Constructing a Real-Time Value-Chain Integration Architecture for Mass Individualized Juice Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Mass Production, Mass Customization, Mass Personalization, and Mass Individualization
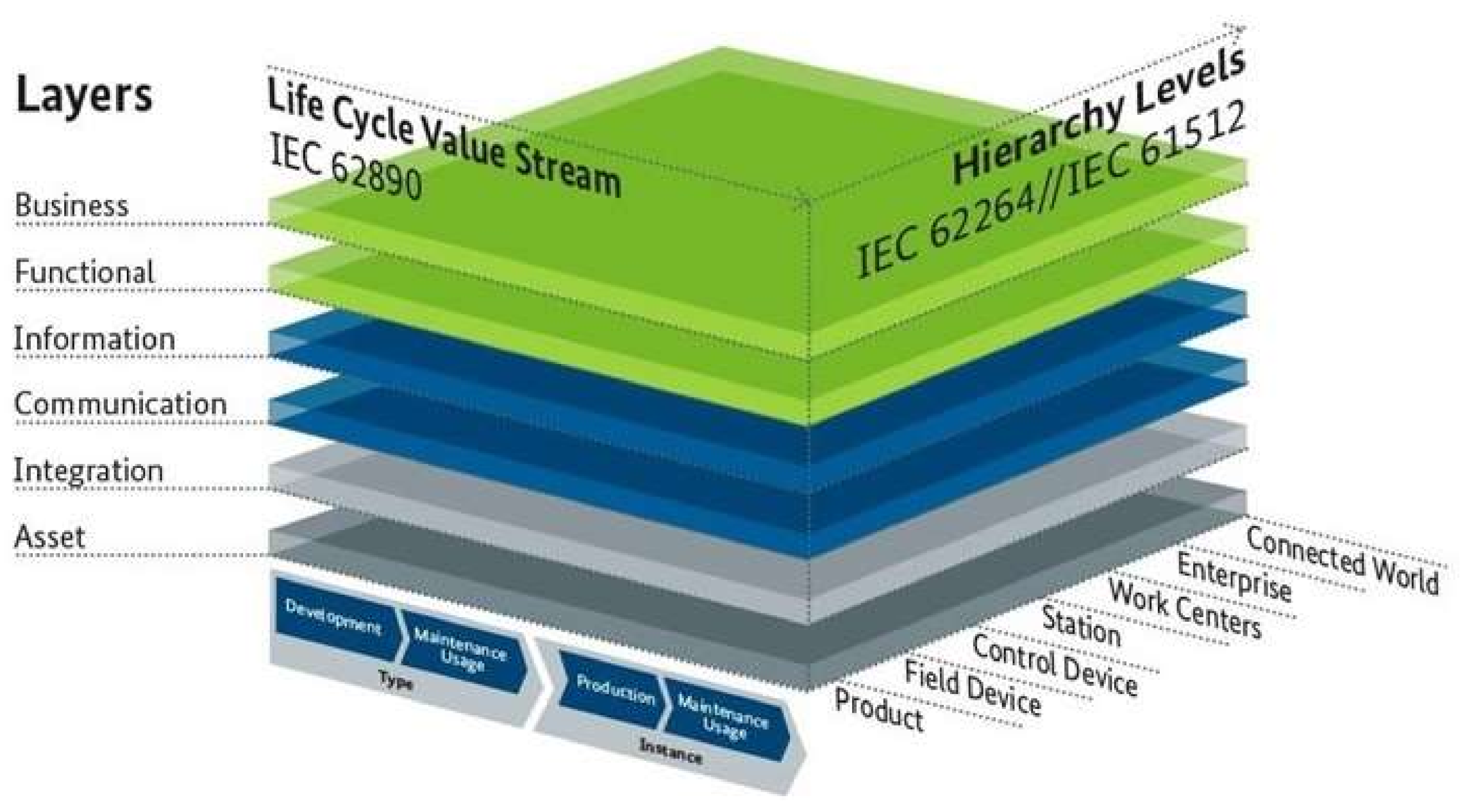
2.2. Reference Architectural Model Industrie 4.0 (RAMI 4.0)
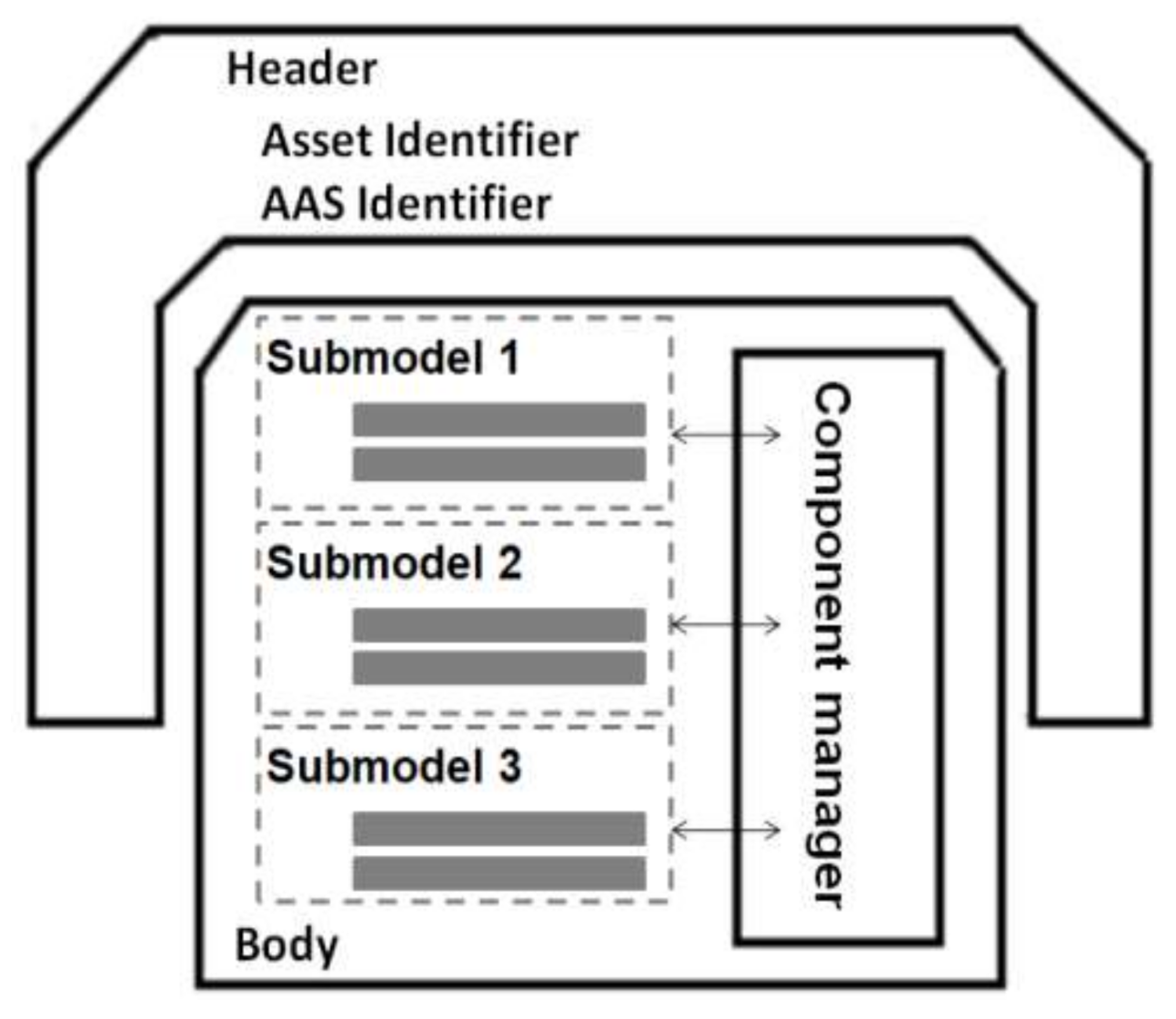
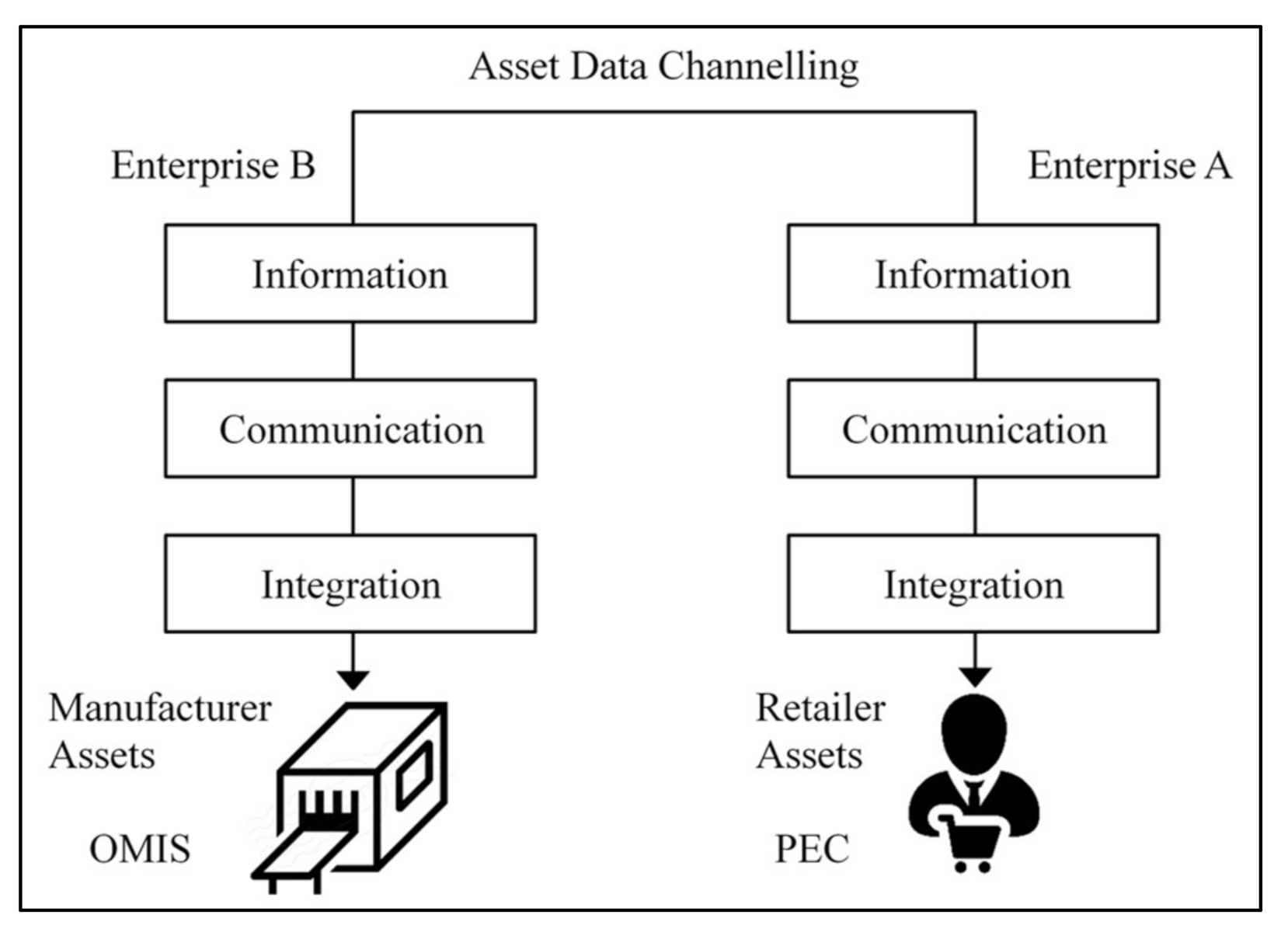
2.3. Data Modeling with Asset and Asset Administration Shell
2.4. Industrial Data Space Reference Architecture Model (IDS-RAM)
- Data Provider/Owner. Data Provider is defined as a person who holds rights to a data that brings value to the organization. The role of which it performs is to offer its data to other participants of the Industrial Data Space.
- Data Consumer/User. They use the data provided by the Data Provider. The Data Consumer can request data from the Data Provider to use that data for providing services or internal purposes.
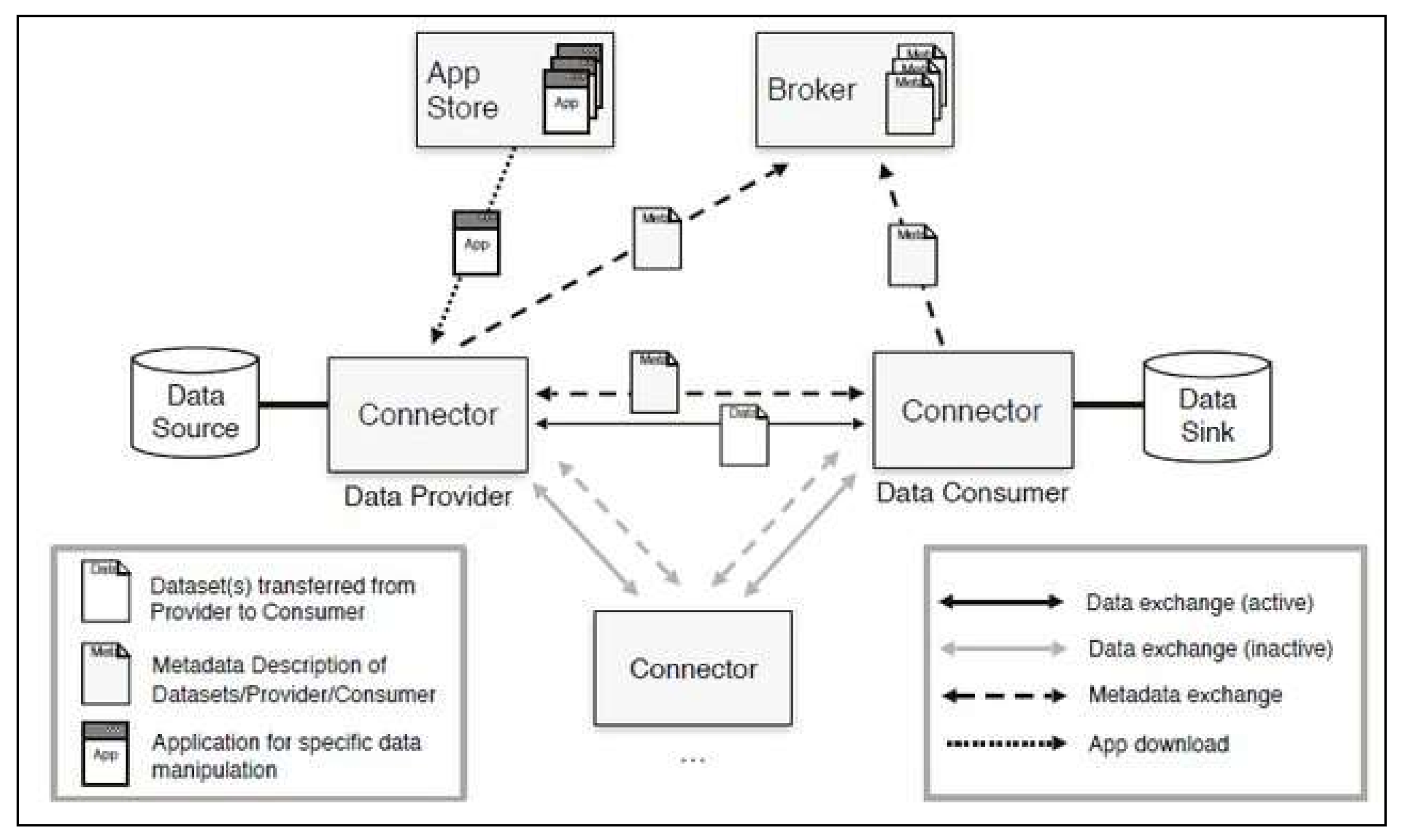
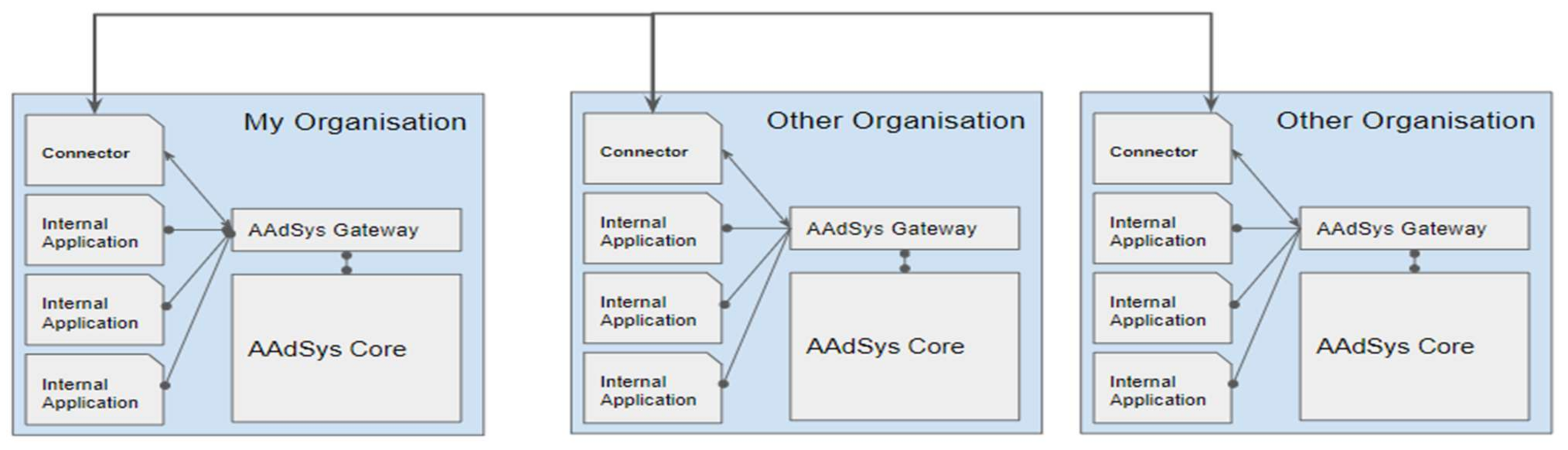
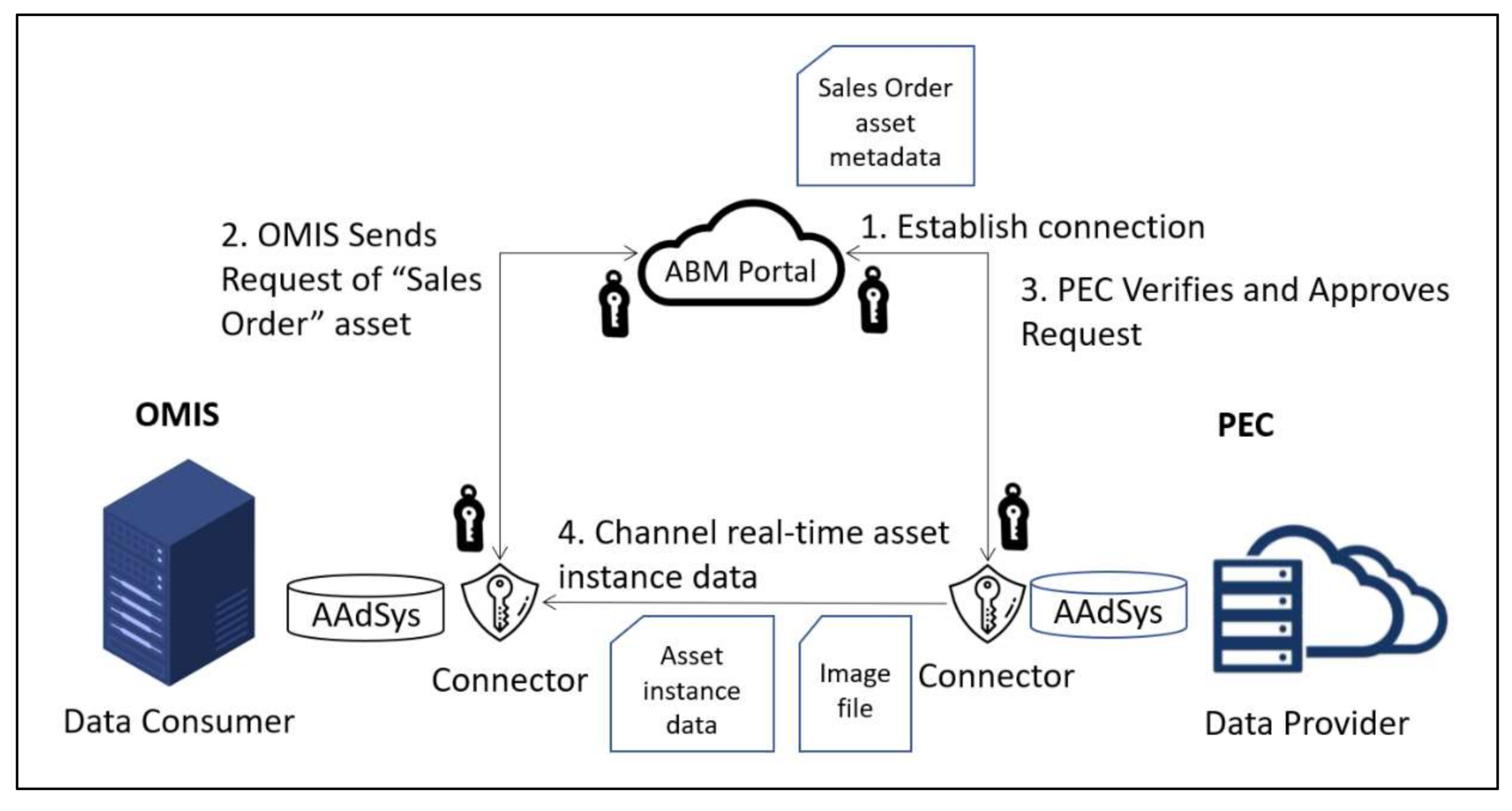
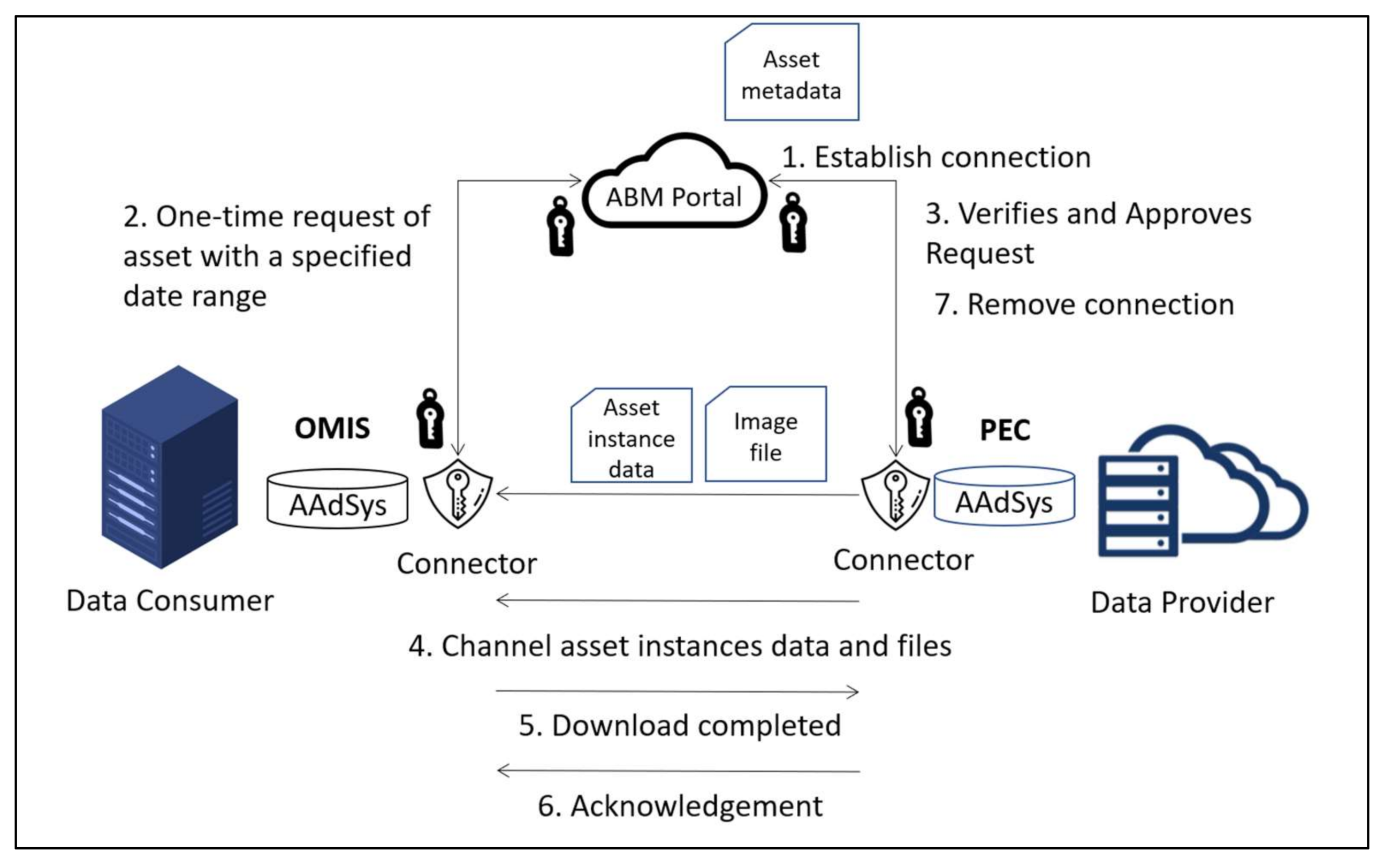
- Broker. Broker is an index-service running in conjunction with an IDS Connector that helps facilitate data exchange between both the Data Provider and the Data Consumer. In IDS, the Broker provides Data Providers with functions to publish their asset metadata, provides Data Consumers with a function to search the data of the Data Providers, and provides functions to both parties to make an agreement for the provision and use of their data. The Broker also acts as a supervisor who will manage the data exchange between both parties by ensuring that all data are transferred to the respective party in a secure manner while maintaining data sovereignty. Data sovereignty refers to the compliance of a set of rules, or terms and conditions, that are created by the Data Provider for the Data Consumer or by a governance body on the data exchange by the three roles. This provides protection to the Data Provider; in the event that any user uses the data without permission, he can take legal action on the unauthorized user. The interaction between both the Data Provider and the Data Consumer and the Broker can be seen in Figure 4.
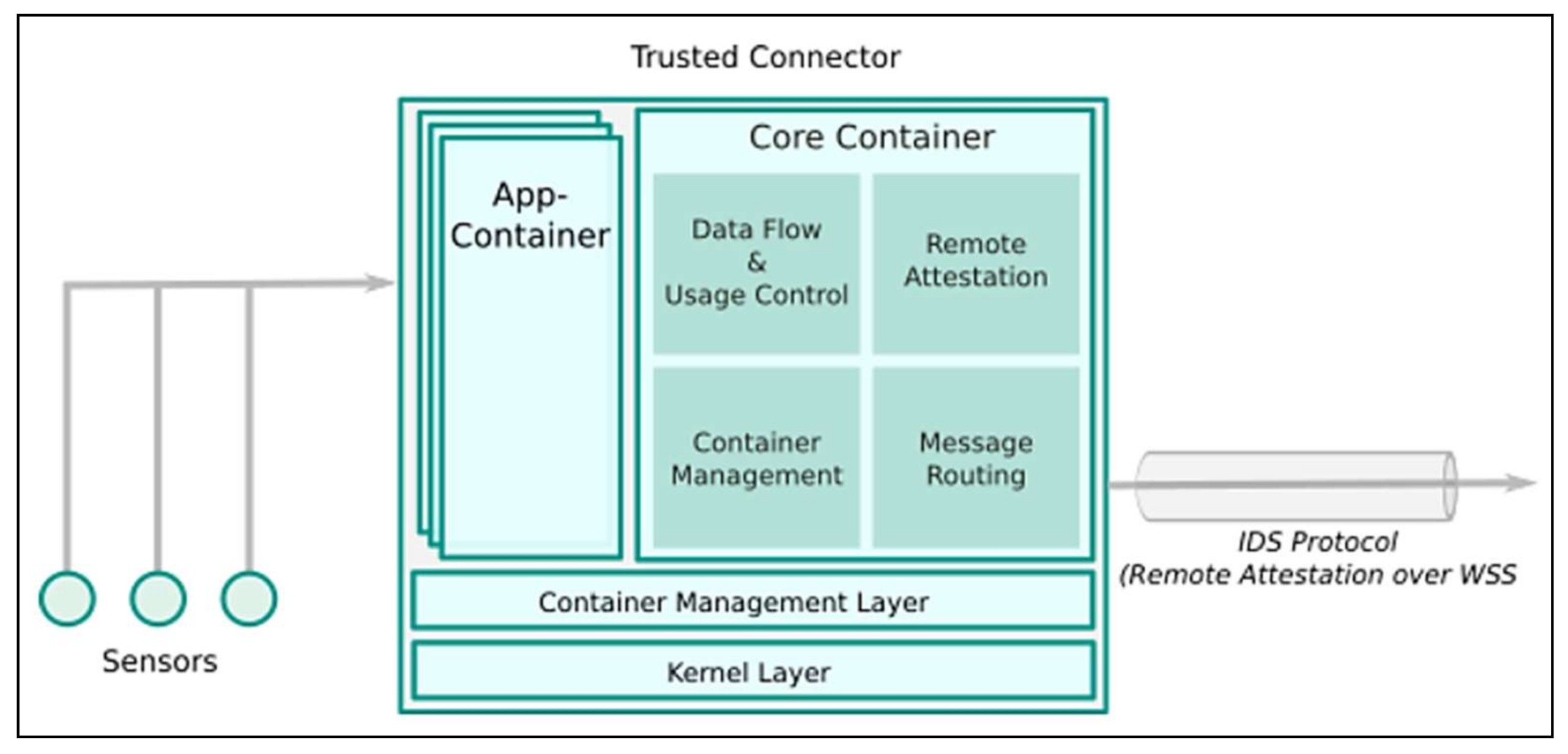
- Trusted Connector. This component is a service in the IDS that allows data to be kept in a container, such as asset data and sensor data, to be processed and transferred to the other party (see Figure 5). The trusted Connector has to work together with the Broker to enable communication between a Data Provider and a Data Consumer.
2.5. Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Microservices
2.6. Brokering System
3. Project Background
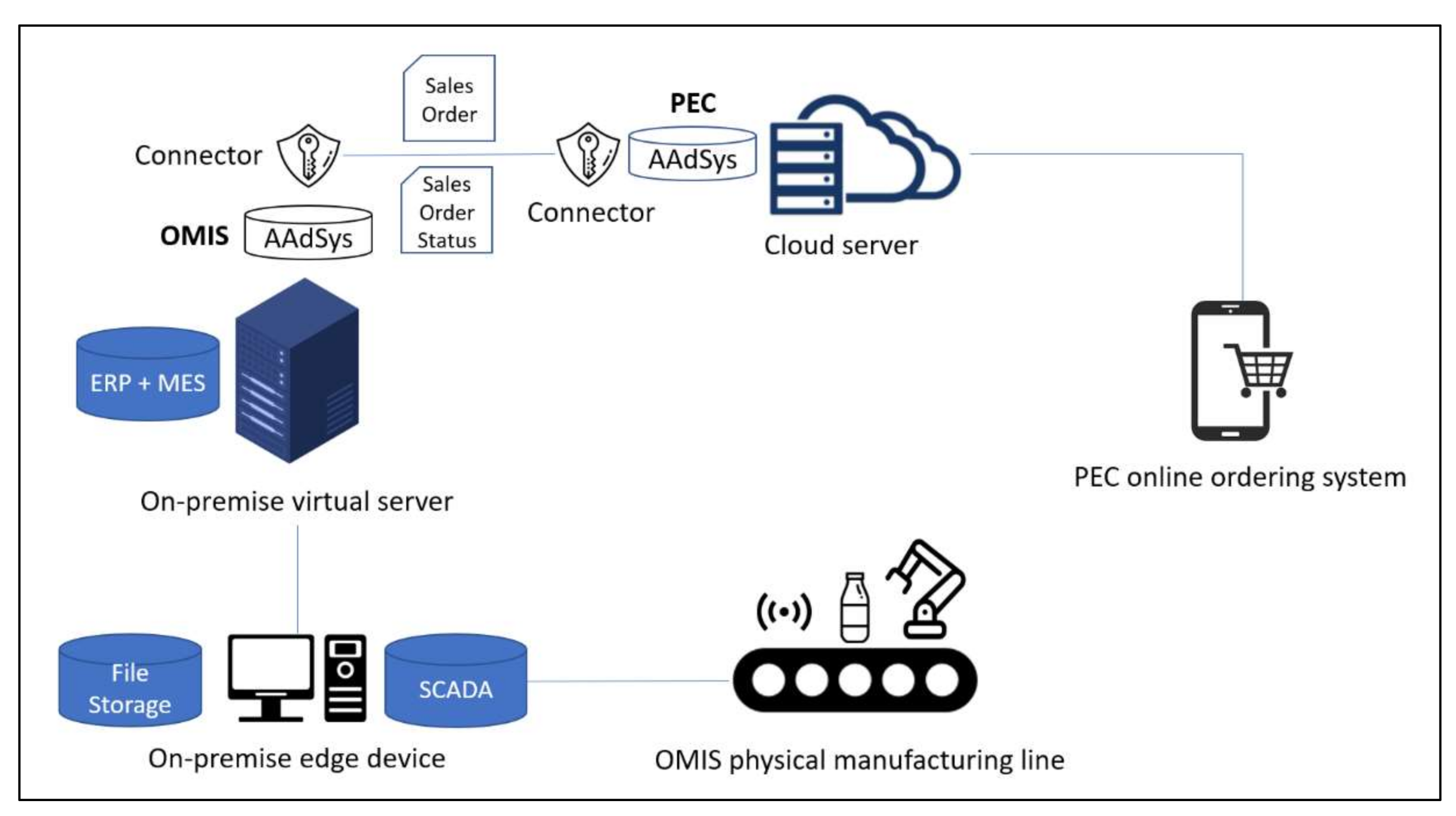
3.1. Personalised E-Commerce (PEC)
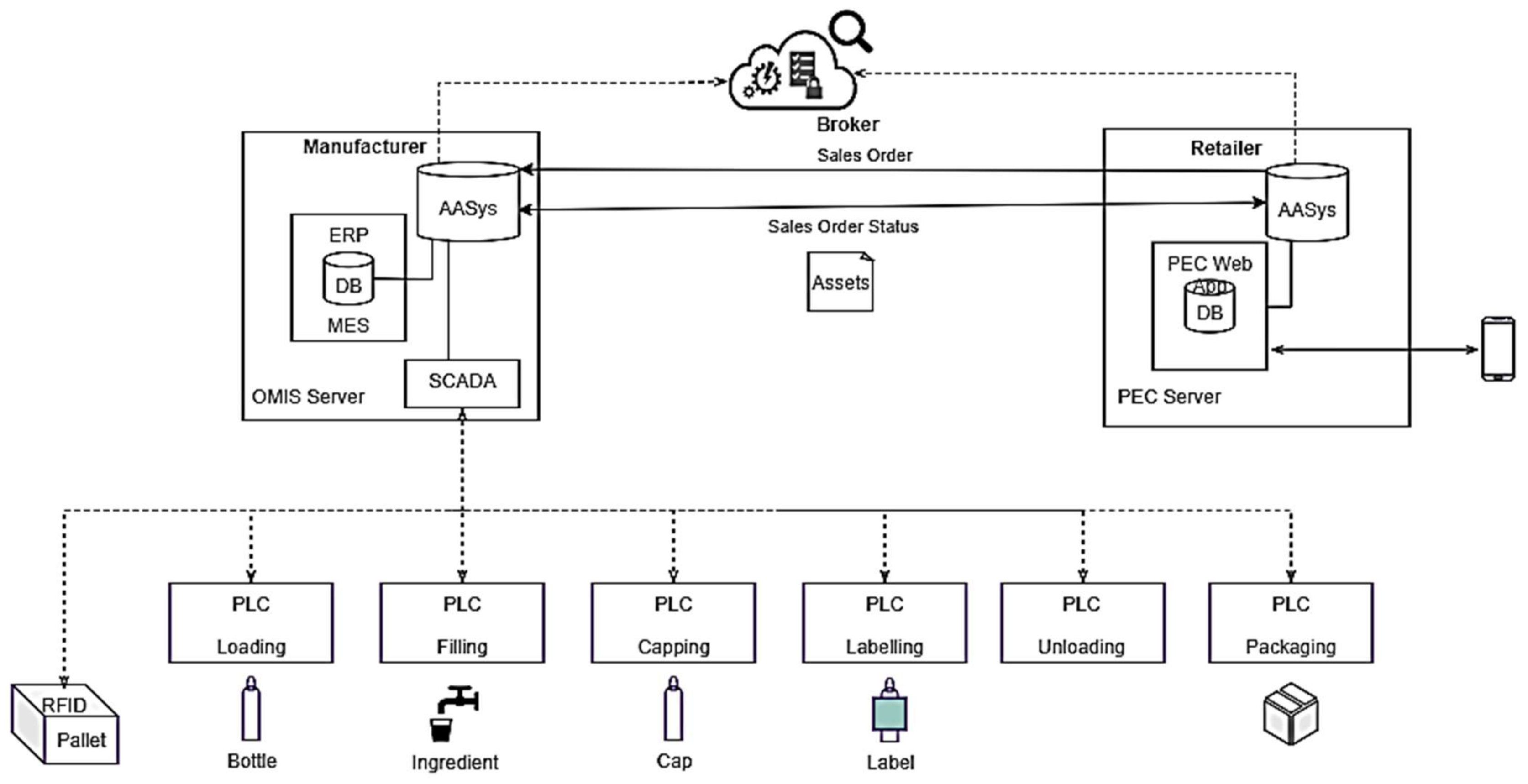
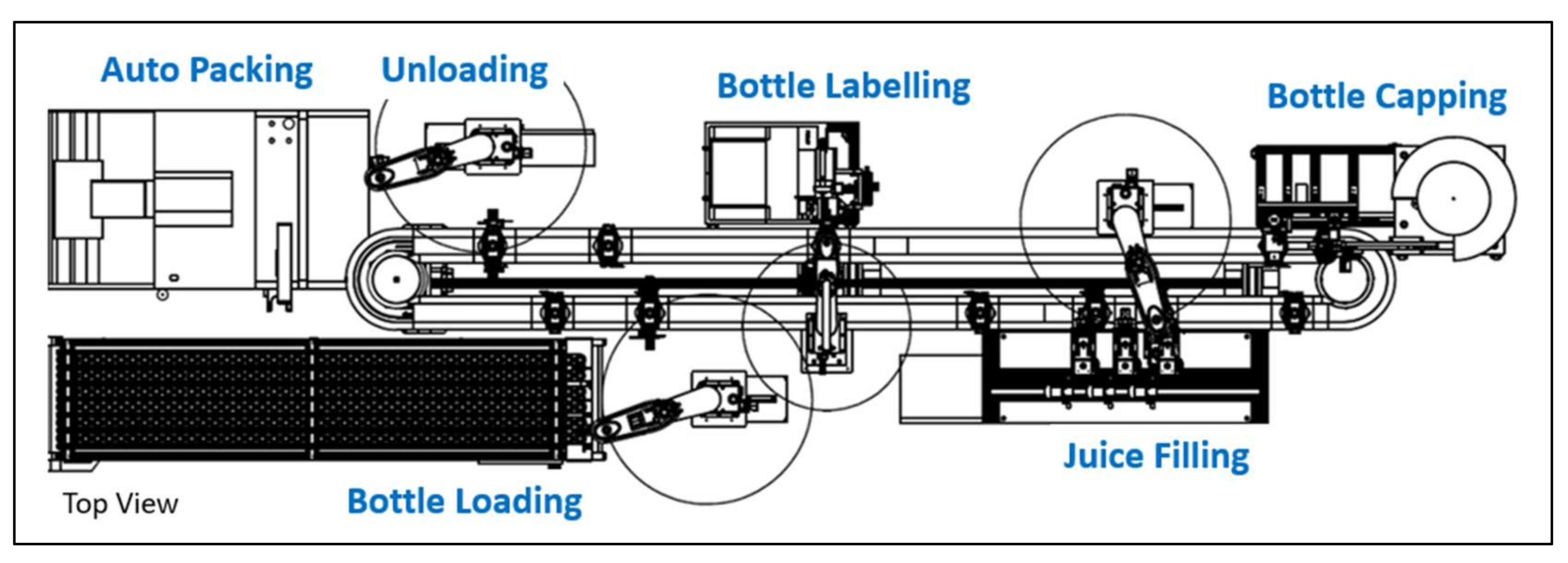
3.2. One-Piece Manufacturing through Individualization Solution (OMIS)
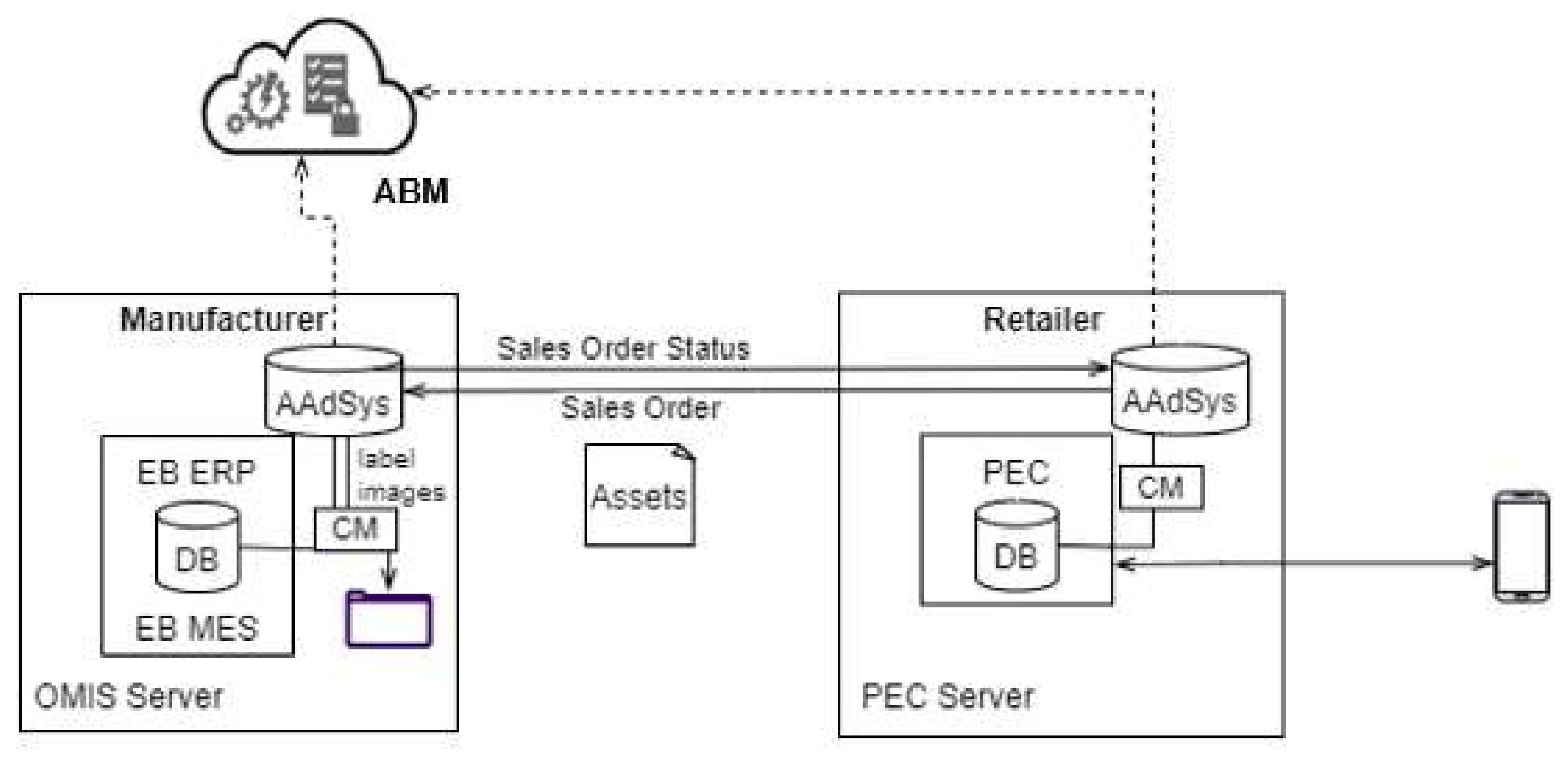
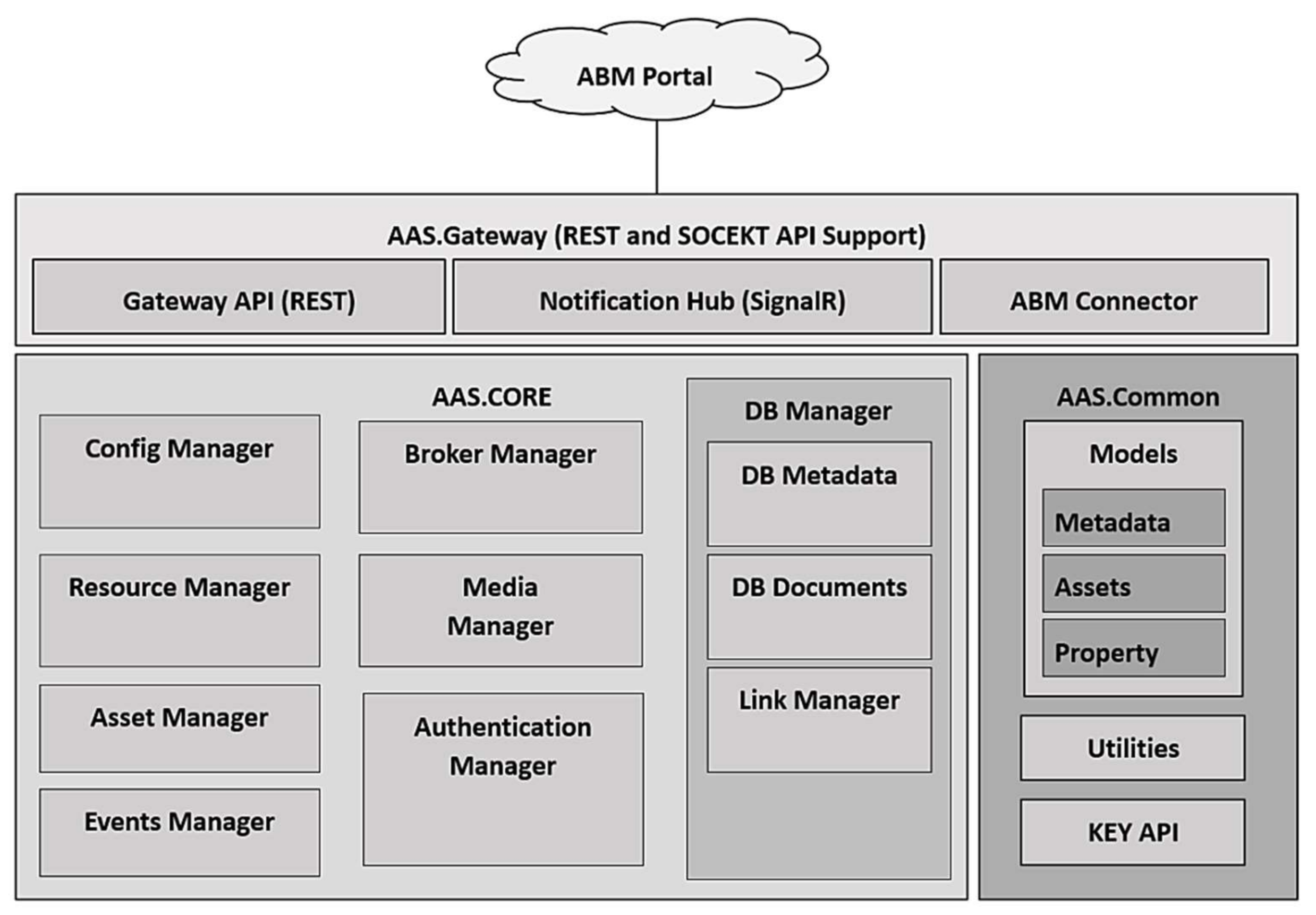
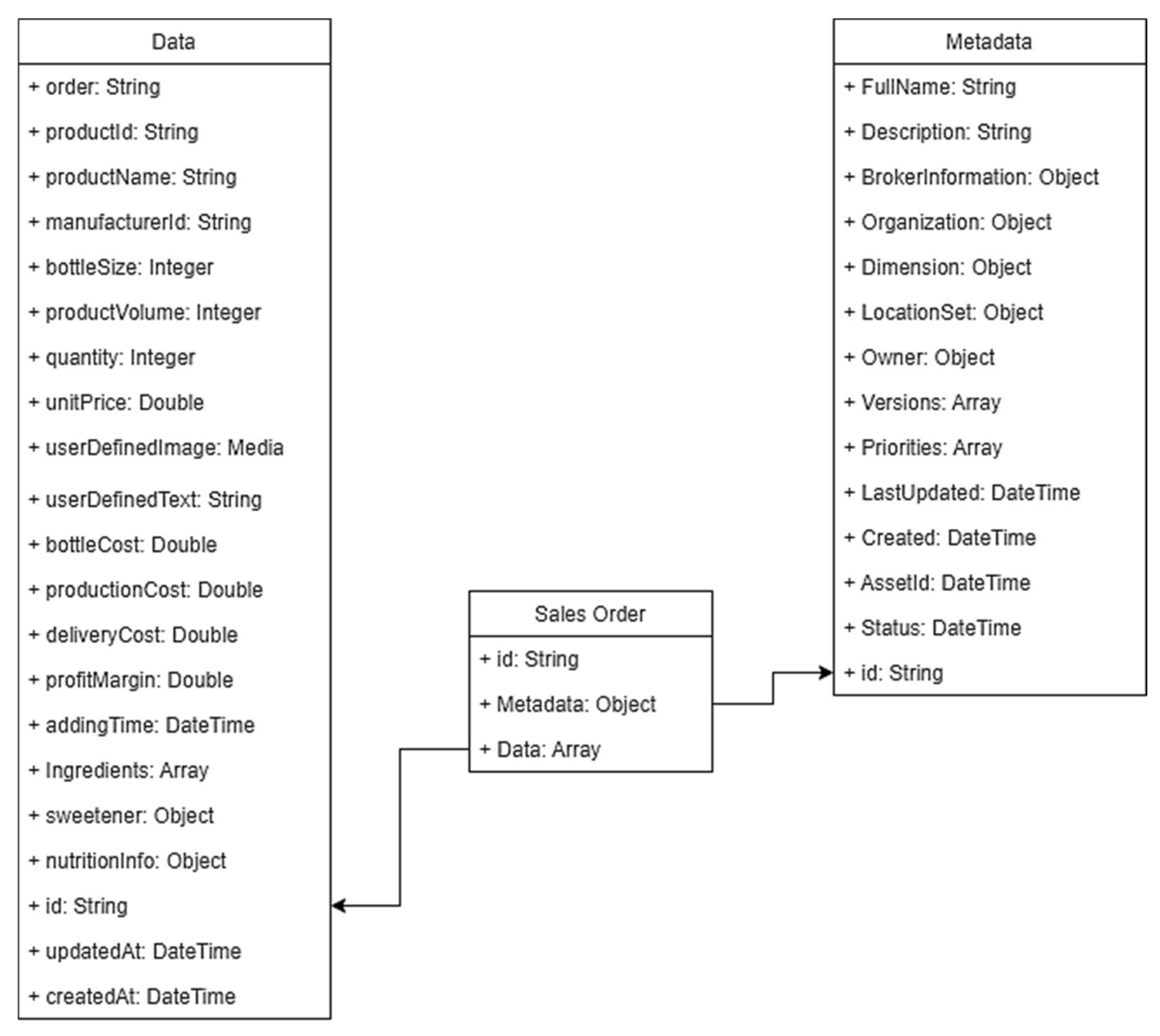
3.3. Asset Administration System (AAdSys)
3.4. Asset Brokering Manager (ABM)
4. Experiment Setup
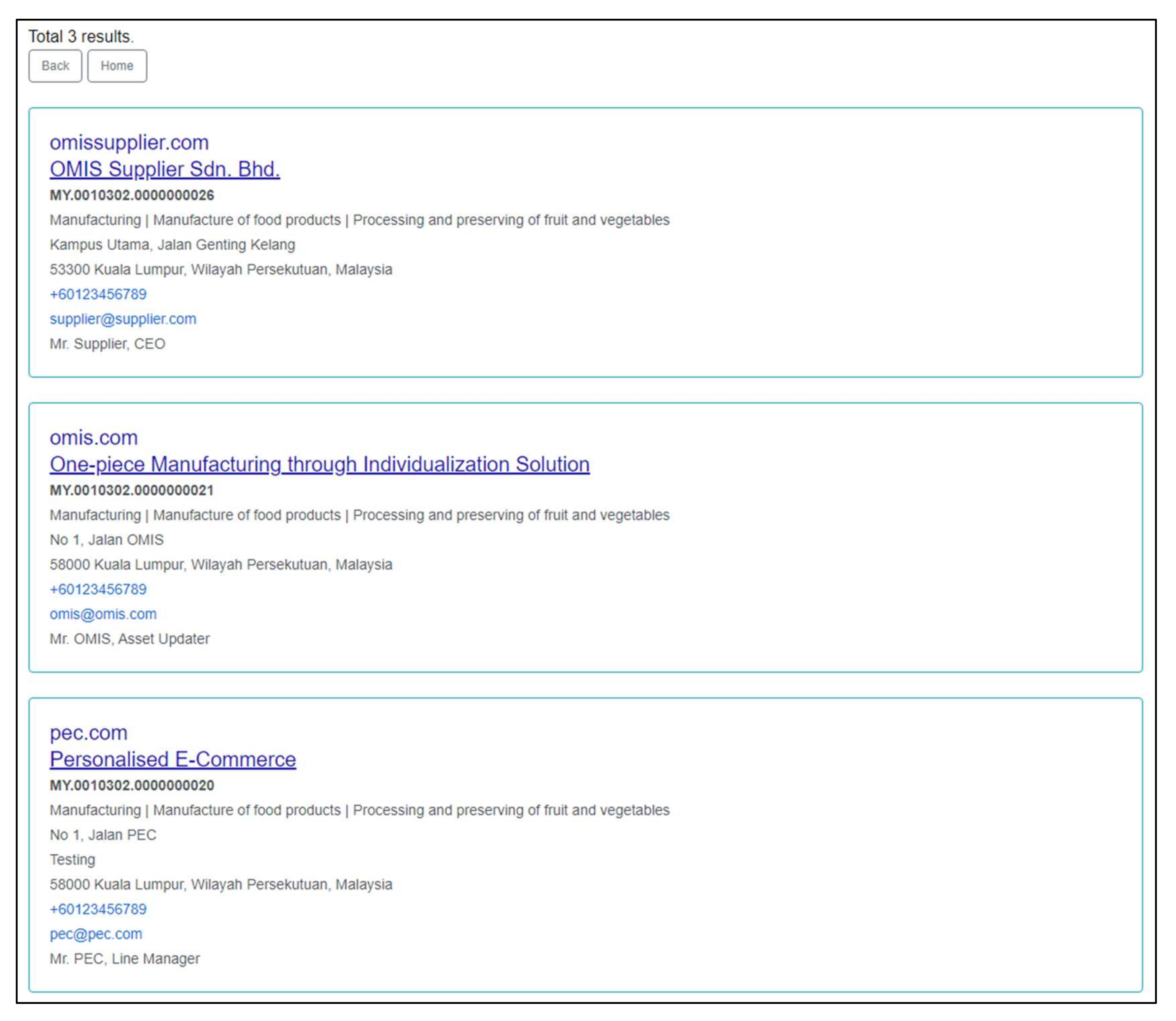
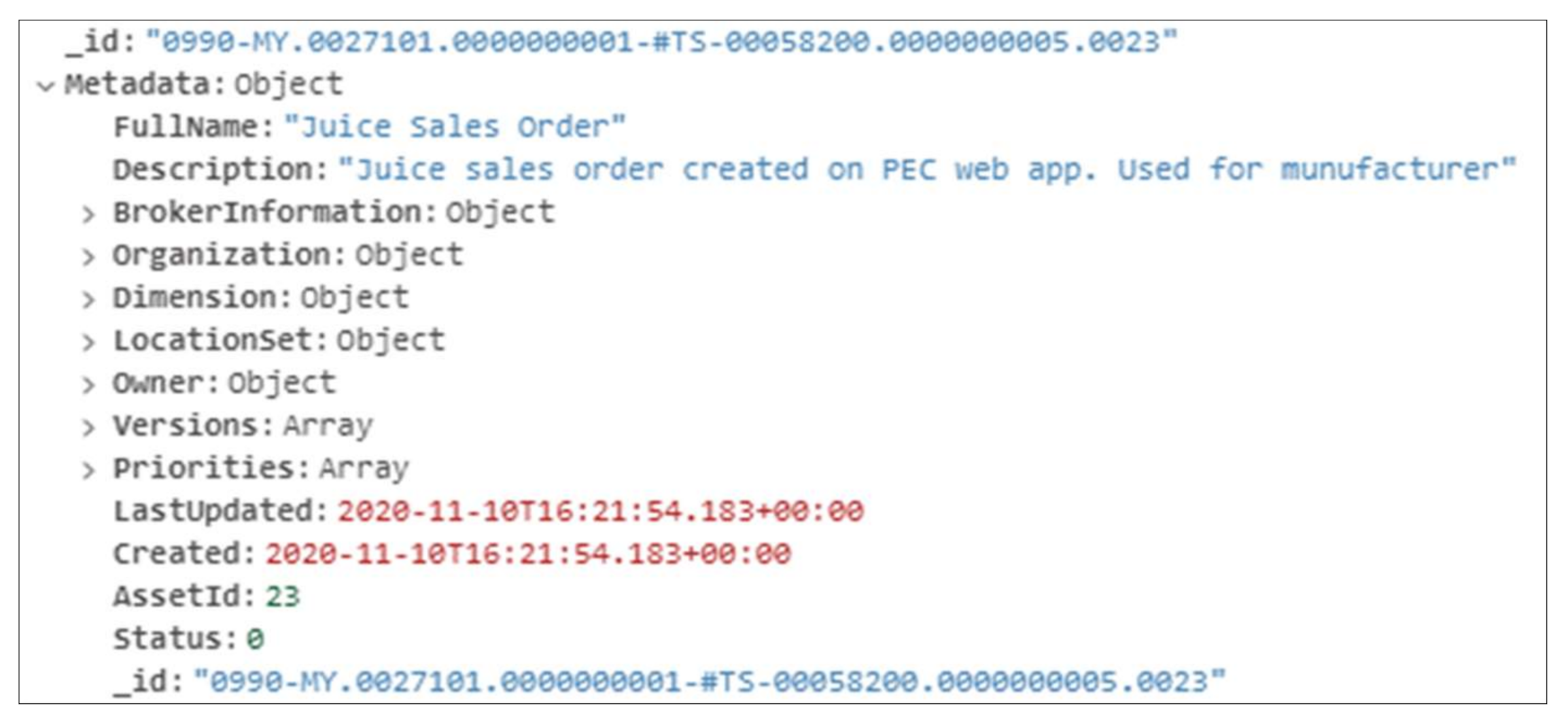
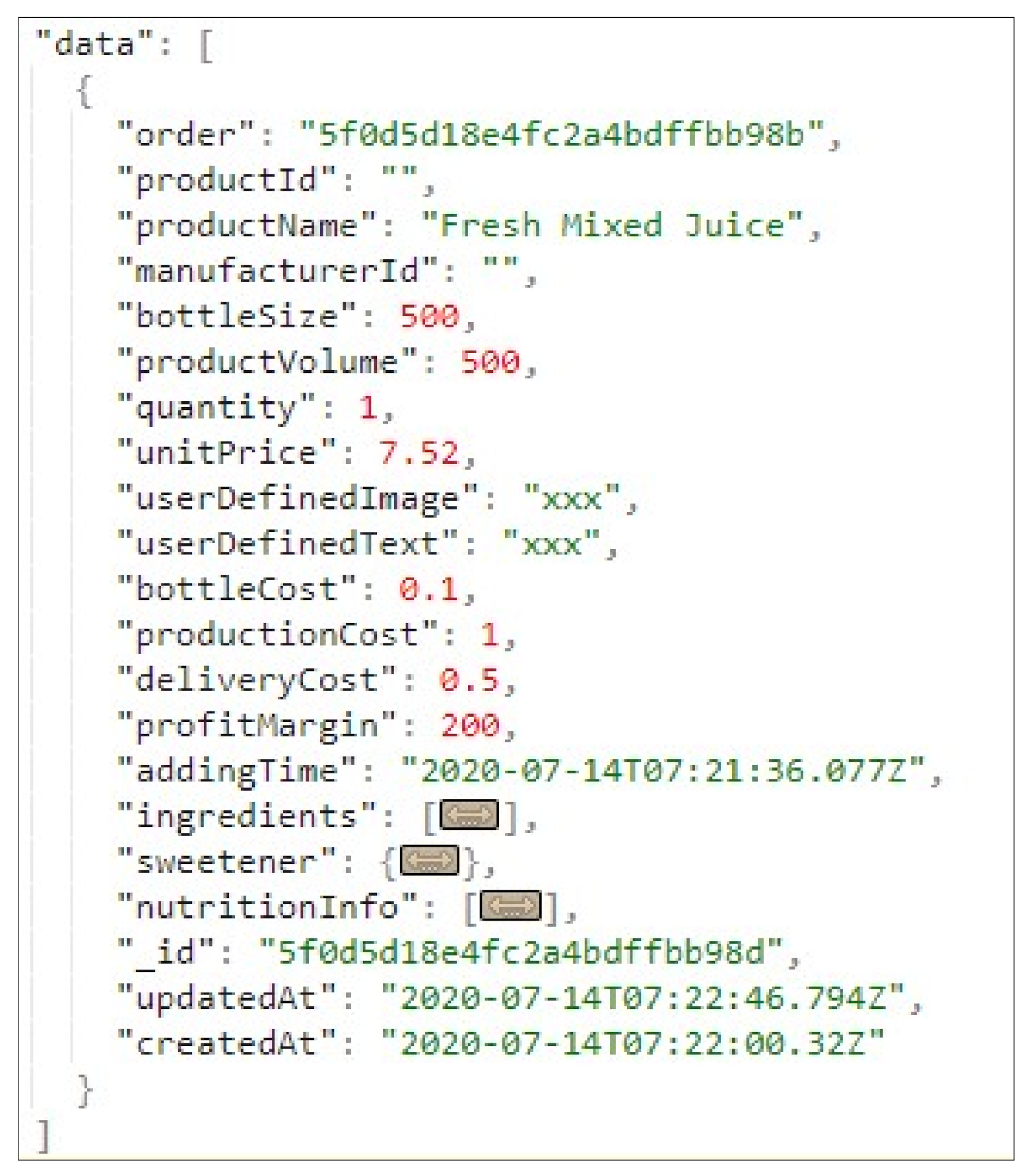
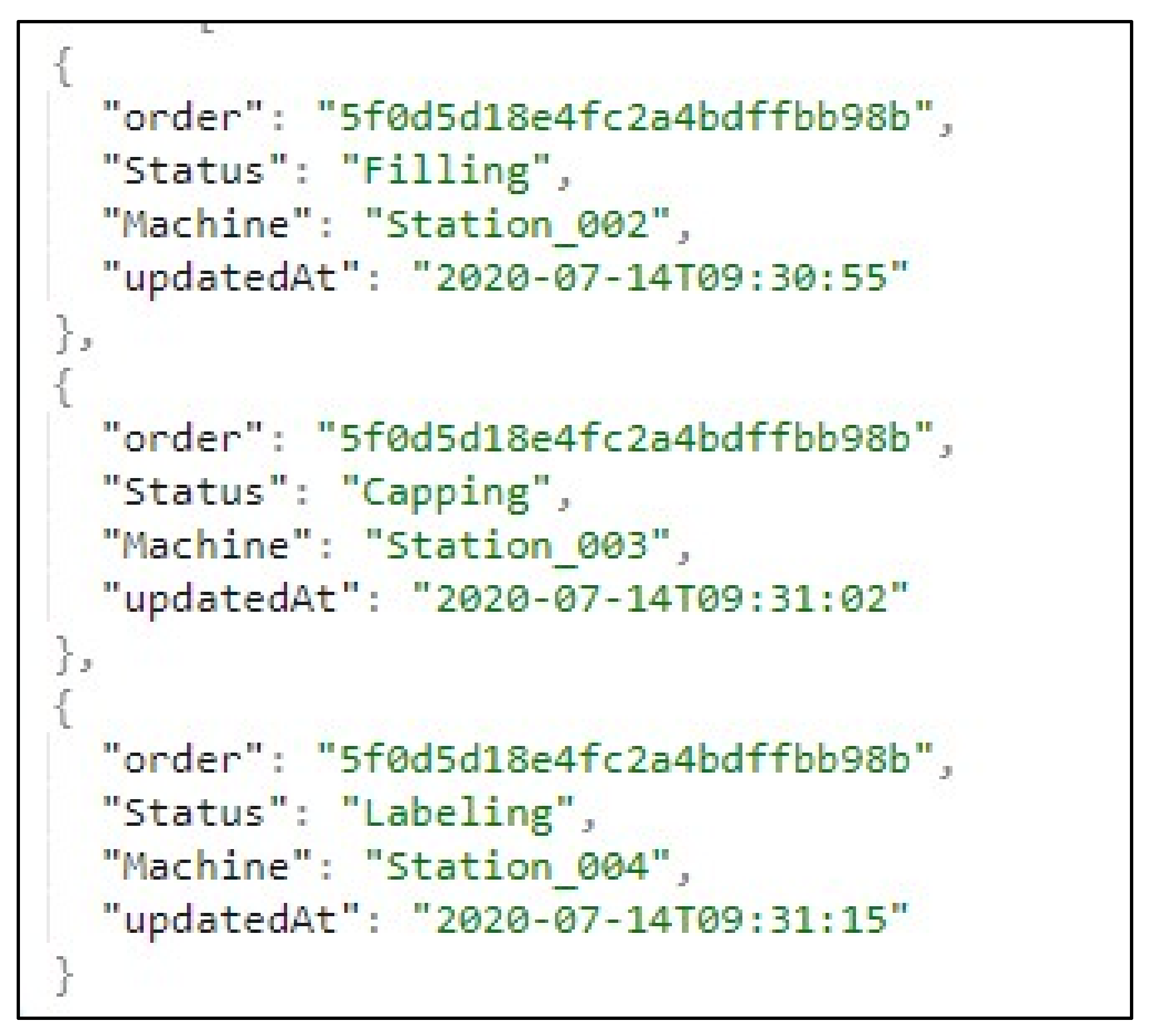
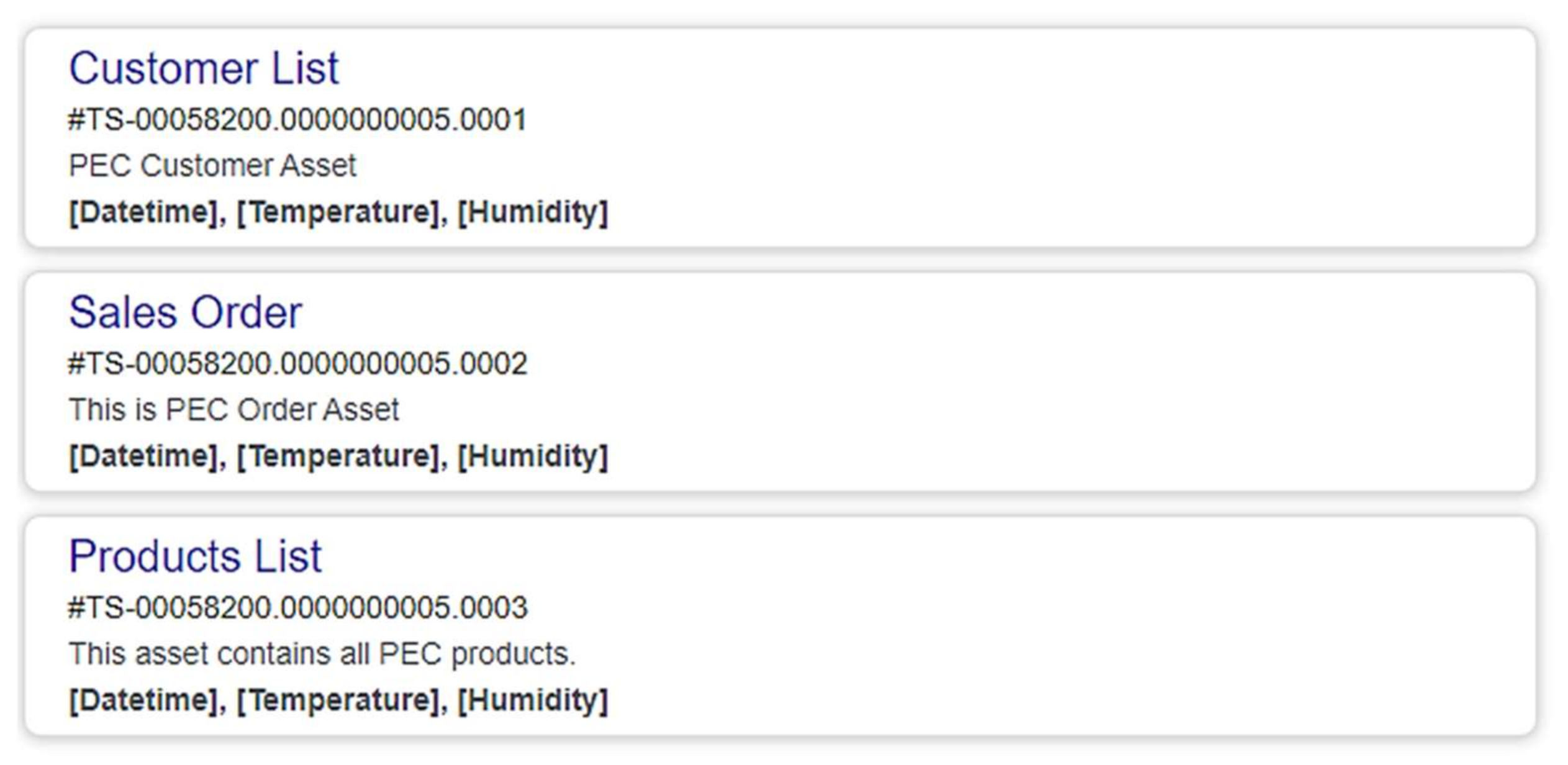
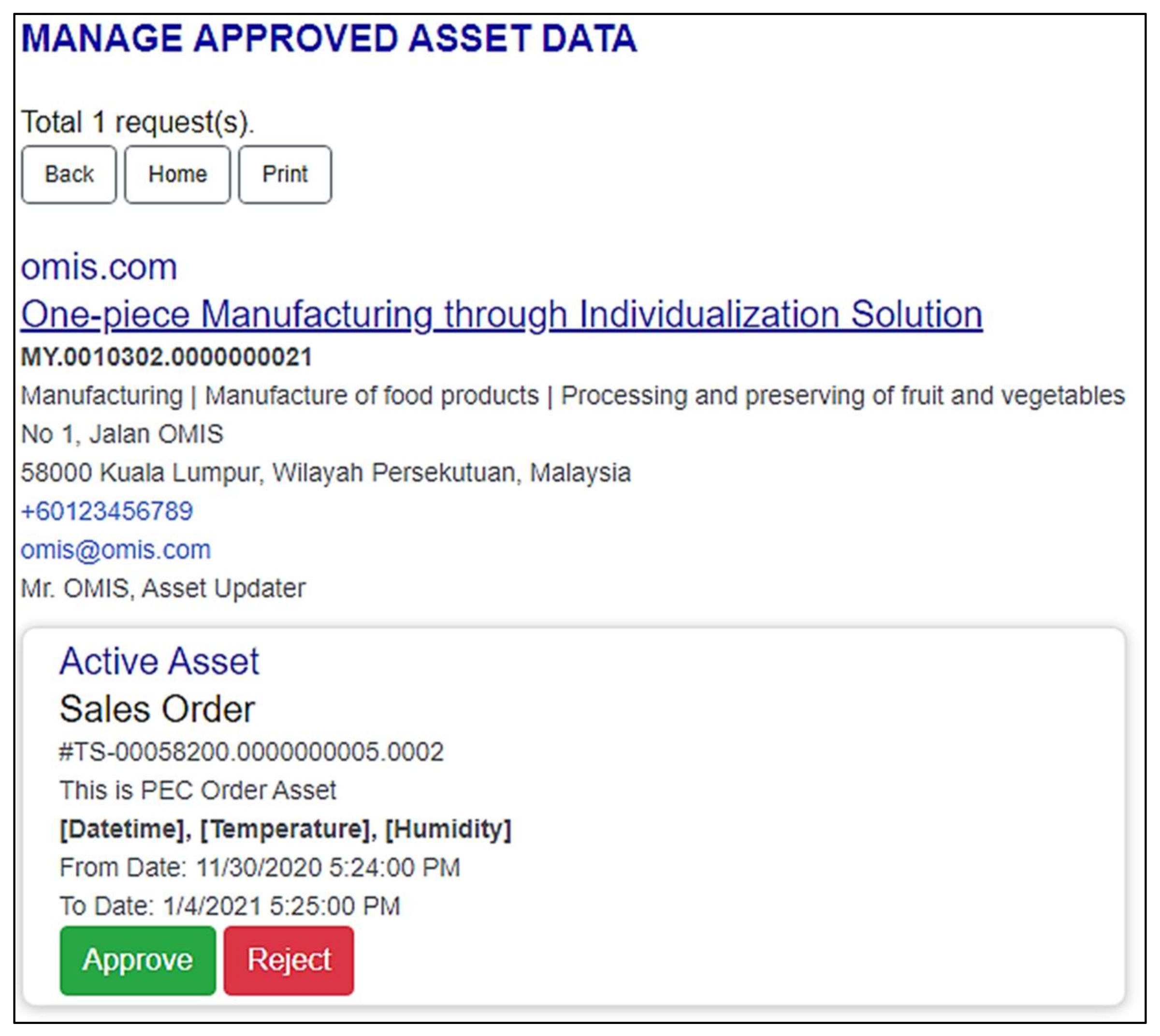
4.1. Testing PEC AAdSys in Creating Assets and Instances
4.2. Connectivity Test between Asset Brokering Manager (ABM) Connector and ABM Portal
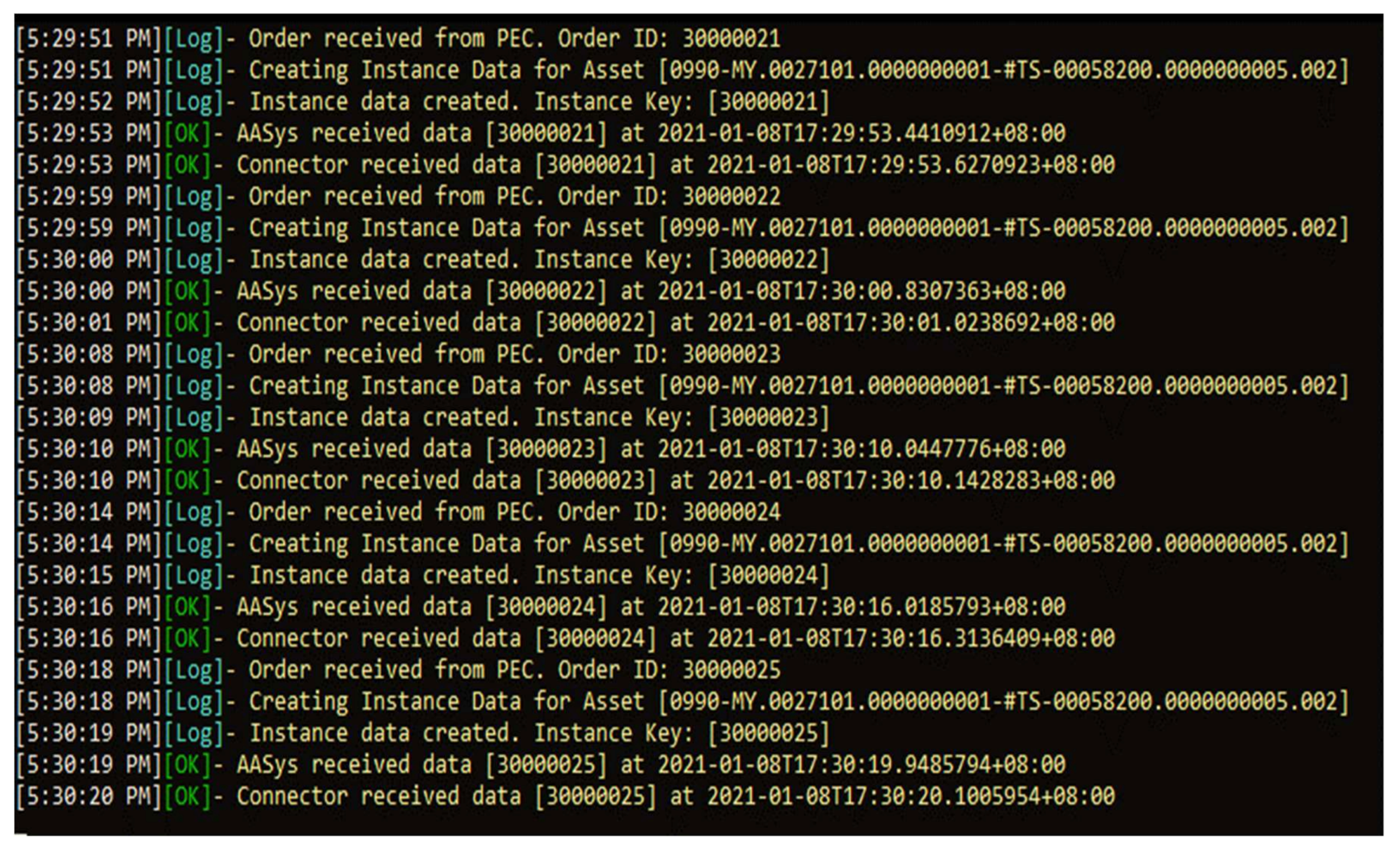
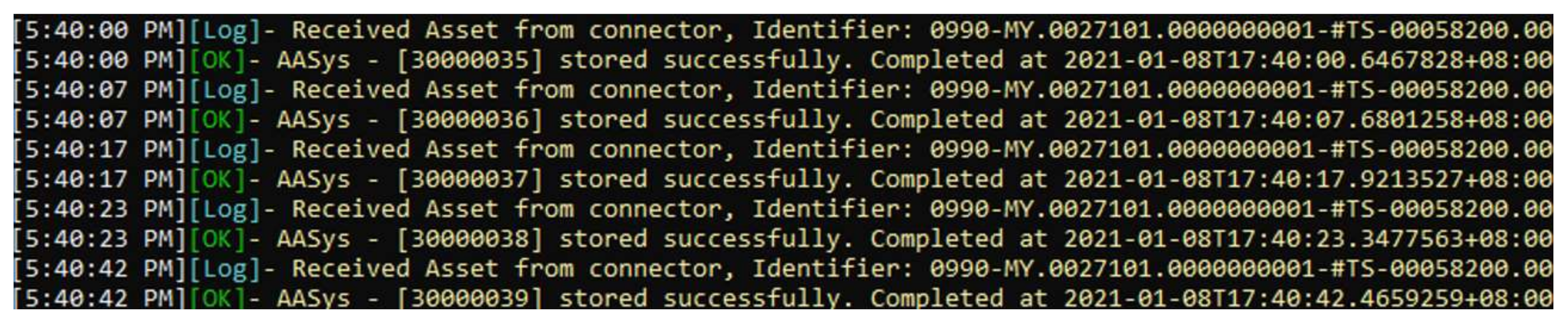
4.3. Connectivity Performance Test between Asset Administration Systems of PEC and OMIS
5. Results
5.1. Testing the PEC AAdSys in Creating Assets and Instances
5.2. Connectivity Test between Asset Brokering Manager (ABM) Connector and ABM Portal
5.3. Connectivity Performance Test between Asset Administration Systems of PEC and OMIS
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Ming, X.; Liu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Yin, D. State-of-the-art review of customer to business (C2B) model. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 132, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torn, I.A.R.; Vaneker, T.H.J. Mass Personalization with Industry 4.0 by SMEs: A concept for collaborative networks. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 28, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, Y. The Global Manufacturing Revolution: Product-Process-Business Integration and Reconfigurable Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Hankel, M.; Rexroth, B. The Reference Architectural Model Industrie 4.0 (Rami 4.0); ZVEI: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schweichhart, K. Reference Architectural Model Industrie 4.0 (Rami 4.0): Introduction. 2016, Volume 40. Available online: https://www.amnytt.no/getfile.php/3901260.2265.akzillql7uuipz/RAMEI+4.0.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Adolphs, P.; Berlik, S.; Dorst, W.; Friedrich, J.; Gericke, C.; Hankel, M.; Heidel, R.; Hoffmeister, M.; Mosch, C.; Pichler, R.; et al. Reference Architecture Model Industrie 4.0 (RAMI 4.0), DIN SPEC 91345:2016-04. DIN. 2016. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/din-spec-91345-reference-architecture-model-industrie-4-0-rami4-0-4/ (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Aheleroff, S.; Mostashiri, N.; Xu, X.; Zhong, R.Y. Mass Personalisation as a Service in Industry 4.0: A Resilient Response Case Study. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheleroff, S.; Philip, R.; Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X. The Degree of Mass Personalisation under Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, H.-S.; Yang, J.-H.; Wang, K.-S. Industry 4.0: A way from mass customization to mass personalization production. Adv. Manuf. 2017, 5, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.H.; Lee, W.P.; Lim, Y.M. Towards Mass Individualized Production: RAMI 4.0 Asset Data Channelling for Manufacturing Value Chain Connectivity. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Computer Communication and the Internet (ICCCI), Nagoya, Japan, 25–27 June 2021; pp. 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P. The Way Forward for SMI/SMEs in Industry 4.0: Industry 4.0 in Germany & Malaysia; Urban Engineering Development Special Interest Group (UEDSIG), Mechanical Engineering Technical Division (METD), The Institution of Engineers: Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Plattform Industrie 4.0. Plattform Industrie 4.0. Digital Transformation, ‘Made in Germany’, Berlin. 2016. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/information_society/newsroom/image/document/2016-27/10__pi40_diemer_16494.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2019).
- SAP News Centre. Open Industry 4.0 Alliance: An Open Ecosystem for the Digital Transformation of Industrial Manufacturing Plants; SAP: Walldorf, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adolphs, P.; Auer, S.; Bedenbender, H.; Meik, B.; Martin, H.; Roland, H. Structure of the Administration Shell-Continuation of the Development of the Reference Model for the Industrie 4.0 Component. Berlin: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi). 2016. Available online: http://sf-eu.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/bmwi-2016-plattform-industrie-4.0-structure-of-the-administration-shell-en.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- DIN SPEC 91345; Reference Architecture Model Industrie 4.0 (RAMI4.0). Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Rojko, A. Industry 4.0 Concept: Background and Overview. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2017, 11, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zezulka, F.; Marcon, P.; Vesely, I.; Sajdl, O. Industry 4.0—An Introduction in the phenomenon. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-W.; Murphy, B.; Clauer, E.; Loewen, U.; Neubert, R.; Bachmann, G.; Hankel, M. Architecture Alignment and Interoperability. An Industrial Internet Consortium and Platform Industrie 4.0; White Paper; Industrial Internet Consortium: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 12, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Alcácer, V.; Cruz-Machado, V. Scanning the Industry 4.0: A Literature Review on Technologies for Manufacturing Systems. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattform Industrie 4.0. Details of the Administration Shell—From Idea to Implementation [UPDATE]. 2019. Available online: https://www.plattform-i40.de/IP/Redaktion/EN/Downloads/Publikation/vws-in-detail-presentation.html (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Chin, C.F.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, W.P. Designing Automated Batch-Processing Production Planning for Manufacturing based on Asset-Oriented Modelling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Transformation and Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 14–16 January 2020; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://www.tarc.edu.my/icdxa/publication (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Cavalieri, S.; Salafia, M.G. Asset Administration Shell for PLC Representation Based on IEC 61131–3. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 142606–142621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, P.; Diedrich, C.; Zezulka, F. The Asset Administration Shell of Operator in the Platform of Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th International Conference on Mechatronics-Mechatronika (ME), Brno, Czech Republic, 5–7 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tantik, E.; Anderl, R. Integrated Data Model and Structure for the Asset Administration Shell in Industrie 4.0. Procedia CIRP 2017, 60, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, M.; Zoitl, A.; Müller, T. Connecting PLCs With Their Asset Administration Shell for Automatic Device Configuration. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 16th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Porto, Portugal, 18–20 July 2018; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Schmidt, J.; Franke, J.; Rehman, K.; Sauer, M.; Karnouskos, S. I4.0-compliant integration of assets utilizing the Asset Administration Shell. In Proceedings of the 2019 24th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Zaragoza, Spain, 10–13 September 2019; pp. 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Grothoff, J.; Epple, U.; Drath, R.; Malakuti, S.; Grüner, S.; Hoffmeister, M.; Zimermann, P. The role of the Industry 4.0 asset administration shell and the digital twin during the life cycle of a plant. In Proceedings of the 2017 22nd IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Limassol, Cyprus, 12–15 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A. Smart manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 56, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattform Industrie 4.0, Relationships between I4.0 Components—Composite Components and Smart Production: Continuation of the Development of the Reference Model for the I4.0 SG Models and Standards. Berlin: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi). 2017. Available online: https://www.plattform-i40.de/PI40/Redaktion/DE/Downloads/Publikation/hm-2018-relationship.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=5 (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- IEC. IEC 62832-1:2020|IEC Webstore. International Electrotechnical Commission. 2020. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/65858 (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Bedenbender, H.; Billmann, M.; Epple, U.; Hadlich, T.; Hankel, M.; Heidel, R.; Zinn, M. Examples of the Asset Administration Shell for Industrie 4.0 Components Basic Part; ZVEI: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, B.; Auer, S.; Cirullies, J.; Jürjens, J.; Menz, N.; Schon, J.; Wenzel, S. Industrial Data Space: Digital Souvereignity over Data; White paper; Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft: Munchen, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Huertas, A.P.; Cantera, J.; Vega, F.; Hierro, J. Industrial Data Space Architecture Implementation Using FIWARE. Sensors 2018, 18, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otto, B.; Steinbuß, S.; Teuscher, A.; Lohmann, S. International Data Space Reference Architecture Model Version 3.0; International Data Spaces Association: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–118. Available online: https://internationaldataspaces.org/wp-content/uploads/IDS-Reference-Architecture-Model-3.0-2019.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Andreas Teuscher, A.; Gerd Brost, G.; Uwe Brettner, U.; Martin Böhmer, M.; Bastian Fraune, B.; Christian Haas, C.; Tina Hardt, T.; Benjamin Heidenreich, B.; Christian Jung, C.; Lutz Jänicke, L.; et al. DIN SPEC 27070:2020-03; Requirements and Reference Architecture of a Security Gateway for the Exchange of Industry Data and Services. DIN German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Erl, T. Service-Oriented Architecture: A Field Guide to Integrating XML and Web Services; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, M.; Lewis, J. Microservices. 2014. Available online: https://martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Xiao, Z.; Wijegunaratne, I.; Qiang, X. Reflections on SOA and Microservices. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on Enterprise Systems (ES), Melbourne, Australia, 2–3 November 2016; pp. 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.; Alencar, B.; Prazeres, C. Microservices: A mapping study for internet of things solutions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications (NCA), Cambridge, MA, USA, 1–3 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Luo, B.; Liu, P.; Lee, D.; Chu, C.-H. Enforcing Secure and Privacy-Preserving Information Brokering in Distributed Information Sharing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2013, 8, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Luo, B.; Liu, P.; Lee, D.; Mitra, P.; Lee, W.-C.; Chu, C.-H. In-broker access control: Towards efficient end-to-end performance of information brokerage systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Sensor Networks, Ubiquitous, and Trustworthy Computing (SUTC’06), Taichung, Taiwan, 5–7 June 2006; Volume 1, p. 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, L.; Doshi, C.; Hu, J.; Seguin, P. Information rich monitoring of interoperating services in privacy enabled B2B networks. Int. J. Adv. Media Commun. 2010, 4, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F. Privacy-preserving data integrity verification by using lightweight streaming authenticated data structures for healthcare cyber–physical system. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 108, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office for Civil Rights. The HIPAA Privacy Rule. HHS.gov. 7 May 2008. Available online: https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/privacy/index.html (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Object Management Group (OMG). Information Exchange Framework Reference Architecture, 1st ed.; Object Management Group, Inc.: Milford, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Object Management Group (OMG). Information Exchange Framework (IEF); Object Management Group, Inc.: Milford, MA, USA; Available online: https://www.omg.org/ief/index.htm (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Charles, D.S.; Wong, T.L.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, W.P. Towards Personalised Manufacturing with Industry 4.0: Asset Brokering in Real Time; UNTAR: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]









| Data Size | Connectivity Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| From | To | Average Time (ms) | |
| 100 kb | OMIS (Manufacturer) | PEC (Retailer) | 114 |
| 100 kb | PEC (Retailer) | OMIS (Manufacturer) | 121 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hang, J.H.; Charles, D.S.; Gan, Z.H.; Gan, S.K.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, W.P.; Wong, T.L.; Goh, C.P. Constructing a Real-Time Value-Chain Integration Architecture for Mass Individualized Juice Production. Information 2022, 13, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13020056
Hang JH, Charles DS, Gan ZH, Gan SK, Lim YM, Lee WP, Wong TL, Goh CP. Constructing a Real-Time Value-Chain Integration Architecture for Mass Individualized Juice Production. Information. 2022; 13(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleHang, Jen Hin, Donovan Sheldon Charles, Zheng Hung Gan, Sze Kai Gan, Yee Mei Lim, Wah Pheng Lee, Thein Lai Wong, and Ching Pang Goh. 2022. "Constructing a Real-Time Value-Chain Integration Architecture for Mass Individualized Juice Production" Information 13, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13020056
APA StyleHang, J. H., Charles, D. S., Gan, Z. H., Gan, S. K., Lim, Y. M., Lee, W. P., Wong, T. L., & Goh, C. P. (2022). Constructing a Real-Time Value-Chain Integration Architecture for Mass Individualized Juice Production. Information, 13(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13020056






