Sex Control in Fish: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities for Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
The Need for Sex Control
| Approach | Technique | Purpose | Representative example species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hormonal manipulation | Administration of exogenous hormones (e.g., 17β-estradiol, 11-α-methyltestosterone) | Monosex | Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua [6] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [7] | |||
| Administration of aromatase inhibitor (e.g., Fadrozole) | Monosex | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [8] | |
| Honeycomb grouper (Epinephelus merra) [9] | |||
| Hybridisation | Cross breeding | Monosex | Tilapia (O. aurea x O. niloticus) [10] |
| Bass (Morone saxatilis x M. mississippiensis) [11] | |||
| Chromosome Ploidy | Gynogenetics | Monosex | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [12] |
| Triploidy | Sterility | Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) [13,14] | |
| Envionmental manipulation | Manipulation of social factors | Production of male broodstock | Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) [15] |
| Temperature treatment during gonadal differentiation | Monosex populations | European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) [16,17,18] | |
| Selection | Marker assisted selection (MAS) | Monosex populations | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [19,20] |
| Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) [21] |
2. Sex Determination and Differentiation in Fish
2.1. Genetic Factors Involved in Fish Sex Determination and Differentiation
2.2. Epigenetic Mechanisms Involved in Fish Sex Determination and Differentiation
2.3. Environmental Factors Involved in Fish Sex Determination
2.4. Sex Reversal and the Labile Period
3. Approaches Used to Manipulate Sex in Farmed Fish
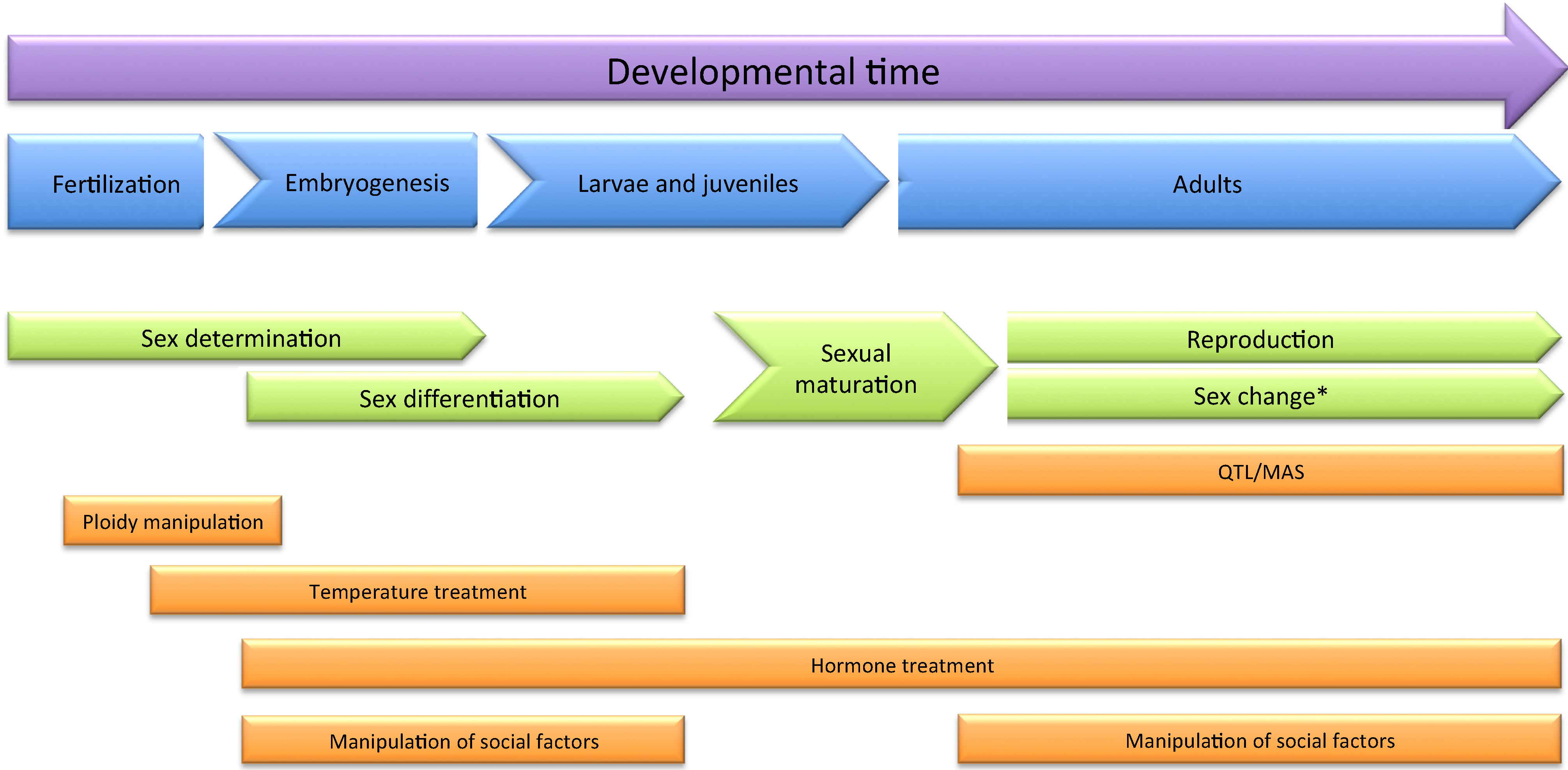
3.1. The Use of Exogenous Hormones and Other Chemicals to Control Sex
3.1.1. Principles of Exogenous Hormones and Other Chemicals Application for Sex Control
3.1.2. Challenges to the Use of Hormones and Other Chemicals in Controlling Sex
3.2. Chromosome Ploidy Manipulation and Sex Control
3.2.1. Principles of Triploidy Induction in Fish
3.2.2. Uses of Triploids in Aquaculture Production
3.2.3. Advantages of Triploidy Induction in Controlling Sex
3.2.4. Challenges of Producing Triploids
3.3. Environmental Manipulations and Opportunities for Sex Control
3.3.1. The Use of Social Factors to Influence Sex Change in Hermaphrodite Fish
3.3.2. The Use of Temperature to Manipulate Sex Ratios
3.3.3. Other Environmental Factors Affecting Fish Sex Ratios
3.3.4. Challenges for Environmental Control of Sex in Fish
3.4. Selection for Altered Sex Ratios
3.4.1. Heritability and Potential for Selection of Altered Sex Ratios
3.4.2. The Use of Quantitative Trait Loci to Improve Sex Control
4. Other Methods and Future Directions
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mires, D. Production of aquatic animals. In The Tilapias; Nash, C.E., Novotony, A.J., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 133–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, C.S.; Morrissy, N.M.; Vercoe, P.E.; Williams, I.H. Hybridization in Australian freshwater crayfish—Production of all-male progeny. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2000, 31, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Beaumont, A.; Falguière, J.-C.; Flajšhans, M.; Haffray, P.; Colombo, L. Polyploid fish and shellfish: Production, biology and applications to aquaculture for performance improvement and genetic containment. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, M.T. Evaluation of monosex culture of GIFT and non-improved strains of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in recirculating tanks. Int. Aquat. Res. 2011, 3, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Coman, F.E.; Sellars, M.J.; Norris, B.J.; Coman, G.J.; Preston, N.P. The effects of triploidy on Penaeus (Marsupenaeus) japonicus (Bate) survival, growth and gender when compared to diploid siblings. Aquaculture 2008, 276, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Benfey, T.J.; Martin-Robichaud, D.J. Hormonal sex reversal in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. Aquaculture 2012, 364, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayamen, M.M.; Shelton, W.L. Inducement of sex reversal in Sarotherodon niloticus (Linnaeus). Aquaculture 1978, 14, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Haghpanah, V.; Kogson-Hurtado, L.M.; McAndrew, B.J.; Penman, D.J. Masculinization of genetic female Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by dietary administration of an aromatase inhibitor during sexual differentiation. J. Exp. Zool. 2000, 287, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.K.; Higa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, M. Aromatase inhibitor induces complete sex change in the protogynous honeycomb grouper (Epinephelus merra). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2004, 67, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruginin, Y.; Rothbard, S.; Wohlfarth, G.; Halevy, A.; Moav, R.; Hulata, G. All-male broods of Tilapia nilotica × T. aurea hybrids. Aquaculture 1975, 6, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, W.R.; de May, R. Production characteristics of striped bass x white bass and striped bass x yellow bass hybrids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1996, 27, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourrout, D.; Quillet, E. Induced gynogenesis in the rainbow trout: Sex and survival of progenies production of all-triploid populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1982, 63, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbreath, P.F.; Thorgaard, G.H. Saltwater performance of all-female triploid Atlantic salmon. Aquaculture 1995, 138, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfey, T.J.; Sutterlin, A.M. Triploidy induced by heat shock and hydrostatic pressure in landlocked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 1984, 36, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y. The influence of social factors on juvenile sexual differentiation in a diandric, protogynous grouper Epinephelus coioides. Ichthyol. Res. 2011, 58, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Martín, L.; Viñas, J.; Ribas, L.; Díaz, N.; Gutiérrez, A.; di Croce, L.; Piferrer, F. DNA methylation of the gonadal aromatase (cyp19a) promoter is involved in temperature-dependent sex ratio shifts in the European sea bass. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koumoundouros, G.; Pavlidis, M.; Anezaki, L.; Kokkari, C.; Sterioti, A.; Divanach, P.; Kentouri, M. Temperature sex determination in the European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L., 1758) (Teleostei, Perciformes, Moronidae): Critical sensitive ontogenetic phase. J. Exp. Zool. 2002, 292, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saillant, E.; Fostier, A.; Haffray, P.; Menu, B.; Thimonier, J.; Chatain, B. Temperature effects and genotype-temperature interactions on sex determination in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). J. Exp. Zool. 2002, 292, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentsen, H.B.; Gjerde, B.; Nguyen, N.H.; Rye, M.; Ponzoni, R.W.; Palada de Vera, M.S.; Bolivar, H.L.; Velasco, R.R.; Danting, J.C.; Dionisio, E.E.; et al. Genetic improvement of farmed tilapias: Genetic parameters for body weight at harvest in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) during five generations of testing in multiple environments. Aquaculture 2012, 338–341, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, H. Studies on the Inheritance of Sex with African Cichlids (Oreochromis Niloticus) (in German); Göttingen University: Göttingen, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, P.; Bouza, C.; Hermida, M.; Fernández, J.; Toro, M.A.; Vera, M.; Pardo, B.; Millán, A.; Fernández, C.; Vilas, R. Identification of the major sex-determining region of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Genetics 2009, 183, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evelyn, G.D.J.-A.; Felix, G.A.; Valentin, T. Early development and seed production of Asian Seabass, Lates calcarifer. In Biology and Culture of Asian Seabass Lates Calcarifer; Jerry, D.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, P.; Blackshaw, A.; Garrett, R. Successful fertility experiments with cryopreserved spermatozoa of barramundi, Lates calcarifer (Bloch), using dimethylsulfoxide and glycerol as cryoprotectants. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 1993, 5, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerry, D.R.; James Cook University, Townsville, Australia. Personal observation, 2014.
- Quinitio, G.F.; Caberoy, N.B.; Reyes, D.M., Jr. Induction of sex change in female Epinephelus coioides by social control. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 1997, 49, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, M.C. Socially controlled sex-change in the half-moon grouper, Epinephelus rivulatus, at Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia. Coral Reefs 2003, 22, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuckey, R.; Finfish Enterprise, Cairns, Australia. Personal communication, 2014.
- Penman, D.J.; Piferrer, F. Fish gonadogenesis. Part I: Genetic and environmental mechanisms of sex determination. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2008, 16, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Blazquez, M.; Navarro, L.; Gonzalez, A. Genetic, endocrine, and environmental components of sex determination and differentiation in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, R.H.; Nagahama, Y. Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 2002, 208, 191–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiguen, Y.; Fostier, A.; Piferrer, F.; Chang, C.-F. Ovarian aromatase and estrogens: A pivotal role for gonadal sex differentiation and sex change in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroiller, J.F.; D’Cotta, H.; Saillant, E. Environmental effects on fish sex determination and differentiation. Sex. Dev. 2009, 3, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Nagahama, Y.; Nakamura, M. Diversity and plasticity of sex determination and differentiation in fishes. Sex. Dev. 2013, 7, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heule, C.; Salzburger, W.; Böhne, A. Genetics of sexual development: An evolutionary playground for fish. Genetics 2014, 196, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piferrer, F.; Ribas, L.; Díaz, N. Genomic approaches to study genetic and environmental influences on fish sex determination and differentiation. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koopman, P.; Gubbay, J.; Vivian, N.; Goodfellow, P.; Lovell-Badge, R. Male development of chromosomally female mice transgenic for sry. Nature 1991, 351, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroiller, J.F.; D'Cotta, H. Environment and sex determination in farmed fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2001, 130, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, H.H. Karyology of three Galaxiid fishes Galaxias maculatus, G. platei, and Brachygalaxias bullocki. Copeia 1972, 1972, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertollo, L.A.; Mestriner, C.A. The X1X2Y sex chromosome system in the fish Hoplias malabaricus. II. Meiotic analyses. Chromosome Res. 1998, 6, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Foresti, F.; Hilsdorf, A. Genetics of neotropical fish: From chromosomes to populations. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosswig, C. Polygenic sex determination. Experientia 1964, 20, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, W.C.; Orban, L. Zebrafish sex: A complicated affair. Brief. Funct. Genomics 2014, 13, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeputte, M.; Dupont-Nivet, M.; Chavanne, H.; Chatain, B. A polygenic hypothesis for sex determination in the European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax. Genetics 2007, 176, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Peichel, C.L. Molecular Cytogenetic Evidence of rearrangements on the Y chromosome of the threespine stickleback fish. Genetics 2008, 179, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, T.; Kai, W.; Tasumi, S.; Oka, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Mizuno, N.; Fujita, M.; Suetake, H.; Suzuki, S.; Hosoya, S. A trans-species missense SNP in amhr2 is associated with sex determination in the tiger pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes (fugu). PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.A.; High, S.K.; McCluskey, B.M.; Amores, A.; Yan, Y.-l.; Titus, T.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Batzel, P.; Carvan, M.J.; Schartl, M. Wild sex in zebrafish: Loss of the natural sex determinant in domesticated strains. Genetics 2014, 114, 1291–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Shinomiya, A.; Sato, T.; Matsuda, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Morrey, C.E.; Shibata, N.; Asakawa, S.; Shimizu, N. Dmy is a Y-specific DM-domain gene required for male development in the medaka fish. Nature 2002, 417, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, I.; Kondo, M.; Hornung, U.; Asakawa, S.; Winkler, C.; Shimizu, A.; Shan, Z.; Haaf, T.; Shimizu, N.; Shima, A. A duplicated copy of dmrt1 in the sex-determining region of the Y chromosome of the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11778–11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, R.S.; Strussmann, C.A.; Fernandino, J.I.; Somoza, G.M. Genotypic sex determination in teleosts: Insights from the testis-determining amhy gene. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, R.S.; Murai, Y.; Oura, M.; Masuda, S.; Majhi, S.K.; Sakamoto, T.; Fernandino, J.I.; Somoza, G.M.; Yokota, M.; Strüssmann, C.A. A Y-linked anti-Müllerian hormone duplication takes over a critical role in sex determination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2955–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myosho, T.; Otake, H.; Masuyama, H.; Matsuda, M.; Kuroki, Y.; Fujiyama, A.; Naruse, K.; Hamaguchi, S.; Sakaizumi, M. Tracing the emergence of a novel sex-determining gene in medaka, Oryzias luzonensis. Genetics 2012, 191, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, A.; Guyomard, R.; Nicol, B.; Jouanno, E.; Quillet, E.; Klopp, C.; Cabau, C.; Bouchez, O.; Fostier, A.; Guiguen, Y. An immune-related gene evolved into the master sex-determining gene in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takehana, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Myosho, T.; Suster, M.L.; Kawakami, K.; Shin-I, T.; Kohara, Y.; Kuroki, Y.; Toyoda, A.; Fujiyama, A.; et al. Co-option of as the male-determining factor on the Y chromosome in the fish Oryzias dancena. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, J.; Wheatley, S.C.; Andrews, J.E.; Sinclair, A.H.; Koopman, P. A male-specific role for sox9 in vertebrate sex determination. Development 1996, 122, 2813–2822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Roeszler, K.N.; Ohnesorg, T.; Cummins, D.M.; Farlie, P.G.; Doran, T.J.; Sinclair, A.H. The avian Z-linked gene dmrt1 is required for male sex determination in the chicken. Nature 2009, 461, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-S.; Kobayashi, T.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Paul-Prasanth, B.; Ijiri, S.; Sakai, F.; Okubo, K.; Morohashi, K.-I.; Nagahama, Y. Foxl2 up-regulates aromatase gene transcription in a female-specific manner by binding to the promoter as well as interacting with Ad4 binding protein/steroidogenic factor 1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutting, A.; Chue, J.; Smith, C.A. Just how conserved is vertebrate sex determination? Dev. Dyn. 2013, 242, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trukhina, A.V.; Lukina, N.A.; Wackerow-Kouzova, N.D.; Smirnov, A.F. The variety of vertebrate mechanisms of sex determination. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 58746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piferrer, F. Epigenetics of sex determination and gonadogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2013, 242, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.E.; Martienssen, R.A.; Riggs, A.D. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Gene Regulation; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.M. Epigenetic responses to environmental change and their evolutionary implications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2009, 364, 3403–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, P.; Lian, J.; Hu, Q.; Sun, B.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. Epigenetic modification and inheritance in sexual reversal of fish. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, D.; Kynard, B. Environmental sex determination: Interaction of temperature and genotype in a fish. Science 1981, 213, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, M.; Fernandino, J.I.; Strobl-Mazzulla, P.; Strüssmann, C.A.; Yoshizaki, G.; Somoza, G.M.; Patiño, R. Characterization and expression profile of the ovarian cytochrome P450 aromatase (cyp19A1) gene during thermolabile sex determination in pejerrey, Odontesthes bonariensis. J. Exp. Zool. Part A 2007, 307, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Piferrer, F. Temperature-dependent sex determination in fish revisited: Prevalence, a single sex ratio response pattern, and possible effects of climate change. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socorro, S.; Martins, R.S.; Deloffre, L.; Mylonas, C.C.; Canario, A.V. A cDNA for European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) 11β-hydroxylase: Gene expression during the thermosensitive period and gonadogenesis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 150, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, N.; Adams, D.C.; Janzen, F.J. Pattern does not equal process: Exactly when is sex environmentally determined? Am. Nat. 2003, 161, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Hourigan, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Nagahama, Y.; Grau, E.G. Histological and ultrastructural evidence for the role of gonadal steroid hormones in sex change in the protogynous wrasse Thalassoma duperrey. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1989, 24, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, J.; Luckenbach, J.A.; Borski, R.J. Ecology meets endocrinology: Environmental sex determination in fishes. Evolut. Dev. 2003, 5, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Arshad, A.; Marimuthu, K.; Ara, R.; Amin, S. Inter-specific hybridization and its potential for aquaculture of fin fishes. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2013, 8, 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.-O. Sex differentiation. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; Volume 3, pp. 117–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.-O. Artificially induced sex-reversal in genotypic males of the medaka (Oryzias latipes). J. Exp. Zool. 1953, 123, 571–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.-O. Artificial induction of functional sex-reversal in genotypic females of the medaka (Oryzias latipes). J. Exp. Zool. 1958, 137, 227–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandian, T.; Sheela, S. Hormonal induction of sex reversal in fish. Aquaculture 1995, 138, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardmore, J.A.; Mair, G.C.; Lewis, R.I. Monosex male production in finfish as exemplified by tilapia: Applications, problems, and prospects. Aquaculture 2001, 197, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.K.; Alam, M.A.; Higa, M.; Soyano, K.; Nakamura, M. Evidence that estrogen regulates the sex change of honeycomb grouper (Epinephelus merra), a protogynous hermaphrodite fish. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2005, 303A, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-L.; Liu, X.-C.; Lin, H.-R. Effects of aromatizable and nonaromatizable androgens on the sex inversion of red-spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 32, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.A.; Forrester, J. Administration of oestradiol to barramundi, Lates calcarifer, induces protandrous sex change. In Perspective in Comparative Endocrinology, Unity and Diversity; Goos, H.I.T., Rastogi, R.K., Vaudry, H., Pierantoni, R., Eds.; Monduzzi Editore: Bologna, Napoli, Italy, 2001; pp. 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Sower, S.A.; Dickhoff, W.W.; Flagg, T.A.; Mighell, J.L.; Mahnken, C.V. Effects of estradiol and diethylstilbesterol on sex reversal and mortality in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 1984, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoa, E. Further observations on the differentiation of sex, normal and modified by the administration of follicular hormone, in the iridée trout (Salmo irideus) (in French). Biomorphosis 1939, 1, 337–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hackmann, E.; Reinboth, R. Delimitation of the critical stage of hormone-influenced sex differentiation in Hemihaplochromis multicolor (Hilgendorf) (Cichlidae). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1974, 22, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Takahashi, H. Gonadal sex differentiation in Tilapia mossambica, with special regard to the time of estrogen treatment effective in inducing complete feminization of genetic males. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1973, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M. Effects of estradiol-17β on gonadal sex differentiation in two species of salmonids, the masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou, and the chum salmon, O. keta. Aquaculture 1984, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Donaldson, E.M. Gonadal differentiation in coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, after a single treatment with androgen or estrogen at different stages during ontogenesis. Aquaculture 1989, 77, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, R.; Slof, G.A. A morphological and experimental study of gonadal sex differentiation in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tissue Res. 1981, 218, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patiño, R.; Davis, K.B.; Schoore, J.E.; Uguz, C.; Strüssmann, C.A.; Parker, N.C.; Simco, B.A.; Goudie, C.A. Sex differentiation of channel catfish gonads: Normal development and effects of temperature. J. Exp. Zool. 1996, 276, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Baker, I.J.; Donaldson, E.M. Effects of natural, synthetic, aromatizable, and nonaromatizable androgens in inducing male sex differentiation in genotypic female Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1993, 91, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piferrer, F. Endocrine sex control strategies for the feminization of teleost fish. Aquaculture 2001, 197, 229–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, M.; Piferrer, F.; Zanuy, S.; Carrillo, M.; Donaldson, E.M. Development of sex control techniques for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) aquaculture: Effects of dietary 17 α-methyltestosterone prior to sex differentiation. Aquaculture 1995, 135, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kajiura-Kobayashi, H.; Nagahama, Y. Induction of XY sex reversal by estrogen involves altered gene expression in a teleost, tilapia. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003, 101, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, T.; Takamune, K.; Nagahama, Y.; Abe, S.-I. Aromatase inhibitor and 17α-methyltestosterone cause sex-reversal from genetical females to phenotypic males and suppression of P450 aromatase gene expression in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2000, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crim, L.W. Methods for acute and chronic hormone administration in fish. In Reproduction and Culture of Milkfish; Lee, C.S., Liao, I.C., Eds.; Tungkang Marine Laboratory: Tungkang, Taiwan, 1985; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chatain, B.; Saillant, E.; Peruzzi, S. Production of monosex male populations of European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. by use of the synthetic androgen 17α-methyldehydrotestosterone. Aquaculture 1999, 178, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. Dosage-dependent changes in the effect of oral administration of methyltestosterone on gonadal sex differentiation in Tilapia mossambica. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1975, 26, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, G.A.; Solar, I.I.; Baker, I.J.; Donaldson, E.M. Feminization of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) by immersion of alevins in a solution of estradiol-17β. Aquaculture 1986, 53, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, G.; Yeoh, C.-G.; Fitzpatrick, M.S.; Schreck, C.B. The production of functional sex-reversed male rainbow trout with 17α-methyltestosterone and 11 β-hydroxyandrostenedione. Aquaculture 1995, 131, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parliament, E. Directive 96/22/EC concerning the prohibition on the use in stockfarming of certain substances having a hormonal or thyrostatic action and of β-agonists, and repealing Directives 81/602/EEC, 88/146/EEC and 88/299/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Union 1996, L25, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Parliament, E. Directive 2003/74/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Council Directive 96/22/EC concerning the prohibition on the use in stockfarming of certain substances having a hormonal or thyrostatic action and of beta-agonists. Off. J. Eur. Union 2003, L262, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, T.J.; Kirankumar, S. Recent advances in hormonal induction of sex-reversal in fish. J. Appl. Aquac. 2003, 13, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, A.; Zanuy, S.; Carrillo, M.; Piferrer, F. Induction of triploidy and gynogenesis in teleost fish with emphasis on marine species. Genetica 2001, 111, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulata, G. Genetic manipulations in aquaculture: A review of stock improvement by classical and modern technologies. Genetica 2001, 111, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwary, B.K.; Kirubagaran, R.; Ray, A.K. The biology of triploid fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2004, 14, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihssen, P.; McKay, L.; McMillan, I.; Phillips, R. Ploidy manipulation and gynogenesis in fishes: Cytogenetic and fisheries applications. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1990, 119, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.M. Tetraploid induction in Oreochromis spp. Aquaculture 1986, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, P.; Dubé, F. Meiotic maturation in mollusc oocytes. Seminars Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 9, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Allen, S.K. Reproductive potential and genetics of triploid Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Biol. Bull. 1994, 187, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuñado, N.; Terrones, J.; Sánchez, L.; Martínez, P.; Santos, J. Sex-dependent synaptic behaviour in triploid turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (Pisces, Scophthalmidae). Heredity 2002, 89, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfey, T.J. The physiology and behavior of triploid fishes. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1999, 7, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, J.R. Managing Aquatic Vegetation with Grass Carp. A Guide for Water Resource Managers; Cassani, J.R., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Varadaraj, K.; Pandian, T. Production of all-female sterile-triploid Oreochromis mossambicus. Aquaculture 1990, 84, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.G.; Chatterji, A.; McAndrew, B.; Johnstone, R. Triploidy induction in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. using pressure, heat and cold shocks. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1991, 81, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, G.C. Chromosome-set manipulation in tilapia—Techniques, problems and prospects. Aquaculture 1993, 111, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byamungu, N.; Darras, V.; Kühn, E. Growth of heat-shock induced triploids of blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus, reared in tanks and in ponds in Eastern Congo: Feeding regimes and compensatory growth response of triploid females. Aquaculture 2001, 198, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, R. Induced polyploidy in Tilapia aurea (Steindachner) by means of temperature shock treatment. J. Fish Biol. 1975, 7, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordham, B.S.; Trippel, E. Feeding behaviour of cod (Gadus morhua) in relation to spawning. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 1999, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, Ø.; Holm, J.C.; Kjesbu, O.S. Effects of periodic starvation on reproductive investment in first-time spawning Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquaculture 1995, 133, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Taranger, G.L.; Carrillo, M.; Schulz, R.W.; Fontaine, P.; Zanuy, S.; Felip, A.; Weltzien, F.-A.; Dufour, S.; Karlsen, Ø.; Norberg, B. Control of puberty in farmed fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 483–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garner, S.; Madison, B.; Bernier, N.; Neff, B. Juvenile growth and aggression in diploid and triploid Chinook salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Walbaum). J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, A.; Zanuy, S.; Carrillo, M.; Martínez, G.; Ramos, J.; Piferrer, F. Optimal conditions for the induction of triploidy in the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 1997, 152, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Cal, R.M.; Álvarez-Blázquez, B.; Sánchez, L.; Martinez, P. Induction of triploidy in the turbot (Scophthalmus maximus): I. Ploidy determination and the effects of cold shocks. Aquaculture 2000, 188, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzi, S.; Chatain, B. Pressure and cold shock induction of meiotic gynogenesis and triploidy in the European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L.: Relative efficiency of methods and parental variability. Aquaculture 2000, 189, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Cal, R.M.; Gómez, C.; Bouza, C.; Martı́, P. Induction of triploidy in the turbot (Scophthalmus maximus): II. Effects of cold shock timing and induction of triploidy in a large volume of eggs. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherfas, N.B.; Gomelsky, B.; Ben-Dom, N.; Peretz, Y.; Hulata, G. Assessment of triploid common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) for culture. Aquaculture 1994, 127, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Wilson White, J.; Warner, R.R. A social basis for the development of primary males in a sex-changing fish. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 273, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mitcheson, Y.S.; Liu, M. Functional hermaphroditism in teleosts. Fish Fish. 2008, 9, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroiller, J.F.; Guiguen, Y.; Fostier, A. Endocrine and environmental aspects of sex differentiation in fish. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 910–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, A.J.; Jellyman, D.J. Sex determination in freshwater eels and management options for manipulation of sex. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2005, 15, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickström, H.; Westin, L.; Clevestam, P. The biological and economic yield from a long-term eel stocking experiment. Ecol. Freshwater Fish 1996, 5, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.A. Effect of pH on sex ratio in cichlids and a poecilliid (Teleostei). Copeia 1985, 1985, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römer, U.; Beisenherz, W. Environmental determination of sex in Apistogrammai (Cichlidae) and two other freshwater fishes (Teleostei). J. Fish Biol. 1996, 48, 714–725. [Google Scholar]
- Papadaki, M.; Piferrer, F.; Zanuy, S.; Maingot, E.; Divanach, P.; Mylonas, C. Growth, sex differentiation and gonad and plasma levels of sex steroids in male-and female-dominant populations of Dicentrarchus labrax obtained through repeated size grading. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 66, 938–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saillant, E.; Chatain, B.; Menu, B.; Fauvel, C.; Vidal, M.O.; Fostier, A. Sexual differentiation and juvenile intersexuality in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Zool. 2003, 260, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, D.; Yamashita, M.; Kitano, T.; Iguchi, T. An aromatase inhibitor or high water temperature induce oocyte apoptosis and depletion of P450 aromatase activity in the gonads of genetic female zebrafish during sex-reversal. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2004, 137, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusslein-Volhard, C.; Dahm, R. Zebrafish; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, E.H.; Yu, R.M.; Wu, R.S. Hypoxia affects sex differentiation and development, leading to a male-dominated population in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3118–3122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, C.; Ebersole, J.P.; Kesseli, R.V. Rapid growth and out-crossing promote female development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2008, 81, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.H. Recent advances of genome mapping and marker-assisted selection in aquaculture. Fish Fish. 2014, 15, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, B.; Egedi, S.; Bártfai, R.; Orbán, L. Male-specific DNA markers from African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Genetica 2000, 110, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandian, T. Sex Determination in Fish; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Palaiokostas, C.; Bekaert, M.; Khan, M.G.Q.; Taggart, J.B.; Gharbi, K.; McAndrew, B.J.; Penman, D.J. Mapping and validation of the major sex-determining region in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) using RAD sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaiokostas, C.; Bekaert, M.; Khan, M.G.; Taggart, J.B.; Gharbi, K.; McAndrew, B.J.; Penman, D.J. A novel sex-determining QTL in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, T.D.; Kole, C. Genome Mapping and Genomics in Fishes and Aquatic Animals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, S.; Hörstgen-Schwark, G. Temperature dependent sex ratios in selected lines and crosses with a YY-male in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2011, 318, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, S.; Hörstgen-Schwark, G. Selection experiments to increase the proportion of males in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by means of temperature treatment. Aquaculture 2007, 272, S80–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magerhans, A.; Hörstgen-Schwark, G. Selection experiments to alter the sex ratio in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by means of temperature treatment. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Lim, P.; Kause, A.; Mulder, H.A.; Martin, K.E.; Barfoot, A.J.; Parsons, J.E.; Davidson, J.; Rexroad, C.E.; van Arendonk, J.A.M.; Komen, H. Genotype-by-environment interaction of growth traits in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): A continental scale study. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5572–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont-Nivet, M.; Vandeputte, M.; Vergnet, A.; Merdy, O.; Haffray, P.; Chavanne, H.; Chatain, B.A. Heritabilities and GxE interactions for growth in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) using a marker-based pedigree. Aquaculture 2008, 275, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfarth, G.W.; Wedekind, H. The heredity of sex determination in tilapias. Aquaculture 1991, 92, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, R.P.; Carpenter, R.H. Monosex Tilapia Production through Androgenesis: Selection of Individuals for Sex Inheritance Characteristics for Use in Monosex Production; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grossen, C.; Neuenschwander, S.; Perrin, N. Temperature dependent turnovers in sex-determination mechanisms: A quantitative model. Evolution 2011, 65, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyniuk, C.J.; Perry, G.M.L.; Mogahadam, H.K.; Ferguson, M.M.; Danzmann, R.G. The genetic architecture of correlations among growth-related traits and male age at maturation in rainbow trout. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 746–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnaani, A. The tilapias’ chromosomes influencing sex determination. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshel, O.; Shirak, A.; Weller, J.I.; Hulata, G.; Ron, M. Linkage and physical mapping of sex region on LG23 of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). G3: Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2012, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukovitis, D.; Sarropoulou, E.; Tsigenopoulos, C.S.; Batargias, C.; Magoulas, A.; Apostolidis, A.P.; Chatziplis, D.; Kotoulas, G. Quantitative trait loci involved in sex determination and body growth in the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) through targeted genome scan. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaiokostas, C.; Bekaert, M.; Davie, A.; Cowan, M.; Oral, M.; Taggart, J.; Gharbi, K.; McAndrew, B.; Penman, D.; Migaud, H. Mapping the sex determination locus in the Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) using RAD sequencing. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirak, A.; Seroussi, E.; Cnaani, A.; Howe, A.E.; Domokhovsky, R.; Zilberman, N.; Kocher, T.D.; Hulata, G.; Ron, M. Amh and dmrta2 genes map to tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) linkage group 23 within quantitative trait locus regions for sex determination. Genetics 2006, 174, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, P.; Viñas, A.M.; Sánchez, L.; Díaz, N.; Ribas, L.; Piferrer, F. Genetic architecture of sex determination in fish: Applications to sex ratio control in aquaculture. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lühmann, L.M.; Knorr, C.; Hörstgen-Schwark, G.; Wessels, S. First evidence for family-specific QTL for temperature-dependent sex reversal in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sex. Dev. 2012, 6, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Pang, R.; Miao, G.; Liao, X.; Shao, C.; Gao, F.; et al. Construction of a high-density microsatellite genetic linkage map and mapping of sexual and growth-related traits in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, P.; Jiang, J.; Liew, W.; Orban, L. Small-scale transcriptomics reveals differences among gonadal stages in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2014, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; You, F.; Wang, L.; Weng, S.; Wu, Z.; Hu, J.; Zou, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, P. Gonadal transcriptome analysis of male and female olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manousaki, T.; Tsakogiannis, A.; Lagnel, J.; Sarropoulou, E.; Xiang, J.; Papandroulakis, N.; Mylonas, C.; Tsigenopoulos, C. The sex-specific transcriptome of the hermaphrodite sparid sharpsnout seabream (Diplodus puntazzo). BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhne, A.; Sengstag, T.; Salzburger, W. Comparative transcriptomics in east african cichlids reveals sex- and species-specific expression and new candidates for sex differentiation in fishes. Genome Biol. Evolut. 2014, 6, 2567–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-C.; Chiu, P.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Lyu, Y.-S.; Lan, D.-S.; Chang, C.-F. Testicular dmrt1 is involved in the sexual fate of the ovotestis in the protandrous black porgy. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.C.; van Eenennaam, A.L. Transgenic approaches for the reproductive containment of genetically engineered fish. Aquaculture 2008, 275, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzbekova, S.; Chyb, J.; Ferriere, F.; Bailhache, T.; Prunet, P.; Alestrom, P.; Breton, B. Transgenic rainbow trout expressed sGnRH-antisense RNA under the control of sGnRH promoter of Atlantic salmon. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 25, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclean, N.; Hwang, G.; Molina, A.; Ashton, T.; Muller, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Iyengar, A. Reversibly-sterile fish via transgenesis. Inf. Syst. Biotechnol. News Rep. 2003, 12, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Maclean, N.; Rahman, M.; Sohm, F.; Hwang, G.; Iyengar, A.; Ayad, H.; Smith, A.; Farahmand, H. Transgenic tilapia and the tilapia genome. Gene 2002, 295, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z. A perspective on fish gonad manipulation for biotechnical applications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budd, A.M.; Banh, Q.Q.; Domingos, J.A.; Jerry, D.R. Sex Control in Fish: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities for Aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 329-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3020329
Budd AM, Banh QQ, Domingos JA, Jerry DR. Sex Control in Fish: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities for Aquaculture. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2015; 3(2):329-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudd, Alyssa M., Quyen Q. Banh, Jose A. Domingos, and Dean R. Jerry. 2015. "Sex Control in Fish: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities for Aquaculture" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 3, no. 2: 329-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3020329
APA StyleBudd, A. M., Banh, Q. Q., Domingos, J. A., & Jerry, D. R. (2015). Sex Control in Fish: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities for Aquaculture. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 3(2), 329-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3020329





