Machine Learning in Maritime Safety for Autonomous Shipping: A Bibliometric Review and Future Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Bibliometric Analysis Method and Tool
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Distribution of Publications
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Publications
3.2.1. Publications Distribution in Pattern of Countries/Regions
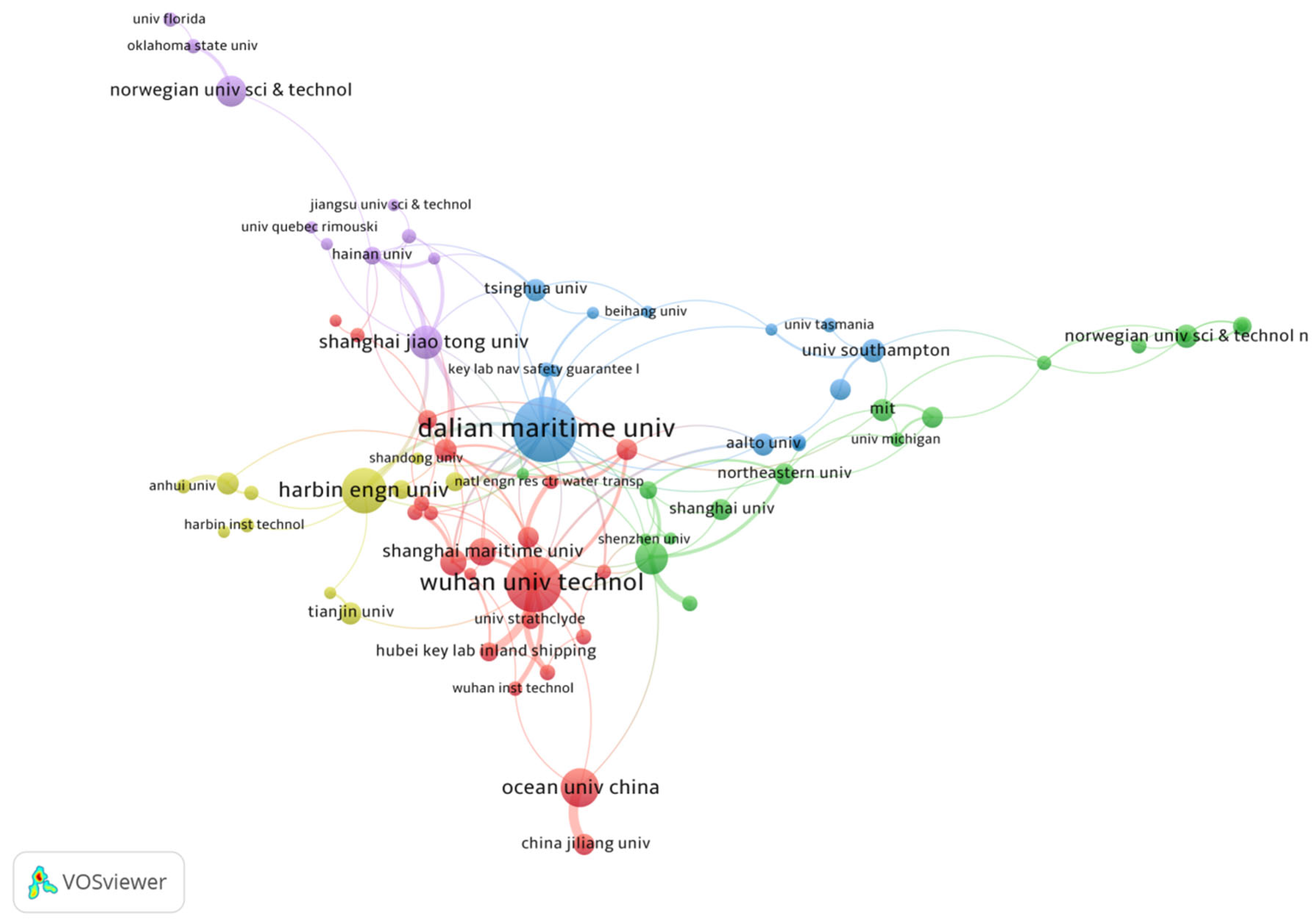
3.2.2. International Cooperation and Influential Research Institutions
3.3. Influential Journal Analysis
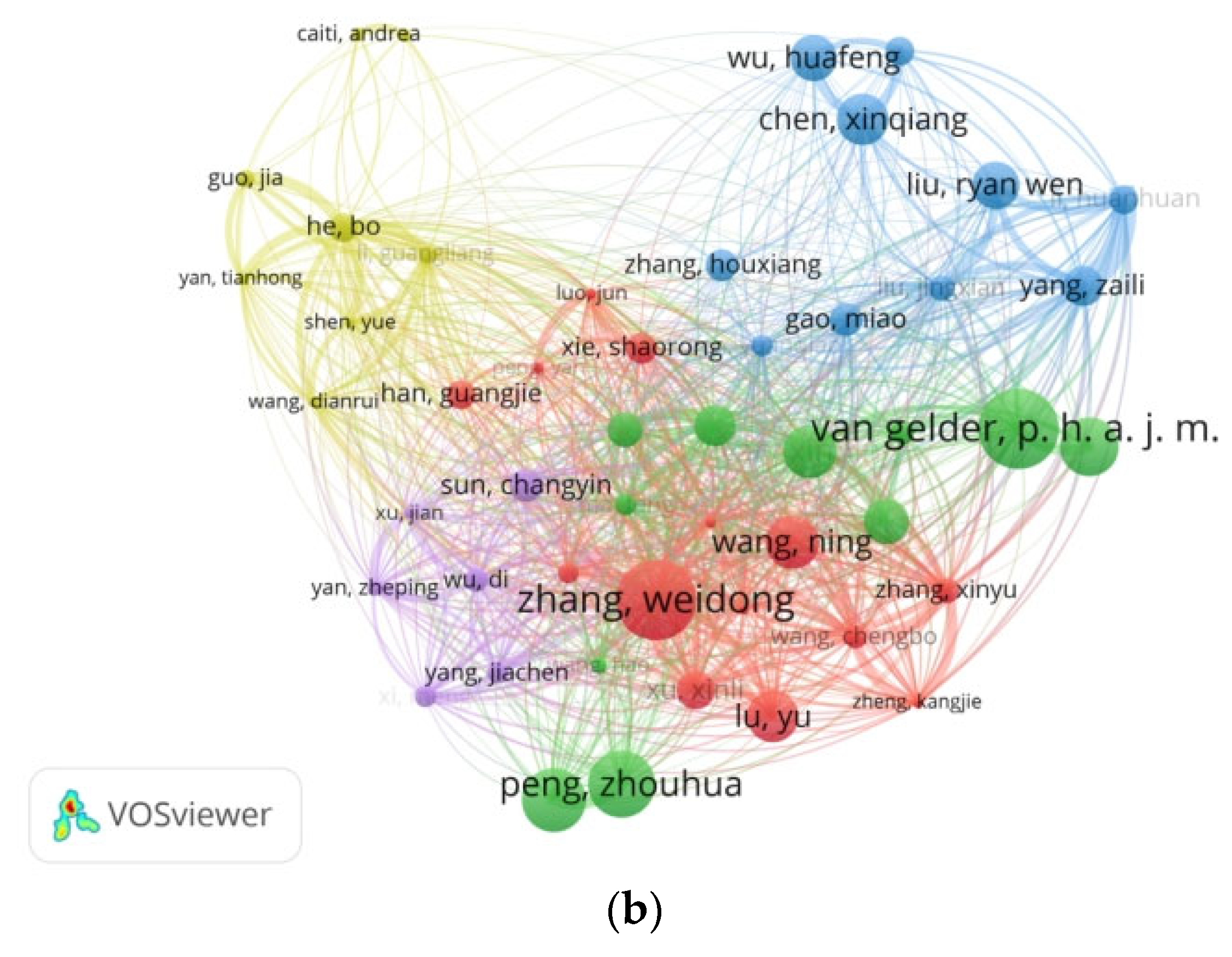
3.4. Cooperation Network Analysis for the Authors
3.5. Citation and Co-Citation Network Analysis for the Publications
3.5.1. Publications Citation Analysis
3.5.2. Publications Co-Citation Analysis
3.6. Research Subject Categories, Hot Topics, and Trends
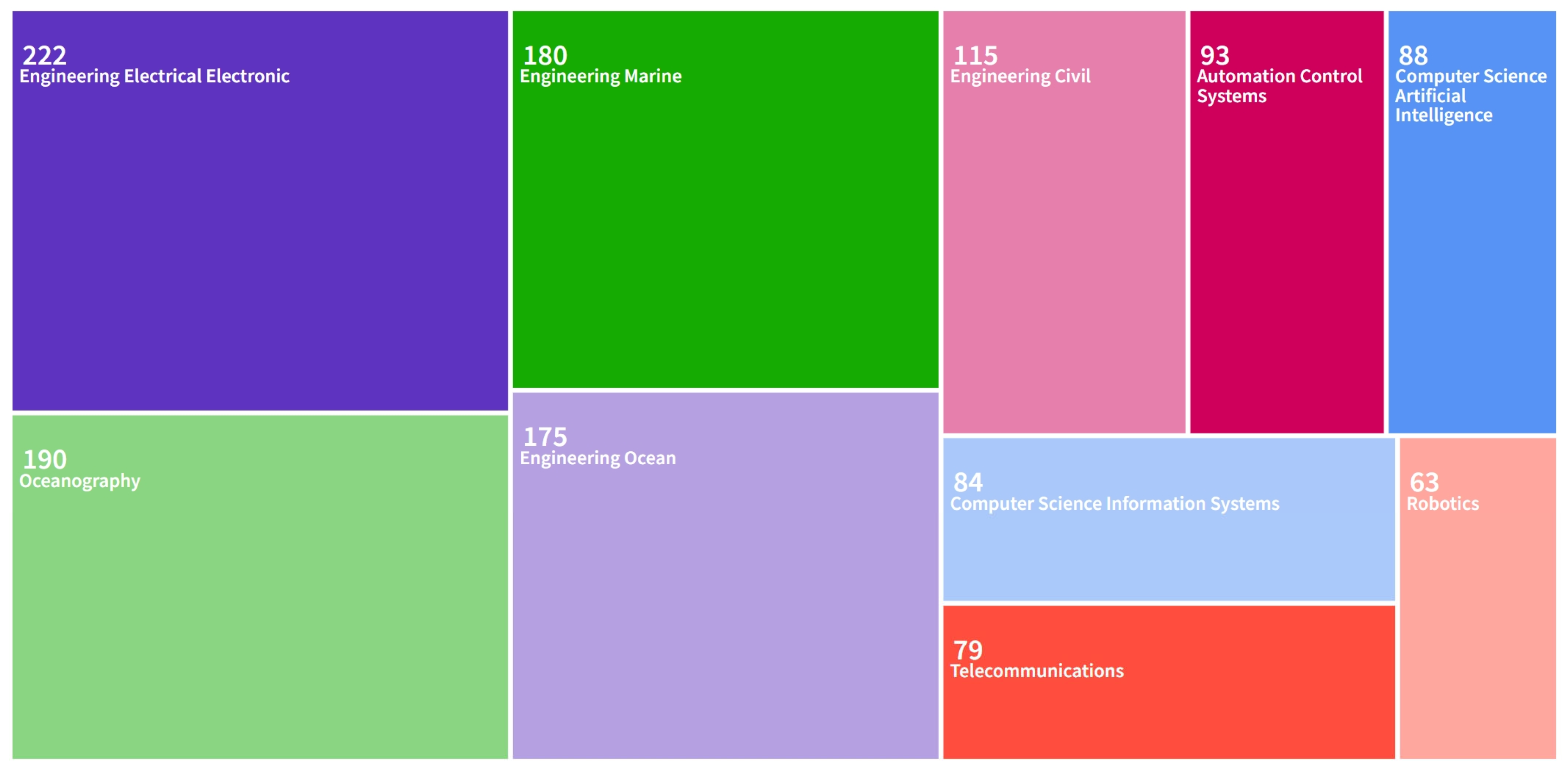
3.6.1. Subject Categories Analysis
3.6.2. Influential Authors’ Research Interests and Domains
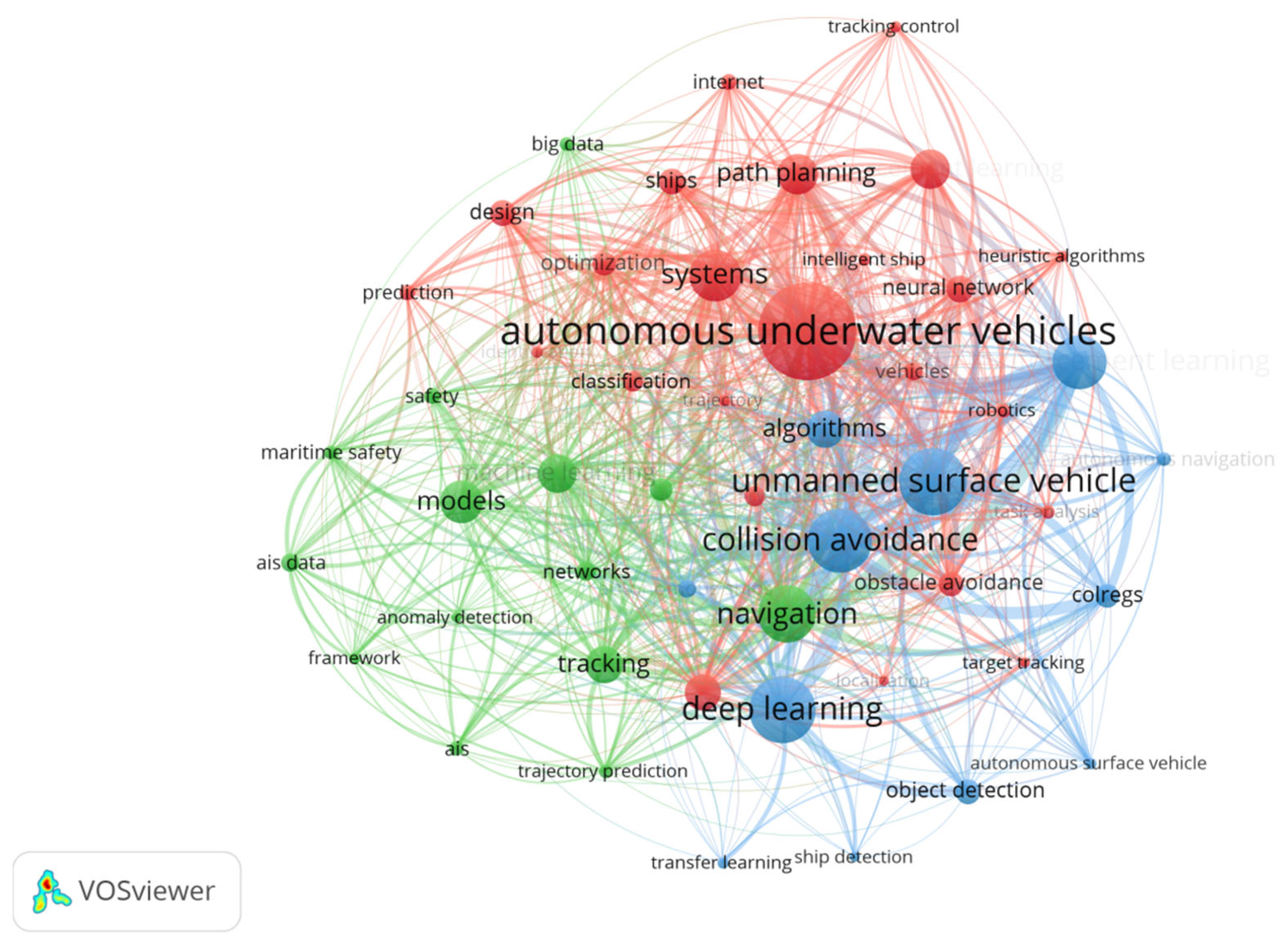
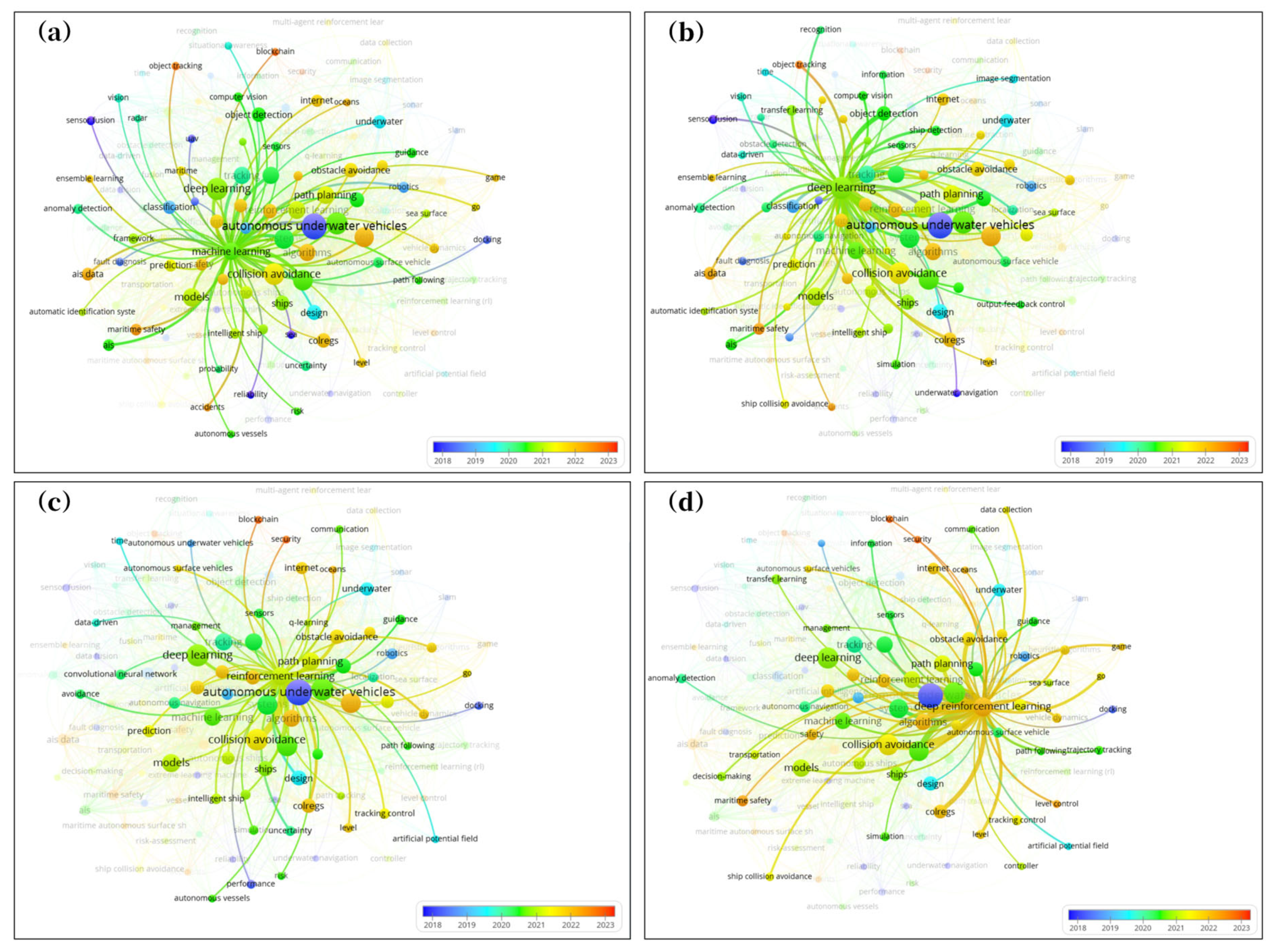
3.6.3. Research Fields Identification and Analysis
3.6.4. Research Frontier and Evolutionary Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Bibliometric Analysis Findings
4.1.1. Past and Current Trends
4.1.2. The Features of Social Structure
4.1.3. Citation and Co-Citation Network Summary
4.2. Comparison Analysis of Research Methods
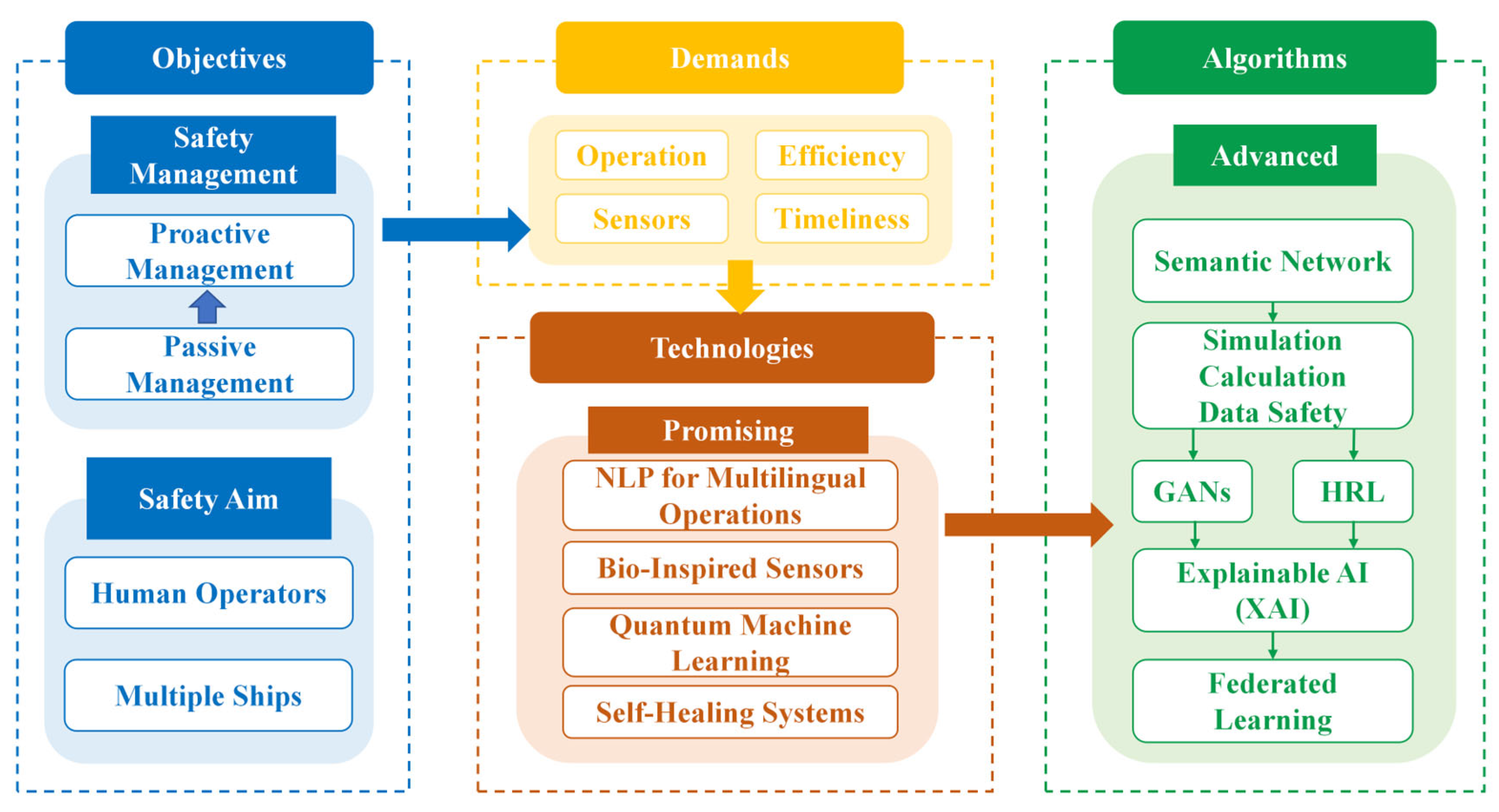
4.3. Future Research Trends
4.3.1. Trends in Safety Objectives
4.3.2. Trends in Safety Technology Based on Machine Learning
4.3.3. Trends in Machine Learning Algorithms
4.3.4. Summary for Future Prospect
4.3.5. Bias and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Step | Keywords/Strings/Topics | Number of Papers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TS = (big data) AND TS = (autonomous shipping OR unmanned shipping) AND TS = (safety OR risk OR security OR reliability) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 26 |
| 2 | TS = (data analytics) AND TS = (autonomous shipping OR unmanned shipping) AND TS = (safety OR risk OR security OR reliability) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 9 |
| 3 | TS = (machine learning) AND TS = (autonomous shipping OR unmanned shipping) AND TS = (safety OR risk OR security OR reliability) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 37 |
| 4 | TS = (data analysis OR data analytics OR data analyst OR data analyzed) AND TS = (autonomous shipping OR unmanned shipping) AND TS = (safety OR risk OR security OR reliability) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 133 |
| 5 | TS = (big data OR data analysis OR data analytics OR data analyst OR data analyzed OR machine learning OR supervised learning OR unsupervised learning OR semi-supervised learning OR ensemble learning OR deep learning OR reinforcement learning OR transfer learning) AND TS = (autonomous shipping OR unmanned shipping) AND TS = (safety OR risk OR security OR reliability) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 222 |
| 6 | TS = (big data OR data analy* OR machine learning OR supervised learning OR unsupervised learning OR semi-supervised learning OR ensemble learning OR deep learning OR reinforcement learning OR transfer learning) AND TS = (autonomous(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR unmanned(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR smart(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR intelligent(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR “autonomous underwater vehicle*” OR “autonomous surface vehicle*” OR “unmanned underwater vehicle*” OR “unmanned surface vehicle*” OR “autonomous marine robotic vehicle*” OR “unmanned marine robotic vehicle*” OR “underwater robotic vehicle*” OR “surface robotic vehicle*” OR “robotic underwater vehicle*” OR “robotic surface vehicle*” OR “untethered underwater vehicle” OR “untethered surface vehicle”) AND TS = (safety OR risk OR security OR reliability) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 775 |
| 7 | TS = (big data OR data analy* OR machine learning OR supervised learning OR unsupervised learning OR semi-supervised learning OR ensemble learning OR deep learning OR reinforcement learning OR transfer learning) AND TS = (autonomous(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR unmanned(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR smart(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR intelligent(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR “autonomous underwater vehicle*” OR “autonomous surface vehicle*” OR “unmanned underwater vehicle*” OR “unmanned surface vehicle*” OR “autonomous marine robotic vehicle*” OR “unmanned marine robotic vehicle*” OR “underwater robotic vehicle*” OR “surface robotic vehicle*” OR “robotic underwater vehicle*” OR “robotic surface vehicle*” OR “untethered underwater vehicle” OR “untethered surface vehicle”) AND TS = (safe* OR risk* OR secur* OR reliab* OR resilience* OR emergen* OR danger* OR hazard* OR maintainab* OR los$ OR accident* OR incident* OR colli* OR encounter* OR ground* OR sink* OR list* OR capsiz* OR dragg* OR contact* OR damag* OR COLREG* OR fire* OR explosion* OR wind* OR “human factor*” OR marine* OR maritime* OR “maritime tra*” OR “maritime transportation system*”) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024 | 2120 |
| 8 | TS = (big data OR data analy* OR machine learning OR supervised learning OR unsupervised learning OR semi-supervised learning OR ensemble learning OR deep learning OR reinforcement learning OR transfer learning) AND TS = (autonomous(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR unmanned(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR smart(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR intelligent(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR “autonomous underwater vehicle*” OR “autonomous surface vehicle*” OR “unmanned underwater vehicle*” OR “unmanned surface vehicle*” OR “autonomous marine robotic vehicle*” OR “unmanned marine robotic vehicle*” OR “underwater robotic vehicle*” OR “surface robotic vehicle*” OR “robotic underwater vehicle*” OR “robotic surface vehicle*” OR “untethered underwater vehicle” OR “untethered surface vehicle”) AND TS = (safe* OR risk* OR secur* OR reliab* OR resilience* OR emergen* OR danger* OR hazard* OR maintainab* OR los$ OR accident* OR incident* OR colli* OR encounter* OR ground* OR sink* OR list* OR capsiz* OR dragg* OR contact* OR damag* OR COLREG* OR fire* OR explosion* OR wind* OR “human factor*” OR marine* OR maritime* OR “maritime tra*” OR “maritime transportation system*”) AND DT = (Article OR Proceedings Paper OR Review) Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024; Search language = English | 2107 |
| 9 | TS = (big data OR data analy* OR machine learning OR supervised learning OR unsupervised learning OR semi-supervised learning OR ensemble learning OR deep learning OR reinforcement learning OR transfer learning) AND TS = (autonomous(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR unmanned(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR smart(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR intelligent(ship* OR vessel$ OR boat*) OR “autonomous underwater vehicle*” OR “autonomous surface vehicle*” OR “unmanned underwater vehicle*” OR “unmanned surface vehicle*” OR “autonomous marine robotic vehicle*” OR “unmanned marine robotic vehicle*” OR “underwater robotic vehicle*” OR “surface robotic vehicle*” OR “robotic underwater vehicle*” OR “robotic surface vehicle*” OR “untethered underwater vehicle” OR “untethered surface vehicle”) AND TS = (safe* OR risk* OR secur* OR reliab* OR resilience* OR emergen* OR danger* OR hazard* OR maintainab* OR los$ OR accident* OR incident* OR colli* OR encounter* OR ground* OR sink* OR list* OR capsiz* OR dragg* OR contact* OR damag* OR COLREG* OR fire* OR explosion* OR wind* OR “human factor*” OR marine* OR maritime* OR “maritime tra*” OR “maritime transportation system*”) AND DT = (Article OR Proceedings Paper OR Review) Manually screened by relevance Indexes = SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH; Timespan = 1 January 2001–31 May 2024; Search language = English | 719 |
| Rank | Top 20 Most Productive Authors | Top 20 Most Citation Authors | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Country | Links | TLS | NP | P (%) | TC | APY | AC | Author | Country | Links | TLS | NP | P (%) | TC | APY | AC | |
| 1 | He, Bo | China | 93 | 1542 | 14 | 1.95% | 98 | 2018.14 | 7.00 | Zhang, Weidong | China | 84 | 2918 | 9 | 1.25% | 373 | 2021.56 | 41.44 |
| 2 | Zhang, Weidong | China | 84 | 2918 | 9 | 1.25% | 373 | 2021.56 | 41.44 | Van Gelder, P. H. A. J. M. | Netherlands | 78 | 1066 | 4 | 0.56% | 370 | 2019.25 | 92.50 |
| 3 | Liu, Yuanchang | England | 96 | 1803 | 8 | 1.11% | 155 | 2020.63 | 19.38 | Peng, Zhouhua | China | 61 | 865 | 5 | 0.70% | 290 | 2019.60 | 58.00 |
| 4 | Wang, Chengbo | China | 76 | 1715 | 8 | 1.11% | 69 | 2022.25 | 8.63 | Wang, Dan | China | 60 | 719 | 4 | 0.56% | 274 | 2018.75 | 68.50 |
| 5 | Yang, Zaili | England | 64 | 3673 | 8 | 1.11% | 149 | 2023.25 | 18.63 | Wu, Chaozhong | China | 46 | 628 | 4 | 0.56% | 246 | 2019.25 | 61.50 |
| 6 | Zhang, Xinyu | China | 90 | 1670 | 8 | 1.11% | 77 | 2021.88 | 9.63 | Yan, Xinping | China | 79 | 1232 | 6 | 0.83% | 216 | 2017.50 | 36.00 |
| 7 | Yan, Tianhong | China | 56 | 598 | 7 | 0.97% | 16 | 2017.43 | 2.29 | Wang, Ning | China | 86 | 981 | 6 | 0.83% | 215 | 2021.83 | 35.83 |
| 8 | Chen, Xinqiang | China | 49 | 803 | 6 | 0.83% | 205 | 2021.33 | 34.17 | Chen, Xinqiang | China | 49 | 803 | 6 | 0.83% | 205 | 2021.33 | 34.17 |
| 9 | Guo, Jia | China | 32 | 576 | 6 | 0.83% | 51 | 2018.50 | 8.50 | Lu, Yu | China | 73 | 792 | 4 | 0.56% | 203 | 2019.00 | 50.75 |
| 10 | Li, Guangliang | China | 80 | 997 | 6 | 0.83% | 52 | 2019.17 | 8.67 | Chen, Zhijun | China | 41 | 418 | 3 | 0.42% | 187 | 2019.33 | 62.33 |
| 11 | Liu, Jingxian | China | 84 | 1326 | 6 | 0.83% | 83 | 2021.00 | 13.83 | Liu, Ryan Wen | China | 58 | 912 | 4 | 0.56% | 185 | 2020.50 | 46.25 |
| 12 | Wang, Ning | China | 86 | 981 | 6 | 0.83% | 215 | 2021.83 | 35.83 | Wu, Huafeng | China | 45 | 548 | 4 | 0.56% | 181 | 2021.00 | 45.25 |
| 13 | Yan, Xinping | China | 79 | 1232 | 6 | 0.83% | 216 | 2017.50 | 36.00 | Li, Zhixiong | China | 80 | 491 | 5 | 0.70% | 175 | 2016.60 | 35.00 |
| 14 | Li, Huanhuan | China | 62 | 2974 | 5 | 0.70% | 98 | 2023.20 | 19.60 | Liang, Maohan | China | 45 | 530 | 3 | 0.42% | 169 | 2019.67 | 56.33 |
| 15 | Li, Zhixiong | China | 80 | 491 | 5 | 0.70% | 175 | 2016.60 | 35.00 | Yang, Yongsheng | China | 42 | 434 | 3 | 0.42% | 168 | 2020.00 | 56.00 |
| 16 | Ma, Feng | China | 76 | 1278 | 5 | 0.70% | 66 | 2019.80 | 13.20 | Liu, Yuanchang | England | 96 | 1803 | 8 | 1.11% | 155 | 2020.63 | 19.38 |
| 17 | Peng, Zhouhua | China | 61 | 865 | 5 | 0.70% | 290 | 2019.60 | 58.00 | Wang, Yang | China | 73 | 622 | 3 | 0.42% | 150 | 2020.67 | 50.00 |
| 18 | Shen, Yue | China | 74 | 692 | 5 | 0.70% | 20 | 2019.40 | 4.00 | Yang, Zaili | England | 64 | 3673 | 8 | 1.11% | 149 | 2023.25 | 18.63 |
| 19 | Sun, Changyin | China | 85 | 1182 | 5 | 0.70% | 113 | 2022.80 | 22.60 | Xu, Xinli | China | 79 | 1540 | 4 | 0.56% | 138 | 2021.75 | 34.50 |
| 20 | Wang, Hao | China | 62 | 353 | 5 | 0.70% | 42 | 2021.00 | 8.40 | Zhang, Mingyang | China | 71 | 617 | 3 | 0.42% | 135 | 2021.67 | 45.00 |
| Rank | All Time | 2000–2010 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword | Frequency | Keyword | Frequency | |
| 1 | AUV | 131 | AUV | 6 |
| 2 | Collision avoidance | 83 | Navigation | 2 |
| 3 | Deep learning | 79 | Reliability | 2 |
| 4 | USV | 77 | UGV | 2 |
| 5 | Navigation | 68 | 3D computer vision | 1 |
| 6 | System | 62 | Acoustic image | 1 |
| 7 | Deep reinforcement learning | 57 | Acoustic ultrashort baseline system | 1 |
| 8 | Reinforcement learning | 45 | Automatic control | 1 |
| 9 | Machine learning | 43 | Autonomous navigation | 1 |
| 10 | Model | 43 | Autonomous underwater navigation | 1 |
| 11 | Tracking | 41 | AUV docking | 1 |
| 12 | Path planning | 39 | Avoidance | 1 |
| 13 | Algorithm | 33 | Basis expansion model | 1 |
| 14 | Ship | 29 | Channels | 1 |
| 15 | Design | 28 | Circular buffe | 1 |
| 16 | Object detection | 26 | Collision avoidance system | 1 |
| 17 | Obstacle avoidance | 26 | Data logging | 1 |
| 18 | COLREGS | 25 | Data reconstruction | 1 |
| 19 | Optimization | 25 | Detection | 1 |
| 20 | Artificial Intelligence | 24 | Diagnosis | 1 |
| 21 | Classification | 21 | Differential detection | 1 |
| 22 | Marine vehicles | 21 | Differential OSTBC | 1 |
| 23 | Marine robotics | 19 | Distant transmission algorithm | 1 |
| 24 | AIS data | 18 | DSSS | 1 |
| 25 | Internet | 16 | Dynamic replanning | 1 |
| 26 | Prediction | 16 | Expert system | 1 |
| 27 | Safety | 16 | Fault detection | 1 |
| 28 | AIS | 15 | Fuzzy fault tree | 1 |
| 29 | Autonomous navigation | 14 | Homing strategies | 1 |
| 30 | Big data | 14 | Image process | 1 |
| 2011–2015 | 2016–2024 | |||
| Keyword | Frequency | Keyword | Frequency | |
| AUV | 20 | AUV | 99 | |
| Design | 5 | USV | 80 | |
| Systems | 4 | Deep learning | 79 | |
| Tracking | 3 | Collision avoidance | 76 | |
| Acoustic communication | 3 | Navigation | 64 | |
| AIS | 2 | Deep reinforcement learning | 63 | |
| Anomaly detection | 2 | System | 55 | |
| Big data | 2 | Models | 46 | |
| Component | 2 | Path planning | 44 | |
| Data assimilation | 2 | Reinforcement learning | 44 | |
| Data fusion | 2 | Algorithms | 42 | |
| Decision support | 2 | Machine learning | 40 | |
| Docking | 2 | Marine robotics | 38 | |
| Instantaneous angular speed | 2 | Tracking | 37 | |
| Intelligent systems | 2 | Neural network | 29 | |
| Machine learning | 2 | Ship | 28 | |
| Marine robotics | 2 | Object detection | 26 | |
| Maritime domain awareness | 2 | COLREGS | 25 | |
| Models | 2 | Obstacle avoidance | 25 | |
| Navigation | 2 | Optimization | 25 | |
| Path planning | 2 | Artificial Intelligence | 24 | |
| Underwater | 2 | Design | 23 | |
| Underwater communication | 2 | Classification | 20 | |
| UUV | 2 | Networks | 20 | |
| 3 axis aquatic flight | 1 | Autonomous ships | 19 | |
| Accumulation | 1 | Underwater | 19 | |
| Acoustic navigation | 1 | Vehicles | 18 | |
| Adriatic sea | 1 | AIS data | 17 | |
| Air launch | 1 | Safety | 16 | |
| AIS data | 1 | Internet | 15 | |
| Number | Machine Learning | Deep Learning | Reinforcement Learning | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sensor fusion | Sensor fusion | - | - |
| 2 | - | Ship detection | - | - |
| 3 | - | Image segmentation | - | - |
| 4 | Reinforcement learning | Reinforcement learning | - | Reinforcement learning |
| 5 | Optimization | Optimization | - | Optimization |
| 6 | Object detection | Object detection | - | - |
| 7 | - | Machine learning | - | Machine learning |
| 8 | - | Transfer learning | - | Transfer learning |
| 9 | - | - | COLREGs | COLREGs |
| 10 | - | - | Autonomous navigation | Autonomous navigation |
| 11 | - | Simulation | Simulation | Simulation |
| 12 | - | - | - | decision-making |
| 13 | Path planning | Path planning | Path planning | Path planning |
| 14 | - | - | Underwater vehicle | - |
| 15 | Fault diagnosis | Fault diagnosis | - | - |
| 16 | - | - | - | Data collection |
| 17 | Classification | Classification | - | - |
| 18 | Prediction | Prediction | Prediction | - |
| 19 | - | Marine robotics | - | Marine robotics |
| 20 | AUV | AUV | AUV | AUV |
| 21 | AIS data | AIS data | - | - |
| 22 | Anomaly detection | Anomaly detection | - | Anomaly detection |
| 23 | Computer vision | Computer vision | - | - |
| 24 | Navigation | Navigation | Navigation | Navigation |
| 25 | Robotics | Robotics | Robotics | Robotics |
| 26 | Tracking | Tracking | Tracking | Tracking |
| 27 | Models | Models | Models | Models |
| 28 | AIS | AIS | - | - |
| 29 | System | System | System | System |
| 30 | Uncertainty | - | Uncertainty | - |
| 31 | Design | Design | Design | Design |
| 32 | Neural network | Neural network | Neural network | Neural network |
| 33 | Algorithm | Algorithm | Algorithm | Algorithm |
| 34 | Marine vehicles | Marine vehicles | Marine vehicles | - |
| 35 | Deep learning | - | Deep learning | Deep learning |
| 36 | Autonomous ship | Autonomous ship | Autonomous ship | Autonomous ship |
| 37 | USV | USV | USV | USV |
| 38 | - | Convolutional neural Network | Convolutional neural Network | - |
| 39 | Collision avoidance | Collision avoidance | Collision avoidance | Collision avoidance |
| 40 | Sensors | Sensors | Sensors | Sensors |
| 41 | Obstacle avoidance | Obstacle avoidance | Obstacle avoidance | Obstacle avoidance |
| 42 | Path following | - | Path following | Path following |
| 43 | Ensemble learning | Ensemble learning | - | - |
| 44 | Maritime safety | Maritime safety | - | Maritime safety |
| 45 | - | Vision | - | - |
| 46 | Blockchain | - | Blockchain | Blockchain |
| 47 | - | - | Management | Management |
References
- Olapoju, O. Autonomous ships, port operations, and the challenges of African ports. Marit. Technol. Res. 2023, 5, 260194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Yang, Z.L. Incorporation of AIS data-based machine learning into unsupervised route planning for maritime autonomous surface ships. Transp. Res. Part E-Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 176, 103171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-C.; Wang, C.-N.; Hsu, H.-P. A novel quantitative and qualitative model for forecasting the navigational risks of Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships. Ocean Eng. 2022, 248, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.Y.N.; Loh, H.S.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Lopez, M.C.R. Adoption of digital technologies in the maritime industry: Insights from Singapore. Marit. Technol. Res. 2025, 7, 275821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, F.W.; Wu, Z.L. A system-theoretic approach to safety and security co-analysis of autonomous ships. Ocean Eng. 2021, 222, 108569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, I.; Percic, M.; Korican, M.; Vladimir, N.; Fan, A.L. Investigation of the Viability of Unmanned Autonomous Container Ships under Different Carbon Pricing Scenarios. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.S.; Roman, D.; Dickie, R.; Robu, V.; Flynn, D. Prognostics and Health Management for the Optimization of Marine Hybrid Energy Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Im, N.K. Development of ship collision avoidance system and sea trial test for autonomous ship. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 113120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.L.; Liu, G.Z.; Lv, T.Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Marine Vision-Based Situational Awareness Using Discriminative Deep Learning: A Survey. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.D.; Gang, L.H.; Zhang, M.H.; Liu, T.; Lan, Z.X. Optimizing Multi-Vessel Collision Avoidance Decision Making for Autonomous Surface Vessels: A COLREGs-Compliant Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.X.; Feng, H.; He, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Li, F.; Yang, Z. Deep reinforcement learning based collision avoidance system for autonomous ships. Ocean Eng. 2024, 292, 116527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.B.; Wang, N.; Gao, H.B.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Fang, M.X. Knowledge transfer enabled reinforcement learning for efficient and safe autonomous ship collision avoidance. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 3715–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, C.B.; Li, Y.K.; Cui, J.L.; Jiang, L.L. Adaptive collision avoidance decisions in autonomous ship encounter scenarios through rule-guided vision supervised learning. Ocean Eng. 2024, 297, 117096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.H.; Zhu, F.X.; Wei, M.X.; Du, Y.F.; Zhai, P.Y. A Multi-Ship Collision Avoidance Algorithm Using Data-Driven Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.L.; Wu, D.F.; Yamashita, A.S.; Li, Z.X. Proximal policy optimization with reciprocal velocity obstacle based collision avoidance path planning for multi-unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2023, 273, 114005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.K.; Pandi, A.R.; Somayajula, A. Collision avoidance for autonomous surface vessels using novel artificial potential fields. Ocean Eng. 2023, 288, 116011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Han, F.L.; Xia, G.H.; Zhao, W.Y.; Zhao, Y.M. Autonomous Obstacle Avoidance in Crowded Ocean Environment Based on COLREGs and POND. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, M.; Paulig, N.; Okhrin, O. 2-level reinforcement learning for ships on inland waterways: Path planning and following. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 274, 126933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Wu, D.F.; Huang, Y.Q.; Yuan, Z.-M. A path planning strategy unified with a COLREGS collision avoidance function based on deep reinforcement learning and artificial potential field. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 113, 102759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, H.M.; Lao, S.H.; Drew, S. Efficient Path Planning and Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance in Edge for Safe Navigation of USV. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 10084–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degorre, L.; Fossen, T.I.; Delaleau, E.; Chocron, O. A Virtual Reference Point Kinematic Guidance Law for 3-D Path-Following of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 109822–109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, M.; Okhrin, O. Spatial-temporal recurrent reinforcement learning for autonomous ships. Neural Netw. 2023, 165, 634–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Cui, E.H.; Fu, X.J. A novel multi-ship collision probability estimation method considering data-driven quantification of trajectory uncertainty. Ocean Eng. 2023, 272, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Q.; Haugen, S.; Utne, I.B. Risk assessment of collisions of an autonomous passenger ferry. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O-J. Risk Reliab. 2023, 237, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, G.W.; Tang, S.H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Alrifaey, M. Toward a Highly Accurate Classification of Underwater Cable Images via Deep Convolutional Neural Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-y.; Lee, T.-h.; Lee, S.-h.; Lee, J.-j.; Lee, W.-k.; Kim, Y.-j.; Park, J.-w. A Study on Deep Learning-Based Fault Diagnosis and Classification for Marine Engine System Auxiliary Equipment. Processes 2022, 10, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Yuan, H.W.; Yu, Q. Autonomous Vessels in the Yangtze River: A Study on the Maritime Accidents Using Data-Driven Bayesian Networks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.H.; Tian, H.; Jiang, R.Z.; Lin, Y.J.; Zhang, J.D. A comparative investigation of data-driven approaches based on one-class classifiers for condition monitoring of marine machinery system. Ocean Eng. 2020, 201, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.B.; Birant, D. GASEL: Genetic algorithm-supported ensemble learning for fault detection in autonomous underwater vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2023, 272, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.I.; Claro, R.M.; Leite, P.N.; Pinto, A.M. Advancing Autonomous Surface Vehicles: A 3D Perception System for the Recognition and Assessment of Docking-Based Structures. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 53030–53045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K. An Intelligent Automatic Sea Forecasting System Targeting Specific Areas on Sailing Routes. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.; Seth, B.; Radulescu, M.; Cilan, T.F.; Serbanescu, L. Optimized Deep Learning with Learning without Forgetting (LwF) for Weather Classification for Sustainable Transportation and Traffic Safety. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Liu, S.H.; Zhao, J.S.; Wu, H.F.; Xian, J.F.; Montewka, J. Autonomous port management based AGV path planning and optimization via an ensemble reinforcement learning framework. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 251, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, S.; Zetterlind, V.; Tougher, B.; Easterday, K. Using machine learning to optimize autonomous tracking of vessels by marine radar. In Proceedings of the OCEANS Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–23 September 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Spatial risk assessment of maritime transportation in offshore waters of China using machine learning and geospatial big data. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 247, 106934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Wrobel, K.; Montewka, J.; Goerlandt, F. A bibliometric analysis and systematic review of shipboard Decision Support Systems for accident prevention. Saf. Sci. 2020, 128, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Zhang, D.; Han, B.; Wan, C.P. Risk and reliability analysis for maritime autonomous surface ship: A bibliometric review of literature from 2015 to 2022. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2023, 187, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatug, C.; Arslanoglu, Y.; Soares, C.G. Review of maintenance strategies for ship machinery systems. J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2023, 22, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaal, M.; Ren, X.; BahooToroody, A.; Basnet, S.; Bolbot, V.; Banda, O.A.V.; Van Gelder, P. Research on risk, safety, and reliability of autonomous ships: A bibliometric review. Saf. Sci. 2023, 167, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.W.; Dhir, S.L.; Das, V.M.; Sharma, A. Bibliometric overview of the Technological Forecasting and Social Change journal: Analysis from 1970 to 2018. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 154, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.T.; Grimes, S. The emerging dynamic structure of national innovation studies: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askun, V.; Cizel, R. Twenty Years of Research on Mixed Methods. J. Mix. Methods Stud. 2020, 1, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukar, U.A.; Sayeed, M.S.; Razak, S.F.A.; Yogarayan, S.; Amodu, O.A.; Mahmood, R.A.R. A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Goerlandt, F.; Reniers, G. Mapping process safety: A retrospective scientometric analysis of three process safety related journals (1999–2018). J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 65, 104141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hale, A. Output distributions and topic maps of safety related journals. Saf. Sci. 2016, 82, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hale, A. Identification of, and knowledge communication among core safety science journals. Saf. Sci. 2015, 74, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nunen, K.; Li, J.; Reniers, G.; Ponnet, K. Bibliometric analysis of safety culture research. Saf. Sci. 2018, 108, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.Y.; Zou, P.X.W.; Piroozfar, P.; Wood, H.; Yang, Y.; Yan, L.B.; Han, Y. A science mapping approach based review of construction safety research. Saf. Sci. 2019, 113, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, R.; Thaheem, M.J.; Nasir, A.R.; Ali, T.H.; Khan, S. Exploring the role of building information modeling in construction safety through science mapping. Saf. Sci. 2019, 120, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Khan, F.; Amyotte, P. A bibliometric review of process safety and risk analysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Reniers, G.; Cozzani, V.; Khan, F. A bibliometric analysis of peer-reviewed publications on domino effects in the process industry. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2017, 49, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Reniers, G.; Chen, G.H.; Goerlandt, F. A bibliometric review of laboratory safety in universities. Saf. Sci. 2019, 120, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Yue, W.L.; Vu, H.L. Visualization and analysis of mapping knowledge domain of road safety studies. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 118, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, H.L.; Hong, R.; Liu, H.G.; You, W.J. Mapping knowledge structure and research trends of emergency evacuation studies. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yang, F.Q.; Qiu, D.Y.; Reniers, G. Analysis of safety leadership using a science mapping approach. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 140, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenon, G.; An, P.E.; Smith, S.M.; Healey, A.J. Enhancement of the inertial navigation system for the Morpheus autonomous underwater vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldieri, L.; Kotsemir, M.; Vinci, C.P. The impact of research collaboration on academic performance: An empirical analysis for some European countries. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2018, 62, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.P.; Xue, M.M.; Zhang, X.F. Characteristics and Trends of Ocean Remote Sensing Research from 1990 to 2020: A Bibliometric Network Analysis and Its Implications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, D. Distributed Containment Maneuvering of Multiple Marine Vessels via Neurodynamics-Based Output Feedback. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3831–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.M.; Chen, L.Y.; Chen, P.F.; Negenborn, R.R.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. Ship collision avoidance methods: State-of-the-art. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.D. Concise deep reinforcement learning obstacle avoidance for underactuated unmanned marine vessels. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, E.M.; Zhang, G.H.; Rachmawati, L.; Rajabally, E.; Huang, G.B. Exploiting AIS Data for Intelligent Maritime Navigation: A Comprehensive Survey From Data to Methodology. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 1559–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Teixeira, A.P.; Soares, C.G. Ship trajectory uncertainty prediction based on a Gaussian Process model. Ocean Eng. 2019, 182, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, L.P.; Oliveira, P.; Soares, C.G. Maritime Traffic Monitoring Based on Vessel Detection, Tracking, State Estimation, and Trajectory Prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 13, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, G.; Vespe, M.; Bryan, K. Vessel Pattern Knowledge Discovery from AIS Data: A Framework for Anomaly Detection and Route Prediction. Entropy 2013, 15, 2218–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.M.; Roh, M.I. COLREGs-compliant multiship collision avoidance based on deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Eng. 2019, 191, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Kim, N. Collision avoidance for an unmanned surface vehicle using deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Eng. 2020, 199, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.Q.; He, K.M.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.F.; Chen, G.H.; Reniers, G.; Goerlandt, F. A bibliometric analysis of process safety research in China:Understanding safety research progress as a basis for making China’s chemical industry more sustainable. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.G.; Yang, Y.; Long, C.L.; Li, H. A bibliometric analysis of research on the risk of engineering nanomaterials during 1999–2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Huang, J.-S.; Ho, Y.-S. Bibliometric analysis of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related research in the beginning stage. Scientometrics 2004, 61, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-L.; Ding, G.H.; Feng, N.; Wang, M.-H.; Ho, Y.-S. Global stem cell research trend: Bibliometric analysis as a tool for mapping of trends from 1991 to 2006. Scientometrics 2009, 80, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.H.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.H.; Liu, Z.J. Research in marine accidents: A bibliometric analysis, systematic review and future directions. Ocean Eng. 2023, 284, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.L.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.C.; Yu, S.S.; He, T.H.; Jin, R.H.; Li, Z.Z.; et al. MLDet: Towards efficient and accurate deep learning method for Marine Litter Detection. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 243, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.R.; Liu, K.Z.; Loughney, S.; Wang, J.; Li, H.H.; Ekere, N.; Yang, Z.L. Multi-scale collision risk estimation for maritime traffic in complex port waters. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 240, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Han, Z.P.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, F. Use of Hybrid Causal Logic Method for Preliminary Hazard Analysis of Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, R.; Gaspar, H.M.; Gausdal, A.H.; Morshedi, M. Human Interactions Framework for Remote Ship Operations. In Proceedings of the 26th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Zadar, Croatia, 19–22 June 2018; pp. 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Weng, J.X.; Fan, S.Q.; Yang, Z.L.; Ding, H.F. Exploring seafarers’ emotional responses to emergencies: An empirical study using a shiphandling simulator. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 243, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Yang, F.K.; Mou, J.M.; Chen, L.Y.; Li, M.X. Regional ship behavior and trajectory prediction for maritime traffic management: A social generative adversarial network approach. Ocean Eng. 2024, 299, 117186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Luo, W.Z.; Cui, Z.W. Intelligent decision-making system for multiple marine autonomous surface ships based on deep reinforcement learning. Rob. Auton. Syst. 2024, 172, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.F.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y. Autonomous decision-making scheme for multi-ship collision avoidance with iterative observation and inference. Ocean Eng. 2020, 197, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simola, J.; Poyhonen, J.; Acad Conf, L.T.D. Emerging Cyber risk Challenges in Maritime Transportation. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security (ICCWS), State Univ New York, Albany, NY, USA, 17–18 March 2022; pp. 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.; Theotokatos, G.; Boulougouris, E. Robust Decision-Making for the Reactive Collision Avoidance of Autonomous Ships against Various Perception Sensor Noise Levels. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandavasi, B.N.J.; Venkataraman, H.; Gidugu, A.R. Machine learning-based electro-magnetic field guided localization technique for autonomous underwater vehicle homing. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.-M. Marine Object Segmentation and Tracking by Learning Marine Radar Images for Autonomous Surface Vehicles. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 10062–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tychola, K.A.; Kalampokas, T.; Papakostas, G.A. Quantum Machine Learning-An Overview. Electronics 2023, 12, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maray, M.; Alghamdi, M.; Alrayes, F.S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Alazwari, S.; Alabdan, R.; Al Duhayyim, M. Intelligent metaheuristics with optimal machine learning approach for malware detection on IoT-enabled maritime transportation systems. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Y.; Teng, J.K.; Hu, T.; Shi, P.; Wang, S.M. Co-communication Protocol of Underwater Sensor Networks with Quantum and Acoustic Communication Capabilities. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 113, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.W.; Liang, M.H.; Nie, J.T.; Lim, W.Y.B.; Zhang, Y.; Guizani, M. Deep Learning-Powered Vessel Trajectory Prediction for Improving Smart Traffic Services in Maritime Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 3080–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Perera, L.P. A dual linear autoencoder approach for vessel trajectory prediction using historical AIS data. Ocean Eng. 2020, 209, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Shi, G.Y.; Li, S. Online Prediction of Ship Behavior with Automatic Identification System Sensor Data Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.; Perera, L.P. Ship behavior prediction via trajectory extraction-based clustering for maritime situation awareness. J. Ocean. Eng. Sci. 2022, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, J.; Krawczyk, B.; Wozniak, M. Fault diagnosis of marine 4-stroke diesel engines using a one-vs-one extreme learning ensemble. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 57, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.; Heiberg, A.; Rasheed, A.; San, O. COLREG-Compliant Collision Avoidance for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 165344–165364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-h.; Liu, Z.-j. Deep Learning in Unmanned Surface Vehicles Collision-Avoidance Pattern Based on AIS Big Data with Double GRU-RNN. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Cao, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, C.-H. Visual Recognition Based on Deep Learning for Navigation Mark Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32767–32775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurowietz, M.; Langenkaemper, D.; Hosking, B.; Ruhl, H.A.; Nattkemper, T.W. MAIA-A machine learning assisted image annotation method for environmental monitoring and exploration. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, A.; Brito, M.; Sabeur, Z.; Tran-Thanh, L. A machine learning approach for monitoring ship safety in extreme weather events. Saf. Sci. 2021, 141, 105336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.Q.; Yang, Z.L. Towards objective human performance measurement for maritime safety: A new psychophysiological data-driven machine learning method. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 233, 109103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Feng, C.; He, B.; Guo, J.; Wang, D.R.; Lv, P.F. Actuator fault diagnosis in autonomous underwater vehicle based on neural network. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2021, 324, 112668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigin, B.; Celik, M. A Prescriptive Model for Failure Analysis in Ship Machinery Monitoring Using Generative Adversarial Networks. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Huang, J.; Cheng, C.; Sha, Q.; He, B.; Li, G.L. Autonomous underwater vehicle formation control and obstacle avoidance using multi-agent generative adversarial imitation learning. Ocean Eng. 2022, 262, 112182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.W.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.X. Deep hierarchical reinforcement learning based formation planning for multiple unmanned surface vehicles with experimental results. Ocean Eng. 2023, 286, 115577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, H.; Ura, T.; Ieee, I. Fast reinforcement learning algorithm for motion planning of non-holonomic Autonomous Underwater Vehicle in disturbance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2002), Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 September–4 October 2002; pp. 903–908. [Google Scholar]
- Gjaerum, V.B.; Rorvik, E.-L.H.; Lekkas, A.M. Approximating a deep reinforcement learning docking agent using linear model trees. In Proceedings of the European Control Conference (ECC), Delft, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1465–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Gizzini, A.K.; Medjahdi, Y.; Ghandour, A.J.; Clavier, L. Towards Explainable AI for Channel Estimation in Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 7389–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zablocki, E.; Ben-Younes, H.; Pérez, P.; Cord, M. Explainability of Deep Vision-Based Autonomous Driving Systems: Review and Challenges. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2425–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.; Fernandes, L.; Fernandes, J.N.D.; Cardoso, J.S. Explaining Bounding Boxes in Deep Object Detectors Using Post Hoc Methods for Autonomous Driving Systems. Sensors 2024, 24, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazat, S.; Arreche, O.; Abdallah, M. On Evaluating Black-Box Explainable AI Methods for Enhancing Anomaly Detection in Autonomous Driving Systems. Sensors 2024, 24, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Development of Intelligent Marine Traffic Service Application Software for Haikou Bay. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 94, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammedi, W.; Brik, B.; Senouci, S.M. Federated Deep Learning-Based Framework to Avoid Collisions Between Inland Ships. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 30 May–3 June 2022; pp. 967–972. [Google Scholar]
- Harish, A.V.; Tam, K.; Jones, K. Literature review of maritime cyber security: The first decade. Marit. Technol. Res. 2024, 7, 273805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
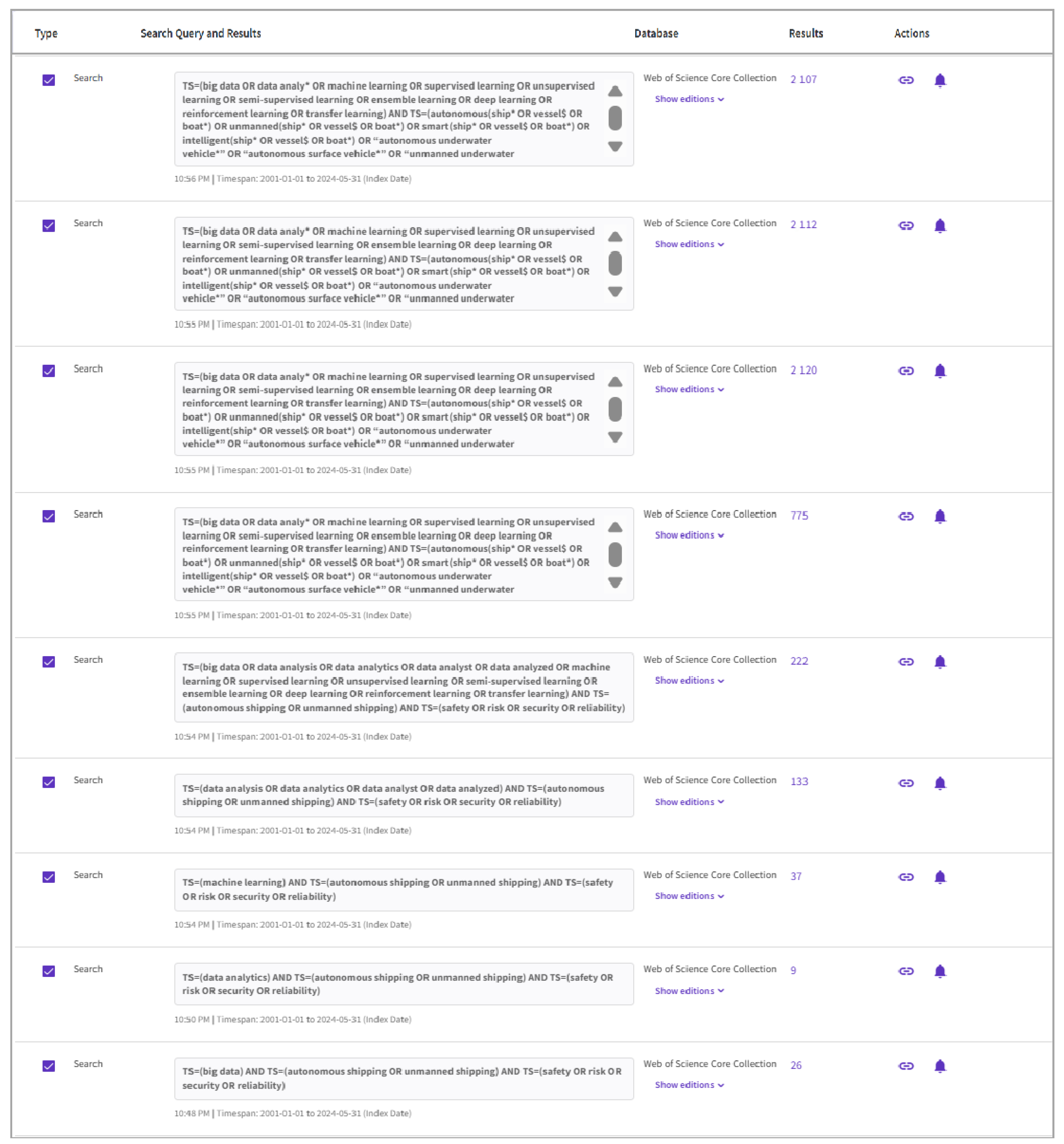

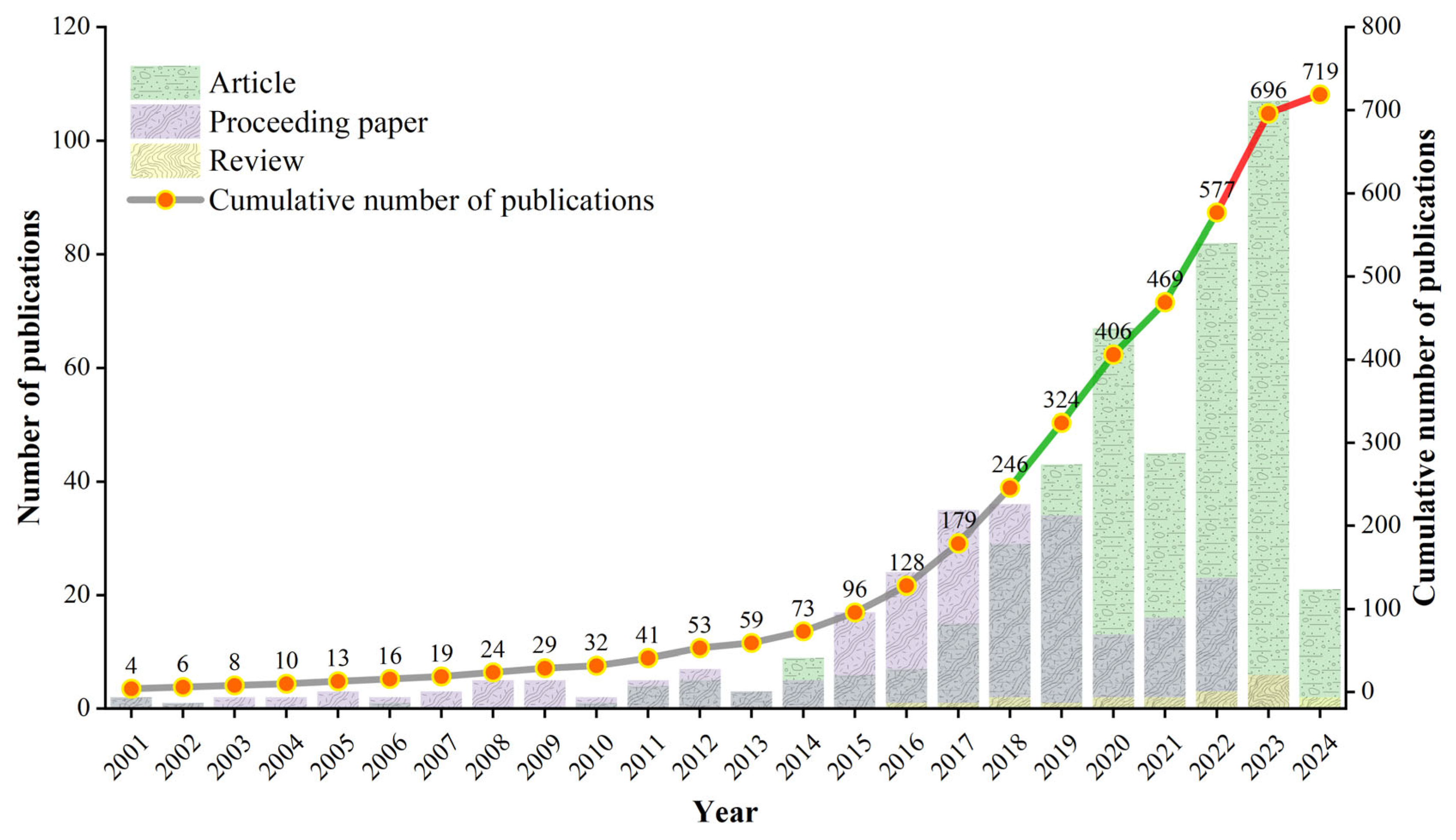

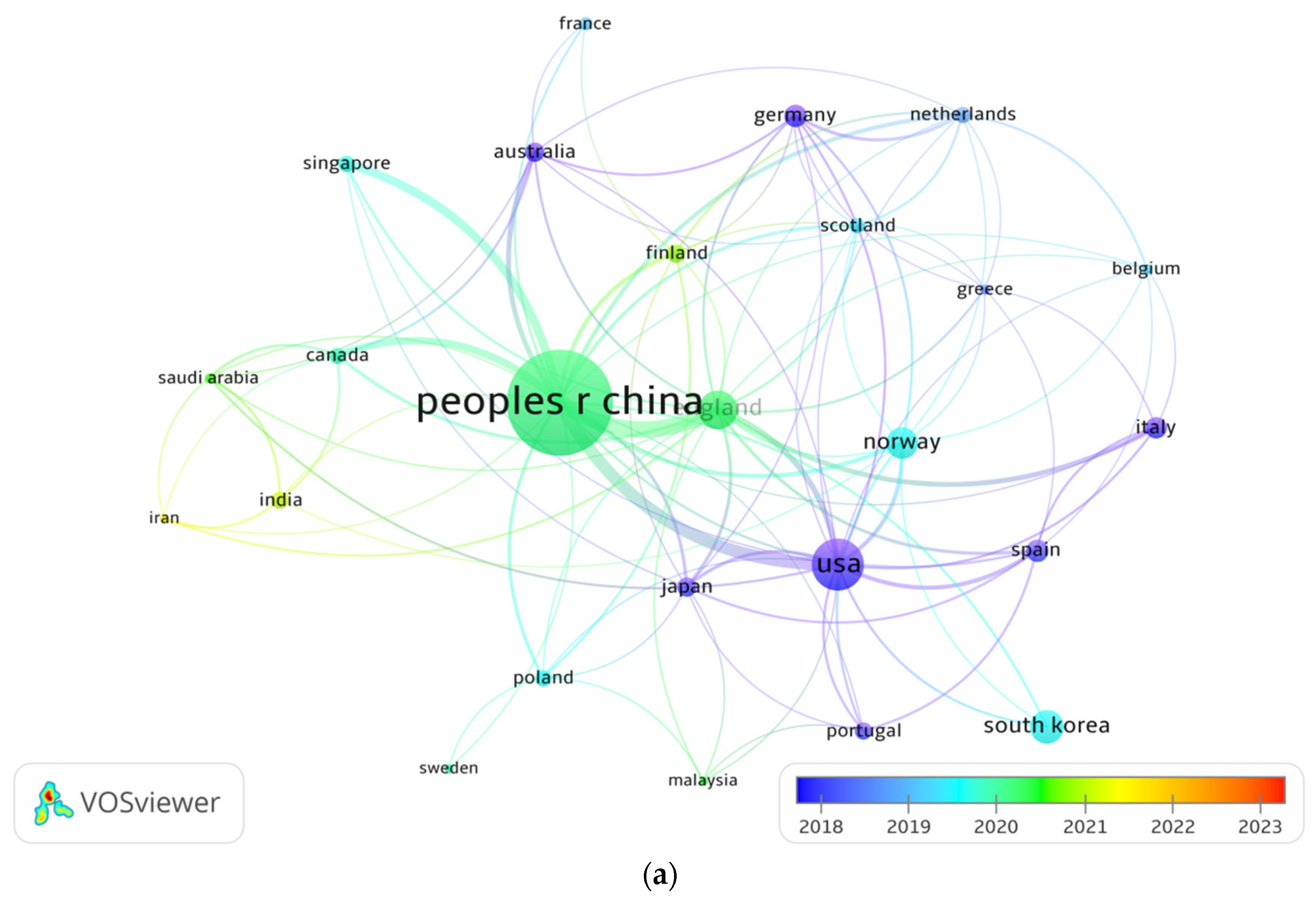
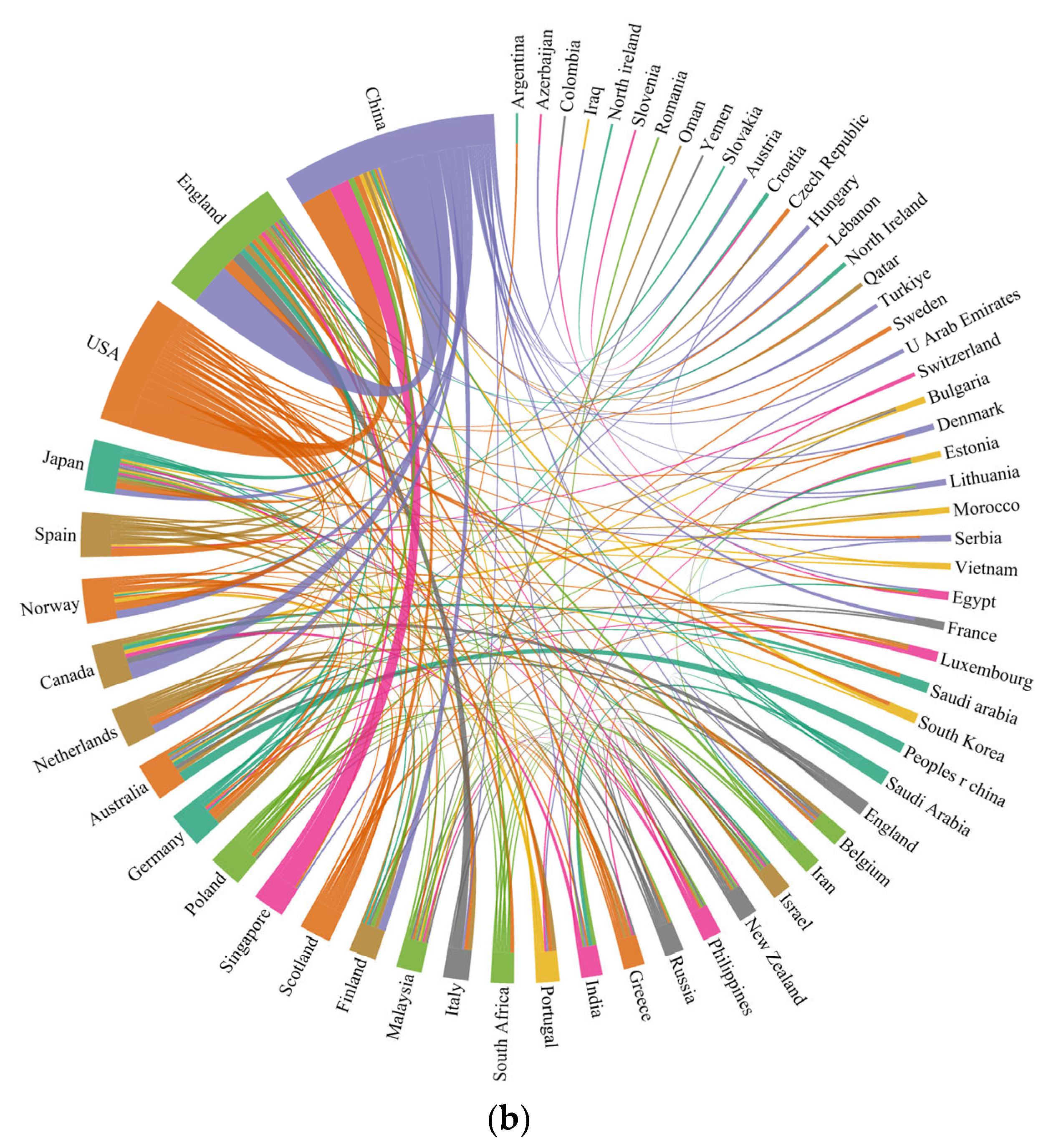






| Criteria | TS | TND | AU | SJP | SC | NI | TC | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | 31 May 2001–31 May 2024 | 719 | 2404 | 399 | 66 | 824 | 11,124 | 8218 |
| Stage | Time Span | Classification Criteria | Number of Articles | Proportion (%) | Number of Proceeding Paper | Proportion (%) | Number of Reviews | Proportion (%) | Total Number | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial germination stage | 2001–2010 | 0 < AINP ≤ 5 | 5 | 0.69% | 27 | 3.76% | 0 | 0 | 32 | 4.44% |
| Initial growth stage | 2011–2015 | 5 < AINP ≤ 25 | 27 | 3.76% | 37 | 5.15% | 0 | 0 | 64 | 8.90% |
| Rapid development stage | 2016 and beyond | AINP > 25 | 416 | 57.86% | 187 | 26.01% | 20 | 2.78% | 603 | 83.86% |
| Total | - | - | 448 | 62.31% | 251 | 34.91% | 20 | 2.78% | 719 | 100.00% |
| Rank | Institution | Country/Region | Links | TLS | NP | P (%) | TC | APY | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dalian Maritime Univ. | China | 53 | 68 | 58 | 8.07% | 1161 | 2020.21 | 20.02 |
| 2 | Wuhan Univ. Technol. | China | 55 | 81 | 44 | 6.12% | 1013 | 2020.30 | 23.02 |
| 3 | Harbin Engn Univ. | China | 17 | 21 | 30 | 4.17% | 449 | 2019.10 | 14.97 |
| 4 | Norwegian Univ Sci and Technol. | Norway | 29 | 36 | 26 | 3.62% | 407 | 2019.75 | 15.65 |
| 5 | Ocean Univ China. | China | 20 | 27 | 23 | 3.20% | 266 | 2018.52 | 11.57 |
| 6 | Chinese Acad. Sci. | China | 25 | 34 | 18 | 2.50% | 211 | 2020.61 | 11.72 |
| 7 | Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. | China | 14 | 26 | 18 | 2.50% | 488 | 2021.06 | 27.11 |
| 8 | Shanghai Maritime Univ. | China | 19 | 20 | 13 | 1.81% | 317 | 2020.00 | 24.38 |
| 9 | Liverpool John Moores Univ. | UK | 13 | 19 | 12 | 1.67% | 169 | 2023.17 | 14.08 |
| 10 | Univ Southampton. | UK | 14 | 16 | 10 | 1.39% | 276 | 2018.60 | 27.60 |
| Rank | Journal Title | Links | TLS | NP | P (%) | TC | APY | AC | IF | 5 Year IF | Journal Category | Corresponding Quartile Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ocean Engineering | 58 | 220 | 68 | 9.45% | 1396 | 2021.76 | 20.53 | 4.6 | 4.8 | Engineering Civil; Engineering Marine; Engineering Ocean; Oceanography | Q1; Q1; Q1; Q1 |
| 2 | Journal of Marine Science and Engineering | 29 | 114 | 36 | 5.00% | 271 | 2022.44 | 7.53 | 2.7 | 2.8 | Engineering Marine; Engineering Ocean; Oceanography | Q1; Q2; Q2 |
| 3 | IEEE Access | 28 | 65 | 29 | 4.03% | 635 | 2019.72 | 21.90 | 3.4 | 3.7 | Computer Science; Electrical and Electronic; Telecommunication | Q2; Q2; Q2 |
| 4 | Sensors | 28 | 69 | 24 | 3.34% | 507 | 2020.83 | 21.13 | 3.4 | 3.7 | Chemistry; Electrical and Electronic; Instruments and Instrumentation | Q2; Q2; Q2 |
| 5 | Applied Sciences | 8 | 8 | 14 | 1.95% | 143 | 2020.93 | 10.21 | 2.5 | 2.7 | Chemistry; Engineering; Materials Science; Physics | Q2; Q1; Q3; Q2 |
| 6 | IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering | 8 | 8 | 14 | 1.95% | 412 | 2015.64 | 29.43 | 3.8 | 4.2 | Engineering Civil; Electrical and Electronic; Engineering Ocean; Oceanography | Q1; Q2; Q2; Q1 |
| 7 | IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems | 22 | 40 | 14 | 1.95% | 327 | 2022.21 | 23.36 | 7.9 | 8.3 | Engineering Civil; Electrical and Electronic; Transportation Science and Technology | Q1; Q1; Q1 |
| 8 | IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems | 16 | 20 | 8 | 1.11% | 243 | 2022.13 | 30.38 | 10.2 | 10.4 | Artificial Intelligence; Hardware and Architecture; Theory and Methods; Electrical and Electronic | Q1; Q1; Q1; Q1 |
| 9 | Reliability Engineering and System Safety | 10 | 21 | 8 | 1.11% | 217 | 2021.63 | 27.13 | 9.4 | 8.1 | Engineering Industrial; Operations Research and Management Science | Q1; Q1 |
| 10 | Applied Ocean Research | 22 | 58 | 7 | 0.97% | 250 | 2021.86 | 35.71 | 4.3 | 4.1 | Engineering Ocean; Oceanography | Q1; Q1 |
| No. | Author | Country | Institution | NP | P (%) | TC | APY | AC | Main Research Interests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zhang, Weidong | China | Shanghai Jiao Tong University | 9 | 1.25% | 373 | 2021.56 | 41.44 | Image restoration; intelligent agriculture; deep learning; image processing and computer vision; control theory and pattern recognition theory and their applications in USV/UAV/AUV |
| 2 | Van Gelder, P. H. A. J. M. | Netherlands | Delft University of Technology | 4 | 0.56% | 370 | 2019.25 | 92.50 | Risk analysis and optimization of systems; processes and structures; infrastructure safety; statistical modelling of high impact low probability (HILP) |
| 3 | Peng, Zhouhua | China | Dalian Maritime University | 5 | 0.70% | 290 | 2019.60 | 58.00 | Guidance, control, and coordination of unmanned surface vehicles; multi-vehicle systems; unmanned surface vehicles; formation control; neural networks |
| 4 | He, Bo | China | Ocean University of China | 14 | 1.95% | 98 | 2018.14 | 7.00 | Mobile robots; unmanned vehicles; precise navigation, and control and communication; AUV design and applications; AUV SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping); AUV control; machine learning |
| 5 | Liu, Yuanchang | England | University College London | 8 | 1.11% | 155 | 2020.63 | 19.38 | Autonomous system; artificial intelligence; marine robotics; statistical machine learning; automation and autonomy; guidance and control of intelligent and autonomous vehicles |
| 6 | Wang, Chengbo | China | Dalian Maritime University | 8 | 1.11% | 69 | 2022.25 | 8.63 | Maritime autonomous surface ships; collision avoidance; decision-making; deep reinforcement learning |
| 7 | Yang, Zaili | England | Liverpool John Moores University | 8 | 1.11% | 149 | 2023.25 | 18.63 | Maritime transport; risk analysis; analysis and modelling of safety; resilience and sustainability of transport networks; maritime and logistics systems |
| 8 | Zhang, Xinyu | China | Dalian Maritime University | 8 | 1.11% | 77 | 2021.88 | 9.63 | Traffic organization optimization; intelligent navigation of USV; analysis and integration of maritime big data; three-dimensional maritime supervision methods; port traffic capability simulation |
| 9 | Yan, Xinping | China | Wuhan University of Technology | 6 | 0.83% | 216 | 2017.50 | 36.00 | Intelligent transport system key technologies; energy efficiency management of vessel; marine system design and control; vessel condition monitoring and fault diagnosis; maritime safety; tribology and safety |
| 10 | Wang, Dan | China | Dalian Maritime University | 4 | 0.56% | 274 | 2018.75 | 68.50 | Marine vehicle control; unmanned surface vehicles; multi-agent system control; tracking control; linear multiagent systems |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, J.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Song, Y.; Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.v.; Papadimitriou, E.; Hu, H. Machine Learning in Maritime Safety for Autonomous Shipping: A Bibliometric Review and Future Trends. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040746
Xue J, Yang P, Li Q, Song Y, Gelder PHAJMv, Papadimitriou E, Hu H. Machine Learning in Maritime Safety for Autonomous Shipping: A Bibliometric Review and Future Trends. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040746
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Jie, Peijie Yang, Qianbing Li, Yuanming Song, P. H. A. J. M. van Gelder, Eleonora Papadimitriou, and Hao Hu. 2025. "Machine Learning in Maritime Safety for Autonomous Shipping: A Bibliometric Review and Future Trends" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040746
APA StyleXue, J., Yang, P., Li, Q., Song, Y., Gelder, P. H. A. J. M. v., Papadimitriou, E., & Hu, H. (2025). Machine Learning in Maritime Safety for Autonomous Shipping: A Bibliometric Review and Future Trends. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040746








