Severity Scoring of Behavioral Responses of Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus) to Novel Continuous versus Conventional Pulsed Active Sonar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Welfare Considerations
2.2. Study Species and General Protocol
2.3. Experimental Exposures
2.4. Data Recording and Processing
2.5. Scoring Severity of Expert-Identified Behavioral Responses
2.6. Behavioral Response Analyses
2.6.1. Quantitative Analysis of the Proportion of Scored Responses and the Maximum Score Per Session Variables
2.6.2. Dose–Response Function Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Scorability of the Data Across the Behavioral Response Categories and Exposure Types
3.2. Overview of the Scoring of Behavioral Responses
3.2.1. Expert Scoring Process
3.2.2. Summary of Scored Behavioral Responses
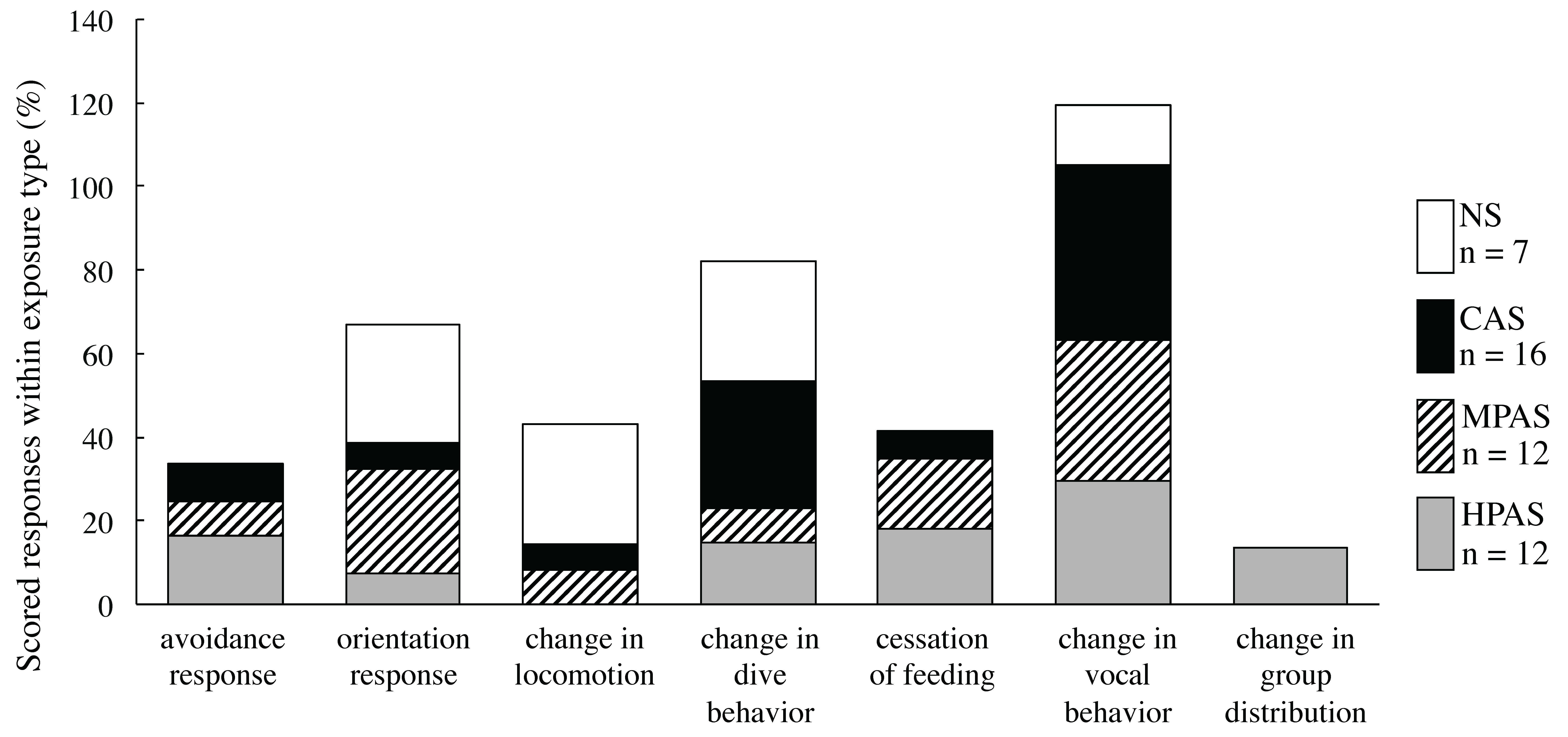
3.3. Description and Distribution of the Types of Behavioral Responses within Exposure Type
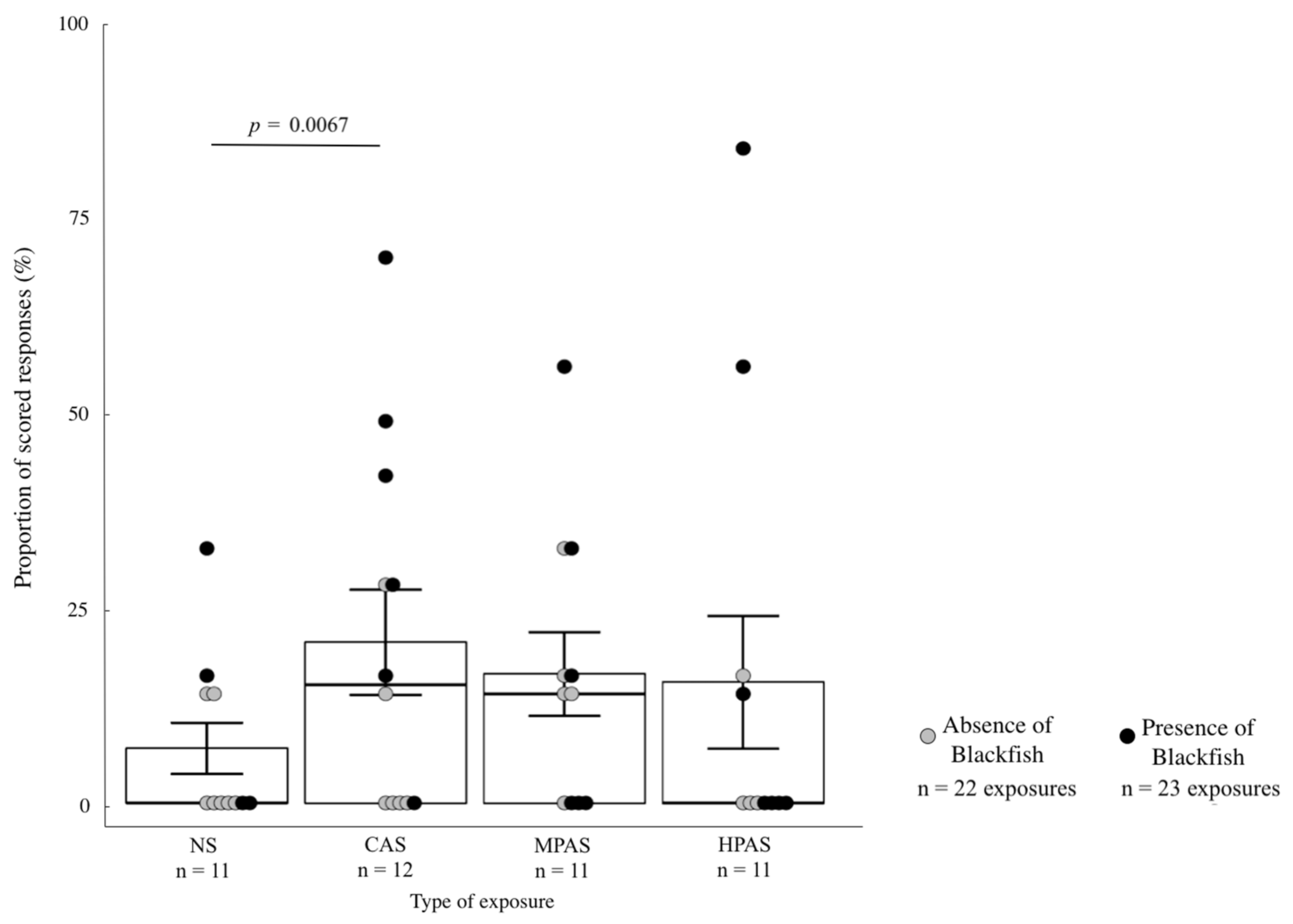
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of the Severity Scoring Variables in Relation to Exposure Type, Order and Recent Exposure to Blackfish
3.5. Severity of Scored Response in Relation to Received sound Pressure Level
4. Discussion
4.1. Responses to NS
4.2. Responses to Sonar and Influence of Exposure Type
4.3. Severity of Response to Sonar Related to RL Thresholds
4.4. Responses Related to Order of Exposures
4.5. Responses Related to Blackfish Presence
4.6. Remarks on the Scoring Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, W.J.; Greene, C.R.; Malme, C.I.; Thomson, D.H. Marine Mammals and Noise; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-12-588441-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tyack, P.L. Convergence of Calls as Animals Form Social Bonds, Active Compensation for Noisy Communication Channels, and the Evolution of Vocal Learning in Mammals. J. Comp. Psychol. 2008, 122, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.O.; Antunes, R.N.; Wensveen, P.J.; Samarra, F.I.P.; Catarina Alves, A.; Tyack, P.L.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Kleivane, L.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Ainslie, M.A.; et al. Dose-Response Relationships for the Onset of Avoidance of Sonar by Free-Ranging Killer Whales. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southall, B.L.; Bowles, A.E.; Ellison, W.T.; Finneran, J.J.; Gentry, R.L.; Greene, C.R.; Kastak, D.; Ketten, D.R.; Miller, J.H.; Nachtigall, P.E.; et al. Marine mammal noise exposure criteria: Initial scientific recommendations. Aquat. Mamm. 2007, 33, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southall, B.L.; Nowacek, D.; Miller, P.J.O.; Tyack, P.L. Experimental Field Studies to Measure Behavioral Responses of Cetaceans to Sonar. Endang. Species Res. 2016, 31, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzis, A. Does Acoustic Testing Strand Whales? Nature 1998, 392, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcomb III, K.C.; Claridge, D.E. A mass stranding of cetaceans caused by naval sonar in the Bahamas. Bahamas J. Sci. 2001, 8, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico, A.; Gisiner, R.C.; Ketten, D.R.; Hammock, J.A.; Johnson, C.; Tyack, P.L.; Mead, J. Beaked Whale Strandings and Naval Exercises. Aquat. Mamm. 2009, 35, 452–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Ketten, D.R. Underwater Hearing. In The Senses: A Comprehensive Reference; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 225–236. ISBN 978-0-12-370880-9. [Google Scholar]
- Erbe, C.; Dunlop, R.; Dolman, S. Effects of Noise on Marine Mammals. In Effects of Anthropogenic Noise on Animals; Slabbekoorn, H., Dooling, R., Popper, A., Fay, R., Eds.; Springer Handbook of Auditory Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 66, pp. 227–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, L.; Clark, J.; Costa, D.; Fleishman, E.; Hindell, M.; Klanjšček, T.; Lusseau, D.; Kraus, S.; McMahon, C.; Robinson, P.; et al. Using Short-Term Measures of Behaviour to Estimate Long-Term Fitness of Southern Elephant Seals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 496, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.P.; Tyack, P.L. A Digital Acoustic Recording Tag for Measuring the Response of Wild Marine Mammals to Sound. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 28, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isojunno, S.; Sadykova, D.; DeRuiter, S.L.; Curé, C.; Visser, F.; Thomas, L.; Miller, P.J.O.; Harris, C.M. Individual, Ecological, and Anthropogenic Influences on Activity Budgets of Long-Finned Pilot Whales. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e02044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.O.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Wensveen, P.J.; Antunes, R.; Alves, A.C.; Visser, F.; Kleivane, L.; Tyack, P.L.; Sivle, L.D. The Severity of Behavioral Changes Observed During Experimental Exposures of Killer (Orcinus Orca), Long-Finned Pilot (Globicephala Melas), and Sperm (Physeter Macrocephalus) Whales to Naval Sonar. Aquat. Mamm. 2012, 38, 362–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensveen, P.J.; Isojunno, S.; Hansen, R.R.; von Benda-Beckmann, A.M.; Kleivane, L.; van IJsselmuide, S.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; DeRuiter, S.L.; Curé, C.; et al. Northern Bottlenose Whales in a Pristine Environment Respond Strongly to Close and Distant Navy Sonar Signals. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2019, 286, 20182592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isojunno, S.; Curé, C.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Tyack, P.L.; Wensveen, P.J.; Miller, P.J.O. Sperm Whales Reduce Foraging Effort during Exposure to 1-2 KHz Sonar and Killer Whale Sounds. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curé, C.; Isojunno, S.; Visser, F.; Wensveen, P.J.; Sivle, L.D.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.; Miller, P.J.O. Biological Significance of Sperm Whale Responses to Sonar: Comparison with Anti-Predator Responses. Endang. Species. Res. 2016, 31, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvadsheim, P.H.; Isojunno, S.; Curé, C.; Siemensma, M.; Wensveen, P.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Hansen, R.R.; Benti, B.; Sivle, L.D.; Burslem, A.; et al. The 3S3 experiment data report–using operational naval sonars to study the effects of continuous active sonar, and source proximity, on sperm whales. FFI Report 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Isojunno, S.; Wensveen, P.J.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; von Benda-Beckmann, A.M.; Martín López, L.M.; Kleivane, L.; Siegal, E.M.; Miller, P.J.O. When the Noise Goes on: Received Sound Energy Predicts Sperm Whale Responses to Both Intermittent and Continuous Navy Sonar. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb219741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivle, L.D.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Curé, C.; Isojunno, S.; Wensveen, P.J.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Visser, F.; Kleivane, L.; Tyack, P.L.; Harris, C.M.; et al. Severity of Expert-Identified Behavioural Responses of Humpback Whale, Mike Whale, and Northern Bottlenose Whale to Naval Sonar. Aquat. Mamm. 2015, 41, 469–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southall, B.L.; DeRuiter, S.L.; Friedlaender, A.; Stimpert, A.K.; Goldbogen, J.A.; Hazen, E.; Casey, C.; Fregosi, S.; Cade, D.E.; Allen, A.N.; et al. Behavioral Responses of Individual Blue Whales (Balaenoptera Musculus) to Mid-Frequency Military Sonar. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb190637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.-P.A.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Isojunno, S.; Wensveen, P.J.; van IJsselmuide, S.; Siemensma, M.L.; Dekeling, R.; Miller, P.J.O. Behavioural response study on the effects of continuous sonar on sperm whales in Norwegian waters-The 3S-2016-CAS cruise report. 2018. Available online: http://publications.tno.nl/publication/34627070/Q3bPWP/TNO-2018-R10802.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Lam, F.-P.A.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Isojunno, S.; Wensveen, P.J.; van IJsselmuide, S.; Siemensma, M.L.; Dekeling, R.; Miller, P.J.O. Behavioural response study on the effects of continuous sonar on sperm whales in Norwegian waters-The 3S-2017-CAS cruise report. 2018. Available online: http://publications.tno.nl/publication/34627071/pohdo8/TNO-2018-R10958.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Miller, P.J.O.; Johnson, M.P.; Tyack, P.L. Sperm Whale Behaviour Indicates the Use of Echolocation Click Buzzes ‘Creaks’ in Prey Capture. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2004, 271, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.O.; Aoki, K.; Rendell, L.E.; Amano, M. Stereotypical Resting Behavior of the Sperm Whale. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R21–R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivle, L.D.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Fahlman, A.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Tyack, P.L.; Miller, P.J.O. Changes in Dive Behavior during Naval Sonar Exposure in Killer Whales, Long-Finned Pilot Whales, and Sperm Whales. Front. Physio. 2012, 3, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Benda-Beckmann, A.M.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Moretti, D.J.; Fulkerson, K.; Ainslie, M.A.; van IJsselmuide, S.P.; Theriault, J.; Beerens, S.P. Detection of Blainville’s Beaked Whales with Towed Arrays. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.O.; Antunes, R.; Alves, A.C.; Wensveen, P.J.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Nordlund, N.; Lam, F.P.; Ijsselmuide, S.; Visser, F.; Tyack, P.; et al. The 3S experiments: Studying the Behavioral Effects of Sonar on Killerwhales (Orcinus orca), Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus), and Long-Finned Pilot Whales (Globicephala melas) in Norwegian Waters; IQOE: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2011; p. 290. [Google Scholar]
- Wensveen, P.J.; Thomas, L.; Miller, P.J.O. A Path Reconstruction Method Integrating Dead-Reckoning and Position Fixes Applied to Humpback Whales. Mov. Ecol. 2015, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzis, A.; Alexiadou, P. Male Sperm Whale (Physeter Macrocephalus) Coda Production and Coda-Type Usage Depend on the Presence of Conspecifics and the Behavioural Context. Can. J. Zool. 2008, 86, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Wahlberg, M.; Johnson, M.; Miller, P.J.O.; Madsen, P.T. The Function of Male Sperm Whale Slow Clicks in a High Latitude Habitat: Communication, Echolocation, or Prey Debilitation? J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 3135–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, D.W.; Würsig, B.; Whitehead, H.; Norris, J.C.; Lynn, S.K.; Davis, R.W.; Clauss, N.; Brown, P. Observations of an interaction between sperm whales and short-finned pilot whales in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Mammal Sci. 1996, 12, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.R.; Berger, J.; Clapham, P.J. Killer Whales as Predators of Large Baleen Whales and Sperm Whales. In Whales, Whaling, and Ocean Ecosystems; Estes, J., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 174–187. ISBN 978-0-520-24884-7. [Google Scholar]
- von Benda-Beckmann, A.M.; Thomas, L.; Tyack, P.L.; Ainslie, M.A. Modelling the Broadband Propagation of Marine Mammal Echolocation Clicks for Click-Based Population Density Estimates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, F.; Miller, P.J.O.; Antunes, R.N.; Oudejans, M.G.; Mackenzie, M.L.; Aoki, K.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Huisman, J.; Tyack, P.L. The Social Context of Individual Foraging Behaviour in Long-Finned Pilot Whales (Globicephala Melas). Behaviour 2014, 151, 1453–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Højsgaard, S.; Halekoh, U.; Yan, J. The R Package geepack for Generalized Estimating Equations. Journal of Statistical Software. 2006, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curé, C.; Sivle, L.D.; Visser, F.; Wensveen, P.J.; Isojunno, S.; Harris, C.M.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Miller, P.J.O. Predator Sound Playbacks Reveal Strong Avoidance Responses in a Fight Strategist Baleen Whale. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 526, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M.; Sadykova, D.; DeRuiter, S.L.; Tyack, P.L.; Miller, P.J.O.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Thomas, L. Dose Response Severity Functions for Acoustic Disturbance in Cetaceans Using Recurrent Event Survival Analysis. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Multiple events per subject. In Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 169–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. Competing risks survival analysis. In Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 425–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T. A package for survival analysis in SR package, 2014, Version 2.37-7. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Ellison, W.T.; Southall, B.L.; Clark, C.W.; Frankel, A.S.A. New Context-Based Approach to Assess Marine Mammal Behavioral Responses to Anthropogenic Sounds. Conserv. Biol. 2012, 26, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curé, C.; Isojunno, S.; Vester, H.I.; Visser, F.; Oudejans, M.; Biassoni, N.; Massenet, M.; Barluet de Beauchesne, L.; Wensveen, P.J.; Sivle, L.D.; et al. Evidence for Discrimination between Feeding Sounds of Familiar Fish and Unfamiliar Mammal-Eating Killer Whale Ecotypes by Long-Finned Pilot Whales. Anim. Cogn. 2019, 22, 863–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M.; Thomas, L.; Falcone, E.A.; Hildebrand, J.; Houser, D.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.-P.A.; Miller, P.J.O.; Moretti, D.J.; Read, A.J.; et al. Marine Mammals and Sonar: Dose-Response Studies, the Risk-Disturbance Hypothesis and the Role of Exposure Context. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 55, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.; McKenna, M.F.; Angeloni, L.M.; Crooks, K.R.; Fristrup, K.M.; Brown, E.; Warner, K.A.; Nelson, M.D.; White, C.; Briggs, J.; et al. A Synthesis of Two Decades of Research Documenting the Effects of Noise on Wildlife: Effects of Anthropogenic Noise on Wildlife. Biol. Rev. 2016, 91, 982–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnot, N.C.; Couriot, O.; Berger, A.; Cagnacci, F.; Ciuti, S.; De Groeve, J.E.; Gehr, B.; Heurich, M.; Kjellander, P.; Kröschel, M.; et al. Fear of the Dark? Contrasting Impacts of Humans versus Lynx on Diel Activity of Roe Deer across Europe. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudman, N.J.; Churski, M.; Bubnicki, J.W.; Nilsson, J.-Å.; Kuijper, D.P.J. Red Deer Allocate Vigilance Differently in Response to Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Risk from Human Hunters and Wolves. Wildl. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieucau, G.; Sivle, L.D.; Handegard, N.O. Herring perform stronger collective evasive reactions when previously exposed to killer whales calls. Behav. Ecol. 2016, 27, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curé, C.; Antunes, R.; Alves, A.C.; Visser, F.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Miller, P.J.O. Responses of Male Sperm Whales (Physeter Macrocephalus) to Killer Whale Sounds: Implications for Anti-Predator Strategies. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deecke, V.B.; Slater, P.J.B.; Ford, J.K.B. Selective Habituation Shapes Acoustic Predator Recognition in Harbour Seals. Nature 2002, 420, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benti, B.; Miller, P.J.O.; Biuw, M.; Curé, C. Indication that the behavioural responses of humpback whales to killer whale sounds are influenced by trophic relationships. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 660, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Score | Behavioral Responses |
|---|---|
| 0 | No observable response |
| 1 | Brief orientation response |
| 2 | Moderate or multiple orientation responses Brief or minor changes in respiration rates Brief cessation/modification of vocal behavior Brief change in dive profile |
| 3 | Prolonged orientation behavior Minor change in locomotion (speed/direction) and or dive profile but no avoidance of sound source Minor cessation/modification of vocal behavior Individual alert behavior Moderate change of respiration rate Brief shift in group distribution |
| 4 | Moderate change in locomotion (speed/direction) and or dive profile but no avoidance of sound source Brief avoidance of sound source Minor shift in group distribution Moderate cessation/modification of vocal behavior Brief cessation of feeding/resting |
| 5 | Extended change in locomotion (speed/direction) and or dive profile but no avoidance of sound source Minor avoidance of sound source Moderate shift in group distribution Change in inter-animal distance and/or group size Prolonged cessation or modification of vocal behavior Minor cessation of feeding/resting |
| 6 | Moderate avoidance of sound source Extended cessation or modification of vocal behavior Visible startle response Moderate cessation of feeding Prolonged shift in group distribution Brief or minor separation of female and dependent offspring Aggressive behavior related to noise exposure Brief cessation of reproductive behavior Moderate cessation of resting behavior |
| 7 | Prolonged cessation of feeding Moderate separation of female and dependent offspring Severe and or sustained avoidance of sound source Extensive or prolonged aggressive behavior Clear antipredator response Moderate cessation of reproductive behavior Prolonged avoidance |
| 8 | Obvious aversion and/or progressive sensitization Long-term avoidance of area Prolonged or significant separation of female and dependent offspring with disruption of acoustic reunion mechanisms Prolonged cessation of reproductive behavior |
| 9 | Outright panic, flight, stampede, or attack Avoidance related to predator detection |
| Whale ID. | Exposure Sessions (by Order of Exposure) |
|---|---|
| Sw16_126a | CAS, MPAS, HPAS |
| Sw16_130a | NS, MPAS, CAS |
| Sw16_131a | NS |
| Sw16_134a | NS |
| Sw16_134b | NS, CAS, HPAS, MPAS |
| Sw16_135a | NS, HPAS, CAS, MPAS |
| Sw16_136a | NS, CAS, MPAS, HPAS |
| Sw17_179a * | MPAS, HPAS, CAS |
| Sw17_180a * | NS, HPAS, MPAS, CAS |
| Sw17_182a * Sw17_182b | NS, MPAS, CAS, HPAS NS, MPAS, CAS, HPAS |
| Sw17_184a * | NS, CAS, HPAS |
| Sw17_186a * Sw17_186b | NS, HPAS, CAS NS, HPAS, CAS, MPAS |
| Sw17_188a | NS, MPAS, HPAS, CAS, CAS |
| Sw17_191a | NS, HPAS, MPAS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curé, C.; Isojunno, S.; Siemensma, M.L.; Wensveen, P.J.; Buisson, C.; Sivle, L.D.; Benti, B.; Roland, R.; Kvadsheim, P.H.; Lam, F.-P.A.; et al. Severity Scoring of Behavioral Responses of Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus) to Novel Continuous versus Conventional Pulsed Active Sonar. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040444
Curé C, Isojunno S, Siemensma ML, Wensveen PJ, Buisson C, Sivle LD, Benti B, Roland R, Kvadsheim PH, Lam F-PA, et al. Severity Scoring of Behavioral Responses of Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus) to Novel Continuous versus Conventional Pulsed Active Sonar. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(4):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040444
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuré, Charlotte, Saana Isojunno, Marije L. Siemensma, Paul J. Wensveen, Célia Buisson, Lise D. Sivle, Benjamin Benti, Rune Roland, Petter H. Kvadsheim, Frans-Peter A. Lam, and et al. 2021. "Severity Scoring of Behavioral Responses of Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus) to Novel Continuous versus Conventional Pulsed Active Sonar" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 4: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040444
APA StyleCuré, C., Isojunno, S., Siemensma, M. L., Wensveen, P. J., Buisson, C., Sivle, L. D., Benti, B., Roland, R., Kvadsheim, P. H., Lam, F.-P. A., & Miller, P. J. O. (2021). Severity Scoring of Behavioral Responses of Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus) to Novel Continuous versus Conventional Pulsed Active Sonar. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(4), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040444








