Abstract
The influence of salinity on the characteristics of individual bubbles (2–4 mm in diameter) in fresh and saline water (up to 40 practical salinity units) was investigated. Bubbles were produced by forcing air through capillary tubes. Aqueous solutions in distilled and filtered tap waters with minimized presence of organic additives were used. Salinity, surface tension, and water temperature were monitored. Parameters measured were the bubble surface lifetime, diameter, and rise velocity. The surface lifetime varies widely (in the range of 0.4–35 s) depending on the salinity concentration and the purity of the solutions. Variations with salinity of size and rise velocity of large individual bubbles are discussed. Interpretation of the results in terms of anti-foaming (negative adsorption), as well as the Marangoni and the Gibbs effects, is helpful in understanding the results.
1. Introduction
Whitecaps visualize the breaking of water waves with air entrainment. Whitecaps comprise both bubble clouds (plumes) below the surface and floating foam layers on the surface. For measurements in marine systems, the electromagnetic properties (e.g., reflection and emission) of these bubble plumes and foam layers enable detection of whitecaps with optical, infrared, or microwave sensors [1]. For marine and climate studies, the importance of these bubble plumes and foam layers is that they enhance the transfer processes across the air–sea interface [2,3,4,5]. Air–sea interaction (ASI) processes are used to model the coupling and boundary conditions between the ocean and the atmosphere in numerical weather predictions and climate models. Reliable, well-constrained parameterizations of ASI processes are thus necessary for accurate model predictions.
Air–sea fluxes of heat and mass (e.g., gasses and particles) are often formulated in terms of whitecap fraction W (defined as the fractional area of whitecaps within unit area of sea surface). Whitecap fraction is usually parameterized as a function of wind speed. However, other variables also influence W, including atmospheric stability, currents, seawater temperature, wave field, salinity, and surface-active materials (surfactants) [6,7]. A better understanding of the relationship of whitecap fraction to each of these variables can facilitate the development of new W parameterizations.
Lower W values can be expected in waters with short-lived whitecaps. Conversely, long-lived (persistent) whitecaps can yield higher W values. Whitecap lifetime depends on the time intervals during which: (i) the whitecaps persist on the surface, and (ii) subsurface bubble plumes replenish the whitecaps on the surface. Bubble surface lifetime t determines the former while bubble size (e.g., diameter d) and its respective rise velocity Vr affect the latter. Water chemical composition—including its salinity and the presence of organic compounds and/or surfactants—influences t, d, and Vr. The objective of the current study is to investigate the impact of salinity variations on bubbles forming the whitecaps.
Most previous measurements in fresh and saline waters have focused on the more stable, equilibrated phase of the bubble population. Less attention has been paid to the characteristics of the transient bubble population during the initial, active phase of wave breaking because of the challenge of resolving individual bubbles. However, bubbles and whitecaps observed during the active phase of wave breaking are also of interest because most dynamic ASI processes occur during this initial period [2,8].
Bubbles formed during the initial stages of the wave breaking show a wide range of sizes with notable prevalence of large ones (larger than 0.5 mm in diameter) [9] compared to the equilibrated bubble population [10] (chapter 4.4). Asher et al. [8] investigated in fresh and sea waters the transient bubble population at the lower size end (diameters of 0.1–2.2 mm). In this study, we focus on the under-sampled, initial stage of whitecaps by characterizing large individual bubbles (above a diameter of 2.2 mm).
Laboratory and field experiments have shown that whitecaps in seawater are more persistent [10,11]. Variables quantifying the lifetime of whitecaps include the decay of whitecap areas and foam layers thickness [10,11,12,13,14] or the lifetime of bubbles on the surface before bursting [15,16,17,18]. Typically, large bubbles persist for less than 0.01 s to about 3 s in fresh or clean water. Bubble surface lifetimes observed in saline water are in striking contrast: 0.3–30 s. These saline-water values are consistent with whitecap lifetimes obtained in a recent field campaign with a completely different measuring technique such as infrared imagery [1].
Salinity affects the formation, behavior, and characteristics of bubbles by changing the ionic strength (a measure of the concentration of ions in a solution) of the water and consequently the surface tension γ at air–water interfaces [19,20]. Generally, bubbles are easily created in aqueous solutions when γ is lower than its value in pure water γ0 (γ < γ0). The surface tension of water is always lower when the water temperature is higher or if the water contains organic additives. However, when adding inorganic salts, the surface tension may either increase or decrease depending on the purity of the water. When added to pure water, salts create negative surface excess (or negative adsorption) of the solute at air–water interfaces, thus increasing γ of the solution above γ0. The negative surface film pressure ∆γ ≡ γ0 − γ < 0, associated with these higher γ values, hinder the formation of bubbles. Inorganic salts thus act as anti-foaming agents in clean aqueous solutions. The anti-foaming role of the salts reverses in presence of organics and surfactants. By increasing the ionic strength of the solutions, salts enhance the positive adsorption created at interfaces by the organic additives. The resulting positive surface film pressure (∆γ > 0) facilitates bubble formation and stabilizes bubbles against bursting. Inorganic salts thus augment the bubbling (foaming) in contaminated aqueous solutions.
Previous salinity experiments have focused primarily on the contrast between fresh and saline waters or on the effect of surfactants in seawater, e.g., [8]. In this study, we aim to examine the salinity effect by systematically varying the salinity concentration (i.e., the ionic strength) in solutions with minimized influence of organic additives. This approach can help to deduce the relative importance of salinity versus surfactant effects, and thus guide the parameterization of whitecap fraction. To this end, we conducted laboratory experiments to observe and quantify the effect of salinity S from 0 to 40 practical salinity units (psu) on the characteristics of individual macro-bubbles of diameter of 2–4 mm. We used video records of individual bubbles to measure their t, d, and Vr in two experiments with salt added to distilled and filtered tap waters. To understand and interpret the impact of salinity on bubbles, we also measured the surface tension γ of the saline solutions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions
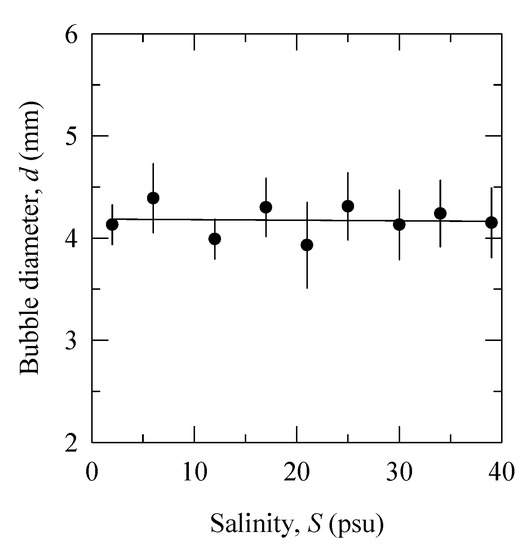
To avoid wall effects, the experiments were performed in transparent plastic tanks with dimensions much larger than individual bubbles. Individual bubbles were generated by forcing atmospheric air through capillary tubes of various inner diameters (Appendix A). The air flow rate F through the capillaries was controlled with a fine valve; a production of 10 bubbles for 30 s assured F < 1 cm3 min−1 (Table 1). The sizes and behavior of the bubbles thus generated were independent of the flow; the only parameter of the experimental setup that influenced the bubbles was the capillary opening. A capillary with an inner diameter 2R = 1.5 mm was used in the experiment with filtered water. Capillaries with different inner diameters (0.5, 1 and 1.15 mm) were used in the experiment with distilled water. The predicted bubble diameters dpred = 2r range between 2.8 and 4 mm (for fresh water with S = 0 at water temperature of 20 °C, Table 1). We thus expect the produced bubbles to be representative of bubbles generated during active wave breaking.

Table 1.
Experimental and bubble parameters for bubbles produced by capillary with different sizes.
Initially, an experiment with filtered tap water was conducted in a large (121.9 cm L × 32.4 cm W × 39.0 cm H), thoroughly cleaned tank filled to a depth of 32.4 cm. Two mechanical filters (5 and 1 μm) and a charcoal canister were used for filtering. It was difficult to maintain the quality of the filtered water in the large tank throughout the experiments. Thus, another experiment with distilled water was conducted in a smaller (30.2 cm L × 30.3 cm W × 27.8 cm H), thoroughly cleaned tank with water depth of 26.5 cm. The use of distilled and filtered tap waters aimed to remove or minimize the presence of organic compounds. Salinity S, surface tension γ, and water temperature T were monitored during all experiments. Table 2 summarizes the experimental conditions.

Table 2.
Summary of the controlled parameters for experiments in distilled and filtered waters: salinity S, water temperature T, calculated surface tension of pure NaCl solutions γ0 (calculated for each S and T with Equation (A3) in Appendix B), measured surface tension γ, standard deviation of the measured surface tension σγ, surface film pressure ∆γ (calculated as ∆γ = γ0 − γ).
A salinity range of 2–40 psu was chosen to span values observed from lakes to estuaries to the open ocean. Salinity differences were achieved using laboratory-grade sodium chloride (NaCl) without additional cleaning procedures [21]. The salinity of the water was varied in steps of δS ≅ 4–6.5 psu by adding an appropriate amount of salt to the water volumes used in each experiment. The salinity was measured with a handheld refractometer (Aquatic Eco-Systems, Inc., Apopka, FL, USA), which relates changes of the water refractive index to varying concentration of added salt. The refractometer was calibrated before each experiment. To check the uniformity of the salinity after salt dissolution, drops taken with a pipette at different locations and depths in the tanks were sampled.
The water temperature was measured with a thermistor thermometer (Cole-Parmer Instrument Company, Vernon Hills, IL, USA). During the experiments, water temperature changed slightly with the diurnal cycle (some experiments lasted a few days) and due to the lighting used for the video records. Strict usage of the lighting only for the period of recording minimized variations of the water temperature. The water temperature fluctuations at a given salinity were δT = 0.2–0.3 °C while those between different salinity steps were δT ≤ 0.4 °C (with one exception, Table 2). Hereafter, we neglect the temperature effect because we established that the temperature impact on the surface tension was much smaller than that of salinity during the experiments (Appendix B).
Surface tension was measured with a tensiometer (Biolar Corp., Brentwood Cir Provo, UT, USA) based on Wilhelmy plate method [19,20]. A thin plate of platinum foil, whose weight is balanced a priori with a built-in Roller-Smith precision balance, is lowered gradually toward the measured liquid sample until it just touches the surface. Surface tension then pulls down the plate, and the increase in the plate weight due to wetting is noted. The weight-change reading, in mg, is multiplied with a coefficient specific for the instrument (0.1909 in our case), and the surface tension is obtained in dynes cm−1 (≡ mN m−1). Mean value γ and standard deviation (SD) σγ of the surface tension were obtained from 10 readings. The relative measuring error σγ/γ is from 0.5% to 10%.
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
Video records of individual bubbles were made for 2–4 min with standard cameras (30 frames per second). Front lighting with two 600-W lamps made the bubbles bright in the video records [22]. The visualization was improved by placing dark screens on the tank back wall and beneath the tank. Images of individual bubbles were digitized with frame grabber (Epix Inc., Buffalo Grove, IL, USA, 4MEG Video Model 10) and processed with image processing software (4MIP).
The bubble diameter d and rise velocity Vr were determined from side view images recorded with a Panasonic AG-160 camera. The camera is a ½-inch charge-coupled device (CCD) sensor equipped with a 6× zoom lens with focus lengths from 9 to 54 mm (where the focus length is defined as the distance between the lens and the image sensor when the subject is in focus). Large camera field of view (FOV) was used to track the rise of the bubble in the tanks. Camera focus length set at ≅ 35 mm and an automatic aperture adjustment provided object distance of 1.2 m (where the object distance is defined as the distance from the object to its image on the camera sensor). The rising bubbles were in focus at all times at working distance of 1 m from the rim of the camera to the tank wall. A ruler within the camera’s FOV gave a reference scale needed to calculate the bubble rise velocity; the ruler was located on the tank wall about 10 cm from the plane of the rising bubbles. Close-up images of individual bubbles were recorded in camera side view with small FOV providing x and y scales in the order of 0.27 mm/pixel and 0.62–0.8 mm/pixel, respectively.
To determine the bubble diameter d, up to 30 video frames with bubble images were digitized for each salinity step. We determined the projected-area equivalent diameter of the bubble from measured major (horizontal) x and minor (vertical) y axes using d = (xy)1/2. This basis for the equivalent diameter was found to be satisfactory due to the small range of aspect ratios: y/x ≈ 0.6–0.8. The percentage difference of projected-area equivalent diameter from the volume-equivalent diameters d = (xyy)1/3 was about 5%.
The travel time for a reference distance traversed by a bubble was obtained by counting the frames and using the time interval between the frames (33 ms). The reference distance was 24–30 cm in different experiments, from the tip of the forming capillary up toward the water surface. For each salinity value, the averaged travel time was determined from tracking 10 bubbles. Rise velocity Vr was calculated for each travel time using the reference distance; the mean and SD of the resulting 10 Vr values are reported.
The bubble surface lifetime t was determined from top view images recorded with a Panasonic WV-3400 camera with a 6× zoom lens with focus lengths from 12.5 to 75 mm. The setting of the focus length and aperture provided an object distance of 1.5 m. With these settings, bubbles on the water surface were in sharp focus at working distance of 28 cm from the camera rim.
The bubble surface lifetime t was obtained either by counting the number of frames a bubble survived on the surface after popping up or using the time recorded from the camera timer. When bubbles coalesced, they were excluded from consideration. For the experiments in filtered water, data were extracted for 50 bubbles at each salinity step. To illustrate the variations of the individual t samples, we obtained their distributions at each salinity step. The distributions were constructed for time range of 0–20 s with bins of 1 s. These individual 50 samples of t were also used to obtain average values of t for each salinity step (these differ from the t values at the distribution peaks), and their SDs, in order to examine trends of surface lifetime at different salinities. For the experiment in distilled water, individual t measurements were obtained for 15 bubbles for each of the three diameters (Table 1) at each salinity step. Distributions were not constructed for t in distilled water as fewer samples were taken.
We did not collect specific data on bubble coalescence. However, the surface lifetime t of a bubble can be used as a proxy for the coalescence rate by noting that the air–water interface itself plays the role of a second very large bubble [17,23]. Thus, for example, short-lived bubbles are indicative of a high coalescence rate, and vice versa: long-lived bubbles point to a low coalescence rate.
3. Results
Figure 1a,b depicts the isothermal variations of surface tension with salinity in distilled and filtered waters. The experimental values of S and T (Table 2) were used to calculate surface tension for pure water (no contamination) γ0 with Equation (A3) (dashed lines in Figure 1a,b). Figure 1a shows the surface tension γ of the distilled water at S = 2 psu is below the respective γ0 value. The implication is that the experiment started with some initial contamination of the distilled water. Contamination may have occurred either from impurities in the added NaCl or during the measuring procedures (Section 2.1). As the salinity increases, we observe that γ increases due to negative adsorption and even exceeds γ0 at S = 19 psu to give a negative film pressure ∆γ = −1.65 mN m−1 (Table 2). The γ values are below γ0 trend for S > 24 psu. Figure 1b shows that the surface tension γ of the experiment in filtered water at S = 2 psu is also below the respective γ0 value, a sign that the experiment began with some initial contamination of the large water volume. Values of γ(S) decrease monotonically over the entire range of S. We discuss the implications of the results in Figure 1a,b in Section 4.1.
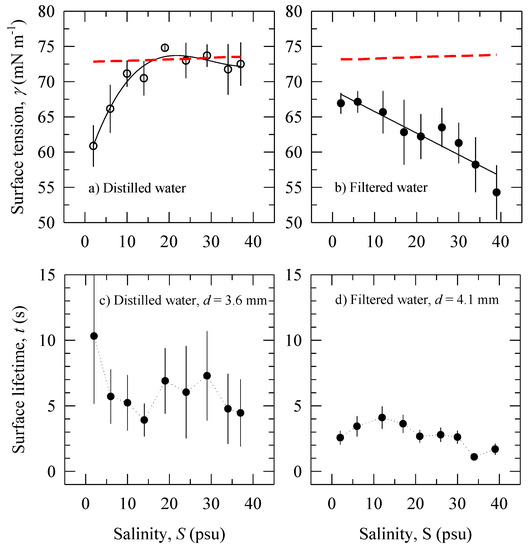
Figure 1.
Surface tension γ as a function of salinity S (Table 2) with error bars of ±95% confidence interval in: (a) distilled water. The error bar at S = 19 psu is 0.37 mN m−1; (b) filtered water. The solid lines are regressions (cubic polynomial and linear, respectively). The dashed lines are surface tension of pure NaCl solutions γ0 calculated with Equation (A3) for each pair of salinity and temperature values (Table 2). Bubble surface lifetime t as a function of salinity S: (c) distilled water (bubble diameter of 3.6 mm); (d) filtered water (bubble diameter of 4.1 mm).
3.1. Bubble Surface Lifetime
Figure 2a presents images of bubbles floating on the water surface before they burst. We observed that bubbles rarely overlap for fresh water or dilute (low salinity) solutions. They either burst before the next bubble surfaced or drifted away from the point of surfacing. However, when a bubble lingered until another one appeared nearby, immediate attraction and coalescence occurred; this is consistent with previous observations [17,23,24]. Several bubbles co-existed on the surface of saltier solutions. Usually they persisted as a cluster until eventual coalescence or bursting.
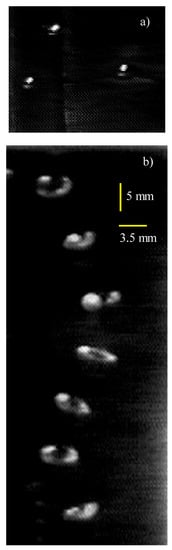
Figure 2.
Images of: (a) Bubbles floating on the water surface before bursting. (b) A bubble in seven consecutive moments (∆t = 33 ms) on its path up (likely helical) towards the water surface.
Bubble surface lifetime t varies widely for the narrow range of bubble diameters investigated here. Figure 3 shows the probability density functions of bubble surface lifetime t for different salinity obtained in the experiment with filtered water. It is seen that in fresh water (2 psu) t values vary up to about 10 s with a pronounced peak around 2 s. The widest range of possible t values, up to 13 s, is for salinity range of 6–17 psu with no pronounced peak. Further increase of the salinity, above 21 psu, confines the lifetime values to below 7–10 s. At the highest salinity (34 and 39 psu), most of the bubbles survive for less than 1–2 s. The variations of t for distilled water are much wider. The individual t samples (Section 2.2) in distilled water for all measured bubble sizes range between 0.4 and 35 s, as opposed to the range of up to 13 s for filtered water.
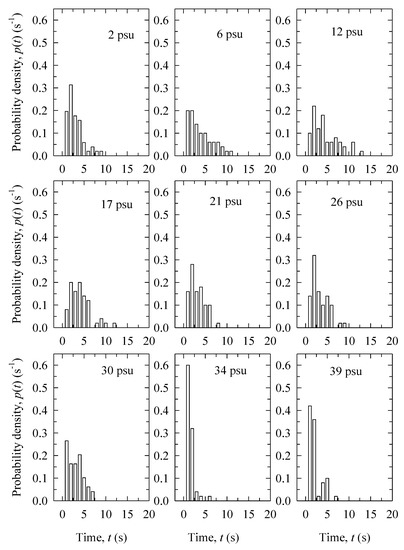
Figure 3.
Probability density distributions of the bubble surface lifetime t values with varying salinity concentrations for the experiment in filtered water.
Using the average t values (Section 2.2), Figure 1c,d presents data on bubble surface lifetimes t within 95% confidence interval (CI) versus salinity in distilled and filtered water. Results for bubbles with comparable diameters for the two experiments are shown: d = 3.6 mm for distilled water experiment and d = 4.1 mm for the filtered water experiment (Table 1). The uncertainty of the averaged values plotted in Figure 1d reflects the variations of the individual samples illustrated in Figure 3. Different number of samples used for SD (15 for distilled water versus 50 for filtered water, Section 2.2) is the reason for the larger uncertainty (error bars) of t in Figure 1c compared to Figure 1d. We discuss the large differences in t variations in Figure 1c,d in Section 4.2.
The large error bars in Figure 1c preclude a definitive conclusion on the trend of the bubbles surface lifetime t with salinity. However, we can determine a range of values for the surface lifetime in contaminated distilled water because the observed maximum and minimum t values have distinct uncertainties: We observe maximum bubble surface lifetime t ≅ 10 s at S = 2 psu; the minimal t ≅ 4 s occurs at S = 14 psu. Figure 1d shows small yet distinct variations in the bubble surface lifetime with salinity for the experiment in filtered water. Bubble surface lifetimes are the longest (up to 4 s) for low salinity (S < 12 psu). The bubbles become increasingly short-lived, attaining lifetimes of 1–2 s, for S > 30 psu.
The main observations in Figure 1c,d are: (i) significantly wider variations of t in distilled water than in filtered water; and (ii) t in distilled water is a factor of two longer than t in filtered water for the salinity range. We discuss these results in conjunction with surface tension measurements (Figure 1a,b) in Section 4.2.
3.2. Bubble Size
The ellipsoidal shape of the bubble in Figure 2b is typical for the large bubbles observed in our experiments. Figure 2b also shows a typical bubble trajectory through the water column. The figure comprises images at seven consecutive moments at time steps of ∆t = 33 ms, overlapped to reveal the bubble motion. The experiments of Tomiyama et al. [25] for similarly sized bubbles and large initial shape deformation (defined in Appendix A) show a zig-zag path for small distances (less than 10 cm) from the capillary. For larger distances, they observed helical bubble paths. The bubble path in Figure 2b is likely to be helical because the visualizations are at locations of 20–30 cm above the capillary.
Table 1 provides mean equivalent bubble diameters d with standard deviation σd; the measured equivalent values for ellipsoidal bubbles agree with the predicted values for idealized spherical bubbles (Equation (A2)). The average relative error σd/d of the measured equivalent bubble diameters is 10%. Note that this error includes not only the experimental uncertainty but also bubble size variations arising from the bubble shape oscillation [25,26,27]. This is especially true for cases with large initial shape deformation where the bubble size depends on the rotation of the bubbles; bubbles seen from different angles will have different shapes due to waves traveling on the bubble-water interface.
Figure 4 shows the bubble diameter as a function of salinity obtained from the experiment in filtered water using capillary diameter 2R = 1.5 mm (Table 1). The bubble diameter (mean value 4.17 ± 0.43 mm) is independent of salinity. This result is consistent with Quinn et al. [26] observations of a constant bubble aspect ratio y/x in aqueous solutions of different inorganic salts. We discuss possible explanation of the bubble size constancy in Section 4.3.
3.3. Bubble Rise Velocity
Table 1 lists the mean Vr values and their respective standard deviations over the salinity range for each measured bubble diameter in distilled and filtered waters. Figure 5 shows these results with 95% CI. The measured mean Vr values are consistent with previously reported terminal velocity for bubbles of comparable sizes in pure water (see Figure 7.3 in [26]). Considering that some contamination occurred during our filtered water experiment (Figure 1b), the position of the mean Vr value close to Clift et al.’s curve for pure water (instead of the curve for surfactant-contaminated water) is unexpected. However, comparison to bubble rise velocity reported by Asher et al. [8] (see their Figure 6) corroborate the comparison to the data of Clift et al. Our Vr values for bubble diameters above 2.54 mm in fresh water (S = 2 psu) are comparable to the Vr values in [8] for bubbles with d ≈ 2.2 mm in fresh, clean water. For any bubble size and salinity, our Vr results are higher than those of Asher et al. [8] for surfactant-contaminated water. We speculate that the surface of large bubbles, like those in the filtered water experiment (Table 1), may not be fully covered by the contaminants and thus such large bubbles can behave like clean bubbles [28]. The fact that contamination during our filtered water experiment did not affect Vr significantly, compared to values in pure solutions (dashed line in Figure 1b), implies that the contaminants are not surfactants.
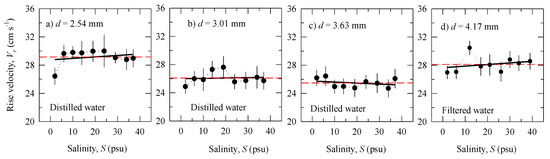
Figure 5.
Bubble rise velocity Vr as a function of salinity S: Experiment in distilled water for different bubble diameters d: (a) d = 2.54 mm; (b) d = 3.01 mm; (c) d = 3.63 mm; (d) d = 4.17 mm for filtered water. Monitored variables are given in Table 2 and Figure 1a,b. The solid (black) lines are linear regression fits Vr(S) to the data. The dashed (red) horizontal lines show the mean Vr values for each bubble diameter (Table 1). The dotted lines connect the data points.
Comparing the plots for distilled water (Figure 5a–c), we observe a decrease of Vr as the bubble diameter increases (Table 1); the trend is statistically significant with p < 0.05 from Student’s t-test. Such a decreasing trend of Vr with d is expected in the intermediate region of the rise velocity for clean water [26].
Figure 5 shows the dependence of the rise velocity Vr on salinity S. The solid (black) lines are linear regression fits Vr(S) through the data, and dashed (red) horizontal lines show the mean value for each bubble diameter (Table 1). The slopes of the regression lines do not differ statistically from the respective means (p > 0.05 from Student’s t-test). That is, the range of salinity variations, from fresh to open ocean waters, has little effect on the rise velocity of large bubbles during the active phase of wave breaking.
4. Discussion
4.1. Salinity Action during Experiments
We seek to examine the role of salinity on bubble characteristics with minimized influence from organic compounds. Because the surface tension of a solution behaves differently in presence of salts and organics (Appendix C), we use the isotherms γ(S) in Figure 1a,b to: (i) assess the role of salinity for foaming of the solutions; and (ii) infer possible mechanisms by which salinity impacts bubble stabilization.
The dependence of γ on S in Figure 1a (Section 3) shows there is an increase of the γ(S) trend. This observation is consistent with negative adsorption taking place in electrolyte solutions (Figure A2). It results in an increasingly less positive film pressure ∆γ, eventually reaching ∆γ < 0 at S ≅ 19 psu. This suggests that the salinity acts progressively as an anti-foaming agent. The decrease of the γ values below this peak for S > 24 psu is small (within the error bars); broadly, the γ(S) trend is approximately constant and remains close to that of γ0. This suggests that the anti-foaming action of the salinity continues to the end of the experiment. The result in Figure 1a therefore indicates that our experiment in contaminated distilled water was partially successful in observing the anti-foaming effect of salinity.
The dependence of γ on S in Figure 1b shows initial contamination and progressively decreasing γ(S) trend. This observation is consistent with positive adsorption taking place in solutions of contaminated filtered water. It results in increasing film pressure ∆γ, from approximately 6 mN m−1 to as much as 20 mN m−1 (Table 2). This suggests that the salinity acts to enhance both the foaming and the stabilization that the contaminants bring up. The result in Figure 1b therefore illustrates two aspects of the salinity role in contaminated filtered water. One aspect is that the salinity action reverses to that of a foaming agent in the presence of organic additives. The second is that salinity enhances the foaming potential of solutions.
The presence of some contaminants during the experiment in distilled water (Figure 1a) implies that some surface film may have formed on interfaces promoting bubble stabilization. We speculate that the anti-foaming action in the diluted solutions (S ≤ 19 psu) may neutralize this stabilization. For the more concentrated solutions (S > 19 psu), the weak slope (with derivative dγ/dS ≈ 0) implies weak stabilization by the small amount of contaminants present. (Strong dγ/dS gradients result in a more elastic film (vide Appendix C)). While the γ(S) trend decreases over the entire range of salinity during the experiment in filtered water (Figure 1b), it does not reach saturation level. We thus infer that the contaminants in this experiment are not surfactants (vide Figure A2), a result consistent with our observation regarding the high Vr values (Section 3.3). The large slope of the γ(S) isotherm (dγ/dS ≠ 0) implies the formation of surface film with elasticity sufficient to provide effective stabilization by the present contaminants. Recognizing the tendencies of the Marangoni elasticity in dilute solutions and the Gibbs elasticity in more concentrated solutions (Appendix C), we infer that both effects are likely to have contributed to stabilization of the bubbles in solutions with different salinity.
4.2. Salinity Role for Bubble Stabilization
Figure 1c,d shows that bubble surface lifetime t in distilled water is a factor of two longer than t in filtered water over the salinity range. To understand and interpret these results, below we consider the bubble lifetime observations together with the respective γ(S) trends (Figure 1a,b and Section 4.1). However, we first discuss the question whether the bubbles were affected by the surface tension of the bulk solutions or by the surface tension of the air–water free surface. This question arises from the observation in Figure 1c,d of significantly larger variations of t in distilled versus those in filtered waters.
One possible reason for differing variations of t between Figure 1c,d could be an effect observed and discussed by Garrett [29]. When a bubble floats on the water surface and bursts, the surface film is perturbed. Locally, the water surface is cleaner for a few seconds as the surface film recovers. If a new bubble appears on the surface during this interval, its lifetime will be determined by the new surface conditions. In such uncontrolled conditions, the competition between the surface tension of the disturbed spot with the surface tension of the bulk solution leads to wide variations of the observations (up to ±60% deviations between measurements [29]). The differing variations between Figure 1c,d suggest that this “Garrett” effect occurs during our experiments with a more pronounced influence on the measurements in distilled than in filtered water. Garrett [29] noted times of at least 30 s (and even minutes) were needed for the recovery of water surface films by surfactants. With our flow rate of 10 bubbles for 30 s (Section 2.1), the bubbles surfaced roughly every 3 s; this impedes full recovery of the water surface films. In absence of a film at the air–water interface, we deduce that the surface tension of the bulk solutions (Figure 1a,b) were determining the observed t values in our experiments.
For the experiment in distilled water (Figure 1c), the minimal t value that we observed is longer than the bubble lifetimes less than 3 s expected in clean water (Section 1). This range of observed t values is consistent with the surface tension trend (Figure 1a) and the corresponding surface film pressure ∆γ (Table 2). The maximum t value is associated with maximum positive film pressure ∆γ ≅ 12 mN m−1 at S = 2 psu; this stabilizes the bubble caps against bursting thus prolonging bubble lifetimes. Because the solution at S = 2 psu is dilute, it is likely that the stabilization is realized by the Marangoni effect (Section 4.1). As the anti-foaming action of salts takes place for S < 19 psu (Section 4.1), t decreases to a minimum value. With small variations of γ and weak potential for stabilization by the present contaminants (Figure 1a and Section 4.1), surface lifetimes settle at 6 s (on average) for S ≥ 19 psu (Figure 1c).
For the experiment in filtered water (Figure 1b,d), relatively low ∆γ values for S < 12 psu (Table 2) promote long surface lifetimes (up to 4 s) of the bubbles. This result is consistent with the expected bubble stabilization by the Marangoni elasticity in dilute solutions (Section 4.1). Further increase of ∆γ with S (Figure 1b and Table 2) does not stabilize the bubbles further; rather, the minimal observed t values are at the highest ∆γ. This observation contrasts with the expected stabilization due to the strong surface tension gradient seen in Figure 1b at high salinities. Considering that the possible contamination in our experiments is weak (or at least not caused by surfactants), we speculate that the increasing ionic strength of the solutions is able to counteract the stabilization to yield low surface lifetime.
4.3. Salinity Effect on Large Bubble Sizes
Observations have established that the bubble size spectrum narrows towards smaller sizes from fresh to more saline waters as the mean bubble radius decreases [30]. Recent results, summarized in [5], confirm that the peak of the bubble size distribution shifts toward smaller bubble sizes with increasing salinity. Our results of bubble sizes being independent of S (Figure 4) differ.
Other processes than salinity variations affect the bubble sizes. Our finding of the constancy of bubble size over the salinity range of the experiments can be explained as the net result of competing processes acting on a bubble while rising through the water column, namely: the effects of pressure, heat transfer, and mass transfer [31]. In the configuration of the experiments—shallow tanks and negligible air/water temperature differentials (Section 2.1)—changes in bubble sizes due to these processes are imperceptibly small.
To help explore the salinity effect on the bubble size, we also need to consider the regime of bubble formation in the experiments. The low air flow rates in our experiments (Table 1) suggest that the bubble formation is in the pinch off (sinuous wave breakup) regime [32]. In this regime, surface tension is the predominant formative force and sets the observed bubble sizes. At a specific capillary size R, Equation (A1) shows that the ratio γ/∆ρ decreases by less than 2% over the salinity range of 0–40 psu. This yields a decrease of the predicted bubble diameter with S by less than 0.6%. In our experiment, γ is decreasing with S by about 20% (Figure 1b); respective changes of the ratio γ/∆ρ would thus lead to a decrease of the bubble size by 7.6% over the S range. Such bubble size variations are less than the uncertainty of 10% and cannot be resolved with a single side-view camera (Section 2.2) because of the dynamics of bubble motion (oscillation, rotation, and advection). We therefore observe a nearly constant bubble diameter for our range of salinities. To reiterate, our bubble diameters are large (Table 1); the dynamics and salinity dependence of diameters of smaller bubbles may differ.
In the field, at any given location, the environmental conditions and water composition (salinity, organics, temperature, etc.) determine the surface tension. Our results imply that a specific surface tension creates a bubble population with a distinctive size distribution. This predetermined bubble size range can evolve through the impact of surface tension on the rate of bubble coalescence (Section 3.1). In fresh water, due to the high rate of coalescence, the number of large bubbles would increase at the expense of smaller bubbles. In contrast, in saline waters, the stabilization of bubble walls and inhibition of coalescence preserve the small bubbles. We infer, therefore, that at a specific site (open ocean, coastal or riverine) the salinity, via its impact on the surface tension, plays a role in determining the bubble size distribution and its subsequent temporal evolution.
Deep-water seeps form large bubbles too [33]. Our result in Figure 5 implies that salinity stratification of the water column would not affect the rise velocity and gas exchange of seep bubbles rising from ocean depth.
5. Conclusions
We present the results of laboratory experiments designed to observe and quantify the effect of salinity S over the range of 0–40 psu on the characteristics of individual bubbles with diameters of 2–4 mm. Salt was added to distilled and filtered tap waters to discriminate the influence of salinity variations (with minimized influence of organic additives) on surface lifetime t (Section 3.1), bubble diameter d (Section 3.2), and rise velocity Vr (Section 3.3). Concurrent measurements of surface tension γ during the experiments (Section 3) allowed interpretation in terms of physico-chemical processes associated with the ionic strength of electrolyte solutions (Section 4.1). These include the anti-foaming action of salts and their role in bubble stabilization by surface films (Section 4.2).
Even with carefully created solutions in the laboratory, contaminants (organic or otherwise) in low concentrations are present. As a result, we were able to isolate the salinity effect from that of contaminants only partially. Definitive understanding of the effects of salinity alone on surface tension remains elusive. Nonetheless, our data provide insights for real-world conditions where the effects of salinity and those of organic compounds coexist. The main conclusions of our study are:
- (1)
- Wide variations of the bubble surface lifetime t are measured with a range of 0.4–35 s. Changing water surface conditions after bubble bursting are most likely causing such wide variations; this effect is more pronounced in cleaner solutions (Figure 1c,d).
- (2)
- Even weakly contaminated solutions can stabilize bubbles at low S (Figure 1c). The anti-foaming action of S decreases bubble surface lifetime when surface tension approaches negative film pressure in a weakly contaminated water (Figure 1a,c). At a given level of contamination, bubbles are short-lived (less stable) at S > 30 psu (Figure 1c,d).
- (3)
For the range of salinity found in the open ocean (28–39 psu), we conclude that there is likely to be a weak direct effect of salinity on the characteristics of large individual bubbles, and its role in sustaining whitecap lifetime. Therefore, explicit parameterization of whitecap fraction, and particularly active whitecap fraction, in terms of salinity is not a high priority.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the help of colleagues at the Air–Sea Interaction Laboratory, University of Delaware, at the time of collection of the data reported here. Part of this work is sponsored by the Office of Naval Research (NRL program element 61153N). Data for the experimental conditions and surface tension are given in tables in the text. More data are available from the first author upon request (maggie.anguelova@nrl.navy.mil).
Author Contributions
M.D.A. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; M.D.A. and P.H. interpreted the results and wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Formation of Individual Bubbles
The bubble radius r that a capillary tube with radius R can produce is determined from the relationship [31]:
where ∆ρ is the air–water density difference, and g is acceleration due to gravity. This relationship is obtained from the balance between the surface tension force at the capillary opening () and the buoyancy force of the spherical bubble equal to . With γ = 72 mN m−1 and ∆ρ ≅ 998 kg m−3, Equation (A1) reduces to (in mm):
The predicted bubble sizes (Table 1) are in the intermediate size range (equivalent diameter typically between 1 and 15 mm), and thus would fall in the ellipsoidal shape regime [26] (see their Figure 2.5).
Capillary with R << r form bubbles with large initial shape deformation [25]. Because in our experiments the ratio R/r is in the range of 0.2–0.4, the produced bubbles would have large initial shape deformation. The motion, shape, and velocity of bubbles with large initial shape deformation are markedly sensitive to the initial conditions, including the method of bubble release. It is therefore important to monitor and characterize the initial conditions of bubble formation. The flow rate F through the capillary tubes is a parameter that influences the initial conditions of bubble formation and sets the size and rise velocity of the generated bubbles [31] (see their Figure 3.5). At high flow rates, the bubbles rise in a stream and coalesce. This leads to non-uniform bubble sizes different from those predicted by Equation (A2). Low flow rates (e.g., F < 10 cm3 min−1) ensure generation of individual bubbles.
Appendix B. Surface Tension Variations
The surface tension γ of aqueous solutions changes with variations of water temperature T and with the presence of dissolved substances (vide Appendix C). The surface tension of clean seawater at temperature T and salinity S can be obtained empirically from the equation [34]:
where T is in °C, and the chlorinity Cl is obtained from our measured salinity values (Table 2) using the relationship S = 1.80655Cl [35]. Figure A1a shows surface tension variations with S at fixed T = 20 °C from Equation (A3). The surface tension excess (surface film pressure) ∆γ is negative (i.e., γ > γ0 where γ0 is for pure water) with a magnitude |∆γ| up to ~0.77 mN m−1 over the salinity range S. Comparison to data (symbols in Figure A1a) shows that ∆γ could be larger. Figure A1b shows changes in surface tension due to variations in both water temperature T and salinity S. At a given salinity, changes of the water temperature in the range of 0–30 °C can suppress the surface tension by ~4 mN m−1.
γ (T, S) = 75.64 − 0.144T + 0.0399Cl
Referring to the values of T and S in our experiments (Table 2), it is seen from Figure A1c that a temperature rise of δT = 0.5 °C would cause a decrease of the surface tension by δγ(δT) = 0.072 mN m−1 at a given salinity (e.g., S = 24 psu). In comparison, a variation of salinity δS = 4 psu (our smallest step-size change of S), would change the surface tension by δγ(δS) ≈ 0.088 mN m−1.
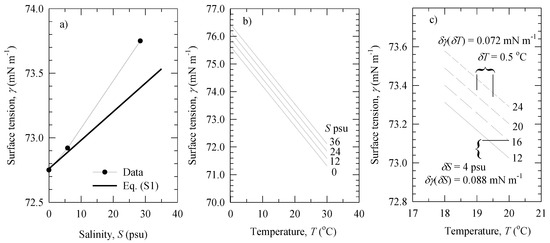
Figure A1.
Dependence of water surface tension γ on: (a) salinity S at fixed T = 20 °C; (b) water temperature T at fixed S values; (c) changes of water surface tension δγ for small changes in temperature (δT = 0.5 °C) or salinity (δS = 4 psu). All lines are derived from Equation (A3). The data points in panel (a) are from [36] (p. f-31).
Appendix C. Stabilization of Air–Water Interfaces by Surface Films
At a given temperature (i.e., isothermal conditions), dissolved substances alter surface tension γ because an excess amount of solute accumulates (or adsorbs) at interfaces (e.g., air–water free surface interface or bubble walls). The isothermal dependence of γ on the solute concentration c (usually termed isotherm) generally displays one of the three trends shown schematically in Figure A2 [20]:
- (1)
- An increase of γ above that of pure water γ0 (solid and dotted lines), typical for inorganic electrolytes (e.g., salts);
- (2)
- A decrease of γ progressively (dash-dot line), typical of simple, un-ionized organic compounds (e.g., alcohols); and
- (3)
- A decrease of γ until a saturation level is reached (dashed line), typical of surface-active materials (surfactants).
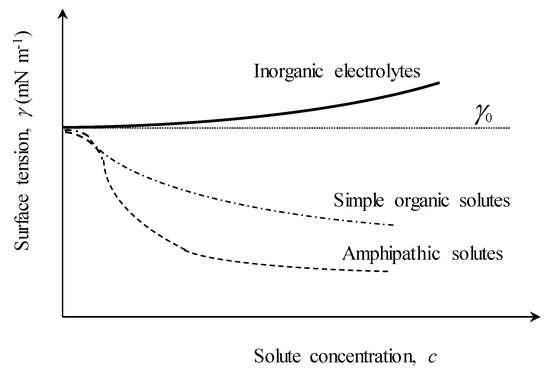
Figure A2.
Schematic representation of the variations of surface tension γ with concentration of different inclusions in aqueous solution: (solid line) inorganic electrolytes (e.g., NaCl); (dash-dot line) simple organics; (dashed line) surfactants. The changes of γ are relative to the surface tension γ0 of pure water (dotted line).
Surfactants suppress γ more effectively than simple organics because of their amphipathic molecular structure [19,20]. The Gibbs adsorption equation predicts the surface excess of the solutes (negative or positive) which then yields an increase or a decrease of γ [19,20]. The high γ values, associated with negative surface film pressure ∆γ ≡ γ0 − γ < 0, make the inorganic salts anti-foaming agents in clean aqueous solutions because the creation of new surfaces and bubbles is hindered even more so than in pure water. The lower γ values, associated with the positive surface film pressure ∆γ > 0 of organic or amphipathic solutes, impart foaming properties of the solution, i.e., bubbles form much more easily than in pure water.
The surface films promoted by positive adsorption stabilize the bubbles and thus further sustain the foaming of the solution. The slope (gradient) dγ/dc of the isotherms in Figure A2 (or dγ/d (ln c) in the Gibbs equation) is a mathematical expression of the film stabilization. The negative slopes dγ/dc of the isotherms for organics and surfactants represent the film elasticity—defined as E ∝ dγ/d(ln A)—because the surface of the film A is related to the solute concentration c. The effectiveness of the surface-active film changes with the inclusion concentration c. The surface-active film is prone to rupturing when dγ/dc ≅ 0. This happens in two cases: in clean or dilute solutions, when inclusion concentration is absent or very low so that the film is thin and patchy; and in solutions with high c, when the film becomes brittle [37].
Two mechanisms (effects) lead to the stabilization of interfaces by the surface films [37,38]: the Marangoni elasticity and the Gibbs elasticity. While providing the same outcome—namely, bubble stabilization—the two effects operate under different conditions. The Marangoni effect explains the film stability to rapid disturbances and is significant in dilute solutions. The Gibbs effect comes into play at a longer time scale of the film stretching and prevails at high inclusion concentrations.
References
- Potter, H.; Smith, G.B.; Snow, C.M.; Dowgiallo, D.J.; Bobak, J.P.; Anguelova, M.D. Whitecap lifetime stages from infrared imagery with implications for microwave radiometric measurements of whitecap fraction. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 7521–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Edson, J.B.; Monahan, E.C.; Rouault, M.P.; Smith, S.D. The spray contribution to the net evaporation from the sea: A review of recent progress. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1995, 72, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, W.K. The role of surface-wave breaking in air-sea interaction. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1996, 28, 279–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninkhof, R.; Asher, W.E.; Ho, D.T.; Sweeney, C.; McGillis, W.R. Advances in quantifying air-sea gas exchange and environmental forcing. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 213–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, G.; Andreas, E.L.; Anguelova, M.D.; Fairall, C.W.; Lewis, E.R.; O’Dowd, C.; Schulz, M.; Schwartz, S.E. Production flux of sea spray aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; O’Muircheartaigh, I.G. Whitecaps and the passive remote sensing of the ocean surface. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.J.; Anguelova, M.D.; Brooks, I.M. On the variability of whitecap fraction using satellite-based observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6201–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, W.E.; Karle, L.M.; Higgins, B.J. On the differences between bubble-mediated air-water transfer in freshwater and seawater. J. Mar. Res. 1997, 55, 813–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D. Scale dependence of bubble creation mechanisms in breaking waves. Nature 2002, 418, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.R.; Schwartz, S.E. Sea Salt Aerosol Production: Mechanisms, Methods, Measurements and Models—A Critical Review; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, E.M.; Zietlow, C.R. Laboratory comparisons of fresh-water and salt-water whitecaps. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 6961–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, R.D.; Griffin, O.M. Stability of a three-dimensional foam layer in seawater. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10804–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, A.H.; Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D.; Ward, B. Observed variation in the decay time of oceanic whitecap foam. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C09015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, A.H.; Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D. Two Regimes of Laboratory Whitecap Foam Decay: Bubble-Plume Controlled and Surfactant Stabilized. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.C. The role of salt in whitecap persistence. Deep Sea Res. 1975, 22, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, S.R.; Blanchard, D.C. The persistence of air bubbles at a seawater surface. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 7724–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struthwolf, M.; Blanchard, D.C. The residence time of air bubbles <400 µm diameter at the surface of distilled water and seawater. Tellus B 1984, 36B, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.A.; Klemas, V.; Hsu, Y.-H.L. Laboratory measurements of water surface bubble life time. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattoraj, D.K.; Birdi, K.S. Adsorption and the Gibbs Surface Excess; Plenum Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemenz, P.C.; Rajagopalan, R. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, W.E.; Pankow, J.F. The interaction of mechanically generated turbulence and interfacial films with a liquid phase controlled gaslliquid transport process. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1986, 38B, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelova, M.D.; Huq, P. Characteristics of bubble clouds at various wind speeds. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C03036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsir, Y.; Marmur, A. Rate of bubble coalescence following quasi-static approach: Screening and neutralization of the electric double layer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pounder, C. Sodium chloride and water temperature effects on bubbles. In Oceanic Whitecaps Their Role in Air-Sea Exchange Processes; Monahan, E.C., MacNiocaill, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyama, A.; Celata, G.P.; Hosokawa, S.; Yoshida, S. Terminal velocity of single bubbles in surface tension force dominant regime. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2002, 28, 1497–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops, and Particles; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, J.J.; Maldonado, M.; Gomez, C.O.; Finch, J.A. Experimental study on the shape-velocity relationship of an ellipsoidal bubble in inorganic salt solutions. Miner. Eng. 2014, 55, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. On the clouds of bubbles formed by breaking wind-waves in deep water, and their role in air-sea gas transfer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1982, A304, 155–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, W.D. Stabilization of air bubbles at the air-sea interface by surface-active material. Deep Sea Res. 1967, 14, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.M. Comments on “Bubbles produced by breaking waves in fresh and salt water”. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1931–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, S.L. Fluid Dynamics of Multiphase Systems; Blaisdel Publishing Company: Waltham, MA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Science and Engineering of Droplets: Fundamentals and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Leifer, I.; Judd, A.G. Oceanic methane layers: The hydrocarbon seep bubble deposition hypothesis. Terra Nova 2002, 14, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, C.D.; Baylor, E.R. Surface tension reductions and urban wastes in the New York Bight. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 2696–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.L.; Perkin, R.G. Salinity: Its definition and calculation. J. Geophys. Res. 1978, 83, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weast, R.C. (Ed.) Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Couder, Y.; Chomaz, J.M.; Rabaud, M. On the hydrodynamics of soap films. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1989, 37, 384–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).