Religiosity as a Mechanism to Control Delinquent Behaviour of School Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- Shah Alam City Plan
- (b)
- Sociologists views on the resilient connection between religion and violence
- (c)
- The use of religiosity by addiction scientists to control antisocial behaviour
2. Method
2.1. Strategy of the Study
2.2. The Sample
2.3. The Instruments and Techniques Used in This Study
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Analysis of Data
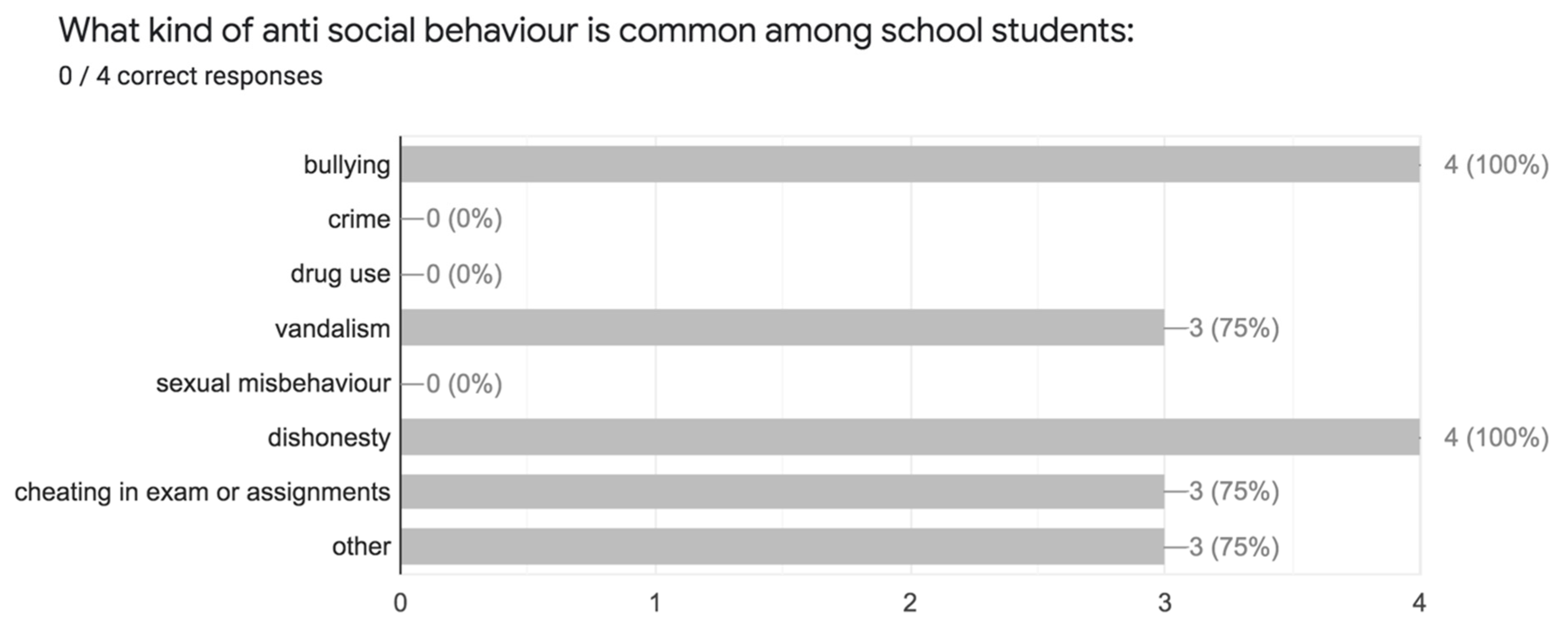
3. Findings
3.1. The Level of Religiosity among Students
- (i).
- The level of religiosity
- (ii).
- Socio-economic reasons and delinquency
3.2. Religiosity Anddelinquency among Students
- (i).
- Aqidah or worldview and delinquency
- (ii).
- Ahlaq or ethics and delinquency
- (iii).
- Ibadat or rituals and delinquency
- (iv).
- Muamalat or social relationship and delinquency
4. Discussion
4.1. The Adolescents’ Delinquency Rate and Socio-Economic Reasons
- (i).
- Gender Differences:
- (ii).
- Parents’ income:
- (iii).
- Parents’ Education Level:
- (iv).
- Parents’ social status:
- (v).
- Urbanisation:
4.2. Religiosity and Adolescents’ Delinquency
- (i).
- Aqidah or worldview and delinquency
- (ii).
- Ahlaq or ethics and delinquency
- (iii).
- Ibadat or rituals and delinquency
- (iv).
- Muamalat or social relationship and delinquency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abou-Youssef, Mariam, Wael Kortam, Ehab Abou-Aish, and Noha El-Bassiouny. 2011. Measuring Islamic-driven buyer behavioral implications: A proposed market-minded religiosity scale. Journal of American Science 7: 728–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Sameera. 2009. Religiosity and presence of character strengths in American Muslim youth. Journal of Muslim Mental Health 4: 104–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisyah, Muniatly. 2016. The Influence of Religious Behavior on Consumers’intention to Purchase Halal-Labeled Products. Business and Entrepreneurial Review 14: 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akiba, Motoko, Gerald K. LeTendre, David P. Baker, and Brian Goesling. 2002. Student victimisation: National and school system effects on school violence in 37 nations. American Educational Research Journal 39: 829–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, Syed Shah, Rohani Mohd, and Badrul Hisham. 2011. Is religiosity an important determinant on Muslim consumer behaviour in Malaysia? Journal of Islamic Marketing 2: 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ammar, Fawziah, Ismaiel Hamid Ahmed, and Mohamad Sahari Nordin. 2012. Moral character of Muslim personality: Scale validation. Journal of Education and Practice 3: 118–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, Abdullah. 2006. Role of Islamic Educational Values in Developing Emotional Intelligence Skills. Master’s thesis, The University of Montana, Missoula, MT, USA. Available online: https://scholarworks.umt.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6015&context=etd (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Ali, Afzaal, Adnan Ali, and Mehkar Sherwani. 2017. Shaping halal into a brand? Factors affecting consumers’ halal brand purchase intention. Journal of International Food & Agribusiness Marketing 29: 234–59. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khalifah, Abdullah H. M. 1994. Religiosity in Islam as a protective mechanism against criminal temptation. American Journal of Islamic Social Sciences 11: 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Fatemeh, Parvaneh Doodman, Ali Edalati, Zhila Abbasi, and Mohd Redzuan. 2014. A study on the relationship between religiosity and forgiveness among students. Applied Science Reports 5: 131–34. [Google Scholar]
- Aute, Dorothy Anyango, Moses Wesang’ula Poipoi, and Okaya Edward Khasakhala. 2020. Family Socioeconomic Status and Deviant Behaviour Among Secondary School Students in Homabay County, Kenya. Science Journal of Education 8: 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbenishty, Rami, and Ron Astor. 2008. School violence in an international context. International Journal 60: 69–79. Available online: http://www.ijvs.org/files/Revue-07/04.-Benbenishty-Ijvs-7.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2021).
- Bernama. 2014. Violent Culture Seeping into Schools. Bernama. Available online: http://www.freemalaysiatoday.com/category/nation/2014/02/24/lee-violent-culture-seeping-into-schools/ (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Berti, Chiara, and Monica Pivetti. 2019. Childhood economic disadvantage and antisocial behavior: Intervening factors and pathways. Children and Youth Services Review 97: 120–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, Walter, Joycem Gall, and Meredith Gall. 1979. Educational Research: An Introduction, 3rd ed. New York: Longman. [Google Scholar]
- Brain. 2013. Malaysia: Among the Most Dangerous Countries in the World? Hornbill Unleashed. Available online: https://hornbillunleashed.wordpress.com/2013/11/24/53436/ (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Browman, Alexander S., Mesmin Destin, Melissa S. Kearney, and Phillip B. Levine. 2019. How economic inequality shapes mobility expectations and behaviour in disadvantaged youth. Nature Human Behaviour 3: 214–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, Noel, Stucky Brian, Sawalani Gita, and Little Todd. 2008. Direct and indirect aggression during childhood and adolescence: A meta-analytic review of gender differences, intercorrelations, and relations to mala adjustment. Child Development 79: 1185–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, Simon. 2004. Learning styles: An overview of theories, models, and measures. Educational Psychology 24: 419–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalfin, Aaron, and Monica Deza. 2019. The intergenerational effects of education on delinquency. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 159: 553–71. [Google Scholar]
- Christians, Clifford G., and James William Carey. 1989. The logic and aims of qualitative research. Research Methods in Mass Communication 2: 354–74. [Google Scholar]
- Christina Low. 2012. Islamic city set to take shape in Shah Alam. The Star. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/news/community/2012/05/14/islamic-city-set-to-take-shape-in-shah-alam (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Cohen, Louis, Lawrence Manion, and Keith Morrison. 2000. Research Methods in Education British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data. Abingdon: The British Library. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, Kathleen. 1989. Neither conflict nor labeling nor paternalism will suffice: Intersections of race, ethnicity, gender, and family in criminal court decisions. Crime & Delinquency 35: 136–68. [Google Scholar]
- Dastagir, Gulam, and Mohammad Ismath Ramzy. 2019. Understanding “The Others”: Buddhist-Islamic Dialogue for Peace with Particular Reference to ‘Moderation’. Al-Shajarah: Journal of the International Institute of Islamic Thought and Civilization (ISTAC) 24: 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, Christiana. 2009. Transcription: Imperatives for qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods 8: 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Statistics Malaysia. 2016. Children Statistic Malaysia 2016; Putrajaya: Department of Statistics Malaysia. Available online: https://www.dosm.gov.my/v1/index.php?r=column/cthemeByCat&cat=333&bul_id=NVYwaEtwM21MempVbWpBZFpxOFZHZz09&menu_id=U3VPMldoYUxzVzFaYmNkWXZteGduZz09 (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Department of Statistics Malaysia. 2019. Press Release Children Statistics Malaysia 2019; Putrajaya: Department of Statistics Malaysia. Available online: https://www.dosm.gov.my/v1/index.php?r=column/pdfPrev&id=c3I4eitkb1RZTlMvUjNLZVRBMExVQT09 (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Education Destination Malaysia. 2019. What you need to know about bullying in school. Education Destination Malaysia Blog. Available online: https://educationdestinationmalaysia.com/blogs/what-you-need-to-know-about-bullying-in-schools (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- El-Menouar, Yasemin. 2014. The five dimensions of Muslim religiosity. Results of an empirical study. Methods, Data, Analyses 8: 53–78. [Google Scholar]
- El Sen, Teoh. 2014. Students Involved in Violent Crime and Gangsterism on the Rise. Astro Awani. Available online: http://english.astroawani.com/malaysia-news/students-involved-violent-crime-and-gangsterism-rise-32766 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Epic Teachers. 2013. What is Merit-demerit system. Epic Teachers Blog. Available online: http://epicteachers.blogspot.com/2013/03/what-is-merit-demerit-system.html (accessed on 24 August 2021).
- Ferdoos, Ahmad, and Ahmad Ashiq. 2015. Impact of urbanisation on juvenile delinquency: A study of Muzaffarabad jail. International Journal of Criminology and Sociological Theory 8: 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, Murray, and Andrea Marshall. 2009. Understanding descriptive statistics. Australian Critical Care 22: 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraenkel, Jack, Wallen Norman, and Hyun Helen. 2012. How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education. Johnproyer.com. Available online: http://www.johnlpryor.com/JP_Digital_Portfolio/EDU_7901_files/EDU%207901%20Data%20Definitions.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Gibbs, Graham R. 2007. Thematic coding and categorising. Analysing Qualitative Data 703: 38–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gorsuch, Richard. 1983. Factor Analysis. Hillsdale: John Wiley & Sons Inc., vol. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Güneş, Tacettin. 2003. The Relationship between Religiosity and Crime: A Case Study on University Students in Turkey. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Middle Eastern Technical University, Ankara, Turkey; p. 43. Available online: https://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/418368/index.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Hair, Joe F., Page Michaeal, and Niek Brunsveld. 2019. Essentials of Business Research Methods. Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, Hanafi Hadi, and Shariff Nadiah Syariani Md. 2020. Fear of crime: Crime perception and coping strategy in Shah Alam. International Journal of Medical Toxicology and Legal Medicine 23: 120–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, H., M. Sadek, and Mohd Wan. 2018. The spatial distribution of “hotspot schools” and the relationship with crime pattern in Mukim Petaling and Klang. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. Bristol: IOP Publishing, vol. 169, p. 012109. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, Veronica, and Laura Ann McCloskey. 2001. Gender differences in the risk for delinquency among youth exposed to family violence. Child Abuse & Neglect 25: 1037–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstaedter, Graham. 2011. Modern Muslim Identities: Negotiating Religion and Ethnicity in Malaysia. Copenhagen: NIAS Press. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, Nik Ahmad Hisham, and Mustafa Tekke. 2015. Development and initial validation of integrative Islamic personality inventory. Advances in Environmental Biology 9: 163–71. [Google Scholar]
- Isralowitz, Richard, and Alexander Reznik. 2015. Impact of religious education and religiosity on adolescent alcohol use and risk-taking behavior. Religious Education 110: 303–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, Anja M., Ellen Giebels, Thomas J. L. van Rompay, and Marianne Junger. 2018. The influence of the presentation of camera surveillance on cheating and pro-social behavior. Frontiers in Psychology 9: 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, Muhammad Iqmal Hisham, and Sofiah MdAuzair. 2019. Integrated Islamic financial accountability model for Islamic social enterprise (ISE). The Journal of Muamalat and Islamic Finance Research 16: 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Jinho. 2021. Gender differences in the educational penalty of delinquent behavior: Evidence from an analysis of siblings. Journal of Quantitative Criminology 37: 179–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, Steven Eric, Azimi Hamzah, and Fazila Idris. 2007. Adaptation of a Muslim religiosity scale for use with four different faith communities in Malaysia. Review of Religious Research 49: 147–64. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, Steven, Al Haj Hamzah, Turiman Suandi, Sidek Mohd Noah, Khairul Anwar Mastor, Rumaya Juhari, and Manap. 2005. The Muslim religiosity-personality measurement inventory (MRPI)’s religiosity measurement model: Towards filling the gaps in religiosity research on Muslims. Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities 13: 131–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kunin, Seth. 2003. Religion: The Modern Theories. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis US. [Google Scholar]
- Malaysian Education Blueprint. 2015. Blueprint 2015–2025 (Higher Education); Putrajaya: Ministry of Education. Available online: https://www.um.edu.my/docs/um-magazine/4-executive-summary-pppm-2015-2025.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- McDermott, Robert J., and Paul Sarvela. 1999. Methods and strategies for sampling. In Health Education Evaluation and Measurement: A Practitioner’s Perspective. Dubuque: William C Brown Pub, pp. 264–89. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, Douglas. 2002. Behavior, belonging, and belief: A theory of ritual practice. Sociological Theory 20: 360–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, Clark. 1994. Phenomenological Research Methods. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt, Terrei, Avshalom Caspi, Micheal Rutter, and Silva Phil. 2001. Sex Differences in Antisocial Behaviour: Conduct Disorder, Delinquency and Violence in the Dunedin Longitudinal Study. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Abul Qassim. 1983. The Ethics of Al-Ghazali: A Composite Ethics in Islam. Selangor: National University of Malaysia. [Google Scholar]
- Nabilah, Hamudin. 2015. Shah Alam crime index shows drop in first four months of 2015. The Sun Daily. Available online: http://www.thesundaily.my/news/1416772 (accessed on 4 April 2021).
- Neto, Fellix. 2007. Forgiveness, personality and gratitude. Personality and Individual Differences 43: 2313–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberg, Andrew. 2016. How God changes your brain: An introduction to Jewish neurotheology. CCAR Journal: The Reform Jewish Quarterly, Winter 19: 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Newberg, Andrew, and Mark Robbert Waldman. 2013. Words Can Change Your Brain: 12 Conversation Strategies to Build Trust, Resolve Conflict, and Increase Intimacy. London: Penguin Books Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Newberg, Andrew B., Nancy A. Wintering, David B. Yaden, Mark Robbert, Waldman, Janet Reddin, and Abass Alavi. 2015. A case series study of the neurophysiological effects of altered states of mind during intense Islamic prayer. Journal of Physiology-Paris 109: 214–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Strait Time. 2019. School Bully: Home Remedy. New Straits Times. Available online: Https://Www.Nst.Com.My/Opinion/Leaders/2019/01/450202/School-Bully-Home-Remedy (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Nunnally, Jum. 1978. Psychometric Theory. New York: McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Nye, Ivan, Short James, and Olson Virgil. 1958. Socio-economic status and delinquent behavior. American Journal of Sociology 63: 381–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshako, Toshio. 1997. Tackling school violence worldwide: A comparative perspective of basic issues and challenges. In Violence at School: Global Isues and Inerventions. Paris: UNESCO/IBE. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, Nooraini. 2011. Exploring the ummatic personality dimensions from the psycho-spiritual paradigm. International Journal of Psychological Studies 3: 37–42. Available online: www.ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/ijps/article/view/13335/9202 (accessed on 21 April 2021).
- Patton, Michael Quinn. 1999. Enhancing the quality and credibility of qualitative analysis. Health Services Research 34, Pt 2: 1189. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, Reed, Bergin Allen, Bielema Kimberly, and Jenkins Paul. 1991. Review of religion and mental health: Prevention and the enhancement of psychosocial functioning. Prevention in Human Services 9: 11–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, John. 2015. Youth Crime and Youth Justice. Youth & Policy 114: 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzy, Mohammad Ismath, Azni Yati, and Faisal Mohammd. 2020. Universal Aspects of Islamic Religious Ethics and Muslim Extremism. Journal of Dharma 45: 437–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzy, Mohammad Ismath. 2015. Training in Islamic Rituals: A Solution to Muslim Extremism. KATHA-The Official Journal of the Centre for Civilisational Dialogue 11: 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, Mohd Fadzil Abdul, and Ishak Ab Ghani. 2011. The Importance of Internal Migration in Urban Planning Process: The Case Study of Klang Valley Region. International Journal of Social Planning and Development 1: 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidiyaan, Somaye, Amrollah Amini, Mohammad Mehdi Mojahedi, and Ali Safdari. 2018. Modelling an Interest Free Economy Through Overlapping Generation Model (OLG). Journal of Economics and Modeling 9: 91–129. [Google Scholar]
- Roid, Gale, and Thomas Haladyna. 1982. A Technology for Test-Item Writing. Cambridge: Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, James, and Graldine Pratt. 1980. A description of the affective quality attributed to environments. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 38: 311–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, Zila van der Meer, and Solange Aparecida Nappo. 2008. Religious intervention and recovery from drug addiction. Revista de Saude Publica 42: 265–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhana, Dass, and Ananthan Rueben. 2019. Crime Trends and Patterns in Malaysia. Kyoto Review of Southeast Asia. Available online: https://kyotoreview.org/trendsetters/crime-trends-and-patterns-in-malaysia/ (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Small, Mario Luis. 2011. How to conduct a mixed-methods study: Recent trends in a rapidly growing literature. Annual Review of Sociology 37: 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, Mazlan, and Bin Che. 2012. Crime and urbanisation: Revisited Malaysian case. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 42: 291–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenberg, Bettina. 2014. Social Integration and Social Involvement from a Societal and Individual Perspective. In Dependencies and Mechanisms of Unemployment and Social Involvement. Wiesbaden: Springer VS, pp. 25–58. [Google Scholar]
- Suhail, Kuasar, and Haroon Rashid Chaudhry. 2004. Predictors of subjective wellbeing in an Eastern Muslim culture. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology 23: 359–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synder, James, and Gerald Patterson. 1987. Family interaction and delinquent behaviour. In Handbook of Juvenile Delinquency. Nueva York: Wiley, pp. 216–43. [Google Scholar]
- The Star. 2014. Tackling school violence. The Star Online. Available online: http://www.thestar.com.my/opinion/letters/2014/08/11/tackling-school-violence/ (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- The Department of Statistics. 2016. Press Release: Children Statistics, Malaysia 2016; Putrajaya: The Office of Chief Statistician Malaysia, Department of Statistics. Available online: https://www.dosm.gov.my/v1/index.php?r=column/pdfPrev&id=NVYwaEtwM21MempVbWpBZFpxOFZHZz09 (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Tiliouine, Habib, Cummins, and Melanie Davern. 2009. Islamic religiosity, subjective wellbeing, and health. Mental Health, Religion & Culture 12: 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Uba, Ikechukwu, Siti Nor Yaacob, Mansor Abu Talib, Rohani Abdullah, and Sakineh Mofrad. 2014. Association among peer substance use, religiosity and substance abuse in high school students. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences 11: 1–6. Available online: http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/36575/1/Association%20among%20peer%20substance%20use.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- UNESCO. 2019. Behind the Numbers: Ending School Violence and Bullying. Paris: UNESCO. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/media/66496/file/Behind-the-Numbers.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2021).
- UNICEF. 2013. The Malaysian Juvenile Justice System: A Study of Mechanisms for Handling Children in Conflict with the Law; Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development and UNICEF Malaysia. Available online: http://www.iccwtnispcanarc.org/upload/pdf/1672867150Malaysian%20Juvenile%20Justice%20System.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Usman, Hardius. 2015. Islamic religiosity scale, and its applied on the relationship between religiosity and selection of Islamic bank. East Asian Journal of Business Economics (EAJBE) 3: 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Vaismoradi, Mojtaba, and Sherrill Snelgrove. 2019. Theme in qualitative content analysis and thematic analysis. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research 20: 1–14. Available online: https://www.qualitative-research.net/index.php/fqs/article/view/3376/4471 (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Vierra, Andrea, and Judith Pollock. 1992. Reading Education Research. Scottsdale: Gorsuch Sewishirch. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, Azna Abdul, Siti Rasidah Md Sakip, and Halmi Zainol. 2018. An assessment of CPTED principles in relation to bullying behaviour. Advances in Applied Sociology 8: 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weber, Max, and Stephen Kalberg. 2013. The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism. Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge. Available online: https://scholar.princeton.edu/sites/default/files/tpavone/files/weberthe_protestant_ethic_and_the_spirit_of_capitalism_summary.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2021).
- WHO. 2020. Youth Violence. WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/youth-violence (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Wiersma, William, and Stephen Jurs. 2000. Research Methods in Education: An Introduction. Boston: Allyn. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, Kevin, and Karen Wright. 1992. Family Life and Delinquency and Crime: A Policy-Makers Guide to the Literature; Unpublished manuscript. Washington: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention. Available online: https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/Digitization/140517NCJRS.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Zhang, Xianquan. 2016. The trends, promises and challenges of urbanisation in the world. Habitat International 54: 241–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Designation | ID | Experience in Years | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Discipline teacher | DT1 | 15 | Male |
| 2 | Discipline teacher | DT2 | 10 | Male |
| 3 | Discipline teacher | DT3 | 03 | Male |
| 4 | Student counsellor | SC1 | 10 | Female |
| Interval Mean | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 1.00–2.33 | Low |
| 2.34–3.67 | Moderate |
| 3.68–5.00 | High |
| Dimension | Mean | SD | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aqidah (worldview) | 3.51 | 1.4 | Moderate |
| Ahlaq (ethics and morals) | 3.45 | 1.3 | Moderate |
| Ibadat (rituals) | 3.41 | 1.2 | Moderate |
| Muammar (social relationship) | 3.52 | 1.2 | Moderate |
| Overall | 3.47 | 1.3 | Moderate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramzy, M.I.; Irfan, P.M.M.; Hussin, Z. Religiosity as a Mechanism to Control Delinquent Behaviour of School Students. Religions 2021, 12, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel12100823
Ramzy MI, Irfan PMM, Hussin Z. Religiosity as a Mechanism to Control Delinquent Behaviour of School Students. Religions. 2021; 12(10):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel12100823
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamzy, Mohammad Ismath, Peer Mohamed Mohamed Irfan, and Zaharah Hussin. 2021. "Religiosity as a Mechanism to Control Delinquent Behaviour of School Students" Religions 12, no. 10: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel12100823
APA StyleRamzy, M. I., Irfan, P. M. M., & Hussin, Z. (2021). Religiosity as a Mechanism to Control Delinquent Behaviour of School Students. Religions, 12(10), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel12100823






