Abstract
Recommendation systems play a key role in everyday life; they are used to suggest items that are selected among many candidates that usually belong to huge datasets. The recommendations require a good performance both in terms of speed and the effectiveness of the provided suggestions. At the same time, one of the most challenging approaches in computer science is quantum computing. This computational paradigm can provide significant acceleration for resource-demanding and time-consuming algorithms. It has become very popular in recent years, thanks to the different tools available to the scientific and technical communities. Since performance has great relevance in recommendation systems, many researchers in the scientific community have recently proposed different improvements that exploit quantum approaches to provide better performance in recommendation systems. This paper gives an overview of the current state of the art in the literature, outlining the different proposed methodologies and techniques and highlighting the challenges that arise from this new approach to the recommendation systems domain.
1. Introduction
The rapid growth of online services and social networks has radically changed people’s lives. In our time, we regularly live under the pressure of information overload, overwhelmed by a multitude of online content, making it extremely difficult to find items that could interest us. Determining what the customer likes in real time is crucial for modern e-commerce systems. Especially after the lockdown due to COVID-19, there has been significant growth in online shopping. In parallel, there has been an increasing need to provide online stores with efficient recommendation systems to guide customers through buying.
Recommendation systems (RSs) were introduced by Goldberg et al. in Ref. [1]; they are classified as information systems aimed at information retrieval and belonging to the subcategory of retrieval tasks and goals [2]. These systems are applied whenever users need to be guided through a choice of items when the offer is large, and the catalog presents an assortment of characteristics. Its typical domains of application are music, movies, and online shopping recommendations [3] These kinds of systems collect information about customers and their purchasing decisions regarding the offered items, as well as about features of the products on sale, and propose the items that can be more relevant for the single user or new possible buyers [4,5,6]. In particular, a recommendation system tries to understand the user’s requirements and preferences and searches on a large repository to find adequate items to suggest. The interaction between the user and the system usually follows a very simple approach: the user’s preferences are roughly computed by taking into account the past observed behavior of the people; the user may also provide feedback to the system. One of the key elements of recommendation systems in this process is the clustering operation. Usually, products are grouped according to their characteristics to the ratings obtained from specific groups of users to propose similar items to users who show the same preferences as the group [7].
Depending on how recommendations are made, recommendation systems can be divided into [4]: collaborative filtering-based systems, content-based systems, and hybrid systems.
Collaborative filtering-based systems only make use of the user-item correlation. They propose recommendations by exploiting the assumption that similar users have similar interests. Recommendations are provided according to a nearest neighbors search given a similarity measure so that an item is suggested to a given user by taking into account the interests of a similar user. The approach suffers from a problem known in the literature as the “cold-start” problem: if an item has never been seen during the training phase, the system cannot generally create an encoding for it. Therefore, it cannot query the model with the new item.
Content-based systems exploit item features and a profile of the user’s preferences based on previous actions or explicit feedback to recommend other items homologous to what the user likes. The model best suits situations where there are data about an item. It does not need data on other users since the recommendations are specific to a given user. The profile of the user is determined to infer the type of item the user likes. The model can capture the particular interests of a user, and it has the advantage that it can recommend items that very few other users are interested in. Furthermore, it suffers less from the cold-start problem. On the other hand, the model has a limited ability to broaden the interests of existing users.
Hybrid methods exploit the advantages of the first two approaches [8]. Furthermore, another kind of approach, mentioned here just for completeness, is provided by knowledge-based recommender systems [9]. This approach is based on explicit knowledge regarding items, user preferences, and context-dependent criteria for recommending items. Such systems are used in complex domains when items are purchased infrequently; therefore, approaches such as collaborative filtering and content-based filtering are not easy to apply. They have disadvantages, such as the need to explicitly acquire the necessary knowledge of the recommendations to be provided. On the other hand, they do not suffer from the cold-start problem when the system has not achieved enough information about a user or item.
Despite the success of recommendation systems, they are continuously facing new challenges, such as the increasing volumes of data that have to be analyzed and the growth of the number of users utilizing online services. In this context, the rise of new techniques, methodologies, and computing paradigms that help the effectiveness and real-time computing of recommendations provided by RSs assume a key role. Given the increasingly compelling need for improved performance, deep learning approaches, which are able to deal with complex data feeds, oriented to recommendation systems have been developed [4].
At the same time, new perspectives are opening up thanks to the innovative paradigm of quantum computing (QC), which in recent years has moved out of the purely theoretical domain and is starting to be used in simple but challenging applications [10]. This innovative paradigm has become increasingly relevant in recent years. It has recently undergone considerable development, especially from the hardware point of view: quantum computers are increasingly available to the scientific community, and they have a steadily increasing number of qubits. Currently, the performance of such systems is still limited; however, the technology is undergoing a rapid development stage. The most popular systems include the IBM Qiskit [11], D-WAVE [12], and Amazon Braket [13]. A remarkably clear introduction to the essential elements of quantum computing that does not require a deep knowledge of advanced mathematics or physics can be found in Ref. [14].
Classical computers use the bit to represent information, and each bit can only assume the state “0” or “1”. In contrast, the basic unit of quantum computing is the qubit. One of the most relevant peculiarities of quantum approaches is that they use the superposition property of quantum information. This feature provides a significant acceleration, in general, of time-consuming algorithms. In a quantum computer, the general state of a qubit can be a coherent superposition of multiple states between “0” and “1” at a given instant. Moreover, while measuring the value of a bit does not alter its state, the process of measuring a qubit destroys its coherence and irrevocably alters the superposition state. Superposition is the root principle of quantum mechanics. This principle allows quantum states to be added together, resulting in a new valid quantum state. As a result of this, each quantum state can be expressed as a linear combination of other distinct quantum states. Due to this property, a quantum algorithm can perform multiple operations simultaneously.
During the last two decades, many interesting and useful applications have been developed by quantum researchers. For example, the Shor [15] and Grover [16] algorithms are two milestones often used to show the potential of a quantum approach to computing. From a computational point of view, there are two main approaches in quantum computing: the circuit model and adiabatic computing. The former is analogous to an electronic circuit-like architecture in which the sequence of state transformations is based on quantum computing techniques, and it is widely used in the quantum computing community. On the other hand, the latter is inspired by a physical system’s tendency to evolve toward a state of minimum energy in which the system persists. Models belonging to such a paradigm are not universal and are called quantum annealers [17]. However, in Ref. [18], it is pointed out that such an approach is beneficial when using optimal sampling, facilitating the resolution of NP-hard and NP-complete problems [19].
This paper provides a survey on quantum computing (QC) approaches for recommender systems. The survey has been conducted by reading and examining the results from different queries from Scopus [20] and ISI-WoS [21] and selecting the most interesting papers to give an overview of the literature in the specific field of quantum-based recommendation systems, which can have a relevant impact on both research and industry. In particular, we report works on QC for matrix decomposition, for clustering, for searching, for swarm intelligence, and adiabatic QC approaches for RS. Moreover, we summarize some approaches inspired by quantum computing for solving recommender systems-related problems. We then provide a list of datasets used by the scientific community to test the approaches. This list could also be a reference for those researchers that would like to propose new quantum-oriented algorithms and techniques for recommendation systems. Finally, future challenges and conclusions are outlined.
2. Quantum Approaches for Recommender Systems
In the next subsections we illustrate an overview of the main quantum computing-related or -inspired techniques that are currently exploited in the recommendation systems field.
2.1. Quantum Computing for Matrix Decomposition
Many recommendation systems exploit previously stored data about purchases or ratings of a number n of products by a group of m users. This information is usually modeled as an preference matrix , which is assumed to have a good rank-k approximation for a small integer constant k. The matrix decomposition of the matrix is based on an assumption, called low-rank assumption, that only a limited portion of the matrix is relevant for the recommendation. A motivation from a cognitive point of view is that people buy a product for a few reasons: the price, the quality, the popularity, and the recognition of the brand [22]. Another reason is that users can be considered as belonging to a small number of ‚“types”, and each individual is a noisy version of these “prototype” users [22].
Since the matrix decomposition operation is typically computationally expensive, exploiting the quantum computing paradigm for manipulating matrices and, in particular, managing their decomposition process is relevant. In the following, we recap the approaches that use QC for matrix decomposition or manipulation in general.
2.1.1. Singular Value Decomposition
In Ref. [22], Kerenidis et al. define a subsample matrix that, with some probability, has elements that are equal to the matrix ; otherwise, they are set to zero. The singular value decomposition technique extracts the top singular vectors that allow the fundamental relationship among users and items to emerge, discarding the co-occurrence noise in data [23]. The authors describe an efficient sampling algorithm that avoids computing the entire matrix and determines if, with a good probability, the value corresponding to the j-th item for the i-th user is equal to one. In particular, the authors compute the approximation of the preference matrix through a quantum algorithm. More precisely, they use an efficient quantum procedure that, having as input a vector, a matrix, and a threshold, computes the quantum state corresponding to the projection of the vector onto the space spanned by the row singular vectors of the matrix. The resulting projection is the vector containing the recommendation for the user. The algorithm proceeds from the quantum walk-based algorithm by Childs [24], and its time cost is polylogarithmic in the dimensions of the matrix; in particular, it is , being k the dimension of the reduced space, m the number of users, and n the number of the items.
Tang proposes in Ref. [25] a quantum-inspired 2D recommendation system modeled by an . The author demonstrated that its time cost is O(poly(k)log(mn)), an exponential increase in speed compared with other classical methods and only polynomially slower than Kerenidis and Prakash’s quantum algorithm [22]. Tang’s 2D recommendation systems algorithm was analyzed in Ref. [26]. This raised the question of whether Tang’s algorithm was actually useful in practice. The authors of Ref. [26] pointed out that Tang’s algorithm is only advantageous for preference matrices with extremely large dimensions and a very low rank, and they question whether these kinds of datasets exist. According to their evaluation, Tang’s algorithm takes more time and suffers higher inaccuracies than the classical exact diagonalization method.
Following a similar approach, Wang et al. [27] introduced a quantum recommendation system through the representation of a third-order tensor of dimension N, where N is computed as the product of the number of users, the number of items, and the contexts used for the recommendation. The contexts, e.g., delimiting the interests to specific time intervals or to a certain episode, can focus the recommendation on a more specific subset of the available items. The rationale is that the product that a user prefers in a specific context is likely to affect the recommendation for the user in other contexts. In the algorithm, the connection among different slices, formed by matrices of users × products elements, are taken into account through the quantum implementation of the Fourier transform. The general idea of the algorithm is to approximate the observed-preference tensor using the truncated T-SVD in the Fourier domain. The quantum parallelism allows for estimating the quantum singular value of all frontal slices after the parallel quantum Fourier transform and sensibly reducing the processing time. The algorithm has a time cost of .
2.1.2. Normalized Non-Negative Models
In 2016, a recommendation system was implemented by Stark through a system–state–measurement quantum paradigm; furthermore, it has also been implemented in the form of normalized non-negative models (NNM) [28]. Each user is represented in terms of a probability distribution on a sample space. The user answers questions such as: “Do you like the item i?”. The normalized non-negative models can be used to interpret user preferences as a mixture of user stereotypes, the computation of hierarchical orderings of tags of users and items, and the fast inference of users’ states [29]. NNMs can be used to compute operational user–user and item–item distance measures. According to the author, the quantum models have been successful in physics due to their relation to probabilistic descriptions and for their high predictive power and interpretability. At the same time, they allow us to draw conclusions starting from users and items representations in the RS domain. As highlighted by the author, the interpretability of quantum models derive from Kolmogorov factorizations. The high interpretability of this kind of model comes at the price of higher dimensionality of representations. The quantum model, which has a reduced dimension, performs recommendations by achieving a trade-off with high interpretability [29].
In Ref. [30], Reafee et al. propose standard quantum-based similarity (SQB), which represents the item-use rating through vectors in the Hilbert space and calculates the influence of explicitly connected friends and implicit friends. The authors extract the item correlation by exploiting social tag information. They proposed a model integrating two regularization terms methods to improve the prediction accuracy and enhance the recommendation quality. SQB is adapted to measure the similarities between users and items in the proposed model. The SQB method is based on the Dirac notation and normalization to re-represent the rating matrix and obtain a new one in Hilbert space. Once represented, the similarity is evaluated through the inner product.
Batra et al. in Ref. [31] propose matrix factorization to predict three types of quantum correlations considered as figures of merit: von Neumann entropy, negativity of a general quantum state, and discord [32]. The system was able to correctly predict about 50% of unknown elements and to determine, using a reference database, if the database was clean/genuine, noisy, or fake. The tests have been carried out with randomly produced states and random evolution, although the approach has the advantage that it is straightforward to extend to real scenarios.
Ouedrhiri et al. adopt quantum methods based on phase estimation [33] (QPE) to generate recommendations. The phase estimation is used to find eigenvalues for unitary operators. The authors adopt three quantum algorithms using the QPE technique as a subroutine: the quantum principal components analysis (PCA) for data visualization, the Harrow–Hassidim–Lloyd (HHL) algorithm to solve linear systems [34], and the quantum singular value thresholding (SVT) [35] for matrix completion in recommendation systems. This study is focused on the theoretical study of the proposed approach.
2.2. Quantum Computing for Clustering
In Ref. [36], Ouedrhiri et al. cast the recommendation as a clustering and matrix completion task. The authors propose a hybrid recommendation system based on a quantum k-means clustering algorithm to extract the users’ clusters and the sets of items. The authors also apply the singular value thresholding (SVT) [37] algorithm to sub-matrices, where an item is missing for a user to estimate the possibility that the user could be interested in the given item. Since the algorithm’s most resource-consuming operation is distance computation, they adopt quantum computing properties to speed up the calculation process. The approach has been tested on the MovieLens dataset [38].
A similar approach based on clustering was proposed by Kolhe et al. [7]. They processed the textual user opinions with lemmatization, the removal of stop-words, and uniform resource locators (URLs). Then, topic modeling with latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and the modified grey wolf optimizer (MGWO) was exploited to identify the best keywords. The extracted keywords were clustered into two forms (positive and negative) by applying a quantum clustering algorithm based on possibilistic fuzzy C-means (QIPFCM). The QIPFCM algorithm was included in the conventional PFCM algorithm to identify the optimal cluster number, helping to reduce system complexity. In this study, a product recommendation system was performed on a reputed Amazon customer review dataset. Using this dataset, the proposed algorithm overcomes similar techniques, such as collaborative filtering, k-means, and fuzzy C-means in terms of precision, recall, and F1-measure.
A work based on a clustering method and empowered with the Grover algorithm is presented in the paper of Andreev and Lazarova [39]. They tackle an image-based recommendation problem to verify if an image can be recommended given a set of reference images. The images are represented through ORB descriptors (using the gray-level value), and they are clusterized with Jaccard-Needham dissimilarity. The obtained representations are processed with quantum procedures, in particular the distance computation, the recommendation step, and finally the step of matching the image representation with other descriptors. The Grover algorithm is used to map the images in the clusters created starting from ORB descriptors. The experiments have been carried out with the Graz-02 dataset [40], which consists of 1096 images with 640 × 480 resolution, split into three categories: bikes, cars, and people. The technique’s performance is evaluated according to the time needed to let the clustering process converge.
2.3. Quantum Computing for Searching
Chakrabarty et al. in Ref. [41] employ the Grover search algorithm for a recommendation system. They use a dynamic search, based on Grover, to define the goals of the recommendation. The goals are represented with a binomial similarity distribution. The recommendation is cast as a similarity searching in an unstructured space and is implemented as Grover’s search with a difference in the selection function.
The authors state that a static selection function can be constructed to select the top M states if the search space is well known. In the case of an unknown or a dynamic search space, it is not easy to build a static selection function. In that case, they dynamically associate the selection to the similarity with the given state .
For each iteration of the proposed dynamic Grover’s search, a set of quantum states is superposed, and each state corresponds to an item through a random number. The oracle is provided as the selection of a given item . According to the authors, the iteration converges toward the Grover search and finds a set of states M related to the desired item. No typical recommendation system dataset has been used, and experiments were devoted to comparing Grover convergence with the proposed dynamic Grover procedure.
Moreover, Sawerwain and Wróblewski proposed in Refs. [42,43] to use the Grover search, coupled with k-NN, for proposing a recommendation. In particular, their technique is focused on data processing—they consider a quantum k-NN based on a Hamming distance. The Grover procedure is used to improve the quality of the recommendations. The authors represent the items in the quantum system as:
where is used to encode the identifier of the recommended element, and the part of the register describes the features of individual database elements. is the description of the features desired by the user, and are additional qubits. The authors use, at first, items points of the database whose features are closest to those indicated by the user. For this purpose, the quantum version of the k-nearest neighbors algorithm is used. If the auxiliary qubit indicates that a match has been found, the Grover algorithm is used to amplify the probability of the best solutions. Otherwise, an uncomputing step is performed and the quantum k-NN is repeated. The auxiliary qubit is determined be the Hamming distance between the features and the user vector. The tests were carried out on the OMDB dataset [44]. The results are presented as probability distributions of the single k-NN samples over the user id and items features after the Grover’s convergence.
2.4. Quantum Computing and Swarm Intelligence
Collaborative filtering was implemented by Logesh et al. in Ref. [45] through swarm techniques and, in particular, with quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (QPSO). This approach was tested on data from the “Yelp!” and “TripAdvisor” websites and evaluated according to hit rate, precision, and f-measure recall. The dataset is not public, and the pre-processing from the online data is not made explicit.
A common technique to enhance collaborative filtering was to endow the recommendation system with clustering techniques to generate personalized recommendations to meet users’ requirements. In the user-based CFRS, the clustering technique employs a similarity measure to group the users based on the similar item ratings given by different users. The authors propose a new user-clustering approach based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (QPSO) for better clustering by addressing the drawbacks of RS based on traditional clustering. Quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (QPSO) is a new swarm intelligence algorithm with improved ability over PSO by producing an effective solution for global optimization problems with fewer adjustable parameters [46]. The authors adopt a quantum-induced clustering ensemble (QICE) approach-based collaborative recommendation system by exploiting multiple swarm intelligence algorithms. The main goal of the user-clustering process of this approach is to enhance the task of creating recommendations. They consider the quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization inspired by the trajectory analysis of PSO and the quantum mechanics. To improve the performance, the mean of the previous best positions has been exploited to frame the QPSO algorithmic model. The quantum algorithm differs from the PSO since it does not require a velocity vector from the particles and only one parameter must be adjusted during the process. The QPSO is adopted to cluster the data and find a similarity matrix from the users’ preference history. A new user is then matched in the existing clusters, and the neighbors are determined. According to the found rating, a recommendation list is generated. Furthermore, a classical version of PSO and k-means mussels wandering optimization is used through an ensemble to obtain the best results from the three techniques. In particular, mussels wandering optimization (MWO) is a meta-heuristic method inspired by the locomotion behavior of mussels during their bed-formation patterns in their home environment. The MWO algorithm is a bio-inspired optimization algorithm that formulates the evolutionary mechanism to distribute the mussels’ bed patterns by Levy walk and a stochastic decision. The proposed method outperforms, in terms of hit-rate, precision, accuracy, and F1 score, the traditional clustering techniques, such as k-means and c-means, and tautologically also the sub-technique forming the ensemble.
2.5. Adiabatic Approaches to Quantum Computing
Quantum annealers have been used in different problems, such as restricted Boltzmann machines for deep learning [47], support vector machines [48], matrix factorization [49], multiple community detection [50], graph isomorphism, and graph partitioning [51,52]. A very interesting quantum annealer solution in the field of recommendation systems has been proposed by the authors of Ref. [18]. They suggest a hybrid feature selection methodology that can be solved by using an adiabatic approach. In particular, the authors focus on selecting the most appropriate set of features that can be used for classification or for making predictive recommendation models. This task is challenging to tackle, being NP-hard and requiring thorough domain knowledge.
The technique proposed in Ref. [18] addresses the feature selection problem through a formulation called QUBO (quadratic unconstrained binary optimization), which allows NP-complete and some NP-hard problems to be described. The authors observe how a QUBO formulation can be solved with a quantum annealer. Specifically, an annealer called D-Wave Advantage, consisting of more than 5000 qubits connected with a sparse graph called Pegasus [53], was used. One notable feature is the annealing times, which are reported to be constant and equal to about s, although more cycles must be run due to the stochastic nature of the problem being treated. Nevertheless, the authors highlight that the best solution can be found in a very short time. Such an approach is called collaborative-driven quantum feature selection (CQFS). According to this methodology, features are selected based on the way users interact with them; this is performed to exploit the domain knowledge implicit in user behavior. Specifically, the approach is based on an already trained collaborative model; features are selected so that the content-based model built by exploiting the selected features simulates a collaborative model in some way. An idea of the relevance of the selected features is obtained by considering all the features with which to build a content-based model. The more similar the items obtained with the collaborative and content-based models are, the more relevant the selected features are.
The system defines a QUBO problem by exploiting a matrix called the “Feature Penalization Matrix”, a matrix of dimension , where F is the feature cardinality of the entire set of items and contains the coefficients of the QUBO objective function. The authors also impose a soft constraint in the objective function to select a certain percentage of the original number of features. When solved, the binary optimization problem provides a selection of features that can be used to train a content-based recommendation model. The quantum annealer employed to solve the optimization problem generates various solutions. The authors sampled 100 answers, selecting the one with the best fitness value according to the QUBO model. In the solution proposed by Ref. [18], the authors rely on a previously trained collaborative model, then feature selection is performed so that the content-based model built with the selected features mimics the collaborative model as closely as possible. Therefore, considering a content-based model built using all features, if the similar elements in this model are also similar in the collaborative model, this indicates that the features are important. Conversely, if the features are similar in the content-based model but not in the collaborative model, this indicates that the features are unimportant and can add noise.
Another interesting approach that exploits the adiabatic computing paradigm implemented by the D-Wave quantum annealer has been illustrated in Ref. [54]. The proposed methodology exploits the D-Wave Advantage quantum annealer to determine the optimal set of recommendations for a user, without assuming anything about the models that generate them. The qubits of the D-Wave Advantage annealer are organized in a graph topology named Pegasus, which is based on a simpler one named Chimera, where qubits are arranged in bipartite 8-qubit graphs, named “unit cells”. The formulation is similar to the one proposed in Ref. [18], exploiting the quadratic unconstrained binary optimization(QUBO):
where is an n-dimensional vector and Q is an matrix containing the parameters of the model. According to Ref. [54], to solve the problem represented in a QUBO format, it is necessary to map it into a quantum processing unit (QPO) of the annealer. This process requires two phases: the embedding phase and the parameter-setting phase. The first finds a subgraph of the problem graph G so that G can be obtained by contracting the edges of the subgraph. The second phase adds constraints to the loss function in order to consider the nodes and edges created during the first phase. Following this methodology, if the problem can be expressed in QUBO, it is feasible to sample optimal solutions in a time of tens of milliseconds.
The goal of the approach is to provide a list of carousels that give the user correct recommendations that are not already present in other lists, ensuring in this manner an adequate diversity among the possible choices. The authors consider a set M of all available recommendation models and a function that provides the number of times the item i has been recommended. The coefficients of the QUBO problem are then determined to provide accurate models and avoid selecting those that are too similar. To reach this goal, the authors introduce some heuristics related to the accuracy (A), measured as the precision of the given model calculated on a validation set, and the diversity (D) of the recommendations computed through two different heuristics, namely correlation measures and the Gini index [55], and, finally, the authors propose the use of a penalty function that is used to select a given number c of models.
The system has been evaluated by using the Netflix [56] and the MovieLens10M [57] datasets. The authors optimized different recommendation models: 21 models for the MovieLens10M dataset (15 collaborative, 3 content-based, and 3 hybrid approaches) and 15 models for Netflix. The authors show that the QUBO carousel selection (QCS) strategy is competitive with the individual greedy strategy on Netflix. It has to combine accuracy and diversity by using the Gini index to be competitive by using the Movielens10 dataset. On the other hand, QCS cannot give better performances than the incremental greedy strategy. The authors suppose that an explanation could be that the incremental greedy considers all user’s recommendation lists while QCS is dependent on the global item distribution. However, a significant advantage of the QUBO carousel selection is its scalability: fractions of a second instead of an hour are required for the incremental greedy. This makes the QCS methodology a promising path for real-time recommendation systems.
2.6. Quantum Computing-Inspired Approaches
A variational bandwidth auto-encoder (VBAE) was proposed for recommendations in Ref. [8]. VBAE first encodes a user’s collaborative and feature information into Gaussian latent variables via deep neural networks that capture non-linear user similarities.
A quantum-inspired uncertainty measurement of the hidden rating embeddings has been proposed by disentangling the uncertainty information contained in the ratings. Through this mechanism, VBAE incorporates adequate auxiliary information from user features if collaborative information is insufficient. Extensive experiments were conducted on three real-world datasets that are available on github [58]. The authors focused on the attention mechanism introduced into recommendation systems to dynamically fuse the user rating and feature information. However, the attention weights are generally calculated by modality embedding and softmax normalization, which may fail to capture the actual relative importance among the found modalities. To overcome this issue, they used a quantum-inspired uncertainty measurement of collaborative information and a channel with user-specific bandwidth to dynamically fuse the user feature and collaborative information.
The paper describes a collaborative module that infers the user latent collaborative variable and the latent channel variable based on user–item interactions. A parameter is the bandwidth of the channel that determines the sufficiency level of the collaborative information. A neural network is used to model the generative model based on Bernoulli distribution, and a collaborative network produces the inferences. To jointly learn the parameters of the generative network and the inference network, the authors maximize the evidence lower bound (ELBO), which approximates the marginal log-likelihood of evidence.
The collaborative model infers the latent variables and channel according to the user–item interactions. The channel bandwidth determines the level of collaborative information and it should disentangle uncertainty and semantic information from the preference attributed by the user. The proposed system adopts a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to embed the sparse rating vector into a compact hidden representation. The length of the representation is a measurement of the uncertainty of collaborative information, and the direction is the representation of semantic information that is used to infer the user collaborative embedding. The hidden embedding is implemented as a quantum superposition state of a physical system. The advantage is that the superposition vector has the property that the norm of the vector is correlated with the probability that this superposition is observed when measuring the system, and the direction of the vector distinguishes a superposition state from other states. The contribution is bound to the quantum algorithms since the authors use a quantum-inspired measurement of the hidden rating embedding to infer the bandwidth of the channel according to the Bayesian model. The bandwidth enhances the model generalization, modulating the information from the user preferences according to the level of collaborative information.
In Ref. [59], a method is proposed to make the recommendation process transparent. The authors start from the assumption that Hilbert space can generalize the representation of the information, and language representation is effectively used with quantum algorithms. Density matrices represent the text snippets about the users’ preferences and quantum measurements are applied to distill information encoded in density matrices. The authors propose a unified model to fuse information in reviews, IDs, and ratings. The quantum measurement can capture the similarity between reviews of users and items. The results of quantum measurements and the embedding vectors of IDs are merged to obtain the rating of the prediction. In particular, the technique is based on the representation of the words of the reviews into a finite vector space, and their normalized direction vectors are viewed as quantum states. From the quantum states, the density matrices are derived with the non-linear weights, and quantum measurements are applied to compute the similarity between user reviews and item reviews. The final step is to put together the results of quantum measurement and the ID of the embeddings to predict the rating through a fully connected layer. This layer is trained with the aim of reducing the square mean error between the actual rating and the layer output.
This approach has been tested on six publicly available datasets that provide reviews and ratings. These six datasets are obtained from Amazon 5-core1 and include Video Games (VG), Tools and Home Improvements (THI), Sports and Outdoors (SO), Toys and Games (TG), Pet Supplies (PS), and Grocery and Gourmet Food (GGF) [60]. The proposed approach outperforms the traditional baseline algorithms.
In Ref. [61], a recommendation system for disruptive innovations is proposed by Trisetyarso et al. The paper starts from the point that, in a market, the incumbents tend to keep their customer until the arrival of a disruption tendency introduced by new entrants. They stated that through a threat-inspired quantum game, it is possible to model this kind of ecosystem. In particular, they use Eisert–Wilkens–Lewenstein quantum strategies [62] that, for example, are shown to solve the case of the Prisoners’ Dilemma, allowing for the removal of the dilemma if quantum strategies are employed. For the recommendation system, the users are the quadruple helix ecosystem members and the items are the innovation trends. The recommendation system, spotting disruptive innovations, is obtained by measuring the strategy over the players. During the gamification with the innovations ecosystem, collaborative ratings on innovation trends are evaluated. Recommendation systems share information via social media, workshops, conferences, or other meetings. The outcomes of this gamification are an evaluation of the innovation trends. The collaborative system attempts to forecast the utility of innovation trends for a particular member of the ecosystem according to the items previously used by other members.
In Ref. [63], Khaliq et al. use a parking recommendation system to propose parking spaces according to parking history. They also focus on privacy issues, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of the stored data. To guarantee data, they adopt distributed ledger technologies (DLT), which are based on the consensus of replicated and shared digital data on multiple servers, without relying on a central authority and providing, at the same time, scalability and privacy. Furthermore, the author assumes that a potential attacker can employ a quantum computer to break both symmetric and asymmetric encryption protocols effectively. An example is Shor’s algorithm combined with a stable quantum computer, which has the potential to break conventional cryptosystems.
Even if the paper is not concerned with a quantum algorithm applied or exploited by a recommendation system, it sheds light on security issues. In particular, to ensure quantum resistance, the work considers the Internet of Things application (IOTA), which employs a Winternitz one-time signature (WOTS) that is blue-judged secure against quantum computing blue attacks. The WOTS algorithm is considered the most efficient method for key generation and signature compression.
2.7. Quantum Computing for Monte Carlo Simulation
An interesting approach, related to both quantum computing and recommendation systems, is that proposed in Ref. [64]. The authors exploit recommendation systems to approach a quantum-oriented Monte Carlo simulation. In particular, the authors construct a classical molecular gas model to reproduce the quantum distributions and molecular simulation techniques. They start from the assumption that recommendation systems have the purpose of building a probabilistic model based on the user’s past behavior to suggest favorable products with high acceptance rates. They model the probability distribution of the QMC configurations with machine learning techniques and propose new updates accordingly.
The technique is based on identifying the correlations in the QMC configurations to build a classical system used as a reference; then, the reference system is used as a recommendation engine to guide future QMC sampling. The QMC simulation is improved through recommendation systems as they can use non-local updates (that in the configuration can vary drastically) and accumulate multiple local updates, generating a global update. Furthermore, since the simulation of the molecular gas is much cheaper than the QMC ( versus operations), the recommendation step provides little overhead and can be efficiently used in the design of new model proposals.
3. Datasets Used in the Literature
The approaches examined in this survey use different datasets; hence, there is no standard and common benchmark to test the different methods. This choice is reasonable, since each technique highlights specific characteristics of the presented method. The list of these datasets has been provided in Table 1.
The OMBd dataset [44] collects information about movies and is accessible through a web service. It contains movie information, content, and images; all the information is contributed to and maintained by users. The dataset includes over 12,000 records.
The Inria Graz-02 dataset [40] is a collection of 1096 natural-scene images, with a resolution of 649 × 480, prepared at Graz University of Technology. The annotations created at INRIA focus on bikes, cars, and people and may present high intra-class variability on cluttered backgrounds. In Ref. [39], the recommendation is to find the dataset image that is more relevant given a test image represented through a given feature. There is no ground truth about this task.
The Amazon dataset [65] was used by Ref. [7]. The dataset contains a set of reviews from Amazon. The reviews are around 35 million from more than 6 million users from June 1995 to March 2013. The reviews are about products, ratings, and plaintext opinions. A subset with eight topics has been selected for the testing of the paper.
The Netflix Prize dataset [66] was used by Ferrari Dacrema et al. in Ref. [54]. The data contain 17770+ files about the preference of 480,189 users on movies. The Kaggle Netflix Prize open competition used the dataset to select the algorithm to predict film user ratings. The grand prize was USD 1,000,000 and was won by BellKor’s Pragmatic Chaos team.
Wang used the Yahoo! Webscope Movies dataset in Ref. [27]. It covers the preference of 7642 users on 11,915 movies and contains 221 K ratings in a scale. A subset with 800 users and 4623 corresponding movies was selected. From the original dataset containing user age and gender features, the user’s birth year was selected as the third dimension.
The Citeulike dataset [58,67] was used by Pan et al. [59]. Data were collected from Citeulike and Google Scholar; the information is related to papers and are in two sub-databases, citeulike-a and citeulike-t. The first contains data for 5551 users and 16,980 items; the user–items pairs are 20,4987. Similarly, Citeulike contains 13,4860 user–items pairs for 7947 users and 52,975 items.
In Ref. [36], the dataset MovieLens 100 k was used. It was created by the GroupLens Research Project at the University of Minnesota and collects movie ratings. It is composed of 100,000 ratings from 943 users on 1682 movies. Furthermore, simple demographic information for the users, such as age, gender, occupation, and zip code, was included. The dataset was released in April 1998.

Table 1.
Used dataset.
Table 1.
Used dataset.
| Year | Paper | Dataset | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Sawerwain et al. [43] | OMBd | [44] |
| 2019 | Andreev et al. [68] | Inria Graz-02 [69,70] | [40] |
| 2021 | Kolhe et al. [7] | Amazon [60,71] | [65] |
| 2021 | Ferrari et al. [54] | Netflix Prize [56] | [66] |
| 2021 | Wang et al. [27] | Yahoo! Webscope | [72] |
| 2022 | Pan et al. [59] | Citeulike [8] | [58,67] |
| 2022 | Ouedrhiri et al. [36] | MovieLens | [38] |
4. Challenges
We have reviewed different approaches that illustrate the advantages of exploiting the quantum computing paradigm in the field of recommendation systems. Some of them explicitly make use of quantum computing to improve the specific aspects of well-known approaches, while others take into account quantum-inspired algorithms. The different contributions analyzed here can be divided into two categories according to input data usage. Among the works based on collaborative filtering there are 15 papers [7,8,18,22,25,27,28,30,31,36,41,45,54,59,61]. The other category of recommender systems is content-based filtering and we considered six works as being related with this approach [39,42,43,63,64,68].
The main advantage of using quantum techniques for recommendation systems is that the quantum algorithms can outperform traditional computations under given conditions. The reviewed papers often are focused on given aspects of the computation and cover all the components of the given problem. Some work is oriented on the computational cost or the theoretical development and does not consider the adherence to user preferences. This issue can be due to the relative youth of the considered field and to the heterogeneity of the scholars in quantum computing. Among the studies taken into consideration, all the works that start from a matrix with information about items and users’ preference fall into the category of collaborative filtering methods. The methods that, given the representation of the items, cluster data or search new items for a single user are typically related to content-based filtering.
The distribution of the considered method for this review is shown in Figure 1, which provides a general snapshot of how the examined approaches can be related more to the collaborative or content-based filtering paradigms. Even if some of the techniques are generally or loosely related to one of the two filtering classes, we have tried to associate them with one of them.
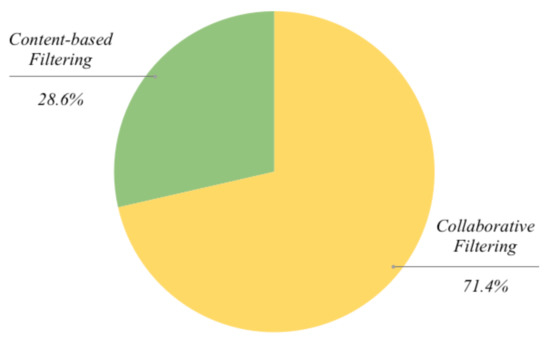
Figure 1.
Overall covering of the examined quantum-related approaches with regard to a subdivision related with collaborative- vs. content-based filtering.
In the following, we highlight as emerging challenges the computational cost, which when reduced, allows us to limit the time, allocated resources, and the performance in terms of the accuracy, precision, and recall of the found items to be recommended.
- Computational Cost: The advantage of using quantum techniques is that these techniques can sensibly reduce computational costs and speed up processing. The paper of Kerenidis et al. focuses on the computational cost of their approach, and they assess their technique as , with m the number of users and n the number of products. k is the low-rank approximation for the global matrix. The technique is also run with constant memory. The SVT algorithm used in Ref. [33] has a cost that is , where is the condition number and depends on the value of the highest and lowest eigenvalue, and is the accuracy of the approximation.Wang et al. [27] adopt a recommendation through a third-order tensor of dimension N. The time complexity of the algorithm is , with k being the low-rank value and N taking into account the number of users, the items, and the number of different contexts. The Tang algorithm in Ref. [25] performs the recommendation with a time cost of .
- Performance The performance of these methodologies is somehow challenging to assess. A metric for evaluating the efficacy of the prediction was to consider the recommendation as a retrieval task and, therefore, use the accuracy, precision, recall, and F-measures. In [7], the average accuracy on the subset of the Amazon data [65] was 71%, the average precision 73.5%, the average recall 70.6%, and the average F-measure 71.5%. In Ref. [18], the precision is evaluated on a different dataset. Keeping constantly in mind that a direct comparison is not fair and that the presented technique outperformed similar techniques, the value for the Netflix [56] and Movielens [38] dataset is less than 10%. The evaluation is performed in Ref. [59] by computing a mean square error among the QINR method and a set of baseline methods. The average MSE for the different Amazon sets [65] was 0.97, outperforming the baseline techniques. In Ref. [36], the results are evaluated according to precision, recall, F1-measure, root mean square error(RMSE), and mean absolute error (MAE). The technique was tested on the dataset in Ref. [38]: precision was , recall , F-measure , RMSE and MAE .
5. Conclusions
We have provided an overview of the most interesting approaches that involve the field of recommendation systems and the fascinating approach of quantum computing. This computational paradigm is potentially disruptive and can dramatically boost recommendation systems research with a highly significant performance improvement. This feature is becoming more and more relevant as the availability of data grows exponentially. All the reported approaches have specific peculiarities and focus on particular aspects of RS. Some of them are just inspired by the quantum computing paradigm; nevertheless, they are interesting and relevant, shedding light on possible new research directions. Furthermore, there is a need for a collection of datasets suited explicitly for highlighting the potentiality of using QC for RS with considerations similar to the ones drawn in Refs. [73,74]. Moreover, in Ref. [75], it is highlighted that quantum algorithms, in many cases, need an input configured as a quantum state encoding a non-quantum dataset; the authors outline a set of interesting challenges to be met for encoding non-quantum data so that they can be effectively used by quantum computers. Such kinds of datasets should be used with the aim of having some standard benchmark that can be used by the scientific community for testing and comparing the different approaches. On the other hand, there is the necessity to make more high-performing quantum systems as available as possible to the scientific community.
Author Contributions
The contributions of the two authors in terms of searching the literature, and analysis, writing, and revision are equivalent. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in the analyzed papers have been listed in Section 3.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CQFS | Collaborative-Driven Quantum Feature Selection |
| DLT | Distributed Ledger Technologies |
| ELBO | Evidence Lower Bound |
| HHL | Harrow Hassidim Lloyd |
| LDA | Latent Dirichlet Allocation |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MGWO | Modified Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| MWO | Mussels Wandering Optimization |
| PCA | Principal Components Analysis |
| QCS | QUBO Carousel Selection |
| QICE | Quantum-Induced Clustering Ensemble |
| QIPFCM | Quantum Possibilistic fuzzy C-means |
| QMC | Quantum Monte Carlo |
| QPO | Quantum Processing Unit |
| QPSO | Quantum-Behaved Particle Swarm Optimization |
| QUBO | Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) |
| RS | Recommendation Systems |
| SQB | Standard Quantum-Based Similarity |
| SVT | Singular Value Thresholding |
| VBAE | Variational Bandwidth Auto-Encoder |
| WOTS | Winternitz One-Time Signature |
References
- Goldberg, D.; Nichols, D.; Oki, B.M.; Terry, D. Using collaborative filtering to weave an information tapestry. Commun. ACM 1992, 35, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2012 ACM Computing Classification System. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/ccs (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Guo, Q.; Zhuang, F.; Qin, C.; Zhu, H.; Xie, X.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A survey on knowledge graph-based recommender systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 3549–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Sun, A.; Tay, Y. Deep Learning Based Recommender System: A Survey and New Perspectives. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 3285029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyaz, P.; Varghese, S.M. A scalable product recommendations using collaborative filtering in hadoop for bigdata. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.; Matuszyk, P.; Krieter, S.; Spiliopoulou, M.; Saake, G. Personalized recommender systems for product-line configuration processes. Comput. Lang. Syst. Struct. 2018, 54, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, L.; Jetawat, A.; Khairnar, V. Robust product recommendation system using modified grey wolf optimizer and quantum inspired possibilistic fuzzy C-means. Clust. Comput. 2021, 24, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z. Variational Bandwidth Auto-encoder for Hybrid Recommender Systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 1, 3155408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R. Knowledge-based recommender systems. Encycl. Libr. Inf. Syst. 2000, 69, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Pilato, G.; Persia, F.; D’Auria, D. New Perspectives on Recommender Systems for Industries. In Proceedings of the IEEE AI4I 2022: 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Industries, Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 19–21 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qiskit. Available online: https://qiskit.org/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- D-Wave Systems. Available online: https://www.dwavesys.com/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Amazon Braket. Available online: https://aws.amazon.com/braket/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Yanofsky, N.S. An introduction to quantum computing. In Proof, Computation and Agency; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 145–180. [Google Scholar]
- Shor, P.W. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–22 November 1994; pp. 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, L.K. Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.K.; Humble, T.S. Adiabatic Quantum Computing and Quantum Annealing; Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Physics: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nembrini, R.; Ferrari Dacrema, M.; Cremonesi, P. Feature selection for recommender systems with quantum computing. Entropy 2021, 23, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A. Ising formulations of many NP problems. Front. Phys. 2014, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/home.uri (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Web of Science. Available online: https://www.webofknowledge.com (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Kerenidis, I.; Prakash, A. Quantum recommendation system. In Proceedings of the 8th Innovations in Theoretical Computer Science Conference (ITCS 2017), Berkeley, CA, USA, 9–11 January 2017; Volume 67, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilato, G.; Vassallo, G. TSVD as a statistical estimator in the latent semantic analysis paradigm. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2014, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M. On the relationship between continuous-and discrete-time quantum walk. Commun. Math. Phys. 2010, 294, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E. A quantum-inspired classical algorithm for recommendation systems. In Proceedings of the STOC 2019: 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 23–26 June 2019; pp. 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazola, J.M.; Delgado, A.; Bardhan, B.R.; Lloyd, S. Quantum-inspired algorithms in practice. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, L.; Lee, H.W.; Zhang, G. Quantum context-aware recommendation systems based on tensor singular value decomposition. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C. Recommender systems inspired by the structure of quantum theory. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.06035. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, C. Expressive recommender systems through normalized nonnegative models. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Reafee, W.; Alhazmi, M.; Salim, N. Two-sided regularization model based on probabilistic matrix factorization and quantum similarity for recommender systems. Int. J. Model. Simul. Sci. Comput. 2020, 11, 20500567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, P.; Singh, A.; Mahesh, T. Efficient Characterization of Quantum Evolutions via a Recommender System. Quantum 2021, 5, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, H.; Zurek, W.H. Quantum discord: A measure of the quantumness of correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 88, 017901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedrhiri, O.; Banouar, O.; Hadaj, S.; Raghay, S. Quantum phase estimation based algorithms for machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Informatics and Software Engineering Conference (IISEC), Ankara, Turkey, 16–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, A.W.; Hassidim, A.; Lloyd, S. Quantum algorithm for linear systems of equations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 150502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Efficient quantum circuit for singular-value thresholding. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 012308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedrhiri, O.; Banouar, O.; El Hadaj, S.; Raghay, S. Intelligent recommender system based on quantum clustering and matrix completion. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, 6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.F.; Candès, E.J.; Shen, Z. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J. Optim. 2010, 20, 1956–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MovieLens 100 k Dataset. 2018. Available online: https://grouplens.org/datasets/movielens/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Andreev, D.; Lazarova, M. Applying a quantum amplification over a system for image feature matching and image recommendation. In Proceedings of the BCI’19: 9th Balkan Conference in Informatics, Sofia, Bulgaria, 26–28 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INRIA Annotations for Graz-02 (IG02). Available online: https://lear.inrialpes.fr/people/marszalek/data/ig02/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Chakrabarty, I.; Khan, S.; Singh, V. Dynamic Grover search: Applications in recommendation systems and optimization problems. Quantum Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawerwain, M.; Wróblewski, M. Recommendation systems with the quantum k-NN and Grover algorithms for data processing. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2019, 29, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawerwain, M.; Wróblewski, M. Application of quantum k-NN and grover’s algorithms for recommendation big-data system. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 852, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMDb Dataset. Available online: http://www.omdbapi.com/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Logesh, R.; Subramaniyaswamy, V.; Vijayakumar, V.; Gao, X.Z.; Indragandhi, V. A hybrid quantum-induced swarm intelligence clustering for the urban trip recommendation in smart city. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 83, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, W.; Fang, W.; Wun, X.; Xu, W. Gene expression data analysis with the clustering method based on an improved quantum-behaved Particle Swarm Optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.H.; Henderson, M.P. Application of quantum annealing to training of deep neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.06356. [Google Scholar]
- Willsch, D.; Willsch, M.; De Raedt, H.; Michielsen, K. Support vector machines on the D-Wave quantum annealer. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020, 248, 107006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, D.; Vesselinov, V.V.; Alexandrov, B.S.; Alexandrov, L.B. Nonnegative/binary matrix factorization with a d-wave quantum annealer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negre, C.F.; Ushijima-Mwesigwa, H.; Mniszewski, S.M. Detecting multiple communities using quantum annealing on the D-Wave system. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamascelli, D.; Zanetti, L. A quantum-walk-inspired adiabatic algorithm for solving graph isomorphism problems. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2014, 47, 325302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushijima-Mwesigwa, H.; Negre, C.F.; Mniszewski, S.M. Graph partitioning using quantum annealing on the d-wave system. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Post Moores Era Supercomputing, Denver, CO, USA, 12–17 November 2017; pp. 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Boothby, K.; Bunyk, P.; Raymond, J.; Roy, A. Next-generation topology of d-wave quantum processors. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.00133. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari Dacrema, M.; Felicioni, N.; Cremonesi, P. Optimizing the selection of recommendation carousels with quantum computing. In Proceedings of the RecSys’21: 15th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Kuscsik, Z.; Liu, J.G.; Medo, M.; Wakeling, J.R.; Zhang, Y.C. Solving the apparent diversity-accuracy dilemma of recommender systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4511–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.; Lanning, S. The netflix prize. In Proceedings of the KDD Cup and Workshop, San Jose, CA, USA, 12 August 2007; Volume 2007, p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, F.M.; Konstan, J.A. The movielens datasets: History and context. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2015, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VBAE: Variational Bandwidth Auto-Encoder Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/yaochenzhu/VBAE (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Pan, T.; Hou, Y.; Tian, T.; Li, Z. QINR: A Quantum-Inspired Network for Interpretable Review-based Recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Information Technology (CECIT), Sanya, China, 27–29 December 2021; pp. 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; McAuley, J. Ups and downs: Modeling the visual evolution of fashion trends with one-class collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, Montr©al, QC, Canada, 11–15 April 2016; pp. 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Trisetyarso, A.; Hastiadi, F. Quantum Game-Based Recommender Systems for Disruptive Innovations. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2019, 11431 LNAI, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisert, J.; Wilkens, M.; Lewenstein, M. Quantum games and quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Anjum, A.; Ajmal, A.; Webber, J.; Mehbodniya, A.; Khan, S. A Secure and Privacy Preserved Parking Recommender System Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography and Local Differential Privacy. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 56410–56426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, L. Recommender engine for continuous-time quantum Monte Carlo methods. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J. Amazon Product Data. Available online: http://jmcauley.ucsd.edu/data/amazon/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Netflix Prize data. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/netflix-inc/netflix-prize-data (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Li, W.J. Collaborative Topic Regression with Social Regularization for Tag Recommendation. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Beijing, China, 3–9 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andreev, D. Quantum Recommendation System for Image Feature Matching and Pattern Recognition. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1069, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszalek, M.; Schmid, C. Accurate Object Localization with Shape Masks. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opelt, A.; Pinz, A.; Fussenegger, M.; Auer, P. Generic object recognition with boosting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, J.; Targett, C.; Shi, Q.; Van Den Hengel, A. Image-based recommendations on styles and substitutes. In Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 9–13 August 2015; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Webscope v1.0. Available online: http://research.yahoo.com/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Perrier, E.; Youssry, A.; Ferrie, C. QDataSet, quantum datasets for machine learning. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Broughton, M.; Mohseni, M.; Babbush, R.; Boixo, S.; Neven, H.; McClean, J.R. Power of data in quantum machine learning. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieferová, M.; Sanders, Y.R. Assume a Quantum Data Set. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 2022, 4. Available online: https://hdsr.mitpress.mit.edu/pub/23gghb1v (accessed on 15 December 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).