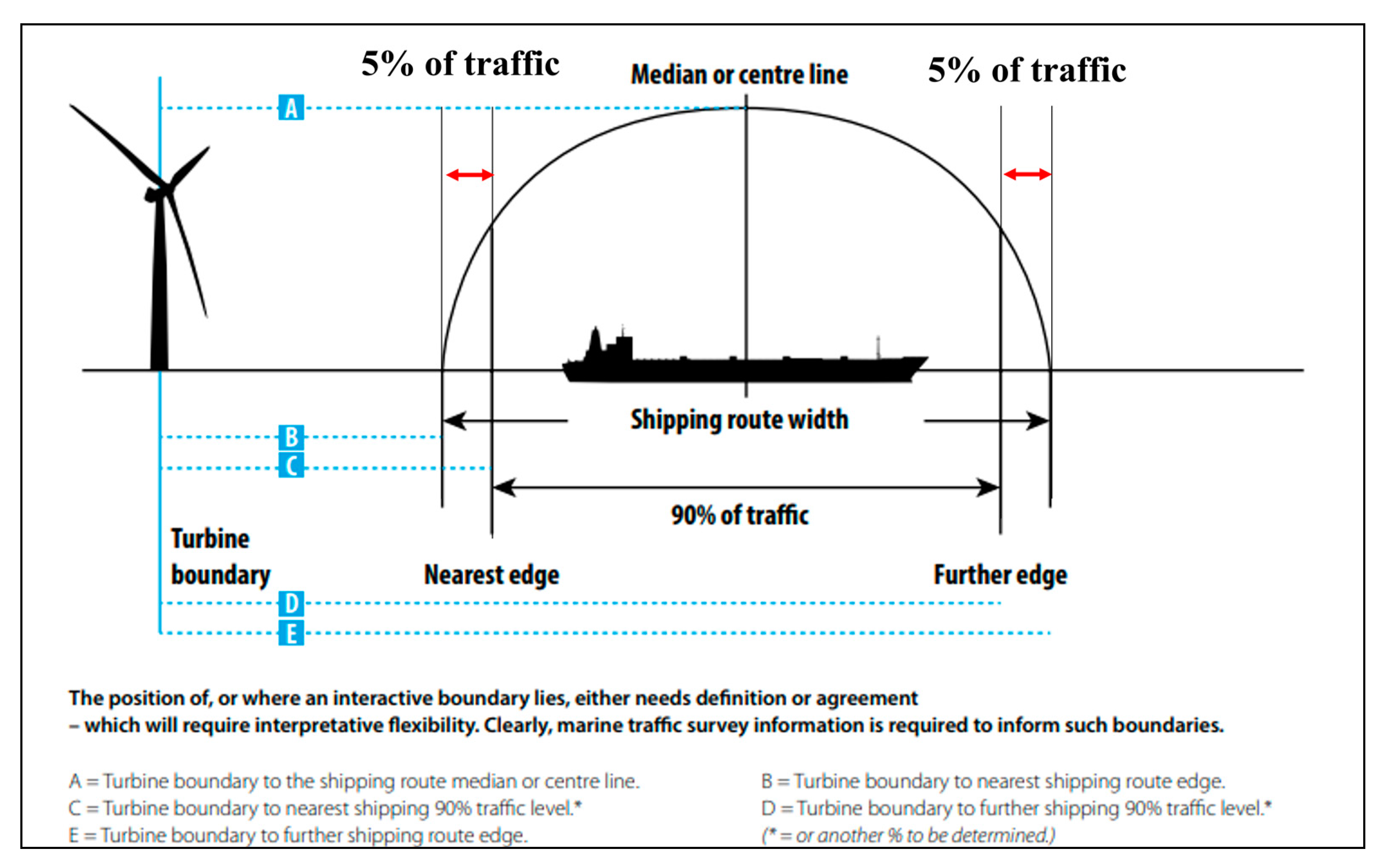
Figure 1.
Safety distance between ship traffic and wind turbines recommended by the UK MCA.
Figure 1.
Safety distance between ship traffic and wind turbines recommended by the UK MCA.
Figure 2.
Overview of data preprocessing and processing method.
Figure 2.
Overview of data preprocessing and processing method.
Figure 3.
Flow chart used for investigating the safety distance between a ship and the bridge pier.
Figure 3.
Flow chart used for investigating the safety distance between a ship and the bridge pier.
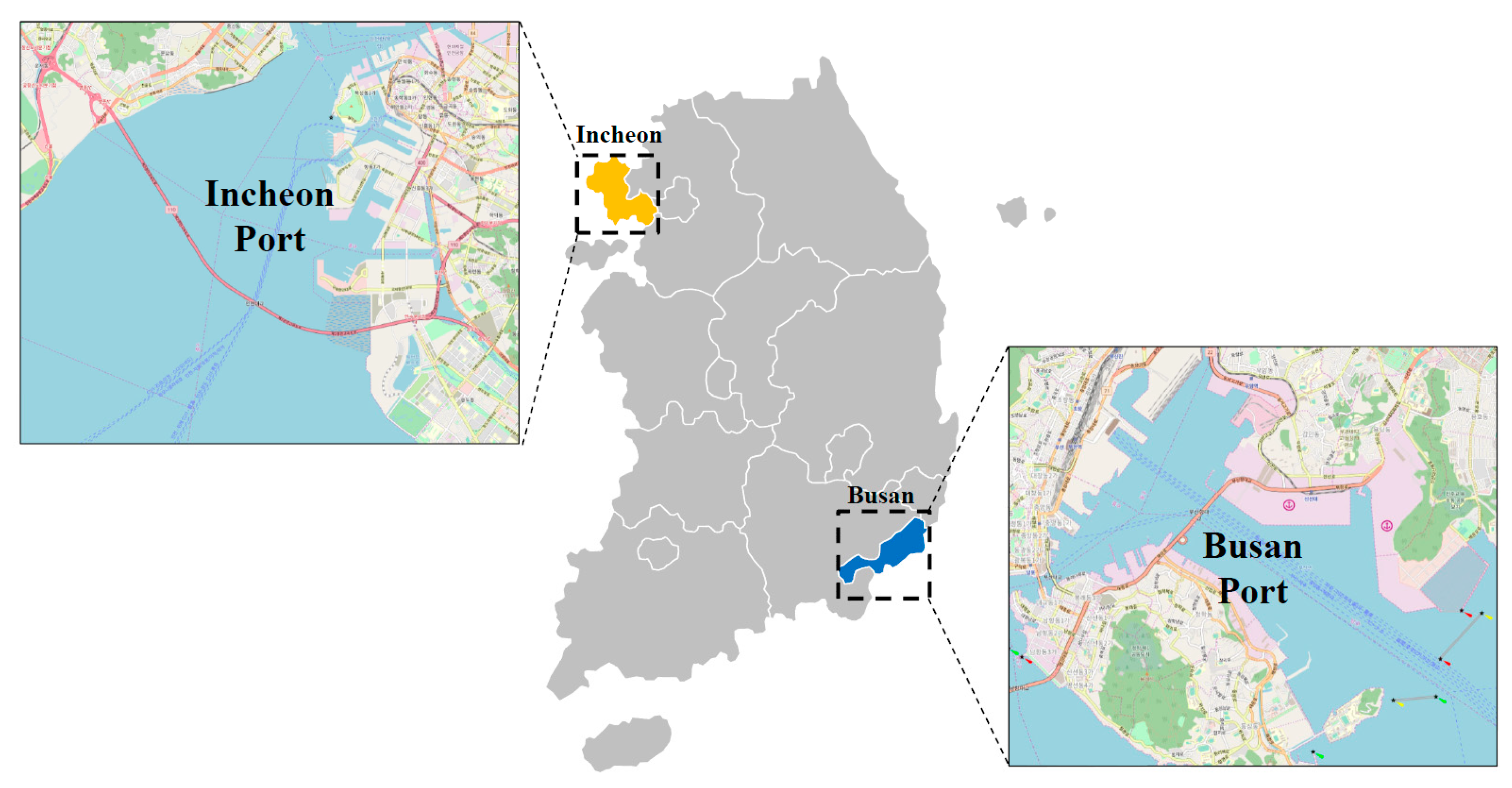
Figure 4.
Geographical locations of the Busan and Incheon ports in the Korean peninsula.
Figure 4.
Geographical locations of the Busan and Incheon ports in the Korean peninsula.
Figure 5.
Historical tracks for the (a) Incheon bridge, (b) Busan harbor bridge and (c) legend.
Figure 5.
Historical tracks for the (a) Incheon bridge, (b) Busan harbor bridge and (c) legend.
Figure 6.
Cable-stayed part of Incheon bridge.
Figure 6.
Cable-stayed part of Incheon bridge.
Figure 7.
Cable-stayed part of Busan harbor bridge.
Figure 7.
Cable-stayed part of Busan harbor bridge.
Figure 8.
Histogram and Normal Q–Q plots for the Incheon bridge data for (a,b) 2-way arrival and (c,d) 2-way departure.
Figure 8.
Histogram and Normal Q–Q plots for the Incheon bridge data for (a,b) 2-way arrival and (c,d) 2-way departure.
Figure 9.
Histogram and Normal Q–Q plots for the Incheon bridge data for (a,b) 1-way arrival, and (c,d) 1-way departure.
Figure 9.
Histogram and Normal Q–Q plots for the Incheon bridge data for (a,b) 1-way arrival, and (c,d) 1-way departure.
Figure 10.
Histogram and Normal Q–Q plots for the Busan harbor bridge data for (a,b) arrival and (c,d) departure.
Figure 10.
Histogram and Normal Q–Q plots for the Busan harbor bridge data for (a,b) arrival and (c,d) departure.
Figure 11.
Method used for analyzing the ship safety distance.
Figure 11.
Method used for analyzing the ship safety distance.
Figure 12.
Traffic distribution at the Incheon bridge for 2-way traffic.
Figure 12.
Traffic distribution at the Incheon bridge for 2-way traffic.
Figure 13.
Traffic distribution at the Incheon bridge for 1-way traffic.
Figure 13.
Traffic distribution at the Incheon bridge for 1-way traffic.
Figure 14.
Traffic distribution for the Busan harbor bridge for 2-way traffic.
Figure 14.
Traffic distribution for the Busan harbor bridge for 2-way traffic.
Figure 15.
Distance difference divided by ship’s maximum breadth at the Incheon bridge for (a,b) 2-way, (c,d) 1-way, and (e,f) Busan harbor bridge 2-way.
Figure 15.
Distance difference divided by ship’s maximum breadth at the Incheon bridge for (a,b) 2-way, (c,d) 1-way, and (e,f) Busan harbor bridge 2-way.
Figure 16.
Variation of distances differences divided by the ship’s maximum breadth.
Figure 16.
Variation of distances differences divided by the ship’s maximum breadth.
Figure 17.
Ship safety distance for 2-way traffic situation at the (a) Incheon bridge and (b) legend.
Figure 17.
Ship safety distance for 2-way traffic situation at the (a) Incheon bridge and (b) legend.
Figure 18.
Ship safety distance for 2-way traffic at the (a) Busan harbor bridge and (b) legend.
Figure 18.
Ship safety distance for 2-way traffic at the (a) Busan harbor bridge and (b) legend.
Table 1.
Classification of the ships according to passage rules at the Incheon bridge.
Table 1.
Classification of the ships according to passage rules at the Incheon bridge.
| Classification | Gross Tonnage |
|---|
| Cargo | Tanker, Passenger |
|---|
| 2-way | 5 K < < 50 K | 1 K < < 50 K |
| 1-way | 50 K < |
Table 2.
Classification of ships by size according to precedent study.
Table 2.
Classification of ships by size according to precedent study.
| Classification | LOA(m) | Standard Deviation |
|---|
| Size | Gross Tonnage |
|---|
| Small | 0–1 K | 48 | ±20 |
| Medium | 1 K–10 K | 104 | ±20 |
| Large | Over 10 K | 240 | ±50 |
Table 3.
Result of missing values treatment according to data preprocessing.
Table 3.
Result of missing values treatment according to data preprocessing.
| Bridge | Collected AIS Data | Missing Values | Target Values |
|---|
| Incheon bridge | 982 (100.0%) | 22 (2.2%) | 960 (97.8%) |
| Busan harbor bridge | 840 (100.0%) | 24 (2.9%) | 816 (97.1%) |
| Total | 1822 (100.0%) | 46 (2.5%) | 1776 (97.5%) |
Table 4.
Port status from 2015–2019 by count and gross tonnage.
Table 4.
Port status from 2015–2019 by count and gross tonnage.
| Unit | Port | Annual Status |
|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|
| Count | Incheon | 37,560 | 37,407 | 36,215 | 31,351 | 29,753 |
| Busan 1 | 98,087 | 100,197 | 99,687 | 94,816 | 93,701 |
| G/T | Incheon | 378,218,349 | 386,789,768 | 391,694,597 | 380,847,451 | 361,696,734 |
| Busan 1 | 1,247,878,352 | 1,324,573,420 | 1,332,261,065 | 1,345,183,479 | 1,361,337,334 |
Table 5.
Summary of marine accidents in the Incheon and Busan ports of Korea from 2015–2019.
Table 5.
Summary of marine accidents in the Incheon and Busan ports of Korea from 2015–2019.
| Unit | Port | Annual Status |
|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|
| Count | Incheon | 22 | 37 | 22 | 43 | 49 |
| Busan | 66 | 85 | 52 | 19 | 59 |
Table 6.
Data collection period and the number of ships used during data collection.
Table 6.
Data collection period and the number of ships used during data collection.
| Date | Bridge | Status | Number of Ships |
|---|
| 1–30 June 2019 | Incheonbridge | 2-way | Arrival | 487 |
| Departure | 412 |
| 1-way | Arrival | 30 |
| Departure | 31 |
| Busan harbor bridge | 2-way | Arrival | 409 |
| Departure | 407 |
Table 7.
Sailing speeds passing through the target bridge.
Table 7.
Sailing speeds passing through the target bridge.
| Bridge | Arrival | Departure |
|---|
| Average (knots) | S.D (knots) | Average (knots) | S.D (knots) |
|---|
| Incheon bridge | 11.4 | 2.0 | 10.8 | 2.5 |
| Busan harbor bridge | 10.5 | 3.6 | 10.7 | 3.1 |
Table 8.
Sample size verification by sample power calculation (one-sample t-test).
Table 8.
Sample size verification by sample power calculation (one-sample t-test).
| Bridge | Status | Number of Ships | Effect Size | Sample Size |
|---|
| Incheon bridge | 2-way | Arrival | 487 | 0.47 | 39 |
| Departure | 412 | 0.67 | 20 |
| 1-way | Arrival | 30 | 0.55 | 28 |
| Departure | 31 | 0.89 | 12 |
| Busan harbor bridge | 2-way | Arrival | 409 | 0.68 | 19 |
| Departure | 407 | 1.93 | 5 |
Table 9.
Summarized data for normality tests of traffic distributions.
Table 9.
Summarized data for normality tests of traffic distributions.
| Classification | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure |
|---|
| Target (Centerline) | E1 | W1 | E1 | W1 | MP3 | MP2 |
| Count | 487 | 412 | 30 | 31 | 409 | 407 |
| Max (m) | 700 | 642 | 574 | 586 | 379 | 453 |
| Min (m) | 163 | 116 | 234 | 228 | 126 | 216 |
| Mean (m) | 350 | 337 | 359 | 335 | 245 | 197 |
| S.D (m) | 107 | 94 | 75 | 73 | 36 | 38 |
| Skewness | 0.66 | 0.98 | 0.69 | 1.39 | 0.44 | 0.41 |
| Ex. Kurtosis | −0.39 | 3.62 | 0.44 | 5.92 | 0.88 | 3.13 |
| K-S test (p-v) | 8.90 × 10−5 | 3.10 × 10−6 | 0.99 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
Table 10.
Summarized data of distances from ship to bridge pier based on the confidence interval.
Table 10.
Summarized data of distances from ship to bridge pier based on the confidence interval.
| Classification | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure |
|---|
| Target (edge) | E1 | W1 | E1 | W1 | MP3 | MP2 |
| Count | 487 | 412 | 30 | 31 | 409 | 407 |
| Mean (m) | 299 | 286 | 300 | 276 | 220 | 171 |
| S.D (m) | 107 | 94 | 75 | 73 | 36 | 38 |
| C (m) | 80% CI | 162 | 165 | 205 | 180 | 173 | 123 |
| 85% CI | 146 | 150 | 194 | 168 | 168 | 117 |
| 90% CI | 124 | 131 | 179 | 153 | 160 | 109 |
| 95% CI | 90 | 101 | 156 | 129 | 149 | 97 |
| 99% CI | 25 | 44 | 111 | 84 | 127 | 74 |
Table 11.
Statistics for ships passing outside the confidence interval (90 to 99%).
Table 11.
Statistics for ships passing outside the confidence interval (90 to 99%).
| Classification | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure |
|---|
| Count | 487 (100%) | 412 (100%) | 30 (100%) | 31 (100%) | 409 (100%) | 407 (100%) |
| 90% CI | 2 (0.5%) | 3 (0.7%) | 1 (3.3%) | 2 (6.5%) | 13 (3.2%) | 16 (3.9%) |
| 95% CI | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (1.5%) | 2 (0.5%) |
| 99% CI | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (0.5%) | 1 (0.2%) |
Table 12.
Maximum breadth of bridge crossing waterway.
Table 12.
Maximum breadth of bridge crossing waterway.
| Classification | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| Max. breadth (m) | 37 | 60 | 38 |
Table 13.
Data for distance divided by ship’s maximum breadth for two bridges across waterways.
Table 13.
Data for distance divided by ship’s maximum breadth for two bridges across waterways.
| Classification | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure |
|---|
| 80% CI | 4.39 B | 4.46 B | 3.42 B | 3.00 B | 4.56 B | 3.24 B |
| 85% CI | 3.93 B | 4.06 B | 3.23 B | 2.80 B | 4.41 B | 3.08 B |
| 90% CI | 3.34 B | 3.54 B | 2.98 B | 2.55 B | 4.21 B | 2.88 B |
| 95% CI | 2.43 B | 2.74 B | 2.59 B | 2.16 B | 3.91 B | 2.56 B |
| 99% CI | 0.68 B | 1.19 B | 1.85 B | 1.40 B | 3.33 B | 1.95 B |
Table 14.
Data for the distance difference divided by the ship’s maximum breadth for two bridges across waterways.
Table 14.
Data for the distance difference divided by the ship’s maximum breadth for two bridges across waterways.
| Classification | |Arrival–Departure| |
|---|
| Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| 80% CI | 0.07 B | 0.42 B | 1.32 B |
| 85% CI | 0.13 B | 0.43 B | 1.33 B |
| 90% CI | 0.20 B | 0.43 B | 1.33 B |
| 95% CI | 0.31 B | 0.43 B | 1.35 B |
| 99% CI | 0.51 B | 0.45 B | 1.38 B |
Table 15.
Data for variation of distances differences divided by the ship’s maximum breadth.
Table 15.
Data for variation of distances differences divided by the ship’s maximum breadth.
| Classification | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| 80% to 85% | 0.06 B | 0.01 B | 0.01 B |
| 85% to 90% | 0.07 B | 0.00 B | 0.00 B |
| 90% to 95% | 0.11 B | 0.00 B | 0.02 B |
| 95% to 99% | 0.20 B | 0.02 B | 0.03 B |
Table 16.
Maritime accidents in Korea associated with bridges for 2010–2019.
Table 16.
Maritime accidents in Korea associated with bridges for 2010–2019.
| Accident Date | Bridge Name | Target Ship (G/T) | Cause |
|---|
| 25 September 2010 | Geoje bridge | Towing (166G/T)
Barge (1968 G/T) | Officer’s carelessness |
| 4 April 2011 | Geoje bridge | Towing (55G/T)
Barge (932 G/T) | Inadequate
passage plan |
| 8 August 2011 | Jangja bridge | Towing (17G/T)
Barge (530 G/T) | Excessive navigation
during bad weather |
| 25 August 2011 | Incheon bridge | Fishing (10G/T) | Neglect of watch |
| 24 August 2012 | Naro 2 bridge | Passenger (228G/T) | Neglect of watch |
| 29 August 2013 | Chunsa bridge | Cargo (1673G/T) | Drunken drowsiness |
| 27 July 2013 | Shinan 1 bridge | Passenger (307G/T) | Excessive navigation
during restricted visibility |
| 13 April 2016 | Jido bridge | Passenger (228G/T) | Speeding
during restricted visibility |
| 27 September 2016 | Chunsa bridge | Tanker (864G/T) | Neglect of watch |
| 2 March 2018 | Geoje bridge | Towing (55G/T)
Barge (932 G/T) | Excessive navigation |
| 28 February 2019 | Gwangan bridge | Cargo (1673G/T) | Drunken negligence |
| 14 October 2019 | Geoje bridge | Towing (55G/T)
Barge (932 G/T) | Inadequate navigation |
Table 17.
Variation of distance difference divided by the ship maximum breadth.
Table 17.
Variation of distance difference divided by the ship maximum breadth.
| 95% CI | Incheon Bridge | Busan Harbor Bridge |
|---|
| 2-Way | 1-Way | 2-Way |
|---|
| Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure | Arrival | Departure |
|---|
| Target pier | E1 | W1 | E1 | W1 | MP3 | MP2 |
| Distance (m) | 90 | 101 | 156 | 129 | 149 | 97 |
| Distance/Breadth | 2.43 B | 2.74 B | 2.59 B | 2.16 B | 3.91 B | 2.56 B |
| Difference from 3.0 B | −0.57 B | −0.26 B | −0.41 B | −0.84 B | +0.91 B | −0.44 B |