Effects of Monsoon Circulation on Bedload Transport in the Qiongzhou Strait and Adjacent Seas Based on SCHISM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
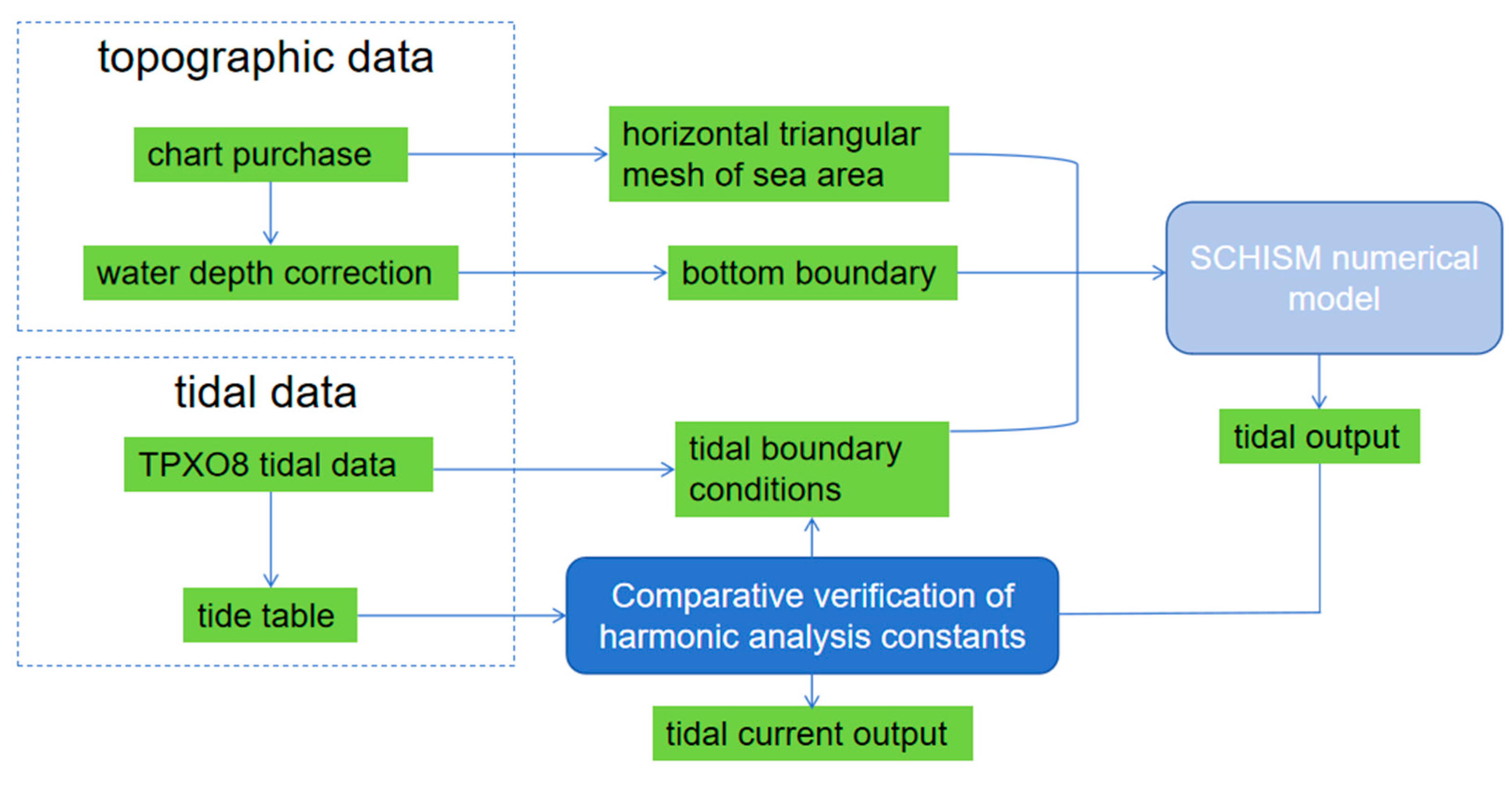
2.1. SCHISM Numerical Mode Settings
2.2. Calculation of Bedload Sediment Transport
3. Results
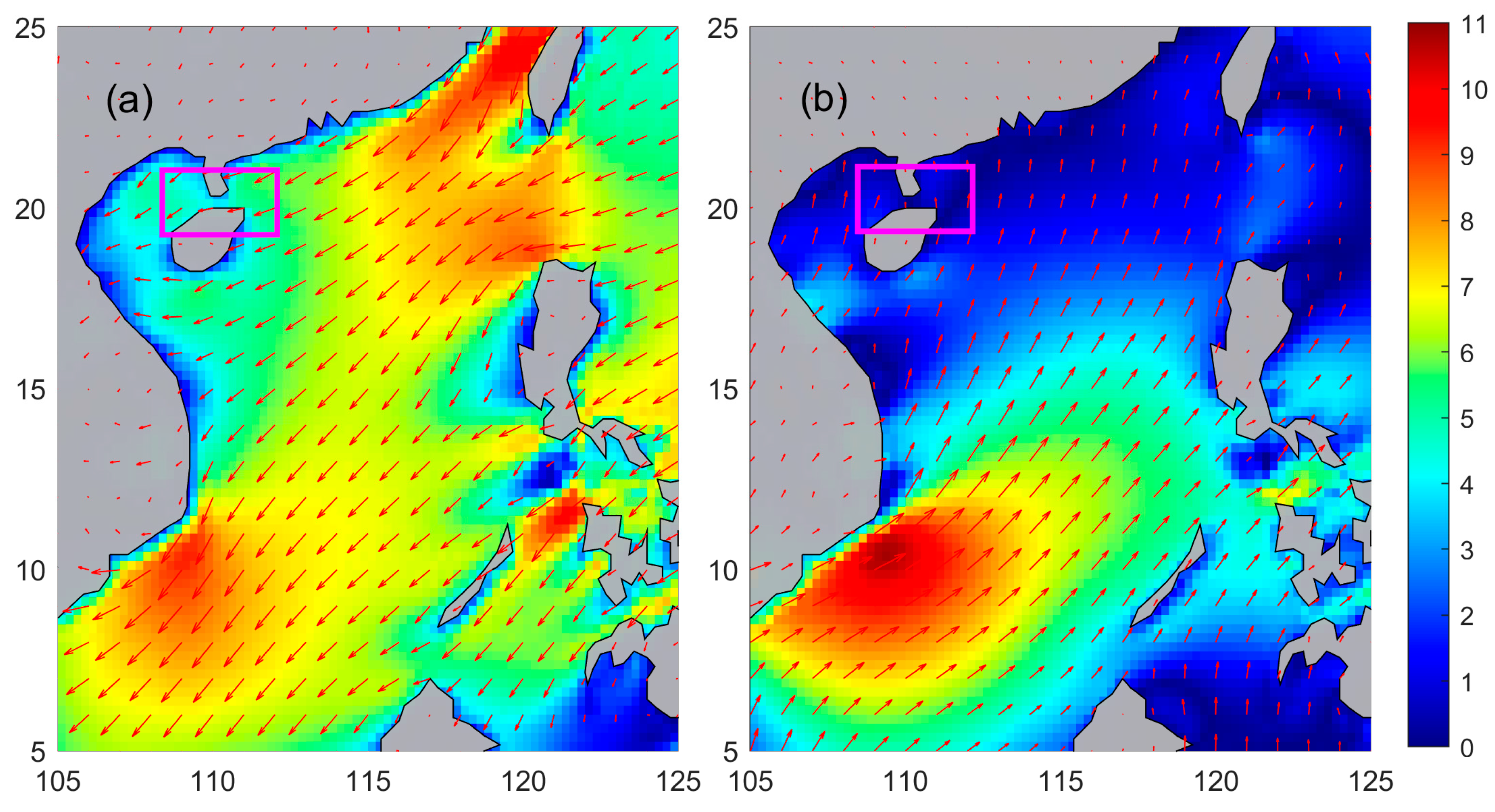
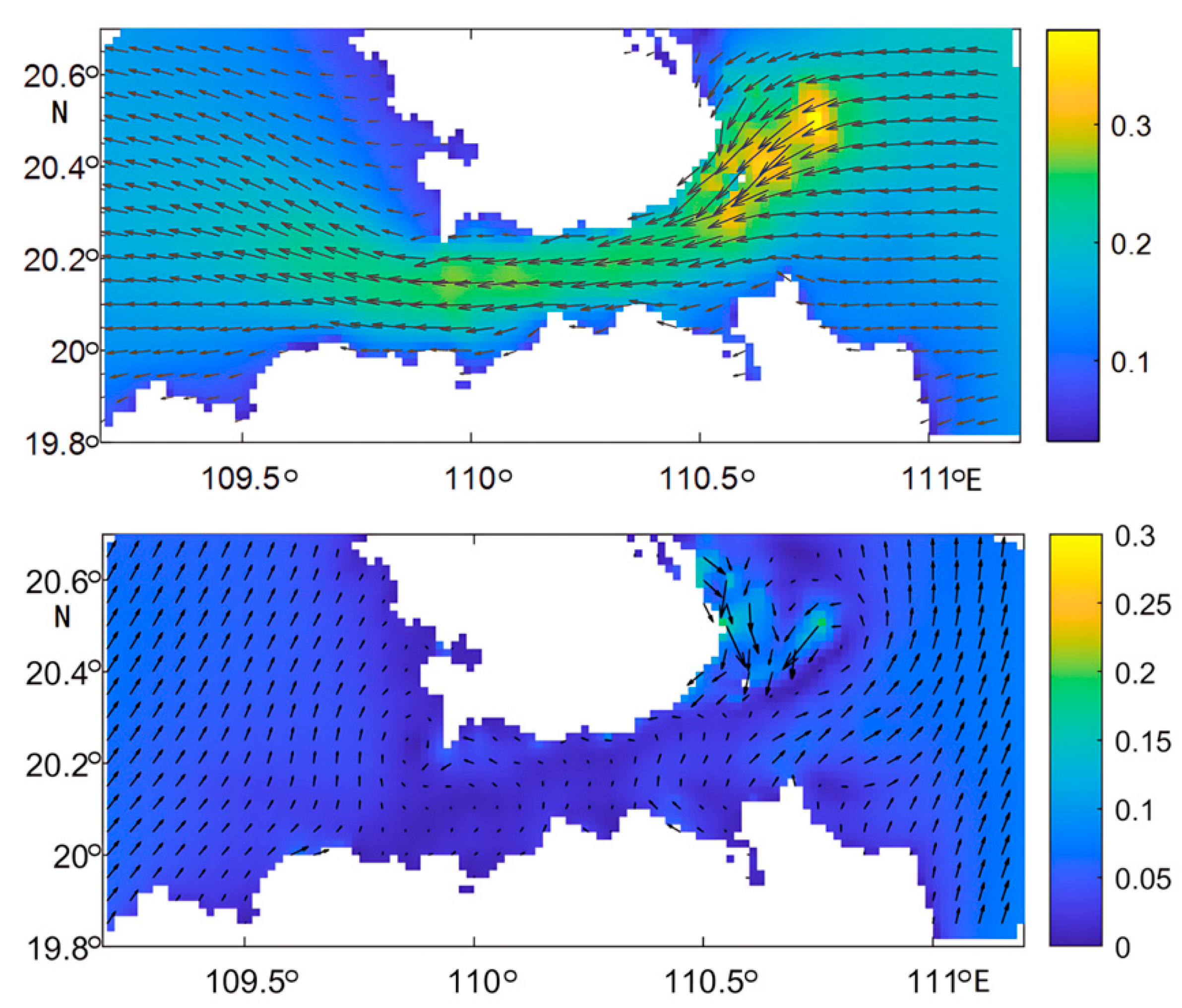
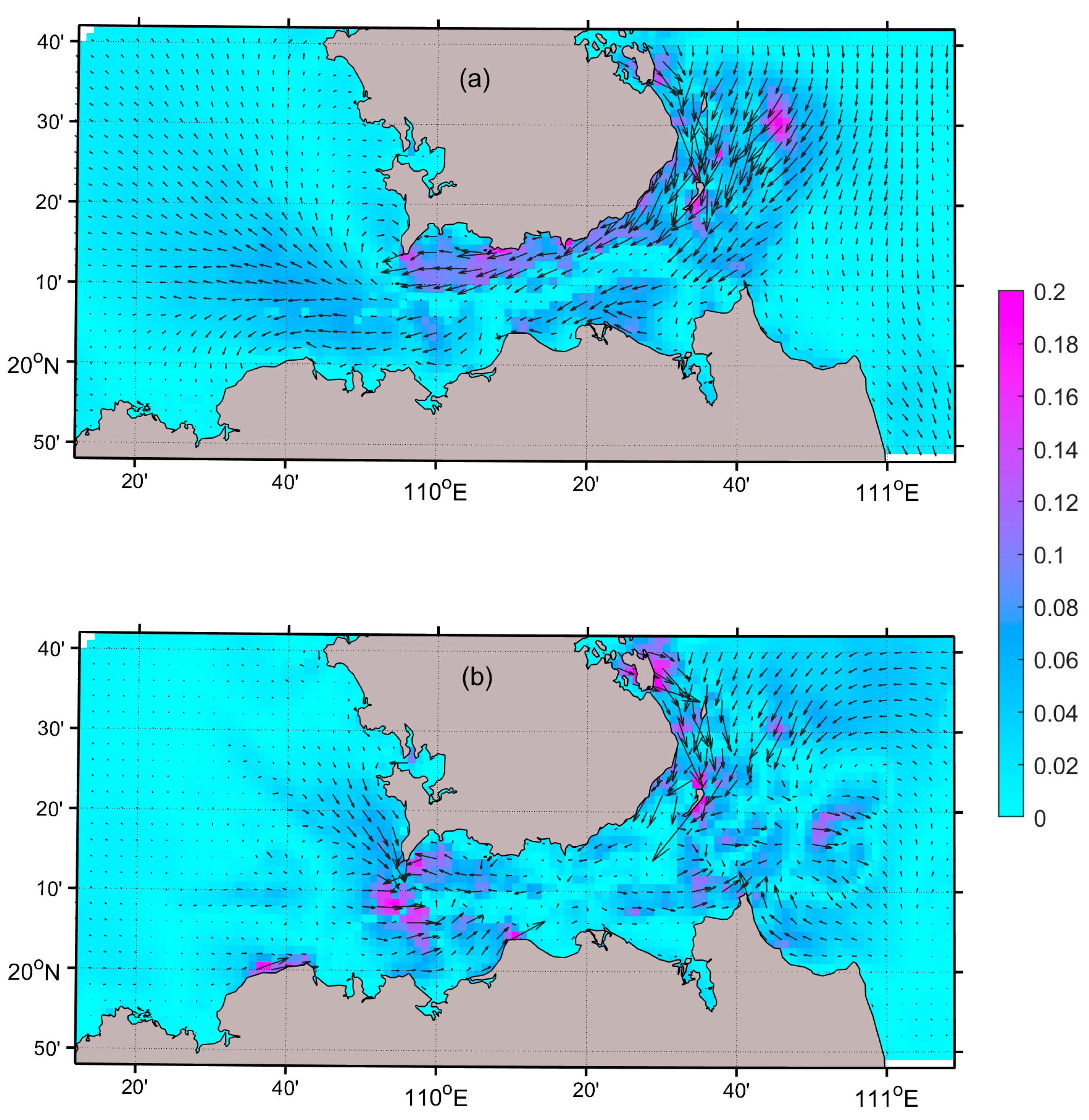
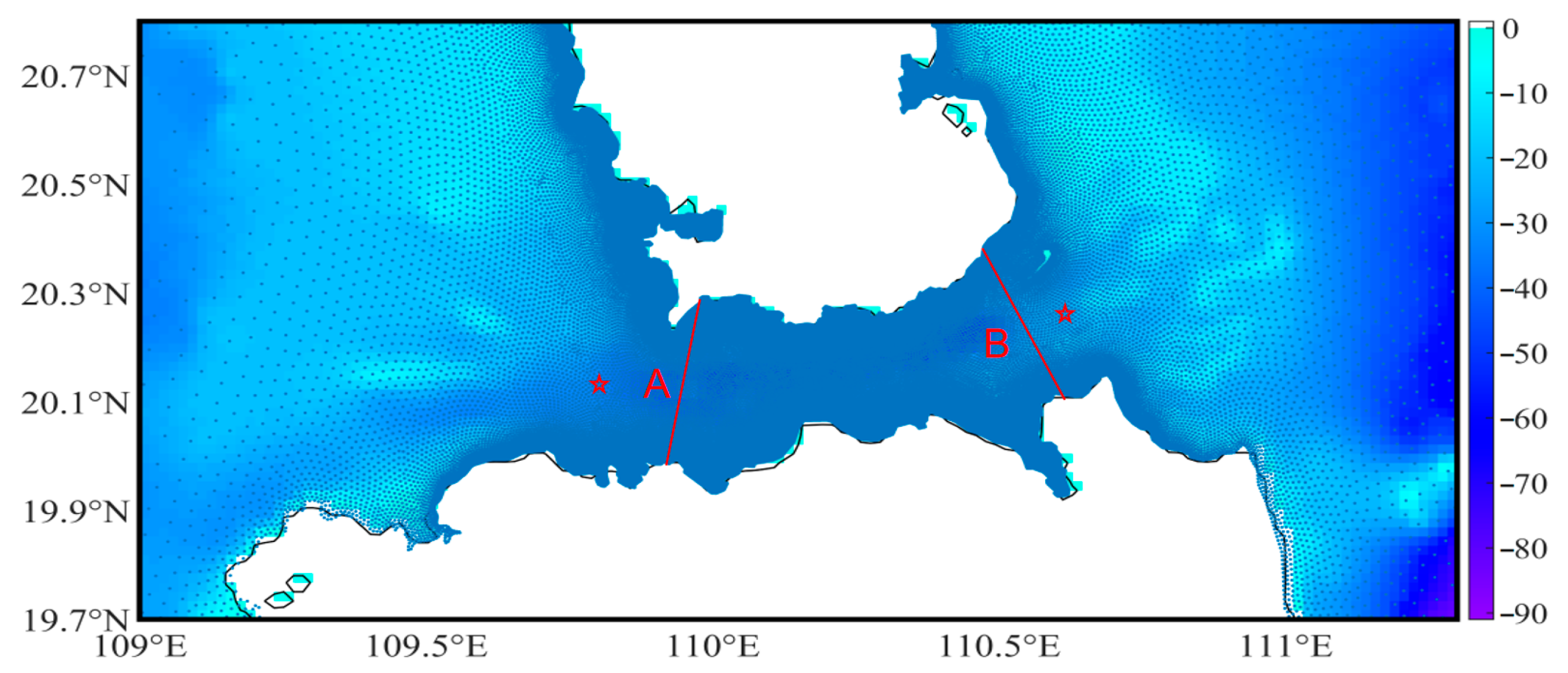
3.1. Monsoon Circulation in the Waters Surrounding the Qiongzhou Strait
3.2. Net Sediment Transport per Unit Width
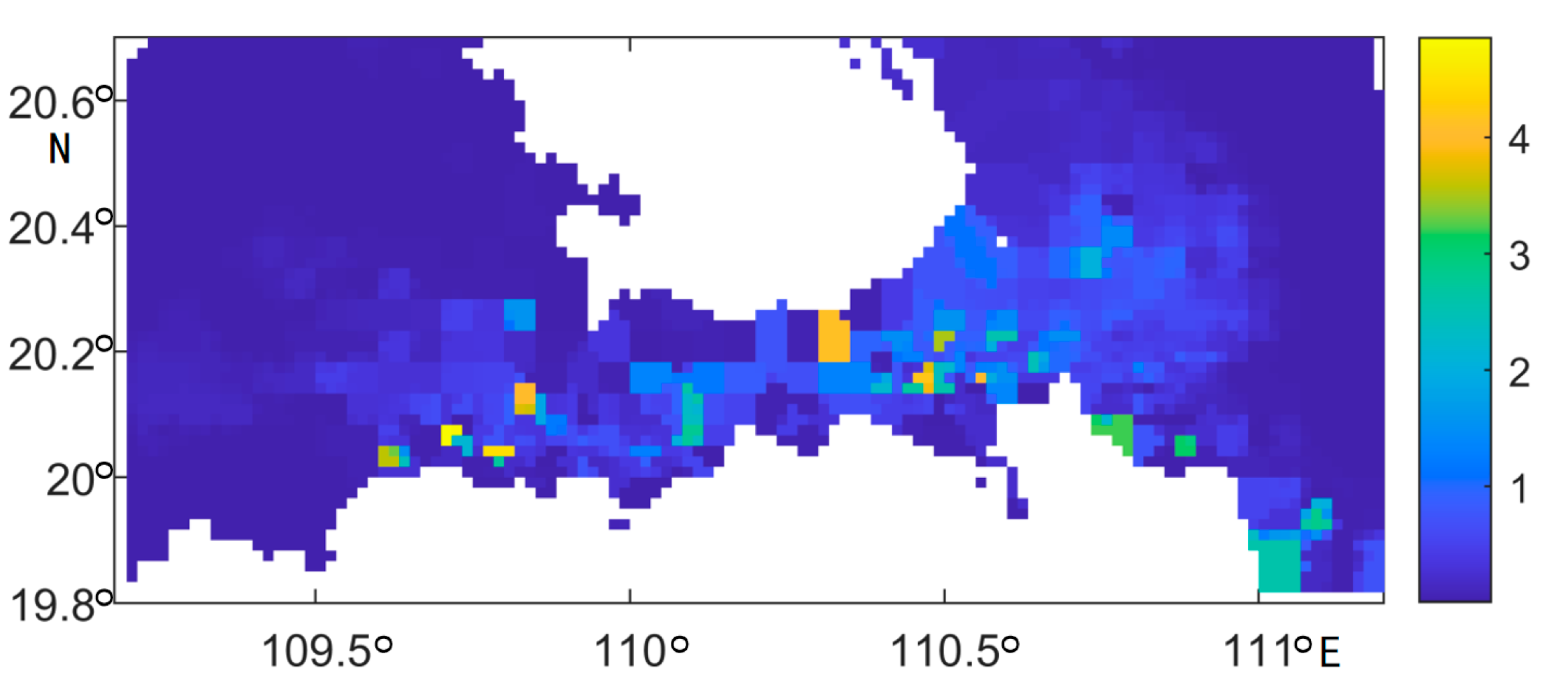
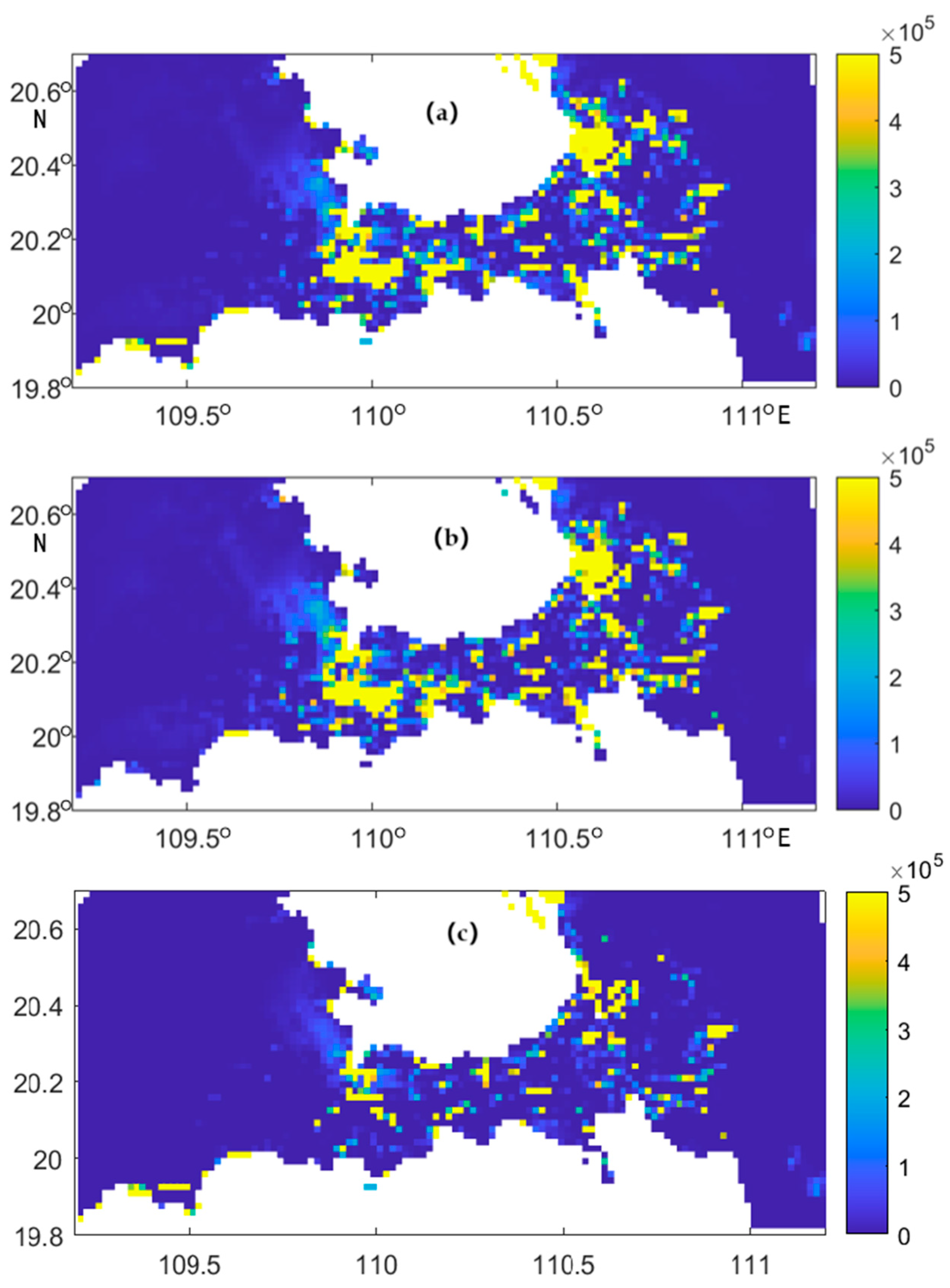
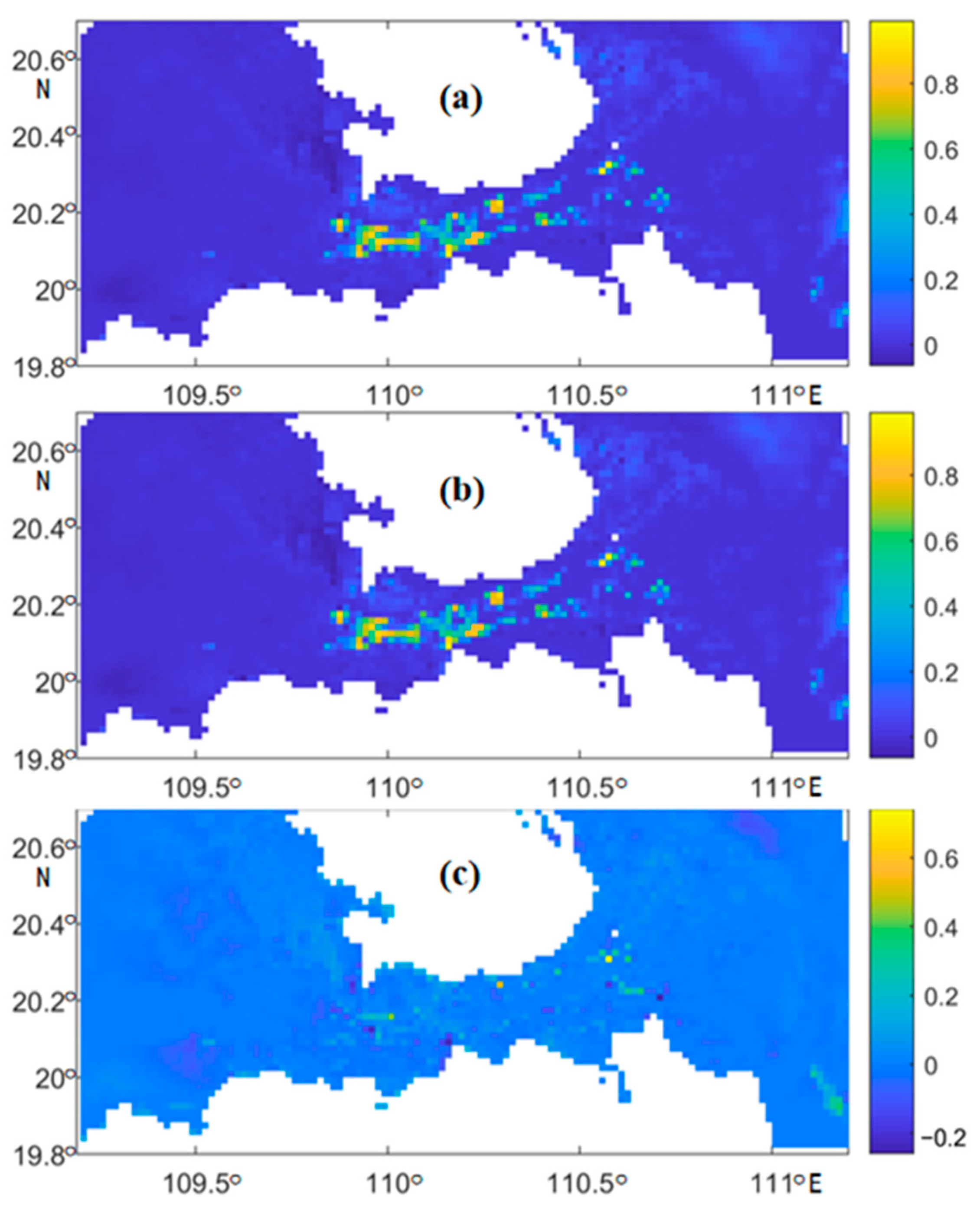
3.3. Analysis of Sediment Mobility
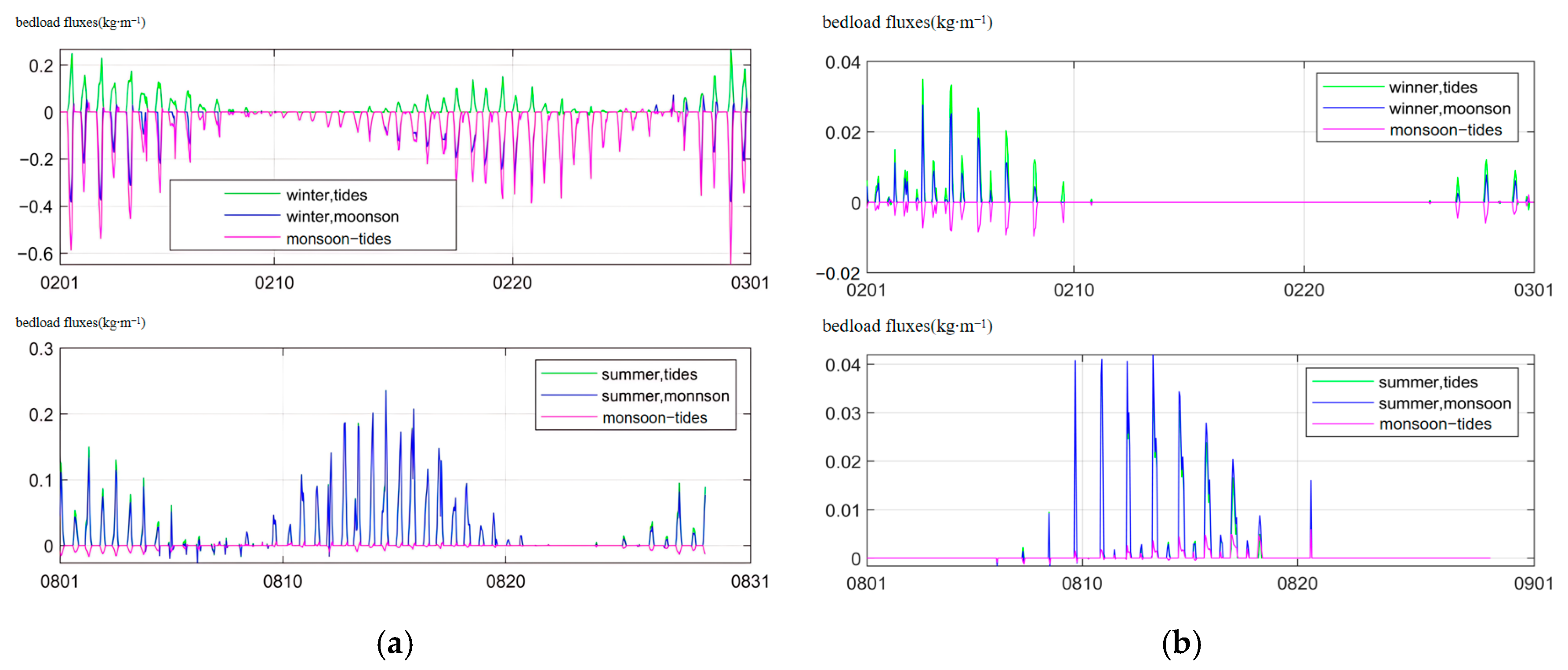
3.4. Time-Series of Bedload Transport Rate
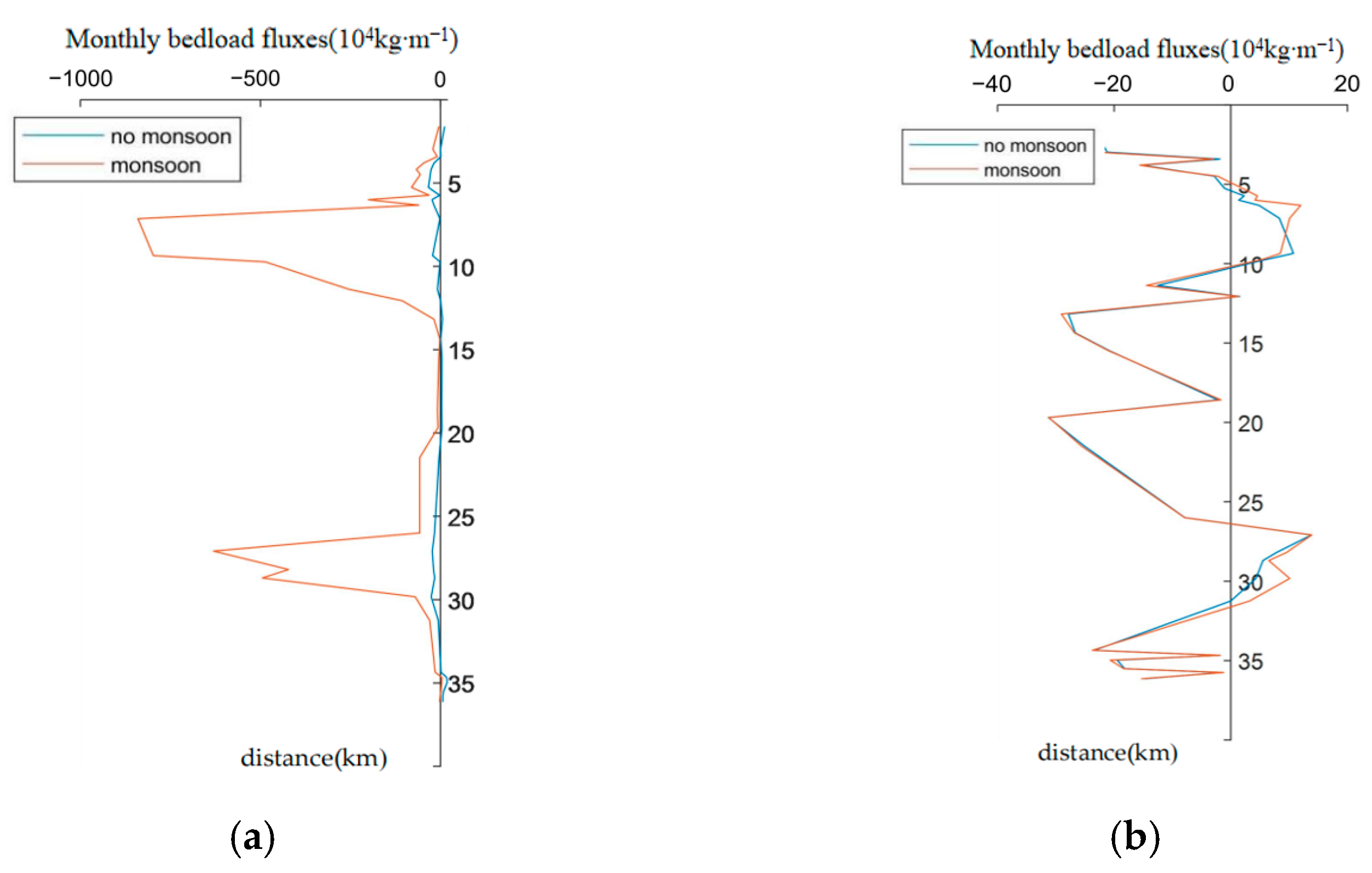
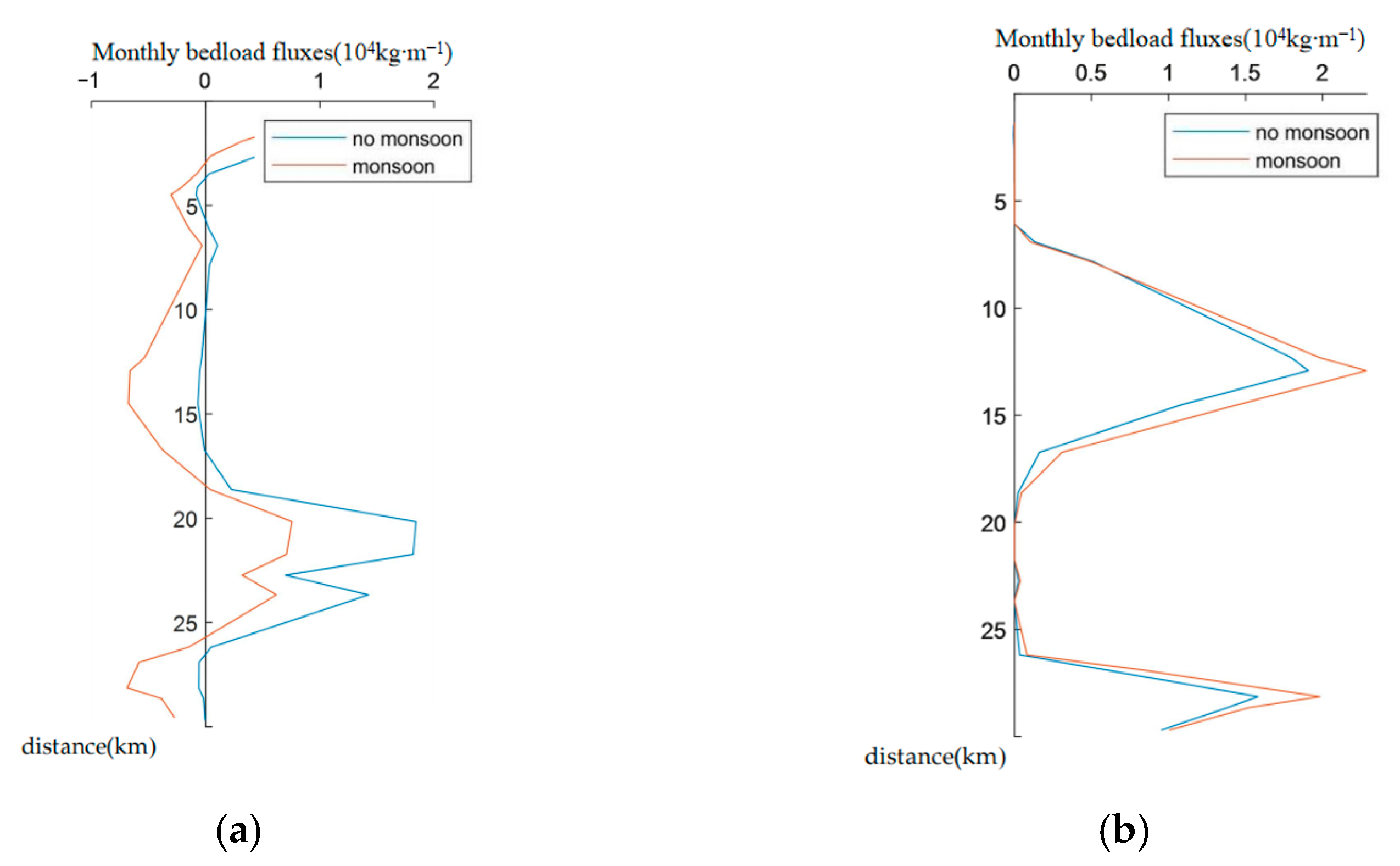
3.5. Bedload Transport Across Sections in the Qiongzhou Strait
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Monsoon Circulation on the Transport of Sediment
4.2. Sediment Supplies
4.3. Global Change Context and Future Projections
4.4. Implications for Regional Marine Environmental Management
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Monsoon seasonality controls net sediment flux through contrasting hydrodynamic regimes: the winter monsoon establishes spatially coherent westward transport pathways, while the summer monsoon induces mutually opposing flows that might suppress net transport.
- (2)
- Tidal and monsoon forcing exhibit counteractive transport vectors at both eastern and western strait entrances during winter, with monsoon-driven bedload transport dominating the western entrance while tidal forcing prevails in the eastern sector.
- (3)
- The summer monsoon influences show reduced hydrodynamic coupling, generating merely 10% or less of the tidal transport magnitude across critical cross-sections.
- Implementation of dynamic downscaling techniques to resolve subgrid-scale atmospheric–oceanic interactions;
- Implementation of multi-physics coupled modeling frameworks integrating wave–current–tide interactions to quantify their synergistic effects on sediment transport partitioning;
- Climate projection experiments quantifying sediment flux sensitivity to IPCC SSP scenarios.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. The type and distribution pattern of geomorphology in the Bohai sea. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2014, 6, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, K.R.; Huntley, D.A. The origin, classification and modelling of sand banks and ridges. Cont. Shelf Res. 1999, 19, 1285–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouillon, S. Why and How Do We Study Sediment Transport? Focus on Coastal Zones and Ongoing Methods. Water 2018, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wang, K.; Xia, D. Tidal Dynamic Geomorphic System in the East Part of the Bohai Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1996, 14, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, Q.; Lin, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Yan, J. The role of Qiongzhou Strait in the seasonal variation of the South China Sea circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Fang, G.; Yu, K.; Jia, J. Methodology for evaluating the stability of sandy seabed controlled by sediment movement with an example of application. In Studia Marina Sinica; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Endler, R.; Xia, Z.; Endler, M.; Harff, J.; Gan, H.; Schulz-Bull, D.E.; Waniek, J.J. The “butterfly delta” system of Qiongzhou Strait: Morphology, seismic stratigraphy and sedimentation. Mar. Geol. 2014, 355, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Coastal dynamic geomorphological researches on south coast of Qiongzhou Strait. Trop. Oceanol. 1998, 3, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Bao, C.; Lin, J. Geomorphic feature and origin of the deltas at the east and west mouthes of Qiongzhou Strait. Mar. Geol. Res. 1982, 4, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, P. A preliminary analysis of currents and water exchanges in the Qiongzhou Strait. Trop. Oceanol. 1983, 1, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C. Distribution of sediments and submarine topography of Qiongzhou Strait. Trop. Geogr. 1986, 4, 346–353. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Cao, Z.; Bao, M. Dynamics of currents in the Qiongzhou strait during spring and summer based on a numerical simulation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1367145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Li, J.; Yin, D.; Li, M.; Wang, B. Nearshore bedform instability in the eastern entrance to the Qiongzhou Strait, South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. China 2008, 2, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ke, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, J. Characteristics of water and sedimenttransport in the Qiongzhou Strait. Geogr. Res. 2003, 2, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Shi, Y.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y. Surface Sediment Characteristics and Dynamics in Beibu Gulf. J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 46, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, J.; Yan, J. Tide-induced bedload transport pathways in a multiple-sand-ridge system offshore of Hainan Island in the Beibu Gulf, northwest South China Sea. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 2738–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Wu, X.; Ge, J.; Bi, N.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, H. Impact of Typhoon Chan-hom on sediment dynamics and morphological changes on the East China Sea inner shelf. Mar. Geol. 2021, 440, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Yang, G.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Ma, X. Response of Sediment Dynamics to Tropical Cyclones under Various Scenarios in the Jiangsu Coast. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Cai, F.; Wu, C.; Lu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Regeneration and anti-migration of sand waves associated with sand mining in the Taiwan Shoal. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Characteristics of tidal current dynamic in Lianyungang nearshore area. Port Waterw. Eng. 2012, 9, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- French, J.R.; Burningham, H.; Benson, T. Tidal and Meteorological Forcing of Suspended Sediment Flux in a Muddy Mesotidal Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomä, A.; Kubicki, A.; Badewien, T.H.; Flemming, B.W. Suspended sediment transport in the German Wadden Sea—Seasonal variations and extreme events. Ocean Dyn. 2009, 59, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, I.; de Vet, P.L.M.; van Maren, D.S.; Reniers, A.J.H.M.; Winterwerp, J.C.; van Prooijen, B.C. The Impact of Wind on Flow and Sediment Transport over Intertidal Flats. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Griffiths, C.; Paraschivoiu, E.; Dyt, C.; Jenkins, C.; Rutherford, M.J. Wind-driven Water Circulation And Its Impact On Seabed Sediment Transport In the Australian Northeast. In Proceedings of the Seventh ISOPE Pacific/Asia Offshore Mechanics Symposium, Dalian, China, 17–21 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Andutta, F.P.; Patterson, R.G.; Wang, X.H. Monsoon driven waves superpose the effect from macro-tidal currents on sediment resuspension and distribution. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 223, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Ralston, D.K.; Bi, N.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, H. Seasonal variation in sediment transport and deposition on a muddy clinoform in the Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 179, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, N.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Fan, D.; Sun, X.; Lei, K. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Seasonal variation of surface currents in the southwestern Taiwan Strait observed with HF radar. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Lang, H.; Xu, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, F. Distribution and bi-directional transport of surface sediments driven by monsoons on the northwest continental shelf of the South China Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2025, 45, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, J. Sedimentary Environment and Its Evolution of Qiongzhou Strait and Nearby Seas since Last Ten Thousand Years. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2014, 39, 696–704. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X. Estimation of Bedload Transport at the Eastern Entrance of the Qiongzhou Strait based on Numerical Simulation. Earth Sci. Front. 2023, 30, 553–566. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, C.; Chen, F.; Zhang, K. Analysis of the distribution and development of marine sand resources in the northeast sea of Hainan island. China Min. Maniz. 2019, 28, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Cen, Z.; Cai, C.; Xu, Y. Analysis on the Sand Wave Stability of the Submarine Cable Route in the Qiongzhou Strait. Sci. Technol. Innov. Her. 2019, 16, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- You, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Yue, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, W.; Wu, F.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, H.; et al. Recent frontiers of climate changes in East Asia at global warming of 1.5 °C and 2 °C. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Ding, Y.; Hu, T. Future changes in East Asian summer monsoon circulation and precipitation under 1.5 to 5 °C of warming. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Stanev, E.V.; Grashorn, S. Seamless cross-scale modeling with SCHISM. Ocean Model. 2016, 102, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhang, Y.; Friedrichs, M.; Wang, H.V.; Irby, I.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. A 3D, cross-scale, baroclinic model with implicit vertical transport for the Upper Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries. Ocean Model. 2016, 107, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, B.; Sandwell, D.T.; Smith, W.H.F.; Olson, C.; Beale, J.R.; Wessel, P. Global bathymetry and topography at 15 arc sec: SRTM15+. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Navy Hydrographic Office. Beibu Gulf (C1316020); China Navigation Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, C.; Qin, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Estimation of the Spring Tide Bedload Transport at the Eastern Entrance of the Qiongzhou Strait. Water 2023, 15, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1940 to present. In Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS); ECMWF: Bonn, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, G.; Bleck, R.; Chassignet, E. Atlantic Ocean simulations performed using a new hybrid-coordinate ocean model. In EOS, Fall 1998 AGU Meeting; AGU Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Large, W.G.; Danabasoglu, G.; Doney, S.C.; McWilliams, J.C. Sensitivity to surface forcing and boundary layer mixing in a global ocean model: Annual-mean climatology. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 2418–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Andrews, P.B.; Lewis, D. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 1970, 13, 937–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Lagoon Inlet Hydraulic Characteristic and Transformation. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2006, 4, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D. Grain size characteristics and transport trends of surface sediment in the bays of northern Hainan Island. Mar. Geol. Front. 2024, 40, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Shi, M. Advances in Study of Beibu Gulf Circulation. Guangxi Sci. 2019, 26, 595–603. [Google Scholar]
- Hardisty, J. An assessment and calibration of formulations for Bagnold’s bedload equation. J. Sediment. Res. 1983, 53, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R. Dynamics of Marine Sands; Thomas Telford Publications: London, UK, 1997; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; McCave, I.; Komar, P.D. Threshold of sediment motion under unidirectional currents. Sedimentology 1977, 24, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S. Modification to the Hardisty equation, regarding the relationship between sediment transport rate and particle. J. Sediment. Res. 2001, 71, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Yu, F.H. Temporal and spatial variation characteristies of residual current and net flux during flood and dry season in inner Lingdingyang estuary. Port Waterw. Eng. 2023, 11, 8–14+22. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Huang, F.; Ye, A. Characteristics of the Residual Current Field at the End of Winter and Beginning of Spring in the Qiongzhou Strait. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1998, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.L.; Chen, B.; Tang, S. Northwest South China Sea Circulation Based on HYCOM Simulation. Guangxi Sci. 2019, 26, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, R.X.; Pan, W.R.; Zhang, G.R.; Luo, Z.B.; Lin, Y.H. Vector EOF analysis of residual current of an anchor station in the Qiongzhou Strait. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2013, 32, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, P.; Shi, M.; Zuo, J. Numerical study of the tides and residual currents in the Qiongzhou Strait. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lou, A.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y. Simulating summer circulation and water exchange in the Beibu Gulf. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Colin, C.; Zhang, H.; Bassinot, F.; Liu, Z.; Fang, X.; Miska, S.; Nouet, J.; et al. Evolution of sediment provenances and transport processes in the central Bay of Bengal since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quatern. Int. 2022, 629, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Colin, C.; Zhang, H.; Bassinot, F.; Liu, Z.; Fang, X.; Miska, S.; Nouet, J.; et al. The impact of changes in sea level and East Asian monsoon on sediment transport on the Sunda Shelf since the last deglaciation. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2023, 128, e2023JF007335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, P.D. Asian monsoon dynamics and sediment transport in SE Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 195, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, P.D.; Jonell, T.N. Monsoon controls on sediment generation and transport: Mass budget and provenance constraints from the Indus River catchment, delta and submarine fan over tectonic and multimillennial timescales. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Asian monsoon variability under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Knutson, T.; Camargo, S.J.; Chan, J.C.; Emanuel, K.; Ho, C.H.; Kossin, J.; Mohapatra, M.; Satoh, M.; Sugi, M.; Walsh, K.; et al. Tropical cyclones and climate change assessment: Part II. Projected response to anthropogenic warming. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E303–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Xie, S.; Primeau, F.; McWilliams, J.; Pasquero, C. Northwestern Pacific typhoon intensity controlled by changes in ocean temperatures. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
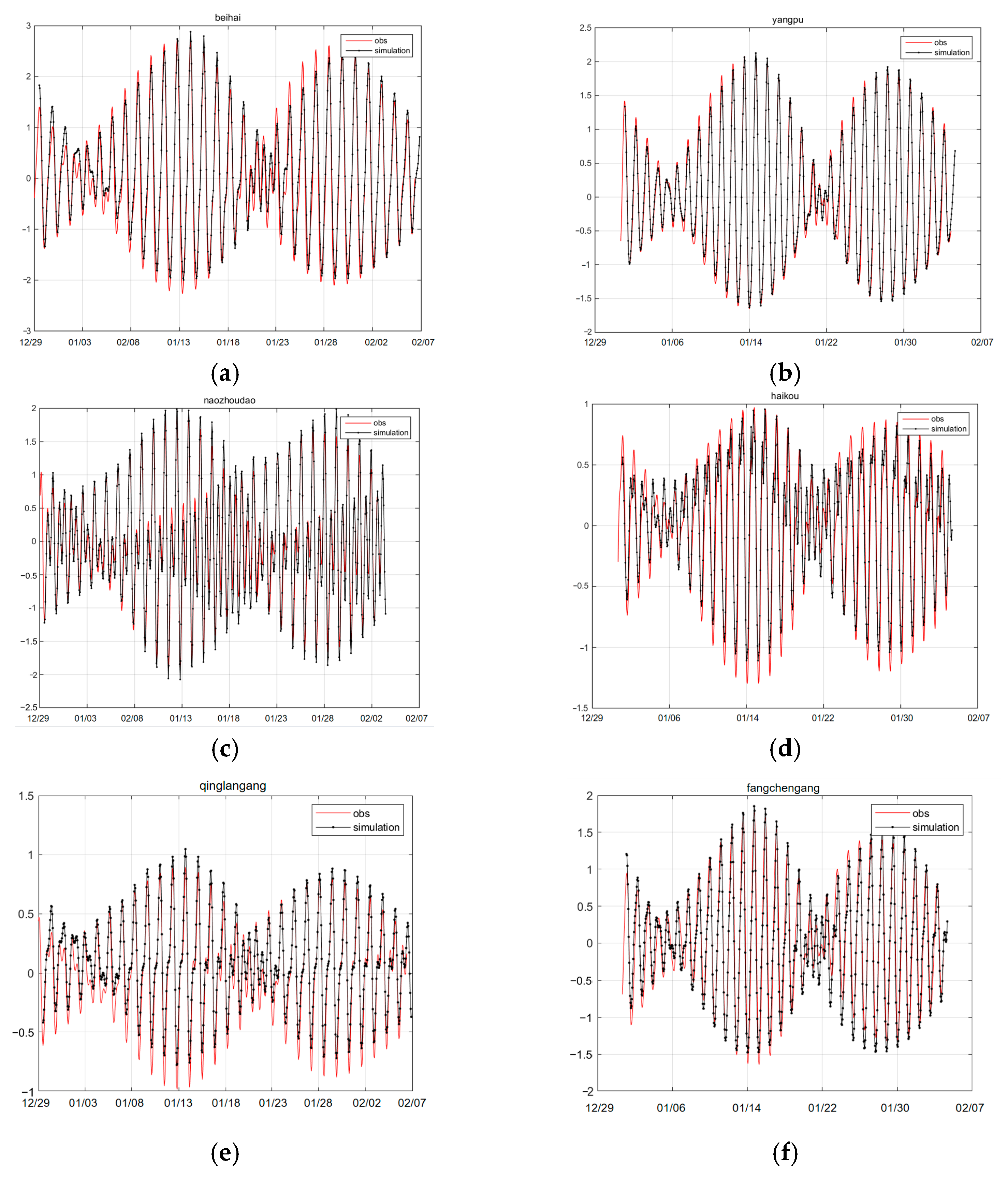
| Beihai | Yangpu | Nanzhoudao | Haikou | Qinglangang | Fangchenggang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (meter) | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.23 |
| Relative RMSE | 0.056 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Year | Data Source | Residual Current Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1998 | In situ observation | westward in winter, surface residual current of approximately 0.12 m/s [46]. |
| 2009 | simulation | westward in winter, the tidally induced surface residual current exceeding 50 cm/s [54]; eastward in summer, 5 to 15 cm/s. |
| 2013 | In situ observation | Westward, in February, the maximum surface residual current 18.6 cm/s, with an average of 8.4 cm/s [55]. |
| 2018 | simulation | westward year-round; maximum reached 25.3 cm/s in August, average of 1.82 cm/s [56]. |
| 2019 | simulation | westward flow in winter and an eastward flow in summer (exceeds 0.2 m/s) [57]. |
| 2019 | Simulation | northeastward in summer, 3 to 12 cm/s; southwestward in winter, 5 to 20 cm/s [58]. |
| 2020 | Simulation | westward in winter,16.2 cm/s; eastward in summer, 8.1 cm/s. (present study) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Mei, H.; Zhu, S.; Tong, C.; La, X. Effects of Monsoon Circulation on Bedload Transport in the Qiongzhou Strait and Adjacent Seas Based on SCHISM. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050854
Huang Y, Wu X, Mei H, Zhu S, Tong C, La X. Effects of Monsoon Circulation on Bedload Transport in the Qiongzhou Strait and Adjacent Seas Based on SCHISM. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050854
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yuxin, Xiangbai Wu, Huan Mei, Shouxian Zhu, Changliang Tong, and Xinyi La. 2025. "Effects of Monsoon Circulation on Bedload Transport in the Qiongzhou Strait and Adjacent Seas Based on SCHISM" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050854
APA StyleHuang, Y., Wu, X., Mei, H., Zhu, S., Tong, C., & La, X. (2025). Effects of Monsoon Circulation on Bedload Transport in the Qiongzhou Strait and Adjacent Seas Based on SCHISM. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050854







