A Generalized Hybrid RANSE/BEM Approach for the Analysis of Hull–Propeller Interaction in Off-Design Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
2.1. Inviscid Flow Model by BEM
2.2. Viscous Flow Model by RANS
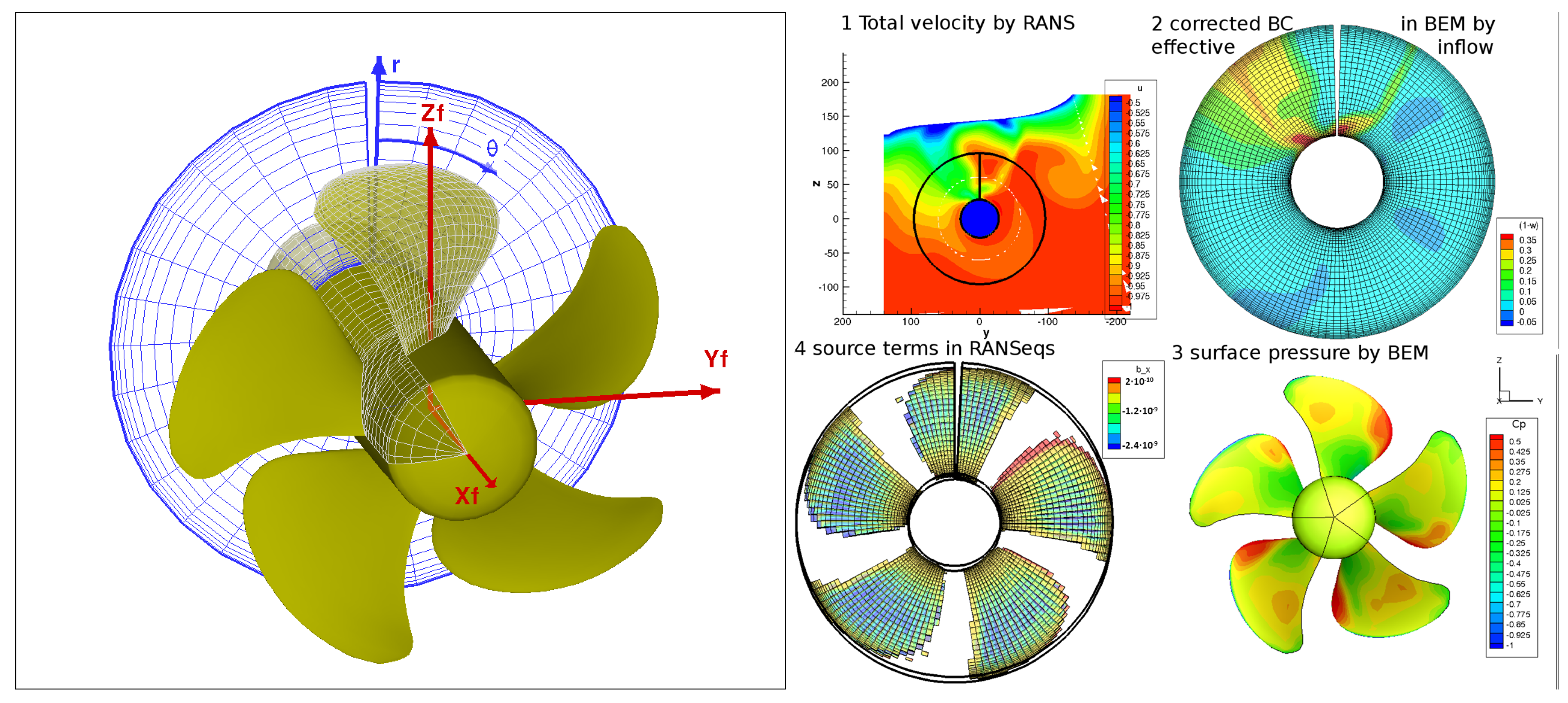
2.3. RANS/BEM Coupling
- volume-forces , derived from the propeller hydrodynamic forces by BEM , are used as forcing terms of the Navier–Stokes equations;
- effective-inflow , which is used in the BEM to impose boundary conditions on propeller surface from the estimation of the total velocity by RANS.
3. Case Study and Experimental Setup
4. Numerical Setup
5. Validation Results
5.1. Straight-Ahead () Motion
5.2. Steady-Drift () Motion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortolani, F.; Mauro, S.; Dubbioso, G. Investigation of the radial bearing force developed during actual ship operations. Part 1: Straight ahead sailing and turning maneuvers. Ocean Eng. 2015, 94, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbioso, G.; Muscari, R.; Ortolani, F.; Di Mascio, A. Analysis of propeller bearing loads by CFD. Part I: Straight ahead and steady turning maneuvers. Ocean Eng. 2017, 130, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, F.; Dubbioso, G. Experimental investigation of blade and propeller loads: Straight ahead motion. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2019, 87, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, F.; Dubbioso, G. Experimental investigation of blade and propeller loads: Steady turning motion. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 91, 101874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbioso, G.; Ortolani, F. Analysis of fretting inception for marine propeller by single blade loads measurement in realistic operating conditions. Straight ahead and turning circle maneuver. Mar. Struct. 2020, 71, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbioso, G.; Muscari, R.; Ortolani, F.; Di Mascio, A. Numerical Analaysis of Marine Propellers Low Frequency Noise during Maneuvering. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 71, 399–419. [Google Scholar]
- Broglia, R.; Dubbioso, G.; Durante, D.; Di Mascio, A. Simulation of Turning Circle by CFD: Analysis of different propeller models and their effect on manoeuvering prediction. Appl. Ocean Res. 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, A.; Carrica, P.M. Simulations of zigzag maneuvers for a container ship with direct moving rudder and propeller. Comput. Fluids 2014, 96, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.M.; Carrica, P.M.; Stern, F. Full scale self-propulsion computations using discretized propeller for the KRISO container ship KCS. Comput. Fluids 2011, 51, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscari, R.; Felli, M.; Di Mascio, A. Analysis of the Flow Past a Fully Appended Hull with Propellers by Computational and Experimental Fluid Dynamics. J. Fluids Eng. 2011, 133, 061104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chen, H. The Influence of Propeller/Hull Interaction on Propeller Induced Cavitating Pressure. In Proceedings of the 15th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE 2005, Seoul, Korea, 19–24 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gaggero, S.; Villa, D.; Viviani, M. An extensive analysis of numerical ship self-propulsion prediction via a coupled BEM/RANS approach. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 66, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Thad, M.; Carrica, P.M. Submarine Maneuvers Using Direct Overset Simulation of Appendages and Propeller and Coupled CFD/Potential Flow Propeller Solver. J. Ship Res. 2015, 59, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, M.; Wockner-Kluwe, K.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.; Rung, T. Viscous-Inviscid Coupling Methods for Advanced Marine Propeller Applications. Int. J. Rotat. Mach. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, S.; Scharf, M.; Gottsche, U.; Neitzel, J.; Angerbauer, R.; Abdel-Maksoud, M. Numerical Simulation of Propeller-Rudder Interaction for Non-Cavitating and Cavitating Flows Using Different Approaches. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Marine Propulsion, SMP’15, Austin, TX, USA, 31 May–4 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rijpkema, D.; Starke, B.; Bosschers, J. Numerical simulation of propeller-hull interaction and of the effective wake field using a hybrid RANS-BEM approach. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Marine Propulsion, SMP’13, Lauceston, Australia, 5–7 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatore, F.; Calcagni, D.; Muscari, R.; Broglia, R. A generalised fully unsteady hybrid RANS/BEM model for marine propeller flow simulations. In Proceedings of the VI International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering, MARINE 2015, Rome, Italy, 15–17 June 2015; pp. 613–626. [Google Scholar]
- Koncoski, J.; Paterson, E.; Zierke, W. A Blade-Element Model of Propeller Unsteady Forces for Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Developments in Marine CFD 2011, London, UK, 22–23 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gaggero, S.; Dubbioso, G.; Villa, D.; Muscari, R.; Viviani, M. Propeller modeling approaches for off–design operative conditions. Ocean Eng. 2019, 178, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagni, D.; Salvatore, F.; Dubbioso, G.; Muscari, R. A generalised unsteady hybrid des/bem methodology applied to propeller-rudder flow simulation. In Proceedings of the VII International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering, MARINE 2017, Nantes, France, 15–17 May 2017; pp. 377–392. [Google Scholar]
- Calcagni, D.; Capone, A.; Ortolani, F.; Broglia, R.; Dubbioso, G.; Pereira, F.; Salvatore, F.; Di Felice, F. A generalised hybrid RANSE/BEM approach for unsteady flow effects in hull/propeller interaction. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Marine Propulsion, SMP’19, Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morino, L. Boundary Integral Equations in Aerodynamics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1993, 46, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P. Detached-Eddy Simulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mascio, A.; Broglia, R.; Muscari, R.; Dattola, R. Unsteady RANS Simulation of a Manoeuvring Ship Hull. In Proceedings of the 25th ONR Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 8–13 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Merkle, C.; Athvale, M. Time-accurate Unsteady Compressible Flow Algorithms Based on Artificial Compressibility. AIAA Pap. 1987, 87, 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Muscari, R.; Di Mascio, A. Simulation of the flow around complex hull geometries by an overlapping grid approach. In Proceedings of the 5th Osaka Colloquium on Advanced Research on Ship Viscous Flow and Hull Form Design by EFD and CFD Approaches, Osaka, Japan, 14–15 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Muscari, R.; Broglia, R.; Di Mascio, A. An overlapping grids approach for moving bodies problems. In Proceedings of the 16th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE 2006, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 May–2 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghi, S.; Di Mascio, A.; Broglia, R.; Muscari, R. Application of dynamic overlapping grids to the simulation of the flow around a fully-appended submarine. Math. Comput. Simul. 2014, 116, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, F.; Capone, A.; Dubbioso, G.; Pereira, F.A.; Maiocchi, A.; Di Felice, F. Propeller performance on a model ship in straight and steady drift motions from single blade loads and flow field measurements. Ocean Eng. 2020, 197, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, A.; Alves Pereira, F.; Maiocchi, A.; Di Felice, F. Analysis of the hull wake of a twin-screw ship in steady drift by Borescope Stereo Particle Image Velocimetry. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 92, 101914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Costa, T.; Felli, M.; Calcagno, G.; Di Felice, F. A versatile fully submersible stereo-PIV probe for tow tank applications. In Proceedings of the ASME/JSME 2003 4th Joint Fluids Summer Engineering Conference, FEDSM 2003, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–10 July 2003; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, F. Iterative image deformation methods in PIV. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 13, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, F.; Dubbioso, G. In-plane and single blade loads measurement setups for propeller performance assessment during free running and captive model tests. Ocean Eng. 2020, 217, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| Parameter | Symbol | Model Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Block coefficient | 0.49 | |
| Drift angle | ||
| Speed | 0.26 | |
| Pitch to diameter ratio | P/D | 1.45 |
| Hub diameter ratio | 0.37 | |
| Prop.s rotation | - | inward |
| Advance coefficient | J | 1.116 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calcagni, D.; Dubbioso, G.; Capone, A.; Ortolani, F.; Broglia, R. A Generalized Hybrid RANSE/BEM Approach for the Analysis of Hull–Propeller Interaction in Off-Design Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050482
Calcagni D, Dubbioso G, Capone A, Ortolani F, Broglia R. A Generalized Hybrid RANSE/BEM Approach for the Analysis of Hull–Propeller Interaction in Off-Design Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(5):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050482
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalcagni, Danilo, Giulio Dubbioso, Alessandro Capone, Fabrizio Ortolani, and Riccardo Broglia. 2021. "A Generalized Hybrid RANSE/BEM Approach for the Analysis of Hull–Propeller Interaction in Off-Design Conditions" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 5: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050482
APA StyleCalcagni, D., Dubbioso, G., Capone, A., Ortolani, F., & Broglia, R. (2021). A Generalized Hybrid RANSE/BEM Approach for the Analysis of Hull–Propeller Interaction in Off-Design Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(5), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050482







