Abstract
With the progressive development of a wide range of applications, interconnect things and internet of things (IoT) became an imperative required trend by industries and academicians. IoT became a base infrastructure for remote access or control depending on internet protocol (IP) networks, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. The huge application domain’s infrastructure, which depends on IoT, requires a trusted connection to guarantee security and privacy while transferring data. This paper proposes a hybrid identity authentication pipeline that integrates three schemes, namely, an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) scheme is integrated with the Ong, Schnorr, and Shamir (OSS) signature scheme and chaotic maps. The latter satisfies both security and guarantee criteria. The novelty of the proposal is in using chaotic mapping and a cyclic group to deduce a substitution box (S-Box) and a reversible matrix as a portion of the OSS signature equation. The ECC-based security part is an efficient public key cryptography mechanism with less computational cost, which makes it the most convenient to be used in IoT devices for authentication and privacy. The strength of the proposed scheme relies on combining the discrete logarithm problem (DLP) and integer factorization problem (IFP). The proposed approach was simulated using Lab-View and compared with other state-of-the art schemes. Extensive simulation results and analysis of the security and time rendering results confirmed its durability against different types of attacks, such as linear and differential attacks.
1. Introduction
In recent years, remote access technology and device control have become an imperative requirement. Particularly, this is evident nowadays due to the increased spread of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19), which necessitated the imposition of some restrictions, including mandatory social distancing in many countries. Therefore, it became clear how developing remote access communication technology is of immense importance depending on the Internet service, especially research in improving the technology of the Internet of things (IoT). The IoT is the technology to assemble devices that need to be monitored, linked, and interacted [1]. IoT is associated with great prospects of physical objects with the cyber world, such as healthcare devices, intelligent transportation systems, home appliances, sensors, and environmental monitoring [2]. Connected devices to the IoT are exponentially increasing [3], which add more security challenges that must be taken into consideration [4]. Cryptosystems based on asymmetric keys play vital roles in the security of diverse communication systems. Cryptanalysis techniques motivate researchers to develop novel signature schemes to dominate the growth in security attacks [5]. The financial field of Bitcoin has become one of the most required research areas for security from cyber-attacks. The blockchain concept succeeded in achieving that, as it provides reliable and secure decentralized solutions [6]. The elliptic curve cryptography (ECC)-based digital signature algorithm (DSA) is used for data signature and verification in wireless devices. Identity-based authentication and access control in wireless network devices help to protect from illegitimate access and preserve the security issues of the wireless nodes [7]. DSA is a robust tool in data authentication and privacy. Since the emergence of public key cryptography in 1970, many schemes have been developed, such as the efficient ECC technique [8]. The cyclic group of order p was also developed, which is isomorphic to the additive group of ((Z/pZ) ∗,.), where Z is the set of all integers, and p is a prime number.
The ECC algorithm has demonstrated a considerable effectiveness on public key cryptography [9]; as a result, an efficient digital signature approach was proposed in [10]. The strength of the scheme in [10] is its dependence on the discrete logarithm problem (DLP). On the contrary, traditional schemes are challenged by more complicated and effective attacks. This paved the way for the robust security schemes previously represented, while the era of the traditional techniques is expired [11].
To ensure a strong and efficient cryptosystem, it is necessary to achieve Shannon properties, where the permutation process is an important operation. Logistic mapping and cyclic groups are very important steps to ensure the randomness of performance. However, for a robust algorithm that can withstand different attacks, it is important to achieve confusion and diffusion properties [12]. Another goal, in addition to robustness, is to minimize execution time to be applicable in real-time applications. Logistic mapping and cyclic groups are used to generate S-Box, which is important to guarantee the cryptographic strength, such as nonlinearity, bijection, strict avalanche criterion, output bits independence criterion (BIC), and equiprobable input/output XOR distribution [13].
This work proposes a novel signature scheme based on the integration of the ECC algorithm with the Ong–Schnorr–Shamir (OSS) scheme. The robustness of the proposed approach relies on using a reversible key matrix of 4×4 as a portion of the OSS signature equation with decoding modification on ECC algorithm. This consolidation increases the degree of complexity and thus increases the confidentiality of the data. To prove the novelty and credibility of the presented technique, the new scheme was tested and demonstrated robustness against other approaches.
The rest of this manuscript is sequenced as follows. Section 2 introduces the previous work related to the proposed pipeline. Section 3 details the proposed methodology and the employed schemes (i.e., the ECC and the OSS signature schemes). Section 4 outlines the details of the proposed OSS–ECC digital signature technique. Robustness measures of the proposed scheme are demonstrated and discussed in Section 5, and conclusions are given is Section 6.
2. Related Work
Many institutions, including the US government, rely on elliptic curve (EC) technology to encrypt their data, as it is a multi-factor robust authentication and encryption technique [14]. Khatoon et al. [15] proposed an efficient and secure, bilinear pairing-based mutual authentication and key agreement protocol based on elliptic curve cryptography hardness for healthcare applications. Nikooghadam and Amintoosi [16] demonstrated the weaknesses of the protocol in [15], as it is vulnerable to known session-specific temporary information attack and is not able to provide perfect forward secrecy. Rahim et al. [17] applied the Ong–Schnorr–Shamir (OSS) subliminal channel scheme in securing data communication, which is a cryptographic method and supports verification based on the OSS digital signature scheme. Depending on OSS, as the basic signature algorithm is no longer possible, Pollard and Schnorr [18] presented an efficacious solution to solve the quadratic equation x2 + ky2 = m mod n. Their technique succeeded in obtaining the signature without any knowledge about the private key. This would be a critical point if we decided to depend on the OSS scheme for authentication. So, the authentication scheme proposed in [18] has shown more robustness and reliability in data security than in previous works.
Recently, Biswas [19] introduced an alternative approach to realize better privacy and lower decentralized identifiers by implementing ring signatures for anonymous authentication. Their approach was implemented based on an android phone with real data, and the signature was designed using the combination of Curve25519 and SHA-512 hashing algorithms. The generation and verification consumed time was 0.875 and 1.06 msec, respectively. An authentication model, called the tree of trust (VTT), for use in IoT was presented by Shingala [20]. The VTT aimed to provide embedded device-friendly entity authentication and limit the trust peripheries. Based on an embedded platform, the public key identifier was evaluated based on the ability of the elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) to verify and SHA-256 digest operations. Chen et al. [21] proposed an authentication scheme applying authenticating identity-based cryptography to protect an entire system from the compromised machine-to-machine service provider (MSP). In their scheme, partial secrets are stored in MSP to prevent it from endangering the whole system.
3. Methodology
The proposed security scheme is based on the integration of (i) the ECC algorithm, (ii) chaotic maps, and (iii) the OSS digital signature algorithm. An overview of the main components of the proposed system is given in the following subsections.
3.1. Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem (ECC)
The elliptic curve cryptosystem, or ECC, provides most of the significant features when compared with other public key algorithms [22]. With fewer mathematics, small key length, and less storage space, the ECC presents an adequate level of data security. This has led researchers to consider ECC as a lightweight authentication scheme in many IoT applications [23,24,25]. Currently, it is the security backbone for many applications and systems, such as mobile devices and network protocols [26,27]. Mathematically, the ECC can be defined using the Weierstrass equation as:
where (x, y) ∈ Zp is the set of all integers; p is a prime number >3; and a and b ∈ Zp are subject to
y2 ≡ x3 + ax + b mod p
4a3 + 27b2 ≠ 0 mod p
The EC group, or E(Zp), contains all points satisfying Equation (1) and the point at the infinity O [28]. In the literature, there are many curves introduced for ECC; see Figure 1.
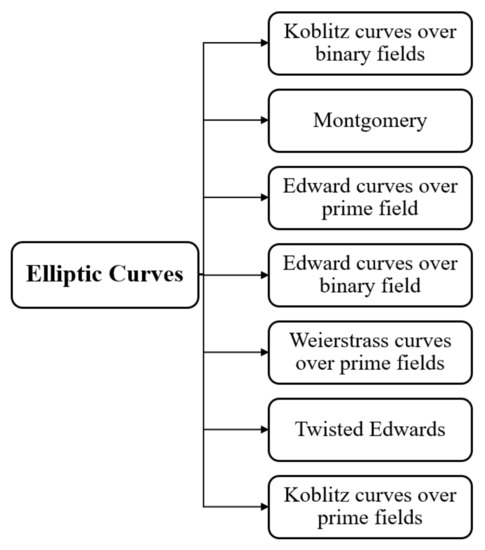
Figure 1.
Illustration of special elliptic curve types, adopted from [29].
Figure 1.
Illustration of special elliptic curve types, adopted from [29].
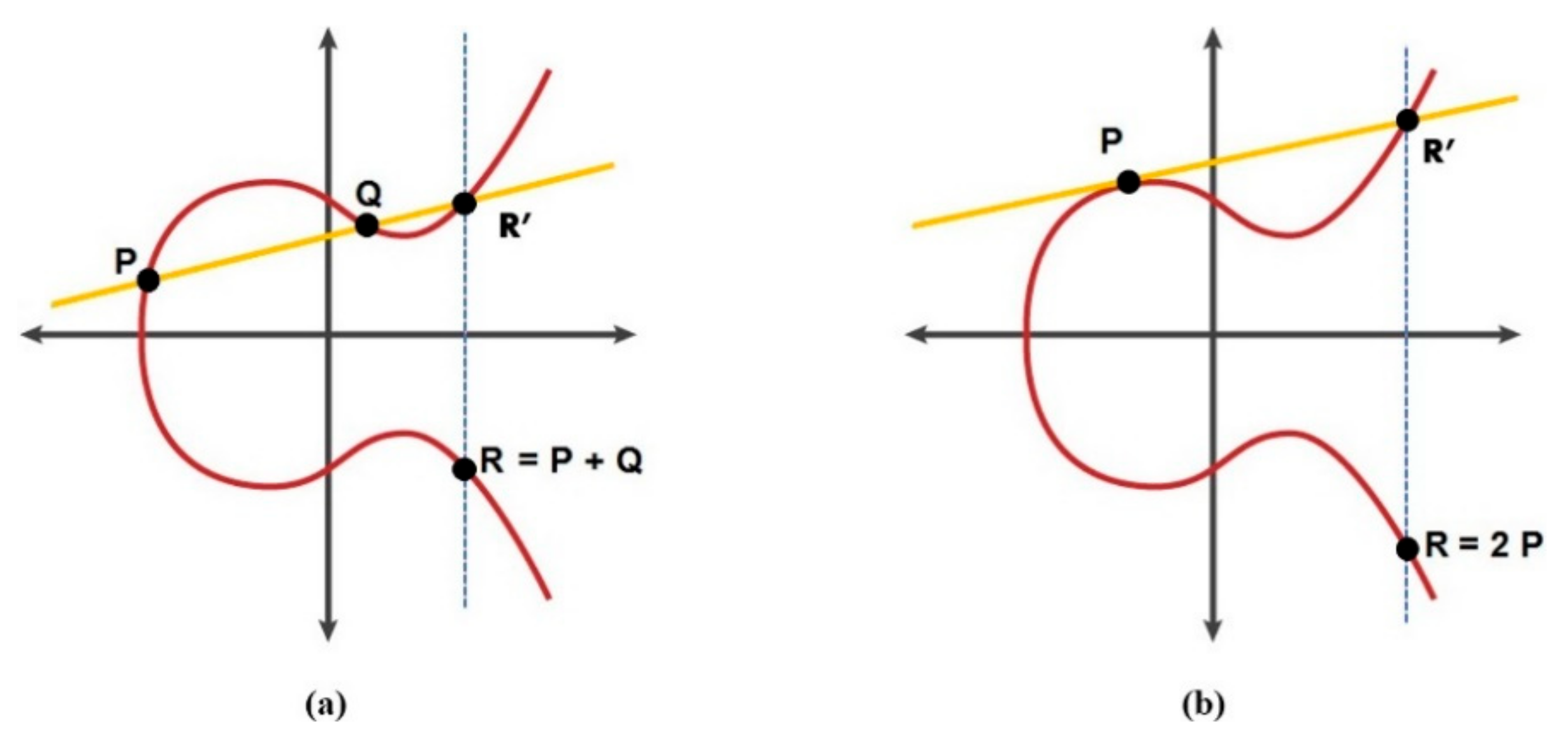
There are two fundamental mathematical point operations for the ECC algorithm: addition and multiplication. Scalar multiplication consists of point summation and doubling [30]. Figure 2 shows both operations. As demonstrated in the figure, two points are used, P = (x1, y1) and Q = (x2, y2), and the summation point R = (x3, y3) can be estimated in two different scenarios:
- (1)
- If P > Q: R = P + Q, which can be calculated by drawing a line passing through P and Q, then R is the mirror point of the third intersection point (R′), as shown in Figure 2a.
- (2)
- If P = Q: R = 2Q, which can be estimated by drawing a tangent line through Q, then the doubling point R is the mirror point of the second intersection point, as clarified in Figure 2b.wherex3 = µ2 − x1 − x2 mod pandy3 = µ (x1 − x3) − y1 mod p
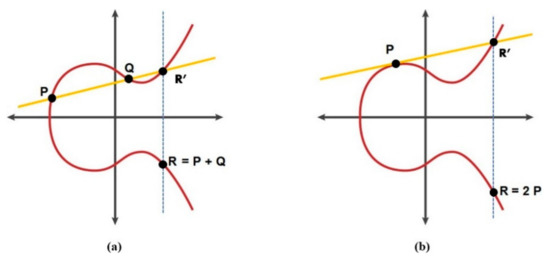
Figure 2.
Demonstration of elliptic curve mathematical operations: (a) point summation and (b) point doubling.
Figure 2.
Demonstration of elliptic curve mathematical operations: (a) point summation and (b) point doubling.
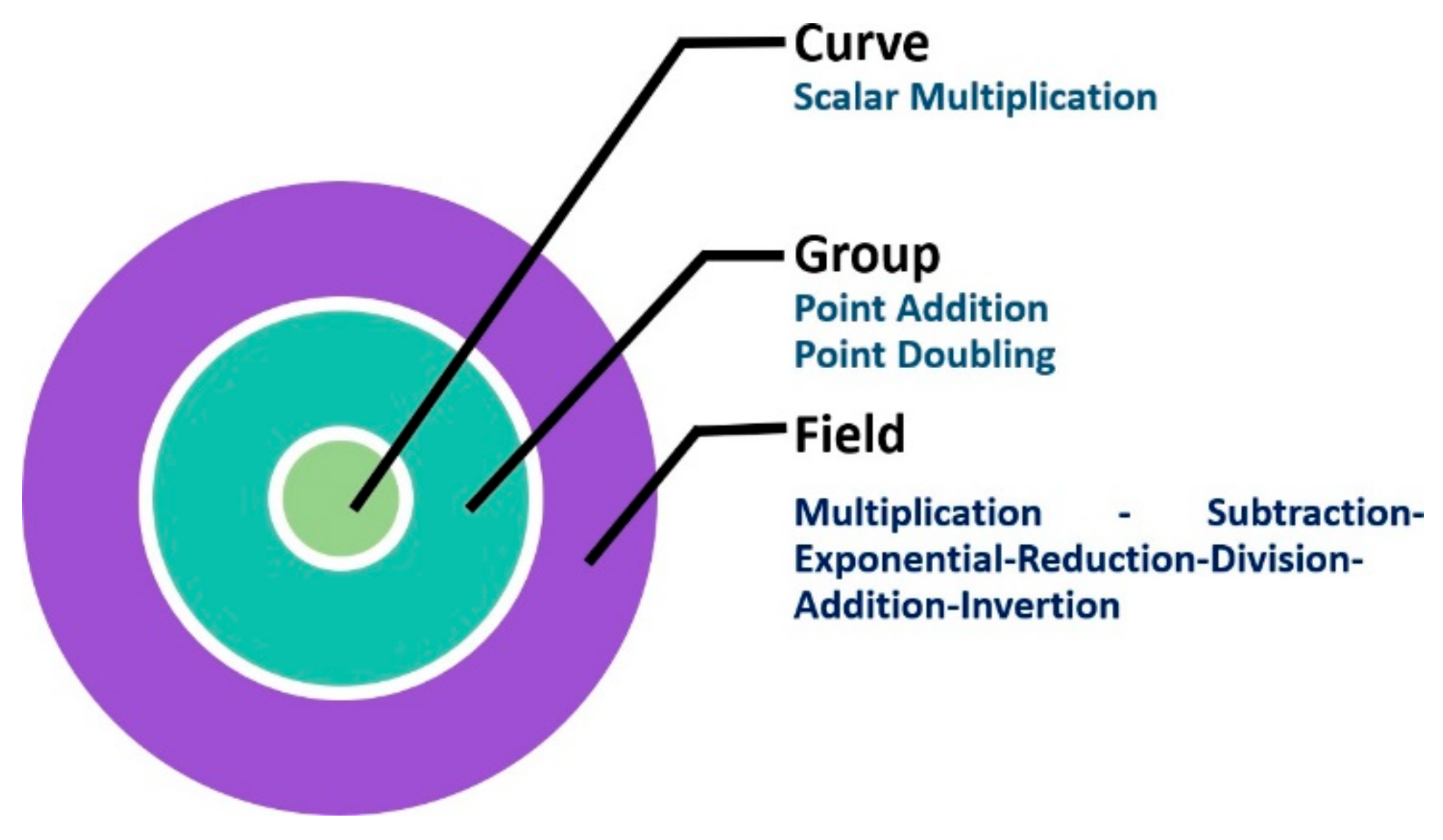
ECC computations depend on the nature that they are defined for, which can be finite field operations, EC group operations, or curve operations. Figure 3 shows the differences between these computations.
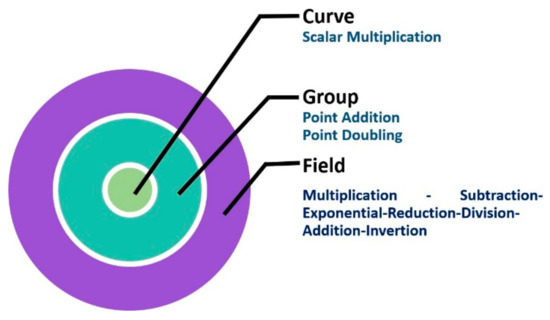
Figure 3.
Illustration of elliptic curve cryptography operations.
3.2. OSS Signature Scheme
Rapidity and guarantee are prime features in any authorized signature scheme. Any technique that satisfies those two features will be realizable and effective in many fields. Ong, Schnorr, and Shamir designed an effective scheme that is based on a functional quadratic equation [31]. Their scheme has an importance advantage of providing speedy signature generation and verification, while requiring only a single inversion and two modular multiplications. However, three multiplications are needed for validation.
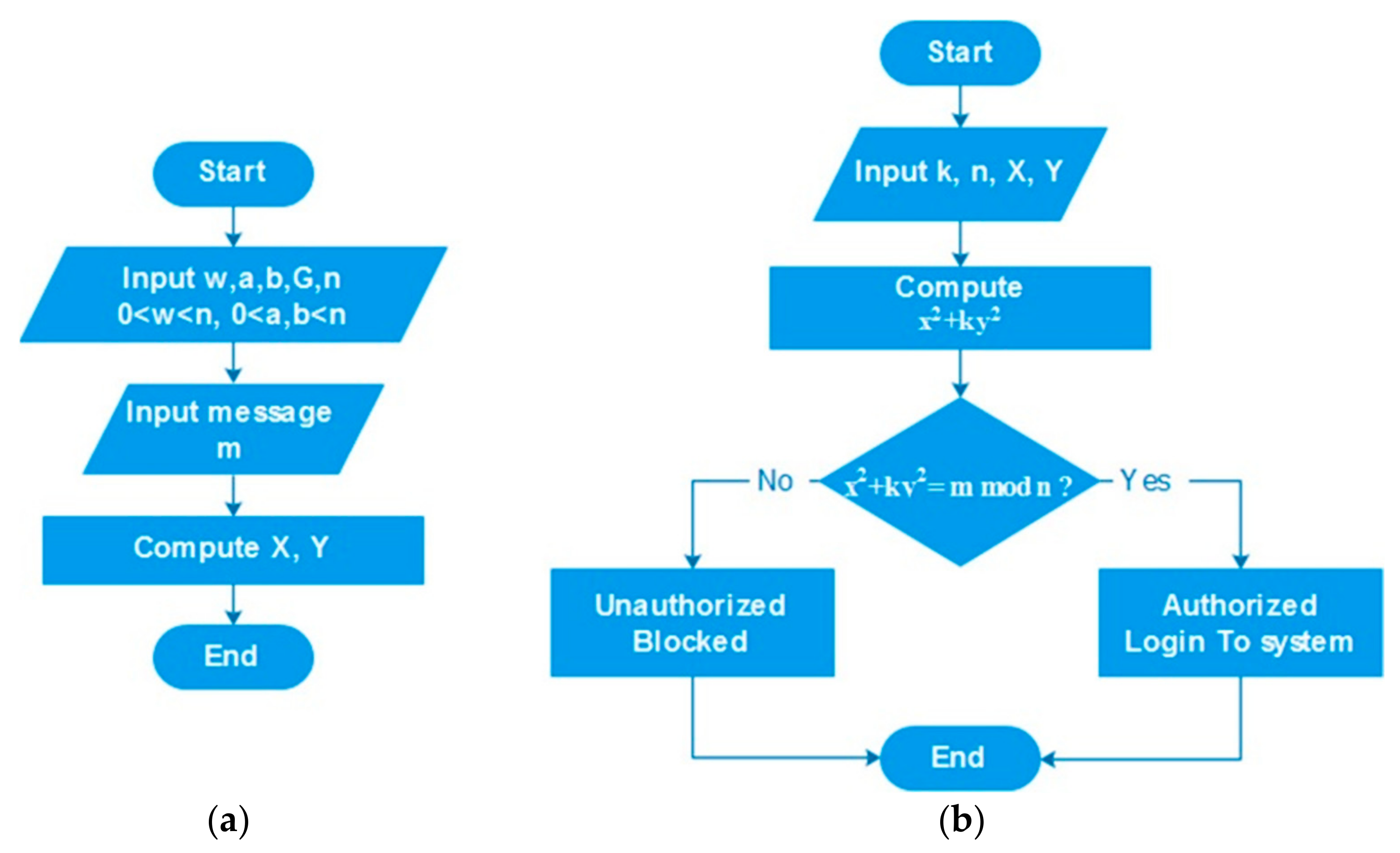
The robustness of the OSS is in its underlying mathematical equation: x2 + ky2 = m mod n, which is hard to solve. Here, m represents the original message, k is the public key, and n is derived from Euler’s theorem [32]. Figure 4 illustrates the OSS scheme’s flowchart. The receiver (interrogator) checks correctness of the previous formula using the received pair (x, y) generated at the receiver. The computation of w−1(mod n) and k = w2(mod n), where k, n, and w are the public key and w−1 is the private key, is illustrated at Figure 4.
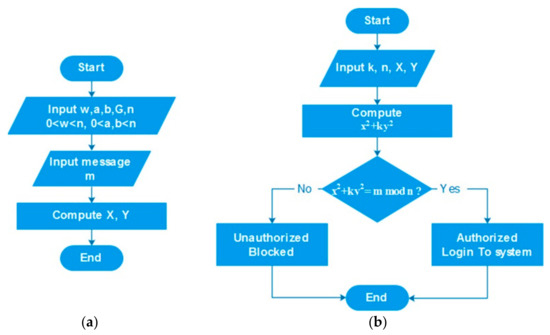
Figure 4.
Traditional Ong–Schnorr–Shamir (OSS) signature scheme: (a) transponder and (b) interrogator flowcharts.
3.3. Logistic Map and Cyclic Group
The third scheme that is utilized in our system is chaotic maps. Chaotic systems are strong tools to select random numbers. They have desirable features, such as ergodicity, complex structural, high randomness, and mixing, according to the following equation:
where x(n) is the initial condition, and λ is the system parameter that is used as a key [33]. The above map is chaotic when 3.9 < λ < 4.0.
x(n + 1) = λx(n)(1 − x(n))
If every element in a given group (G) can be represented as a power αr (r is integer) of a fixed element , then G is said to be a cyclic group. Here, α is known as the generator of group, which can be finite or infinite [34]: αr modulo p; here, r and p is a prime number. By considering p = 17, each number in {3, 5, 6, 7,10, 11, 12, 14} is said to be a generator.
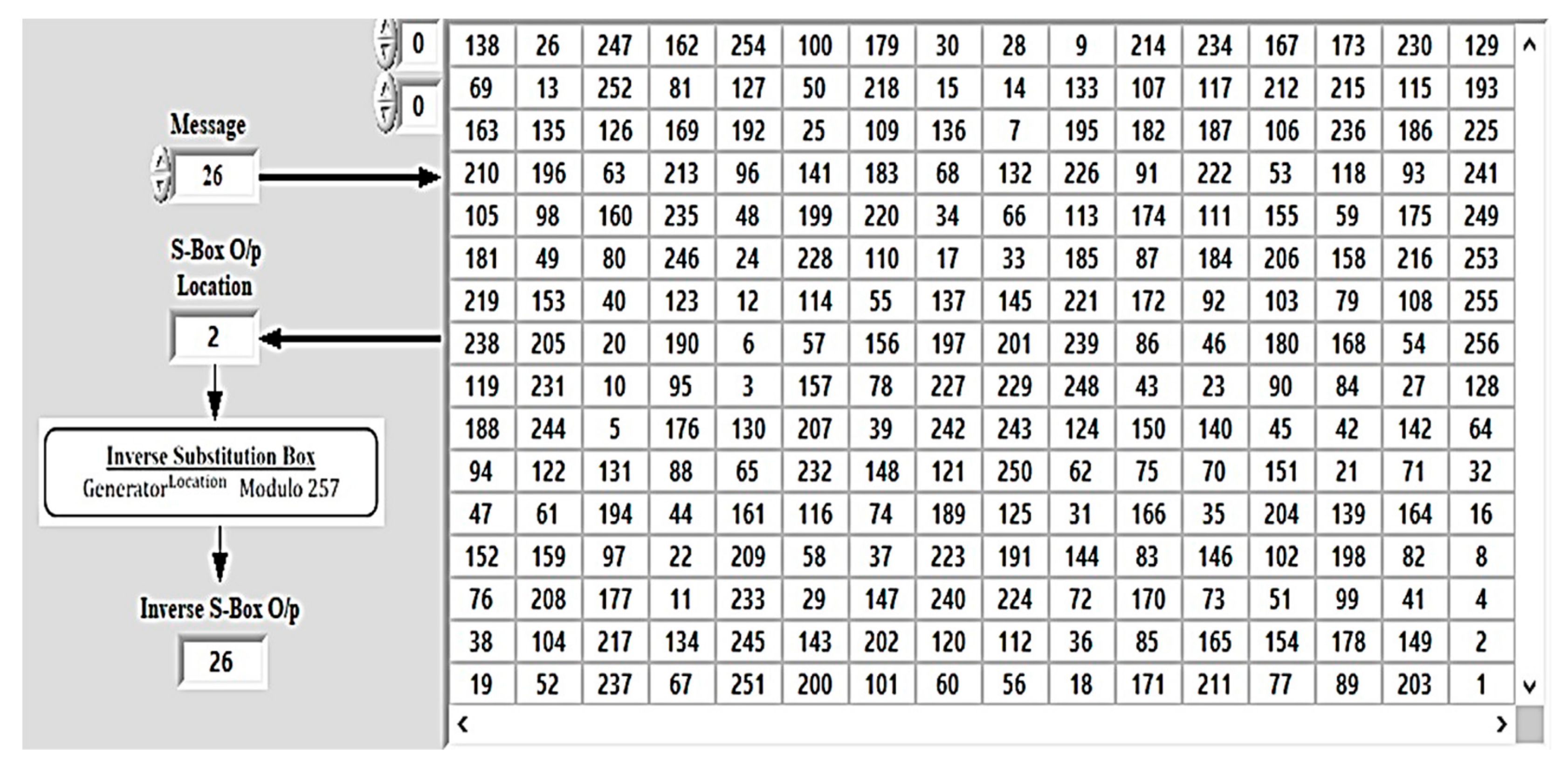
According to the cyclic group theory, it can be noticed that the prime number 257 has 128 generators, and we can choose between them. A chaotic equation is used to choose randomly between the 128 generators, and the seed number for this chaotic equation is considered as the key. Table 1 contains the 128 generators of 257.

Table 1.
The generator list of the prime number 257.
4. The Proposed Oss–ECC Digital Signature
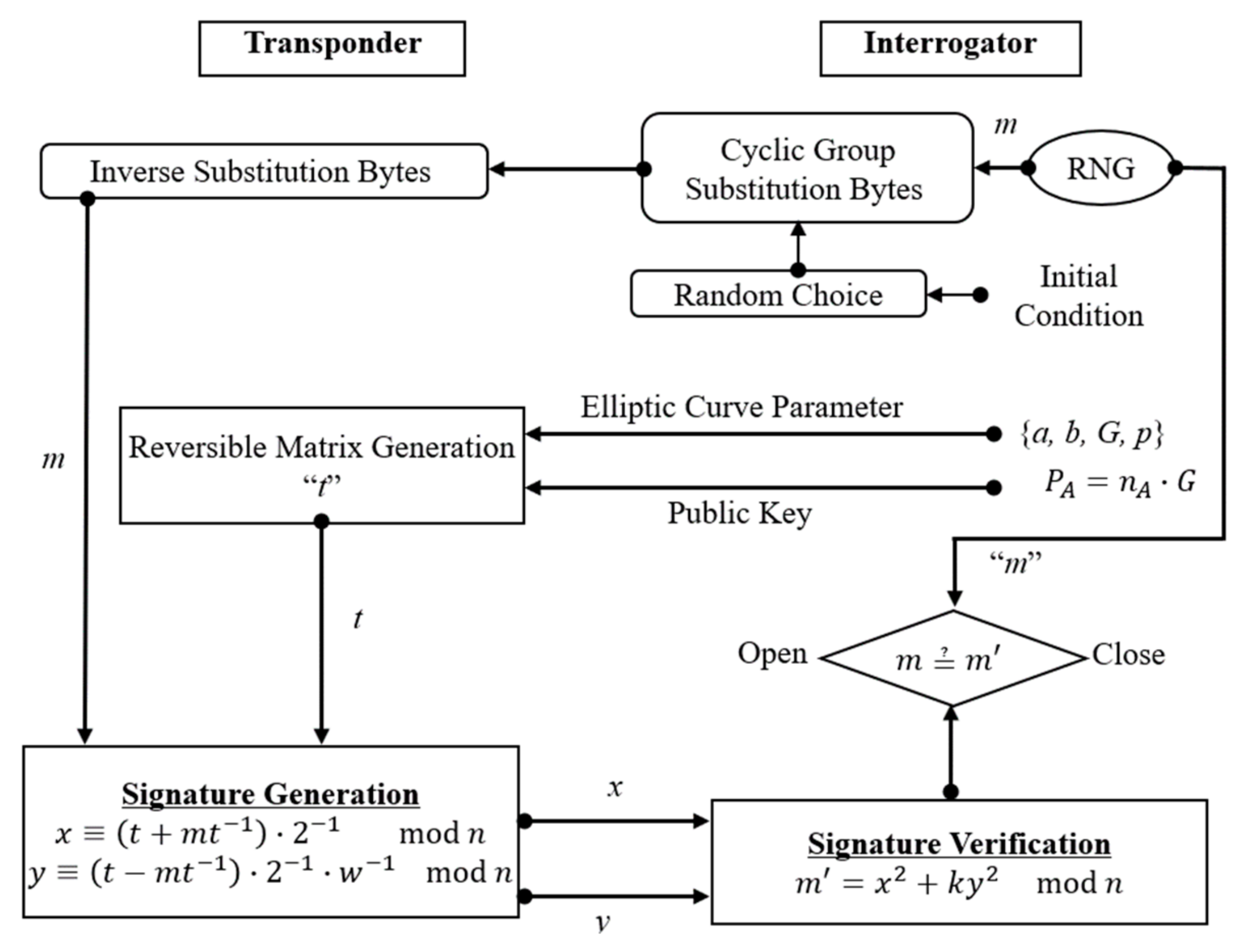
Figure 5 presents the flowchart of the proposed data signature. The interrogator sends data to the transponder, which are the S-Box output with EC parameters and the public key. The transponder receives the data and performs inverse S-Box to obtain the message “m” and uses the public key and EC parameters to calculate “t”. Using t and m, the transponder generates the signature x, y and sends it to the interrogator, which verifies the signature of the transponder and produces m. As mentioned above, the proposed pipeline utilizes three hybrid authentication schemes: the ECC algorithm, chaotic maps, and the OSS digital signature algorithm. The robustness of the proposed technique depends on the hardness of the ECDLP and the modifications using chaotic mapping and cyclic groups. The integration of those three schemes is intended to increase the privacy and makes it more efficient than traditional authentication schemes. Additionally, the signature generation became faster than before and the inverse of the key matrix became unnecessary.
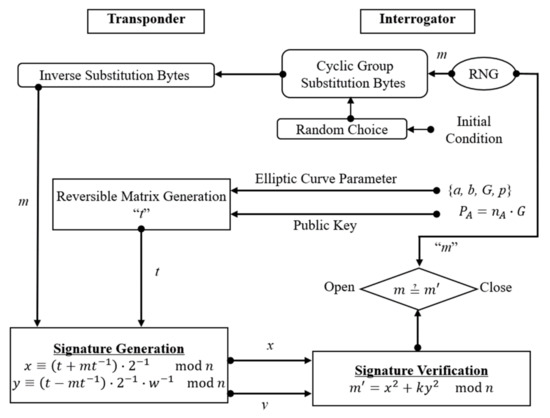
Figure 5.
The proposed OSS digital signature flowchart based on elliptic curve cryptography (ECC).
4.1. Substitution-Box (S-Box) Construction
Substitution-Box (S-Box) is an important concern in constructing any secure cryptosystem. S-Boxes are used to provide diffusion and confusion [35]. Various work has been proposed in the literature. For example, Ruming et al. [36] proposed an S-box that depended on the iteration of continuous chaotic maps. Their key-dependent S-box was constructed with the logistic map. Guo et al. [37] presented an extended method for designing S-Box based on three-dimensional chaotic Baker maps. This depends on obtaining strong 8 × 8 S-boxes. Three-dimensional chaotic Baker maps present an intensive chaotic character in addition to resist several attacks. In this paper, an 8-bit input/output S-box was constructed based on the cyclic group. Unlike previous work, it is a 16 × 16 S-box. Table 1 presents all possible generators for prime number 257, which was used to construct the required S-Box based on Equation (8) of the 2D logistic equation.
4.2. Random Choice
In this process, one random generator (RNG, α) is chosen from Table 1, which is used to construct the required S-Box, by using the 2D logistic equation to select the random generator as follows:
where x(n) is the initial (integer number) condition, and λ is the system parameter, which works as the secret key. The map is chaotic for 3.9 < λ < 4.0, which is used as a key. The S-Box of each round is computed by calculating the cyclic group of the generator using:
where r . The substitution process is based on replacing the 8-bit input with the “location of the similar 8 bits from the cyclic group-1”. The inverse of the substitution process relies on computing:
x (n + 1) = [λx(n) (1 − x(n)) Modulo 128] + 1
αr modulo 257
α((8 bits)input+1) modulo 257
The resulted data output is the same as the original data input. Figure 6 presents the cyclic group outputs with length 256. This process is simulated using Lab-View, and the results are organized as shown.
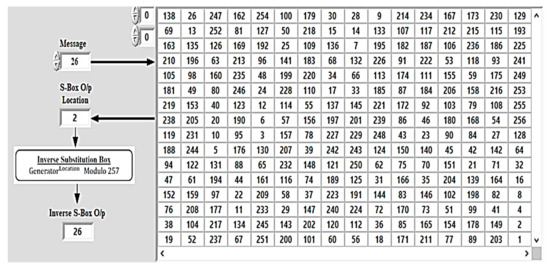
Figure 6.
Substitution-box (S-Box) construction using Lab-View.
4.3. Signature Generation and Verification
The interrogator (User A) shares information from the ECDSA with the transponder (User B). Information that is shared is {a, b, G, p}, where a and b are the coefficients of the ECC mentioned in (1), G is the generator basepoint, and p is the prime number equal to n = [P × Q], which is the Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman (RSA) moduli. Both interrogator and transponder select their private key {nA, nB} randomly from the interval [1, p − 1]. Equation (11) shows the generation of the interrogator’s public key.
PA = nA·G
The transponder uses the interrogator’s public key to generate the key pair (KP) matrix to generate the initial key VI = (x, y), by multiplying its private key by the public key of the interrogator.
where
KP = nB·PA = nB·nA·G = (x, y)
V1 = x·G = (V11, V12)
V2 = y·G = (V21, V22)
Now, the transponder (User B) uses the resulted KP matrix to generate a reversible matrix “t”, where t = t−1. Then, the inverse of the KP matrix is not needed. The reversible matrix “t” is a 4 × 4 matrix that is generated as follows:
which can be partitioned as .
The proposed technique considers that VA equals , then the values of the other sections can be calculated by solving VB = I − VA, VC = I + VA, VA + VD = 0, where I is the identity matrix. Then, the transponder generates the signature by both main equations
where m is the message to be signed, w is the random integer with a range 1 to p − 1, and t is the reversible matrix, so that the great common divisor or GCD (t, n) =1. The signature {x, y} must be sent back to the interrogator, which must test whether
x ≡ (t + mt−1)·2−1 mod n
x ≡ (t − mt−1)·2−1w−1 mod n
x2 + ky2 ≡ m mod n
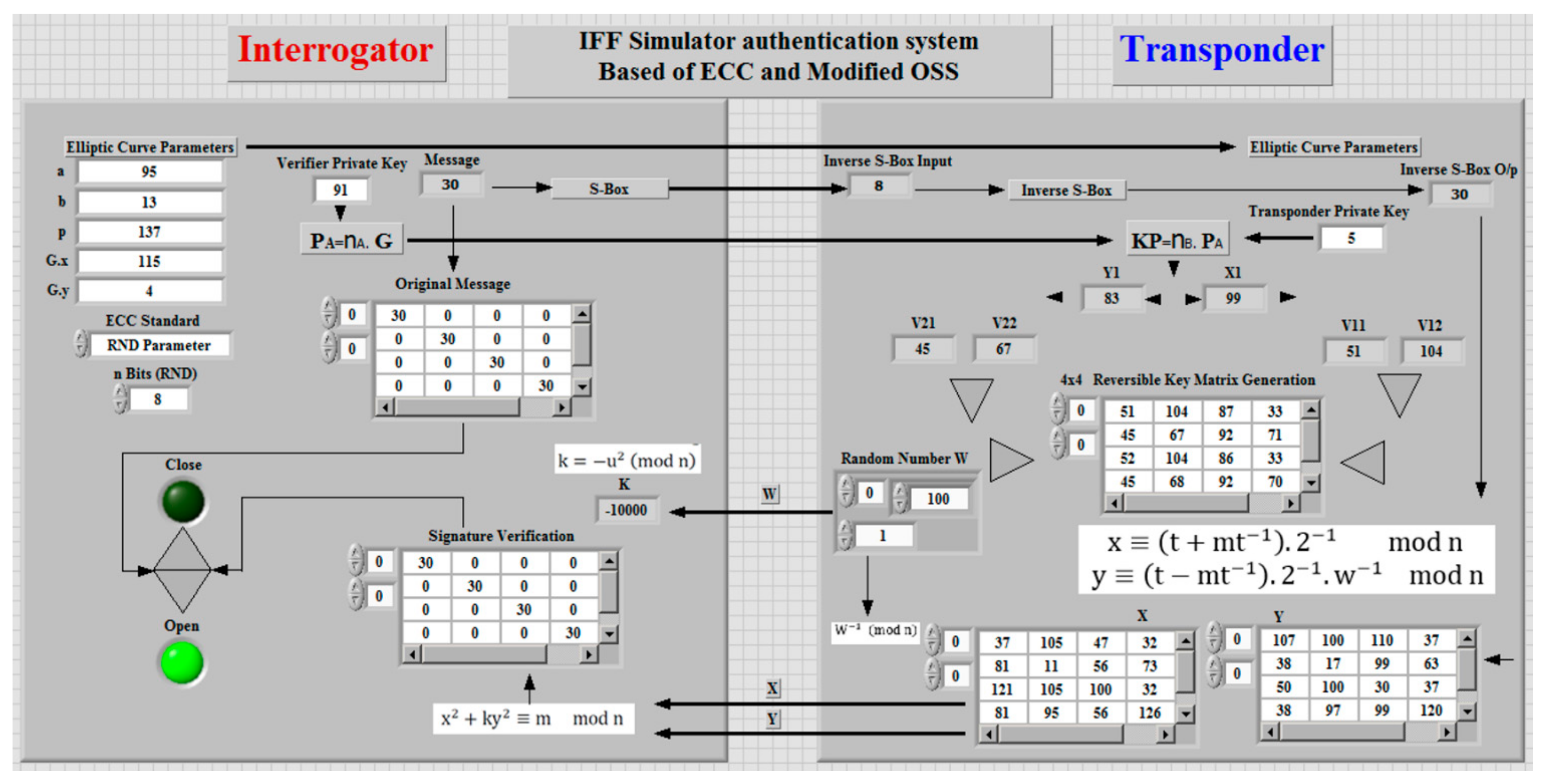
A simulation of the proposed system with Lab-View is demonstrated in Figure 7. The processes can be summarized as follows:
- Transponder and interrogator agree on parameters of the elliptic curve function;
- The transponder sends a signal with digital signature to interrogator;
- Interrogator verifies the signature.
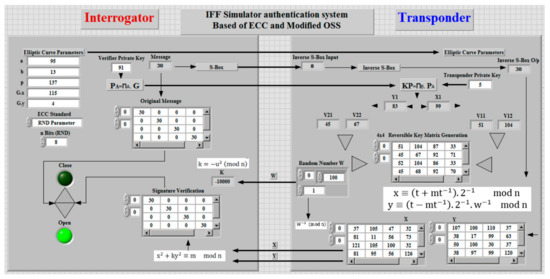
Figure 7.
The proposed system layout implemented with Lab-View.
Figure 7.
The proposed system layout implemented with Lab-View.
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
The quantitative/qualitative performance evaluation of both the traditional and proposed technique could be measured using various parameters, including (i) timing analysis, (ii) security analysis, and (iii) robustness to security attacks. In particular, timing analysis is among the critical points in any digital signature’s schemes, namely, the encryption speed plays a vital role in real-time applications. The longer the encryption/decryption process is, the less suitable the method for some applications, such as video conferencing and live streaming. Thus, a comparison of the execution time of the proposed scheme and different digital signature schemes (signature generation) was conducted.
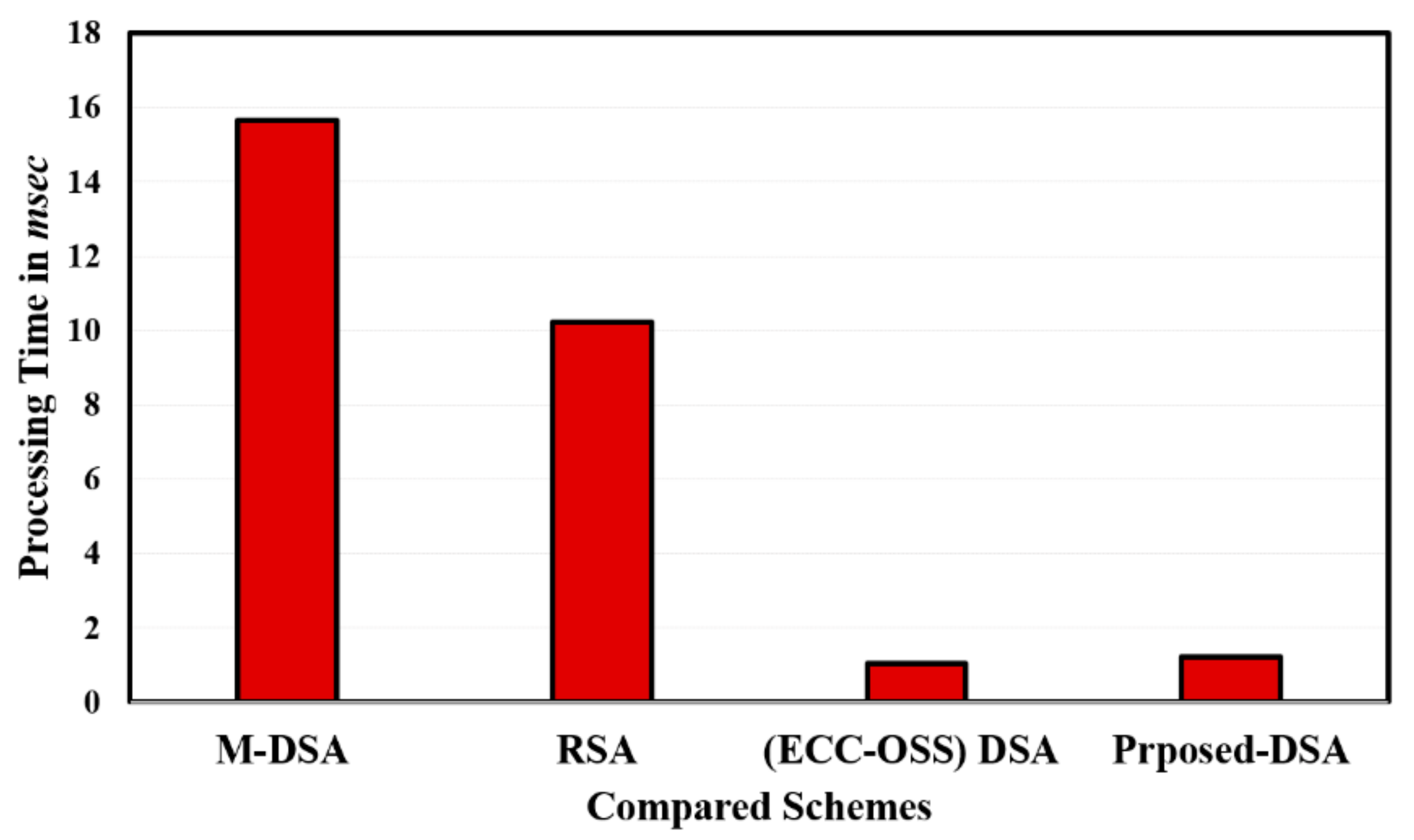
Figure 8 summarizes the comparison with the approach proposed by Al-Sewadi et al. [36], where their authentication algorithm based on NIST-DSA is performed. As readily seen in the figure, the resulting data highlight the high speed of applying the ECC with the OSS scheme with a key length of 1024. However, the proposed method is slightly faster than OSS–ECC as an additional level of S-Box is added to the total processing time. It is worth mentioning that for the RSA algorithm to achieve the same level of security as the ECC technique, it basically requires an increased key length. Although RSA introduces simple computations, the ECC depends on DLP with a lesser key length [37]. Table 2 summarizes the comparative results between RSA, OSS–ECC, and the modified OSS–ECC in signature computation time with respect to key length, which achieved the same security level for all compared schemes. Moreover, Table 2 shows the signature time between RSA, OSS–ECC, and modified OSS–ECC. It is clear that the proposed modification cost is slightly higher than OSS–ECC, as an additional step of S-box and reversible matrix is added to the traditional OSS–ECC scheme. Table 3 summarizes the performance comparison between RSA, EC–DSA, OSS–ECC, and the proposed digital signature. As can be seen, the OSS–ECC and the modified OSS–ECC have the best performance.
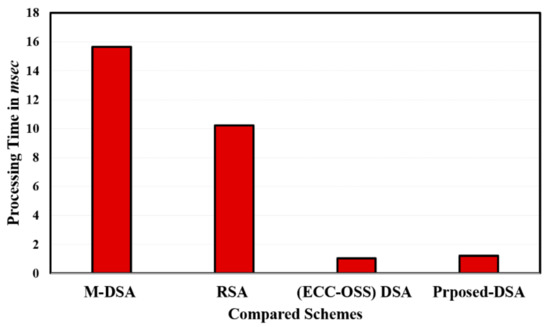
Figure 8.
Comparison of total processing time of the proposed scheme and other state-of the-art schemes proposed in [32]. Note that “RSA”, “DSA”, “OSS”, and ““ECC” stand for Rivest, Shamir and Adleman; digital signature algorithm, Ong, Schnorr, and Shamir; and elliptic curve cryptography, respectively.

Table 2.
Signature generation computational cost (in milliseconds) of different signature schemes and the proposed scheme. Note that “RSA”, “DSA”, “OSS”, and ““ECC” stand for Rivest, Shamir and Adleman; digital signature algorithm, Ong, Schnorr, and Shamir; and elliptic curve cryptography, respectively.

Table 3.
Performance comparison between RSA, DSA, OSS–ECC, and proposed digital signature.
In addition to the timing analysis, the strength of the proposed S-Box was measured using two strong cryptanalytic attacks: differential and linear attacks. Typically, differential cryptanalysis aims to detect the “difference” between related encrypted plaintexts. The plaintexts may vary by a few bits. It attacks depending on a chosen plaintext: the attacker chooses the plaintext to be encrypted without the key, and then encrypts the related plaintexts [38]. The difference distribution tables of cyclic group sub-bytes were constructed, a worst case assumption was made in our consideration, which has a probability of 22/256 with input data difference = {0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, as illustrated in Table 4, except the cases of a one bit input/output difference, which are considered to be impossible (probability is zero). On the other hand, linear cryptanalysis exploits the high probability occurrences in bits of plaintext, ciphertext, and sub-key [39]. Such an expression takes the form:
where x represents the input x = [x1, x2…] and y represents corresponding output y = [y1, y2…]. Equation (18) represents the exclusive-OR “sum” of u input bits and v output bits [40]. If the scheme shows a tendency to hold with high probability or not for Equation (18), this illustrates failure in randomization abilities [41,42]. The main factor that assesses the efficiency of the scheme is the linear probability bias, which is the amount of probability of a linear expression deviating from . The higher the magnitude of the probability bias, |PL|, the worse the security is [36]. In linear cryptanalysis, the relations between two bits of cyclic group sub-bytes can be found; the probability ( P) of these relations is restricted by as illustrated in Algorithm 1.
x1 ⊕x2 · xu ⊕ y1 ⊕ y2 · yv = 0

Table 4.
Difference distribution table for input difference ΔX = {0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0}.
Finally, the performance of the proposed technique can be evaluated by its robustness to security attacks, such as (i) brute-force, (ii) password sniffing, (iii) man-in-the-middle, and (iv) replay attacks. The former is the most popular public key attack, which tries to derive the private key from the know public key [43]. A given system is said to be secured against this type of attack if its key length is ≥70 bits with a probability of 270 [44]. In the proposed scheme, the key length is considered to be the summation of the ECC key length with a probability of 2163 bits in addition to 27 generators of the proposed S-Box. Thus, the robustness of the proposed scheme implies that if a third party has the main parameters of EC function, {a, b, p, G} and {PA, k}, which are the public keys, it is not possible to estimate the signature {x, y} using trial and error with a probability of 2(163+7) bits. Second, the password sniffing attack eavesdrops the network to intercept keys or passwords by capturing passing data. Attackers analyze data to predict keys. Encryption algorithms are the best way to be resilient against sniffing attack. The proposed scheme basically depends on the ECC, which works as a firewall against that types of attack.
Third, Pollard and Schnorr [18] succeeded in forging the signature without solving the quadratic equation. Their scheme approves its strength, as the signatures x and y are a 4 × 4 matrix with a large key length, which makes it hard to estimate. If a third party tried to estimate the second part of signature y where the attacker intercepts and/or modifies the data in transit, a constant value of x could be assumed. Here is a quadratic equation with a complex term. It is hard to calculate the square root to obtain y, while estimating x and fixing the second part y equals factoring n. Such quadratic equation is difficult to solve, which can be explained in the following algorithm (Algorithm 1):
| Algorithm 1 Steps for calculating quadratic equation roots |
| 1. Given n = P × Q, where {P, Q} are unknown prime numbers; |
| 2. Choose w and Compute w−1(mod n); |
| 3. Scheme A: requires signatures of random messages (m) to run, and m must be signed using the private key w−1; |
| 4. Recall Scheme (A) using the signatures and the public keys {k, n}; |
| 5. w′ is computed by scheme (A) as follows: |
| 6. With a probability of, the are the two prime numbers {P, Q}; |
| 7. According to the previous steps, if, then choose another (w) and reiterate all steps; |
| 8. After (n) rounds, the possibility of computing the factorization is. |
Last, in replay attacks, the attackers try to intercept and record the plaintext. The captured data are used another time to try and recreate authentication. The hybrid ECC is used in the declared scheme, as the main parameters a, b, p, and G are generated randomly for each iteration, i.e., it has completely different signatures in each round. Therefore, the modified ECC–OSS approved its strength against this type of attack.
6. Conclusions
A hybrid scheme of an elliptic curve cryptosystem with a modified digital signature scheme was presented in this paper. A logistic map was used to produce the S-Box in addition to a reversible matrix as a portion of the OSS signature equation. The goal was to propose a robust scheme with minimal execution time. The illustrated results documented the robustness and efficiency of our technique against cryptanalysis in terms of implementation and security standardization. However, it requires a slightly longer processing time than DSA without S-Box due to the added complexity of combining the integer factorization problem and discrete logarithm problem. Moreover, the proposed scheme has a high immunity to resist the differential cryptanalysis. This scheme is comparable to existing, related schemes; it is also applicable to resource constrained devices, such as IoT network devices.
Author Contributions
A.T., M.A.M., A.S.S., and F.K.: conceptualization. S.H.A.E. and A.T.: methodology, formal analysis, and visualization. S.H.A.E., A.T., and F.K.: original draft preparation. S.H.A.E.: software and data curation. A.T., M.A.M., A.S.S., and F.K.: validation and supervision. A.T. and F.K.: investigation. A.T., S.H.A.E., M.A.M., A.S.S., and F.K.: review and editing final version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DLP | Discrete Logarithm Problem |
| DSA | Digital Signature Algorithm |
| ECC | Elliptic Curve Cryptography |
| ECDLP | Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem |
| ECDSA | Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm |
| GCD | Great Common Divisor |
| IFP | Integer Factorization Problem |
| IOT | Internet of Things |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| KP | Key Pair |
| MSP | Machine Service Provider |
| OSS | Ong, Schnorr, and Shamir |
| RNG | Random Generator |
| RSA | Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman |
| S-Box | Substitution Box |
| TTV | The Tree of Trust |
References
- El-hajj, M.; Fadlallah, A.; Chamoun, M.; Serhrouchni, A. A survey of internet of things (IoT) Authentication schemes. Sensors 2019, 19, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaila, M.G.; Neto, M.; Fernandes, D.A.; Freire, M.M.; Inácio, P.R. Challenges of securing Internet of Things devices: A survey. Secur. Priv. 2018, 1, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symanovich, S. The future of IoT: 10 predictions about the internet of things. Cyber Secur. Blog Nort. Symantec Accessed 2019, 2–17. Available online: https://us.norton.com/internetsecurity-iot-5-predictions-for-the-future-of-iot.html (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Naeem, M.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Mahmood, K.; Karuppiah, M.; Kumari, S. A scalable and secure RFID mutual authentication protocol using ECC for Internet of Things. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2019, 33, e3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, S.; Li’skiewicz, M. Algorithm Substitution Attacks from a Steganographic Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, TX, USA, 30 October–3 November 2017; pp. 1649–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Raikwar, M.; Gligoroski, D.; Kralevska, K. SoK of Used Cryptography in Blockchain. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 148550–148575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahmud, A.; Morogan, M. Identity-based Authentication and Access Control in Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 41, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Dutta, M.; Granjal, J. A survey of key bootstrapping protocols based on public key cryptography in the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 27443–27464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Reiser, H.P. Distributed Applications and Interoperable Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ghofar, A.; Hardi, M.; Firdaus, M.N.; Shidik, G.F. Digital Signature Based on PlayGamal Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication (iSemantic), Semarang, Indonesia, 7–8 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rabah, K. Security of the Cryptographic Protocols Based on Discrete Logarithm Problem. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 5, 1692–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Farah, M.A.B.; Farah, A.; Farah, T. An Image Encryption Scheme Based on a New Hybrid Chaotic Map and Optimized Substitution Box. Nonlinear. Dyn. 2020, 99, 3041–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesmi, R.; Farah, M.; Kachouri, A.; Samet, M. Chaos-Based Designing of a Highly Nonlinear S-Box Using Boolean Functions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 12th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD15), Mahdia, Tunisia, 16–19 March 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Khatwani, C. Cryptanalysis and improvement of ECC based authentication and key exchanging protocols. Cryptography 2017, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Alrubaian, M.; Alamri, A. Privacy-Preserved, Provable Secure, Mutually Authenticated Key Agreement Protocol for Healthcare in a Smart City Environment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47962–47971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikooghadam, M.; Amintoosi, H. Cryptanalysis of Khatoon et al.’s ECC-based Authentication Protocol for Healthcare Systems. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08424. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, R.; Pranolo, A.; Hadi, R.; Asyidah, R.R.; Nurdiyanto, H.; Napitupulu, D.; Ahmar, A.; Abdillah, L.; Abdullah, D. Digital Signature Security in Data Communication. Adv. Intell. Syst. Res. (AISR) 2017, 144, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, J.; Schnorr, C. An efficient solution of the congruence x2 + ky2 = m(mod n). IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1987, 33, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S. Enhancing the Privacy of Decentralized Identifiers with Ring Signatures. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shingala, K. An Alternative to the Public Key Infrastructure for the Internet of Things. Master’s Thesis, Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskaplige Universitet, Trondheim, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shuo, C.; Ma, M.; Luo, Z. An authentication scheme with identity-based cryptography for M2M security in cyber-physical systems. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2016, 9, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Solanki, A.; Nayyar, A.; Qureshi, B. Elliptic Curve Signcryption-Based Mutual Authentication Protocol for Smart Cards. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletsky, K. RSA vs. ECC Comparison for Embedded Systems. 2015. Available online: http://ww1.microchip.com/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Seok, B.; Park, J.; Park, J. A Lightweight Hash-Based Blockchain Architecture for Industrial IoT. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, B.A.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Barnawi, A.; Al-Barakati, A.; Shon, T. An Anonymous Device to Device Authentication Protocol Using ECC and Self Certified Public Keys Usable in Internet of Things Based Autonomous Devices. Electronics 2020, 9, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Zou, X.; Lin, H.; Cheng, J. Design of an elliptic curve cryptography processor for rfid tag chips. Sensors 2014, 14, 17883–17904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, U.; Mohanta, B.K.; Jena, D.; Sobhanayak, S. An Ecc Based Lightweight Authentication Protocol for Mobile Phone in Smart Home. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Rupnagar, India, 1–2 December 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A. Computational Number Theory; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Azarderakhsh, R.; Reyhani-Masoleh, A. Efficient FPGA implementations of point multiplication on binary Edwards and generalized Hessian curves using Gaussian normal basis. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2011, 20, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlwend, J. Elliptic Curve Cryptography: Pre and Post Quantum; Technical Report; MIT, Tech. Rep: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Coppersmith, D.; Stern, J.; Vaudenay, S. Attacks on the Birational Permutation Signature Schemes. In Annual International Cryptology Conference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, H.; Schnorr, C.P.; Shamir, A. An Efficient Signature Scheme Based on Quadratic Equations. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, New York, NY, USA, 30 April–2 May 1984; pp. 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; He, H. A pseudorandom number generator based on piecewise logistic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 83, 2373–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logachev, O.A.; Salnikov, A.A.; Yashchenko, V.V. Boolean Functions in Coding Theory and Cryptography; American Mathematical Soc.: North Providence, RI, USA, 2012; Volume 241. [Google Scholar]
- Ruming, Y.; Jian, Y.; Jian, W.; Xiuming, S.; Xiqin, W. Designing key-dependent chaotic S-box with larger key space. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Yong, C.; Xiaofeng, L. An extended method for obtaining S-boxes based on three-dimensional chaotic Baker maps. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 31, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, I.; Hayat, U.; Bustamante, M.D. Image Encryption Using Elliptic Curves and Rossby/Drift Wave Triads. Entropy 2020, 22, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sewadi, H.A.; Rifaat, M.M. Reduced time complexity variant of digital signature algorithm. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bafandehkar, M.; Yasin, S.M.; Mahmod, R.; Hanapi, Z.M. Comparison of ECC and RSA Algorithm in Resource Constrained Devices. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on IT Convergence and Security (ICITCS), Macao, China, 16–18 December 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, E.; Misenar, S.; Feldman, J. CISSP Study Guide; Newnes: New South Wales, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Standaert, F.X.; Piret, G.; Quisquater, J.J. Cryptanalysis of Block Ciphers: A Survey; UCL Crypto Group: Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Chen, S. Cryptanalysis of Reduced-Round SPECK. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63045–63056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heys, H.M. A tutorial on linear and differential cryptanalysis. Cryptologia 2002, 26, 189–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tilborg, H.C.; Jajodia, S. Encyclopedia of Cryptography and Security; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).