Topic Classification of Interviews on Emergency Remote Teaching
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- How effectively can transformer-based models classify thematic content from Modern Greek interview datasets?
- 2.
- How do ML and DL models compare in their effectiveness for TC in multi-class and domain-specific datasets?
- 3.
- How do models pre-trained in Greek perform in TC tasks?
2. Related Work
2.1. NLP in Greek
2.2. Topic Classification Techniques in Modern Greek Datasets
2.3. Classification Models
2.4. Topic Classification and Decision-Making Approaches
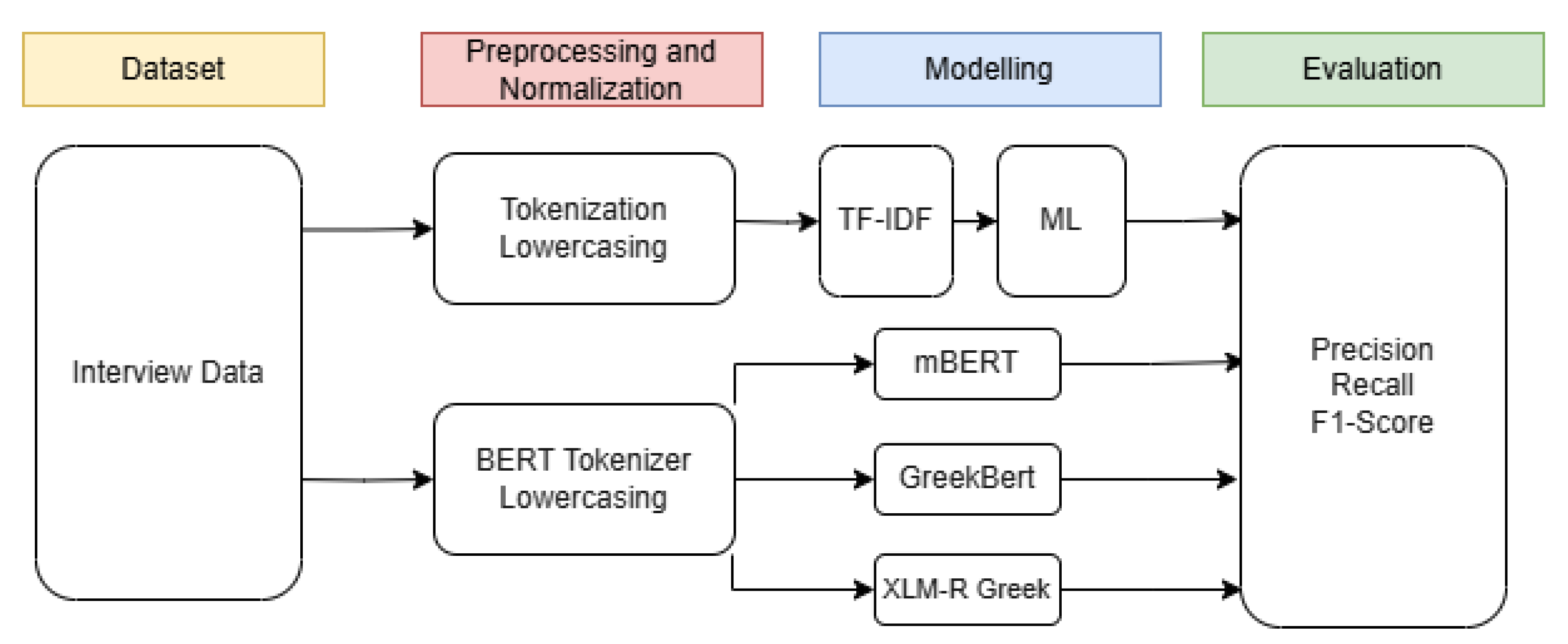
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Participants and Statistics
3.2. Data Preprocessing and Normalization
3.3. Licensing and Data Availability
4. Results
4.1. ML Models
4.2. Classification Performance
4.3. Comparison
5. Discussion
Limitations
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model | Parameters |
|---|---|
| XGBoost | Learning Rate: 0.4 |
| Max Depth: 6 | |
| Number of Estimators: 50 | |
| Subsample Ratio: 1.0 | |
| Gamma: 0.0 | |
| Early Stopping: None | |
| Objective Function: Multi-Class Classification | |
| Test Size: 0.2 | |
| Feature Extraction:TF-IDF | |
| mBERT | Learning Rate: |
| Batch Size: 8 | |
| Maximum Sequence Length: 128 | |
| Number of Epochs: 10 | |
| Dropout: 0.1 | |
| Test Size: 0.2 | |
| XLM-R Greek | Learning Rate: |
| Batch Size: 8 | |
| Maximum Sequence Length: 128 | |
| Number of Epochs: 10 | |
| Dropout: 0.1 | |
| Test Size: 0.2 | |
| GreekBERT | Learning Rate: |
| Batch Size: 8 | |
| Maximum Sequence Length: 128 | |
| Number of Epochs: 10 | |
| Dropout: 0.1 | |
| Test Size: 0.2 |
References
- Khurana, D.; Koli, A.; Khatter, K.; Singh, S. Natural language processing: State of the art, current trends and challenges. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 3713–3744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelrazek, A.; Eid, Y.; Gawish, E.; Medhat, W.; Hassan, A. Topic modeling algorithms and applications: A survey. Inf. Syst. 2023, 112, 102131. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Cambria, E.; Nikzad, N.; Chenaghlu, M.; Gao, J. Deep learning–based text classification: A comprehensive review. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Xia, C.; Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Yu, P.S.; He, L. A survey on text classification: From traditional to deep learning. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2022, 13, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparetto, A.; Marcuzzo, M.; Zangari, A.; Albarelli, A. A survey on text classification algorithms: From text to predictions. Information 2022, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satu, M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Mahmud, M.; Uddin, S.; Summers, M.A.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. TClustVID: A novel machine learning classification model to investigate topics and sentiment in COVID-19 tweets. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 226, 107126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikiforos, M.N.; Deliveri, K.; Kermanidis, K.L.; Pateli, A. Vocational Domain Identification with Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing on Wikipedia Text: Error Analysis and Class Balancing. Computers 2023, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelodar, H.; Wang, Y.; Orji, R.; Huang, S. Deep sentiment classification and topic discovery on novel coronavirus or COVID-19 online discussions: NLP using LSTM recurrent neural network approach. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2020, 24, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Lavanya, P.; Sasikala, E. Deep learning techniques on text classification using Natural language processing (NLP) in social healthcare network: A comprehensive survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICPSC), Coimbatore, India, 13–14 May 2021; pp. 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Palani, S.; Rajagopal, P.; Pancholi, S. T-BERT–Model for Sentiment Analysis of Micro-blogs Integrating Topic Model and BERT. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.01097. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, A.; Mahmoud, T.M.; Abd-El-Hafeez, T.; Mahfouz, A. Multi-label arabic text classification in online social networks. Inf. Syst. 2021, 100, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapis, C.M.; Kyritsis, K.; Perikos, I.; Spatiotis, N.; Paraskevas, M. A Hybrid Ensemble Approach for Greek Text Classification Based on Multilingual Models. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papantoniou, K.; Tzitzikas, Y. NLP for the Greek language: A brief survey. In Proceedings of the 11th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 2–4 September 2020; pp. 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, C.B.; Moore, S.; Lockee, B.B.; Trust, T.; Bond, M.A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educ. Rev. 2020, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vagelatos, A.; Stamatopoulos, J.; Fountana, M.; Gavrielidou, M.; Tsalidis, C. Natural Language Processing Environment to Support Greek Language Educational Games. In Interactive Mobile Communication, Technologies and Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 525–536. [Google Scholar]
- Krasadakis, P.; Sakkopoulos, E.; Verykios, V.S. A survey on challenges and advances in natural language processing with a focus on legal informatics and low-resource languages. Electronics 2024, 13, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papantoniou, K.; Tzitzikas, Y. NLP for The Greek Language: A Longer Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.10962. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Markuzon, N.; Patel, N.; Rueda, J.D. Natural language processing for automated classification of qualitative data from interviews of patients with cancer. Value Health 2022, 25, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Inzer, S.; Leung, A.; Shen, X.; Perlmutter, M.; Lindstrom, M.; Chew, J.; Presner, T.; Needell, D. Multi-scale Hybridized Topic Modeling: A Pipeline for analyzing unstructured text datasets via Topic Modeling. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.13496. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Sun, M. From Voices to Validity: Leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Textual Analysis of Policy Stakeholder Interviews. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.01202. [Google Scholar]
- Papaloukas, C.; Chalkidis, I.; Athinaios, K.; Pantazi, D.A.; Koubarakis, M. Multi-granular legal topic classification on greek legislation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.15298. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrokostas, C.; Giarelis, N.; Karacapilidis, N. Social Media Topic Classification on Greek Reddit. Information 2024, 15, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, G.; Varlamis, I.; Korovesis, K.; Caridakis, G.; Tsantilas, P. A survey on sentiment analysis and opinion mining in greek social media. Information 2021, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitenis, Z.; Zampieri, M.; Ranasinghe, T. Offensive language identification in Greek. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.07459. [Google Scholar]
- Michailidis, P.D. A Comparative Study of Sentiment Classification Models for Greek Reviews. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, L.; Stogiannidis, I.; Diamantopoulos, O.; Malakasiotis, P.; Vassos, S. Making llms worth every penny: Resource-limited text classification in banking. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 November 2023; pp. 392–400. [Google Scholar]
- Voukoutis, L.; Roussis, D.; Paraskevopoulos, G.; Sofianopoulos, S.; Prokopidis, P.; Papavasileiou, V.; Katsamanis, A.; Piperidis, S.; Katsouros, V. Meltemi: The first open large language model for greek. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.20743. [Google Scholar]
- Mylonas, N.; Stylianou, N.; Tsikrika, T.; Vrochidis, S.; Kompatsiaris, I. A Multi-Task Text Classification Pipeline with Natural Language Explanations: A User-Centric Evaluation in Sentiment Analysis and Offensive Language Identification in Greek Tweets. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.10290. [Google Scholar]
- Kydros, D.; Argyropoulou, M.; Vrana, V. A content and sentiment analysis of Greek tweets during the pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkidis, I.; Fergadiotis, M.; Androutsopoulos, I. MultiEURLEX—A multi-lingual and multi-label legal document classification dataset for zero-shot cross-lingual transfer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.00904. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforos, M.N.; Voutos, Y.; Drougani, A.; Mylonas, P.; Kermanidis, K.L. The modern Greek language on the social web: A survey of data sets and mining applications. Data 2021, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoyiannis, A.; Koukis, N. Exploring teachers’ readiness and beliefs about emergency remote teaching in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2023, 32, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kostas, A.; Paraschou, V.; Spanos, D.; Sofos, A. Emergency Remote Teaching in K-12 Education During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research in Greece. In Research on E-Learning and ICT in Education: Technological, Pedagogical, and Instructional Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 235–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lavidas, K.; Apostolou, Z.; Papadakis, S. Challenges and opportunities of mathematics in digital times: Preschool teachers’ views. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Adoma, A.F.; Henry, N.M.; Chen, W. Comparative analyses of bert, roberta, distilbert, and xlnet for text-based emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing (ICCWAMTIP), Chengdu, China, 18–20 December 2020; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Jojoa, M.; Eftekhar, P.; Nowrouzi-Kia, B.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Natural language processing analysis applied to COVID-19 open-text opinions using a distilBERT model for sentiment categorization. AI Soc. 2024, 39, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, L.; Amjad, A.; Ashraf, N.; Chang, H.T. Multi-class sentiment analysis of urdu text using multilingual BERT. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggrainingsih, R.; Hassan, G.M.; Datta, A. BERT based classification system for detecting rumours on Twitter. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.02975. [Google Scholar]
- Giarelis, N.; Mastrokostas, C.; Siachos, I.; Karacapilidis, N. A review of Greek NLP technologies for Chatbot development. In Proceedings of the 27th Pan-Hellenic Conference on Progress in Computing and Informatics, New York, NY, USA, 24–26 November 2023; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsikakis, J.; Chalkidis, I.; Malakasiotis, P.; Androutsopoulos, I. Greek-bert: The greeks visiting sesame street. In Proceedings of the 11th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 2–4 September 2020; pp. 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Βικιπαίδεια: Aντίγραφα της βάσης δεδομένων. Available online: https://el.wikipedia.org/wiki/%CE%92%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%B9%CF%80%CE%B1%CE%AF%CE%B4%CE%B5%CE%AF%CE%B1:%CE%91%CE%BD%CF%84%CE%AF%CE%B3%CF%81%CE%B1%CF%86%CE%B1_%CF%84%CE%B7%CF%82_%CE%B2%CE%AC%CF%83%CE%B7%CF%82_%CE%B4%CE%B5%CE%B4%CE%BF%CE%BC%CE%AD%CE%BD%CF%89%CE%BD (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Europarl. Europarl: A Parallel Corpus for Statistical Machine Translation. Available online: https://www.statmt.org/europarl/ (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- OSCAR Project. OSCAR: Open Super-Large Crawled Aggregated Repository. Available online: https://oscar-project.org/ (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Athinaios, K.; Chalkidis, I.; Pantazi, D.A.; Papaloukas, C. Named Entity Recognition Using a Novel Linguistic Model for Greek Legal Corpora Based on BERT Model. 2020. Available online: https://pergamos.lib.uoa.gr/uoa/dl/object/2927727 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Apostolopoulou, A.G.; Briakos, S.A.; Pantazi, D.A. Nlp Tasks with Greeklegalbert v2. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Sciences Department of Informatics and Telecommunications, Athens, Greece, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsifakou, K.M.; Sotiropoulos, D.N. Greek political speech classification using BERT. In Proceedings of the 2023 14th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), Volos, Greece, 10–12 July 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Evdaimon, I.; Abdine, H.; Xypolopoulos, C.; Outsios, S.; Vazirgiannis, M.; Stamou, G. Greekbart: The first pretrained greek sequence-to-sequence model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.00869. [Google Scholar]
- Giarelis, N.; Mastrokostas, C.; Karacapilidis, N. GreekT5: Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Greek News Summarization. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, D.; Metropoulou, K.; Papadakis, N.; Matsatsinis, N. FarFetched: Entity-centric Reasoning and Claim Validation for the Greek Language based on Textually Represented Environments. In Proceedings of the 12th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–9 September 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- LightEternal. Lighteternal/nli-xlm-r-greek. 2023. Available online: https://huggingface.co/lighteternal/nli-xlm-r-greek (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Cao, J.; Xu, X.; Yin, X.; Pan, B. A risky large group emergency decision-making method based on topic sentiment analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 195, 116527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahne, A.; Fagherazzi, G.; Tannier, X.; Czernichow, T.; Orchard, F. Improving diabetes-related biomedical literature exploration in the clinical decision-making process via interactive classification and topic discovery: Methodology development study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e27434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, R.; Huang, B.; Wei, B.; Zheng, S.L.; Chen, M. Sentiment classification of crowdsourcing participants’ reviews text based on LDA topic model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 108131–108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimiris, S.; Nikiforos, M.N.; Nikiforos, S.; Kermanidis, K.L. Challenges and Opportunities of Emergency Remote Teaching: Linguistic Analysis on School Directors’ Interviews. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2023, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvale, S. Interviews: Learning the Craft of Qualitative Research Interviewing; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Joffe, H. Thematic analysis. In Qualitative Research Methods in Mental Health and Psychotherapy: A Guide for Students and Practitioners; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Grimmer, J.; Stewart, B.M. Text as data: The promise and pitfalls of automatic content analysis methods for political texts. Polit. Anal. 2013, 21, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commons, C. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. 2025. Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Tzimiris, S.; Nikiforos, S.; Kermanidis, K.L. Post-pandemic pedagogy: Emergency remote teaching impact on students with functional diversity. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 10285–10328. [Google Scholar]
- Jimoyiannis, A.; Koukis, N.; Tsiotakis, P. Shifting to emergency remote teaching due to the COVID-19 pandemic: An investigation of Greek teachers’ beliefs and experiences. In Proceedings of the Technology and Innovation in Learning, Teaching and Education: Second International Conference, TECH-EDU 2020, Vila Real, Portugal, 2–4 December 2020; Proceedings 2. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 320–329. [Google Scholar]
- Zagkos, C.; Kyridis, A.; Kamarianos, I.; Dragouni, K.E.; Katsanou, A.; Kouroumichaki, E.; Papastergiou, N.; Stergianopoulos, E. Emergency remote teaching and learning in Greek universities during the COVID-19 pandemic: The attitudes of university students. Eur. J. Interact. Multimed. Educ. 2022, 3, e02207. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, C.; Booth, H.; El-Assady, M.; Butt, M. Representation problems in linguistic annotations: Ambiguity, variation, uncertainty, error and bias. In Proceedings of the 14th Linguistic Annotation Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 12 December 2020; pp. 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jusoh, S. A study on NLP applications and ambiguity problems. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Haviana, S.F.C.; Mulyono, S.; Badie’Ah. The Effects of Stopwords, Stemming, and Lemmatization on Pre-trained Language Models for Text Classification: A Technical Study. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI), Palembang, Indonesia, 20–21 September 2023; pp. 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Nijhawan, L.P.; Janodia, M.D.; Muddukrishna, B.; Bhat, K.M.; Bairy, K.L.; Udupa, N.; Musmade, P.B. Informed consent: Issues and challenges. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2013, 4, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, B.; Kitzinger, J.; Kitzinger, C. Anonymising interview data: Challenges and compromise in practice. Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 616–632. [Google Scholar]
- HiLab, I.U. HiLab Datasets. 2025. Available online: https://hilab.di.ionio.gr/index.php/en/datasets/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Cateni, S.; Colla, V.; Vannucci, M. Improving the stability of the variable selection with small datasets in classification and regression tasks. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 5331–5356. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.B.C.; Karunaratne, T. Learning Analytics with Small Datasets—State of the Art and Beyond. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforos, S.; Anastasopoulou, E.; Pappa, A.; Tzanavaris, S.; Kermanidis, K.L. Motives and barriers in Emergency Remote Teaching: Insights from the Greek experience. Discov. Educ. 2024, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforos, S.; Anastasopoulou, E.; Pappa, A.; Tzanavaris, S.; Kermanidis, K.L. Teachers’ Needs for Support during Emergency Remote Teaching in Greek Schools: Role of Social Networks. Computers 2024, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lu, X.Z.; Chen, K.Y.; Zhou, Y.C.; Lin, J.R. Pretrained domain-specific language model for natural language processing tasks in the AEC domain. Comput. Ind. 2022, 142, 103733. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Su, J.; Luo, D. Improving bert-based text classification with auxiliary sentence and domain knowledge. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 176600–176612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
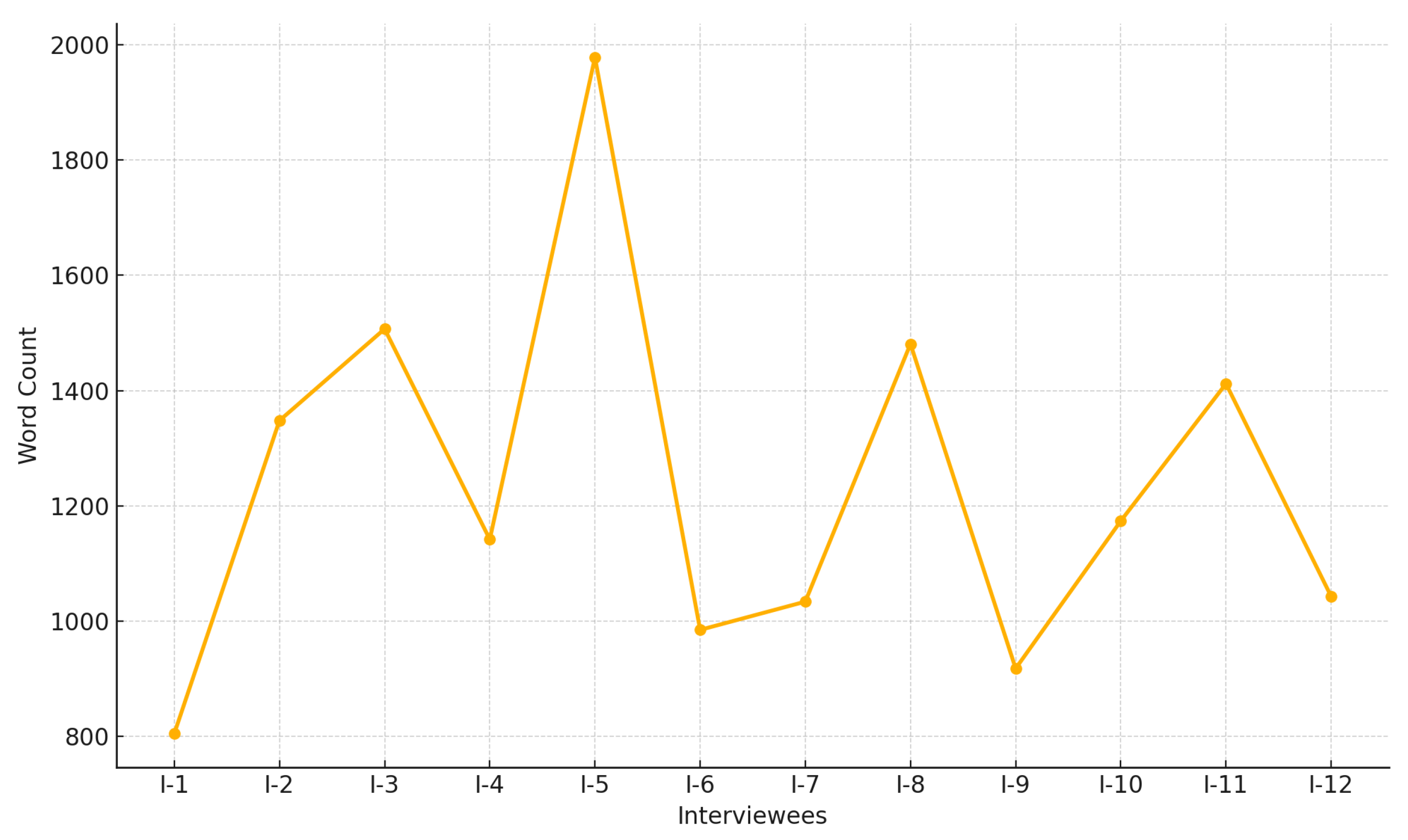

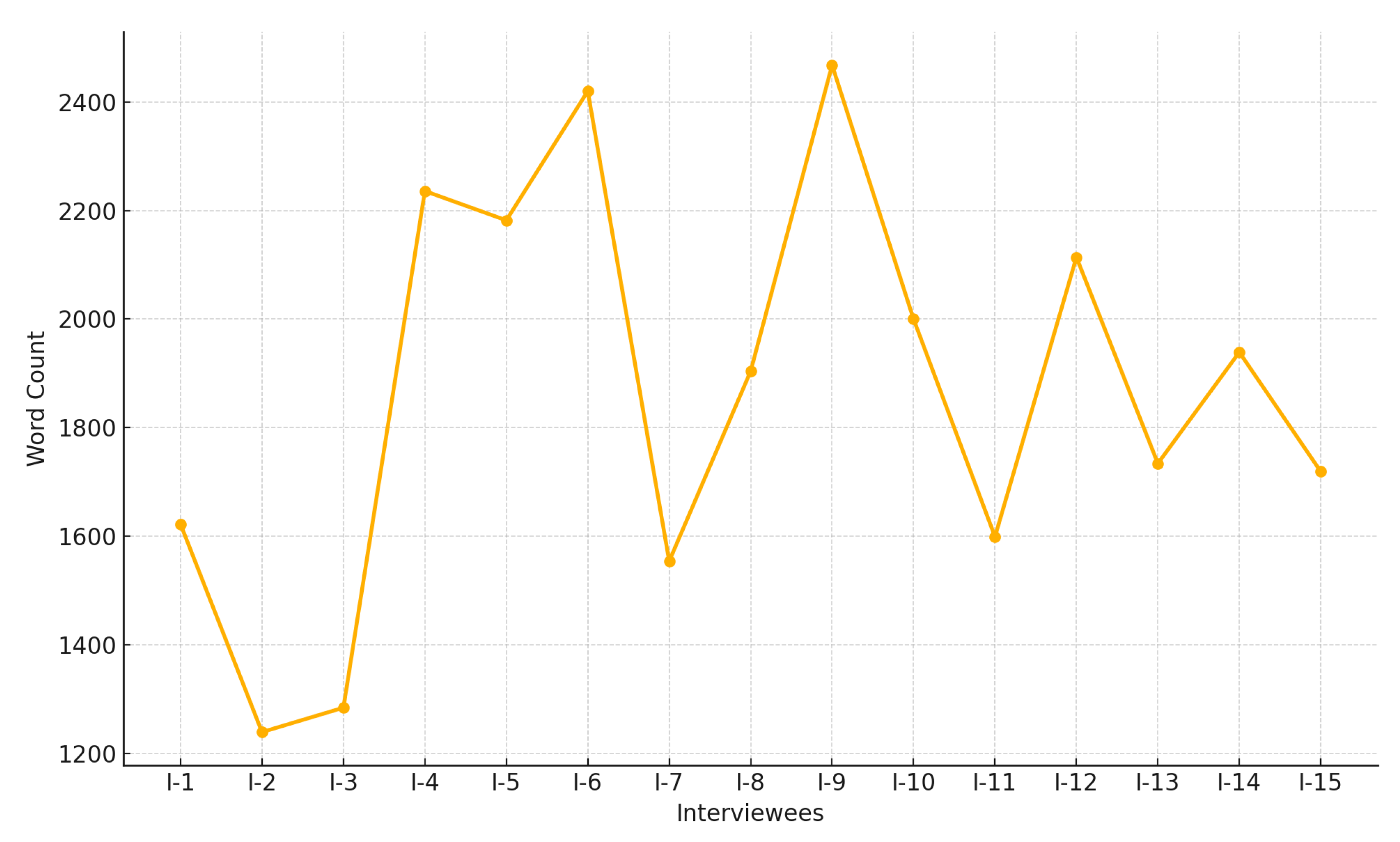

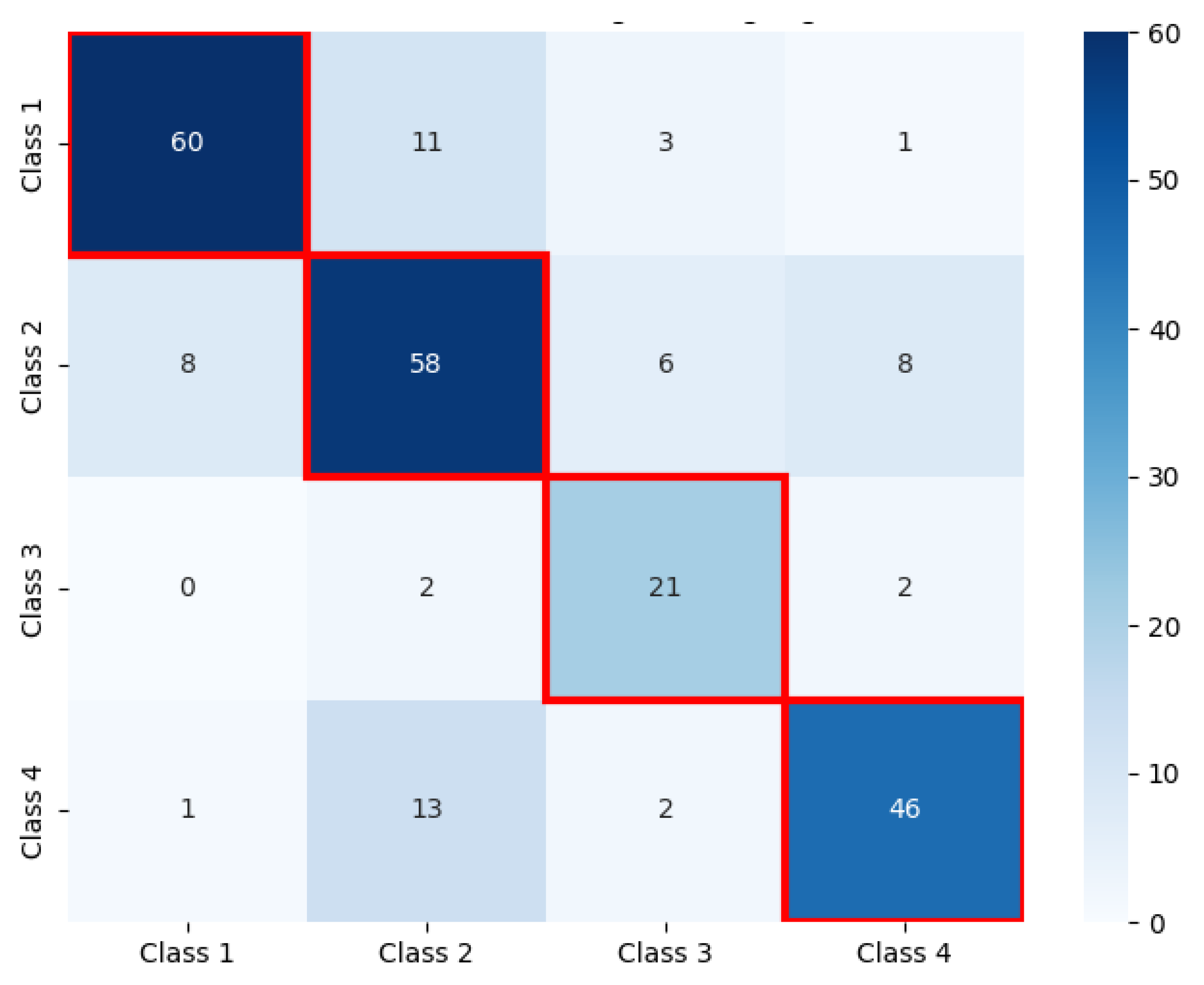
| Interviewees | Word Count | Functional Diversity of Their Child |
|---|---|---|
| I-1 | 805 | Speech Disorder (stuttering, dysarthria), Physical Disability |
| I-2 | 1348 | General Learning Difficulties (GLDs) |
| I-3 | 1507 | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) |
| I-4 | 1142 | Dyslexia, Developmental Dyscalculia |
| I-5 | 1978 | General Learning Difficulties (GLDs) |
| I-6 | 985 | Dyslexia, Speech Disorder (stuttering) |
| I-7 | 1034 | General Learning Difficulties (GLDs) |
| I-8 | 1481 | General Learning Difficulties (GLDs) |
| I-9 | 918 | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Aggressiveness |
| I-10 | 1174 | General Learning Difficulties (GLDs) |
| I-11 | 1412 | Vision Disability |
| I-12 | 1043 | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) |
| Total | 14,827 | |
| Mean | 1236 | |
| Median | 1158 | |
| Standard Deviation | 325.9 | |
| Range | 1173 | |
| Minimum | 805 | |
| Maximum | 1978 |
| Interviewees | Word Count | Age | Years of Service as School Directors |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-1 | 1338 | 50 | 5 |
| I-2 | 1240 | 52 | 1 |
| I-3 | 1410 | 62 | 12 |
| I-4 | 899 | 45 | 7 |
| I-5 | 1464 | 54 | 3 |
| I-6 | 1080 | 40 | 4 |
| I-7 | 1328 | 49 | 7 |
| I-8 | 1098 | 57 | 5 |
| I-9 | 1040 | 56 | 1 |
| I-10 | 1153 | 55 | 8 |
| I-11 | 1081 | 51 | 10 |
| I-12 | 981 | 52 | 6 |
| I-13 | 1243 | 50 | 2 |
| I-14 | 921 | 45 | 15 |
| I-15 | 895 | 48 | 2 |
| Total | 17,171 | ||
| Mean | 1145 | ||
| Median | 1098 | ||
| Standard Deviation | 185.8 | ||
| Range | 569 | ||
| Minimum | 895 | ||
| Maximum | 1464 |
| Interviewees | Word Count | Age | Years of Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-1 | 1622 | 32 | 6 |
| I-2 | 1239 | 45 | 20 |
| I-3 | 1284 | 38 | 10 |
| I-4 | 2236 | 50 | 25 |
| I-5 | 2182 | 62 | 39 |
| I-6 | 2420 | 55 | 30 |
| I-7 | 1554 | 40 | 15 |
| I-8 | 1904 | 48 | 22 |
| I-9 | 2468 | 60 | 37 |
| I-10 | 2000 | 52 | 28 |
| I-11 | 1599 | 36 | 9 |
| I-12 | 2114 | 46 | 21 |
| I-13 | 1734 | 42 | 16 |
| I-14 | 1939 | 49 | 23 |
| I-15 | 1719 | 35 | 8 |
| Total | 28,014 | ||
| Mean | 1868 | ||
| Median | 1904 | ||
| Standard Deviation | 377.1 | ||
| Range | 1229 | ||
| Minimum | 1239 | ||
| Maximum | 2468 |
| Dataset | Model | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCHD Dataset | XGBoost | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.44 |
| mBERT | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.68 | |
| XLM-R Greek | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.72 | |
| GreekBERT | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.76 | |
| PSFD Dataset | XGBoost | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.58 |
| mBERT | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.67 | |
| XLM-R Greek | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | |
| GreekBERT | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.74 | |
| TCH Dataset | XGBoost | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.53 |
| mBERT | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.70 | |
| XLM-R Greek | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.79 | |
| GreekBERT | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.76 |
| Model | Dataset | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | SCHD dataset | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.44 |
| PSFD dataset | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.58 | |
| TCH dataset | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.53 | |
| mBERT | SCHD dataset | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| PSFD dataset | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.67 | |
| TCH dataset | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.70 | |
| XLM-R Greek | SCHD dataset | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.72 |
| PSFD dataset | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | |
| TCH dataset | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.79 | |
| GreekBERT | SCHD dataset | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.76 |
| PSFD dataset | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.74 | |
| TCH dataset | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.76 |
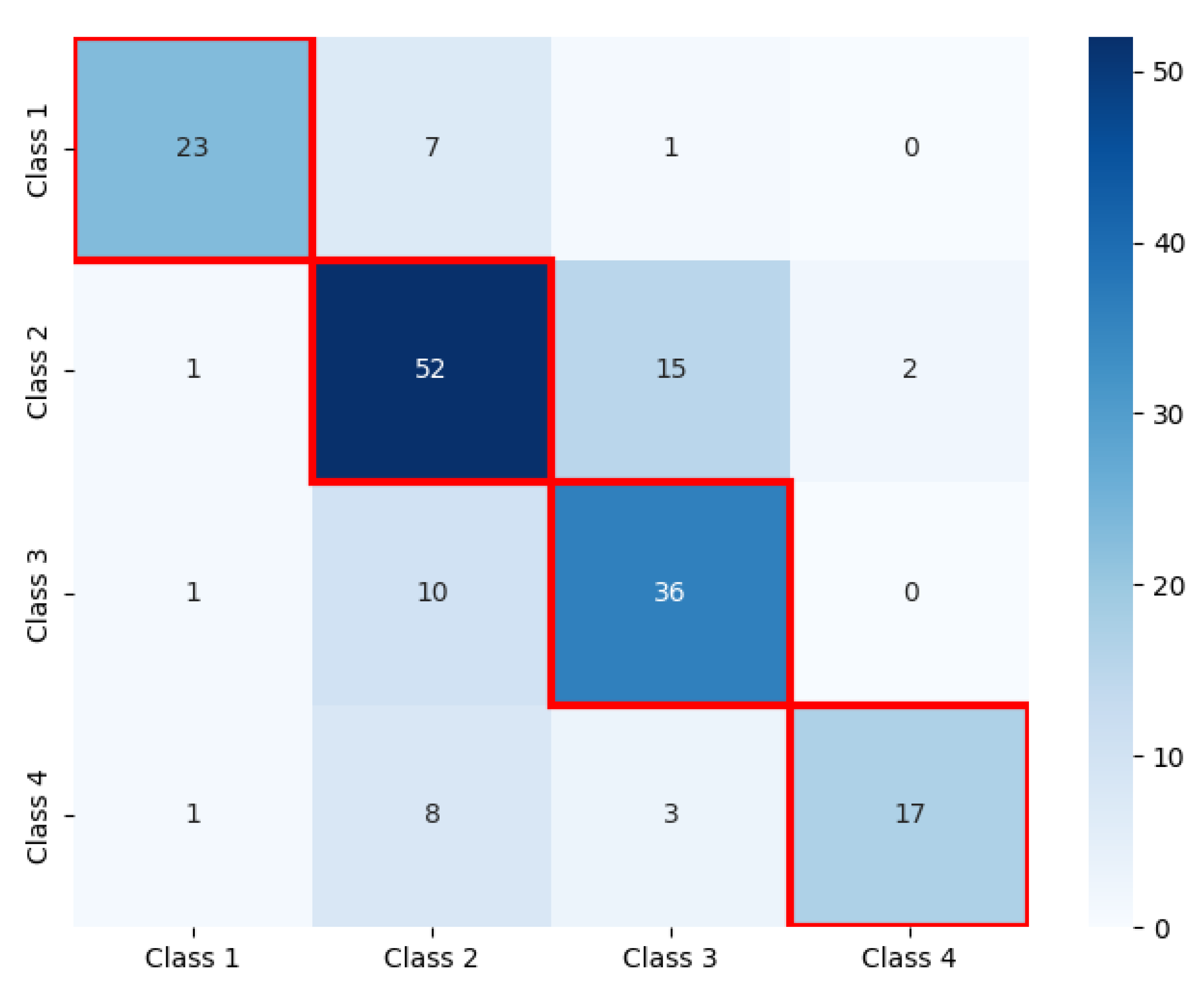
| SCHD Dataset | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.84 |
| Class 2 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.49 |
| Class 3 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.83 |
| Class 4 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.88 |
| PSFD Dataset | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
| Class 1 | 0.88 | 0.74 | 0.81 |
| Class 2 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.71 |
| Class 3 | 0.65 | 0.77 | 0.71 |
| Class 4 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.71 |
| TCH Dataset | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
| Class 1 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.83 |
| Class 2 | 0.69 | 0.72 | 0.71 |
| Class 3 | 0.66 | 0.84 | 0.74 |
| Class 4 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.77 |
| Research | Data | Task | Classes | Model | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [22] | Greek Reddit posts | TC | 10 | GreekBERT | F1: 0.79 |
| [21] | Greek legislation | Legal TC | 50 | GREEK-LEGAL-BERT | F1: 0.89 |
| [25] | Greek reviews | SC | 3 | BERT, GPT-4 | F1: 0.96 |
| This paper | Greek Interviews | TC | 4 | GreekBERT | F1: 0.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tzimiris, S.; Nikiforos, S.; Nikiforos, M.N.; Mouratidis, D.; Kermanidis, K.L. Topic Classification of Interviews on Emergency Remote Teaching. Information 2025, 16, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040253
Tzimiris S, Nikiforos S, Nikiforos MN, Mouratidis D, Kermanidis KL. Topic Classification of Interviews on Emergency Remote Teaching. Information. 2025; 16(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleTzimiris, Spyridon, Stefanos Nikiforos, Maria Nefeli Nikiforos, Despoina Mouratidis, and Katia Lida Kermanidis. 2025. "Topic Classification of Interviews on Emergency Remote Teaching" Information 16, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040253
APA StyleTzimiris, S., Nikiforos, S., Nikiforos, M. N., Mouratidis, D., & Kermanidis, K. L. (2025). Topic Classification of Interviews on Emergency Remote Teaching. Information, 16(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040253











