Comparison of the Results of a Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Logit Model in Assessing Business Financial Health †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Material and Methods
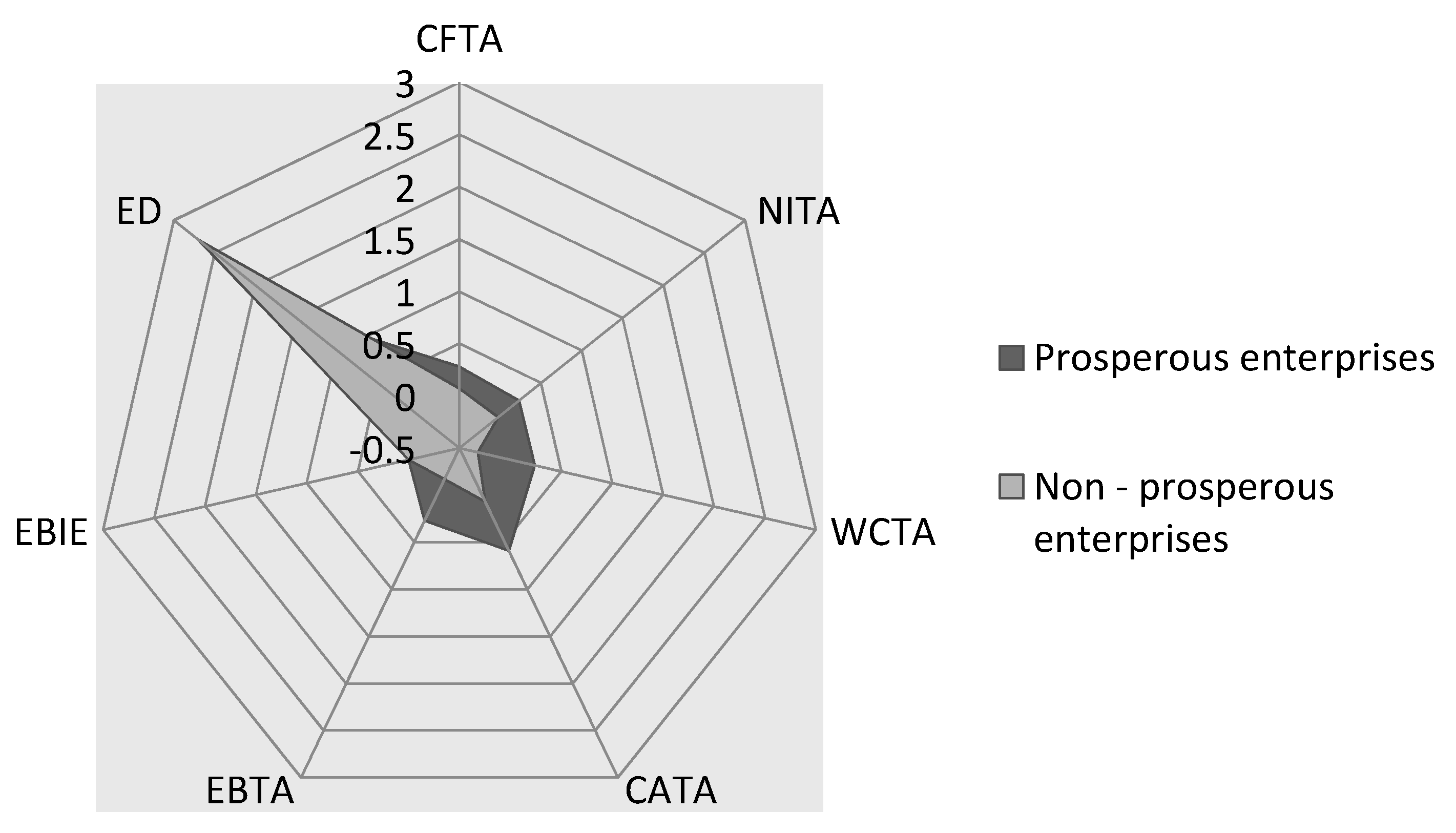
4. Results
Managerial Implications
- ▪
- is significant for managing its efficiency as a part of operational management;
- ▪
- is an important part of its strategic management and a prerequisite for future growth, prosperity, and competitiveness;
- ▪
- identifies key efficiency indicators;
- ▪
- allows the use of multiple inputs and outputs;
- ▪
- is characterized by good data availability;
- ▪
- creates a benchmarking tool for comparing businesses and entire networks;
- ▪
- allows businesses to be ranked;
- ▪
- provides peer units and goal values;
- ▪
- allows lessons to be learned from successful businesses;
- ▪
- is easily applicable in practice.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denis, D.; Denis, D. Causes of Financial Distress Following Leveraged Recapitalizations. J. Financ. Econ. 1995, 37, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, H.; Platt, M. Predicting Corporate Financial Distress: Reflection on Choice—Based Sample Bias. J. Econ. Financ. 2002, 26, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcaen, S.; Ooghe, H. 35 Years of Studies on Business Failure: An Overview of the Classic Statistical Methodologies and Their Related Problems. Br. Account. Rev. 2006, 38, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldson, M. The Turnaround Prescription: Repositioning Troubled Companies; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Michalková, L.; Valašková, K.; Frajtová Michalíková, K.; Drugau, A.C. The Holistic View of the Symptoms of Financial Health of Businesses. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Economic and Business Management (FEBM 2018), Honhot, China, 20–22 October 2018; Skitmore, M., Huang, X., Eds.; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, R.; Bose, I.; Chen, X. Prediction of financial distress: An empirical study of listed Chinese companies using data mining. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 241, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.S.; Song, X.P.; Zen, Y.M. Forecasting Financial Condition of Chinese Listed Companies Based on Support Vector Machine. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klieštik, T. Predikcia Finančného Zdravia Podnikov Tranzitívnych Ekonomík; EDIS: Žilina, Slovakia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dambolena, I.G.; Khoury, S.J. Ratio Stability and Corporate Failure. J. Financ. 1980, 35, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombola, M.B.; Ketz, J.E. A note on cash flow and classification patterns of financial ratios. Account. Rev. 1983, 3, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, H.; Han, I.; Lee, H. Bankruptcy prediction using case-based reasoning, neural networks and discriminant analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 1997, 13, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. The probability of bankruptcy. A comparison of empirical predictions and theoretical models. J. Bank. Financ. 1981, 5, 317–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.M.; Tam, K.Y. A comparative analysis of inductive learning algorithms. Intell. Syst. Account. Financ. Manag. 1993, 2, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Han, I. Integration of cased-based forecasting, neural network and discriminant analysis for bancruptcy prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 1996, 11, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bešlić, D.; Jakšić, D.; Bešlić, I.; Andrić, M. Insolvency prediction model of the company: The case of the Republic of Serbia. Econ. Res. -Ekon. Istraživanja 2018, 31, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, M.A.; Dar, H.A. Predicting corporate bankruptcy: Where we stand? Corp. Gov. 2006, 6, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araghi, K.; Makvandi, S. Evaluating Predictive power of Data Envelopment Analysis Technique Compared with logit and probit Models in Predicting Corporate Bankruptcy. Aust. J. Bus. Manag. Res. 2012, 2, pp. 38–46. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/8f45/3a426e86abf328e836bfbc9216eff2dac75d.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Sun, J.; Li, H.; Huang, Q.H.; He, K.Y. Predicting Financial Distress and Corporate Failure: A Review from the State-of-the-art Definitions, Modeling, Sampling, and Featuring Approaches. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 57, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalovič, M. Využitie skóringových modelov pri predikcii úpadku ekonomických subjektov v Slovenskej republike. Politická Ekon. 2018, 66, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaver, W.H. Financial ratios as predictors of failure. J. Account. Res. 1966, 4, 71–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarlija, N.; Jeger, M. Comparing financial distress prediction models before and during recession. Croat. Oper. Res. Rev. 2011, 2, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kidane, H.W. Predicting Financial Distress in IT and Services Companies in South Africa. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Economics and Management Sciences, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2004. Available online: http://scholar.ufs.ac.za:8080/xmlui/handle/11660/1117 (accessed on 18 June 2018).
- Spuchľáková, E.; Frajtová Michalíková, K. Comparison of LOGIT, PROBIT and neural network bankruptcy prediction models. In Proceedings of the 2016 ISSGBM International Conference on Information and Business Management, Hong Kong, China, 3–4 September 2016; Singapore Management and Sports Science Institute: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, E.I. Financial Ratios, Discriminant Analysis and the Prediction of Corporate Bankruptcy. J. Financ. 1968, 23, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, E.I.; Haldeman, R.G.; Narayanan, P. ZETA ANALYSIS, a new model to identify bankruptcy risk of corporations. J. Bank. Financ. 1977, 1, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M. Failing company discriminant analysis. J. Account. Res. 1974, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, E.B. A Discriminant Analysis of Predictors of Business Failure. J. Account. Res. 1972, 10, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elam, R. The effect of lease data on the predictive ability of financial ratios. Account. Rev. 1975, 5, 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, C.L.; Smith, R.E. A comparison of general price level and historical cost financial statemnets in the prediction of bankruptcy. Account. Rev. 1979, 54, 72–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, J.W. A prediction of business failure using accounting data. J. Account. Res. Sel. Stud. 1973, 11, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffler, R.J. The assessment of company solvency and performance using a statistical model. Account. Bus. Res. 1983, 13, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisko, S.; Klieštik, T. Finančný Manažment; Edis Publishing, University of Žilina: Žilina, Slovakia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalovič, M. The Assessment of Corporate Financial Performance via Discriminant Analysis. Acta Oeconomica Cassoviensia Sci. J. 2015, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klieštik, T.; Majerová, J.; Lyakin, A.N. Metamorphoses and Semantics of Corporate Failures as a Basal Assumption of a Well-founded Prediction of a Corporate Financial Health. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Economics and Social Science ICESS 2015, Changsha, China, 28–29 December 2015; Lee, G., Ed.; Volume 86, pp. 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gundová, P. Verification of the selected prediction methods in Slovak companies. Acta Acad. Karviniensia 2015, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, D. Early warning of bank failure. A logit regression approach. J. Bank. Financ. 1977, 1, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlson, J. Financial ratios and the probabilistic prediction of bankruptcy. J. Account. Res. 1980, 18, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kliestik, T.; Lyakin, A.N.; Valaskova, K. Stochastic calculus and modelling in economics and finance. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economics and Social Science ICESS 2014, Shenzhen, China, 29–30 July 2014; Lee, G., Ed.; pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Mišanková, M.; Spuchľáková, E.; Frajtová-Michalíková, K. Determination of Default Probability by Loss Given Default. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 26, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloubos, G.; Grammatikos, T. The success of bankruptcy prediction models in Greece. Stud. Bank. Financ. 1988, 7, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zmijewski, M. Methodological issues related to the estimation of financial distress prediction models. J. Account. Res. 1984, 22, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, J. What Is the Difference Between Logit and Probit Models? 2015. Available online: https://www.methodsconsultants.com/tutorial/what-is-the-difference-between-logit-and-probit-models/ (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Adamko, P.; Švábová, L. Prediction of the risk of bankruptcy of Slovak companies. In Proceedings of the 8th International Scientific Conference on Managing and Modelling of Financial Risks, Ostrava, Czech Republic, 5–6 September 2016; VSB-Technical University: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2016; pp. 15–20. Available online: https://www.ekf.vsb.cz/export/sites/ekf/rmfr/cs/sbornik/Soubory/Part_I.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Jakubík, P.; Teplý, P. The Prediction of Corporate Bankruptcy and Czech Economy’s Financial Stability through Logit Analysis; IES Working Paper 19/2008; IES FSV, Univerzita Karlova: Prague, Czech Republic, 2008; Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/83366/1/578585421.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Valecký, J.; Slivková, E. Microeconomic Scoring Model of Czech Firms’ Bankruptcy. Ekonomická Revue 2012, 15, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hand, D.J. Artificial Intelligence and Psychiatry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, R.; Jackson, W.M.; Jones, T.W. A Comparison of the Classical and the Linear Programming Approaches to the Classification Problem in Discriminant Analysis. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1992, 41, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváthová, J.; Mokrišová, M. Risk of Bankruptcy, its Determinants and Models. Risks. 2018, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Štefko, R.; Gavurová, B.; Kočišová, K. Healthcare efficiency assessment using DEA analysis in the Slovak Republic. Health Econ. Rev. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.J. The Measurement of Productive Efficiency. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1957, 120, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debreu, G. The coefficient of resource utilization. Econometrica 1951, 19, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, T.C. Analysis of production as an efficient combination of activities. In Activity Analysis of Production and Allocation; Koopmans, T.C., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1951; pp. 33–97. [Google Scholar]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lovell, C.A. Measurement of Efficiency of Production; Kluwer-Nijhoff Publishing Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J. DEA Based Benchmarking Models. In Data Envelopment Analysis. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science; Zhu, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 221, pp. 291–308. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Margaritis, D. Advances in Data Envelopment Analysis; World Scientific Books; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Chin, K.S.; Yang, J.B. Measuring the performances of decision-making units using geometric average efficiency. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2007, 58, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, T.R.; Silkman, R.H.; Hogan, A.J. Data Envelopment Analysis: Critique and Extensions. In Measuring Efficiency: An Assessment of Data Envelopment Analysis; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1986; Volume 1986, pp. 73–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.; Hwang, S.N. Efficiency decomposition in twostage data envelopment analysis: An application to non-life insurance companies in Taiwan. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 185, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradi, J.C.; Rouatt, S.; Zhu, H. Two-stage evaluation of bank branch efficiency using data envelopment analysis. Omega 2011, 39, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnes, J. Data envelopment analysis and its application to the measurement of efficiency in higher education. Econ. Educ. Rev. 2006, 25, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanassoulis, E. Introduction to the Theory and Application of Data Envelopment Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Thrall, R.M. What Is the Economic Meaning of FDH? J. Product. Anal. 1999, 11, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.J.; Omrani, H. Data envelopment analysis with uncertain data: An application for Iranian electricity distribution companies. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezalkotob, A.; Haji-Sami, E.; Omrani, H. Robust DEA under discrete uncertain data: A case study of Iranian electricity distribution companies. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2015, 11, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrier, G.D.; Rosko, M.D.; Valdmanis, V.G. Analysis of uncompensated hospital care using a DEA model of output congestion. Health Care Manag. Sci. 2006, 9, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, S.; Ruchita, R. Efficiencies of health insurance business in India: An application of DEA. Am. J. Soc. Manag. Sci. 2011, 2, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljevic, M.B.; Vukovic, M.; Fontanesi, J. Life expectancy and health expenditure evolution in Eastern Europe—DiD and DEA analysis. Expert Rev. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 2016, 16, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabrani, G.; Irfan, M.; Mesta, H.A.; Arifah, L. Efficiency Analysis of Local Government Health Service in West Sumatra Province Using Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Economics, Business, Entrepreneurship, and Finance (ICEBEF 2018), Bandung, Indonesia, 19 September 2018; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 783–789. [Google Scholar]
- Simak, P.C. DEA Based Analysis of Coporate Failure. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Applied Sciences and Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cielen, A.; Peeters, L.; Vanhoof, K. Bankruptcy prediction using a data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 154, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradi, J.C.; Asmild, M.; Simak, P.C. Using DEA and worst practice DEA in credit risk evaluation. J. Product. Anal. 2004, 21, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premachandra, I.M.; Bhabra, G.S.; Sueyoshi, T. DEA as a tool for bankruptcy assessment: A comparative study with logistic regression technique. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 193, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Goto, M. Methodological comparison between DEA and DEA-DA from the perspective of bankruptcy assessment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 188, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premachandra, I.M.; Chen, Y.; Watson, J. DEA as a Tool for Predicting Corporate Failure and Success: A Case of Bankruptcy Assessment. Omega 2011, 3, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, U.; Pakkala, T.; Mallikarjunappa, T. A modified directional distance formulation of DEA to assess bankruptcy: An application to IT/ITES companies in India. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 9, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roháčová, V.; Kráľ, P. Corporate failure prediction using DEA: An application to companies in the Slovak Republic. In Proceedings of the 18th International Scientific Conference Applications of Mathematics and Statistics in Economics (AMSE), Jindřichúv Hradec, Czech Republic, 2–6 September 2015; Hronová, S., Vltavská, K., Eds.; Oeconomica Publishing House, University of Economics: Prague, Czech Republic, 2015. Available online: http://amse-conference.eu/history/amse2015/doc/Rohacova_Kral.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Vavřina, J.; Hampel, D.; Janová, J. New approaches for the financial distress classification in agribusiness. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2013, 61, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visani, F.; Barbieri, P.; Di Lascio, F.M.L.; Raffoni, A.; Vigo, D. Supplier’s total cost of ownership evaluation: A data envelopment analysis approach. Omega 2016, 61, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanke, P.; Azad, M.A.K.; Emrouznejad, A.; Antunes, J. A dynamic network DEA model for accounting and financial indicators: A case of efficiency in MENA banking. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2019, 61, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gherghina, S.C. An Artificial Intelligence Approach towards Investigating Corporate Bankruptcy. Rev. Eur. Stud. 2015, 7, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altman, E.I.; Marco, G.; Varetto, F. Corporate distress diagnosis: Comparisons using linear discriminant analysis and neural networks (the Italian experience). J. Bank. Financ. 1994, 18, 505–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiya, A.F. Bankruptcy prediction for credit risk using neural networks: A survey and new results. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2001, 12, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abid, F.; Zouari, A. Predicting corporate financial distress: A new neural networks approach. Financ. India 2002, 16, 601–612. [Google Scholar]
- Du Jardin, P. Predicting bankruptcy using neural networks and other classification methods: The influence of variable selection techniques on model accuracy. Neurocomputing 2010, 73, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zouari, A. Discriminating Firm Financial Health Using Self-Organizing Maps: The Case of Saudi Arabia; Department of Finance and Investment, College of Economics and Administrative Sciences, Imam Muhammad Bin Saud Islamic University: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- CRIF. Financial Statements of Businesses; Slovak Credit Bureau, s.r.o.: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Csikósová, A.; Janošková, M.; Čulková, K. Limitation of Financial Health Prediction in companies from Post-Communist Countries. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2019, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kočišová, K. Technical efficiency of top 50 world banks. J. Appl. Econ. Sci. 2013, 8, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kočišová, K. Aplikácia DEA modelov pri analýze technickej efektívnosti pobočiek komerčnej banky. Ekonomický Časopis 2012, 60, 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Barišic, P.; Cvetkoska, V. Analyzing the Efficiency of Travel and Tourism in the European Union. In Advances in Operational Research in the Balkans, Proceedings of the 13th Balkan Conference on Operational Research, Belgrade, Serbia, 25–28 May 2018; Mladenovic, N., Sifaleras, A., Kuxmanovic, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 167–186. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, E.I. Corporate Financial Distress. A Complete Guide to Predicting, Avoiding, and Dealing with Bankruptcy; Wiley Interscience, John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Klieštik, T. Kvantifikácia efektivity činností dopravných podnikov pomocou Data Envelopment Analysis. E+M Ekon. Manag. 2009, 1, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Vincová, K. Využitie DEA modelov na hodnotenie efektívnosti. Biatec 2005, 13, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kováčová, M.; Klieštik, T. logit and probit application for the prediction of bankruptcy in Slovak companies. Equilib. Q. J. Econ. Econ. Policy 2017, 12, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelová, V.; Stachová, M. Comparing DEA and logistic regression in corporate financial distress prediction. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference FERNSTAT 2016, Banská Bystrica, Slovakia, 22–23 September 2016; Boďa, M., Ed.; Slovak Statistical and Demographic Society: Banská Bystrica, Slovakia, 2016; pp. 95–104. Available online: http://fernstat.ssds.sk/proceedings/ (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Valášková, K.; Švábová, L.; Ďurica, M. Verifikácia predikčných modelov v podmienkach slovenského poľnohospodárskeho sektora. Ekon. Manag. Inovace 2017, 9, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Boďa, M.; Úradníček, V. The portability of Altman’s Z-score model to predicting corporate financial distress of Slovak companies. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2016, 22, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperandei, S. Understanding logistic regression analysis. Biochem. Med. 2014, 24, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebák, J. Statistické Myšlení a Nástroje Analýzy Dat; Informatorium: Prague, Czech Republic, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J. DEA Frontier Software; Foisie Business School, Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelová, V.; Bieliková, T. Diagnostikovanie finančného zdravia podnikov pomocou metódy DEA: Aplikácia na podniky v Slovenskej republike. Politická Ekon. 2017, 65, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, C.X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. AUC: A statistically consistent and more discriminating measure than accuracy. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, Acapulco‚ Mexico‚, 9−15 August 2003; pp. 519–526. Available online: https://cling.csd.uwo.ca/papers/ijcai03.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2020).
- Anouze, A.L.M.; Bou-Hamad, I. Data envelopment analysis and data mining to efficiency estimation and evaluation. Int. J. Islamic Middle East. Financ. Manag. 2019, 12, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Input-Oriented | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| BCC Model | |||
| DMU Name | Efficiency | Benchmarks | |
| F34 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F34 |
| F40 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F40 |
| F89 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F89 |
| F91 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F91 |
| F101 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F101 |
| F120 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F120 |
| F132 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F132 |
| F139 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F139 |
| F147 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F147 |
| F156 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F156 |
| F161 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F161 |
| F236 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F236 |
| F250 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F250 |
| F254 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F254 |
| F269 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F269 |
| F288 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F288 |
| Input-Oriented | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| BCC Model | |||
| DMU Name | Efficiency | Benchmarks | |
| F23 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F23 |
| F33 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F33 |
| F41 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F41 |
| F88 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F88 |
| F106 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F106 |
| F107 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F107 |
| F136 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F136 |
| F137 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F137 |
| F140 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F140 |
| F165 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F165 |
| F169 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F169 |
| F173 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F173 |
| F179 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F179 |
| F212 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F212 |
| F215 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F215 |
| F221 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F221 |
| F227 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F227 |
| F231 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F231 |
| F238 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F238 |
| F261 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F261 |
| F271 | 1.00000 | 1.000 | F271 |
| BCC DEA | Peer Units for DMUs | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRS | ||||||||||
| DMU No. | DMU Name | Efficiency | ||||||||
| 23 | F23 | 1.23075 | 0.190 | F40 | 0.061 | F89 | 0.748 | F126 | ||
| 33 | F33 | 1.14391 | 0.640 | F34 | 0.201 | F40 | 0.159 | F236 | ||
| 41 | F41 | 1.18367 | 0.181 | F40 | 0.146 | F89 | 0.143 | F126 | 0.530 | F288 |
| 88 | F88 | 1.15604 | 0.099 | F34 | 0.211 | F40 | 0.690 | F132 | ||
| 106 | F106 | 1.19726 | 0.122 | F40 | 0.874 | F126 | 0.004 | F156 | ||
| 107 | F107 | 1.13749 | 0.198 | F40 | 0.073 | F91 | 0.730 | F132 | ||
| 136 | F136 | 1.06418 | 0.093 | F40 | 0.022 | F236 | 0.709 | F250 | 0.176 | F254 |
| 137 | F137 | 1.19797 | 0.270 | F40 | 0.002 | F126 | 0.728 | F132 | ||
| 140 | F140 | 1.10508 | 0.084 | F40 | 0.177 | F126 | 0.739 | F132 | ||
| 165 | F165 | 1.16846 | 0.143 | F40 | 0.429 | F126 | 0.428 | F132 | ||
| 169 | F169 | 1.16080 | 0.051 | F40 | 0.514 | F89 | 0.436 | F126 | ||
| 173 | F173 | 1.14813 | 0.446 | F34 | 0.238 | F40 | 0.316 | F132 | ||
| 179 | F179 | 1.18514 | 0.142 | F40 | 0.268 | F89 | 0.589 | F126 | ||
| 212 | F212 | 1.22325 | 0.182 | F40 | 0.482 | F89 | 0.336 | F126 | ||
| 215 | F215 | 1.11866 | 0.598 | F34 | 0.159 | F40 | 0.244 | F132 | ||
| 221 | F221 | 1.21425 | 0.134 | F40 | 0.809 | F89 | 0.058 | F126 | ||
| 227 | F227 | 1.14343 | 0.740 | F34 | 0.241 | F40 | 0.020 | F132 | ||
| 231 | F231 | 1.18273 | 0.244 | F40 | 0.160 | F126 | 0.597 | F132 | ||
| 238 | F238 | 1.18128 | 0.112 | F40 | 0.640 | F89 | 0.248 | F126 | ||
| 261 | F261 | 1.10447 | 0.040 | F40 | 0.478 | F126 | 0.482 | F132 | ||
| 271 | F271 | 1.24384 | 0.043 | F40 | 0.956 | F89 | 0.001 | F156 | ||
| Parameter | Estimate | Standard Error | Wald stat. | Lower and Upper Confidence Limit 95.0% | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.9778 | 0.77374 | 1.59710 | −2.4943 | 0.5387 | 0.206315 |
| NITA | −40.9544 | 12.48770 | 10.75566 | −65.4299 | −16.4790 | 0.001040 |
| WCTA | −6.1530 | 1.89538 | 10.53842 | −9.8679 | −2.4381 | 0.001169 |
| EBIE | −1.4028 | 0.50667 | 7.66528 | −2.3958 | −0.4097 | 0.005629 |
| ED | 0.0653 | 0.13258 | 0.24270 | −0.1945 | 0.3252 | 0.622262 |
| CLTA | −1.0043 | 1.58714 | 0.40041 | −4.1150 | 2.1064 | 0.526875 |
| Predicted Value: Non-prosperous | Correct Percentage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| Observed value: Non-prosperous | Yes | 10 | 12 | 45 |
| No | 3 | 265 | 99 | |
| Parameter | BCC Model | Logit Model |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | 41 | 45 |
| Specificity (%) | 96 | 99 |
| Overall estimation accuracy (%) | 91 | 95 |
| Error type 1 (%) | 59 | 55 |
| Error type II (%) | 4 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horváthová, J.; Mokrišová, M. Comparison of the Results of a Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Logit Model in Assessing Business Financial Health. Information 2020, 11, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11030160
Horváthová J, Mokrišová M. Comparison of the Results of a Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Logit Model in Assessing Business Financial Health. Information. 2020; 11(3):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11030160
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorváthová, Jarmila, and Martina Mokrišová. 2020. "Comparison of the Results of a Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Logit Model in Assessing Business Financial Health" Information 11, no. 3: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11030160
APA StyleHorváthová, J., & Mokrišová, M. (2020). Comparison of the Results of a Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Logit Model in Assessing Business Financial Health. Information, 11(3), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11030160




