A Bacteria Acclimation Technology Based on Nitrogen Source Regulation and Its Application in the Reinforcement of Island and Reef Slopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Sporosarcina pasteurella Test Protocol
2.2.2. MICP/EICP Aqueous Solution Experiments
2.2.3. MICP/EICP Sand Column and Scouring Experiments
2.2.4. SEM–EDS and XRD Tests
3. Results
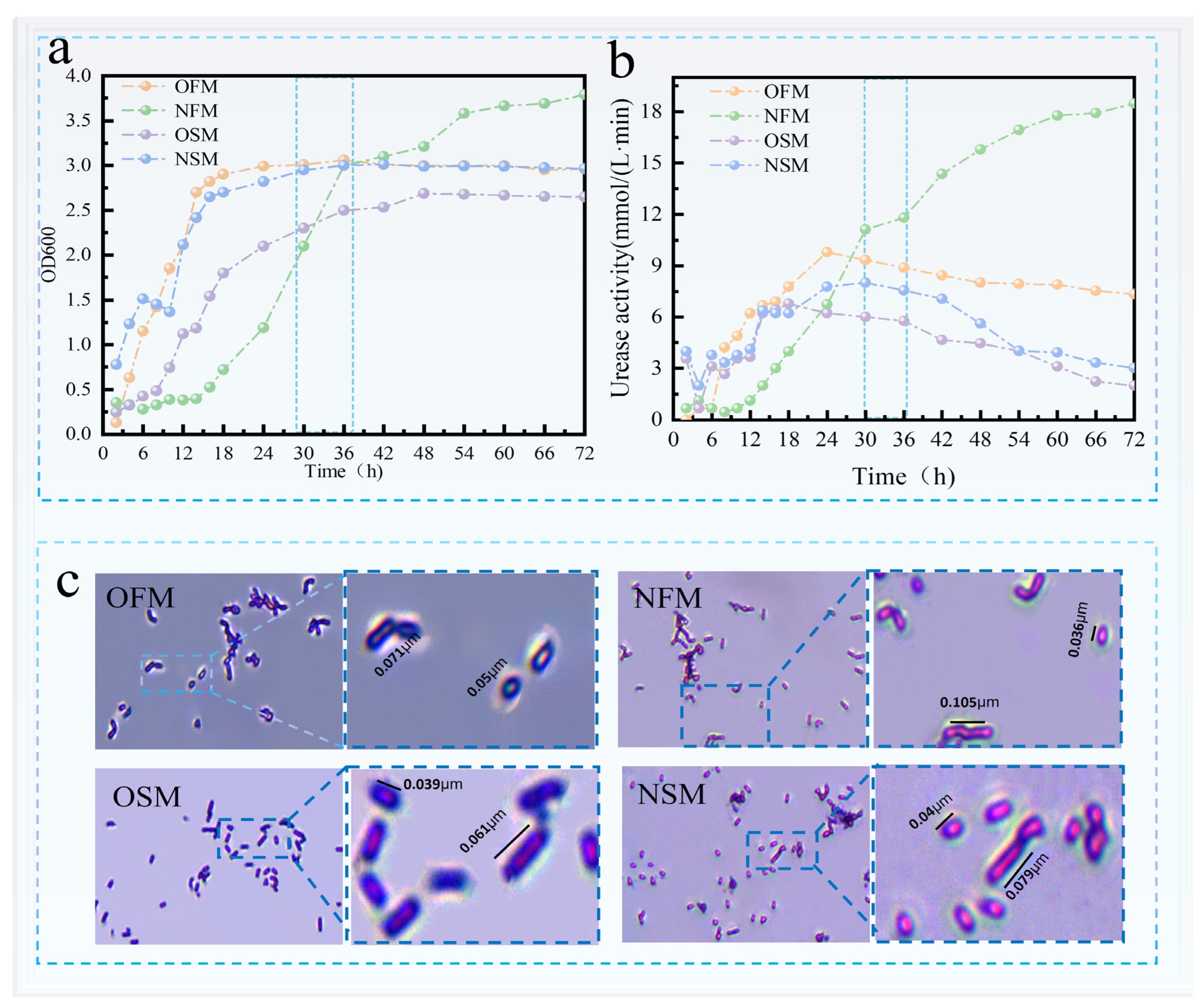
3.1. Analysis of the Results of Bacterial Acclimation Under Novel Nitrogen Source Regulation
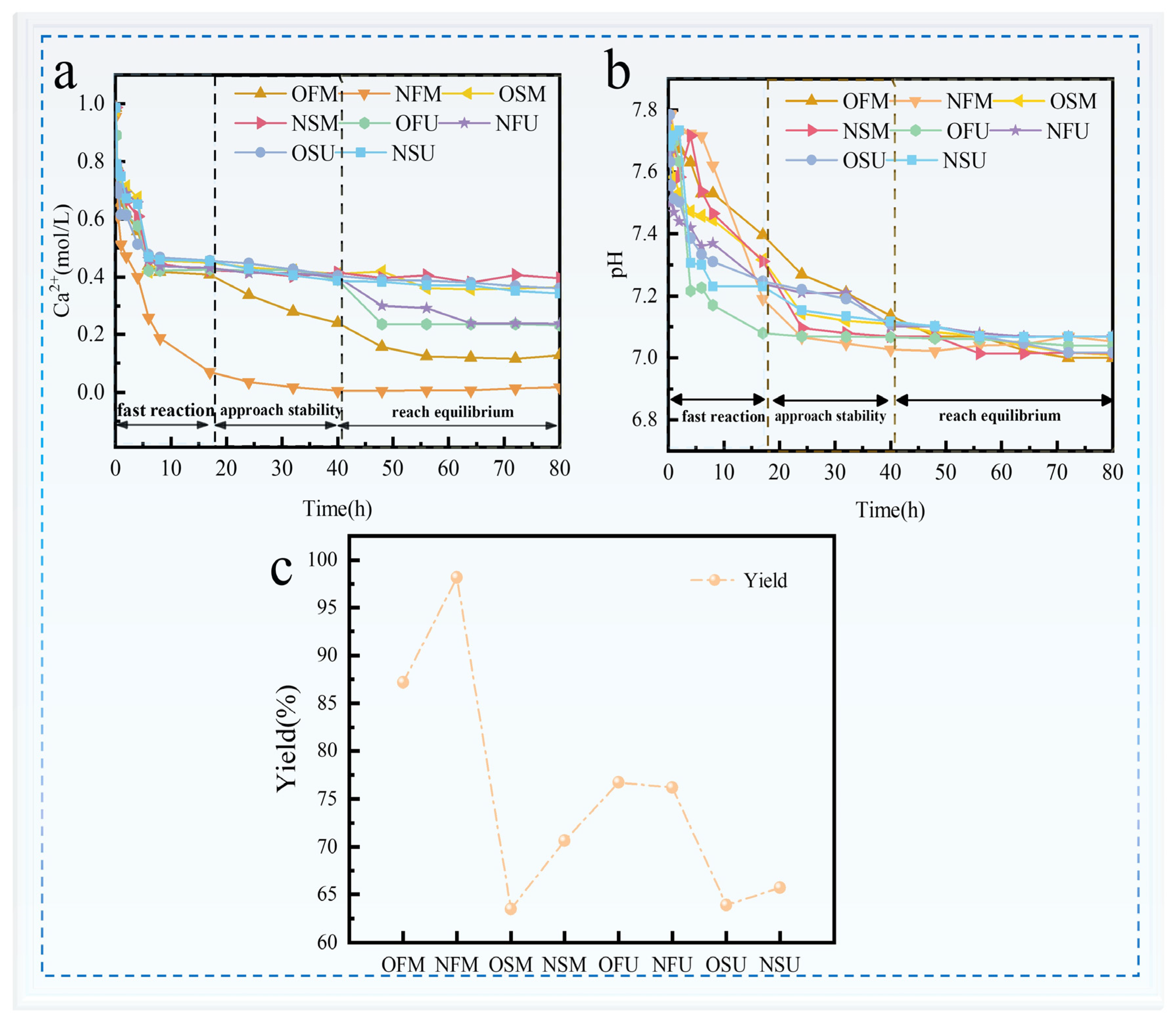
3.2. Analysis of MICP and EICP Aqueous Solution Test Results
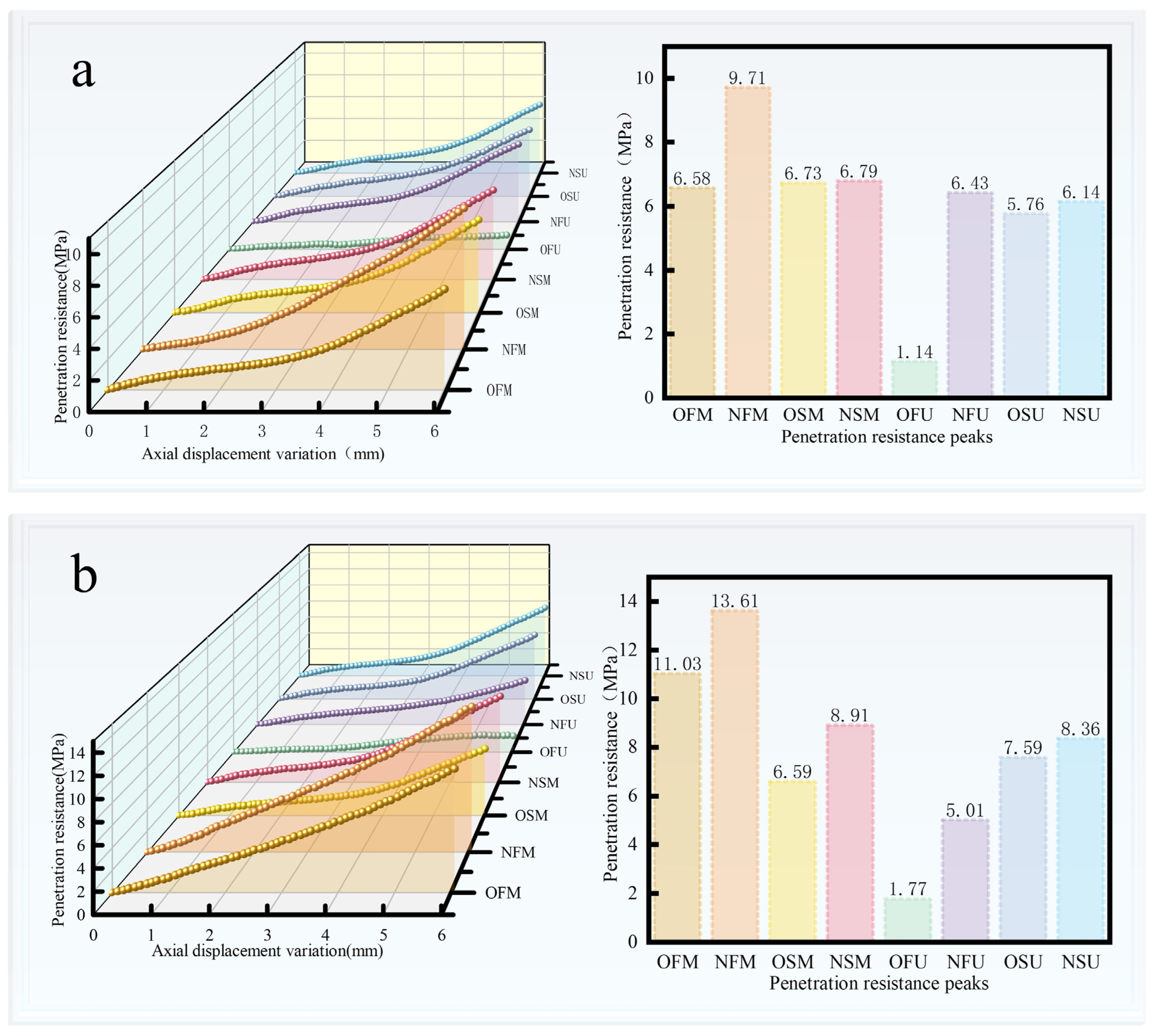
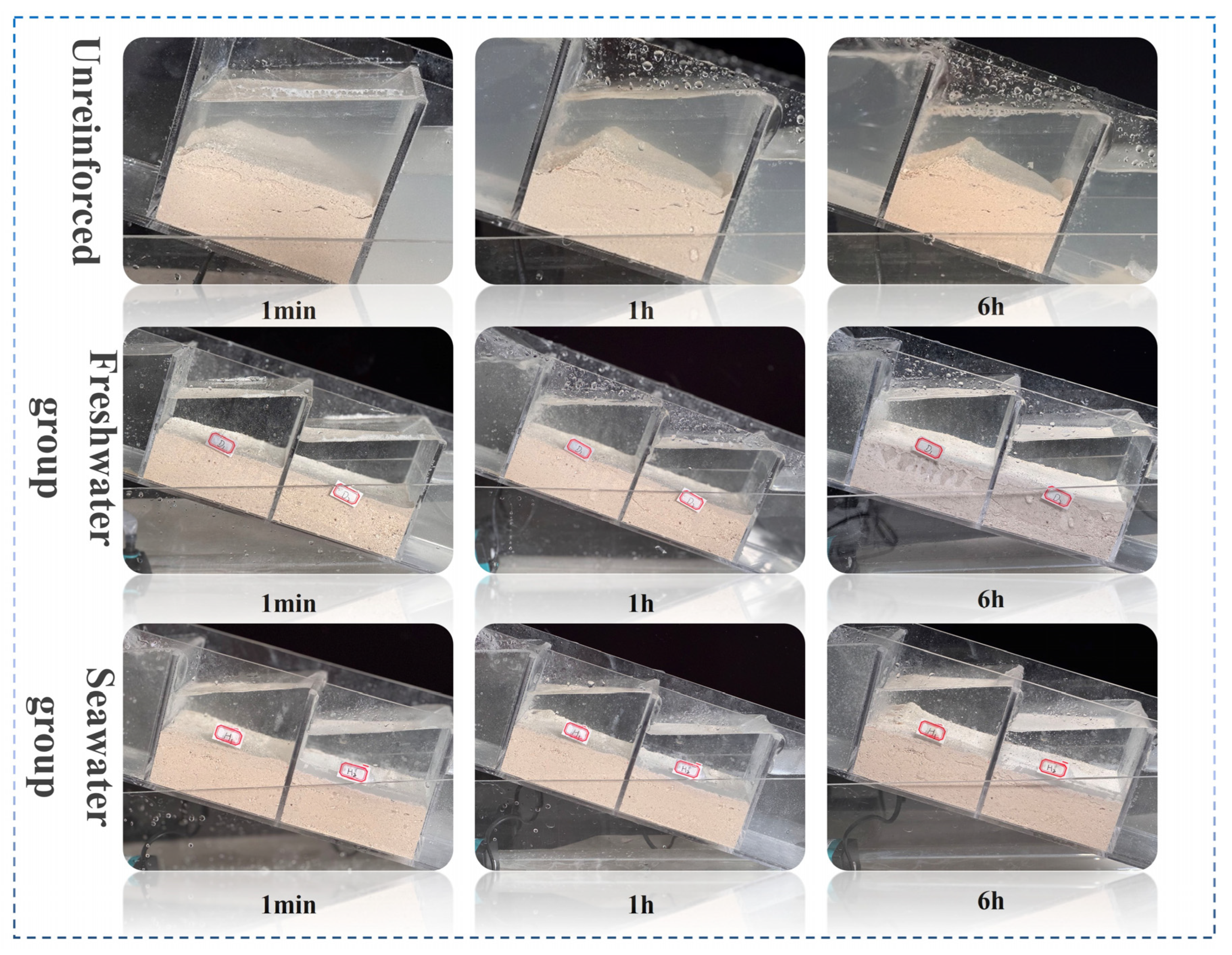
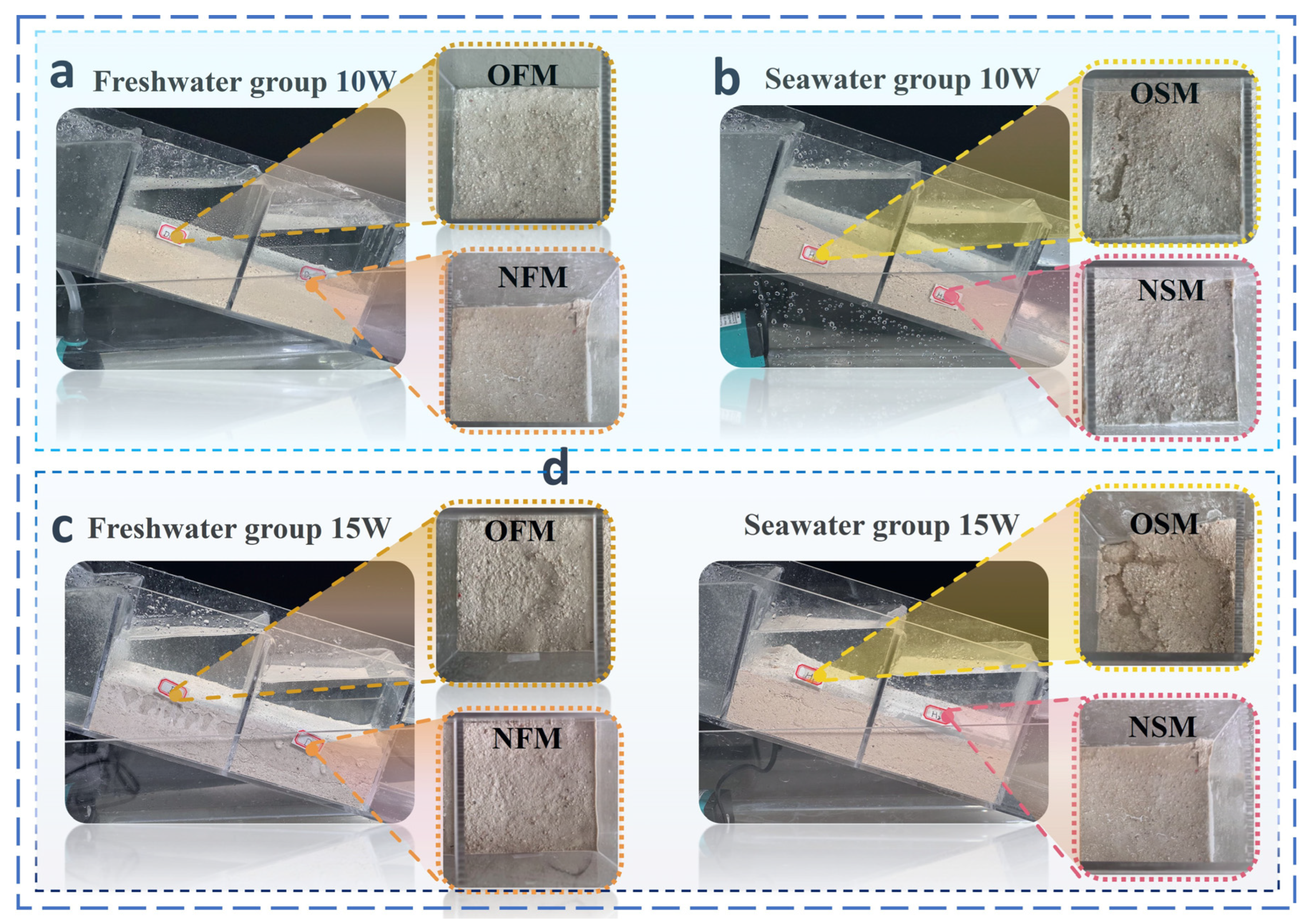
3.3. Analysis of the Results of MICP and EICP Solidified Shore Slope Sand and Simulated Scouring Tests
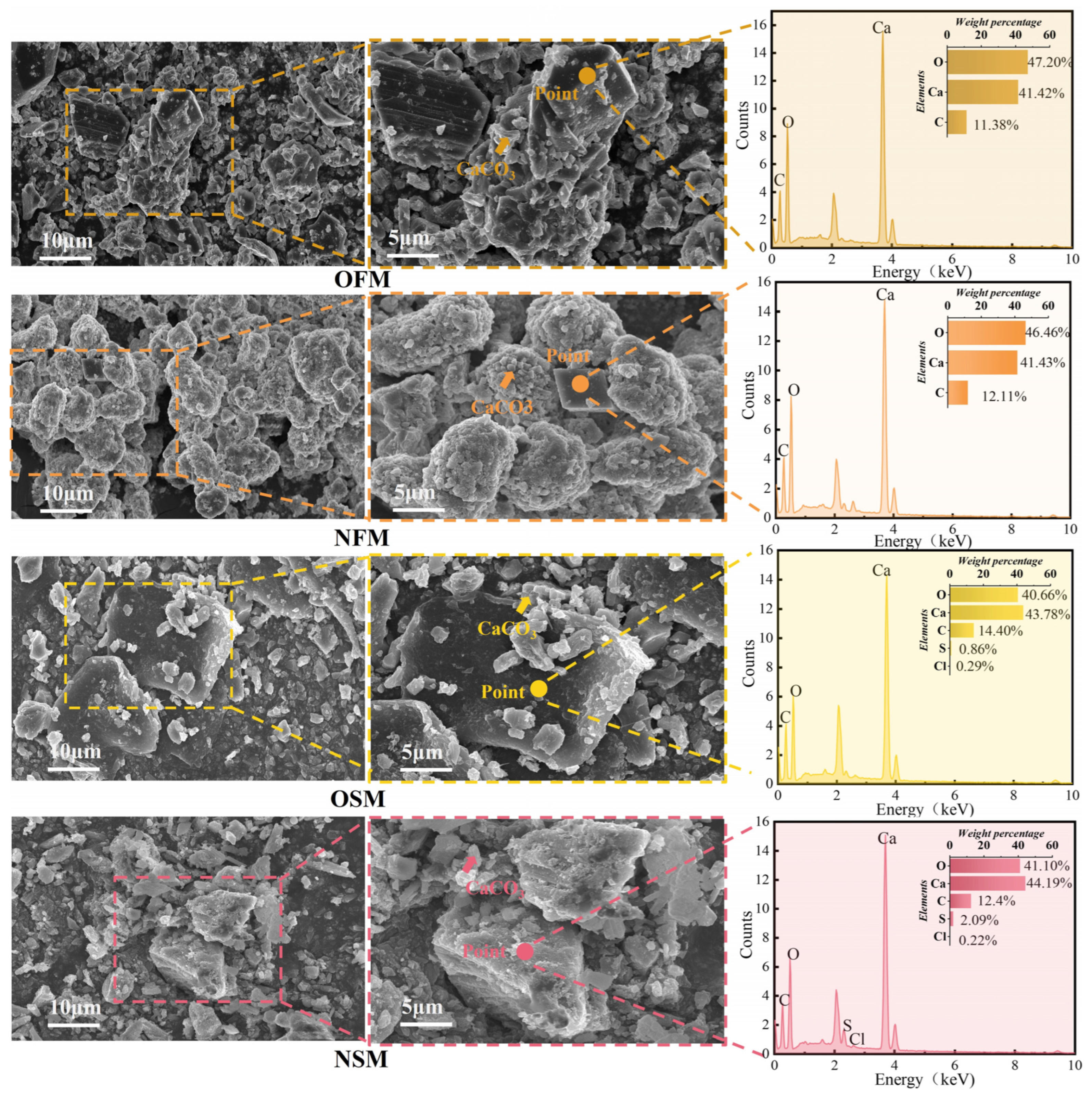
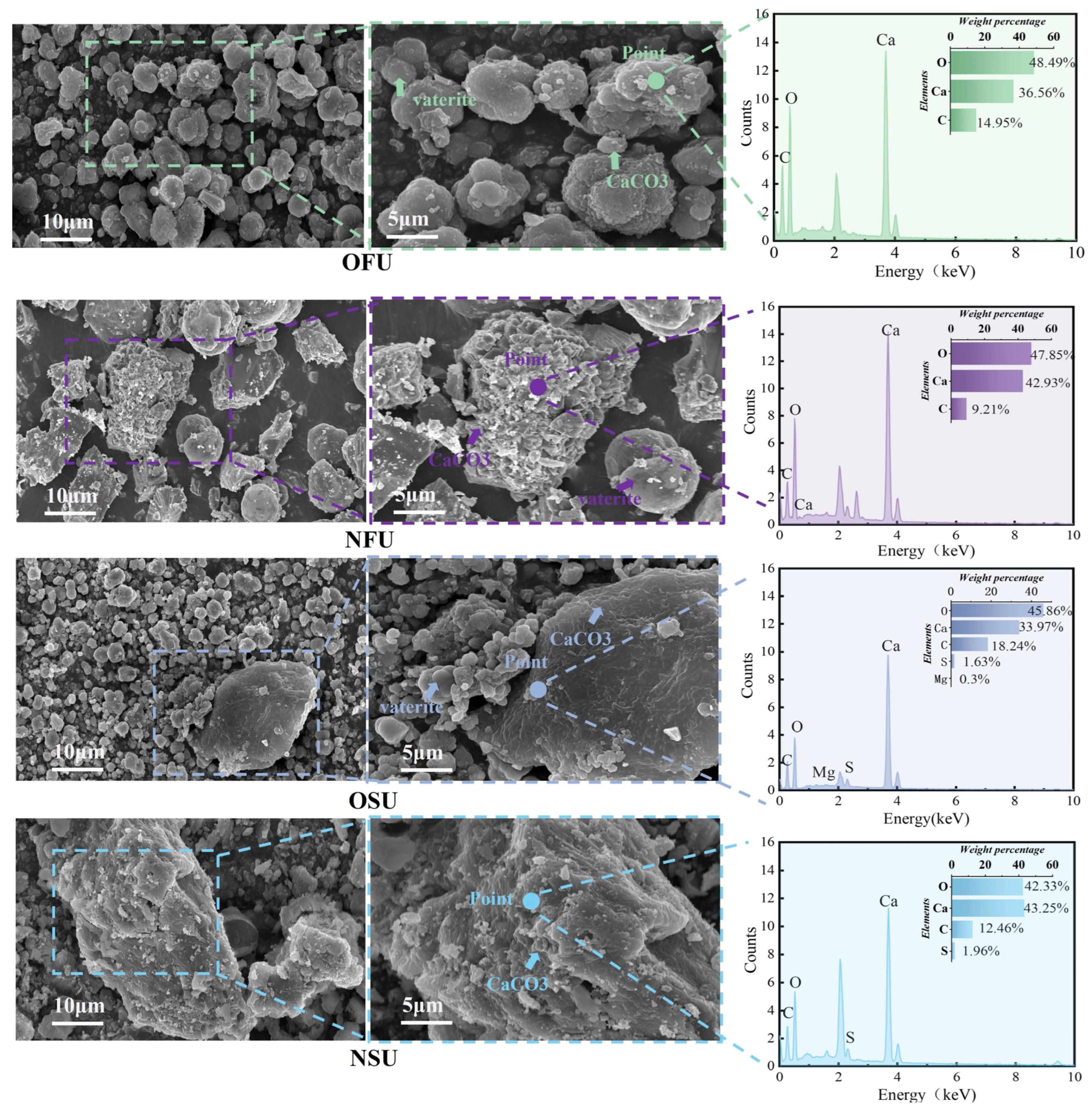
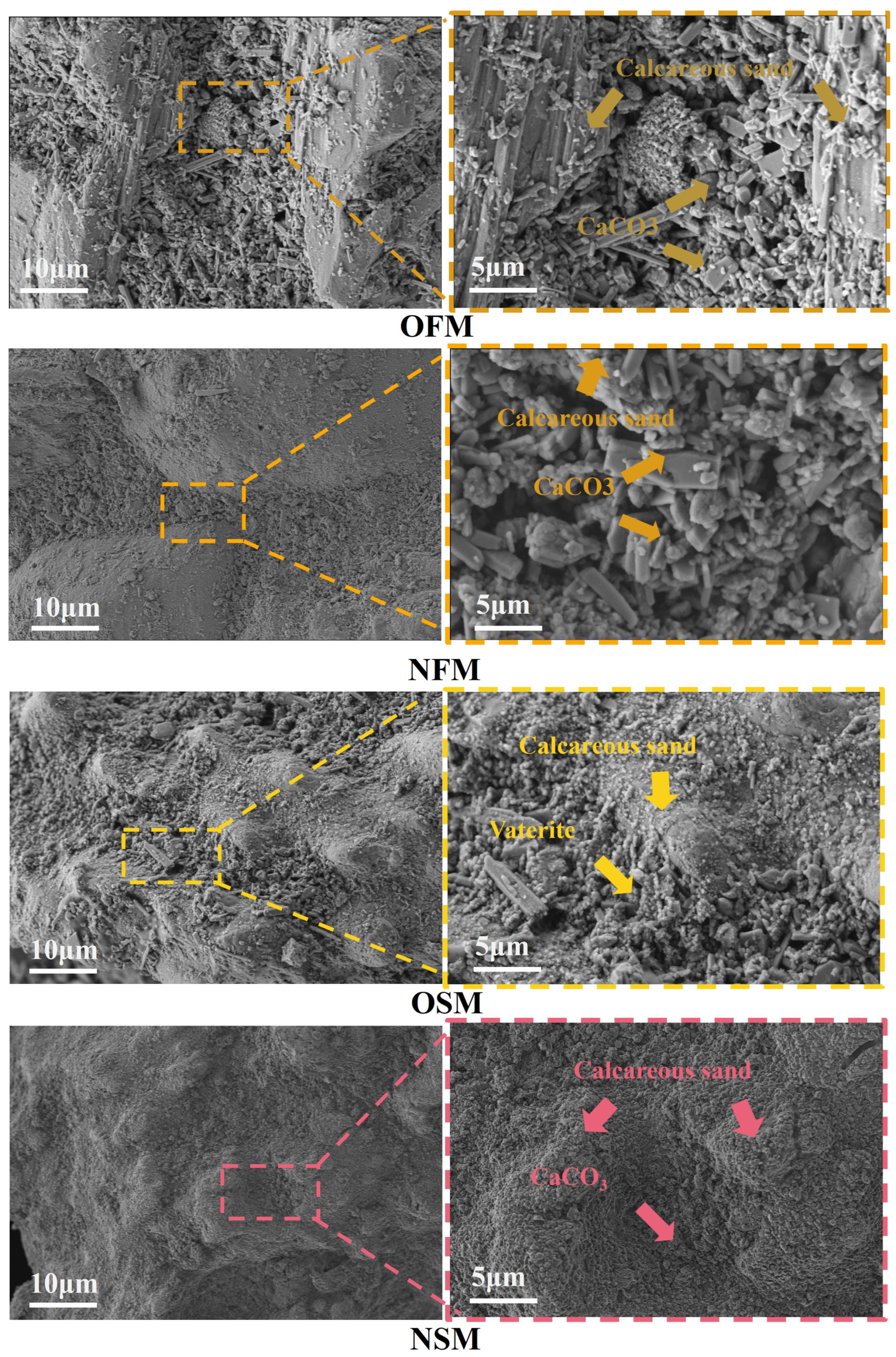
3.4. Microstructure Characterization Analysis
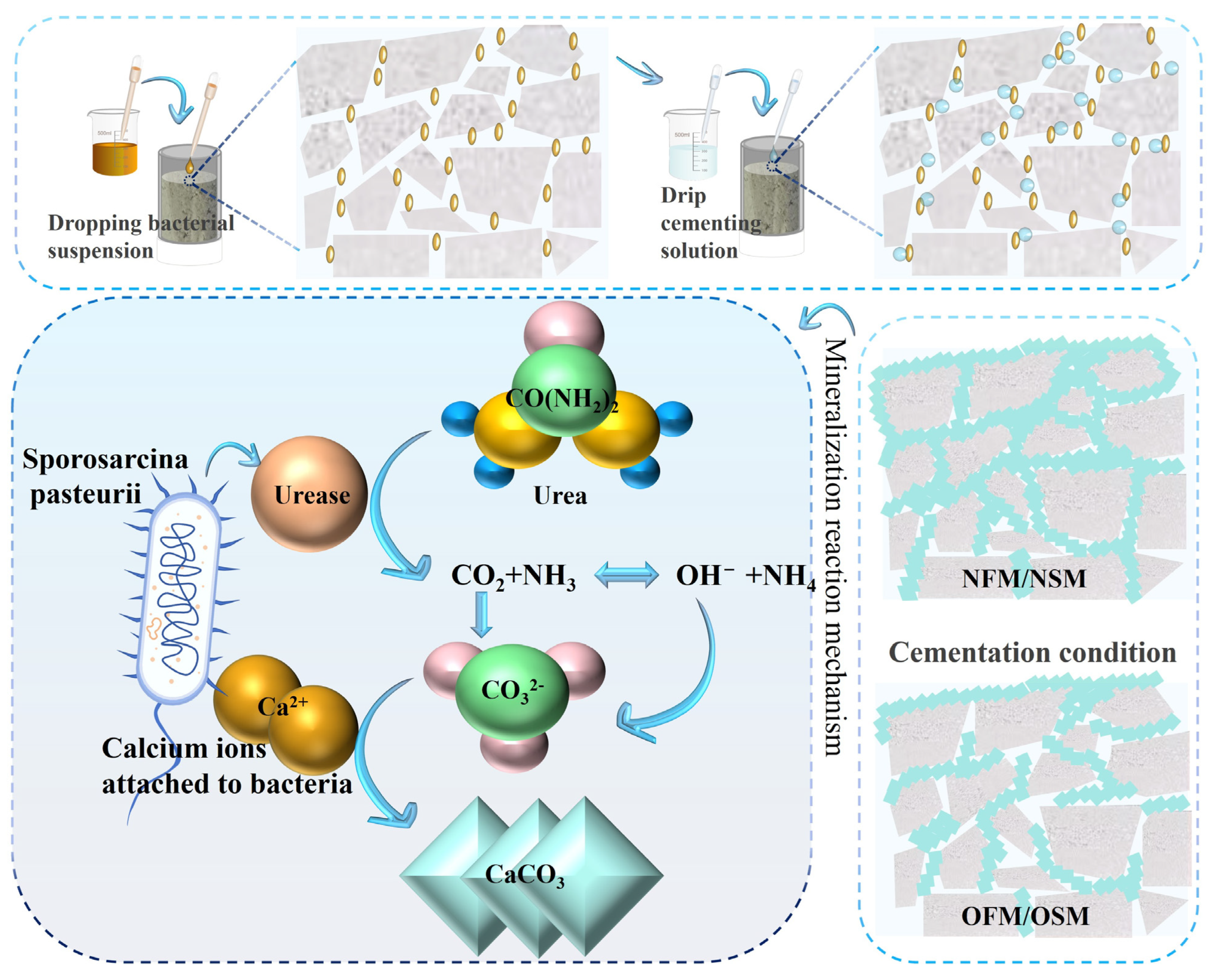
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Behavior and Particle Crushing of Calcareous Sand Retrieved from South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Calcinai, B.; Lim, J.; Schönberg, C.H.L. Bioerosion Research in the South China Sea: Scarce, Patchy and Unrepresentative. Oceans 2023, 4, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, L.T.; Courtney, T.A.; Colella, M.A.; Kupfner Johnson, S.A.; Ruzicka, R.R. The Past, Present, and Future of Coral Reef Growth in the Florida Keys. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5294–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, K.K.; Fehr, Z.; Johnson, S.; Zawada, D. Impact of Hurricane Irma on Coral Reef Sediment Redistribution at Looe Key Reef, Florida, USA. Ocean. Sci. 2024, 20, 661–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohari, A.; Nishigaki, M.; Komatsu, M. Laboratory Rainfall-Induced Slope Failure with Moisture Content Measurement. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, A.; Van Assche, K.; Hornidge, A.-K.; Văidianu, N. Land-Sea Interactions and Coastal Development: An Evolutionary Governance Perspective. Mar. Policy 2020, 112, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumpoulis, V.; Depountis, N.; Dimas, A.; Papatheodorou, G. Presentation and Analysis of the Geotechnical Coastal Vulnerability Index and Validation of Its Application to Coastal Erosion Problems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Williams, A.T.; Anfuso, G. Hard Protection Structures as a Principal Coastal Erosion Management Strategy along the Caribbean Coast of Colombia. A Chronicle of Pitfalls. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonees, T.; Gijón Mancheño, A.; Scheres, B.; Bouma, T.J.; Silva, R.; Schlurmann, T.; Schüttrumpf, H. Hard Structures for Coastal Protection, Towards Greener Designs. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1709–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, A.; Pumijumnong, N.; Arunrat, N.; Punwong, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Chareonwong, U. Nature-Based Solution for Coastal Erosion Protection in the Muddy Coasts: Empirical Perceptibility from the Upper Gulf of Thailand. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 259, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranzini, E. Shore Protection in Italy: From Hard to Soft Engineering … and Back. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y. Multifunctional Integration of Breakwaters: Taking Ecological Protection and Restoration as an Example. E3S Web Conf. 2025, 606, 05006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, A.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Oakley, J.A.; Williams, A.T. Use of Ecosystems in Coastal Erosion Management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Hou, C.; Song, K.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y. Numerical and Experimental Investigation on the Hydrodynamic Characteristics of an Arc-Shaped Plate-Type Breakwater under the Action of Long-Period Waves. Ocean Eng. 2021, 219, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Kuang, C.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, L.; Zou, Q. Effect of Open-Area Ratios on Wave Attenuation over a Submerged Reef Breakwater: An Experimental Study. Ocean Eng. 2024, 312, 119221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xaviour, S.; Shirlal, K.G. Experimental Study of Pipe Artificial Reef on Wave Attenuation. In Proceedings of the Water and Environment, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 19–22 May 2024; Janardhan, P., Choudhury, P., Kumar, D.N., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; Volume 2, pp. 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Shi, L.; Liu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Kuang, C.; Peng, Y.; Qi, H. Experimental Study on the Evolution of Submerged Artificial Sandbar-Beach Profile under the Regular Waves Condition. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 11, 1530904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindeberg, T.; Almström, B.; Skoog, M.; Olsson, P.A.; Hollander, J. Toward a Multifunctional Nature-Based Coastal Defense: A Review of the Interaction between Beach Nourishment and Ecological Restoration. Nord. J. Bot. 2023, 2023, e03751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, D.; Akib, S. A Review of Coastal Protection Using Artificial and Natural Countermeasures—Mangrove Vegetation and Polymers. Eng 2023, 4, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.-J.; Zheng, J.-J.; Chu, J.; Wu, C.-C.; Lai, H.-J. Bio-Mediated Calcium Carbonate Precipitation and Its Effect on the Shear Behaviour of Calcareous Sand. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayananda, N.R.; Wijesinghe, J.; Botheju, S.M.; Perera, W.P.R.T.; Liyanage, J.A. Ocean Warming, Acidification, Plastic Pollution, and Water Quality Deterioration. In Coastal and Marine Pollution; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 111–138. [Google Scholar]
- Rottmueller, M.E.; Storlazzi, C.D.; Frick, F. Coral Reef Restoration Can Reduce Coastal Contamination and Pollution Hazards. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, B.; Pinho, J.; Barros, J.; Antunes do Carmo, J. Optimizing Coastal Protection: Nature-Based Engineering for Longitudinal Drift Reversal and Erosion Reduction. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 256, 107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, E.M.; Aberkan, M.; Saadane, A.; Nmiss, M. Erosion and Shoreline Retreat Indicators in the Rabat-Salé Littoral and Their Impact on Coastal Planning. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2025, 223, 105534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Zhu, D.; Hu, P. Coastal Erosion Risk Assessment of Hainan Island, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, C.-S.; Jiang, N.-J.; Pan, X.-H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shi, B. Microbial-induced Carbonate Precipitation (MICP) Technology: A Review on the Fundamentals and Engineering Applications. Env. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, V.L.; Bragagnolo, L.; Reginatto, C.; Thomé, A. Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP): Review from an Engineering Perspective. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2022, 40, 2379–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ali, A.; Su, J.; Huang, T.; Hou, C.; Li, X. Microbial-Induced Calcium Precipitation: Bibliometric Analysis, Reaction Mechanisms, Mineralization Types, and Perspectives. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, X.; Wu, S.; Chu, J. Presence of Mg-Calcite and Its Influence on MICP and EICP Processes. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Song, Y.; Fang, H.; Wang, D.; Lu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, L.; Song, X. Fiber-Reinforced Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation (MICP) for Enhancing Soil Stability: Mechanisms, Effects, and Future Prospects. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Miao, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Shi, W.; Kawasaki, S. State-of-the-Art Review of Soil Erosion Control by MICP and EICP Techniques: Problems, Applications, and Prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Satyam, N.; Reddy, K.R. Effect of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Engineering Properties of Biocemented Sand under Different Treatment Conditions. Eng. Geol. 2021, 284, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, C.; Tang, C.-S.; Xie, Y.-H.; Yin, L.-Y.; Cheng, Q.; Shi, B. Bio-Remediation of Desiccation Cracking in Clayey Soils through Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP). Eng. Geol. 2020, 264, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Li, S.-K.; Li, Z.-Y.; Garg, A. Exploring the Application of the MICP Technique for the Suppression of Erosion in Granite Residual Soil in Shantou Using a Rainfall Erosion Simulator. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 3273–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarà Saracho, A.; Haigh, S.K.; Ehsan Jorat, M. Flume Study on the Effects of Microbial Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation (MICP) on the Erosional Behaviour of Fine Sand. Géotechnique 2021, 71, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lyu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Huan, C.; Jiang, X.; Yan, Z.; Tan, Z. Microbiologically Induced Calcite Precipitation for in Situ Stabilization of Heavy Metals Contributes to Land Application of Sewage Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y. An Optimum Condition of MICP Indigenous Bacteria with Contaminated Wastes of Heavy Metal. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Application of Microbial-Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation in Wave Erosion Protection of the Sandy Slope: An Experimental Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, M.D.; Ruffo, S.; Lacambra, C.; Meliane, I.; Hale, L.Z.; Shepard, C.C.; Beck, M.W. The Role of Ecosystems in Coastal Protection: Adapting to Climate Change and Coastal Hazards. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 90, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Cord-Ruwisch, R.; Shahin, M.A. Cementation of Sand Soil by Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation at Various Degrees of Saturation. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryono, L.R.; Titisari, A.D.; Warmada, I.W.; Kawasaki, S. Comparative Characteristics of Cement Materials in Natural and Artificial Beachrocks Using a Petrographic Method | Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 3943–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayanthara, P.G.N.; Dassanayake, A.B.N.; Nakashima, K.; Kawasaki, S. Microbial Induced Carbonate Precipitation Using a Native Inland Bacterium for Beach Sand Stabilization in Nearshore Areas. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salifu, E.; MacLachlan, E.; Iyer, K.R.; Knapp, C.W.; Tarantino, A. Application of Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation in Erosion Mitigation and Stabilisation of Sandy Soil Foreshore Slopes: A Preliminary Investigation. Eng. Geol. 2016, 201, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; Wu, C.; Ni, P.; Jang, B.-A. Assessment of Erosion Resistance of Biocemented Sandy Slope Subjected to Wave Actions. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 105, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.A.; Jamieson, K.; Cheng, L. Microbial-Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Coastal Erosion Mitigation of Sandy Slopes. Géotechnique Lett. 2020, 10, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-P.; Ye, J.-H.; Ko, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-R. An Experimental Investigation of Microbial-Induced Carbonate Precipitation on Mitigating Beach Erosion. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Cao, P.; Chen, X.; Chen, W. Experimental Study on Coastal Sediment Reinforcement by Induced Carbonate Precipitation by Different Enzyme Sources. Water 2023, 15, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, V.; Satyam, N. Enhancing the Durability of Coastal Soil Treated with Fiber-Reinforced Microbial-Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP). Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 150, 104106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Efficiency and Characteristics of MICP in Environments with Elevated Salinity, Diminished Oxygen, and Lowered Temperature: A Microfluidics Investigation. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2025, 151, 04024151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Ran, Y.; Shi, J.; Duan, M.; Ouyang, Z. Physical Property of MICP-Treated Calcareous Sand under Seawater Conditions by CPTU. Biogeotechnics 2025, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, C.; Lu, X.; Zhu, D.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Q. Soil Improvement by Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP): A Review about Mineralization Mechanism, Factors, and Soil Properties. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-S.; Yin, L.; Jiang, N.; Zhu, C.; Zeng, H.; Li, H.; Shi, B. Factors Affecting the Performance of Microbial-Induced Carbonate Precipitation (MICP) Treated Soil: A Review. Env. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Du, K.; Wen, K.; Armwood-Gordon, C.; Li, L. Influence of Rainfall-Induced Erosion on the Stability of Sandy Slopes Treated by MICP. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Wang, H.; Zha, F.; Liu, C.; Zhou, A.; Ban, R. Exploring the Uniformity of MICP Solidified Fine Particle Silt with Different Sample Preparation Methods. Biogeotechnics 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, P.; Cao, L.; Chen, W. Mechanical Properties and Constitutive Model of Calcareous Sand Strengthened by MICP. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Tong, Z.; Wu, W.; Chen, X.; Deng, X.; Xie, Y. Research on the Effect of Natural Seawater in Domesticating Bacillus pasteurii and Reinforcing Calcareous Sand. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Cao, P.; Wang, Z.; Tan, Z.; Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. Application of SCMs and Seawater to Cement-Bonded Calcareous Sand: Macro Performance, Micro Mechanism, and Strength Prediction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 419, 135560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Xu, S.; Zhao, X.; Cao, P.; Wang, J. Strength Mechanism and Electrochemical Characterization of Cement-Bonded Calcareous Sand in Different Water Environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarun, A.; Jha, A.K. Influence of Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation Technique on Mitigating Rainfall-Induced Surface Erosion of the Ganga River Sand. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2025, 29, 04024046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Minerals. In Geology and Mineral Resources; Upadhyay, R.K., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 293–350. ISBN 978-981-96-0598-9. [Google Scholar]
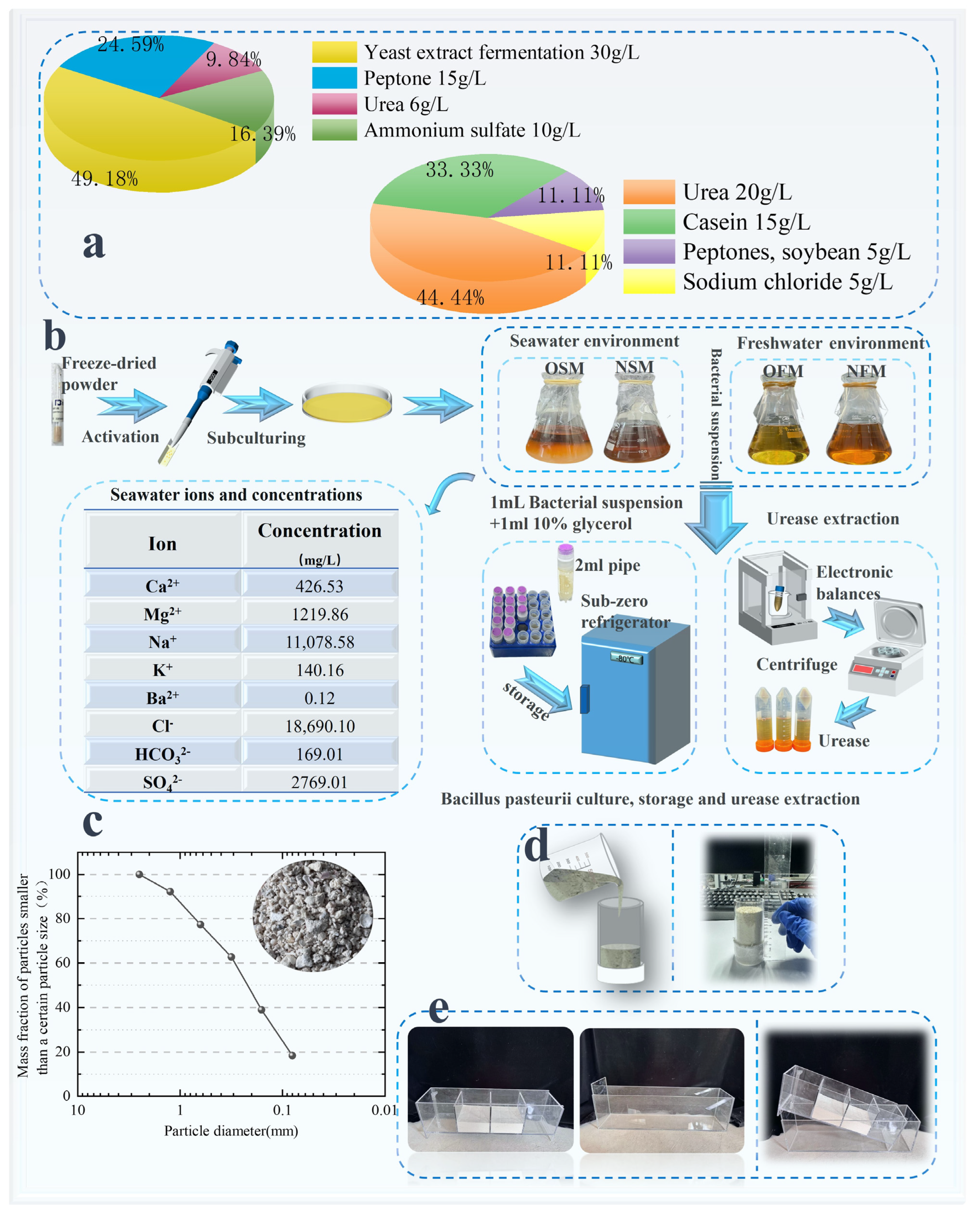




| Culture Medium | Group | Liquid Medium Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Deionized Water Seawater | ||
| The traditional urea medium with deionized water | OFM | 250 -- |
| The traditional urea medium with seawater water | OSM | -- 250 |
| The modified medium with deionized water | NFM | 250 -- |
| The modified medium with seawater water | NSM | -- 250 |
| Group | Bacterial Volume (mL) | Cemented Volume (mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OFM | 40 mL | 160 mL | 1:1 |
| OSM | |||
| NFM | |||
| NSM |
| Group | Bacterial Volume (mL) | Cemented Volume (mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OFU | 40 mL | 160 mL | 1:1 |
| OSU | |||
| NFU | |||
| NSU |
| Group | Number of Injections | Inject Volume (mL) | Number of Times the Cementation Solution Is Injected | Cemented Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFM | 1 | 10 | 2 | 20 |
| 2 | 5 | |||
| OSM | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2 | 5 | |||
| NFM | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2 | 5 | |||
| NSM | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2 | 5 |
| Group | Number of Injections | Inject Volume (mL) | Number of Times the Cementation Solution Is Injected | Cemented Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFU | 1 | 10 | 2 | 20 |
| 2 | 5 | |||
| OSU | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2 | 5 | |||
| NFU | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2 | 5 | |||
| NSU | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Cao, P.; Liu, S.; Xie, Y.; Xie, Y. A Bacteria Acclimation Technology Based on Nitrogen Source Regulation and Its Application in the Reinforcement of Island and Reef Slopes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050848
Chen X, Wang Z, Cao L, Cao P, Liu S, Xie Y, Xie Y. A Bacteria Acclimation Technology Based on Nitrogen Source Regulation and Its Application in the Reinforcement of Island and Reef Slopes. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050848
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xin, Ziyu Wang, Liang Cao, Peng Cao, Shuyue Liu, Yu Xie, and Yingqi Xie. 2025. "A Bacteria Acclimation Technology Based on Nitrogen Source Regulation and Its Application in the Reinforcement of Island and Reef Slopes" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050848
APA StyleChen, X., Wang, Z., Cao, L., Cao, P., Liu, S., Xie, Y., & Xie, Y. (2025). A Bacteria Acclimation Technology Based on Nitrogen Source Regulation and Its Application in the Reinforcement of Island and Reef Slopes. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050848







