Investigation of Spoken-Language Detection and Classification in Broadcasted Audio Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Problem Definition and Motivation
2.2. Proposed Use Scenario Framework
2.3. Data Collection—Content Preprocessing
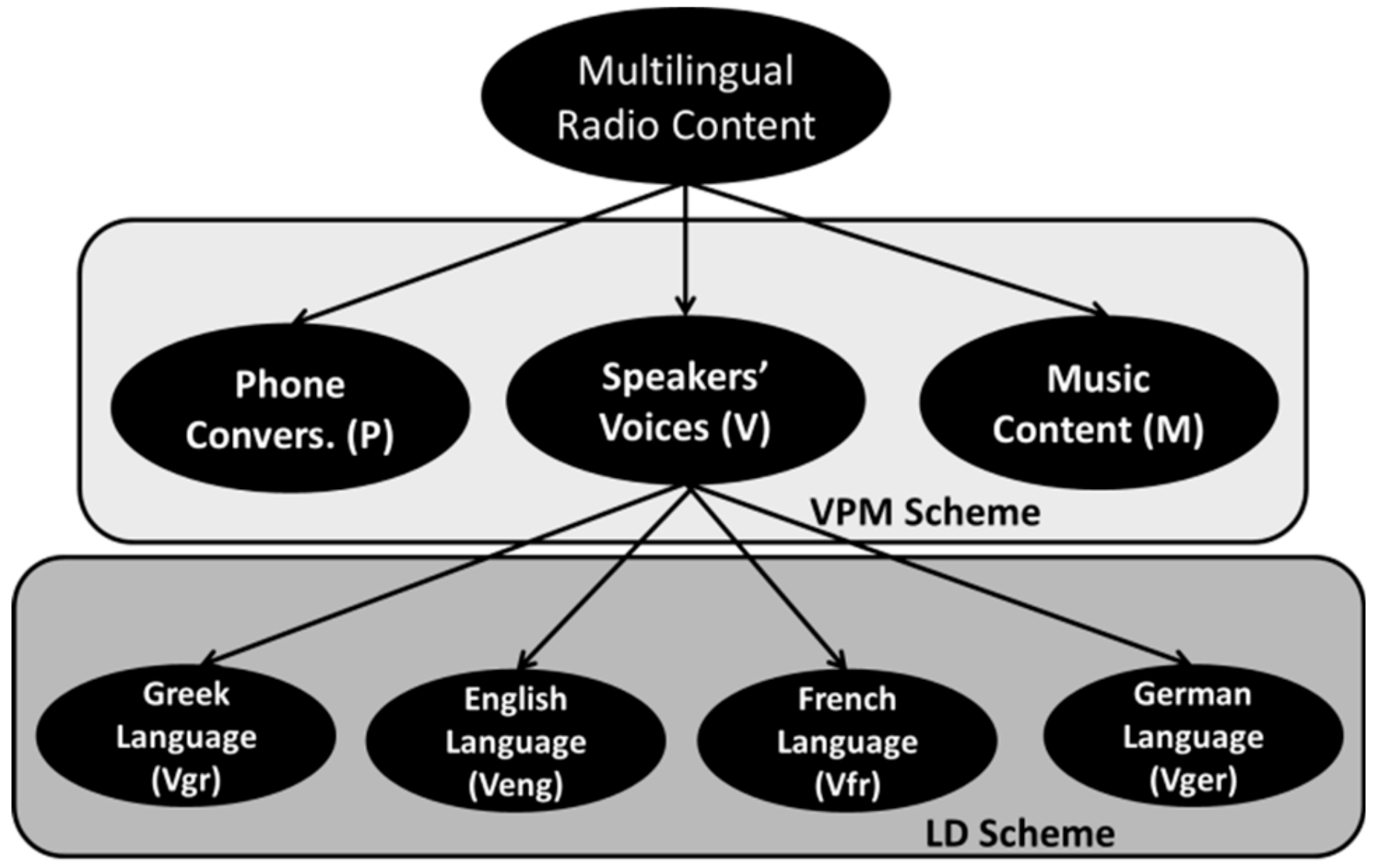
2.4. Definition of Classification Taxonomies
2.5. Windowing Process—Annotation
- M, P, V for Music, Phone and Voice samples, respectively.
- Vgr, Veng, Vfr, Vger for Greek, English, French, German Voice samples, respectively.
2.6. Feature Engine—Feature Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Configuration and Validation of the Training and Evaluation Procedures
3.2. Performance Evaluation Results
4. Discussion and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotsakis, R.; Kalliris, G.; Dimoulas, C. Investigation of broadcast-audio semantic analysis scenarios employing radio-programme-adaptive pattern classification. Speech Commun. 2012, 54, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakis, R.; Kalliris, G.; Dimoulas, C. Investigation of salient audio-features for pattern-based semantic content analysis of radio productions. In Proceedings of the 132nd AES Convention, Budapest, Hungary, 26–29 April 2012; pp. 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsakis, R.G.; Dimoulas, C.A.; Kalliris, G.M. Contribution of Stereo Information to Feature-Based Pattern Classification for Audio Semantic Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 Seventh International Workshop on Semantic and Social Media Adaptation and Personalization, Luxembourg, 3–4 December 2012; pp. 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrysis, L.; Tsipas, N.; Thoidis, I.; Dimoulas, C. 1D/2D Deep CNNs vs. Temporal Feature Integration for General Audio Classification. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2020, 68, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoidis, I.; Vrysis, L.; Pastiadis, K.; Markou, K.; Papanikolaou, G. Investigation of an Encoder-Decoder LSTM model on the enhancement of speech intelligibility in noise for hearing-impaired listeners. In Audio Engineering Society Convention 146; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kostek, B. Perception-Based Data Processing in Acoustics: Applications to Music Information Retrieval and Psychophysiology of Hearing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Korvel, G.; Treigys, P.; Tamulevičius, G.; Bernatavičienė, J.; Kostek, B. Analysis of 2D Feature Spaces for Deep Learning-based Speech Recognition. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2018, 66, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalampiras, S. Toward Language-Agnostic Speech Emotion Recognition. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2020, 68, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrysis, L.; Tsipas, N.; Dimoulas, C.; Papanikolaou, G. Extending Temporal Feature Integration for Semantic Audio Analysis. In Audio Engineering Society Convention 142; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bountourakis, V.; Vrysis, L.; Konstantoudakis, K.; Vryzas, N.N. An Enhanced Temporal Feature Integration Method for Environmental Sound Recognition. Acoustics 2019, 1, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimoulas, C.; Vegiris, C.; Avdelidis, K.; Kalliris, G.; Papanikolaou, G. Automated Audio Detection, Segmentation, and Indexing with Application to Postproduction Editing. In Proceedings of the 122nd AES Convention, Vienna, Austria, 5–8 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vegiris, C.; Dimoulas, C.; Papanikolaou, G. Audio Content Annotation, Description and Management Using Joint Audio Detection, Segmentation and Classification Techniques. In Proceedings of the 126th AES Convention, Munich, Germany, 7–10 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vrysis, L.; Tsipas, N.; Dimoulas, C.; Papanikolaou, G. Crowdsourcing audio semantics by means of hybrid bimodal segmentation with hierarchical classification. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2016, 64, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzel, H.J.; Alexander, P. Forensic Automatic Speaker Recognition with Degraded and Enhanced Speech. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2014, 62, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korvel, G.; Treigys, P.; Tamulevičius, G.; Bernatavičienė, J.; Bożena, K. Borrowing 2D Feature Maps from Audio Signal Analysis to Deep Learning-based Speech Recognition. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2019. (accepted, in editorial process). [Google Scholar]
- Barras, C.; Zhu, X.; Meignier, S.; Gauvain, J.-L. Multistage speaker diarization of broadcast news. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zewoudie, A.W.; Luque, I.; Hernando, J. The use of long-term features for GMM-and i-vector-based speaker diarization systems. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Long, Y.; Li, Y.; Mao, H. Addressing Text-Dependent Speaker Verification Using Singing Speech. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-vectors: Robust DNN embeddings for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimoulas, C.; Kalliris, G. Investigation οf wavelet approaches for joint temporal, spectral and cepstral features in audio semantics. In Proceedings of the 134th AES Convention, Rome, Italy, 4–7 May 2013; pp. 509–518. [Google Scholar]
- Barbedo, J.; Lopes, A. A robust and computationally efficient speech/music discriminator. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2006, 54, 571–588. [Google Scholar]
- Tsipas, N.; Vrysis, L.; Dimoulas, C.; Papanikolaou, G. Efficient audio-driven multimedia indexing through similarity-based speech/music discrimination. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipas, N.; Vrysis, L.; Dimoulas, C.; Papanikolaou, G. Content-Based Music Structure Analysis using Vector Quantization. In Proceedings of the 138th AES Convention, Warsaw, Poland, 7–10 May 2015; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Hellmuth, O.; Allamanche, E.; Kastner, J.H.T.; Lefebvre, N.; Wistorf, R. Music Genre Estimation from Low Level Audio Features. In Proceedings of the 25th AES International Conference, London, UK, 17–19 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dimoulas, C.A.; Symeonidis, A.L. Syncing Shared Multimedia through Audiovisual Bimodal Segmentation. IEEE Multimed. 2015, 22, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, A. An Introduction to Audio Content Analysis: Applications in Signal Processing and Music Informatics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781118393550. [Google Scholar]
- Vryzas, N.; Kotsakis, R.; Liatsou, A.; Dimoulas, C.; Kalliris, G. Speech Emotion Recognition for Performance Interaction. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2018, 66, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, N.; Vrysis, L.; Matsiola, M.; Kotsakis, R.; Dimoulas, C.; Kalliris, G. Continuous Speech Emotion Recognition with Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2020, 68, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakis, R.; Dimoulas, C.; Kalliris, G.; Veglis, A. Emotional Prediction and Content Profile Estimation in Evaluating Audiovisual Mediated Communication. Int. J. Monit. Surveill. Technol. Res. 2014, 2, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharan, R.V.; Moir, T.J. An overview of applications and advancements in automatic sound recognition. Neurocomputing 2016, 200, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Otero, P.; Docio-Fernandez, L.; Garcia-Mateo, C. Ensemble audio segmentation for radio and television programmes. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 7421–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strisciuglioa, N.; Ventob, M.; Petkova, N. Learning sound representations using trainable COPE feature extractors. Pattern Recognition. 2019, 92, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotsakis, R.; Kalliris, G.; Dimoulas, C. Extending radio broadcasting semantics through adaptive audio segmentation automations. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020. (prepared for submission). [Google Scholar]
- Dweik, B.; Qawar, H. Language choice and language attitudes in a multilingual Arab Canadian community: Quebec-Canada: A sociolinguistic study. Br. J. Engl. Linguist. 2015, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaiah, V.S.; Rao, R.R. Speaker diarization system using HXLPS and deep neural network. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakis, R.; Mislow, A.; Kalliris, G.; Matsiola, M. Feature-Based Language Discrimination in Radio Productions via Artificial Neural Training. In Proceedings of the 10th Audio Mostly, ACM, New York, NY, USA, 7–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segbroeck, M.; Travadi, R.; Narayanan, S. Rapid Language Identification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.G.; Doddington, G.R. Doddington, Automatic Language Discrimination; No. TI-08-77-46; Texas Instruments Inc.: Dallas, TX, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy, Y.K.; Barnard, E.; Cole, R.A. Reviewing automatic language identification. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1994, 11, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.M.; Campbell, J.P.; Reynolds, D.A.; Singer, E.; Torres-Carrasquillo, P.A. Support vector machines for speaker and language recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 2006, 20, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncheva, L.I. Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1-118-31523-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Goldberg, A.B. Introduction to Semi-supervised Learning. In Synthesis Lectures on Artificial Intelligence ad Machine Learning; Brachman, R.J., Dietterich, T.G., Eds.; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1598295474. [Google Scholar]
- Lartillot, O.; Toiviainen, P. Mir in matlab (ii): A toolbox for musical feature extraction from audio. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Music Information Retrieval, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.; Frank, E.; Holmes, G.; Pfahringer, B.; Reutemann, P.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA Data Mining Software: An Update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2009, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zim, H.S. Codes & Secret Writing: Authorized Abridgement; Scholastic Book Service: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- English Letter Frequency Counts: Mayzner Revisited or Etaoin Srhldcu. 2018. Available online: https://norvig.com/mayzner.html (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Corpus de Thomas Tempé. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20070930194046/http://gpl.insa-lyon.fr/Dvorak-Fr/CorpusDeThomasTemp%C3%A9 (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Beutelspacher, A. Kryptologie, 7th ed.; Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2014; p. 10. ISBN 3-8348-0014-7. [Google Scholar]


| Notation | 100 ms | 500 ms | 1000 ms | 2000 ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 2400 | 480 | 240 | 120 |
| P | 2400 | 480 | 240 | 120 |
| V | 19,200 | 3840 | 1920 | 960 |
| Vgr | 4800 | 960 | 480 | 240 |
| Veng | 4800 | 960 | 480 | 240 |
| Vfr | 4800 | 960 | 480 | 240 |
| Vger | 4800 | 960 | 480 | 240 |
| Sum | 24,000 | 4800 | 2400 | 1200 |
| Time-Domain | Spectral-Domain |
|---|---|
| rms | Npeaks_spectral |
| Npeaks_temporal | flux_avr, flux_std |
| lowenergy | rolloff_0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 0.9, 0.99 |
| Nonsets | bright_500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 3000, 4000, 8000 |
| event_density | sp_roughness, sp_irregularity |
| rthythm_clarity | Npitch, pitch_avr, pitch_std |
| zerocross | fundam_freq, inharmonicity |
| attacktime_avr,std | mode |
| attackslope_avr,std | Nhcdf, hcdf_avr, hcdf_std |
| sp_centroid, sp_spread | |
| Cepstral-Domain | sp_skewness, sp_kurtosis |
| mfcc1…13 | sp_flatness |
| entropy |
| # | W = 100 ms | W = 500 ms | W = 1000 ms | W = 2000 ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | bright_4000 | bright_4000 | bright_4000 | mfcc1 |
| 2 | mfcc7 | rolloff_0.9 | bright_8000 | bright_8000 |
| 3 | mfcc2 | mfcc2 | rolloff_0.9 | hcdf_avr |
| 4 | rolloff_0.9 | mfcc7 | sp_flatness | sp_flatness |
| 5 | bright_3000 | bright_8000 | mfcc1 | mfcc2 |
| 6 | bright_8000 | bright_3000 | mfcc2 | bright_4000 |
| 7 | mfcc1 | mfcc1 | rolloff_0.99 | rolloff_0.99 |
| 8 | rolloff_0.2 | rolloff_0.99 | mfcc7 | mfcc7 |
| 9 | mfcc10 | sp_flatness | sp_centroid | rolloff_0.9 |
| 10 | rolloff_0.8 | sp_centroid | bright_3000 | sp_centroid |
| # | W = 100 ms | W = 500 ms | W = 1000 ms | W = 2000 ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rolloff_0.99 | rolloff_0.99 | rolloff_0.99 | rolloff_0.99 |
| 2 | bright_8000 | bright_8000 | rolloff_0.9 | rms |
| 3 | rolloff_0.9 | rolloff_0.9 | rms | sp_spread |
| 4 | bright_4000 | rms | bright_8000 | rhythm_clarity |
| 5 | rolloff_0.8 | sp_spread | sp_spread | attackslope_avr |
| 6 | sp_centroid | rolloff_0.8 | rhythm_clarity | rolloff_0.9 |
| 7 | bright_3000 | sp_centroid | attackslope_avr | bright_8000 |
| 8 | Rms | sp_flatness | rolloff_0.8 | attackslope_std |
| 9 | Entropy | flux_avr | flux_avr | flux_avr |
| 10 | sp_flatness | entropy | attackslope_std | sp_roughness |
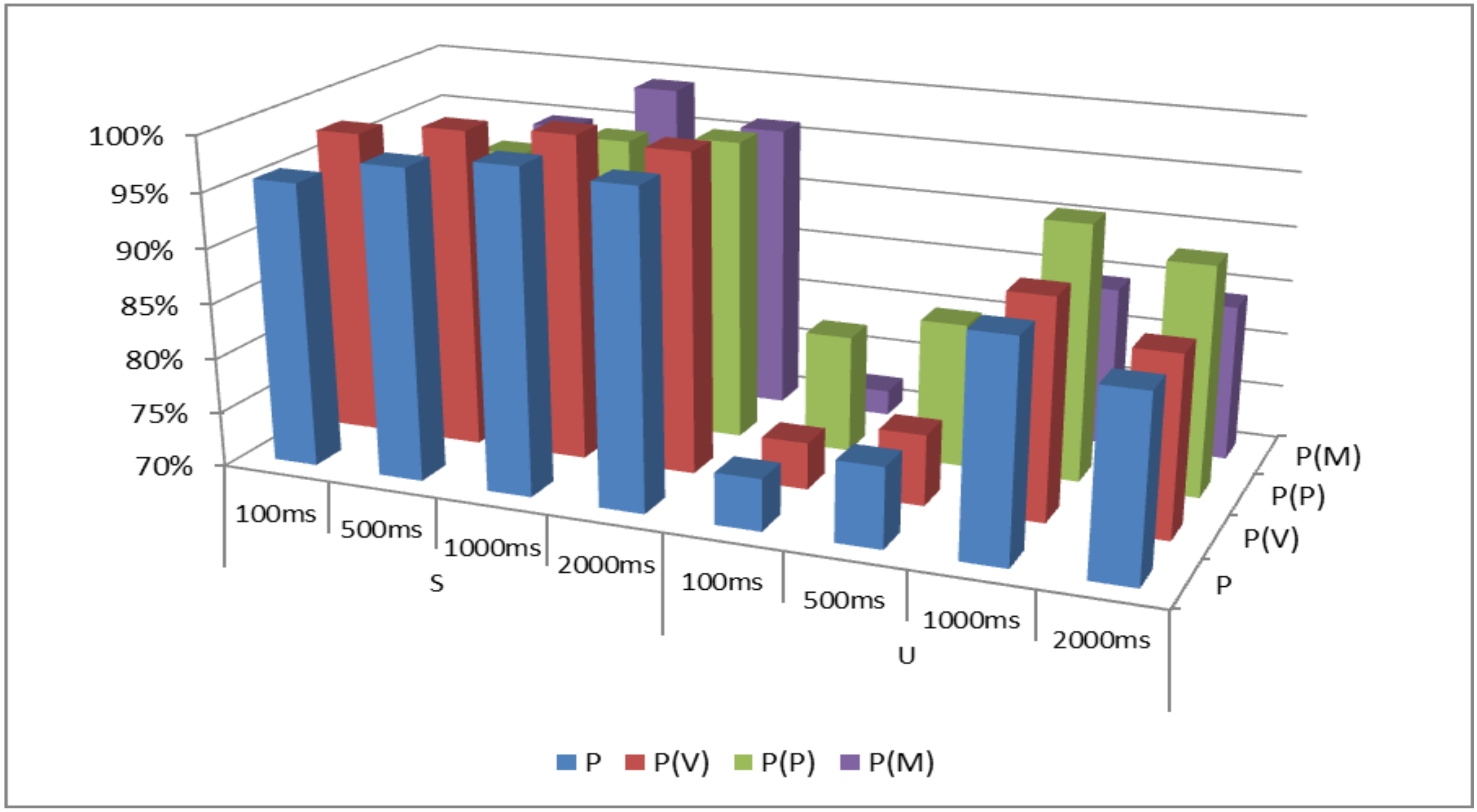
| Window-Length | P | P(V) | P(P) | P(M) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 100 ms | 95.81 | 97.80 | 85.04 | 90.67 |
| 500 ms | 98.15 | 99.01 | 94.58 | 94.79 | |
| 1000 ms | 99.25 | 99.58 | 96.67 | 99.17 | |
| 2000 ms | 98.63 | 99.06 | 97.50 | 96.25 | |
| U | 100 ms | 74.73 | 74.28 | 80.71 | 72.29 |
| 500 ms | 77.31 | 76.46 | 83.13 | 78.33 | |
| 1000 ms | 89.75 | 89.95 | 93.33 | 84.58 | |
| 2000 ms | 86.58 | 86.35 | 90.83 | 84.17 |
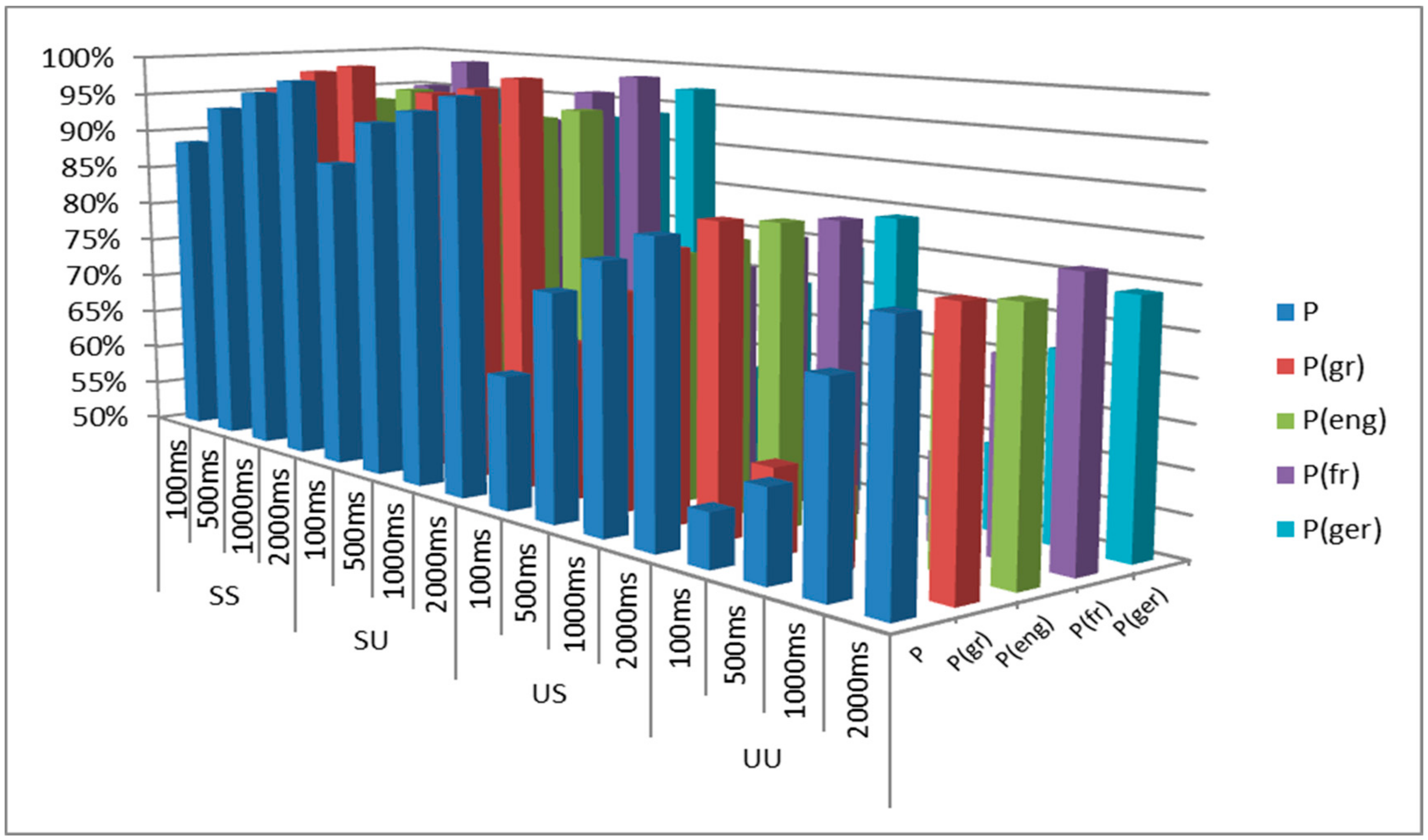
| Win. | P | P(gr) | P(eng) | P(fr) | P(ger) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | 100 ms | 88.53 | 91.99 | 87.97 | 84.29 | 89.85 |
| 500 ms | 93.59 | 95.92 | 92.68 | 92.47 | 93.31 | |
| 1000 ms | 96.08 | 98.54 | 94.56 | 96.03 | 95.19 | |
| 2000 ms | 98.01 | 99.58 | 96.23 | 99.58 | 96.65 | |
| SU | 100 ms | 88.11 | 91.10 | 87.72 | 82.93 | 90.69 |
| 500 ms | 93.72 | 96.99 | 92.47 | 92.71 | 92.71 | |
| 1000 ms | 95.60 | 97.91 | 93.98 | 96.76 | 93.75 | |
| 2000 ms | 97.80 | 99.54 | 95.37 | 99.07 | 97.22 | |
| US | 100 ms | 65.98 | 68.77 | 65.38 | 66.99 | 62.78 |
| 500 ms | 76.78 | 75.84 | 79.60 | 77.20 | 74.48 | |
| 1000 ms | 81.28 | 81.80 | 82.01 | 81.59 | 79.71 | |
| 2000 ms | 84.83 | 85.77 | 84.94 | 84.52 | 84.10 | |
| UU | 100 ms | 56.35 | 59.93 | 56.13 | 57.57 | 51.78 |
| 500 ms | 60.63 | 62.80 | 59.33 | 60.30 | 60.07 | |
| 1000 ms | 73.42 | 74.01 | 75.23 | 72.45 | 71.99 | |
| 2000 ms | 80.67 | 81.02 | 80.09 | 82.41 | 79.17 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotsakis, R.; Matsiola, M.; Kalliris, G.; Dimoulas, C. Investigation of Spoken-Language Detection and Classification in Broadcasted Audio Content. Information 2020, 11, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040211
Kotsakis R, Matsiola M, Kalliris G, Dimoulas C. Investigation of Spoken-Language Detection and Classification in Broadcasted Audio Content. Information. 2020; 11(4):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040211
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotsakis, Rigas, Maria Matsiola, George Kalliris, and Charalampos Dimoulas. 2020. "Investigation of Spoken-Language Detection and Classification in Broadcasted Audio Content" Information 11, no. 4: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040211
APA StyleKotsakis, R., Matsiola, M., Kalliris, G., & Dimoulas, C. (2020). Investigation of Spoken-Language Detection and Classification in Broadcasted Audio Content. Information, 11(4), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040211








