Joint Inversion for Sound Speed Field and Moving Source Localization in Shallow Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A State-Space Model for Joint Inversion
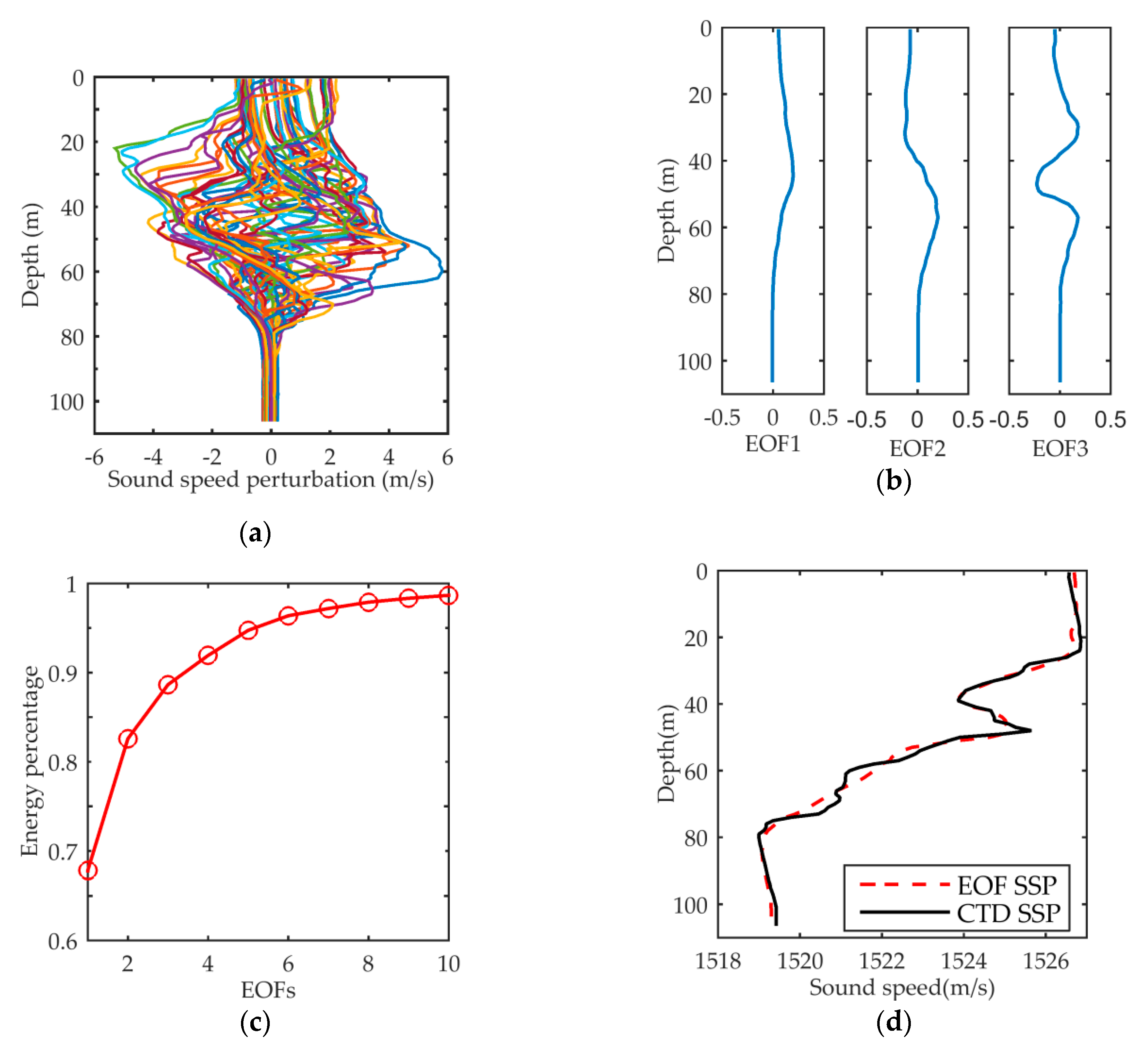
2.1. Sound Speed Field Parameterization
2.2. The Mathematical Model of the Joint Inversion
3. Nonlinear Kalman Filter as an Inversion Processor
3.1. EKF Model
3.2. EnKF Model
4. Results and Discussion
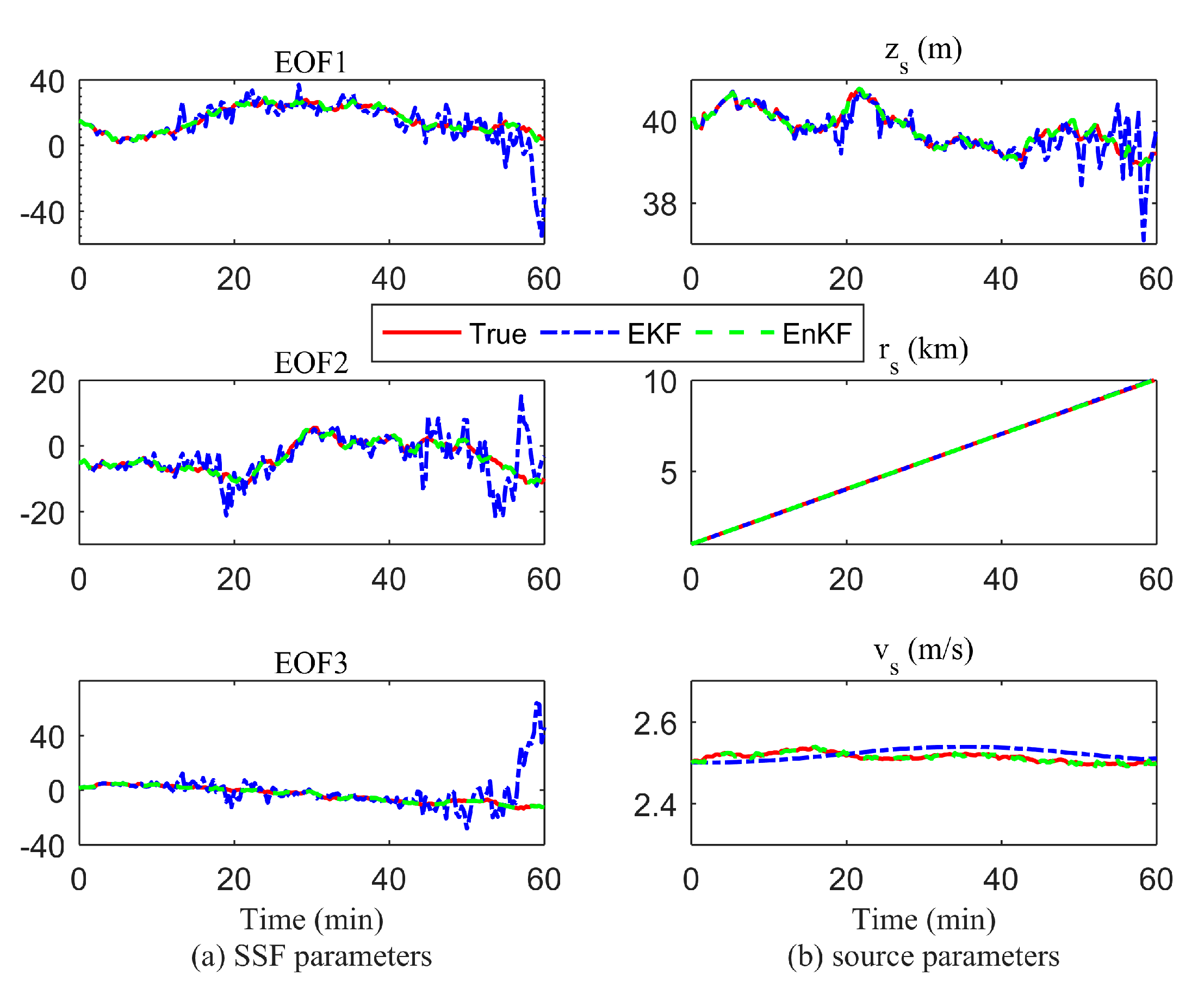
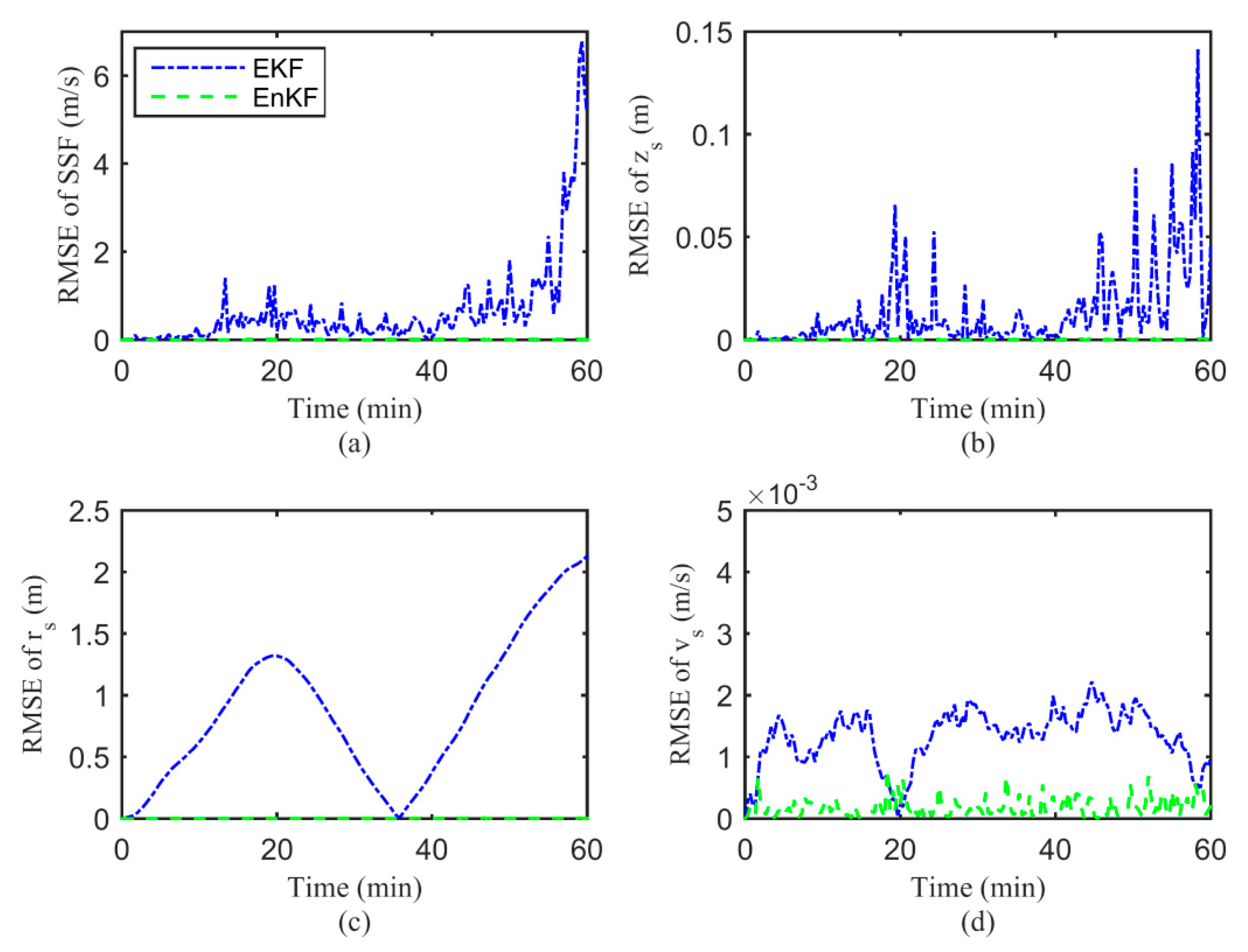
4.1. Estimation of EKF and EnKF for SSF and Moving Source Localization
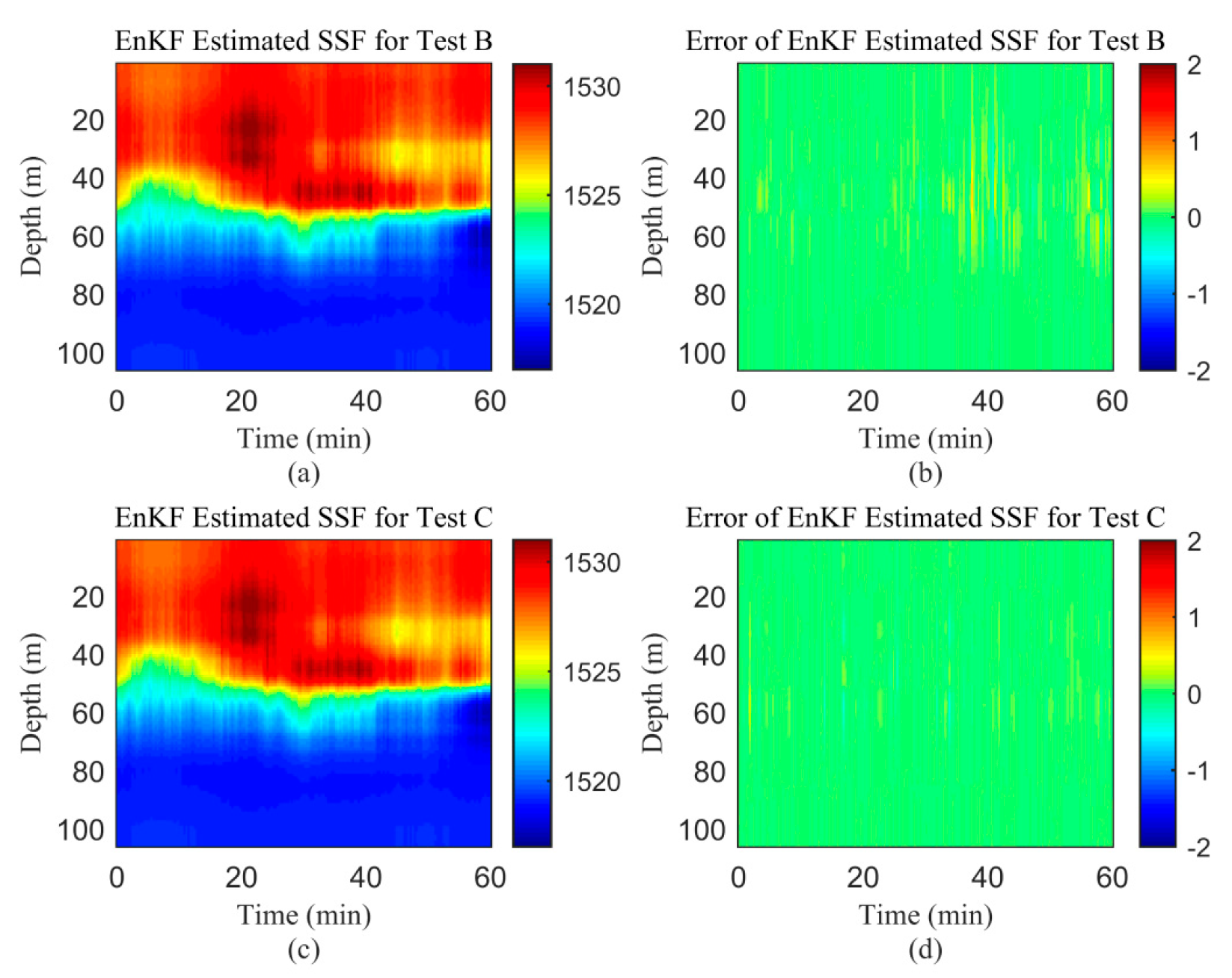
4.2. Sparse Array Configuration
4.3. Impact of the Source-VLA Deployment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, K.; Xiao, P.; Duan, R.; Ma, Y. Bayesian inversion for geoacoustic parameters from ocean bottom reflection loss. J. Comput. Acoust. 2017, 25, 1750019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shi, Y. Passive broadband source localization based on a riemannian distance with a short vertical array in the deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Michalopoulou, Z.H. Sound speed estimation and source localization with linearization and particle filtering. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatté, S.M. Sound Transmission through a Fluctuating Ocean; Dashen, R., Munk, W.H., Watson, K.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, J.F.; Newhall, A.E.; Sperry, B.; Gawarkiewicz, G.; Fredricks, A.; Tyack, P.; Chiu, C.S.; Abbot, P. Spatial and temporal variations in acoustic propagation characteristics at the New England shelfbreak front. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 28, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, L.R.; Middleton, F.H. An underwater acoustic sound velocity data model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 67, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, K.; Duan, R.; Ma, Y. Sequential inversion for geoacoustic parameters in the south China sea using modal dispersion curves. Acoust. Aust. 2017, 45, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.H.; Zhang, R.H. Inversion for sound speed profile by using a bottom mounted horizontal line array in shallow water. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2010, 27, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, K.; Lei, B.; He, Z. Research on the temporal-spatial distribution and the physical mechanisms for the sound speed profiles in north-central Indian ocean. Acta. Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 084301. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, M.; Gerstoft, P. Compressive acoustic sound speed profile estimation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candy, J.V.; Sullivan, E.J. Sound velocity profile estimation a system theoretic approach. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1993, 18, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, O.; Hermand, J.P.; Le Gac, J.C.; Rixen, M. Full-field tomography and kalman tracking of the range-dependent sound speed field in a coastal water environment. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorych, I.; Michalopoulou, Z.H. Particle filtering for dispersion curve tracking in ocean acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardim, C.; Michalopoulou, Z.H.; Gerstoft, P. An overview of sequential Bayesian filtering in ocean acoustics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 36, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Tracking of geoacoustic parameters using Kalman and particle filters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, O.; Hermand, J.P.; Candy, J.V. Inversion for time-evolving sound-speed field in a shallow ocean by ensemble Kalman filtering. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2009, 34, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, H. Tracking of time-evolving sound speed profiles in shallow water using an ensemble Kalman-particle filter. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, O.; Hermand, J.P. Sequential bayesian geoacoustic inversion for mobile and compact source-receiver configuration. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 2668–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dosso, S.E.; Sun, D. Motion-compensated acoustic localization for underwater vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 41, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. A bayesian sparse-plus-low-rank matrix decomposition method for direction-of-arrival tracking. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 4894–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Schmidt, H. System-orthogonal functions for sound speed profile perturbation. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2006, 31, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, P.H.; Zhang, R.; Miller, J.H.; Bartek, L.R.; Peng, Z.; Ramp, S.R.; Zhou, J.X.; Chiu, C.S.; Lynch, J.F.; Simmen, J.A. Overview of results from the asian seas international acoustics experiment in the east China sea. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2005, 29, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B. The Kraken Normal Mode Program; SACLANT Undersea Research Centre: La Spezia, Italy, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Evensen, G. The ensemble Kalman filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean Dyn. 2003, 53, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Principles |
|---|
| Predict: |
| Update: |
| Kalman gain: |
| Jacobians: |
| Principles |
|---|
| Definitions |
| Background ensemble member: Where is the ensemble member index and is the time frame |
| Background ensemble mean value at |
| Analysis ensemble member |
| Analysis ensemble mean value at |
| Ensemble of observation |
| Ensemble covariance matrix |
| Predict: |
| Update: |
| Kalman gain: |
| Test No. | #Hydrophones | Depths |
|---|---|---|
| A | 16 | 15–75 m, 4 m spacing |
| B | 8 | 15–75 m, 8.57 m spacing |
| C | 8 | 30–58 m, 4 m spacing |
| Test No. | SSF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m/s) | (10−4m) | (m) | (10−4m/s) | |
| A | 0.0045 | 1.0731 | 0.0013 | 1.7084 |
| B | 0.0354 | 9.7445 | 0.0109 | 3.9471 |
| C | 0.0186 | 2.9726 | 0.0031 | 1.8864 |
| 16-VLA | 8-VLA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source Depths | VLA Depths | SSF | VLA Depths | SSF | ||||||
| (m) | (m) | (m/s) | (10−4m) | (m) | (10−4m/s) | (m) | (m/s) | (10−4m) | (m) | (10−4m/s) |
| 10 | 1–61 | 0.0108 | 4.9886 | 0.0012 | 3.1329 | 17–45 | 0.0454 | 5.8863 | 0.0060 | 2.5132 |
| 23–83 | 0.0022 | 0.4614 | 0.0005 | 1.3260 | 39–67 | 0.0130 | 3.4522 | 0.0023 | 1.5162 | |
| 45–105 | 0.0030 | 1.3979 | 0.0006 | 1.3952 | 61–89 | 0.0257 | 4.0057 | 0.0025 | 1.6202 | |
| 96 | 1–61 | 0.0041 | 2.6118 | 0.0007 | 1.5324 | 17–45 | 0.0232 | 5.1153 | 0.0049 | 2.1093 |
| 23–83 | 0.0028 | 1.8307 | 0.0007 | 1.5090 | 39–67 | 0.0175 | 3.7058 | 0.0047 | 2.0468 | |
| 45–105 | 0.0861 | 9.6187 | 0.0107 | 18 | 61–89 | 0.1325 | 18 | 0.0281 | 9.0554 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, K. Joint Inversion for Sound Speed Field and Moving Source Localization in Shallow Water. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7090295
Dai M, Li Y, Yang K. Joint Inversion for Sound Speed Field and Moving Source Localization in Shallow Water. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2019; 7(9):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7090295
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Miao, Yaan Li, and Kunde Yang. 2019. "Joint Inversion for Sound Speed Field and Moving Source Localization in Shallow Water" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 7, no. 9: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7090295
APA StyleDai, M., Li, Y., & Yang, K. (2019). Joint Inversion for Sound Speed Field and Moving Source Localization in Shallow Water. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 7(9), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7090295





