Abstract
While much attention has been given to the role of animal intestinal microbes, few studies have focused on microbial communities and associated functions in cultured aquatic animals. In this study, high–throughput sequencing was used to analyze intestinal microbial communities and functions in fish, shrimp, crab and razor clams. Alpha diversity analyses showed significant differences in intestinal microbial diversity amongst these aquatic animals, and that shrimp intestines harbored the highest diversity and species numbers. T–test analyses (p < 0.05) showed significant differences in dominant microbial operational taxonomic units (OTUs) between all aquatic animals. Predominant intestinal bacteria included; Gammaproteobacteria, Fusobacteria, Mollicutes, Spirochaetia, Cyanobacteria, Bacteroidia and Bacilli. Similarly, anaerobic bacteria were highly diverse in animal intestines and included; Vibrio, Photobacterium, Cetobacterium, Propionigenium, Candidatus Hepatoplasma, Paraclostridium, and Lactobacillus. Principal co–ordinate analysis indicated that the distribution characteristics of intestinal microbes varied with animal species; in particular, we observed a high variability among shrimp intestinal samples. This variability indicated these genera had suitability for the different intestinal environment. Function prediction analysis indicated significant differences amongst different animals in the major functional groups, and that microbial functional profiles were strongly shaped by the intestinal environment. Thus, this study provides an important reference for future studies investigating crosstalk between aquatic animal hosts and their intestinal microbiota.
1. Introduction
Microbes play important roles in the material cycle and energy flow of aquaculture ecosystems [1]. Similarly, complex microbial communities play important roles in the digestive tracts of aquatic animal hosts [2,3,4]. Several studies have shown that intestinal microbial composition in such animals, contribute to vitamin synthesis, growth and development, material metabolism, and is related to intestinal development, immune responses and host resistance to disease [5,6].
The intestinal tract is the most important digestive and absorptive organ in animals. Large numbers of microbes live in this compartment and are interdependent and restricted with the host. It has been reported that intestinal microbes play important roles in nutritional metabolic processes [3,4]. They absorb energy from nutrients, such as starch and fiber, which they adapt for their own growth. Similarly, microbial metabolic activities also lead to the production of important nutrients, such as short chain fatty acids, vitamins and amino acids. Studies have shown that intestinal microbial communities with different structures and compositions, directly affect host nutritional metabolism and sensitivity to pathogenic bacterial infections [7,8]. Thus, a balanced microbial community in intestinal tracts is believed to contribute to the maintenance of host intestinal function. With ongoing developments in high–throughput sequencing, researchers are now more aware of aquatic microbial composition. The gut of aquaculture animals primarily contains aerobic bacteria, facultative and transitional anaerobes [9]. Similarly, different culture environments and foodstuffs can change the structures of these intestinal communities [10,11,12,13].
While several reports have investigated relationships between culture environments and intestinal microbial communities in aquatic animals, the composition and potential function of intestinal microbes of such animals in the same aquaculture area, remains unclear. In this study, we used high–throughput sequencing to investigate intestinal microbiome in several economically vital species, i.e., fish, shrimp, crab and razor clams. We analyzed differences in intestinal community structures and their potential functions in these animals. This study would help to establish the relationship between different host and their associated intestinal microbe, improve the understanding of the health status and nutritional level of the host, and provide reference for disease prevention in cultured aquatic animals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Four main economic animals were collected from a seawater aquaculture area, Putian City, China, in September 2018. All the polyculture ponds have the same seawater source, and the seawater enters the culture system through an inlet. Aquatic animal information is shown (Table S1). A total of 14 samples (fishes, shrimps, crabs and razor clams) were collected, of which eight parallel individuals of each sample were randomly collected from different cultured ponds. Then, under laboratory conditions, the intestines were dissected from each animal using conventional aseptic techniques, then pooled intestinal samples of the same animal. After this, intestinal tract contents were placed in sterile tubes, and stored in liquid nitrogen until DNA extraction.
2.2. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing of Intestinal Bacterial Communities
Total DNA from intestinal samples was extracted according to manufacturer’s instructions from the Soil DNA Extraction Kit (Omega, GA, USA). For amplification, we used 16S rRNA V4 primers 515F (5′–GTG CCA GCM GCC GCGGTA A–3′) and 806R (5′–GGA CTA CHV GGG TWTCTA AT–3′). PCR parameters were: total reaction volume = 25 μL, 5×FastPfu buffer = 4 μL, 2.5 mmol/L dNTPs = 2 μL, 5 U/μL FastPfu polymerase = 0.5 μL, 1.0 μL each primer (5.0 μmol/L) and 10 ng DNA template. PCR conditions were: 30 cycles; 95 °C for 3 min; 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 45 s and 72 °C for 10 min. The library was constructed using the TruSeq DNA PCR–Free Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), and quantified by Qubit and quantitative PCR. After purification, the library was loaded onto the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 Sequencer (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) for sequencing.
2.3. Data Analysis
For pair–ended reads generated by Illumina MiSeq sequencing, the data were first classified according to barcodes, and then spliced using FLASH (V1.2.7), according to overlap relationships. Quality filtering was performed on joined sequences. Sequences < 200 base pairs (bp) in length, or with a mean quality score ≥ 20 were discarded. Then, sequences were compared with RDP reference database, using VSEARCH (1.9.6) to detect chimeric sequences. Once identified, they were removed.
Confirmed sequences were grouped into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using UPARSE (v7.0.1001), and pre–clustered at 97% sequence identity. The highest OTU frequencies were selected as representative OTU sequences. These were annotated using Mothur against the SILVA132 database for taxonomic annotation (threshold value of 0.8–1). This approach generated taxonomic information at each taxonomic level. Sequences were also rarefied prior to the calculation of alpha and beta diversity statistics. QIIME software (Version 1.9.1) was used to calculate observed species, Chao1 and Shannon indices. Principal co–ordinate analysis (PCoA) was used to explore differences in communities amongst samples or groups, based on Bray–Curtis distances. T–tests were used to assess for significant differences (p < 0.05) in microbial communities, between samples. Microbial community functions were predicted and analyzed by FAPROTAX (Version 1.1) software [14].
3. Results
3.1. High–Throughput Sequencing Analysis
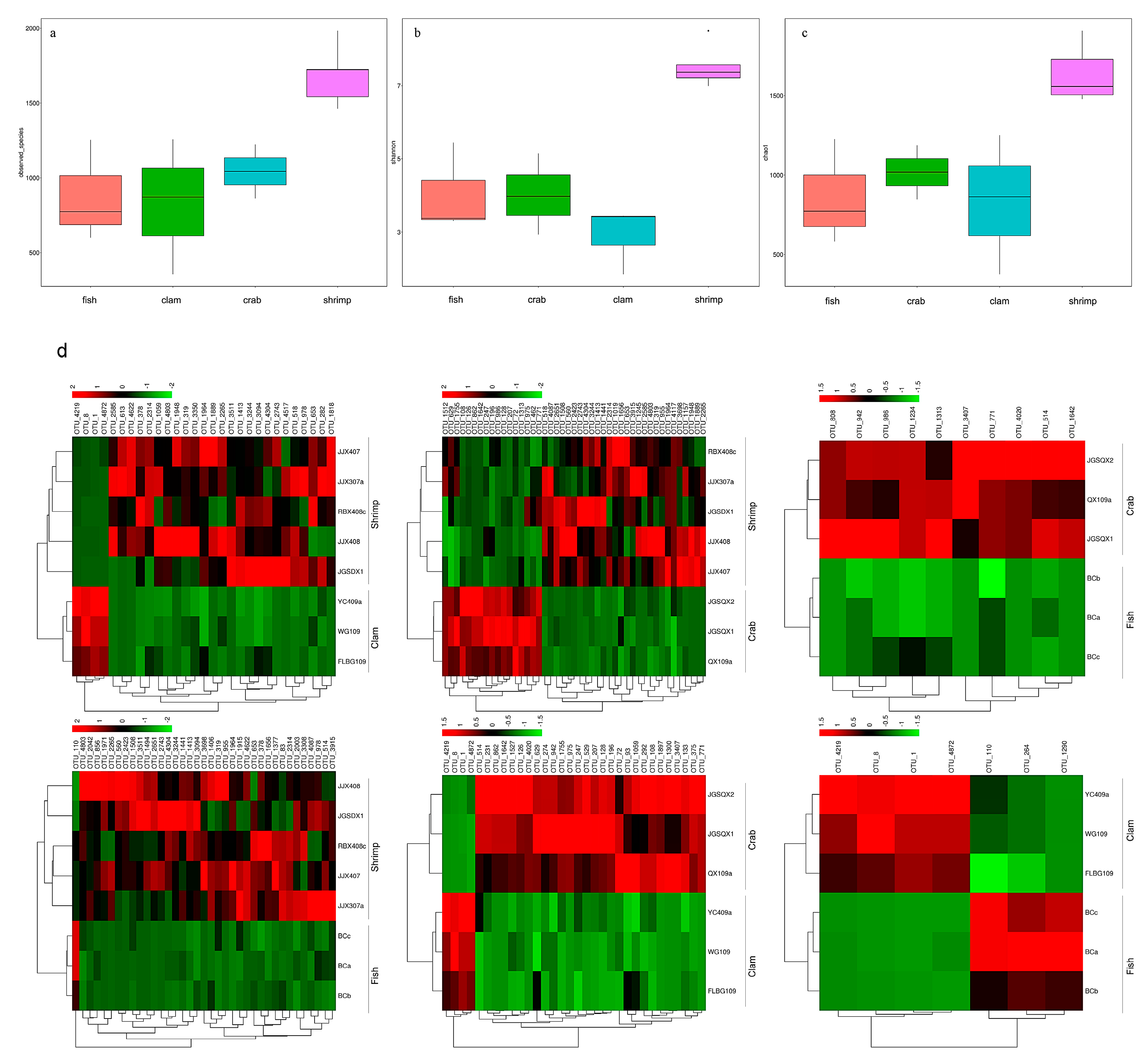
Using Illumina sequencing, 954,755 sequences were identified from 14 intestinal samples, and 4814 OTUs were observed at the 97% similarity level (Table S1). We observed the highest number of bacterial species in shrimp intestines (1686.60 ± 201.16), followed by crab intestines (1043.67 ± 181.00), whereas fish and razor clam intestines recorded the lowest bacterial numbers (Figure 1a). The Shannon index (Figure 1b) for shrimp intestinal bacteria was the highest (7.55 ± 0.58), followed by fish intestines (4.05 ± 1.22) and crab intestines (4.02 ± 1.11), whereas razor clam intestinal bacteria recorded the lowest index (2.91 ± 0.92). The richness index for shrimp intestinal bacteria was the highest (1831.38 ± 249.18), followed by the crab intestinal tract (1182.33 ± 195.13). In contrast, the richness index of intestinal bacteria in fish (988.67 ± 374.40) and razor clam (938.95 ± 507.32) were the lowest (Figure 1c).
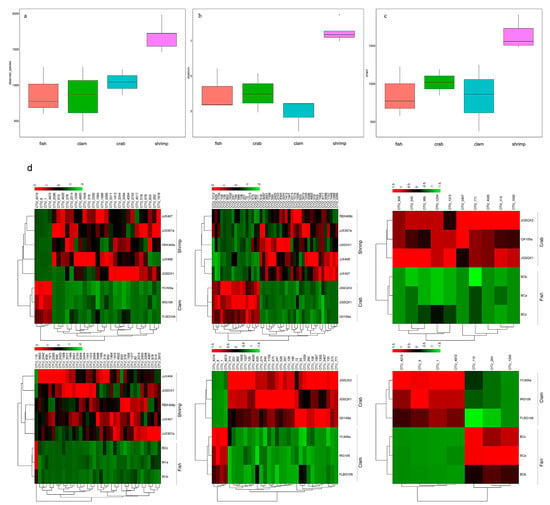
Figure 1.
Species (a), Shannon (b), and Chao1 indices (c) of bacterial intestinal communities in different aquatic animal groups. Significant differences were observed in operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in different aquatic animal intestines (d).
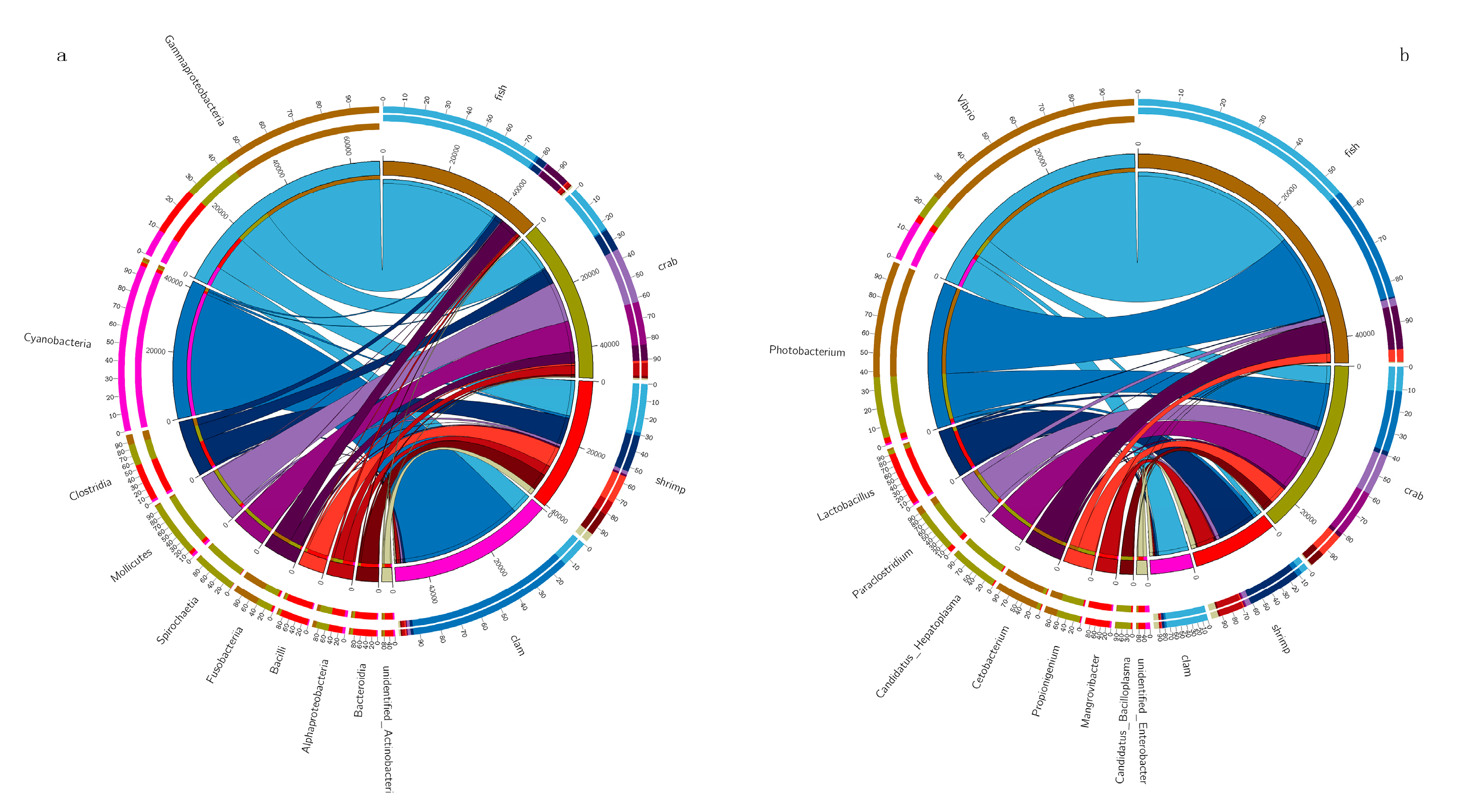
The dominant taxa in different intestinal samples at the genus level (abundance > 2%) are shown (Figure 2). The dominant genera in fish intestines were Vibrio (46.46%), Photobacterium (23.97%), Cetobacterium (9.00%) and Propionigenium (2.55%). The dominant genera in crab intestines were Photobacterium (12.53%), Candidatus Hepatoplasma (9.76%), Paraclostridium (8.60%), Vibrio (5.03%), Propionigenium (4.86%) and Candidatus Bacilloplasma (3.10%). Vibrio (8.45%) dominated in razor clam intestines. Finally, Lactobacillus (11.08%), Mangrovibacter (4.99%) and Fusibacter (2.18%) were the dominant genera in shrimp intestines.
Figure 2.
Dominant bacteria in the intestines of shrimp, crab, fish and razor clam, at phylum (a) and genus (b) levels.
3.2. Differences in Bacterial Communities from Intestinal Samples Identified by PCoA Analysis
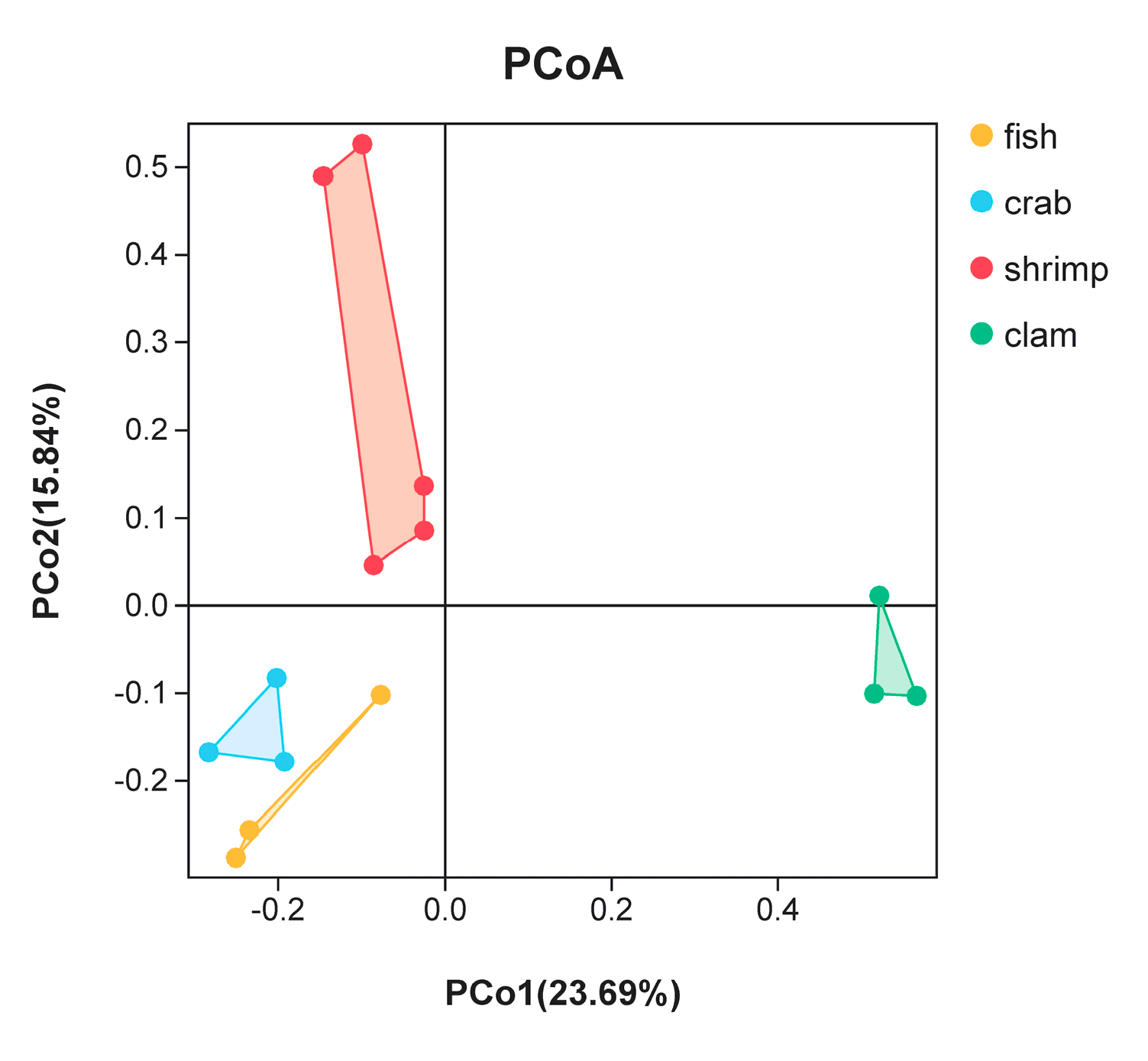
PCoA was used to highlight differences in bacterial communities in intestinal samples (Figure 3). The smaller the distance between the samples on the PCoA figure, the more similar the bacterial community of the intestinal samples. Intestinal samples of the same animal (fishes, crabs and razor clams) were gathered together. There was a large distance on the PCoA figure among fishes, crabs and razor clams’ intestinal samples. Whereas, the distance on the PCoA figure between different shrimp samples is large. In general, samples from the same animals gathered together, reflecting bacterial changes with different animals’ intestine. In addition, crab samples are close to the fish samples in PCoA, but far from the shrimps and razor clam samples.
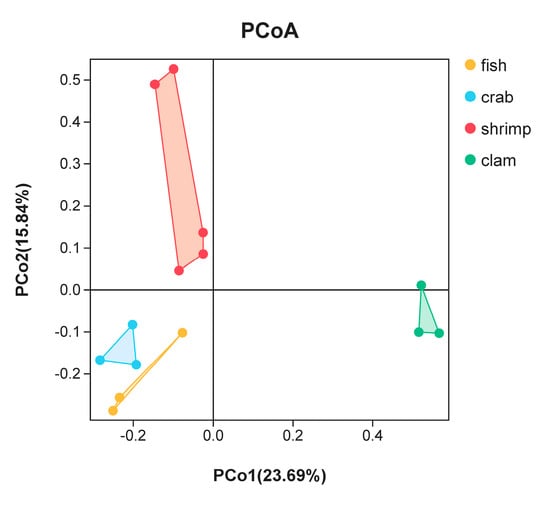
Figure 3.
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of bacterial community differences in the intestines of different aquatic animals.
3.3. Microbial Functional Prediction Analyses
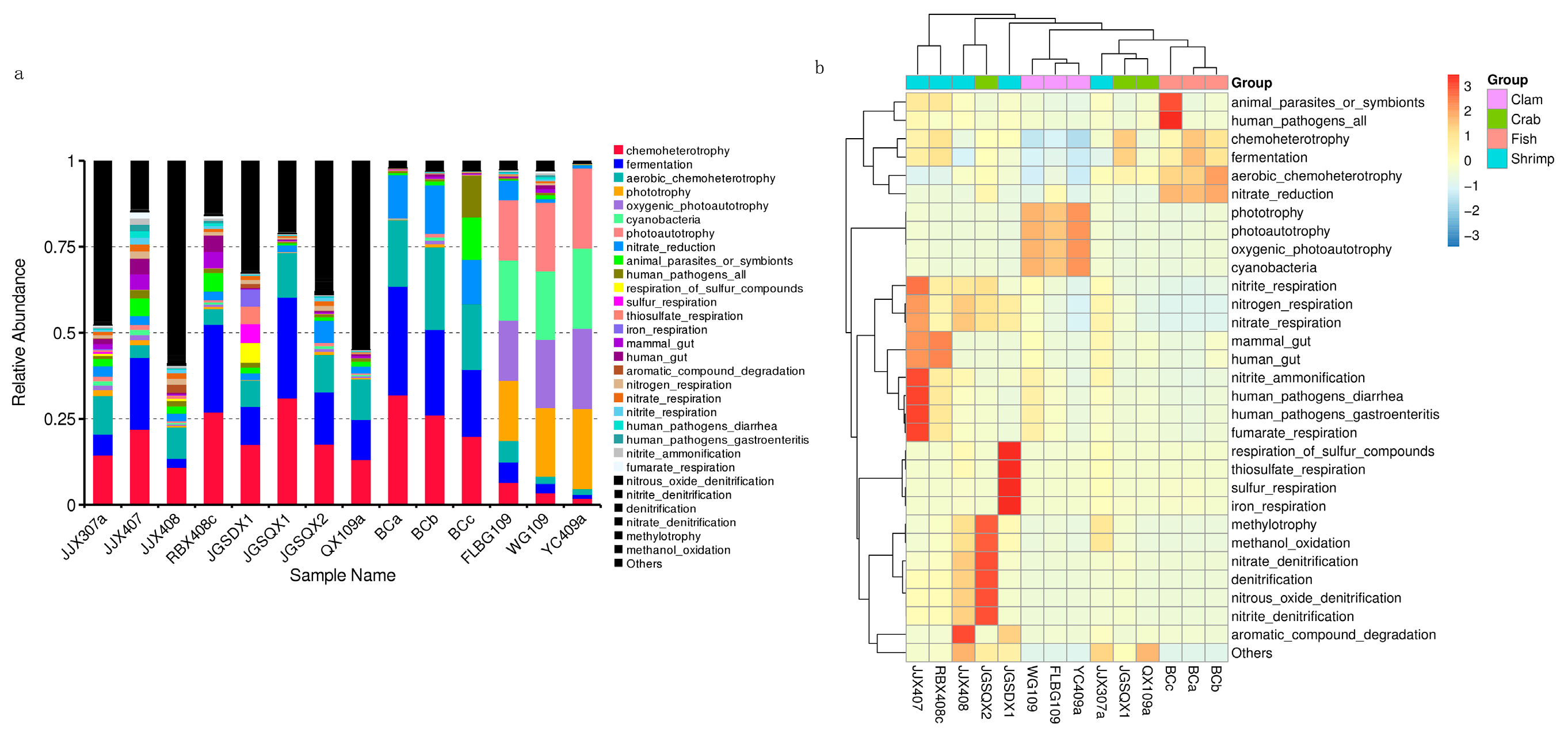
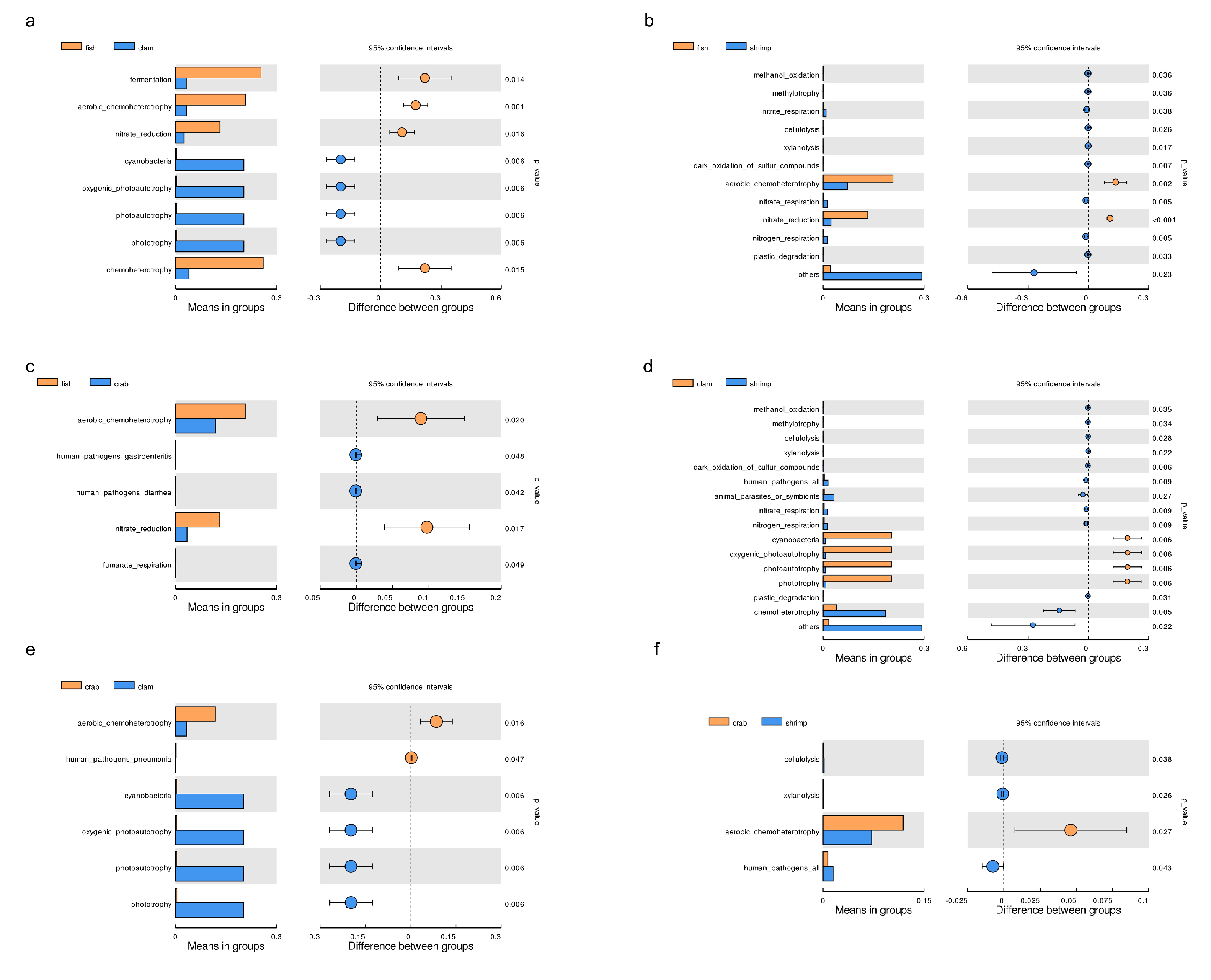
Microbial functions were predicted using FAPROTAX and were based on bacterial relative abundance. Overall, 75 functional groups were identified in intestinal bacterial communities (Figure 4a). Dominant functional groups in fish included chemoheterotrophy (26.01%), fermentation (25.26%), aerobic chemoheterotrophy (20.77%), nitrate reduction (13.19%), animal parasites or symbionts (4.71%) and human pathogens (4.45%). Dominant functional groups in crab included chemoheterotrophy (20.65%), fermentation (18.68%), aerobic chemoheterotrophy (11.86%) and nitrate reduction (3.46%). Dominant functional groups in razor clam included phototrophy (20.23%), photoautotrophy (20.23%), oxygenic photoautotrophy (20.23%) and cyanobacteria (20.23%). Dominant functional groups in shrimp included chemoheterotrophy (18.42%), fermentation (13.23%), aerobic chemoheterotrophy (7.24%), animal parasites or symbionts (3.27%) and nitrate reduction (2.48%).
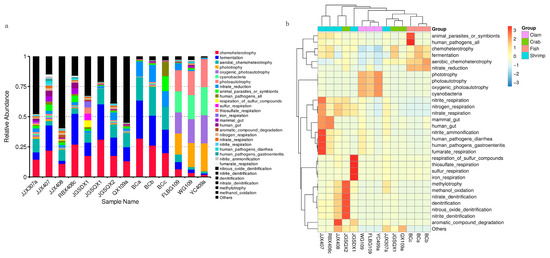
Figure 4.
Microbial functional predictions using FAPROTAX between samples (a) and groups (b), based on the relative abundance of bacterial taxa.
After functional predictions in each group, a cluster analysis revealed that bacterial community functional profiles in fish and crab were highly similar to each other. Microbial functional profiles in razor clam and shrimp intestines exhibited large distances with fish and crabs (Figure 4b). T–tests (p < 0.05) indicated that chemoheterotrophy, fermentation, aerobic chemoheterotrophy, nitrate reduction, phototrophy, photoautotrophy, oxygenic photoautotrophy and animal parasites were the significant functional differences between intestinal samples (Figure 5).
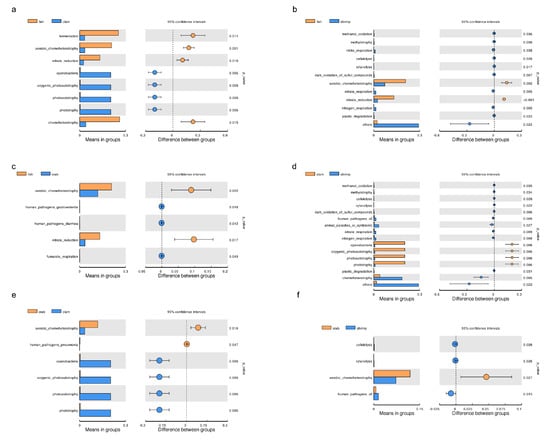
Figure 5.
Significant differences (t–tests) were observed for microbial functions in the intestines of aquatic animals. (a) fish vs. clam; (b) fish vs. shrimp; (c) fish vs. crab; (d) clam vs. shrimp; (e) crab vs. clam; (f) crab vs. shrimp.
4. Discussion
Identifying intestinal microbiome composition provides insights on how these microbial structures are formed, and how they potentially impact their hosts. In this study, we investigated intestinal microbiome compositional and functional differences in shrimp, crab, razor clam and fish taken from an aquaculture area. We also analyzed the potential impact of microbial functions on hosts.
4.1. Intestinal Microbiome Composition in Aquatic Animals May Reflect Specific Host Physiological Selection
Our data showed that microbial intestinal composition was significantly different between the four study animals. In particular for shrimp, bacterial diversity and richness were significantly higher than for fish, crab and razor clam. Previous studies have demonstrated the main source of intestinal microbial composition in cultured aquatic animals is the surrounding environment [11,12,15]. However, intestinal microbiome composition is not simply a reflection of microbes in local habitats, but also reflects host selection pressures at the intestine level [16,17]. We believe these reasons, and possibly feeding pattern, accounted for dominant microbe differences across our sample selection.
PCoA analyses revealed that microbes in different shrimp intestines were highly variable when compared to fish, crab and razor clam. OTU abundance in these intestines was also significantly higher when compared to other animals. In terms of physiology, shrimp intestines are relatively proximal to the body surface, thus intestinal microbes may be more affected by changes in external environments. This could be a reason for the significant differences in intestinal bacteria populations in shrimp samples. In addition, when the environment is relatively constant, obviously changes of dominant microbial taxa were observed among different animals, suggesting that host physiology significantly impacts on intestinal microbiota. Thus, intestinal microbiome may be affected by multiple factors [11,18]. Contributing to these factors is the host genetic background, which determines host nutritional levels, potentially affecting intestinal microbiome diversity [10,19].
4.2. Distinct Dominant Bacterial Taxa in Different Aquatic Intestines
In this study, Gammaproteobacteria, Fusobacteria, Clostridia, Mollicutes and Cyanobacteria were dominant taxa across all animal intestines. These commonalities indicated these microbes are important contributors to host intestinal function, i.e., digestion, absorption and immune responses [20,21,22]. Cyanobacteria were dominant in razor clam intestines, with a relative abundance of 77.71%. Previous studies have indicated that the Cyanobacteria, Prochlorococcus may be a food source for benthic shellfish, such as razor clam [11,12]. These bacteria are found in most aquatic habitats, providing food for aquatic animals.
We also observed that intestinal bacteria (genus level) were primarily anaerobic and facultative anaerobes. In this study, Cetobacterium was the most dominant bacterial genus in fish intestines. Cetobacterium is anaerobic in nature [23], and belongs to the core microbiome of several fish intestines [24,25]. It has been reported that Cetobacterium, and the protease–producing bacteria, Halomonas [26] are enriched in carnivores, suggesting bacteria with such degrading enzyme activities are affected by nutritional levels. The anaerobic bacteria, Propionigenium has been shown to produce propionate and acetate, via fermentation [27]. Propionate is involved in regulatory functions in intestinal physiology and immune systems [28]. Several members of the Vibrio genus are considered primary disease pathogens, causing death in aquaculture animals, and seriously endangering aquaculture systems [29,30]. In this study, Vibrio abundance was observed at 46.44% in fish intestines. However, Vibrio may also be beneficial to hosts. Vibrio also secretes amylases, proteases, lecithinases and chitinases to help digest nutrients in the host, such as fats, proteins and carbohydrates [31,32].
Lactobacillus was observed in the intestines of all aquatic animals, especially in shrimp, where the highest abundance (11%) was recorded. The genus is common to gastrointestinal tracts of most aquatic animals, where via glycolysis, they convert large hexose substrates into pyruvate, and then to lactic acid [33]. In terms of fish health, Lactobacillus have been widely reported as beneficial probiotics [34]. High levels of Lactobacillus lactis produce antimicrobial peptides and proteins in aquaculture ponds, and may exert antibacterial activities against some Gram–positive and negative bacteria [35]. Therefore, L. lactis appears to regulate the intestinal tract e.g., by inhibiting specific microbes by production compounds and competition for nutrients and energy [36,37,38]. Tenericutes, from the genus Candidatus Hepatoplasma, exhibited a high abundance in crab intestines, in line with previous studies [11,12]. Another study also observed that Candidatus Hepatoplasma was beneficial to its isopod host intestinal tract under low–nutrient conditions [39]. In this study, the high abundance of Candidatus Hepatoplasma in the crab’s intestine may indicate that the intestinal absorption of nutrients is abnormal.
4.3. Intestinal Microbiota Functional Profiles and Potential Effects on Aquatic Animal
FAPROTAX analyses indicated significant differences amongst aquatic animal groups, in terms of functional output. Chemoheterotrophy, fermentation and nitrate reduction were the primary functions of intestinal microbes in fish, crab and shrimp. Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria were the main executors of chemoheterotrophy and aerobic chemoheterotrophy. In a healthy animal state, bacteria provide nutrients and energy to hosts via fermentation of indigestible food ingredients, thus maintaining a balanced metabolism and immune system [21]. Previous studies have reported that gut Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria and Bacteroides have important roles in carbohydrate fermentation, polysaccharide catabolism, and amino acid and protein utilization [21,22]. FAPROTAX analysis indicated that microbes in similar environments exert similar ecological functions, but the microbial communities performing these functions may be different [40]. However, for razor clam intestinal microbiome, photoautotrophy functions were highly abundant, and were mainly contributed by Cyanobacteria. This phenomenon indicated that Cyanobacteria were important food sources for razor clams [12]. Thus, our data suggested that microbial functional profiles were strongly shaped by intestinal conditions. This study also exemplified the importance of ascertaining functional characteristics of microbial communities, in addition to identifying which microbes exist in the intestinal tract.
5. Conclusions
This study explored intestinal bacterial composition and functional profiles in different aquatic animals and provided a key reference for future studies investigating crosstalk between these hosts and their microbiota. Future work, incorporating ecological and physiological intestinal microbiota studies, must delineate how microbe are coordinated in the intestines, and how these microbes crosstalk with their aquatic hosts.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2077-1312/9/2/104/s1, Table S1: Aquatic animals and sequence information in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S. and Z.X.; methodology, F.S.; software, Z.X.; validation, Z.X. and F.S.; formal analysis, F.S.; investigation, F.S.; resources, F.S. and Z.X.; data curation, Z.X.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.; writing—review and editing, F.S.; visualization, F.S. and Z.X.; supervision, Z.X.; project administration, F.S. and Z.X.; funding acquisition, F.S. and Z.X. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Project of Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2017A020216008), Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (GML2019ZD0602 and GML2019ZD0305), Key deployment project of Marine Science Research Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences (COMS2019J10), and National Science &Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2018FY100100).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on the NCBI Sequence Read Archive Database with number SUB8798017.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Moriarty, D.J. The role of microorganisms in aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 1997, 151, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatesoupe, F.J. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsen, J.A. Interactions between fish larvae and bacteria in marine aquaculture. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B. The bacterial microflora of fish, revised. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Davies, S.J.; Waines, P.; Emery, M.; Castex, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O.; Bickerdike, R.; Romero, J.; Merrifield, D.L. Dietary synbiotic application modulates Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) intestinal microbial communities and intestinal immunity. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahenzli, J.; Koller, Y.; Wyss, M.; Geuking, M.B.; Mccoy, K.D. Intestinal Microbial Diversity during Early-Life Colonization Shapes Long-Term IgE Levels. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.B.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost microbiomes: The state of the art in their characterization, manipulation and importance in aquaculture and fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.K.; Kelly, S.A.; Legge, R.; Ma, F.; Low, S.J.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M.; Oh, P.L.; Nehrenberg, D.L.; Hua, K. Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18933–18938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Weng, G.; Zheng, Z. The intestinal bacterial community of healthy and diseased animals and its association with the aquaculture environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Tu, K.; Zheng, Z. Insights into the intestinal microbiota of several aquatic organisms and association with the surrounding environment. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyapechara, S.; Rungrassamee, W.; Suriyachay, I.; Kuncharin, Y.; Klanchui, A.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Jiravanichpaisal, P. Bacterial community associated with the intestinal tract of P. monodon in commercial farms. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 938–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lin, G.; Yan, T.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, B.; Sun, F. The cellular community in the intestine of the shrimp Penaeus penicillatus and its culture environments. Fish. Sci. 2014, 80, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, J.F.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I. Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4596–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.D.; Rawls, J.F. Intestinal microbiota composition in fishes is influenced by host ecology and environment. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Maibunkaew, S.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Characterization of intestinal bacteria in wild and domesticated adult black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P. Links between diet, gut microbiota composition and gut metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, C.; Sakata, T.; Sugita, H. Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeselers, G.; Mittge, E.; Stephens, W.Z.; Parichy, D.M.; Cavanaugh, C.M.; Guillemin, K.; Rawls, J.F. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.M.; Mohammed, H.H.; Arias, C.R. Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Gooneratne, R.; Lai, R.; Zeng, C.; Zhan, F.; Wang, W. The gut microbiome and degradation enzyme activity of wild freshwater fishes influenced by their trophic levels. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, B.; Pfennig, N. Propionigenium modestum gen. nov. sp. nov. a new strictly anaerobic, nonsporing bacterium growing on succinate. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 133, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Willemsen, D.; Popkes, M.; Metge, F.; Gandiwa, E.; Reichard, M.; Valenzano, D.R. Regulation of life span by the gut microbiota in the short-lived African turquoise killifish. eLife 2017, 6, e27014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Zhang, X.-H. Vibrio harveyi: A significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Maibunkaew, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Bacterial dynamics in intestines of the black tiger shrimp and the Pacific white shrimp during Vibrio harveyi exposure. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 133, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.H.; Olafsen, J.A. Bacterial Interactions in Early Life Stages of Marine Cold Water Fish. Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 38, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, A.; Sakata, T.; Kakimoto, D. Microflora in the Alimentary Tract of Gray Mullet-IV Estimation of Enzymic Activities of the Intestinal Bacteria. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1979, 45, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.E.; Zeyniyev, A.; Kuipers, O.P.; Kok, J. From meadows to milk to mucosa—adaptation of Streptococcus and Lactococcus species to their nutritional environments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 949–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcázar, J.L.; Blas, I.d.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Cunningham, D.; Vendrell, D.; Múzquiz, J.L. The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 114, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, D.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, M.; Meaney, B.; Hill, C. Lantibiotics Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Structure, Function and Applications. In Lactic Acid Bacteria: Genetics, Metabolism and Applications: Proceedings of the Seventh Symposium on Lactic Acid Bacteria: Genetics, Metabolism and Applications, Egmond aan Zee, The Netherlands, 1–5 September 2002; Siezen, R.J., Kok, J., Abee, T., Schasfsma, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, S.; Carmen Castro, M.; Berdasco, M.; de la Banda, I.G.; Moreno-Ventas, X.; de Rojas, A.H. Isolation and Partial Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria from the Gut Microbiota of Marine Fishes for Potential Application as Probiotics in Aquaculture. Probiotics Antimicro 2019, 11, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Delshad, S.T.; Adel, M.; Tiwari, R.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K.; Lazado, C.C. Probiotics as beneficial microbes in aquaculture: An update on their multiple modes of action: A review. Vet. Quart. 2016, 36, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, L.; Rombaut, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. Probiotic Bacteria as Biological Control Agents in Aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraune, S.; Zimmer, M. Host-specificity of environmentally transmitted Mycoplasma-like isopod symbionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.M. Microbial community ecology function over phylogeny. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).