Generation of an EDS Key Based on a Graphic Image of a Subject’s Face Using the RC4 Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Coupling algorithms based on fractional-order-PCA-SVM [4] in order to achieve recognition accuracies above 98% with relatively high execution speed and without the requirement of high quality images as the input;
- Genetic algorithms which are capable of recognizing a face only by its parts, with an accuracy of up to 93% [5];
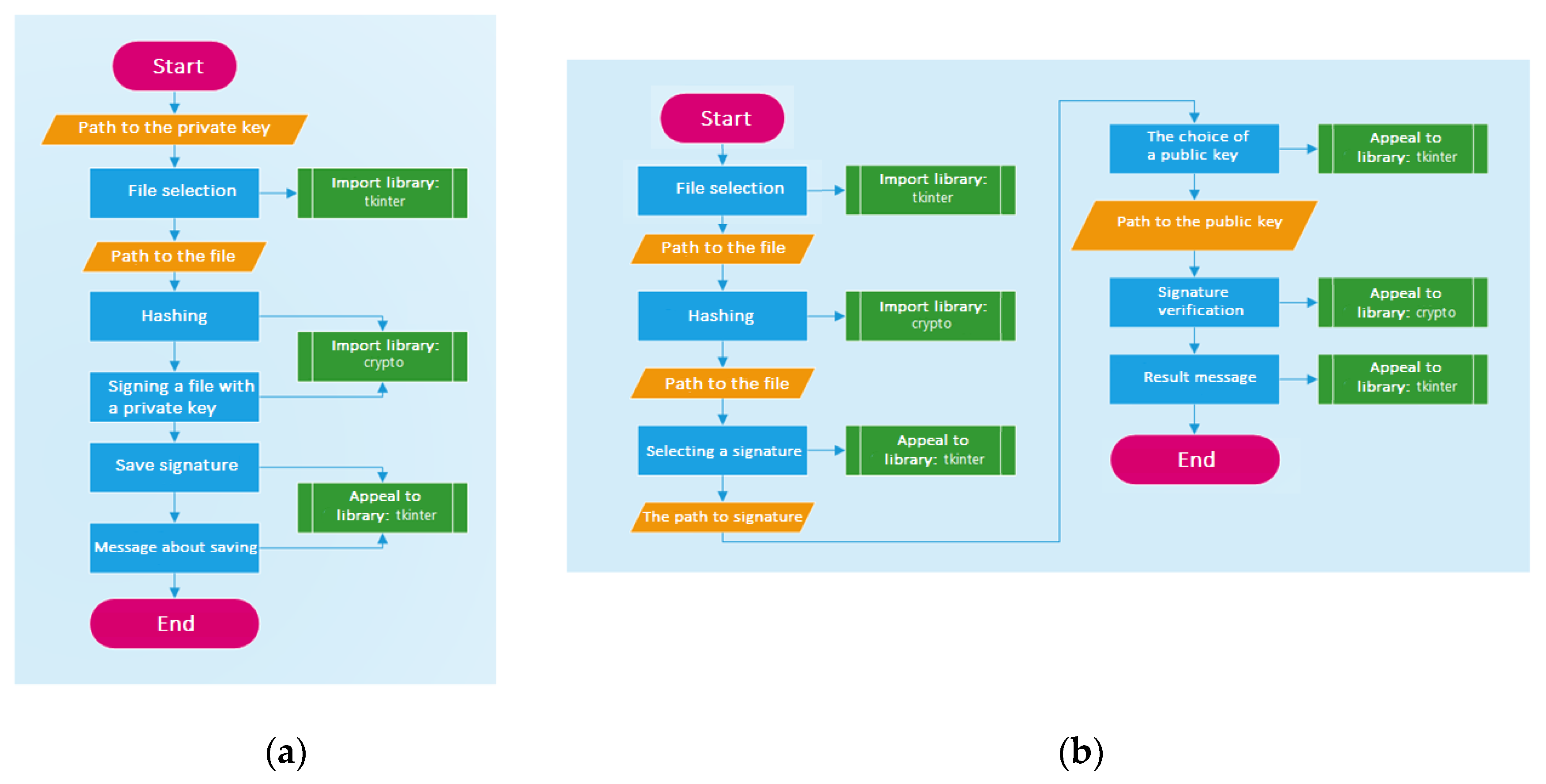
2. Materials and Methods
- Python Imaging Library (PIL for short), for work with bitmap graphics.
- Datetime allows you to work with date and time.
- PyCryptodome is an independent package of Python low-level cryptographic primitives.
- NumPy is an open source library for the Python programming language. Functions: support for multidimensional arrays and for high-level mathematical functions designed to work with multidimensional arrays.
- Time is a module for working with time.
- Face_recognition is a face recognition library.
- OpenCV is a library of computer vision and machine learning with open source code.
- Random provides functions with which to generate random numbers and letters or make random selections of sequence elements.
- Pickle implements a powerful algorithm for the serialization and deserialization of objects.
- provides access to a web-camera;
- identifies faces;
- records frames containing the face on the disk;
- performs training using a neural network;
- stores the learning results separately for each subject.
- The processed facial data are retrieved and uploaded to a list;
- Each real number in the list is raised to a square and multiplied by 1014;
- All list elements are concatenated;
- Random bytes are generated bitwise, a random byte is selected from the concatenated list, and if it is even, a 0 bit is written to the resulting sequence; otherwise a 1 bit is written.
- “Facial PRNG” generates 2048 bits;
- ARC4 encryptor is initialized by the generated bits;
- “Facial PRNG” generates the requested number of bytes;
- The generated bytes are additionally encrypted with the previously initialized ARC4 cipher and returned.
3. Results
Testing Statistical Hypotheses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konen, W.K.; Maurer, T.; von der Malsburg, C. A Fast Dynamic Link Matching Algorithm for Invariant Pattern Recognition. Neural Netw. 1994, 7, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollicelli, D.; Coscarella, M.; Delrieux, C. RoI Detection and Segmentation Algorithms for Marine Mammals Photo-Identification. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 56, 101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Z.; Muhammad, N.; Bibi, N.; Ali, T. A Review on State-of-the-Art Face Recognition Approaches. Fractals 2017, 25, 1750025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Cui, J. Digital Image Recognition Based on Fractional-Order-PCA-SVM Coupling Algorithm. Measurement 2019, 145, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsmadi, M.; Hamed, A.; Badawi, U.; Almarashdeh, I.; Salah, A.; Farag, T.; Hassan, W.; Alomari, Y.; Alsmadi, H.; Jaradat, G. Face image recognition based on partial face matching using genetic algorithm. Sust J. Eng. Comput. Sci. (JECS) 2017, 18, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, F.; Liao, R.; Wang, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhu, X. Improvement of Face Recognition Algorithm Based on Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), Changsha, China, 10–11 February 2018; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.U.; Shahzad, A.; Mahmood, Z.; Shah, A.A. Boosting the Face Recognition Performance of Ensemble Based LDA for Pose, Non-Uniform Illuminations, and Low-Resolution Images. Ksii Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2019, 13, 3144–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrus, S.Z.S.; Cherrier, E.; Rosenberger, C.; Schwartzmann, J.-J. A Review on Authentication Methods. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, Q.; Dai, Y.; Xu, X. Voice Biometric Identity Authentication System Based on Android Smart Phone. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 7–10 December 2018; pp. 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, A.; Rad, P. Voice Biometrics: Deep Learning-Based Voiceprint Authentication System. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th System of Systems Engineering Conference (SoSE), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 18–21 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelupanov, A.; Evsyutin, O.; Konev, A.; Kostyuchenko, E.; Kruchinin, D.; Nikiforov, D. Information security methods-Modern research directions. Symmetry 2019, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodashinsky, I.A.; Kostyuchenko, E.Y.; Sarin, S.K.; Anfilofiev, E.A.; Bardamova, M.B. User Authentication Based on Signature Dynamics Based on Fuzzy Classifier. Comput. Optics. 2018, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, K.S.; Hodashinsky, I.A. Bagged ensemble of fuzzy classifiers and feature selection for handwritten signature verification. Comput. Opt. 2019, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, M.; Fischer, A.; Riesen, K. A Novel Graph Database for Handwritten Word Images; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuchenko, E.; Gurakov, M.; Krivonosov, E.; Tomyshev, M.; Mescheryakov, R.; Hodashinskiy, I. Integration of Bayesian classifier and perceptron for problem identification on dynamics signature using a genetic algorithm for the identification threshold selection. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2016, 9719, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, L.C.F.; Sucupira, L.H.R.; Lizarraga, M.G.; Ling, L.L.; Yabu-Uti, J.B.T. User Authentication through Typing Biometrics Features. IEEE Trans. Signal. Process. 2005, 53, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankovskaya, A.E.; Shelupanov, A.A.; Hodashinsky, I.A.; Gorbunov, I.V. Development of hybrid intelligent system of express-diagnostics for detection potential attacker. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technologies (AICT), Rostov on Don, Russia, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, Z.; Yu, T. On Mouse Dynamics as a Behavioral Biometric for Authentication. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security, ASIACCS ’11, Hong Kong, China, 22–24 March 2011; pp. 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, Q.; Liu, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, F.; Hassan, M.M. AFA: Adversarial fingerprinting authentication for deep neural networks. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmanenko, I.; Shelupanov, A.; Kostyuchenko, E. Fusion of BiLSTM and GMM-UBM Systems for Audio Spoofing Detection. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 6, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozaid, A.; Haggag, A.; Kasban, H.; Eltokhy, M. Multimodal Biometric Scheme for Human Authentication Technique Based on Voice and Face Recognition Fusion. Multimed Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 16345–16361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaas, F.; Serpen, G. Evaluation of Biometric User Authentication Using an Ensemble Classifier with Face and Voice Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.00548. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, K.; Tharewal, S. Development of Face and Signature Fusion Technology for Biometrics Authentication. Int. J. Emerg. Res. Manag. Technol. 2018, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journal, I. Random Keypad and Face Recognition Authentication Mechanism. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Review of High-Quality Random Number Generators. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41781-019-0034-3 (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Pirbhulal, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Zhang, Y.-T. Heartbeats Based Biometric Random Binary Sequences Generation to Secure Wireless Body Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martin, L.; Picazo-Sanchez, P.; Peris-Lopez, P.; Tapiador, J. Heartbeats Do Not Make Good Pseudo-Random Number Generators: An Analysis of the Randomness of Inter-Pulse Intervals. Entropy 2018, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchlert, B.; Hasegawa, H. Using a Low-Cost Electroencephalogram (EEG) Directly as Random Number Generator. In Proceedings of the 2014 IIAI 3rd International Conference on Advanced Applied Informatics, Kitakyushu, Japan, 31 August–4 September 2014; pp. 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokar, E.; Mikaili, M. Assessment of Human Random Number Generation for Biometric Verification. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2012, 2, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OSA. Quantum Random Number Generator Based on Twin Beams. Available online: https://www.osapublishing.org/ol/abstract.cfm?uri=ol-42-5-895 (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Technical Review on Symmetric and Asymmetric Cryptography Algorithms-ProQuest. Available online: https://search.proquest.com/openview/94f3a444d3f907bdb0adfc7ed6ba770c/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1606379 (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Saračević, M.; Adamović, S.; Macek, N.; Elhoseny, M.; Sarhan, S. Cryptographic Keys Exchange Model for Smart City Applications. In IET Intelligent Transport Systems; IET: London, UK, 2020; Volume 14, pp. 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelled Faces in the Wild (LFW) Dataset. Available online: https://kaggle.com/jessicali9530/lfw-dataset (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Pak, M.; Kim, S. A Review of Deep Learning in Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Computer Applications and Information Processing Technology (CAIPT), Kuta Bali, Indonesia, 8–10 August 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Pareschi, F.; Rovatti, R.; Setti, G. Second-Level NIST Randomness Tests for Improving Test Reliability. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 27–30 May 2007; pp. 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G.; Bisogni, C.; Maio, L.D.; Nappi, M. An Encryption Approach Using Information Fusion Techniques Involving Prime Numbers and Face Biometrics. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2020, 5, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. A Novel Iris and Chaos-Based Random Number Generator. Comput. Secur. 2013, 36, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, V.; Chen, B. Simultaneous Biometric Verification and Random Number Generation. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Internet, Telecommunications and Signal Processing, Hobart, Australia, 11–13 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, R.; Dey, S.; Sharma, M.A.; Goel, A. A Fingerprint Based Crypto-Biometric System for Secure Communication. J. Ambient Intell Hum. Comput. 2020, 11, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanitis, A.; Taylor, C.; Cootes, T. Automatic Face Identification System Using Flexible Appearance Models. Image Vis. Comput. 1995, 13, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracevic, M.; Adamovic, S.; Miskovic, V.; Macek, N.; Sarac, M. A novel approach to steganography based on the properties of Catalan numbers and Dyck words. In Future Generation Computer Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 100, pp. 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test Name | Success Rate | Minimal Score | Average Score | Maximal Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monobit | 0.992 | 0.0031 | 0.4973 | 1.0000 |
| Frequency Within Block | 0.989 | 0.0001 | 0.4926 | 0.9999 |
| Runs | 0.989 | 0.0018 | 0.4967 | 0.9996 |
| Longest Run Ones In A Block | 0.994 | 0.0003 | 0.4978 | 0.9999 |
| Discrete Fourier Transform | 0.994 | 0.0014 | 0.4838 | 0.9771 |
| Nonoverlapping Template Matching | 1.000 | 0.9558 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 |
| Serial | 0.988 | 0.0088 | 0.4933 | 0.9976 |
| Approximate Entropy | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Random Excursion | 0.007 | 0.0000 | 0.0889 | 0.7119 |
| Random Excursion Variant | 0.732 | 0.1054 | 0.5601 | 3.6442 |
| Method | Correct Class | Correct Class. within Best 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Shape model | 70.0 | 82.0 |
| Shape-free grey model | 84.5 | 93.0 |
| Local grey-level models | 84.0 | 93.5 |
| Shape + Shape-free grey model | 94.0 | 99.0 |
| Shape + Local grey-level models | 91.5 | 97.0 |
| All three methods | 95.5 | 99.0 |
| Method | Correct Class |
|---|---|
| Face recognition | 93.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semenkov, A.; Bragin, D.; Usoltsev, Y.; Konev, A.; Kostuchenko, E. Generation of an EDS Key Based on a Graphic Image of a Subject’s Face Using the RC4 Algorithm. Information 2021, 12, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12010019
Semenkov A, Bragin D, Usoltsev Y, Konev A, Kostuchenko E. Generation of an EDS Key Based on a Graphic Image of a Subject’s Face Using the RC4 Algorithm. Information. 2021; 12(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemenkov, Alexey, Dmitry Bragin, Yakov Usoltsev, Anton Konev, and Evgeny Kostuchenko. 2021. "Generation of an EDS Key Based on a Graphic Image of a Subject’s Face Using the RC4 Algorithm" Information 12, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12010019
APA StyleSemenkov, A., Bragin, D., Usoltsev, Y., Konev, A., & Kostuchenko, E. (2021). Generation of an EDS Key Based on a Graphic Image of a Subject’s Face Using the RC4 Algorithm. Information, 12(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12010019





