Abstract
Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) has its benefits compared to other biometric verification methods, such as face recognition. It is convenient, low cost, and more privacy protected, so it can start being used for various practical applications. However, voice verification systems are vulnerable to unknown spoofing attacks, and need to be upgraded with the pace of forgery techniques. This paper investigates a low-cost attacking scenario in which a playback device is used to impersonate the real speaker. The replay attack only needs a recording and playback device to complete the process, so it can be one of the most widespread spoofing methods. In this paper, we explore and investigate some spectral clues in the high sampling rate recording signals, and utilize this property to effectively detect the replay attack. First, a small scale genuine-replay dataset of high sample rates are constructed using some low-cost mobile terminals; then, the signal features are investigated by comparing their spectra; machine learning models are also applied for evaluation. The experimental results verify that the high frequency spectral clue in the replay signal provides a convenient and reliable way to detect the replay attack.
1. Introduction
Biometric authentication technologies, such as face recognition, fingerprint recognition, iris recognition, and voice recognition, are widely applied to verify or identify according to certain biometrics. However, there are worries about these technologies because they can easily divulge privacy. For example, people are using the sensors of mobile devices to authenticate for the requirement of various application [1,2] and they rarely have different authentication alternatives; therefore, there is no choice for people who want to keep their privacy. Among these methods, voice verification has advantages because of its non-contact, multi-scene, easy sampling, and low-cost properties. Speaker authentication can be combined with speech content authentication at the same time in order to improve the security and accuracy of the authentication system effectively. At the same time, the speaker authentication methods are applicable to a wider range of ages and are easy to update; that is especially convenience for the elderly and disabled people. Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) systems have gradually become the large-scale applied techniques and are widely deployed in scenarios with security requirements.
However, the ASV systems, which are convenient and low-cost, are also prone to the same security risk as low-cost playback spoofing attacks, and counterattack measures could be expensive. This kind of easy spoofing attacks also exist in other biometric authentication systems, so security information needs to be upgraded and updated constantly [3,4]. Even the most advanced ASV systems are vulnerable to unknown (or unseen) spoofing attacks. Therefore, research on the detection of spoofing attacks is related to investigating not only the model accuracy, but also various scenarios and clues. Currently, spoofing attacks against ASV systems can be divided into four types:
- (1)
- Impersonation attack. The attacker deceives by imitating high-level speaker characteristics of the target speaker such as the prosody, accent, and pronunciation.
- (2)
- Replay attack (RA). The attacker records the real voice of the target speaker through a recording device, then the attack is carried out by playing back the copied voice.
- (3)
- Speech Synthesis (SS) attack. The attacker uses speech synthesis technology to generate the fake speech of the target speaker to deceive the ASV system.
- (4)
- Voice Conversion (VC) attack. The attacker converts the voice signal of the non-target speaker into the voice signal of the target speaker through conversion technology.
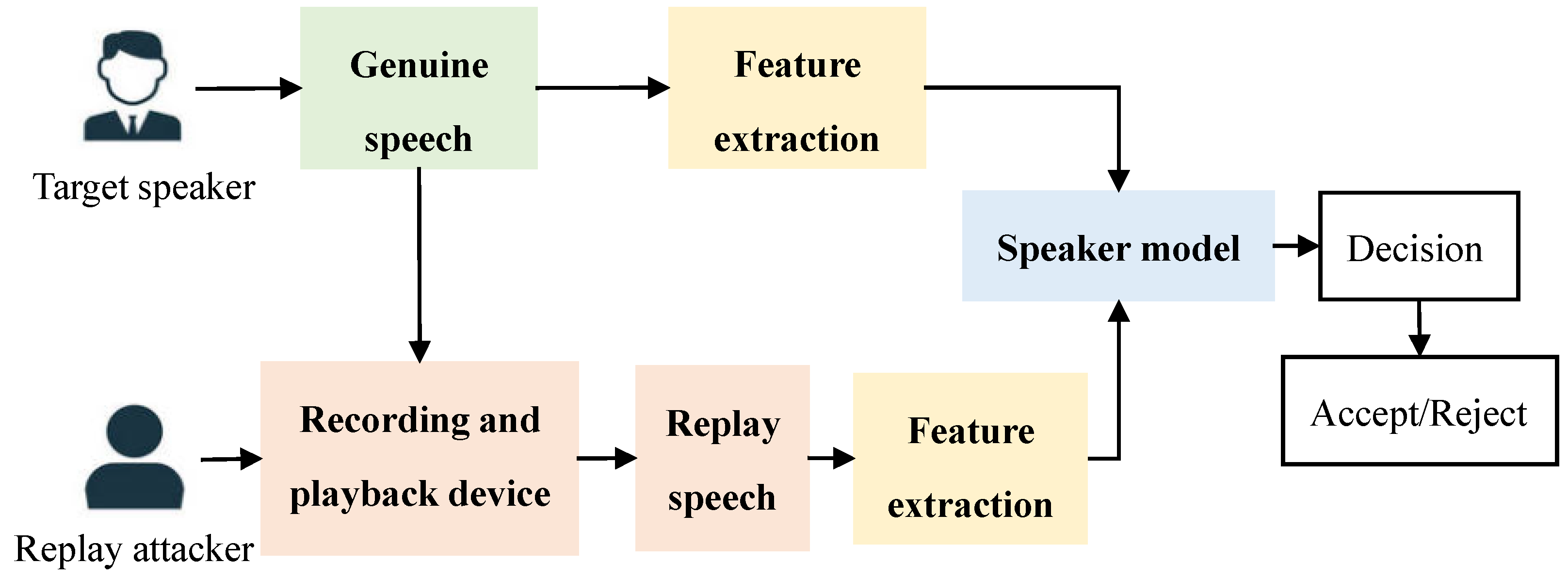
In the replay attack, the attacker uses the pre-recorded voice of the attacked person for illegal authentication [5]; the process is shown in Figure 1. The actual authentication process is carried out while the target speaker provides his/her real voice to the system for identity. Because replay attacks only need recording technology, attackers may only employ a high-quality recording and playback device to achieve the deception purpose. Therefore, it can be the easiest way to implement the threatening attempt for the ASV system.
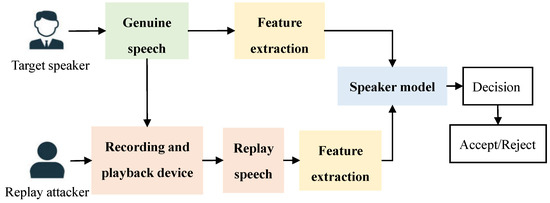
Figure 1.
The process of replay attack.
The research on anti-spoofing attack can be traced back to 1996 when S. Furui put forward the subject of identifying fake speech in the PRL journal [6]. Earlier research was conducted mainly on their own data sets, with no uniform criteria for evaluation. In 2011, J. Koppell et al. included the intrusion attack of the speaker verification system into the ISO and IEC standards [7]. Since 2013, INTERSPEECH has held four consecutive ASV spoofing challenges, and brings this research subject into broad public intention and standardization. Among them, the extensive research on replay attack detection mainly started from the 2017 ASVspoof challenge [8,9]. The ASVspoof 2017 challenge has formulated corresponding countermeasures against replay attacks, and constructed the earliest database with unified tags and evaluation standards. The following ASVspoof 2019 challenge is aimed at formulating general countermeasures for logical access (speech synthesis attacks, voice conversion attacks) and physical access (replay attacks) scenarios. The ASVspoof 2021 challenge is aimed at formulating corresponding countermeasures for logical access (TTS, VC, across telephony and VoIP networks), physical access (RA), and voice deep forgery scenarios.
A small-scale genuine speech with high sampling rate, and corresponding replay datasets, are constructed in this research. This research investigates some important spectral clues in replay speech signals in the high frequency spectrum. A phenomenon of high-frequency information loss in the replay signal is observed compared to the original genuine voice. Experiments are carried out to confirm this clue by using pattern recognition models. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Related work on the replay attack problem is discussed in Section 2. Section 3 describes the datasets and the phenomenon of the spectral loss of replay signals at high sampling rates. Section 4 discusses the related experiments and results. Section 5 provides a summary and future work.
2. Related Work
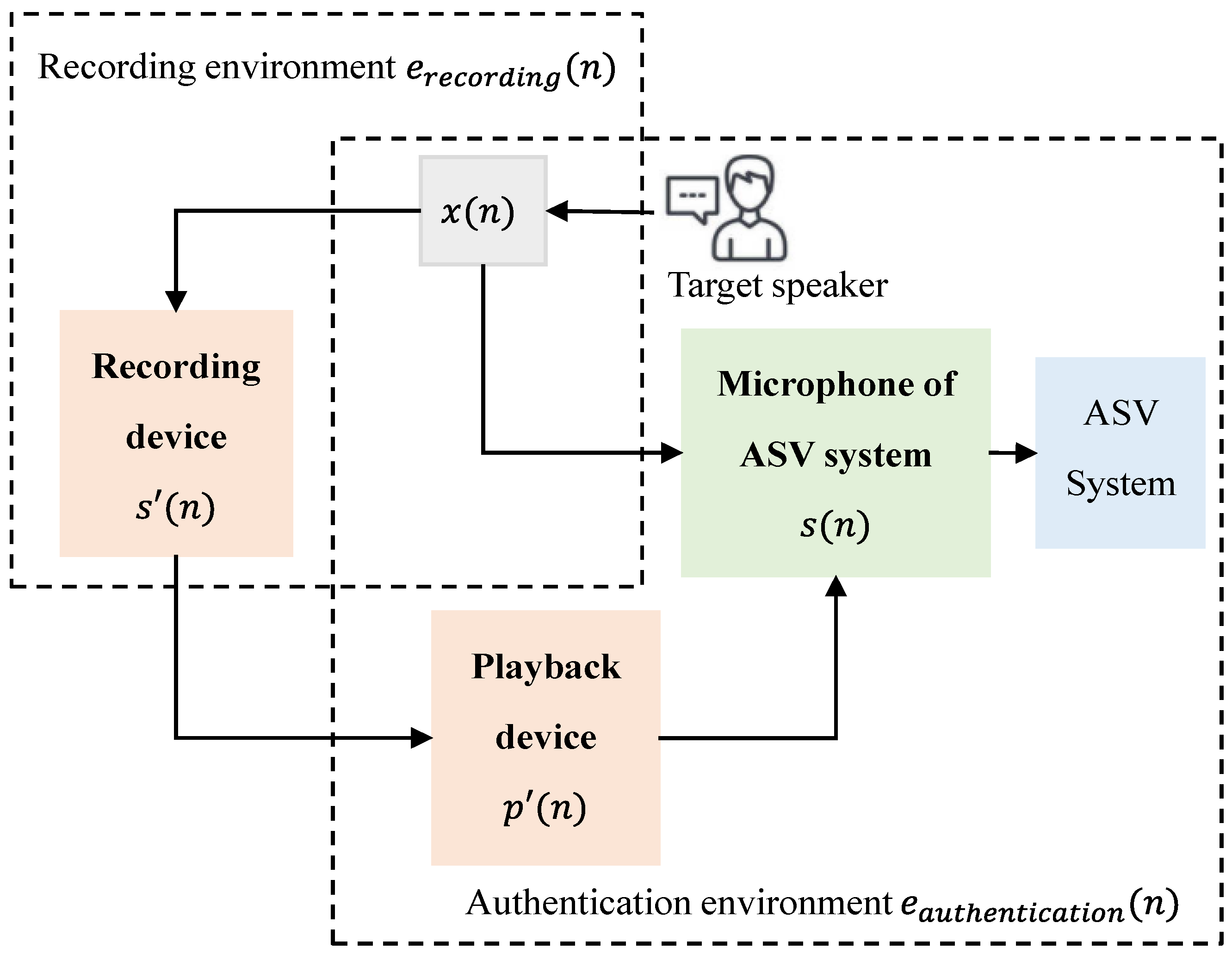
The basic task of replay attack detection is to determine whether the voice signal comes from a genuine speaker or a playback device. The replay signal generating is a process in which the attacker employs recording devices and playback devices to imitate the original signal. The generation and authentication process is shown in Figure 2. Under the perspective of signal processing, the genuine signal and the replay signal can be defined as:
where represents the signal by the target speaker. and represent the microphone response and authentication environment response of the ASV system. and represent the recording device response and the recording environment response, respectively. indicates that the playback device response.
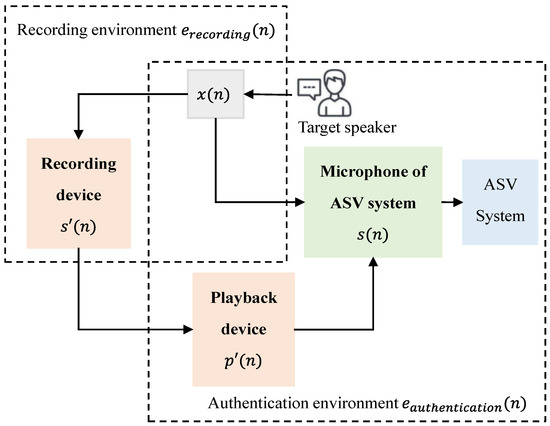
Figure 2.
The generation and authentication process of the replay signal.
For now, the research on replay attack detection can be divided into the following two categories:
(1) Feature-based method. This method is mainly developed on two different signal features, one is based on a special physical phenomena, as we discussed in this paper, and another is based on characteristics that can indirectly explore the difference between original signal and replayed signal like the challenge-response based detection methods [10]. Detection methods based on speech randomness [11] and some detection methods based on other clues (lip movement phenomenon [12], voice liveness detection [13]). In addition to looking for some indirect features, researchers also consider distortion and some additional noise mixed in speech signal after being replayed. Therefore, researchers start to investigate the signal itself and explore the acoustic characteristics that can directly reflect the difference between the genuine signal and the replayed signal. These include: spectral features [14] (CQCC [15], MFCC [16,17], LPCC [18], SFFCC [19], etc.), modulation features (AM-FM based features [20], MCFCC and MSECC features [21], SCD, SCMC, SCF features [22]), excitation source features (RMFCC and LPRHEMFCC feature [23]), and phase features (PBSFVT [24]).
(2) Model-based approaches. In addition to a series of well-designed features to characterize the difference between the genuine signal and the replayed signal, researchers also proposed some model-based methods to detect the replayed signal. For the model-based methods, statistical models [16,25] (SVM, GMM, i-vector and x-vector) and deep neural network models [26,27] (ResNet, Siamese) are mainly used to classify real signals and replayed signals.
3. Spectral Cues in High Sampling Rate Replayed Signal
3.1. Spectrum Loss Phenomenon
For the replay attack detection task, previous works were conducted on the public dataset of the ASV spoofing challenge. The official datasets are all composed of a commonly used sampling rate of 16 kHz, and there has been no report on replay voice with a high sampling rate. In this paper, we investigate for the first time that the frequency spectrum loss exists in the high frequency part of the replayed signals. However, the common sample rate frequency for terminals is set to 16 KHz, which may not be sufficient for the presumed high frequency clue.
To prepare the dataset, we selected readily available mobile devices and recorded in a wide and closed space environment like a university hall or corridor. Various mobile devices are used to first record voices with high sample rate of 48 kHz. Then, these voice samples are replayed using speaker devices and recorded again as the attack voice at same sample rate.
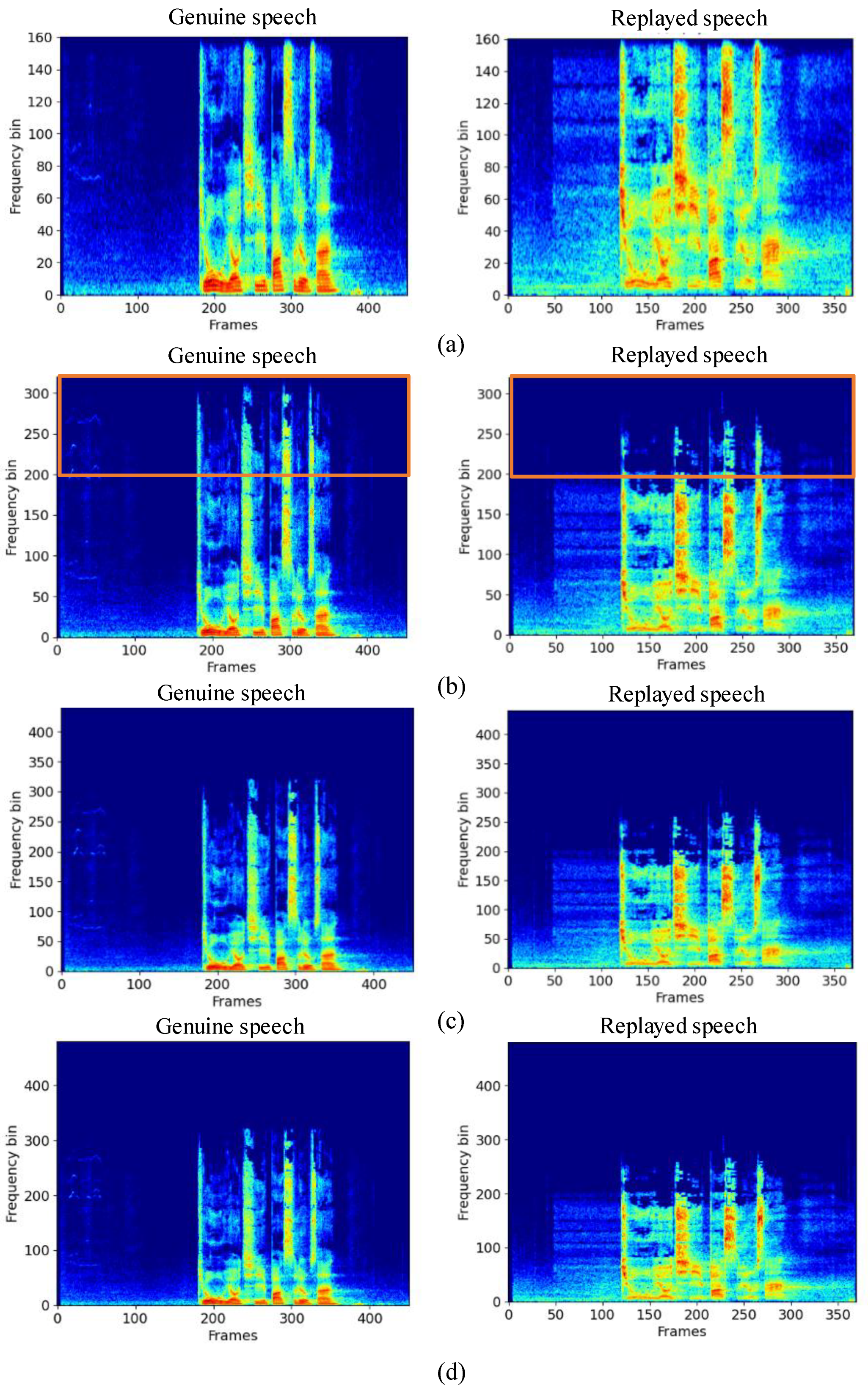
While the high sample rate (48 kHz) is set in order to preserve the high frequency clue, the down sampling is applied to observe the spectra and to simulate the reality scenarios used for ASV authentication. The 48 kHz sample rate dataset twins are down sampled to commonly used sampling frequencies (16 kHz, 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz), thus, three more different sample rate datasets are produced. Then, spectrum differences between genuine speech and replayed speech were compared at four sampling frequencies, as shown in Figure 3.
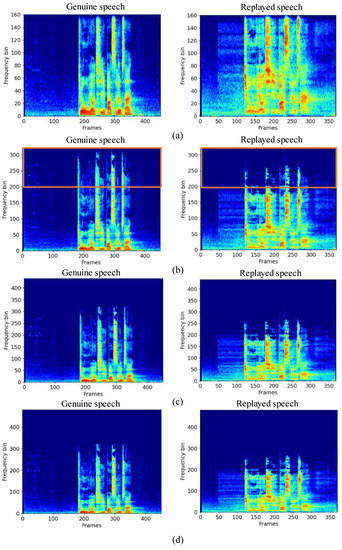
Figure 3.
The spectral difference between genuine speech and replayed speech at the sampling rate between 16 kHz—48 kHz. (a–d) are the spectrum at different sampling rates of 16 kHz, 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, and 48 kHz, respectively.
According to the spectrograms of genuine and replay data in Figure 3, we can see that at around 32 kHz the spectrum difference between genuine speech and replayed speech is most obvious. When the sampling rate is both smaller (16 kHz) or bigger (above 44.1 khz) frequencies, the spectrum clue is difficult to see. This phenomenon shows that when the attacker chooses mobile devices such as mobile phones for replay attack, the playback device may lose the high frequency information of the genuine signal. Therefore, in the case of high sampling rate, spectrum loss may occur in the replayed signal, which provides a new clue for replay attack detection.
3.2. High Sampling Rate Database
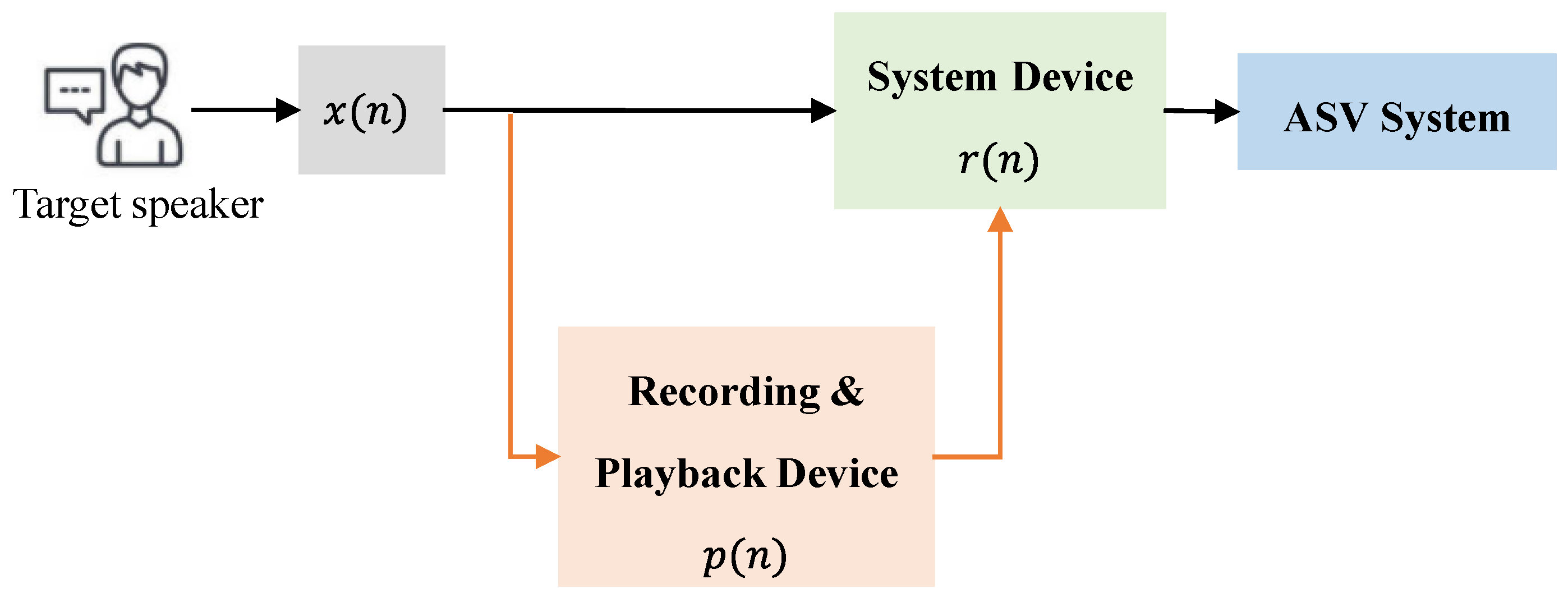
According to the generation process of the replayed signal, as shown in Figure 2, three terminal acquisition devices are necessary, namely: system device, recording device, and playback device. The system device is the microphone of the ASV authentication system, which is deployed to collect the voice to be authenticated from the target speaker.
The recording device is mainly used to record the voice of a genuine speaker. The playback device is mainly utilized to play the recorded voice of the target speaker to the system authentication device. However, attackers typically may choose a device which has both microphone and loudspeaker as the recording device and the playback device to save the cost. Therefore, during the construction of this dataset, the default playback device and recording device are the same device. Figure 4 shows the complete data collection process.
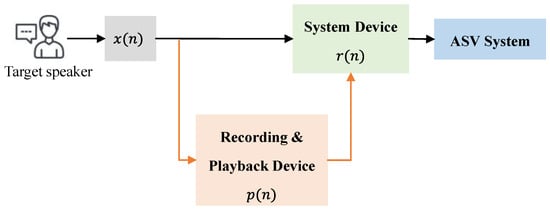
Figure 4.
High sampling rate replayed data collection process.
In order to reliably investigate the phenomenon, we choose 16 mobile devices for this experiment, and each device acts as both the system authentication device and the playback device. The data corpus takes the code form of 8-digit strings. The set of device names (brands) are: HONOR 9 Lite, HONOR H60, HUAWEI mate20X, IPHONE 6s, Mi 5, Redmi note5, Samsung galaxy J7, HUAWEI p30 pro, HUAWEI p20 pro, IPHONE Xs, HUAWEI nova3, Redmi K30, MEIZU 16T, Mi10, IPHONE 11, IPHONE XR. In real scenarios, there are a variety of low-cost attack devices, the mobile phone is the easily available one.
It is not difficult to notice that the replay signal while going through an extra cycle of another microphone and speaker leaves some clues in the signal. Thus, this work is to find the trace left by the additional extra channel while filtering the genuine signal. The spectrograms reveal a notable energy attenuation at the low frequencies—as could be intuitively expected from small piezo speakers. This clue can help to greatly reduce the cost of expensive counterattack measures.
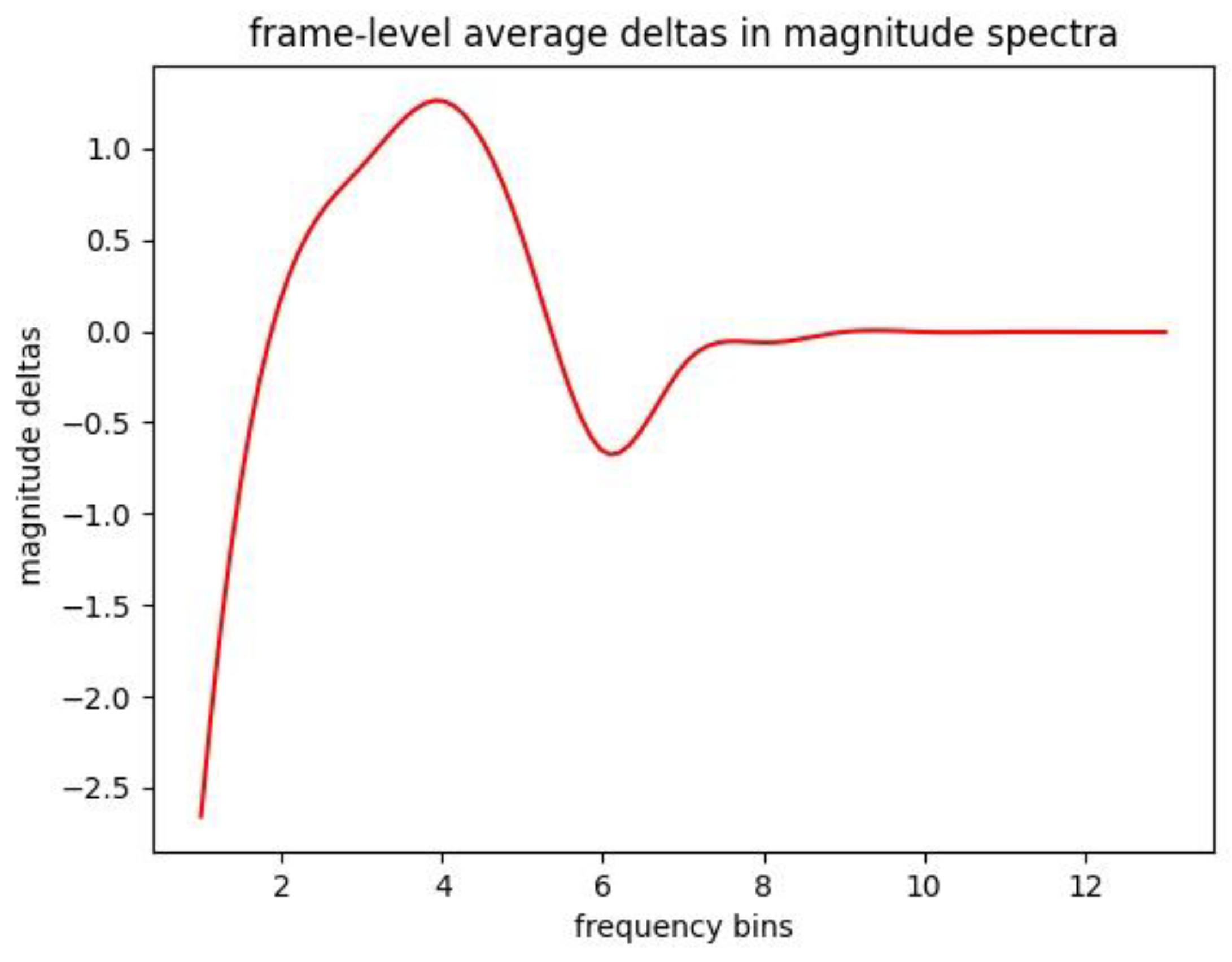
In order to quantitatively display the spectrum difference between the genuine-replay twins, we statistically calculate the frequency domain difference of a few samples. From the twin signals cut a window and calculate the frequency domain difference, and obtain the quantitative average deltas at different frequency point. The results are shown in Figure 5. We divide the frequency domain data into 12 frequency bins, and averaged the several sample windows to calculate the delta differences. These bins represent the linear scale of frequency. The results show that the deltas will have an obvious fluctuation in the high frequency part before it becomes stable. This trend further verifies that with the genuine-replay twin signals have spectrum difference in certain parts.
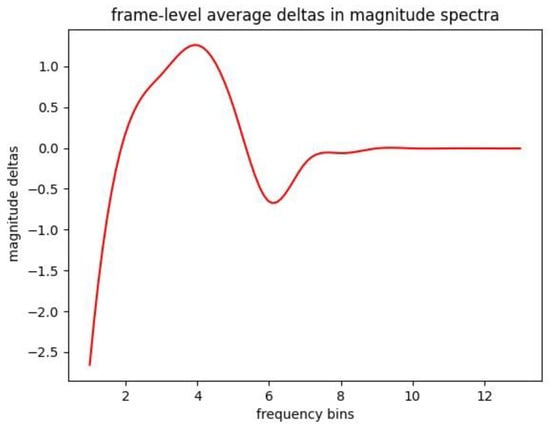
Figure 5.
The average spectrum difference between genuine and replayed signals.
To objectively test the effect of the frequency clue, this research also conducts some simple classification tasks, based on machine learning models. The datasets are separated into training and test sets to train and to highlight reliability of the test results. Thus, some machine learning models are investigated as a new prove of the spectrum clue. The specific data information is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The information of high sampling rate database.
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Configuration
4.1.1. Feature Selection
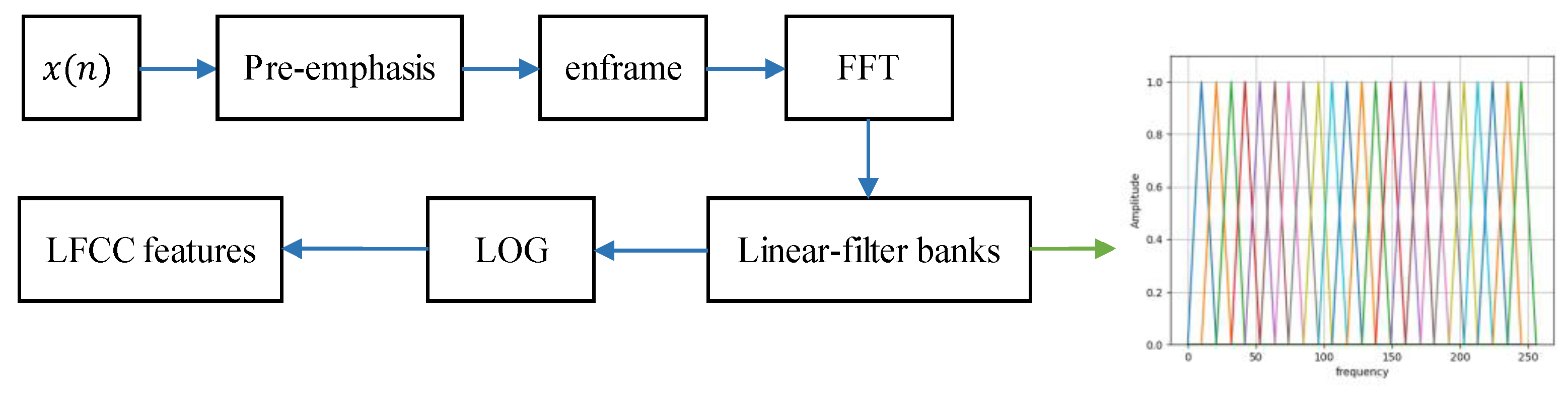
To verify the detection performance of replayed signals at high sampling rate, linear-frequency cepstral coefficients (LFCC) with uniform distribution of linear-filter banks are selected as front-end features. The LFCC feature is used specially to express the spectral difference between the genuine signal and the replayed signal at different spectrums. The speech signal is split using “Hamming” window with 20 ms and step-size of 10 ms, and 23 linear-filters are applied. The extraction process of LFCC features is shown in Figure 6.
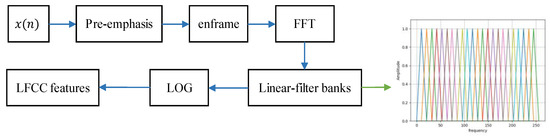
Figure 6.
The extraction process of LFCC features.
4.1.2. Model Selection
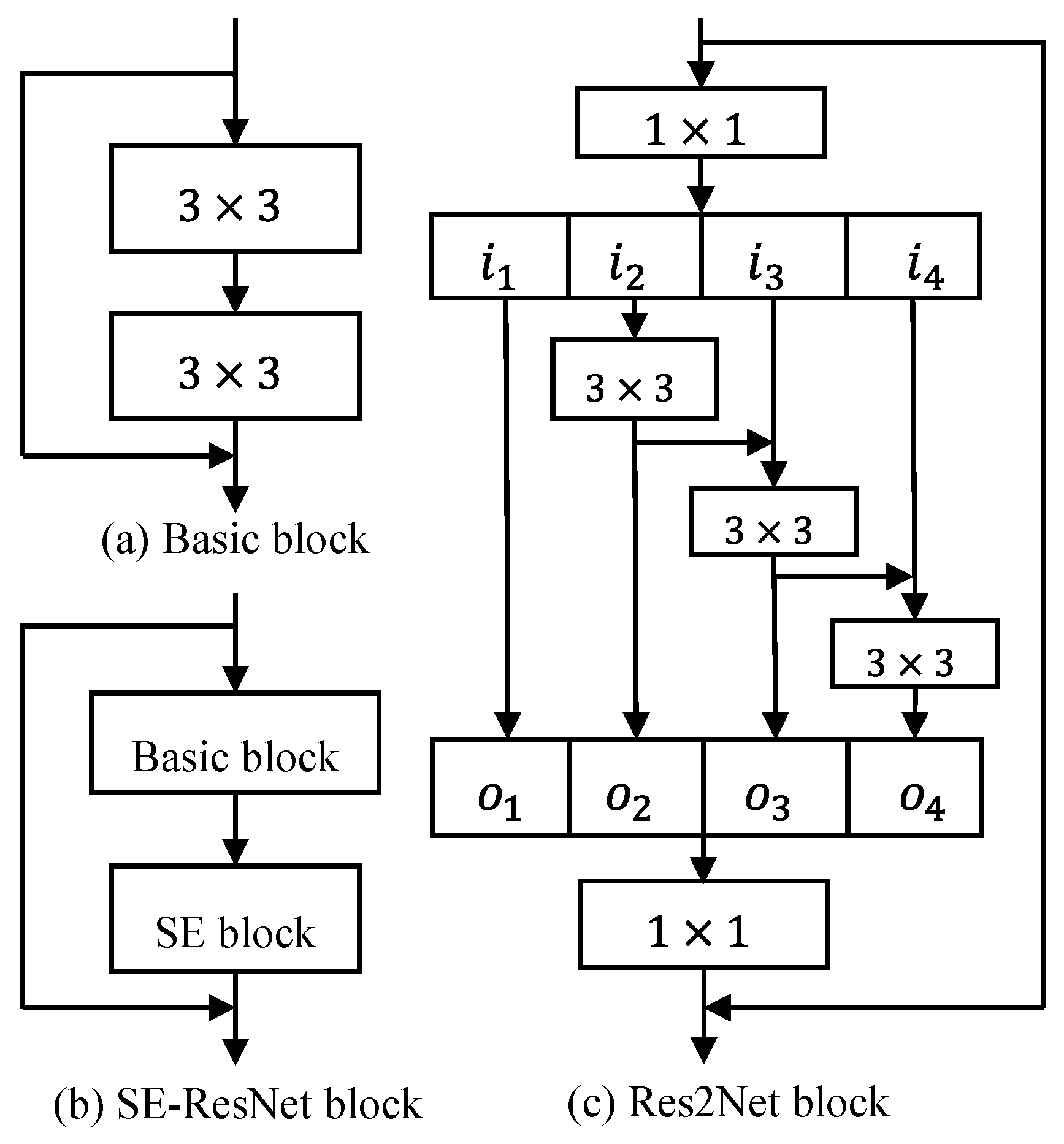
In terms of models, we mainly selected three models to verify the detection performance. First, we select support vector machines (SVM) to compare the performance at different sampling rates and probe the differences across frequency bands. Then, we choose ResNet model and two variants of ResNet models (Res2Net and SE-ResNet) to compare the consistency of experiment results, which are used in attack detection [28]. Res2Net mainly revises the ResNet block to achieve multi-feature scales. It divides the feature maps within one block into multiple channel groups and designs a residual connection across different channel groups. This connection increases the possible receptive fields, resulting in multiple feature scales. SE-ResNet is the integration of the ResNet block and the squeeze-and-excitation (SE) block. The SE block adaptively recalibrates the feature response in terms of the channel by explicitly modeling the interdependencies between the channels. This interdependent modeling assigns different influence weights to channels, improving the model’s ability to focus on the channel information that is most related with replay cues. The same architecture in [28] was adopted in this experiment, as shown in Table 2. Among them, the structures of different residual blocks are shown in Figure 7.

Table 2.
The overall model architectures of ResNet34, SE-ResNet34, and Res2Net50. The type of residual block, and the number of channels, are specified inside the brackets, the repeat times of each block on one stage are specified outside the brackets.
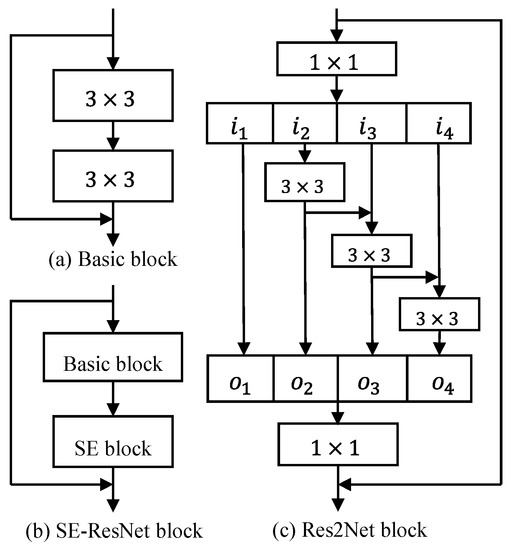
Figure 7.
The different structures in the modules: (a) basic block; (b) SE-ResNet block; (c) Res2Net block.
4.1.3. Evaluation Metric
In this paper, EER (Equal Error Rate) is used as the performance evaluation metric. EER refers to the value when the false acceptation rate (FAR) and false reject rate (FRR) are equal. Among them, FAR refers to the statistics that the replayed speech is identified as genuine speech. Similarly, FRR refers to the genuine speech classified to be the replayed speech. So, the process of calculating EER is actually to find an appropriate threshold for the discriminant system, which makes FAR and FRR equal, the smaller EER means a better detection performance.
4.2. Results and Discussion
4.2.1. Replay Detection Performance at Different Sampling Rate
For the self-constructed genuine and replay datasets with four frequencies (48 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 32 kHz, and 16 kHz) including the down-sampled sets, the SVM model is used to identify the replay detection. The results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The performance under different sampling rates.
Results show that as the sampling rate increases, the EER is decreasing. This further proves that properly increasing the sampling frequency of the system device can help resist the replay attack.
4.2.2. Comparison of Differences among Frequency Bands
The LFCC features in frequency bands are divided into frequency ranges to reflect the spectrum weights of different filter banks, so as to give an optimal frequency range. The 23 linear filter banks divide into 11 linear filter groups, five frequency bins in each group, each with a width of 4 kHz. Subsequently, SVM model was used to detect the features extracted from each frequency range, and the results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The performance among each frequency range.
The results show that in the frequency range of 16 kHz–20 kHz (of sample rate 32 kHz–40 kHz), the two SVM models with different kernel functions achieve the best result at the same time. Therefore, the frequency range of 16 kHz–20 kHz can fully reflect the difference between the genuine signal and the replayed signal. It further proves that there is good discrimination in the high-frequency part of the signal at high sampling rates.
4.2.3. Replay Detection Performance at High Sampling Rate
In addition to two SVM models with different kernel functions, we also investigated ResNet model with two variants, Res2Net and SE-ResNet models, to perform replay detection experiments on a high sampling rate dataset of 48 kHz. The results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
The performance at high sampling rate.
Results show that the neural network models have better detection performance than the SVM model. and also proves the consistency of our observation of the spectrum clue.
4.3. Limitation
According to above experiments, a small-scale high sampling rate dataset initially verify the feasibility of our idea. The spectrum analysis and the machine learning results can conclude the clue left by the additional speaker channel. However, the diversity of replay devices is very important to the replay detection, especially the high fidelity (quality) devices, which are not included in this experiment. High quality and diversity should include both the recording channel and the speaker channel for complete comparison. Because of the limitations of the available experiment conditions, this research choose widely available mobile phones, thus the results are applicable to the low-cost attacking tools, as mentioned in Section 3.2. We hope a more through experiment will have reliable results in the future.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper investigates a spectrum clue in the replay speech signal by using signal analysis and classification models. To objectively verify the ideas proposed in this paper, a genuine and replay dataset with high sampling rate is constructed, and detection experiments are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the high-frequency clue proposed in this paper. The experiments conclude that the frequency rate between 16 kHz–20 kHz is most helpful for reliable detection of replay attacks. Increasing the sampling rate helps distinguish genuine speech from replay speech.
In the future, this work will focus on expending the datasets on different terminal devices and various environments to have more reliable results, and investigate new clues and better detection models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y. and M.A.; methodology, J.Y. and A.H.; software, J.Y.; validation, M.A. and A.H.; formal analysis, J.Y.; investigation, J.Y. and M.A.; resources, M.A. and A.H.; data curation, A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.A. and A.H.; visualization, J.Y., M.A., and A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (U2003207) and the Strengthening Plan of National Defense Science and Technology Foundation of China (2021-JCJQ-JJ-0059).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
We were unable to release our data in time due to the need to obtain authorization from the speakers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Das, R.K.; Tian, X.; Kinnunen, T.; Li, H. The attacker’s perspective on automatic speaker verification: An overview. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08849. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, P.; Yan, Y. Interrelate training and searching: A unified online clustering framework for speaker diarization. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.13760. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, N.W.; Kinnunen, T.; Yamagishi, J. Spoofing and countermeasures for automatic speaker verification. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Lyon, France, 25–29 August 2013; pp. 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Evans, N.; Kinnunen, T.; Yamagishi, J.; Alegre, F.; Li, H. Spoofing and countermeasures for speaker verification: A survey. Speech Commun. 2015, 66, 130–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Pati, D. Countermeasures to replay attacks: A review. IETE Tech. Rev. 2020, 37, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furui, S. Recent advances in speaker recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1997, 18, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppell, J. International organization for standardization. Handb. Transnatl. Gov. Inst. Innov. 2011, 41, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, H.; Todisco, M.; Sahidullah, M.; Evans, N.; Kinnunen, T.; Lee, K.A.; Yamagishi, J. ASVspoof 2017 Version 2.0: Meta-data analysis and baseline enhancements. In Proceedings of the Odyssey 2018—The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop, Les Sables d’Olonne, France, 26–29 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, T.; Evans, N.; Yamagishi, J.; Lee, K.A.; Sahidullah, M.; Todisco, M.; Delgado, H. Asvspoof 2017: Automatic speaker verification spoofing and countermeasures challenge evaluation plan. Training 2017, 10, 1508. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.; Boult, T.E.; Scheirer, W.J. Voice authentication using short phrases: Examining accuracy, security and privacy issues. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), IEEE, Washington, DC, USA, 29 September–2 October 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gałka, J.; Grzywacz, M.; Samborski, R. Playback attack detection for text-dependent speaker verification over telephone channels. Speech Commun. 2015, 67, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, H.; Miguel, A.; Witten, I.H.; Chollet, G. Detecting replay attacks in audiovisual identity verification. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2006 Proceedings—2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, S.; Shiota, S.; Kiya, H. Voice liveness detection using phoneme-based pop-noise detector for speaker verifcation. Threshold 2018, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Lee, K.A.; Chen, X.; Dang, J. Replay-attack detection using features with adaptive spectro-temporal resolution. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6374–6378. [Google Scholar]
- You, C.H.; Yang, J.; Tran, H.D. Device Feature Extractor for Replay Spoofing Detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 2933–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Zheng, T.F. A study on replay attack and anti-spoofing for automatic speaker verification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02101. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, A.R.; Alam, M.J.; O’Shaughnessy, D.D.; Falk, T.H. Blind channel response estimation for replay attack detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 2893–2897. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, M.; Kacprzak, S.; Zelasko, P.; Kowalczyk, K.; Galka, J. Audio Replay attack detection using high-frequency features. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Alluri, K.R.; Achanta, S.; Kadiri, S.R.; Gangashetty, S.V.; Vuppala, A.K. SFF Anti-spoofer: IIIT-H submission for automatic speaker verification spoofing and countermeasures challenge 2017. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, M.R.; Tak, H.; Patil, H.A. Effectiveness of speech demodulation-based features for replay detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 641–645. [Google Scholar]
- Suthokumar, G.; Sethu, V.; Wijenayake, C.; Ambikairajah, E. Modulation dynamic features for the detection of replay attacks. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 691–695. [Google Scholar]
- Gunendradasan, T.; Wickramasinghe, B.; Le, P.N.; Ambikairajah, E.; Epps, J. Detection of replay-spoofing attacks using frequency modulation features. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 636–640. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Pati, D. Linear prediction residual based short-term cepstral features for replay attacks detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 751–755. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Dang, J.; Liu, M.; Oo, Z.; Nakagawa, S.; Guan, H.; Li, X. Multiple phase information combination for replay attacks detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 656–660. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Rownicka, J. Speech replay detection with X-vector attack embeddings and spectral features. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.10324. [Google Scholar]
- Parasu, P.; Epps, J.; Sriskandaraja, K.; Suthokumar, G. Investigating light-resnet architecture for spoofing detection under mismatched conditions. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Shangai, China, 14–18 September 2020; pp. 1111–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Ye, J. Siamese convolutional neural network using gaussian probability feature for spoofing speech detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Shangai, China, 14–18 September 2020; pp. 1116–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, N.; Weng, C.; Liu, X.; Su, D.; Yu, D.; Meng, H. Replay and synthetic speech detection with res2net architecture. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6354–6358. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).