Zero-Shot Topic Labeling for Hazard Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
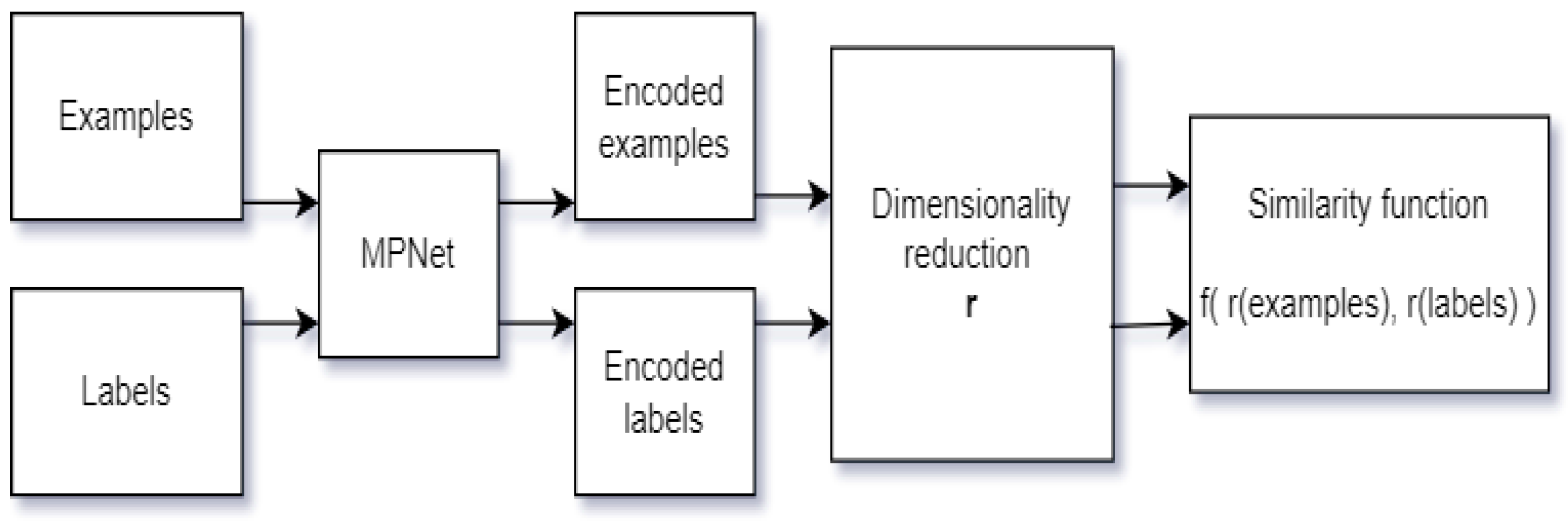
3. Methodology
3.1. PCA Dimensionality Reduction
3.2. Linear Projection onto Word Embeddings
3.3. Autoencoder Projection on Latent Space
4. Datasets
4.1. Benchmark Datasets
4.2. Twitter Handcrafted Datasets
- 1.
- Gold dataset: the tweet is effectively about the hazard associated to the keyword;
- 2.
- Keyword-out-of-context dataset: the tweet is not at all about a hazard and the keyword is just used with another meaning;
- 3.
- Multiple-keywords dataset: the tweet mentions multiple hazards but it has been only associated with the one keyword it was retrieved for.
5. Results
5.1. Benchmark Results
5.2. Twitter Dataset Results
5.3. Keyword-out-of-Context Dataset Results
5.4. Multiple-Keywords Dataset Results
“heavy rainfall from #grace will result in significant flash and urban flooding as well as mudslides.high surf generated by grace will affect the southern gulf of mexico coastline through the weekend.”
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Florio, K.; Basile, V.; Polignano, M.; Basile, P.; Patti, V. Time of your hate: The challenge of time in hate speech detection on social media. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.R.; Le, Q.V. Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 5753–5763. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Lu, J.; Liu, T.Y. Mpnet: Masked and permuted pre-training for language understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 16857–16867. [Google Scholar]
- Ganzha, M. Practical Aspects of Zero-Shot Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.15158. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Hay, J.; Roth, D. Benchmarking zero-shot text classification: Datasets, evaluation and entailment approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.00161. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Y.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. Zero-shot learning-the good, the bad and the ugly. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4582–4591. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lertvittayakumjorn, P.; Guo, Y. Integrating semantic knowledge to tackle zero-shot text classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.12626. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, K.; Akbik, A.; Krapac, J.; Vollgraf, R. Task-aware representation of sentences for generic text classification. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 8–13 December 2020; pp. 3202–3213. [Google Scholar]
- Harrando, I.; Troncy, R. Explainable Zero-Shot Topic Extraction Using a Common-Sense Knowledge Graph. In Open Access Series in Informatics (OASIcs), Proceedings of the 3rd Conference on Language, Data and Knowledge (LDK 2021); Gromann, D., Sérasset, G., Declerck, T., McCrae, J.P., Gracia, J., Bosque-Gil, J., Bobillo, F., Heinisch, B., Eds.; Schloss Dagstuhl—Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik: Dagstuhl, Germany, 2021; Volume 93, pp. 17:1–17:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, A.; Kavuluru, R. Few-shot and zero-shot multi-label learning for structured label spaces. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; Volume 2018, p. 3132. [Google Scholar]
- Dauphin, Y.N.; Tur, G.; Hakkani-Tur, D.; Heck, L. Zero-shot learning for semantic utterance classification. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1401.0509. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.; Seo, J. Automatic text categorization by unsupervised learning. In Proceedings of the COLING 2000 Volume 1: The 18th International Conference on Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Haj-Yahia, Z.; Sieg, A.; Deleris, L.A. Towards unsupervised text classification leveraging experts and word embeddings. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July– 2 August 2019; pp. 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Bojanowski, P.; Grave, E.; Joulin, A.; Mikolov, T. Enriching Word Vectors with Subword Information. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.04606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J.; Isele, R.; Jakob, M.; Jentzsch, A.; Kontokostas, D.; Mendes, P.N.; Hellmann, S.; Morsey, M.; Van Kleef, P.; Auer, S.; et al. Dbpedia—A large-scale, multilingual knowledge base extracted from wikipedia. Semant. Web 2015, 6, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuggener, D.; von Däniken, P.; Peetz, T.; Cieliebak, M. LEDGAR: A Large-Scale Multi-label Corpus for Text Classification of Legal Provisions in Contracts. In Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Online, 13–15 May 2020; European Language Resources Association: Marseille, France, 2020; pp. 1235–1241. [Google Scholar]
| Hazard | Keywords |
|---|---|
| Extreme weather | heatwave, hot weather, hot summer, cold weather cold winter, extreme weather, extreme cold, extreme hot, hottest summer, hottest weather, coldest winter, coldest weather, drought |
| COVID-19 | covid dead, covid deaths, covid infected, covid hospitalized, covid recovered, covid hospitals, covid cases, covid outbreak, covid-19, pandemic virus, virus dead, virus deaths, virus infected, virus hospitalized, virus recovered, virus hospitals, virus outbreak |
| Avalanche | avalanche, avalanches, icefall, icefalls, avalanche victims |
| Fire | forest fire, forest fires, wildfire, wildfires, bushfire, bushfires, conflagration, high flames, burned, explosion fire, firefighter, firefighters, fire fighters, fireman, firemen |
| Flood | flood, floods, flooding, floodings, flash flood, deluge, inundation, inundated, flood victims, flood affected, flood dead, flood missing, flood warnings, help flood, rescue flood |
| Earthquake | earthquake, earthquakes, seismic, magnitude, epicentre, epicenter, building collapsed, quake victims, earthquake dead, earthquake injured, help earthquake, missing earthquake |
| Storm | storm rain, storm rains, storm wind, storm winds, winter storm, summer storm, autumn storm, storm lightning, storm lightnings, severe storm, incoming storm, spring storm, cloud storm, storm clouds, eye storm, storms, heavy rain alert, heavy rains, lightnings, thunderstorm, thunderstorms, thunder storm, thunder storms, windstorm, windstorms, wind storm, wind storms, snowstorm, snow blizzard, blizzards, strong wind, hurricane, tornado, typhoon, rainfall, hurricane category |
| Terrorism | terrorist attack, terrorists attack, terrorist deaths, terrorist injured, terrorist hostages, terrorists dead, terrorist bomb, terrorism bomb, terrorism attack |
| Landslide | landslide mud, landslide rain, landslide buried, landslide kills, landslide erosion, mudslide, mudslides, mudflow, mudflows, debris fall |
| Subsidence | subsidence |
| Label | Support |
|---|---|
| Extreme weather | 105 |
| COVID-19 | 101 |
| Avalanche | 10 |
| Fire | 110 |
| Flood | 114 |
| Earthquake | 102 |
| Storm | 100 |
| Terrorism | 122 |
| Landslide | 124 |
| Subsidence | 112 |
| Reduction Technique | Yahoo Answer | DBPedia | Lexglue/Ledgar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline MPNet | 0.520 | 0.648 | 0.227 |
| LinearProjection (FastText) | 0.343 | 0.286 | 0.067 |
| LinearProjection (Word2Vec) | 0.519 | 0.688 | 0.158 |
| PCA | 0.580 | 0.795 | 0.279 |
| Generalized autoencoder | 0.259 | 0.514 | 0.029 |
| Ad-hoc autoencoder | 0.223 | 0.298 | 0.113 |
| Word2Vec autoencoder | 0.283 | 0.299 | 0.042 |
| Hazard | F1@3 | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme weather | 0.934 | 105 |
| COVID-19 | 0.966 | 101 |
| Avalanche | 1.0 | 10 |
| Fire | 0.982 | 110 |
| Flood | 0.927 | 114 |
| Earthquake | 0.971 | 102 |
| Storm | 0.960 | 100 |
| Terrorism | 0.976 | 122 |
| Landslide | 0.976 | 124 |
| Subsidence | 0.982 | 112 |
| Macro-average | 0.961 | 1000 |
| Micro-average | 0.957 | 1000 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPNet@1 | 0.822 | 0.798 | 0.794 | 0.814 |
| MPNet + PCA@1 | 0.805 | 0.839 | 0.808 | 0.830 |
| MPNet@3 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.950 | 0.943 |
| MPNet + PCA@3 | 0.961 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.957 |
| Keyword-out-of-Context Dataset | Gold Dataset | |
|---|---|---|
| MPNet | 0.220 | 0.416 |
| MPNet + PCA | 0.175 | 0.326 |
| Hazard | MPNet | PCA |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme weather | 0.22 | −0.14 |
| COVID-19 | 0.16 | −0.06 |
| Avalanche | 0.14 | −0.03 |
| Fire | 0.13 | −0.25 |
| Flood | 0.49 | 0.38 |
| Earthquake | 0.35 | 0.15 |
| Storm | 0.42 | 0.36 |
| Terrorism | 0.12 | −0.25 |
| Landslide | 0.37 | 0.26 |
| Subsidence | 0.25 | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rondinelli, A.; Bongiovanni, L.; Basile, V. Zero-Shot Topic Labeling for Hazard Classification. Information 2022, 13, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13100444
Rondinelli A, Bongiovanni L, Basile V. Zero-Shot Topic Labeling for Hazard Classification. Information. 2022; 13(10):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13100444
Chicago/Turabian StyleRondinelli, Andrea, Lorenzo Bongiovanni, and Valerio Basile. 2022. "Zero-Shot Topic Labeling for Hazard Classification" Information 13, no. 10: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13100444
APA StyleRondinelli, A., Bongiovanni, L., & Basile, V. (2022). Zero-Shot Topic Labeling for Hazard Classification. Information, 13(10), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13100444







