A Novel Iterative Water Refraction Correction Algorithm for Use in Structure from Motion Photogrammetric Pipeline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Previous Work
2. Methodology
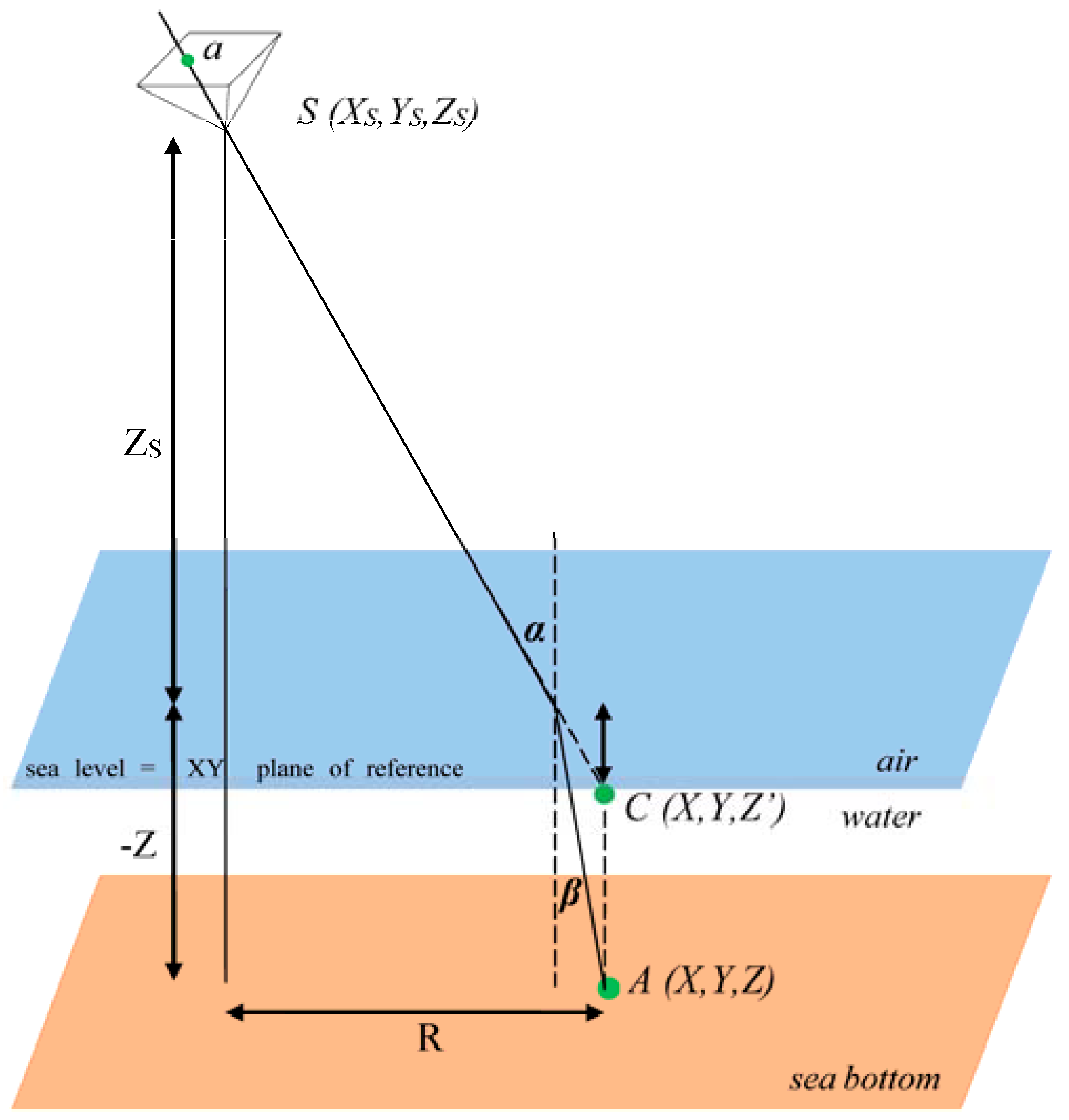
2.1. Discrepancy Estimation
2.1.1. Shan’s Model
2.1.2. Examination of Water Refraction Effect in Drone Photography
- The water surface is planar, without waves;
- The water surface level is the reference (Z = 0) of the coordinate system;
- The photo coordinates have been already corrected with respect to principal center and lens distortion.
2.1.3. Snell’s Law in Vector Form
2.1.4. Vector Intersection
2.1.5. Validation and Error Evaluation
2.2. Proposed Correction Model
2.3. Implementation Aspects of the Proposed Methodology
2.4. Other Assumptions
2.4.1. Bundle Adjustment
2.4.2. Wave Effect
3. Application and Verification on Test Sites
3.1. Amathounta Test Site
3.2. Agia Napa Test Site
3.3. Flight Planning
3.4. LiDAR Reference Data
3.5. Evaluation with Reference Data
3.5.1. Cloud-to-Cloud Distances
3.5.2. Seabed Cross Sections
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karara, H.M. Non-Topographic Photogrammetry, 2nd ed.; American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Menna, F.; Agrafiotis, P.; Georgopoulos, A. State of the art and applications in archaeological underwater 3D recording and mapping. J. Cult. Herit. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlatos, D.; Savvidou, E. Coastal Survey of archaeological sites using drones. Skyllis 2015, 15, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos, A.; Agrafiotis, P. Documentation of a submerged monument using improved two media techniques. In Proceedings of the 2012 18th International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, Milan, Italy, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.B.; Lane, S.N.; Chandler, J.H.; Porfiri, E. Through-water close range digital photogrammetry in flume and field environments. Photogramm. Rec. 2002, 17, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlazeck, A.; Koch, R. Perspective and non-perspective camera models in underwater imaging—Overview and error analysis. In Outdoor and Large-Scale Real-World Scene Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 212–242. [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou, C.C.; Loizou, S.G.; Georgiades, G.P.; Potyagaylo, S.; Skarlatos, D. Adaptive calibration of an underwater robot vision system based on hemispherical optics. In Proceedings of the IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV), Oxford, MS, USA, 6–9 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, J.G.; Fraser, C.S. On the calibration of underwater cameras. Photogramm. Rec. 1986, 12, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavest, J.; Rives, G.; Lapresté, J. Underwater camera calibration. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2000; Vernon, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 654–668. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, J.G.; Kniest, H.T. Errors in Depth Determination Caused by Waves in Through-Water Photogrammetry. Photogramm. Rec. 1985, 11, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A. Wave influences in two-media photogrammetry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1982, 48, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Georgopoulos, A. Camera constant in the case of two media photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewinkel, G.C. Water depths from aerial photographs. Photogramm. Eng. 1963, 29, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Shmutter, B.; Bonfiglioli, L. Orientation problem in two-medium photogrammetry. Photogramm. Eng. 1967, 33, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Principles of Photogrammetry (with Remote Sensing); Publishing House of Surveying and Mapping: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J. Relative orientation for two-media photogrammetry. Photogramm. Rec. 1994, 14, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, J.F. Photogrammetry through shallow waters. Aust. J. Geod. Photogramm. Surv. 1983, 38, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, H.-G. On the Accuracy Potential in Underwater/Multimedia Photogrammetry. Sensors 2015, 15, 18140–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whittlesey, J.H. Elevated and airborne photogrammetry and stereo photography. Photogr. Archaeol. Res. 1975, 223–259. [Google Scholar]
- Westaway, R.; Lane, S.; Hicks, M. Remote sensing of clear-water, shallow, gravel-bed rivers using digital photogrammetry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Elfick, M.H.; Fryer, J.G. Mapping in shallow water. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1984, 25, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, R.; Costeira, J.P.; Silvestre, C.; Sousa, I.; Santos, J.A. Using stereo image reconstruction to survey scale models of rubble-mound structures. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling to Port and Coastal Protection, Porto, Portugal, 8–10 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muslow, C. A flexible multi-media bundle approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, K.; Forstner, W. Exploiting the multi view geometry for automatic surfaces reconstruction using feature based matching in multi media photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 900–907. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Sutton, M.A.; Lessner, S.M.; Yost, M. Robust stereo vision and calibration methodology for accurate three-dimensional digital image correlation measurements on submerged objects. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 2008, 43, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.M.; Honey, F.R. Air survey and satellite imagery tools for shallow water bathymetry. In Proceedings of the 20th Australian Survey Congress, Shrewsbury, UK, 20 May 1977; pp. 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, W.D.; Umbach, M.J. Underwater mapping. Photogramm. Eng. 1972, 38, 765. [Google Scholar]
- Masry, S.E. Measurement of water depth by the analytical plotter. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 1975, 52, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, J.T. Bathymetric Structure-from-Motion: Extracting shallow stream bathymetry from multi-view stereo photogrammetry. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telem, G.; Filin, S. Photogrammetric modeling of underwater environments. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.K. Handbuch der Vermessungskunde; J.B. Metzlersche Verlagsbuchhandlung: Stuttgart, Germany, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- StarkEffects.com. Snell’s Law in Vector Form. 2018. Available online: http://www.starkeffects.com/snells-law-vector.shtml (accessed on 26 June 2018).
- Quan, X.; Fry, E. Empirical equation for the index of refraction of seawater. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 3477–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masry, S.E.; MacRitchie, S. Different considerations in coastal mapping. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1980, 46, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Mandlburger, G.; Otepka, J.; Karel, W.; Wagner, W.; Pfeifer, N. Orientation and Processing of Airborne Laser Scanning data (OPALS)—Concept and first results of a comprehensive ALS software. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Proceedings of the ISPRS Workshop Laserscanning ’09, Paris, France, 1–2 September 2009; Bretar, F., Pierrot-Deseilligny, M., Vosselman, G., Eds.; Société Française de Photogrammétrie et de Télédétection: Marne-la-vallée, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbacher, F.; Pfennigbauer, M.; Aufleger, M.; Ullrich, A. High resolution airborne shallow water mapping. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Proceedings of the XXII ISPRS Congress, Melbourne, Australia 25 August–1 September 2012; 2012; Volume 39, p. B1. [Google Scholar]
- CloudCompare (Version 2.10.alpha) [GPL Software]. 2018. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 26 June 2018).

























| Test Site | Photos | Average Height (m) | GSD (m) | Control Points | SfM-MVS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSX (m) | RMSY (m) | RMSZ (m) | Reprojection Error on All Points (Pixel) | Reprojection Error in Control Points (Pixel) | Total Number of Tie Points | Dense Points | Coverage Area (sq. Km) | ||||
| Amathounta | 182 | 103 | 0.033 | 0.0277 | 0.0333 | 0.0457 | 0.645 | 1.48 | 28.5 K | 17.3 M | 0.37 |
| Agia Napa | 383 | 209 | 0.063 | 5.03 | 4.74 | 7.36 | 1.106 | 0.76 | 404 K | 8.5 M | 2.43 |
| Test Site | Number of LiDAR Points Used | LiDAR Points Density (Points/m2) | Average Pulse Spacing (m) | LiDAR Flight Height (m) | Accuracy (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amathouda | 6.030 | 0.4 | - | 960 | 0.1 |
| Agia Napa | 1.288.760 | 1.1 | 1.65 | 960 | 0.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skarlatos, D.; Agrafiotis, P. A Novel Iterative Water Refraction Correction Algorithm for Use in Structure from Motion Photogrammetric Pipeline. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6030077
Skarlatos D, Agrafiotis P. A Novel Iterative Water Refraction Correction Algorithm for Use in Structure from Motion Photogrammetric Pipeline. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2018; 6(3):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6030077
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkarlatos, Dimitrios, and Panagiotis Agrafiotis. 2018. "A Novel Iterative Water Refraction Correction Algorithm for Use in Structure from Motion Photogrammetric Pipeline" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 6, no. 3: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6030077
APA StyleSkarlatos, D., & Agrafiotis, P. (2018). A Novel Iterative Water Refraction Correction Algorithm for Use in Structure from Motion Photogrammetric Pipeline. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 6(3), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6030077






