Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatial Regularization Correlation Filter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Correlation Filtering
2.2. ADMM Solution
3. The Proposed Algorithm
3.1. Spatial Regularization-Based Correlation Filter SRDCF
3.2. Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatially Regularized Correlation Filter
3.2.1. Improvement of the Optimization Method for Solving the Filter
3.2.2. Occlusion Detection
| Algorithm 1: Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatial Regularization Correlation Filter |
| Input: initial target bounding box (X, Y, W, H) and other initialization parameters Output: target bounding box1. Enter the first frame and initialize the target filter model; 2. for the 2, 3,… until the last frame do 3. Establish 5 scales around the tracking target, and extract Gray and HOG features; 4. Use formula (2) to calculate the filter response value; 5. Determine the optimal scale of the target; 6. Use formula (14) to calculate the APCE value; 7. if APCE > 0.5 * APCE_Average and F_max > 0.6 * F_(max)Average then 8. While ADMM iterative do 9. use formulas (7) and (12) to solve auxiliary variables and respectively; 10. use formula (13) to update the Lagrangian vector ς; 11. end while 12. Update the filter model; 13. end if 14. Update APCE_Average; 15. end for |
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Dataset and Evaluation Criteria
4.1.1. Experimental Dataset
4.1.2. Experimental Evaluation Criteria
4.2. Comparative Experiments on the OTB2015 Dataset
4.2.1. Quantitative Analysis
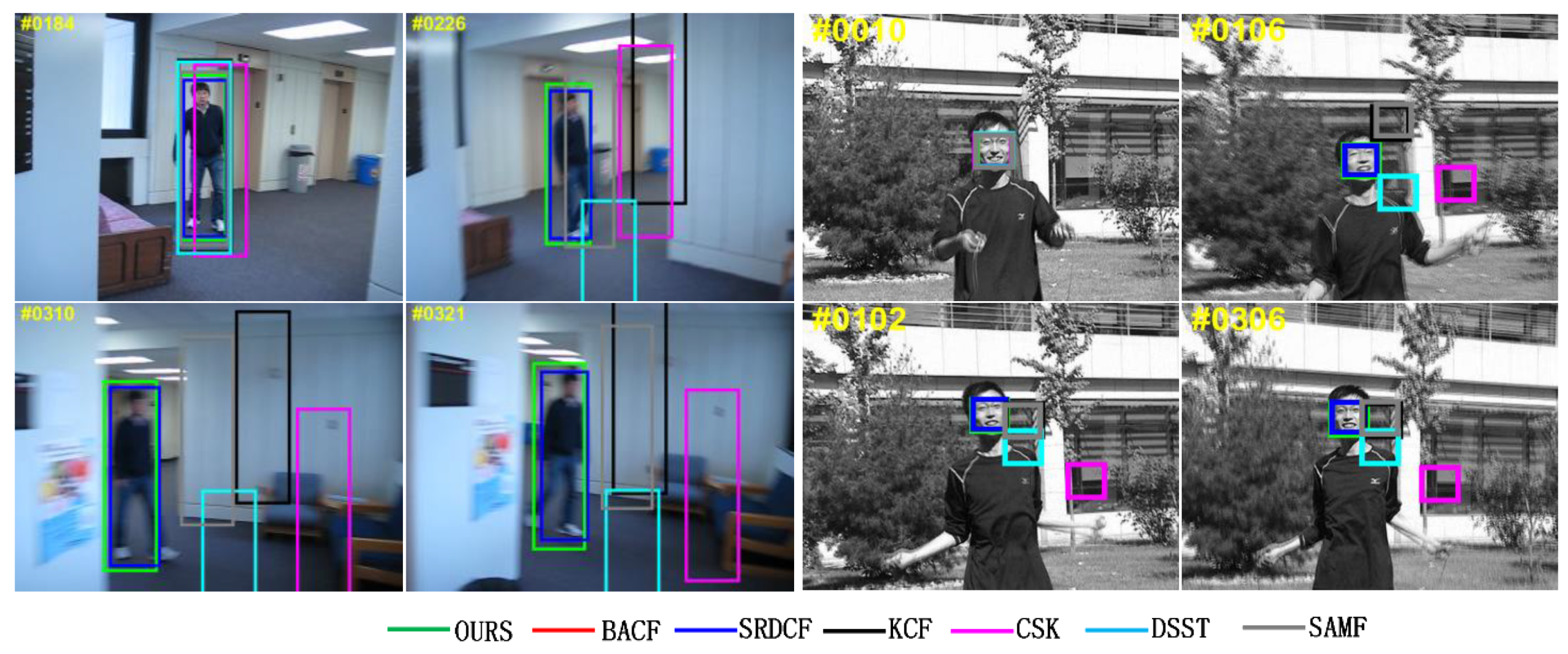
4.2.2. Qualitative Analysis
a: Short-Term Target Occlusion
b: Long-Term Target Occlusion
c: Illumination Change
d: Scale Variation
e: Background Clutter
f: Deformation
g: Motion Blur
h: Fast Motion
i: In-Plane Rotation
j: Out-of-Plane Rotation
4.3. Comparative Experiments on the OTB2013 Dataset
4.4. Comparative Experiments on the UAV123 Dataset
4.5. Comparative Experiments on the TC128 Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, C.; Hu, R.; Jiang, J. Multi-correlation filters with triangle-structure constraints for object tracking. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 21, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, N.A. Self-driving cars and the law. IEEE Spectr. 2016, 53, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautaray, S.S.; Agrawal, A. Vision based hand gesture recognition for human computer interaction: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 43, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.-S.; Mou, X.; Mou, W.; Wang, H. Vision-based navigation of an unmanned surface vehicle with object detection and tracking abilities. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2018, 29, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Smith, N.; Ghanem, B. A Benchmark and Simulator for Uav Tracking. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 445–461. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Kang, W.; He, Z. Robust visual tracking with correlation filters and metric learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 195, 105697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Lu, X.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X. Particle filter re-detection for visual tracking via correlation filters. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 14277–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Yang, Q. Real-Time Part-Based Visual Tracking via Adaptive Correlation Filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4902–4912. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Chang, X.; Huang, P.-Y.; Liu, Q.; He, Z. Self-Supervised Deep Correlation Tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolme, D.S.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A.; Lui, Y.M. Visual Object Tracking Using Adaptive Correlation Filters. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2544–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. Exploiting the Circulant Structure of Tracking-by-Detection with Kernels. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 702–715. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danelljan, M.; Hager, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Learning Spatially Regularized Correlation Filters for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4310–4318. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2011, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z. Large Margin Object Tracking with Circulant Feature Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4021–4029. [Google Scholar]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in C; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M.; Van de Weijer, J. Adaptive Color Attributes for Real-Time Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1090–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Possegger, H.; Mauthner, T.; Bischof, H. In Defense of Color-Based Model-Free Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2113–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Häger, G.; Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Accurate Scale Estimation for Robust Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Voigtlaender, P.; Luiten, J.; Torr, P.H.; Leibe, B. Siam r-cnn: Visual tracking by re-detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6578–6588. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Häger, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 254–265. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Liu, F. Online Learning of Discriminative Correlation Filter Bank for Visual Tracking. Information 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Golodetz, S.; Miksik, O.; Torr, P.H. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1401–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Robinson, A.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. Beyond correlation filters: Learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 472–488. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Hager, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Adaptive decontamination of the training set: A unified formulation for discriminative visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1430–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Eco: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6638–6646. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, G.; Johnander, J.; Danelljan, M.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. Unveiling the power of deep tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 483–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kiani Galoogahi, H.; Sim, T.; Lucey, S. Correlation filters with limited boundaries. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4630–4638. [Google Scholar]
- Kiani Galoogahi, H.; Fagg, A.; Lucey, S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Lukezic, A.; Vojir, T.; Cehovin Zajc, L.; Matas, J.; Kristan, M. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6309–6318. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Tian, C.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.-H. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4904–4913. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Sun, C.; Li, J. Visual tracking via adaptive spatially-regularized correlation filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4670–4679. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Object Tracking Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.-H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Lu, H.; Yang, M.-H. Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1822–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D.A.; Lim, J.; Lin, R.-S.; Yang, M.-H. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Mei, X.; Prokhorov, D.; Tao, D. Multi-store tracker (muster): A cognitive psychology inspired approach to object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 749–758. [Google Scholar]












| Tracker | Precision (Threshold) | Success Rate (AUC) | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OURS | 80.3% | 75.8% | 29.86 |
| BACF | 80.1% | 75.3% | 34.49 |
| SRDCF | 77.2% | 70.9% | 7.71 |
| SAMF | 74.6% | 66.4% | 28.12 |
| KCF | 68.1% | 54.1% | 306.51 |
| DSST | 68.0% | 52.6% | 42.93 |
| CSK | 51.6% | 41.0% | 589.15 |
| Tracker | Precision (Threshold) | Success Rate (AUC) | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OURS | 81.3% | 78.3% | 28.75 |
| SRDCF | 82.2% | 76.2% | 8.10 |
| Staple | 79.3% | 75.4% | 44.90 |
| SAMF | 77.3% | 71.6% | 33.49 |
| KCF | 72.5% | 61.2% | 333.15 |
| DSST | 72.2% | 58.4% | 41.48 |
| CSK | 54.1% | 44.0% | 627.53 |
| BACF | 83.5% | 80.5% | 36.07 |
| MUSTER | 85.0% | 76.8% | 5.61 |
| ASLA | 59.3% | 54.4% | 2.22 |
| IVT | 48.3% | 41.3% | 43.19 |
| Tracker | Precision (Threshold) | Success Rate (AUC) | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OURS | 64.1% | 54.0% | 35.78 |
| BACF | 66.3% | 55.5% | 39.44 |
| SRDCF | 64.9% | 53.2% | 12.62 |
| Staple | 64.1% | 53.7% | 81.16 |
| SAMF | 59.9% | 48.6% | 11.53 |
| KCF | 52.3% | 36.9% | 560.31 |
| DSST | 58.6% | 38.9% | 84.04 |
| CSK | 48.8% | 32.9% | 1076.03 |
| MUSTER | 59.3% | 45.4% | 1.88 |
| ASLA | 54.7% | 47.3% | 2.76 |
| IVT | 43.3% | 36.7% | 42.81 |
| Tracker | Precision (Threshold) | Success Rate (AUC) | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OURS | 66.7% | 63.1% | 35.11 |
| BACF | 64.9% | 61.5% | 39.73 |
| SRDCF | 66.6% | 59.8% | 8.57 |
| Staple | 67.0% | 61.7% | 80.07 |
| SAMF | 63.7% | 58.5% | 20.95 |
| KCF | 55.1% | 46.2% | 454.76 |
| DSST | 53.9% | 44.1% | 67.38 |
| CSK | 39.8% | 32.1% | 847.83 |
| MUSTER | 63.5% | 56.0% | 5.62 |
| ASLA | 48.6% | 40.0% | 2.28 |
| IVT | 35.5% | 29.2% | 37.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Ibrayim, M.; Hamdulla, A. Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatial Regularization Correlation Filter. Information 2022, 13, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13040184
Liu C, Ibrayim M, Hamdulla A. Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatial Regularization Correlation Filter. Information. 2022; 13(4):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13040184
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Caihong, Mayire Ibrayim, and Askar Hamdulla. 2022. "Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatial Regularization Correlation Filter" Information 13, no. 4: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13040184
APA StyleLiu, C., Ibrayim, M., & Hamdulla, A. (2022). Fast Tracking Algorithm Based on Spatial Regularization Correlation Filter. Information, 13(4), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13040184






