Face Recognition Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
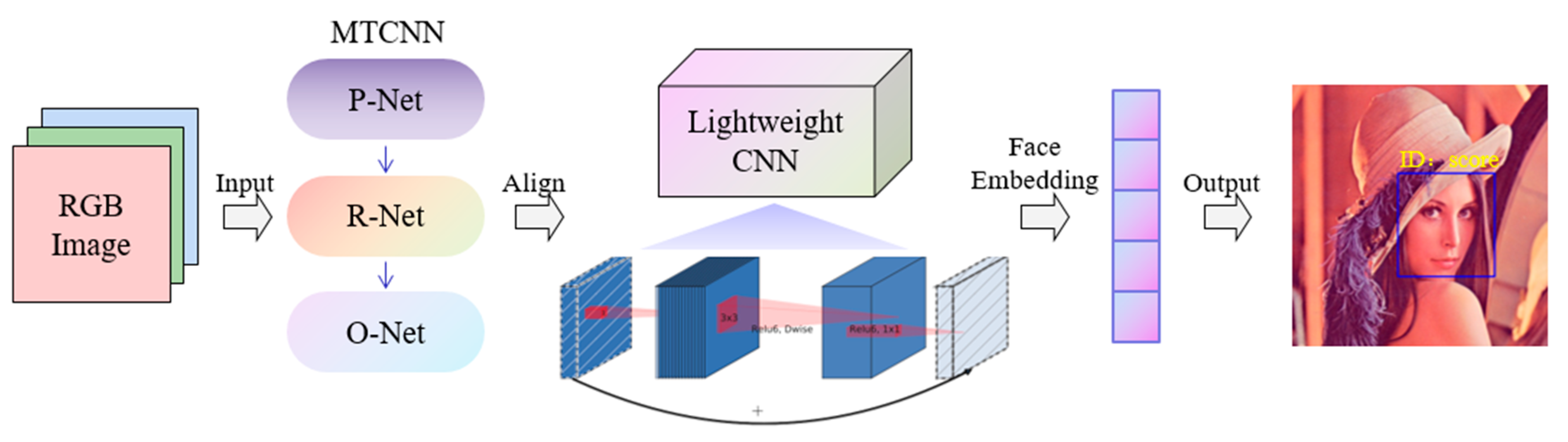
:1. Introduction
- We propose three improved structures based on the channel attention mechanism: the depthwise SE module, depthwise separable SE module, and linear SE module. We applied these to the lightweight network, adding a small number of parameters and calculations, and verified their effectiveness on various datasets.
- Combined with the additive angular margin loss function, we propose a novel training method for the face recognition task, which improves the feature extraction ability of the student network, and realizes the compression and knowledge transfer of the deep network for face recognition.
- We combined the teacher–student training pattern with the improved structures using the channel attention mechanism, further improving the model’s performance on the basis of MobileFaceNet [15]. Through corresponding experiments and analysis, we promoted the accuracy on different datasets while maintaining the lightweight characteristic of the network. The results showed accuracy of 99.67% on LFW, with storage occupation of 5.36 MB and 1.35M parameters.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Approach
3.1. Network Design Strategy
3.2. Training Pattern
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metric
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taigman, Y.; Yang, M.; Ranzato, M.A.; Wolf, L. Deepface: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1701–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Mattar, M.; Berg, T.; Learned-Miller, E. Labeled faces in the wild: A database forstudying face recognition in unconstrained environments. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Faces in ‘Real-Life’ Images: Detection, Alignment, and Recognition, Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1891–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face representation by joint identification-verification. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.4773. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deeply learned face representations are sparse, selective, and robust. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2892–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deepid3: Face recognition with very deep neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.00873. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhi, O.M.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Swansea, UK, 7–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Shen, L.; Xie, W.; Parkhi, O.M.; Zisserman, A. Vggface2: A dataset for recognising faces across pose and age. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M. Large-margin softmax loss for convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.02295. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Raj, B.; Song, L. Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017; pp. 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, H. Additive margin softmax for face verification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4690–4699. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Han, Z. Mobilefacenets: Efficient cnns for accurate real-time face verification on mobile devices. In Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 428–438. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Com-puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Le, Q.V. Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobil. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 2820–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, C.N.; Quach, K.G.; Jalata, I.; Le, N.; Luu, K. Mobiface: A lightweight deep learning face recognition on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Tampa, FL, USA, 23–26 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. SeesawFaceNets: Sparse and robust face verification model for mobile platform. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.09124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Seesaw-Net: Convolution Neural Network with Uneven Group Convolution. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.03672. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep face recognition: A survey. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.06655. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, H.R.; Yu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, S. Triplet distillation for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 808–812. [Google Scholar]
- Karlekar, J.; Feng, J.; Wong, Z.S.; Pranata, S. Deep face recognition model compression via knowledge transfer and distillation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.00619. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Su, Z. Vargfacenet: An efficient variable group convolutional neural network for lightweight face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; Gao, J. Ms-celeb-1m: A dataset and benchmark for large-scale face recognition. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Liao, S.; Li, S. Learning face representation from scratch. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.7923. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Deng, W. Cross-pose lfw: A database for studying cross-pose face recognition in unconstrained environments. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. Tech. Rep. 2018, 5. Available online: http://www.whdeng.cn/CPLFW/Cross-Pose-LFW.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Zheng, T.; Deng, W.; Hu, J. Cross-age lfw: A database for studying cross-age face recognition in unconstrained environments. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.08197. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Chen, J.C.; Castillo, C.; Patel, V.M.; Chellappa, R.; Jacobs, D.W. Frontal to profile face verification in the wild. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–9 March 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Moschoglou, S.; Papaioannou, A.; Sagonas, C.; Deng, J.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. Agedb: The first manually collected, in-the-wild age database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, L.; Hassner, T.; Maoz, I. Face recognition in unconstrained videos with matched background similarity. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I.; Seitz, S.M.; Miller, D.; Brossard, E. The megaface benchmark: 1 million faces for recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4873–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; He, R.; Sun, Z.; Tan, T. A light cnn for deep face representation with noisy labels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 2884–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Input | Operator | t | c | n | s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 112 × 112 × 3 | conv3 × 3 | - | 64 | 1 | 2 |
| 56 × 56 × 64 | depthwise conv3 × 3 | - | 64 | 1 | 1 |
| 56 × 56 × 64 | bottleneck | 2 | 64 | 5 | 2 |
| 28 × 28 × 64 | bottleneck | 4 | 128 | 1 | 2 |
| 14 × 14 × 128 | bottleneck | 2 | 128 | 6 | 1 |
| 14 × 14 × 128 | bottleneck | 4 | 128 | 1 | 2 |
| 7 × 7 × 128 | bottleneck | 2 | 128 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 × 7 × 128 | conv1 × 1 | - | 512 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 ×7 × 512 | linear GDConv7 × 7 | - | 512 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 × 1 × 512 | linear conv1 × 1 | - | 128 | 1 | 1 |
| Datasets | ids | Images/Videos | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| CASIA-WebFace [42] | 10K | 0.5M | train |
| MS-Celeb-1M [40] | 100K | 10M | train |
| VGGFace [8] | 2.6K | 2.6M | train |
| VGGFace2 [9] | 9.1K | 3.3M | train and test |
| LFW [2] | 5749 | 13,233 | test |
| CPLFW [43] | 5749 | 11,652 | test |
| CALFW [44] | 5749 | 12,174 | test |
| CFP-FP [45] | 500 | 7000 | test |
| Aged [46] | 568 | 16,488 | test |
| YTF [47] | 1595 | 3425 | test |
| MegaFace [48] | 690K | 1M | test |
| Model | Train_acc | LFW | AgeDB-30 | VGG2-FP | CALFW | CPLFW | CFP-FF | CFP-FP | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 0.9229 | 0.9947 | 0.9603 | 0.9236 | 0.9522 | 0.8833 | 0.9949 | 0.9269 | 4.8M |
| Model | Train_acc | LFW | AgeDB-30 | VGG2-FP | CALFW | CPLFW | CFP-FF | CFP-FP | Average | STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 0.9229 | 0.9947 | 0.9603 | 0.9236 | 0.9522 | 0.8833 | 0.9949 | 0.9269 | 0.9480 | 0.0404 |
| ours_LSE | 0.9237 | 0.9957 | 0.9607 | 0.9188 | 0.9547 | 0.8852 | 0.9950 | 0.9247 | 0.9478 | 0.0409 |
| ours_DSSE | 0.9369 | 0.9943 | 0.9662 | 0.9228 | 0.9527 | 0.8942 | 0.9946 | 0.9419 | 0.9524 | 0.0368 |
| ours_DSE | 0.9354 | 0.9950 | 0.9652 | 0.9252 | 0.9547 | 0.8952 | 0.9953 | 0.9384 | 0.9527 | 0.0366 |
| ours_DSSE+LSE | 0.9371 | 0.9953 | 0.9675 | 0.9308 | 0.9545 | 0.8932 | 0.9946 | 0.9429 | 0.9541 | 0.0363 |
| ours_DSE+LSE | 0.9300 | 0.9940 | 0.9603 | 0.9254 | 0.9550 | 0.8900 | 0.9950 | 0.9333 | 0.9504 | 0.0378 |
| Model | Train_Acc | LFW | AgeDB-30 | VGG2-FP | CALFW | CPLFW | CFP-FF | CFP-FP | Average | STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 0.9229 | 0.9947 | 0.9603 | 0.9236 | 0.9522 | 0.8833 | 0.9949 | 0.9269 | 0.9480 | 0.0404 |
| ours_distill | 0.9267 | 0.9960 | 0.9625 | 0.9204 | 0.9547 | 0.8883 | 0.9956 | 0.9314 | 0.9498 | 0.0396 |
| ours_distill+LSE | 0.9170 | 0.9953 | 0.9677 | 0.9248 | 0.9555 | 0.8862 | 0.9960 | 0.9226 | 0.9497 | 0.0408 |
| ours_distill+DSSE | 0.9329 | 0.9957 | 0.9672 | 0.9274 | 0.9573 | 0.8898 | 0.9949 | 0.9341 | 0.9523 | 0.0383 |
| ours_distill+DSE | 0.9441 | 0.9957 | 0.9698 | 0.9326 | 0.9580 | 0.8987 | 0.9946 | 0.9439 | 0.9562 | 0.0347 |
| ours_distill+DSSE+LSE | 0.9361 | 0.9953 | 0.9698 | 0.9302 | 0.9580 | 0.8938 | 0.9954 | 0.9387 | 0.9545 | 0.0368 |
| ours_distill+DSE+LSE | 0.9367 | 0.9967 | 0.9683 | 0.9304 | 0.9563 | 0.8968 | 0.9960 | 0.9419 | 0.9552 | 0.0360 |
| Model | Size (MB) | MACs (G) | Params (M) | Speed (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 4.78 | 0.23 | 1.20 | 5.71 ± 0.57 |
| ours_LSE | 4.90 | 0.23 | 1.23 | 6.31 ± 0.59 |
| ours_DSSE | 4.88 | 0.23 | 1.22 | 8.15 ± 0.69 |
| ours_DSE | 5.24 | 0.23 | 1.32 | 8.28 ± 0.84 |
| ours_DSSE+LSE | 5.01 | 0.23 | 1.26 | 8.68 ± 0.58 |
| ours_DSE+LSE | 5.36 | 0.23 | 1.35 | 8.74 ± 0.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J. Face Recognition Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks. Information 2021, 12, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050191
Liu W, Zhou L, Chen J. Face Recognition Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks. Information. 2021; 12(5):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050191
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenting, Li Zhou, and Jie Chen. 2021. "Face Recognition Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks" Information 12, no. 5: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050191
APA StyleLiu, W., Zhou, L., & Chen, J. (2021). Face Recognition Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks. Information, 12(5), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050191




