Which Are the Most Influential Cited References in Information?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
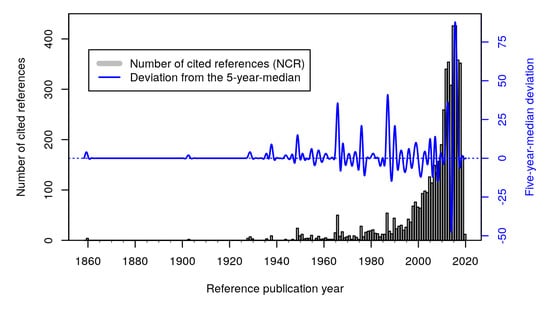
3.1. RPYS Analysis for the Time Frame 1858–1990
3.2. RPYS Analysis for the Time Frame 1990–2019
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brief Introdction about Journal Information. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/information/about (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- Bornmann, L.; Marx, W. The proposal of a broadening of perspective in evaluative bibliometrics by complementing the times cited with a cited reference analysis. J. Informetr. 2013, 7, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A.; Marx, W.; Bornmann, L.; Mutz, R. On the origins and the historical roots of the Higgs boson research from a bibliometric perspective. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marx, W.; Haunschild, R.; Thor, A.; Bornmann, L. Which early works are cited most frequently in climate change research literature? A bibliometric approach based on Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy. Scientometrics 2017, 110, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Wong, N.S.M.; Leung, Y.Y. Are coronectomy studies being cited? A bibliometric study. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, e12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K. Identification of seminal works that built the foundation for functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of taste and food. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Li, X.; Luo, F.; Yang, L.P.; Liu, C.J.; Sun, J. The historical roots and seminal research on health equity: A referenced publication year spectroscopy (RPYS) analysis. Int. J. Equity Health 2019, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haunschild, R.; Barth, A.; Marx, W. Evolution of DFT studies in view of a scientometric perspective. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haunschild, R.; Barth, A.; French, B. A comprehensive analysis of the history of DFT based on the bibliometric method RPYS. J. Cheminform. 2019, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haunschild, R.; Marx, W. Discovering Seminal Works with Marker Papers. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Bibliometric-Enhanced Information Retrieval, Cologne, Germany, 14 April 2019; pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ballandonne, M. The historical roots (1880–1950) of recent contributions (2000–2017) to ecological economics: Insights from reference publication year spectroscopy. J. Econ. Methodol. 2019, 26, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunschild, R.; Bauer, J.; Bornmann, L. Influential cited references in FEMS Microbiology Letters: Lessons from Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy (RPYS). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bornmann, L.; Haunschild, R.; Leydesdorff, L. Reference publication year spectroscopy (RPYS) of Eugene Garfield’s publications. Scientometrics 2018, 114, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thor, A.; Bornmann, L.; Marx, W.; Mutz, R. Identifying single influential publications in a research field: New analysis opportunities of the CRExplorer. Scientometrics 2018, 116, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thor, A.; Marx, W.; Leydesdorff, L.; Bornmann, L. Introducing CitedReferencesExplorer (CRExplorer): A program for Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy with Cited References Standardization. J. Informetr. 2016, 10, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thor, A.; Marx, W.; Leydesdorff, L.; Bornmann, L. New features of CitedReferencesExplorer (CRExplorer). Scientometrics 2016, 109, 2049–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marx, W.; Haunschild, R.; Bornmann, L. Climate change and viticulture—A quantitative analysis of a highly dynamic research field. Vitis 2017, 56, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CR Number | RPY | Cited Reference | NCRs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR1 | 1859 | Darwin, C., 1859, On the Origin of Species | 4 |
| CR2 | 1902 | Muirhead, R.F., 1902, Proc. Edinburgh Math. Soc., V21, P144, DOI: 10.1017/S001309150003460X | 2 |
| CR3 | 1928 | Hartley, R.V.L., 1928, Bell Syst. Tech. J., V7, P535, DOI: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1928.tb01236.x | 4 |
| CR4 | 1928 | Bohr, N., 1928, Nature, V121, P580 | 3 |
| CR5 | 1935 | Einstein, A., 1935, Phys. Rev., V47, P0777, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRev.47.777 | 3 |
| CR6 | 1937 | Turing, A.M., 1937, Proc. London Math. Soc., V42, P230 | 5 |
| CR7 | 1943 | McCulloch, W.S., 1943, Bull. Math. Biophys., V5, P115, DOI: 10.1007/BF02478259 | 2 |
| CR8 | 1946 | Ryle, G., 1946, Symposium: Why are the calculuses of logic and arithmetic applicable to reality? In Proceedings of the Logic and Reality, Symposia Read at the Joint Session of the Aristotelian Society and the Mind Association, Manchester, P20 | 2 |
| CR9 | 1948 | Shannon, C.E., 1948, Bell Syst. Tech. J., V27, P623, DOI: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x | 16 |
| CR10 | 1950 | Turing, A.M., 1950, Mind, V49, P433, DOI 10.1093/MIND/LIX.236.433 | 6 |
| CR11 | 1957 | Everett, H., 1957, Rev. Mod. Phys., V29, P454 | 4 |
| CR12 | 1959 | Popper, K.R., 1959, The Logic of Scientific Discovery | 3 |
| CR13 | 1960 | Cohen, J., 1960, Educ. Psychol. Measurement, V20, P37, DOI: 10.1177/001316446002000104 | 3 |
| CR14 | 1965 | Zadeh L.A., 1965, Information and Control, V8, P338, DOI: 10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X | 38 |
| CR15 | 1967 | MacQueen, J., 1967, Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, P281 | 6 |
| CR16 | 1970 | Kuhn, T.S., 1970, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions | 4 |
| CR17 | 1970 | Bellman, R.E., 1970, Management Science, V17, P141, DOI: 10.1287/MNSC.17.4.B141 | 3 |
| CR18 | 1972 | Anderson, P.W., 1972, Science, V177, P393, DOI: 10.1126/science.177.4047.393 | 3 |
| CR19 | 1975 | Zadeh, L.A., 1975, Information Sciences, V8, P199, DOI: 10.1016/0020-0255(75)90036-5 | 14 |
| CR20 | 1980 | Saaty, T., 1980, The Analytic Hierarchy Process | 7 |
| CR21 | 1980 | Porter, M.F., 1980, Program: Electr. Lib. Inform. Sys., V14, P130, DOI: 10.1108/eb046814 | 5 |
| CR22 | 1986 | Atanassov, K.T., 1986, Fuzzy Sets Syst., V20, P87, DOI: 10.1016/S0165-0114(86)80034-3 | 32 |
| CR23 | 1989 | Atanassov, K.T., 1989, Fuzzy Sets Syst., V31, P343, DOI: 10.1016/0165-0114(89)90205-4 | 13 |
| CR Number | RPY | Cited Reference | NCRs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR24 | 1994 | Bengio, Y., 1994, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks, V5, P157, DOI: 10.1109/72.279181 | 6 |
| CR25 | 1995 | Kennedy, J., 1995, IEEE ICNN, VOL 4, P1942, DOI: 10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968 | 8 |
| CR26 | 1995 | Cortes C., 1995, Machine Learning, V20, P273, DOI: 10.1007/BF00994018 | 6 |
| CR27 | 1996 | Herrera F., 1996, Fuzzy Sets Systems, V78, P73, DOI: 10.1016/0165-0114(95)00107-7 | 7 |
| CR28 | 1997 | Hochreiter S., 1997, Neural Comput., V9, P1735, DOI: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 | 19 |
| CR29 | 1998 | Smarandache F., 1998, Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic | 12 |
| CR30 | 1999 | Smarandache F., 1999, A Unifying Field in Logics: Neutrosophy Logic | 14 |
| CR31 | 2001 | Breiman L., 2001, Machine Learning, V45, P5, DOI: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 | 16 |
| CR32 | 2001 | Lafferty J., 2001, Proc. 18th Int. Conf. Mach. Learn., P282 | 9 |
| CR33 | 2003 | Blei D.M., 2003, J Mach. Learn. Res., V3, P993 | 9 |
| CR34 | 2004 | Lowe D.G., 2004, Int. J. Comput. Vision, V60, P91, DOI: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 | 9 |
| CR35 | 2004 | Wang Z., 2004, IEEE Trans. Image Proc, V13, P600, DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 | 8 |
| CR36 | 2004 | Xu Z.S., 2004, Information Sciences, V168, P171, DOI: 10.1016/j.ins.2004.02.003 | 8 |
| CR37 | 2005 | Wang H., 2005, Interval neutrosophic sets and logic: Theory and applications in computing | 11 |
| CR38 | 2006 | Demšar J., 2006, J. Mach. Learn. Res., V7, P1 | 7 |
| CR39 | 2006 | Bishop C., 2006, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning | 6 |
| CR40 | 2010 | Wang H., 2010, Multispace Multistructure, V4, P410 | 18 |
| CR41 | 2011 | Collobert R., 2011, J. Mach. Learn. Res., V12, P2493 | 11 |
| CR42 | 2012 | Logan R., 2012, Information, V3, P68, DOI: 10.3390/info3010068 | 9 |
| CR43 | 2013 | Mikolov T., 2013, Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, P3111 | 20 |
| CR44 | 2013 | Ye J., 2013, Int. J. Gen. Syst., V42, P386, DOI: 10.1080/03081079.2012.761609 | 12 |
| CR45 | 2014 | Pennington J., 2014, Proc. Conf. Emp. Meth. Nat. Lang. Proc. (EMNLP), P1532, DOI: 10.3115/V1/D14-1162 | 11 |
| CR46 | 2014 | Ye J., 2014, J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst., V26, P2459, DOI: 10.3233/IFS-130916 | 11 |
| CR47 | 2015 | LeCun Y., 2015, Nature, V521, P436, DOI: 10.1038/nature14539 | 10 |
| CR48 | 2017 | Krizhevsky A., 2017, Commun. ACM, V60, P84, DOI: 10.1145/3065386 | 10 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haunschild, R. Which Are the Most Influential Cited References in Information? Information 2019, 10, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120395
Haunschild R. Which Are the Most Influential Cited References in Information? Information. 2019; 10(12):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120395
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaunschild, Robin. 2019. "Which Are the Most Influential Cited References in Information?" Information 10, no. 12: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120395
APA StyleHaunschild, R. (2019). Which Are the Most Influential Cited References in Information? Information, 10(12), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120395