The Effects of Temperature and Salinity Stressors on the Survival, Condition and Valve Closure of the Manila Clam, Venerupis philippinarum in a Holding Facility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Acclimation
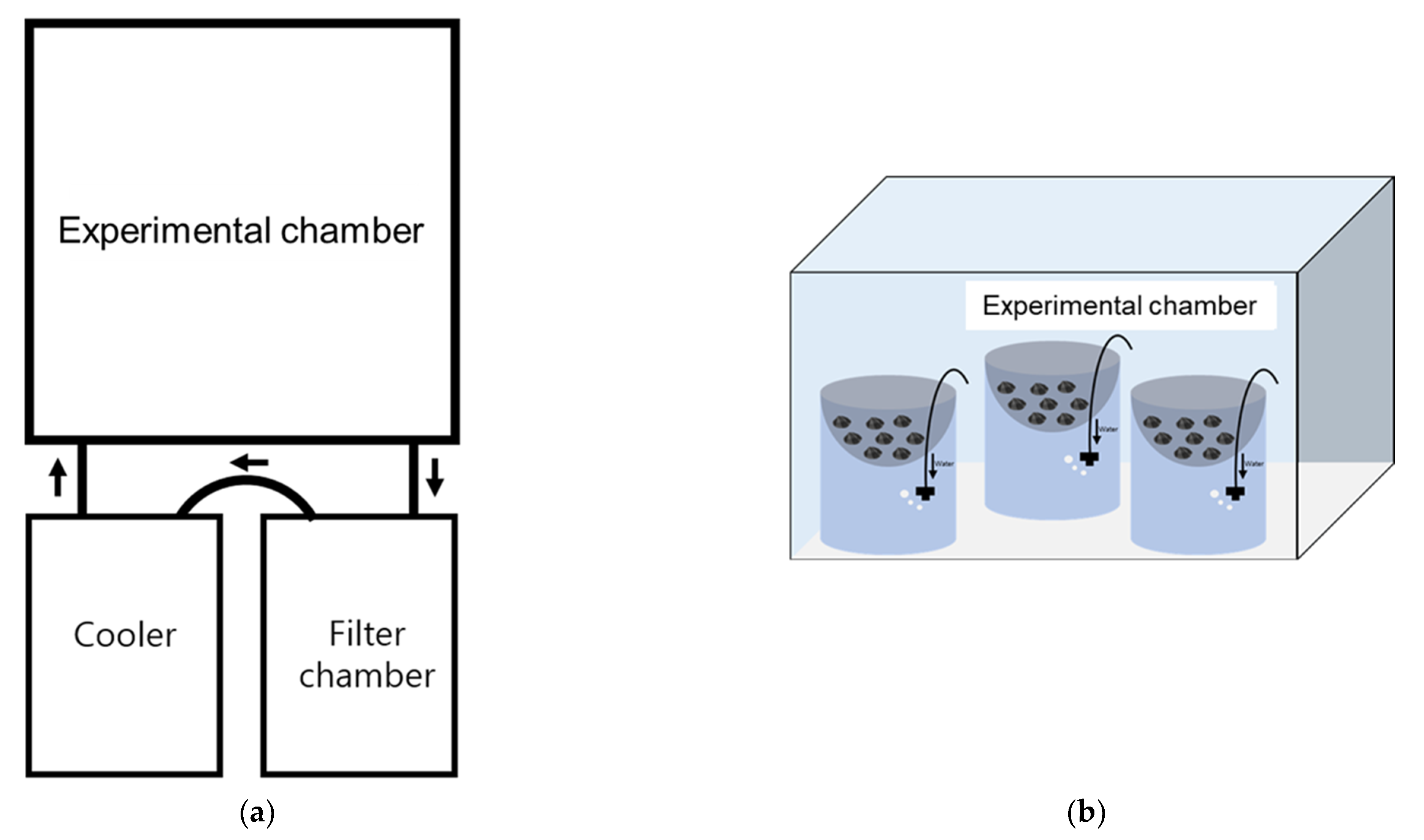
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.2.1. Temperature (Experiment 1)
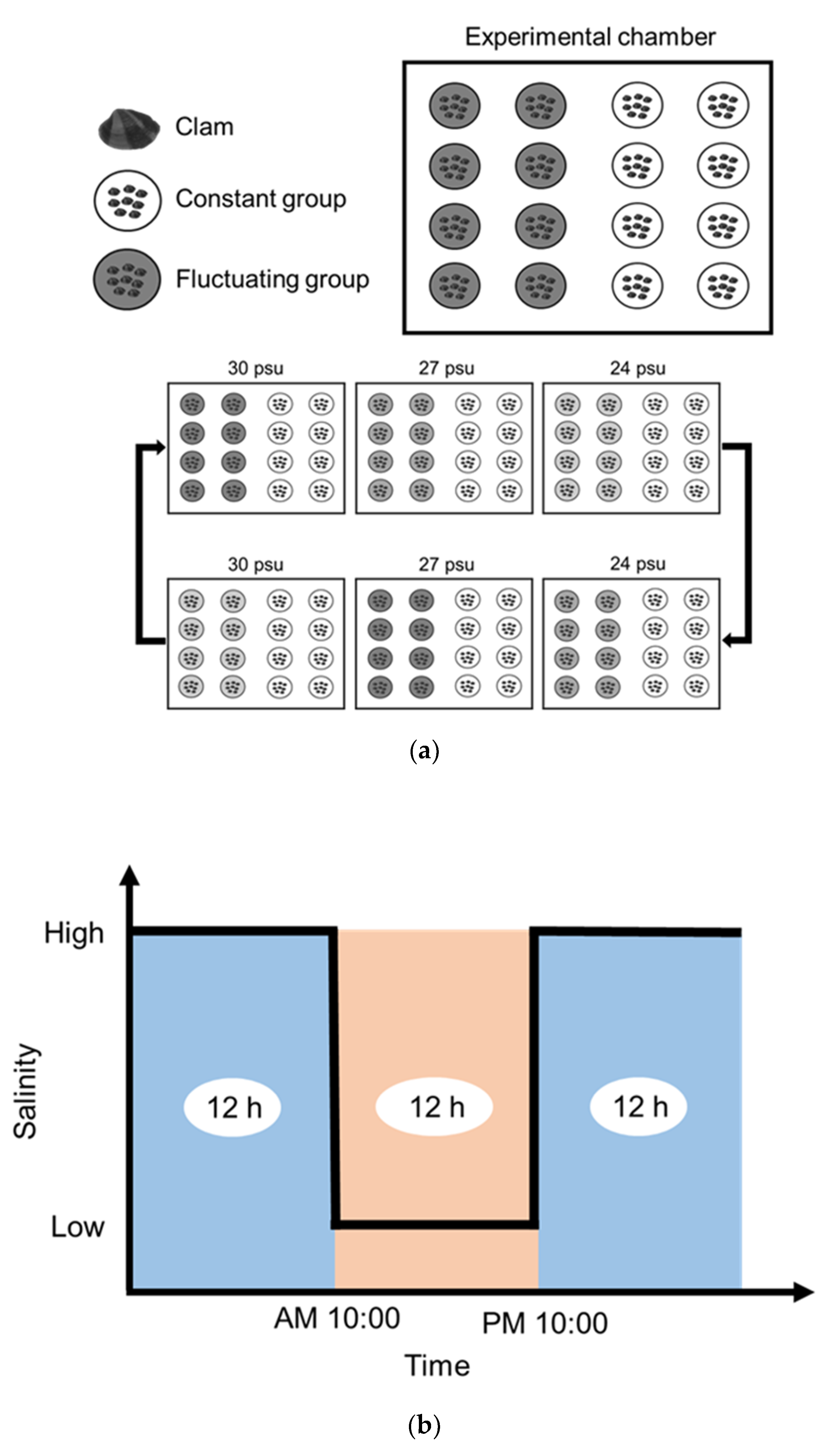
2.2.2. Salinity (Experiment 2)
2.2.3. Temperature and Salinity (Experiment 3)
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Mortality
2.3.2. Condition Index (CI)
2.3.3. Valve Closure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
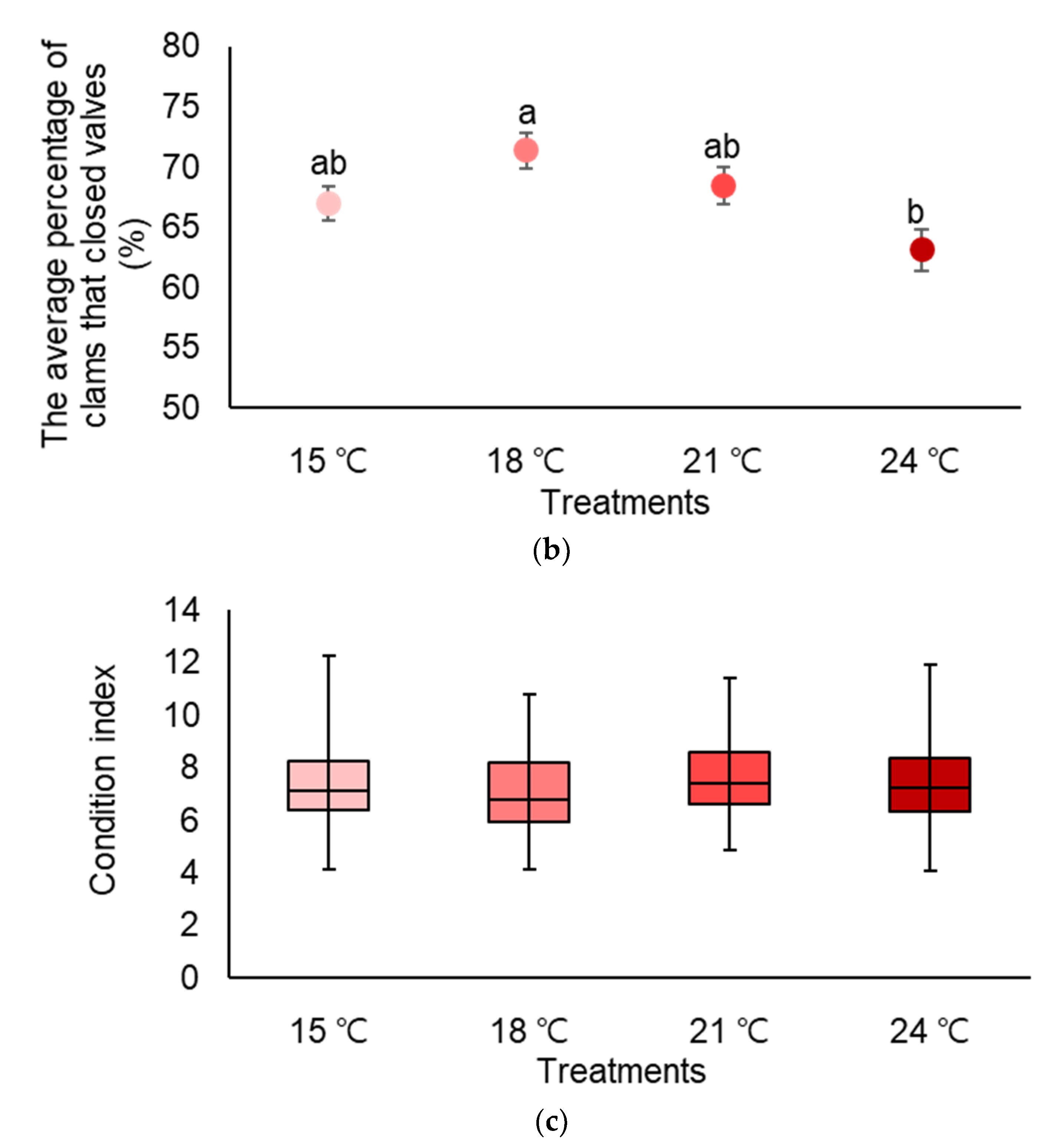
3.1. Temperature (Experiment 1)
3.2. Salinity (Experiment 2)
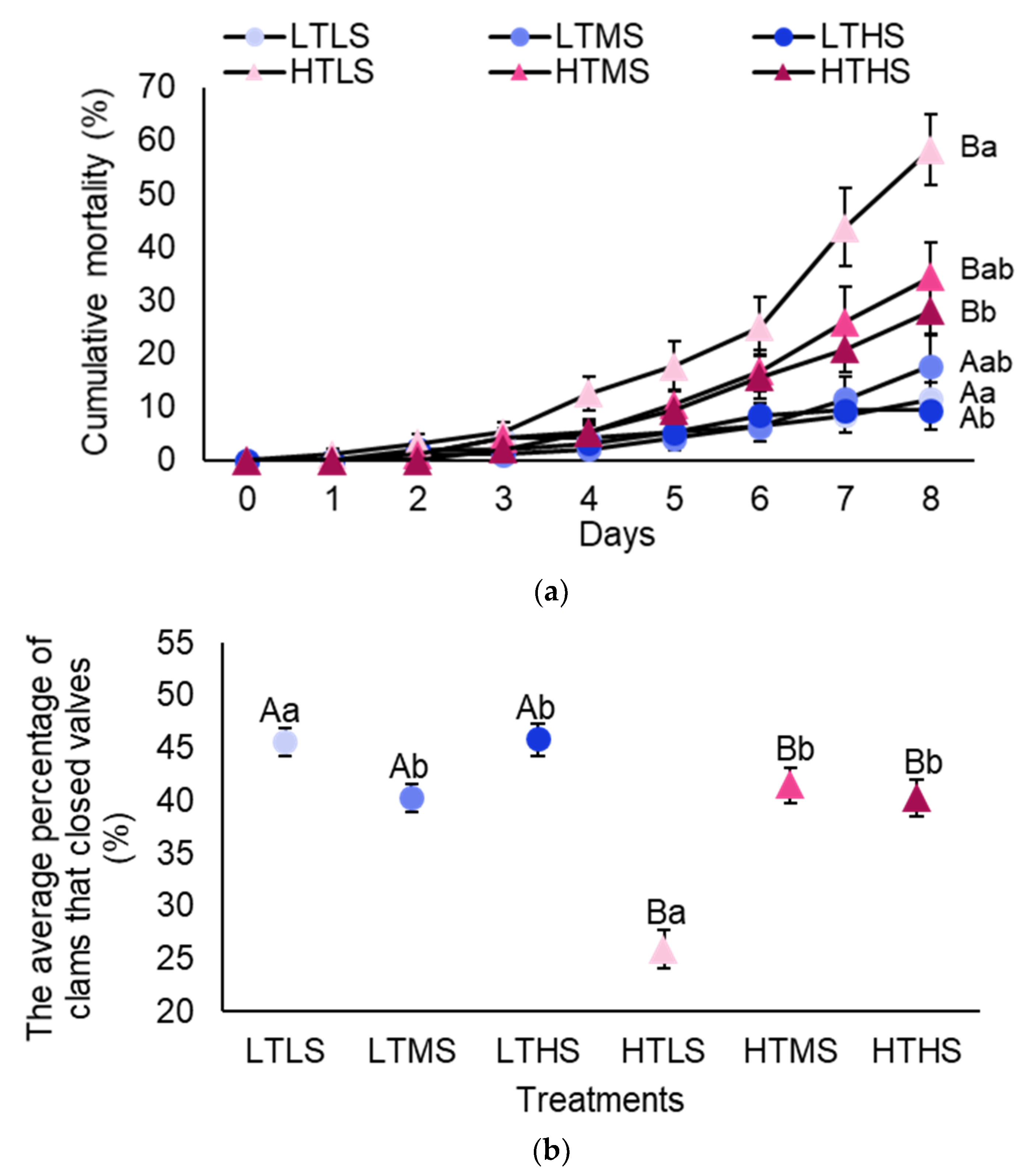
3.3. Temperature and Salinity (Experiment 3)
4. Discussion
4.1. Temperature
4.2. Salinity
4.3. Temperature and Salinity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.; Engelbrecht, F.; et al. Chapter 3: Impacts of 1.5 °C Global Warming on Natural and Human Systems. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C: An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Preindustrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways [...]; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 175–311. [Google Scholar]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups i, ii and iii to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Labat, D.; Goddéris, Y.; Probst, J.L.; Guyot, J.L. Evidence for Global Runoff Increase Related to Climate Warming. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skliris, N.; Marsh, R.; Josey, S.A.; Good, S.A.; Liu, C.; Allan, R.P. Salinity Changes in the World Ocean since 1950 in Relation to Changing Surface Freshwater Fluxes. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 709–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.D.; Ganachaud, A.; Gehrke, P.C.; Griffiths, S.P.; Hobday, A.J.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Johnson, J.E.; Le Borgne, R.; Lehodey, P.; Lough, J.M.; et al. Mixed Responses of Tropical Pacific Fisheries and Aquaculture to Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Fulton, E.A.; Hobday, A.J.; Matear, R.J.; Possingham, H.P.; Bulman, C.; Christensen, V.; Forrest, R.E.; Gehrke, P.C.; Gribble, N.A.; et al. Effects of Climate-Driven Primary Production Change on Marine Food Webs: Implications for Fisheries and Conservation. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1194–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basset, A.; Barbone, E.; Elliott, M.; Li, B.-L.; Jorgensen, S.E.; Lucena-Moya, P.; Pardo, I.; Mouillot, D. A Unifying Approach to Understanding Transitional Waters: Fundamental Properties Emerging from Ecotone Ecosystems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 132, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, R.G.; Pyke, C.R.; Adams, M.B.; Breitburg, D.; Hershner, C.; Kemp, M.; Howarth, R.; Mulholland, M.R.; Paolisso, M.; Secor, D.; et al. Potential Climate-Change Impacts on the Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E. Marine Bivalve Molluscs, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Lee, S.; Wang, S. The Effect of Temperature on the Energy Budget of the Manila Clam, Ruditapes Philippinarum. Aquac. Int. 2008, 16, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Micheli, F. Decreased Solar Radiation and Increased Temperature Combine to Facilitate Fouling by Marine Non-Indigenous Species. Biofouling 2013, 29, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestis, A.; Lazou, A.; Pörtner, H.O.; Michaelidis, B. Behavioral, Metabolic, and Molecular Stress Responses of Marine Bivalve Mytilus Galloprovincialis during Long-Term Acclimation at Increasing Ambient Temperature. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Yoo, C. Change of Foraging and Hiding Behaviors in the Pacific Abalone Haliotis Discus Hannai in Response to Elevated Seawater Temperature. Ocean Sci. J. 2020, 55, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestis, A.; Pörtner, H.O.; Karagiannis, D.; Angelidis, P.; Staikou, A.; Michaelidis, B. Response of Mytilus Galloprovincialis (L.) to Increasing Seawater Temperature and to Marteliosis: Metabolic and Physiological Parameters. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 156, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, E.; Min, W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T. Respiration of the Sea Urchin Mesocentrotus Nudus in Response to Large Temperature Fluctuations. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 144, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Park, S.; Sin, E. At the Tipping Point: Differential Influences of Warming and Deoxygenation on the Survival, Emergence, and Respiration of Cosmopolitan Clams. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4860–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Huh, H.; Huh, S.; Lee, T. Effects of Salinity on Endogenous Rhythm of the Manila Clam, Ruditapes Philippinarum (Bivalvia: Veneridae). Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Im, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, T. Ocean Freshening Adversely Affects the Food Detection Ability of the Gammarid Amphipod Haustorioides Koreanus. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 72, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Ahn, I.; Sin, E.; Shim, J.; Kim, T. Ocean Freshening and Acidification Differentially Influence Mortality and Behavior of the Antarctic Amphipod Gondogeneia Antarctica. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 154, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdelhos, T.; Marques, J.C.; Anastácio, P. Behavioral and Mortality Responses of the Bivalves Scrobicularia Plana and Cerastoderma Edule to Temperature, as Indicator of Climate Change’s Potential Impacts. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, R.M. The Potential Impacts of Low and High Salinities on Salinity Tolerance and Condition Index of the Adult Pearl Oyster Pinctada Imbricata Radiata (Leach, 1814). J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2018, 79, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, E.; Ahn, I.; Park, S.; Kim, T. Effects of Low PH and Low Salinity Induced by Meltwater Inflow on the Behavior and Physical Condition of the Antarctic Limpet, Nacella Concinna. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carregosa, V.; Velez, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Figueira, E.; Freitas, R. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Three Veneridae Clams Exposed to Salinity Changes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 177–178, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Bally, M.; Chevaldonné, P.; Cigliano, M.; Diaz, D.; Harmelin, J.G.; Gambi, M.C.; Kersting, D.K.; et al. Mass Mortality in Northwestern Mediterranean Rocky Benthic Communities: Effects of the 2003 Heat Wave. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Peyre, M.K.; Eberline, B.S.; Soniat, T.M.; La Peyre, J.F. Differences in Extreme Low Salinity Timing and Duration Differentially Affect Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea Virginica) Size Class Growth and Mortality in Breton Sound, LA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 135, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resgalla, C., Jr.; Brasil, E.d.S.; Salomão, L.C. The Effect of Temperature and Salinity on the Physiological Rates of the Mussel Perna Perna (Linnaeus 1758). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.S.; Walters, L.J.; Brodsky, S.A.; Schneider, K.R.; Hoffman, E.A. Synergistic Effects of Salinity and Temperature on the Survival of Two Nonnative Bivalve Molluscs, Perna Viridis (Linnaeus 1758) and Mytella Charruana (d’orbigny 1846). J. Mar. Biol. 2016, 2016, 9261309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.; Barry, J.P.; Micheli, F. The Effects of Intermittent Exposure to Low-PH and Low-Oxygen Conditions on Survival and Growth of Juvenile Red Abalone. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7255–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przeslawski, R.; Byrne, M.; Mellin, C. A Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Multiple Abiotic Stressors on Marine Embryos and Larvae. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 2122–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barange, M.; Bahri, T.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Cochrane, K.L.; Funge Smith, S.; Poulain, F. Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries and Aquaculture: Synthesis of Current Knowledge, Adaptation and Mitigation Options; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 627; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; p. 628. [Google Scholar]
- Doney, S.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Emmett Duffy, J.; Barry, J.P.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Marine Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrento, S.; Lupatsch, I.; Keay, A.; Christophersen, G. Metabolic Rate of Blue Mussels (Mytilus Edulis) under Varying Post-Harvest Holding Conditions. Aquat. Living Resour. 2013, 26, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallardi, D.; Hobbs, K.; Mills, T.; Couturier, C.; Parrish, C.C.; Murray, H.M. Effects of Extended Ambient Live Holding on Cultured Blue Mussels (Mytilus Edulis L.) with Reference to Condition Index, Lipid Profile, Glycogen Content and Organoleptic Testing. Aquaculture 2014, 430, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayücel, S.; Karayücel, İ. The Effect of Environmental Factors, Depth and Position on the Growth and Mortality of Raft-Cultured Blue Mussels (Mytilus Edulis L.). Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, J.; Kenny, S.; Hobbs, K.D.; Mills, T.; Marshall, H.D.; Murray, H.M. The Effect of Extended Wet-Storage on the Condition, Physiology and Stress Response of Cultured Blue Mussels (Mytilus Edulis L. 1758) during Summer and Fall in Northeastern Newfoundland. Aquaculture 2013, 372–375, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, J.; Kenny, S.; Mills, T.; Marshall, D.H.; Murray, H.M. Condition Index and Neutral Red Assay Response of Cultured Mytilus Edulis l. Stored in a Wet Holding Facility during Winter and Spring in Northeastern Newfoundland. Fish. Aquac. J. 2014, 5, 1000091. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Lee, Y.; Choi, K.; Park, H.; Yun, S.; Kang, C. Combined Effects of Temperature and Seston Concentration on the Physiological Energetics of the Manila Clam Ruditapes Philippinarum. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponurovsky, S.K.; Yakovlev, Y.U.M. The Reproductive Biology of the Japanese Littleneck, Tapes Philippinarum (A. Adams and Reeve, 1850) (Bivalvia: Veneridae). J. Shellfish Res. 1992, 11, 265–277. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, R.; Vázquez, E.; Woodin, S.A.; Wethey, D.S.; Peteiro, L.G.; Macho, G.; Olabarria, C. Sublethal Responses of Four Commercially Important Bivalves to Low Salinity. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Jo, K.; Bae, H.; Seo, H.; Kim, T. Optimal Sediment Grain Size and Sorting for Survival and Growth of Juvenile Manila Clams, Venerupis Philippinarum. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, T. Effects of Potential Future CO2 Levels in Seawater on Emerging Behaviour and Respiration of Manila Clams, Venerupis Philippinarum. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walne, P.R. Experiments on the Culture in the Sea of the Butterfish Venerupis Decussata L. Aquaculture 1976, 8, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Chen, P.; Huo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, F.; Yan, X. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on Oxygen Consumption and Ammonia Excretion in Different Colour Strains of the Manila Clam, Ruditapes Philippinarum. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.; Li, Y.; Golam Rbbani, M.; Wu, Q.; Yan, X. Temperature Challenge on Larvae and Juveniles of the Manila Clam Ruditapes Philippinarum. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Olabarria, C.; Woodin, S.A.; Wethey, D.S.; Peteiro, L.G.; Macho, G.; Vázquez, E. Contrasting Responsiveness of Four Ecologically and Economically Important Bivalves to Simulated Heat Waves. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 164, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Martínez, O.; Aldana-Aranda, D.; Quintana, P.; Pichardo, J.L.; Alvarado-Gil, J.J. Photoacoustic Determination of the Thermal Properties of Bivalve Mollusk Shells. Mar. Biol. 2002, 141, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, B.M.; Moroney, G.A.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; O’Brien, N.M.; Davenport, J.; O’Halloran, J. The Effects of Salinity on the Manila Clam (Ruditapes Philippinarum) Using the Neutral Red Retention Assay with Adapted Physiological Saline Solutions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, J.M.; Molares, J.; Otero, X. Multispecies Mortality Patterns of Commercial Bivalves in Relation to Estuarine Salinity Fluctuation. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisman, N.; Istiqomah, N.; Oka, H.; Yoshimatsu, T. Temporal Change of Salinity Stress in Manila Clam Ruditapes Philippinarum: Implication for Biodefense Mechanism in Response to Climate Change. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2017, 10, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, A. Individual and Combined Effects of Salinity and Temperature on Embryos and Larvae of the Coot Clams, Mulinia Lateralis (Say). Biol. Bull. 1969, 137, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, N.M.; Mackenzie, C.L. Physiological responses of marine invertebrates to thermal stress. In Stressors in the Marine Environment; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, Y.; Chung, E.; Hur, S. Temperature and salinity tolerance of the manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 33, 213–218. [Google Scholar]


| Valve Closure | |
|---|---|
| Within-subject effect | |
| Day | F380.987,5.773 = 14.900 |
| p < 0.001 | |
| Day × Temperature | F380.987,5.773 = 5.674 |
| p < 0.001 | |
| Day × Salinity | F380.987,11.545 = 4.542 |
| p < 0.001 | |
| Day × Temperature × Salinity | F380.987,11.545 = 4.932 |
| p < 0.001 | |
| Between-subject effect | |
| Temperature | F66,1 = 28.418 |
| p < 0.001 | |
| Salinity | F66,2 = 8.584 |
| p < 0.001 | |
| Temperature × Salinity | F66,2 = 16.076 |
| p < 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, H.; Im, J.; Joo, S.; Cho, B.; Kim, T. The Effects of Temperature and Salinity Stressors on the Survival, Condition and Valve Closure of the Manila Clam, Venerupis philippinarum in a Holding Facility. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070754
Bae H, Im J, Joo S, Cho B, Kim T. The Effects of Temperature and Salinity Stressors on the Survival, Condition and Valve Closure of the Manila Clam, Venerupis philippinarum in a Holding Facility. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(7):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070754
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Hyeonmi, Jibin Im, Soobin Joo, Boongho Cho, and Taewon Kim. 2021. "The Effects of Temperature and Salinity Stressors on the Survival, Condition and Valve Closure of the Manila Clam, Venerupis philippinarum in a Holding Facility" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 7: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070754
APA StyleBae, H., Im, J., Joo, S., Cho, B., & Kim, T. (2021). The Effects of Temperature and Salinity Stressors on the Survival, Condition and Valve Closure of the Manila Clam, Venerupis philippinarum in a Holding Facility. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(7), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070754







