Taxonomic and Functional Beta Diversity Patterns and Their Driving Factors of the Fish Assemblages Around Marine Islands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
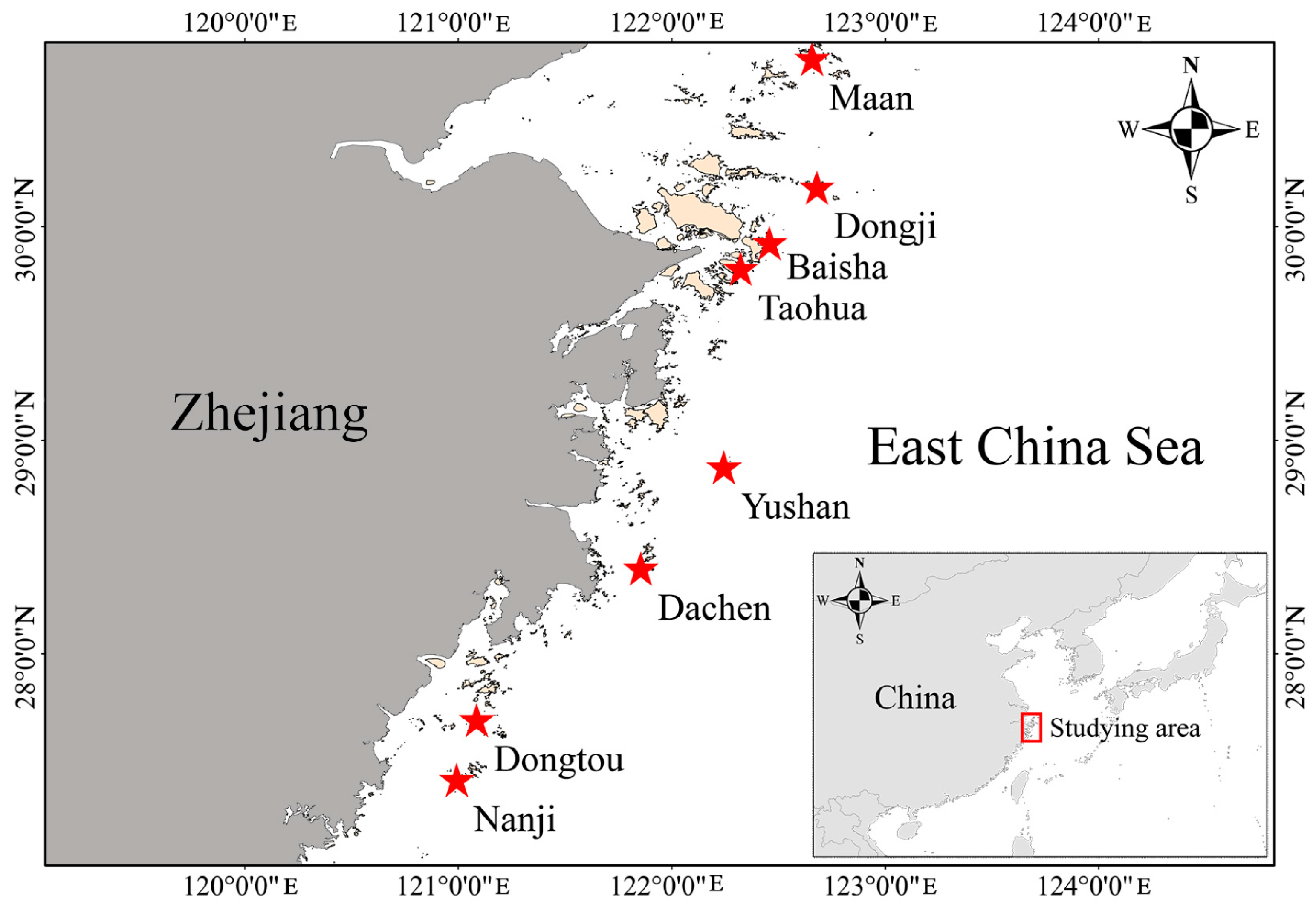
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Taxonomic and Functional Beta Diversity and Decomposition
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
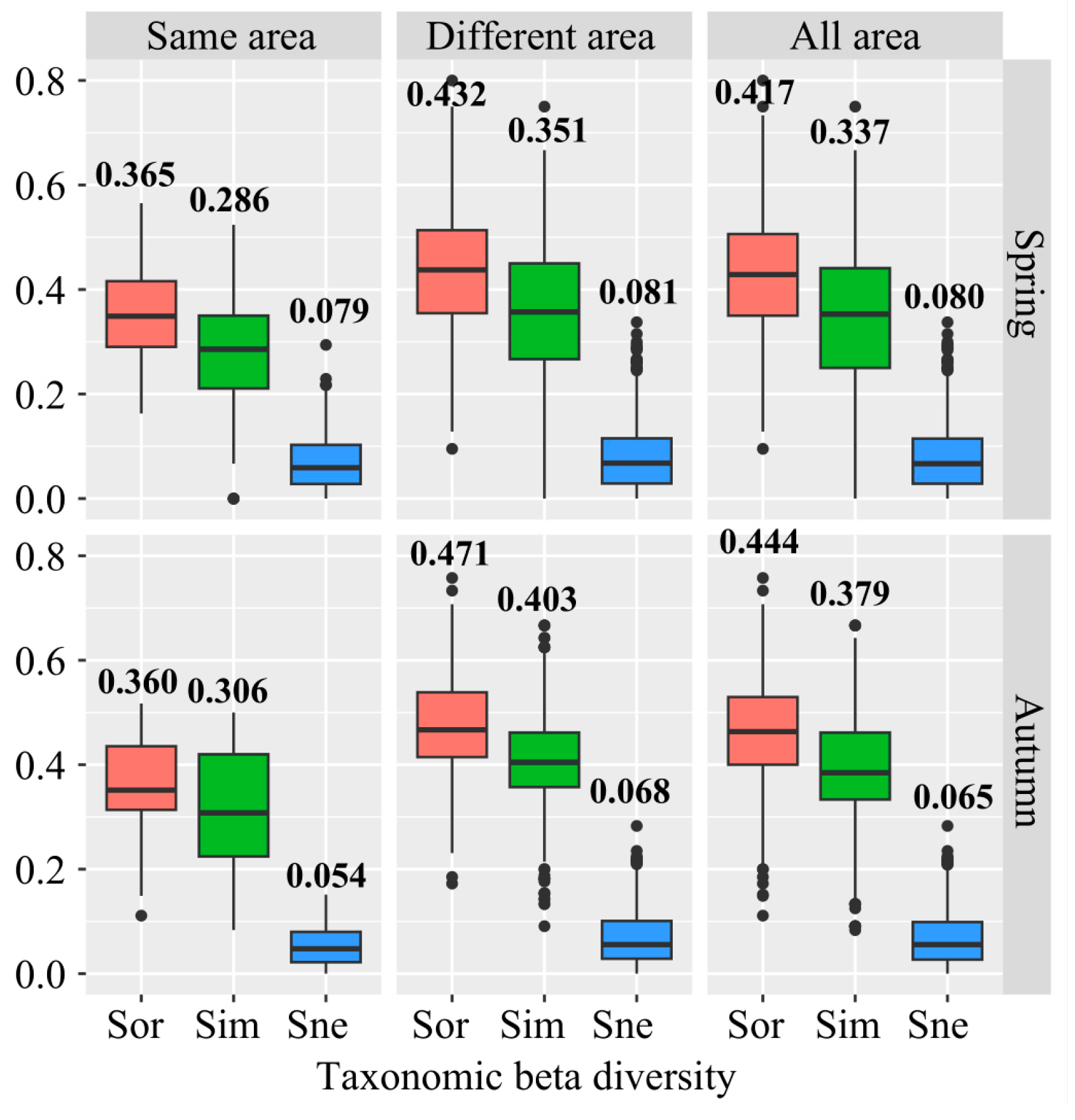
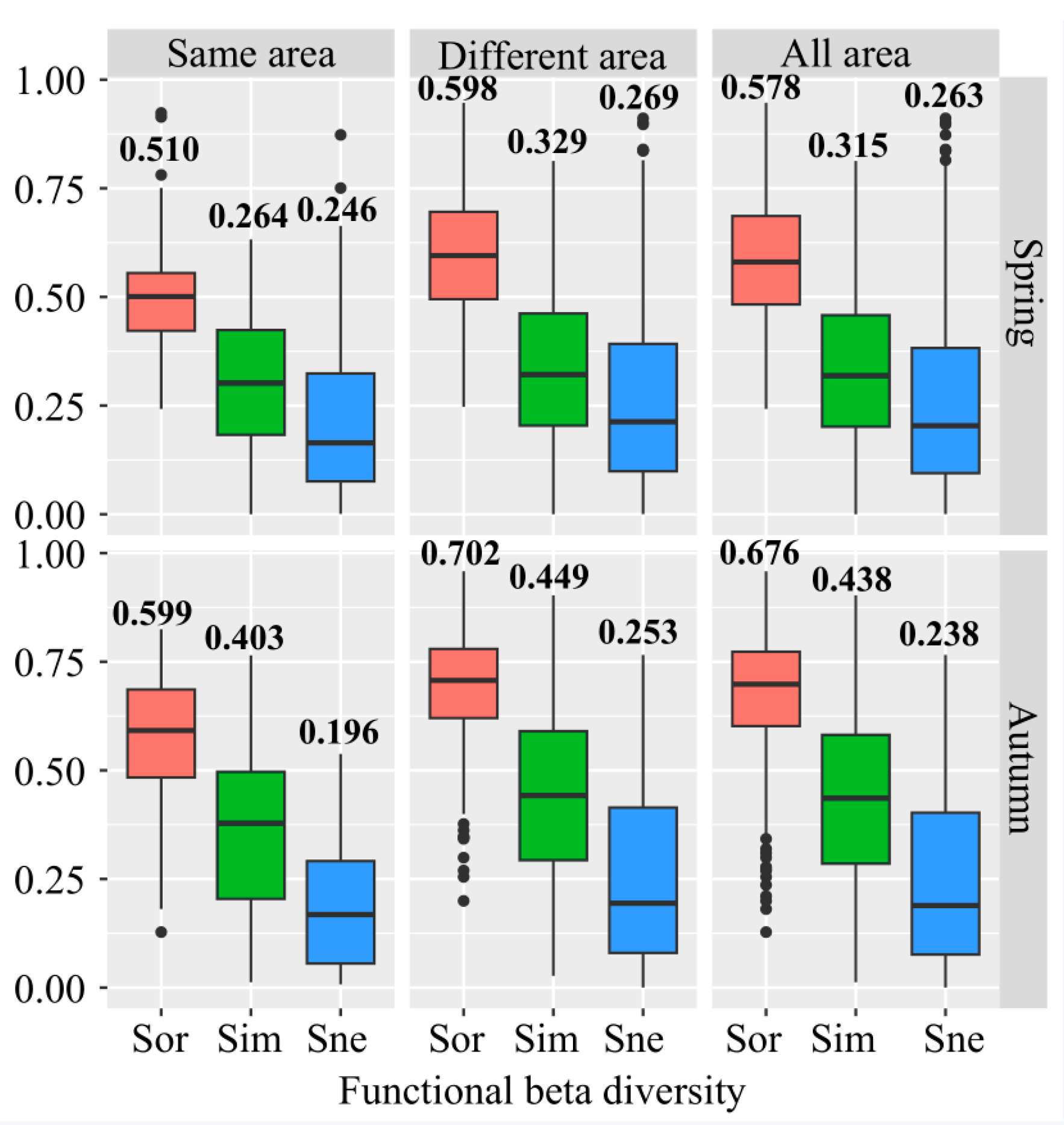
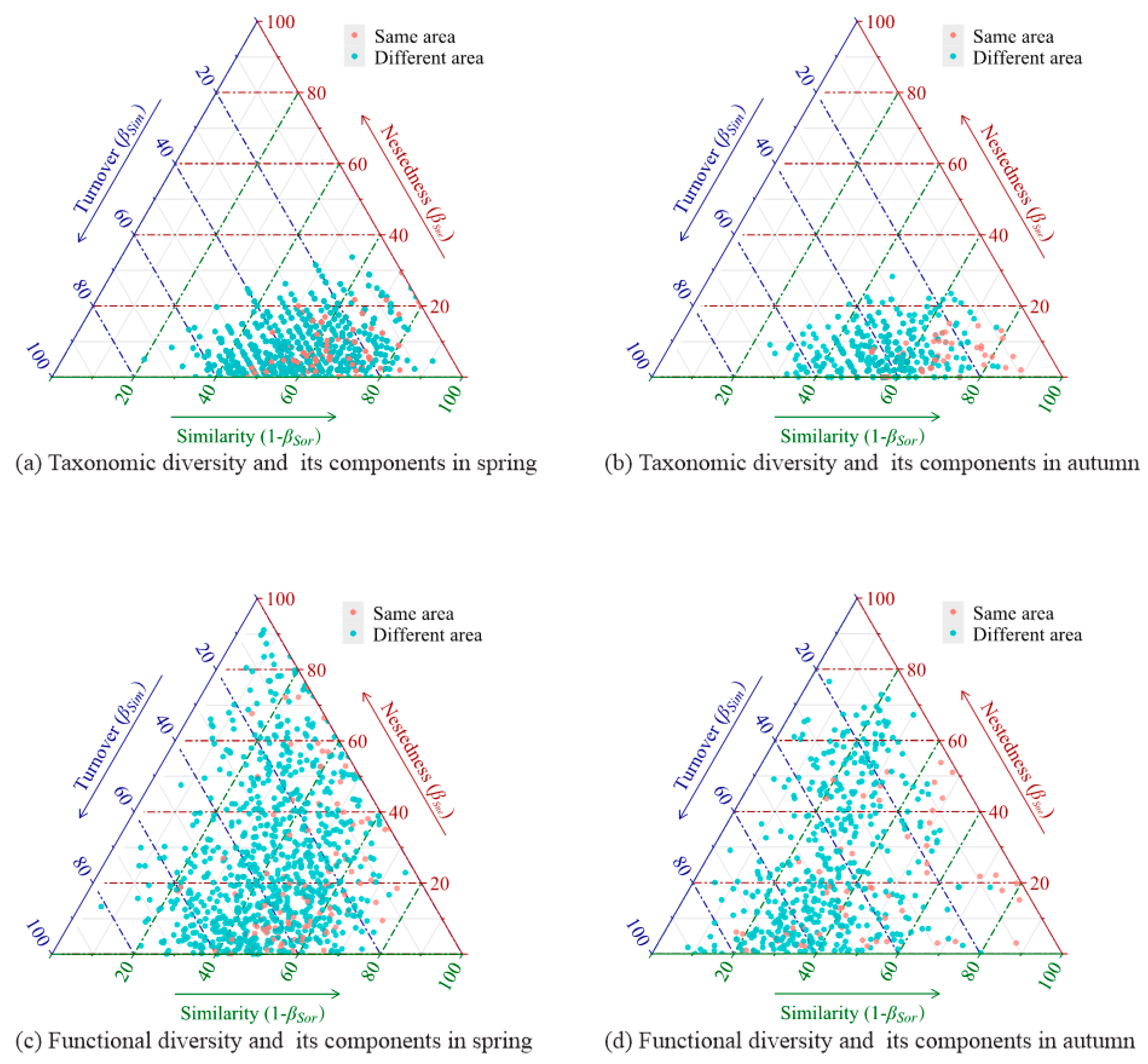
3.1. Beta Diversity and Its Components of Fish Assemblages Around Islands
3.2. The Driving Mechanism of Beta Diversity and Its Components
4. Discussion
4.1. Beta Diversity Patterns of Fish Assemblages Around Islands
4.2. The Impacts of Environmental Factors on Beta Diversity and Its Components in Fish Assemblages
4.3. The Impacts of Geographical Distance on Beta Diversity and Its Components in Fish Assemblages
4.4. Management Implications and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, C.M.; Agusti, S.; Barbier, E.; Britten, G.L.; Castilla, J.C.; Gattuso, J.-P.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Hughes, T.P.; Knowlton, N.; Lovelock, C.E.; et al. Rebuilding marine life. Nature 2020, 580, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baselga, A. Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.F.; Casey, J.M.; Knowlton, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Brandl, S.J. Examining the diversity, stability and functioning of marine fish communities across a latitudinal gradient. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2023, 32, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, N.; Lepage, M.; Chevillot, X.; Lobry, J. Environmental drivers of taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity (alpha, beta and gamma components) in estuarine fish communities. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, S.; Plicanti, A.; Sandulli, R.; Terlizzi, A. Measuring more of β-diversity: Quantifying patterns of variation in assemblage heterogeneity. An insight from marine benthic assemblages. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta Núñez, J.; Romero, M.A.; Ocampo Reinaldo, M.; González, R.; Magurran, A.; Svendsen, G.M. Species turnover drives functional turnover with balanced functional nestedness in a Patagonian demersal assemblage. J. Sea Res. 2023, 196, 102452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque Correa, C.M.; Da Silva, P.G.; Lara, M.A.; Puker, A. Spatiotemporal patterns of β-diversity of flower chafer beetles in urban park and natural reserve sites in Brazilian Cerrado. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.J.; Koleff, P.; Greenwood, J.J.D.; Gaston, K.J. The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. J. Anim. Ecol. 2001, 70, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Heino, J.; Wang, J. A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianuca, A.T.; Declerck, S.A.; Lemmens, P.; De Meester, L. Effects of dispersal and environmental heterogeneity on the replacement and nestedness components of β-diversity. Ecology 2017, 98, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xiang, W.S.; Li, X.K.; Cao, K.F. Environmental filtering and dispersal limitation jointly shaped the taxonomic and phylogenetic beta diversity of natural forests in southern China. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, C.; Meynard, C.N.; Devictor, V.; Guizien, K.; Labrune, C.; Guarini, J.M.; Mouquet, N. Disentangling the role of connectivity, environmental filtering, and spatial structure on metacommunity dynamics. Oikos 2013, 122, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Heino, J.; Quirino, B.A.; Moresco, G.A.; Peláez, O.; Meira, B.R.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Jati, S.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Velho, L.F.M. Differently dispersing organism groups show contrasting beta diversity patterns in a dammed subtropical river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.B.; Oliveira, F.J.M.; De Marco Júnior, P.; Lima-Junior, D.P. Local environmental variables are the best beta diversity predictors for fish communities from the Brazilian Cerrado streams. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 86, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.; Rigal, F.; Carvalho, J.C.; Fortelius, M.; Borges, P.A.V.; Podani, J.; Schmera, D. Partitioning taxon, phylogenetic and functional beta diversity into replacement and richness difference components. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez, O.; Pavanelli, C.S. Environmental heterogeneity and dispersal limitation explain different aspects of β-diversity in Neotropical fish assemblages. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lv, G.; Yue, M. The relative importance of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on the multidimensional Beta diversity of desert plant communities depends on sampling scales. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5608–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q. Geographic patterns and environmental correlates of taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional β-diversity of wetland plants in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlund, C.M.; Hammer, M. Ecosystem services generated by fish populations. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouy, C.; Archambault, P.; Appeltans, W.; Araújo, M.B.; Beauchesne, D.; Cazelles, K.; Cirtwill, A.R.; Fortin, M.-J.; Galiana, N.; Leroux, S.J.; et al. The marine fish food web is globally connected. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villéger, S.; Brosse, S.; Mouchet, M.; Mouillot, D.; Vanni, M.J. Functional ecology of fish: Current approaches and future challenges. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K. Marine biodiversity conservation. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, C.; Villegas-Ríos, D.; Moland, E.; Olsen, E.M. Sea temperature effects on depth use and habitat selection in a marine fish community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grorud-Colvert, K.; Sullivan-Stack, J.; Roberts, C.; Constant, V.; Horta e Costa, B.; Pike, E.P.; Kingston, N.; Laffoley, D.; Sala, E.; Claudet, J.; et al. The MPA Guide: A framework to achieve global goals for the ocean. Science 2021, 373, eabf0861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, S.; Boero, F.; De Leo, F.; Guarnieri, G.; Mačić, V.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Terlizzi, A.; Fraschetti, S. β-diversity reveals ecological connectivity patterns underlying marine community recovery: Implications for conservation. Ecol. Appl. 2023, 33, e2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fluharty, D.L. Marine protected area networks in China: Challenges and prospects. Mar. Policy 2017, 85, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Cliquet, A. Challenges for protected areas management in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrush, S.F.; Hewitt, J.E.; Lohrer, A.M.; Chiaroni, L.D. When small changes matter: The role of cross-scale interactions between habitat and ecological connectivity in recovery. Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.N. Island and island-like marine environments. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, H.T.; Bernardi, G.; Simon, T.; Joyeux, J.-C.; Macieira, R.M.; Gasparini, J.L.; Rocha, C. Island biogeography of marine organisms. Nature 2017, 549, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzan, M.V.; Potschin-Young, M.; Haines-Young, R. Island ecosystem services: Insights from a literature review on case-study island ecosystem services and future prospects. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2018, 14, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, A.; Stewart-Koster, B.; Burford, M.A.; Brown, C.J. A global review of the critical link between river flows and productivity in marine fisheries. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2022, 32, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Medrano, R.; Vega-Cendejas, M.E. Implications of the environmental heterogeneity on the distribution of the fish functional diversity of the Campeche Bank, Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 1913–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, S.J.; Emslie, M.J.; Ceccarelli, D.M.; Richards, Z.T. Habitat degradation increases functional originality in highly diverse coral reef fish assemblages. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Girón, J.; Heino, J.; Baastrup-Spohr, L.; Bove, C.P.; Clayton, J.; de Winton, M.; Feldmann, T.; Fernández-Aláez, M.; Ecke, F.; Grillas, P.; et al. Global patterns and determinants of lake macrophyte taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic beta diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevilacqua, S.; Terlizzi, A. Nestedness and turnover unveil inverse spatial patterns of compositional and functional β-diversity at varying depth in marine benthos. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, B.; Tang, Q. Fish assemblage structure in the East China Sea and southern Yellow Sea during autumn and spring. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 62, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, S.; Tamura, O.S. Fine structure of the skin of the amphibious fishes, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris and Periophthalmus cantonensis, with special reference to the location of blood vessels. J. Morphol. 1992, 214, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, L.; Boom, H.A.; Barbarossa, V.; van Bodegom, P.M. Climate change threats to the global functional diversity of freshwater fish. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3781–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.W.; Graham, N.A.J.; Jones, G.P. Depth gradients in diversity, distribution and habitat specialisation in coral reef fishes: Implications for the depth-refuge hypothesis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 540, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantoussan, J.; Ecoutin, J.M.; Simier, M.; Tito de Morais, L.; Laë, R. Effects of salinity on fish assemblage structure: An evaluation based on taxonomic and functional approaches in the Casamance estuary (Senegal, West Africa). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, E.R.; Winemiller, K.O.; da Silva, J.C.B.; Lopes, T.M.; Gomes, L.C.; Thomaz, S.M.; Agostinho, A.A. α and β diversity of fishes in relation to a gradient of habitat structural complexity supports the role of environmental filtering in community assembly. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rbiai, O.; Badaoui, B.; Chlaida, M. Temporal β-diversity decomposition: Insights into fish biodiversity dynamics in the Moroccan South Atlantic. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.; Roy, D. Patterns of functional diversity along latitudinal gradients of species richness in eleven fish families. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2023, 32, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissi, E.; Manea, E.; Mazaris, A.D.; Fraschetti, S.; Almpanidou, V.; Bevilacqua, S.; Coll, M.; Guarnieri, G.; Lloret-Lloret, E.; Pascual, M.; et al. A review of the combined effects of climate change and other local human stressors on the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddagangaiah, S.; Chen, C.F.; Hu, W.-C.; Akamatsu, T.; Pieretti, N. Assessing the influence of offshore wind turbine noise on seasonal fish chorusing. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 0, fsae061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabinyi, M.; Belton, B.; Dressler, W.H.; Knudsen, M.; Adhuri, D.S.; Abdul Aziz, A.; Akber, M.A.; Kittitornkool, J.; Kongkaew, C.; Marschke, M.; et al. Coastal transitions: Small-scale fisheries, livelihoods, and maritime zone developments in Southeast Asia. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 91, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.; Turiel, A.; Solé, J.; Berdalet, E.; Sabatés, A.; Olivares, A.; Gili, J.-M.; Vila-Subirós, J.; Sardá, R. Unravelling the ecological impacts of large-scale offshore wind farms in the Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Cen, W.; Xu, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y. Ecological impacts of the expansion of offshore wind farms on trophic level species of marine food chain. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, M.F.; Leprieur, F.; Quimbayo, J.P.; Floeter, S.R.; Bender, M.G. Global patterns and drivers of beta diversity facets of reef fish faunas. J. Biogeogr. 2022, 49, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, E.M.V.; Eme, D.; Liggins, L.; Harvey, E.S.; Roberts, C.D.; Anderson, M.J. Functional beta diversity of New Zealand fishes: Characterising morphological turnover along depth and latitude gradients, with derivation of functional bioregions. Austral Ecol. 2021, 46, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzen, V.; Anderson, M.J.; Roberts, C.D.; Harvey, E.S.; Stewart, A.L. Effects of latitude and depth on the beta diversity of New Zealand fish communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Delgado, E.O.; Winemiller, K.O.; Villa-Navarro, F.A. Local environmental factors influence beta-diversity patterns of tropical fish assemblages more than spatial factors. Ecology 2020, 101, e02940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.W.; White, P.S. Scale Dependence and the Species-Area Relationship. Am. Nat. 1994, 144, 717–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, P.S.; Cunningham, S.A.; Manning, A.D.; Gibb, H.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Didham, R.K. The spatial scaling of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa-Fuentes, C.A.; Heino, J.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Ferraz, S.; Zeni, J.O.; Casatti, L. Taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic β-diversity patterns of stream fish assemblages in tropical agroecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.E.L.; Fabré, N.N. Rare Species Enhance Niche Differentiation Among Tropical Estuarine Fish Species. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, F.; Fasola, E.; Marziali, L.; Tirozzi, P.; Schiavon, A.; Bocchi, S.; Gomarasca, S. Response of functional diversity of fish communities to habitat alterations in small lowland rivers. Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 33, 1439–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, C.P.; De Bello, F.; Mason, N.W.; Lepš, J. Traits without borders: Integrating functional diversity across scales. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zheng, P.; Cao, L.; Pan, B. Effects of long-term floodplain disconnection on multiple facets of lake fish biodiversity: Decline of alpha diversity leads to a regional differentiation through time. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 144177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fastré, C.; Possingham, H.P.; Strubbe, D.; Matthysen, E. Identifying trade-offs between biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services delivery for land-use decisions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aglieri, G.; Baillie, C.; Mariani, S.; Cattano, C.; Calò, A.; Turco, G.; Spatafora, D.; Di Franco, A.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Guidetti, P.; et al. Environmental DNA effectively captures functional diversity of coastal fish communities. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallet, D.; Dominique, P. Underwater video techniques for observing coastal marine biodiversity: A review of sixty years of publications (1952–2012). Fish. Res. 2014, 154, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M. Environmental DNA metabarcoding: A novel method for biodiversity monitoring of marine fish communities. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2022, 14, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Schobernd, C.M.; Schobernd, Z.H.; Mitchell, W.A.; Berrane, D.J.; Kellison, G.T.; Reichert, M.J.M. Comparison of trap and underwater video gears for indexing reef fish presence and abundance in the southeast United States. Fish. Res. 2013, 143, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, A.; Bellisario, B.; Cimmaruta, R. A review of fish diversity in Mediterranean seagrass habitats, with a focus on functional traits. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2024, 34, 1329–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.S.; Meaghan, E.E.; Joshua, P.K.; Jonathan, A.P.; Kara, R.W.; Williams, I.; Stallings, C.D. Reef fish assemblages differ both compositionally and functionally on artificial and natural reefs in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 81, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, M.E.; Hughes, A.R. Functional trait analysis reveals the hidden stability of multitrophic communities. Ecology 2025, 106, e70001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Beta Diversity | Season | Coefficient | R2 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | Temperature (°C) | Salinity | Chlorophyll-a (µg/L) | Turbidity (FTU) | Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | Distance (m) | ||||
| Taxonomic beta diversity (TβSor) | Spring | 0.2199 ** | 0.2565 ** | −0.1307 * | 0.1049 | 0.0010 | ||||
| Turnover (TβSim) | 0.1568 * | 0.2372 ** | −0.2114 *** | 0.0902 | 0.0016 | |||||
| Nestedness (TβSne) | 0.1785 ** | 0.0319 | 0.0024 | |||||||
| Taxonomic beta diversity (TβSor) | Autumn | - | 0.1372 * | 0.3402 *** | 0.1977 | 0.0001 | ||||
| Turnover (TβSim) | 0.1706 ** | −0.2058 ** | 0.3390 *** | 0.1746 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Nestedness (TβSne) | 0.4679 *** | −0.1562 ** | 0.1621 * | −0.1456 * | 0.2464 | 0.0001 | ||||
| Functional beta diversity (FβSor) | Spring | 0.2031 ** | 0.3477 *** | 0.1565 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Turnover (FβSim) | 0.2449 ** | −0.2845 *** | 0.0966 | 0.0001 | ||||||
| Nestedness (FβSne) | 0.1567 * | 0.2988 *** | 0.1146 | 0.0001 | ||||||
| Functional beta diversity (FβSor) | Autumn | 0.3340 *** | −0.1988 * | 0.1755 * | 0.1186 * | 0.2464 | 0.0008 | |||
| Turnover (FβSim) | −0.2480 ** | 0.1779 * | 0.0686 | 0.0037 | ||||||
| Nestedness (FβSne) | 0.4012 *** | −0.1314 * | 0.1488 | 0.0004 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, G.; Liang, J.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, M.; Zhou, Y. Taxonomic and Functional Beta Diversity Patterns and Their Driving Factors of the Fish Assemblages Around Marine Islands. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040674
Fang G, Liang J, Jiang R, Zhang Y, Chen J, Chen C, Yang M, Zhou Y. Taxonomic and Functional Beta Diversity Patterns and Their Driving Factors of the Fish Assemblages Around Marine Islands. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040674
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Guangjie, Jun Liang, Rijin Jiang, Yazhou Zhang, Junlin Chen, Chuanxi Chen, Mingda Yang, and Yongdong Zhou. 2025. "Taxonomic and Functional Beta Diversity Patterns and Their Driving Factors of the Fish Assemblages Around Marine Islands" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040674
APA StyleFang, G., Liang, J., Jiang, R., Zhang, Y., Chen, J., Chen, C., Yang, M., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Taxonomic and Functional Beta Diversity Patterns and Their Driving Factors of the Fish Assemblages Around Marine Islands. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040674






