Abstract
The intricate microenvironment at the wound site, coupled with the multi-phase nature of the healing process, pose significant challenges to the development of wound repair treatments. In recent years, applying the distinctive benefits of hydrogels to the development of wound repair strategies has yielded some promising results. Multifunctional hydrogels, by meeting the different requirements of wound healing stages, have greatly improved the healing effectiveness of chronic wounds, offering immense potential in wound repair applications. This review summarized the recent research and applications of multifunctional hydrogels in wound repair. The focus was placed on the research progress of diverse multifunctional hydrogels, and their mechanisms of action at different stages of wound repair were discussed in detail. Through a comprehensive analysis, we found that multifunctional hydrogels play an indispensable role in the process of wound repair by providing a moist environment, controlling inflammation, promoting angiogenesis, and effectively preventing infection. However, further implementation of multifunctional hydrogel-based therapeutic strategies also faces various challenges, such as the contradiction between the complexity of multifunctionality and the simplicity required for clinical translation and application. In the future, we should work to address these challenges, further optimize the design and preparation of multifunctional hydrogels, enhance their effectiveness in wound repair, and promote their widespread application in clinical practice.
1. Introduction
The skin, a crucial organ that envelops the body’s surface and directly interacts with the external surroundings, serves multiple functions, including sensing external stimuli, maintaining body temperature, and safeguarding the body against external harm. Damage to its structural integrity and function can lead to diverse forms of wounds. Research indicated that the process of skin wound repair is recognized as a dynamic and intricate journey, encompassing four consecutive stages, primarily categorized as hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and tissue remodeling [1,2,3,4]. In the early stage of skin damage, platelets are recruited to the trauma site and begin to aggregate while releasing thrombin to initiate the coagulation cascade reaction, catalyzing the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, which combines with aggregated platelets to form a blood clot. During the inflammatory phase, the release of inflammatory factors triggers the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages to the injury site to phagocytose necrotic tissue, foreign debris and bacteria, and to provide local hemostasis. The proliferative phase is primarily characterized by the development of granulation tissue, neovascularization, the deposition of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and the re-epithelialization of the neo-epidermis. In the proliferative phase, newly generated blood vessels are embedded into the granulation tissue, providing ample oxygen and nutrients for cellular activity. Cytokines further activate fibroblasts, thereby enhancing cell proliferation and stimulating the secretion of collagen into the ECM. Epithelial cells begin migrating inward from the wound edge, ultimately covering the entire wound area. Finally, during the wound remodeling process, various cellular components (primarily macrophages), growth factors, as well as the nerve and immune systems, work in concert to regulate the synthesis and degradation of connective tissue. This allows for the repetitive dissolution, deposition, and renewal of collagen, leading to the gradual disappearance of scars and the continuous restructuring of the ECM, ultimately resulting in complete wound healing [5,6,7]. Currently, skin wound repair continues to be a prominent and formidable subject in both clinical and scientific research.
Common wound treatment strategies include ultrasound [8], electrotherapy [9], hyperbaric oxygen therapy [10], negative pressure therapy [11], stem cell therapy [12], dressings containing growth factors, etc. For skin injuries that involve the deeper layers of the dermis but are not extensive in size, if tissue repair can be accelerated and scar formation reduced using skin dressings, it would greatly facilitate the clinical treatment of skin injuries. Gauze, as a traditional dry dressing, is still widely used in clinical practice. However, it tends to adhere to the wound site, cause discomfort when removed due to its high water absorption, and offer limited protection against microbial invasion [13]. An ideal skin wound dressing should possess good tissue compatibility and moisturizing properties and be able to absorb tissue exudate while also having a certain level of mechanical strength, tissue adhesiveness, and surface microstructure [14,15]. It should stably remain on the wound surface, preventing external contamination, inhibiting bacterial growth, and promoting cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation [16,17]. Based on the aforementioned characteristics, hydrogels have gained prominence as the most promising skin wound dressings among numerous candidate materials due to their soft consistency, high porosity, excellent biocompatibility, and resilience [18,19,20]. It can maintain a moist environment for the wound, promoting cell regeneration and wound healing. Additionally, the excellent adhesive property of the hydrogel allows it to tightly adhere to the wound surface without causing secondary damage due to easy detachment. Most importantly, the hydrogel dressing possesses unique permeation regulation capabilities, enabling it to automatically adjust the permeation rate based on the wound condition, providing appropriate humidity and oxygen supply, thus accelerating wound healing. With innovative advancements in hydrogel design and synthesis techniques, coupled with in-depth research into skin wound repair mechanisms, the functionality of hydrogels has evolved from their early role of simple wound coverage to today’s multifunctional and intelligent repair capabilities, and the types of hydrogel dressings have also shown a trend of increasing year by year.
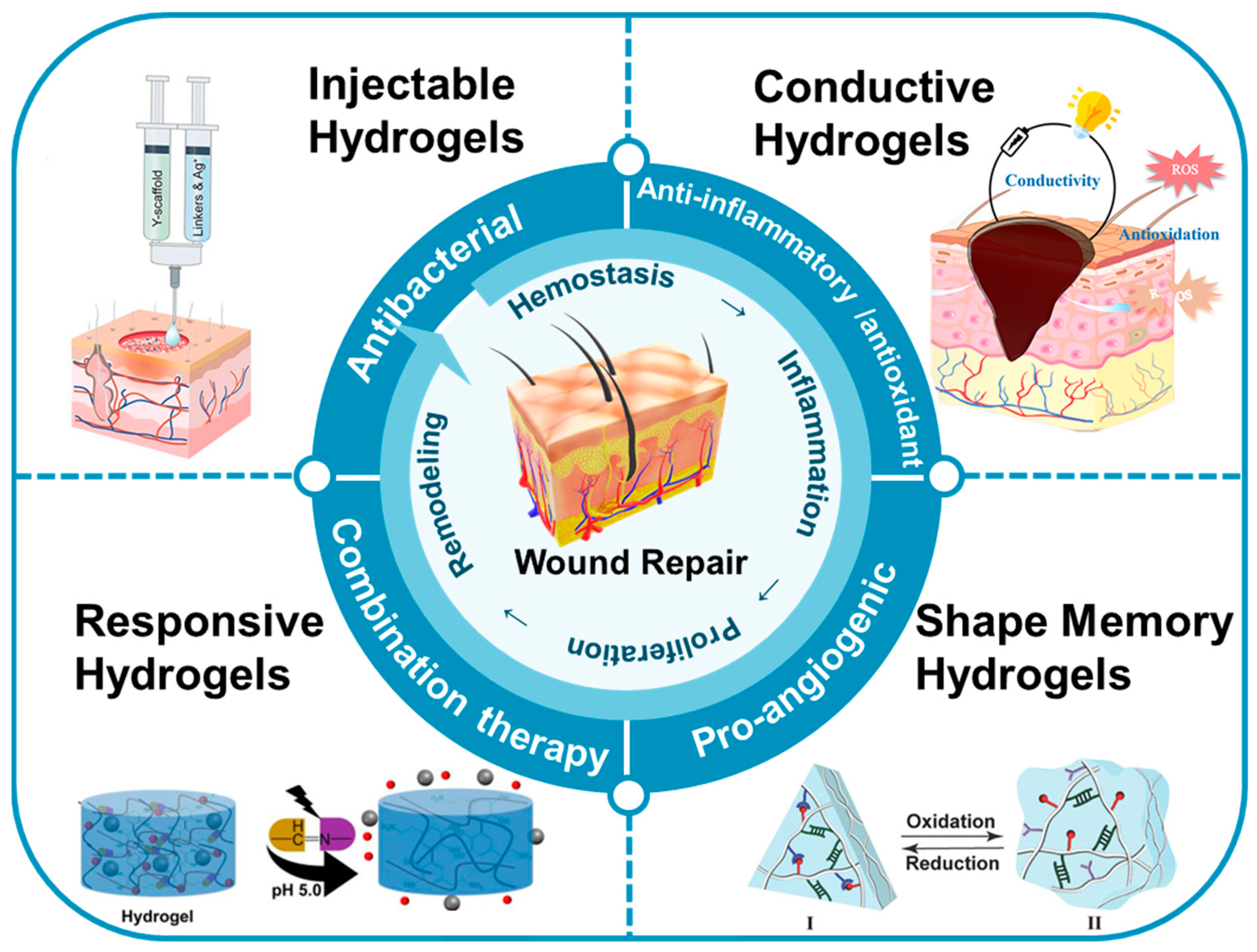
This review focused on the recent research and advancements in utilizing multifunctional hydrogels for wound repair (Figure 1). Firstly, we summarize the preparation and mechanisms of various types of multifunctional hydrogels, including injectable, responsive, conductive, shape-memory, and other types of hydrogels. Secondly, we discuss the diverse roles of these multifunctional hydrogels in wound repair, encompassing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, pro-angiogenic, and combined therapeutic effects, demonstrating their efficacy. Finally, considering the current research landscape and clinical needs, we address the challenges associated with the use of multifunctional hydrogels in wound repair, with the objective of offering valuable insights for future research and applications of multifunctional hydrogels in the field.
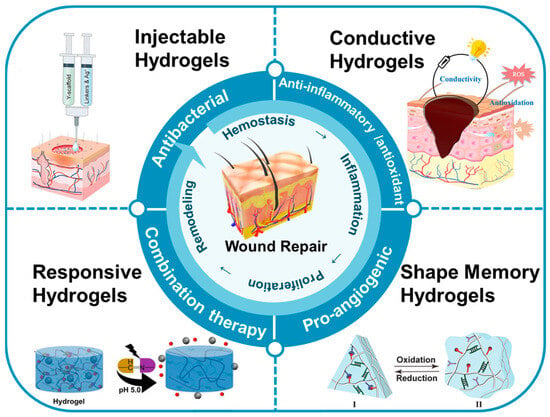
Figure 1.
The applications of multifunctional hydrogels in the context of wound repair.
2. Types of Multifunctional Hydrogels
Hydrogels are large polymer molecules composed of a network of crosslinked polymer chains [21]. The physicochemical properties and network structures of hydrogels vary depending on the preparation methods employed [22]. Based on the different crosslinking mechanisms, the preparation methods of hydrogels can be broadly classified into two categories: physical crosslinking and chemical crosslinking [23]. Physical crosslinking mainly involves non-covalent bonding interactions such as hydrophobic interactions [24,25], hydrogen bonding [26], subject–object interactions [27], electrostatic interactions [28], and biomolecular recognition [29]. These interactions are relatively mild and fast in response, but they are typically reversible, capable of being disrupted and restored under certain conditions, thus imparting shear-thinning and self-healing properties to the gel. However, hydrogels that are purely physically crosslinked tend to have lower mechanical strength and poorer stability. Chemical crosslinking refers to the formation of a hydrogel network through the establishment of covalent bonds. Common chemical crosslinking strategies include free radical polymerization [30], click reactions [31], Schiff base formation as dynamic covalent bonds [32], and enzymatic crosslinking reactions [33]. In comparison to physical crosslinking, chemical crosslinking typically requires precise structural design of the polymers, and the gelation rate and mechanical properties are directly influenced by the chemical reactivity between specific functional groups. Chemical crosslinked hydrogels exhibit higher strength and stability. However, they can also result in residual initiators, crosslinking agents, and unreacted monomers, which can potentially induce adverse reactions in living organisms and reduce the biocompatibility of the synthesized hydrogel materials. Therefore, they are not suitable for medical applications that require high biocompatibility standards.
The preparation method of hydrogels is a crucial factor that determines their physicochemical properties and applications. Researchers have developed various advanced functional hydrogels by applying different preparation methods to meet the different requirements of wound healing at different stages. With the pursuit of precision therapy, the development of more advanced hydrogels has attracted considerable attention. Different types of skin wounds have different shapes (size, thickness, etc.) and clinical manifestations (necrosis, decay, etc.), and the ideal hydrogel wound dressing should have the functions of rapidly forming an anti-infective barrier, promoting rapid blood coagulation, absorbing wound exudate, blocking nerve endings to reduce pain, and providing nutrients to promote tissue regeneration, etc. To meet these varying requirements for wound repair, researchers have developed various functional types of hydrogels, and the common ones include injectable, smart-response, conductive, and shape-memory.
2.1. Injectable Hydrogels
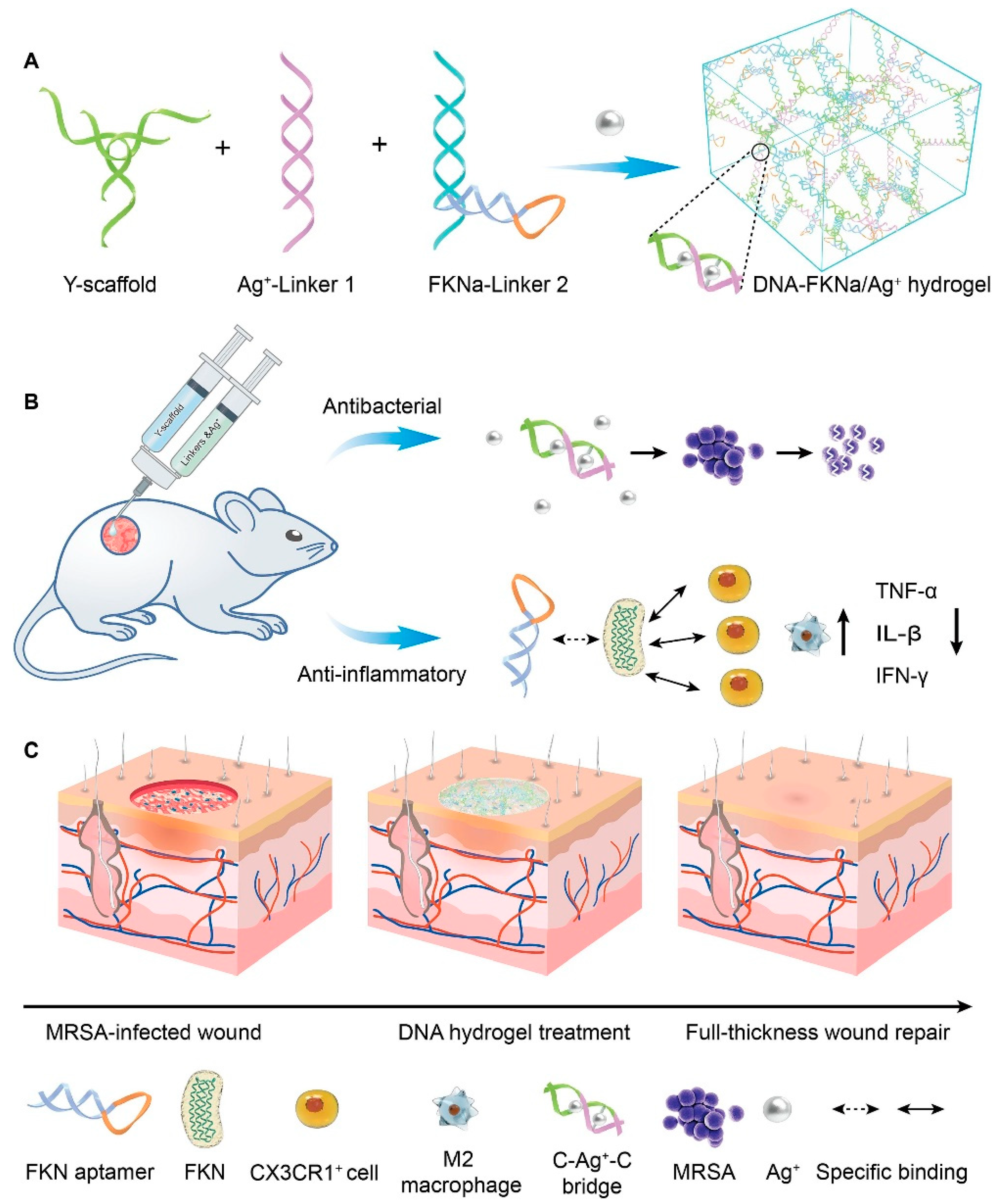
The significant advantage of injectable hydrogels is their ability to conform to irregular wound shapes and serve as a platform for the delivery of drugs/cells and bioactive molecules (genes, proteins, growth factors, etc.), rendering them exceptionally promising for various wound repair applications. Injectable hydrogels can be categorized into two distinct types based on their gelation state and injection behavior: in situ gel-forming and shear-thinning hydrogels [34,35]. Among them, in situ gel-forming hydrogels mainly form a polymer network through certain physical effects or chemical crosslinking of two or more precursor solutions in vivo. A shear-thinning hydrogel is in a solid state (formed through reversible physical crosslinking) before injection. It transforms into a sol under the action of shear force, allowing flow injection in the needle tube. After the injection is completed, it can quickly self-repair to its original gel state. Amphiphilic block copolymers have been widely reported for preparing injectable hydrogels through self-assembly behaviors [36]. For example, Segura et al. [37] synthesized a tetra-armed poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(propylene sulfide) (PEG-PPS) block copolymer, where the hydrophobic self-assembly of PPS at the ends of the molecular chains could act as physical crosslinks to form injectable hydrogels, and this dynamic physical action could confer the gel with both shear-thinning and injectable properties. Injectable hydrogels have been extensively investigated as viable cell delivery systems due to their capability to mimic the extracellular matrix, uniformly encapsulate cells, facilitate effective mass transfer, accommodate chemical and physical modifications, and enable minimally invasive delivery. For instance, Chen et al. [28] synthesized polyglutamic acid-polyethylene glycol-polyglutamic acid (PGA-PEG-PGA) and polylysine-polyethylene glycol-polylysine (PLL- PEG-PLL) two block polymers. Among them, polyglutamic acid and polylysine have negative and positive charges, respectively. After mixing the two, they can quickly form an injectable hydrogel by relying on electrostatic interaction to achieve cell loading and passed function. Hu et al. [38] synthesized an injectable hydrogel that can demonstrate controlled delivery of the drug curcumin (Cur) and customized recombinant humanized collagen type III, precisely targeting the site of myocardial infarction. Chi et al. [39] developed an injectable hydrogel using thioglutamic acid (γ-glutamic acid) (γ-PGA- SH) and oxidized glycidyl methacrylate modified hyaluronic acid (OHA-GMA). This hydrogel exhibited remarkable properties such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, self-healing ability, and robust mechanical strength. Additionally, it demonstrated the capability to regulate fibroblast migration and infiltration through stiffness modulation, serving as an effective in situ scaffold for skin tissue regeneration. Wang et al. [40] constructed a straightforward, injectable, and multifunctional hydrogel (DNA-FKNa/Ag+) dressing by grafting DNA subunits, comprising cytosine (C)-rich strands and an fractalkine aptamer (FKNa), and it demonstrates remarkable suitability and significant potential for clinical translation in promoting and accelerating the healing of a methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-infected wound (Figure 2).
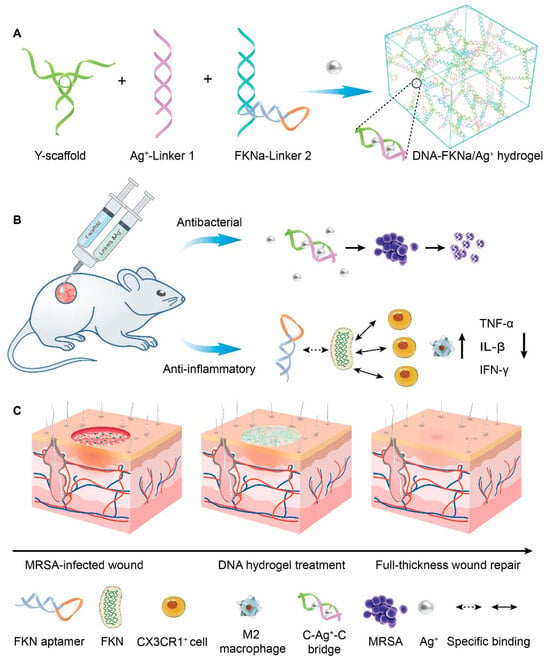
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram depicts the DNA-FKNa/Ag+ hydrogel, which is designed for the treatment of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-infected wounds. (A) The compositions of the DNA-FKNa/Ag+ hydrogel. The enlarged picture presents the structure of C-Ag+-C bridges. (B) DNA-FKNa/Ag+ hydrogels were formed in situ by injecting DNA subunits into the bacterial infection defect using a three-way syringe. (C) MRSA-infected full-thickness wound repair using the dual functionalized DNA-FKNa/Ag+ hydrogel in an animal experiment. Adapted with permission from Ref. [40]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier.
2.2. Responsive Hydrogels
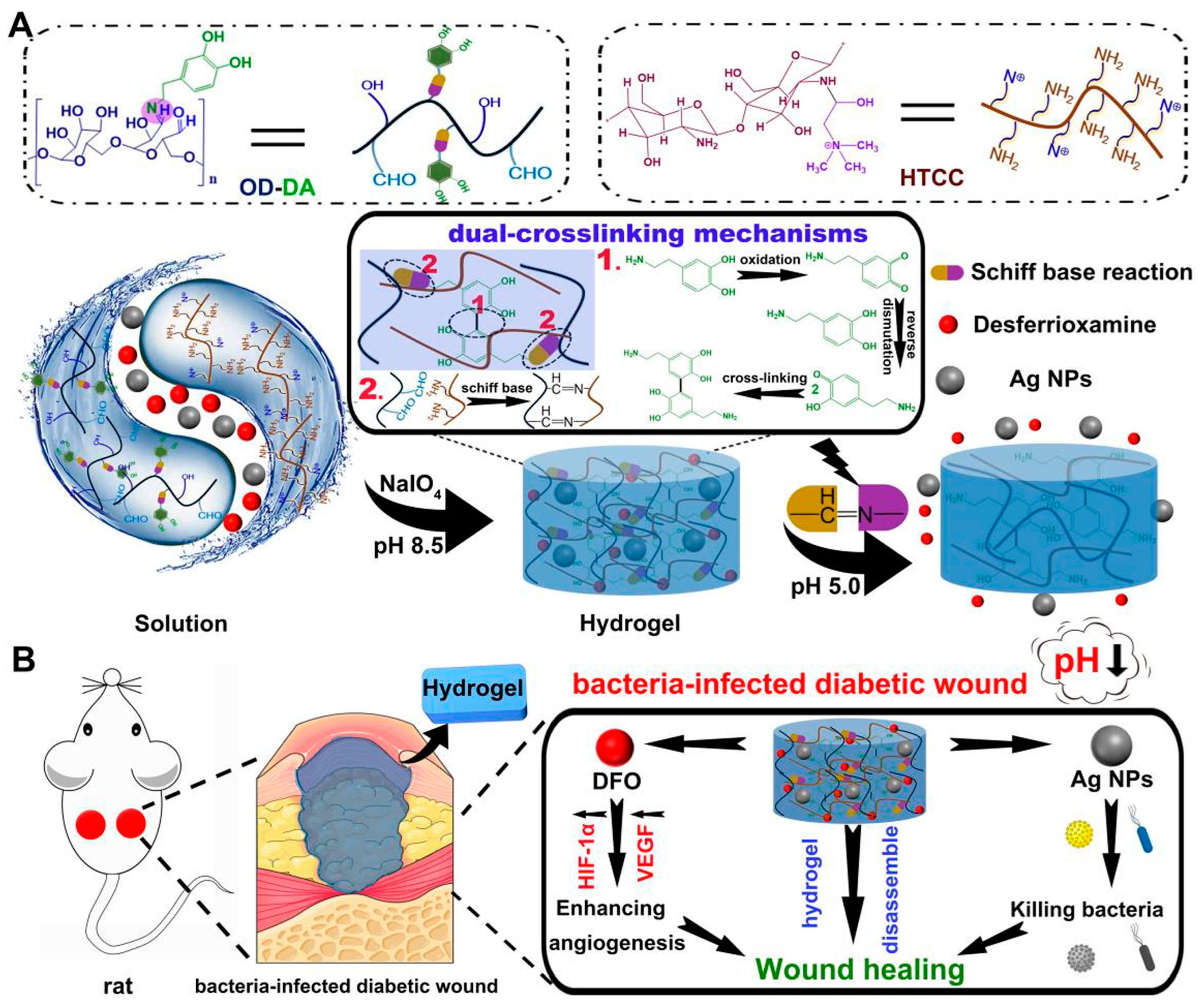
Responsive hydrogels are novel smart biomaterials capable of undergoing polymer chain conformational transitions or network changes under external environmental stimuli (e.g., specific temperature, light, pH, magnetic field, etc.), resulting in a series of specific responses, such as significant volume contraction/expansion, color change, and phase transition, making them injectable and self-healing with other properties [41]. These characteristics endow them with injectability, self-healing properties, shape memory, and more. The factors influencing wound healing include environmental factors (light, temperature, pH, CO2, etc.) that encounter the wound’s surface and physiological factors (cells, extracellular matrix, growth factors, ROS, enzymes, etc.) within the wound. Based on this, researchers have developed a series of responsive hydrogels in recent years, including physically responsive hydrogels responding to physical signals (temperature, light, electric fields, ultrasound, etc.) [42,43,44,45,46], chemically responsive hydrogels reacting to chemical signals (pH and ROS, etc.) [47,48,49,50], biologically responsive hydrogels responsive to biomolecules (enzymes and glucose, etc.) [51,52,53], and multi-responsive hydrogels [54,55]. For instance, Hu et al. [56] utilized caffeic acid-grafted ε-polylysine and phenylboronic acid-grafted oxidized dextran as the foundation to fabricate an injectable hydrogel. This hydrogel exhibits dual responsiveness to pH and ROS, and it encapsulates pH-responsive micelles (MIC@MF) that effectively promotes angiogenesis and anti-inflammatory DS. This feature facilitated the precise release of drugs at specific times and locations, aligning with the well-coordinated progression of wound healing in diabetic wounds. In another work, they exploited a pH-responsive, mussel-inspired, double-crosslinking injectable, and adhesive smart hydrogel to address the challenges associated with chronic diabetic wound repair. Importantly, the hydrogel exhibits antibacterial and angiogenesis-promoting characteristics, achieved through effective encapsulation of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and the pro-angiogenic drug deferoxamine (DFO), respectively [57] (Figure 3). Guo et al. [58] prepared a series of multi-stimulus response (NIR, ROS, and temperature) cryogels with controllable NO release capability based on methacryloyl carboxymethyl chitosan, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), and composite nanoparticle enzyme (MSPA) for the adaptive treatment of drug-resistant bacterial-infected wounds.
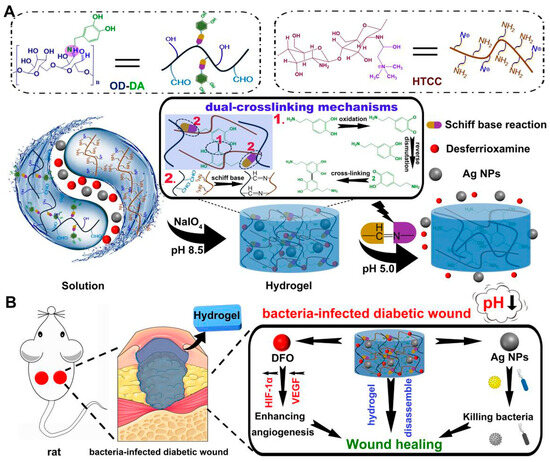
Figure 3.
(A) The formation and mechanisms of the smart hydrogels. (1) Oxidative self-cross-linking mechanism of dopamine. (2) Schiff base cross-linking mechanism. (B) The antibacterial and wound healing mechanisms of the smart hydrogels. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [57]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier.
2.3. Conductive Hydrogels
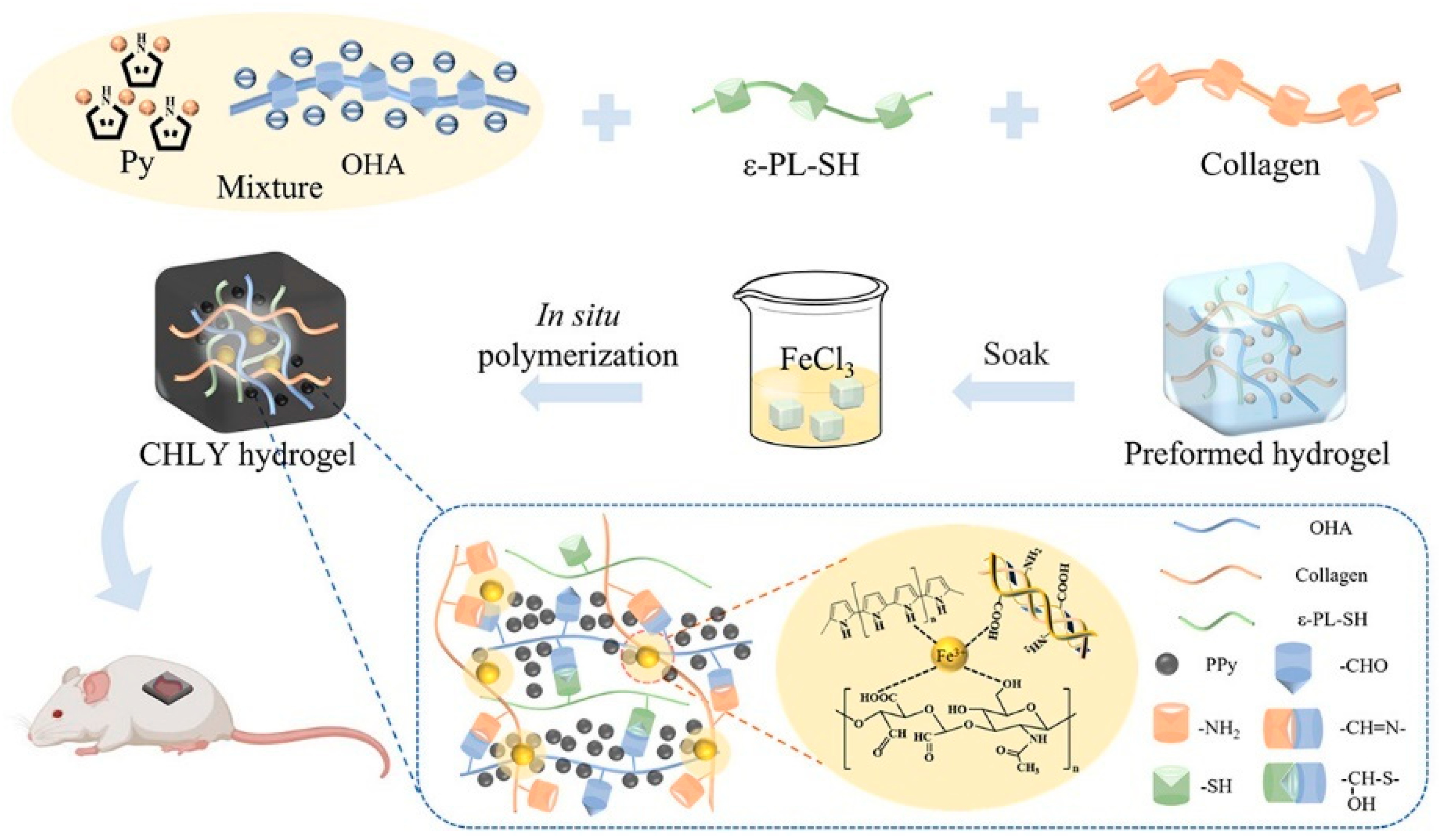
Electrical stimulation expedites wound healing processes across all stages by engaging in multiple ways [59,60]. It relieves peri-electrode edema, directs keratinocyte migration, enhances re-epithelialization, directs cutaneous angiogenesis, modulates a range of genes related to wound healing, and produces antimicrobial action [61,62]. Consequently, strategies related to electrical stimulation for wound treatment have emerged. Conductive hydrogel is a novel composite material that combines a hydrophilic matrix organically combined with conductive fillers. Hydrogel with appropriate conductivity can maintain the wet environment of skin-defective wounds in a variety of mammals and enhance the electrical signaling of wounds, re-establish physiological functions related to electrical conduction, and promote wound healing [6]. The conductive mechanism can be classified into two categories: The first is through the introduction of ionic conductive materials (salt solution, ionic liquids, or polyelectrolytes) into the hydrogel network, in which the t network structure of the hydrogel provides a channel for the migration of ions so that the free ions are transmitted within it, and ultimately achieve ionic conductivity [63,64]. Secondly, it is a combination of electronically conductive polymers (ECPs) [65,66], carbon-based materials (e.g., carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide (GO)) [67,68], MXene [69], and metal-based materials [70], to establish the network of electron transport in hydrogel and realize electronically conductive. As an instance, Zhao et al. [71] presented a self-healing and highly conductive organogel composite. This composite structure was constructed by incorporating a permeable network of Ag microflakes and Ga liquid metal (LM) alloy microdroplets into a poly (vinyl alcohol)-sodium borate gel. It demonstrated remarkable conductivity of 7 × 104 S m−1 and exhibited rapid and effective self-healing properties. Guo et al. [72] proposed a “deswelling in situ aggregation” method to induce colloidal particles of conductive polymer (PEDOT: PSS) to in situ aggregate into a continuous conductive network within a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) network, resulting in a hydrogel with high electrical conductivity and high stretchability (breaking strain of 150%). Recently, Ge et al. [73] successfully created collagen-based hydrogels (CHLY) with multiple functionalities for inducing full-thickness wound healing. They achieved this by incorporating cysteine-modified ε-poly(l-lysine) (ε-PL-SH) and in situ-polymerized polypyrrole (PPy) nanoparticles into the hydrogel formulation (Figure 4). The resulting hydrogels demonstrated adhesive properties, conductivity, as well as antibacterial and antioxidant activities, making them highly versatile in promoting wound healing. Zuo et al. [74] successfully constructed SF/TA@PPy conductive hydrogels with stretchability, skin compliance, antimicrobial properties, and biocompatibility by introducing the conductive polymer polypyrrole (PPy) into the same gel network with filipin protein (SF) and tannic acid (TA) via in situ polymerization. Guo et al. [75] constructed a series of double dynamic bonded crosslinked hydrogels by combining sodium alginate oxide with dopamine/carboxymethyl chitosan/Fe3+. These hydrogels exhibited excellent electrical conductivity, self-healing capabilities, and photothermal antibacterial properties, thereby significantly enhancing the process of wound healing.
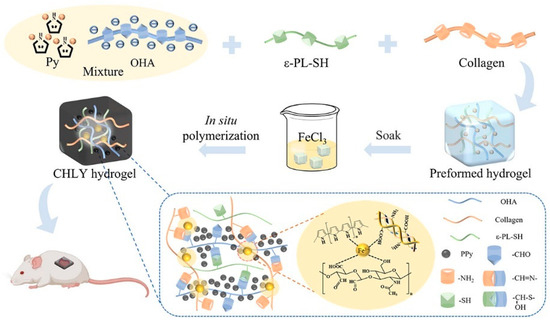
Figure 4.
The preparation route of collagen-based hydrogels with multiple functionalities for inducing full-thickness wound healing. Adapted from Ref. [73].
2.4. Shape Memory Hydrogels
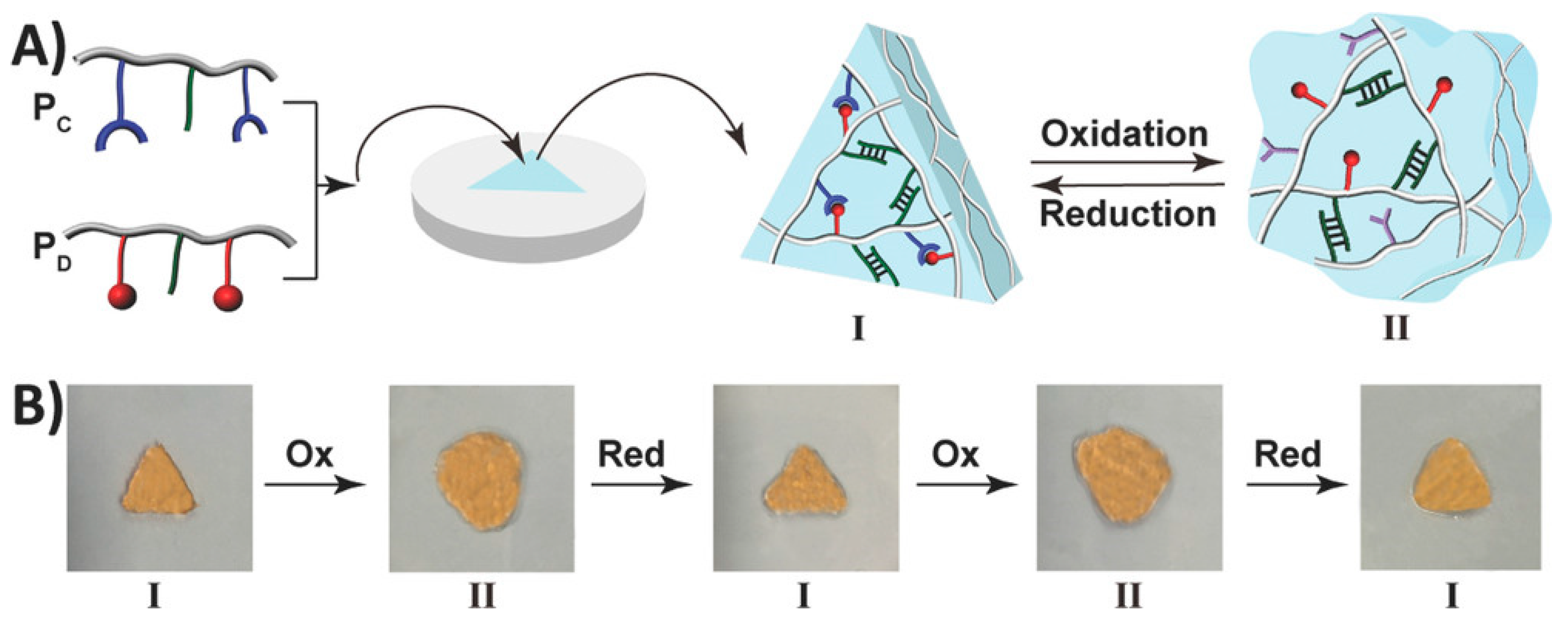
Shape memory hydrogels (SMHs) can retain a temporary shape and restore their initial shape under specific stimuli, displaying a shape memory capability [76,77]. They have extensive applications in various fields, including drug delivery, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and sensors [78,79]. SMHs rely on two special crosslinking structures within their 3D network to achieve shape memory functionality: The first type of crosslinking structure is called permanent crosslinking (e.g., irreversible chemical bonds), and SMHs form their initial shape under the action of this crosslinking agent. The second crosslinking structure is reversible dynamic crosslinking characterized by the stimulus response [76,80,81], including hydrogen bonds, host–guest interactions, coordination interactions, and reversible chemical bonds (dynamic borate bonds, dynamic Schiff base bonds, etc.). This dynamic crosslinking structure allows SMHs to break and reassemble reversibly under external forces, giving them the ability of shape memory. For example, Liu et al. [82] constructed a novel type of radiopaque dual-stimulus-responsive shape memory hydrogels through a straightforward one-step polymerization process. The hydrogels were prepared by combining acrylonitrile (AN), N-acryloyl 2-glycine (ACG), and the crosslinker poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (Mn = 700, PEGDA700). Mano et al. [83] reported a facile method to convert non-thermally responsive hydrogels into thermally responsive hydrogel systems with shape memory capability. As a proof of concept, they provided hydrogel composites with shape memory capabilities by embedding polyurethane networks in heat-sensitive polyurethane chitosan methacrylate, gelatin, laminin, or hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Along this line, researchers have developed shape memory hydrogels with a high shape fixation rate (50–90%) and exceptional shape recovery rate (nearly 100% with almost instantaneous recovery). Willner et al. [84] presented a redox switchable shape memory hydrogel system composed of bipyridinium, which complexes as crosslinking units of carboxymethyl cellulose and dopamine (Figure 5). Xing et al. [85] reported the development of a physical crosslinked PVA hydrogel by introducing a high concentration of sodium hydroxide to a high-density PVA polymer, thereby inducing crystallization. The resulting hydrogel exhibited remarkable mechanical properties, reduced water content, enhanced damage resistance, and demonstrated shape memory capabilities.
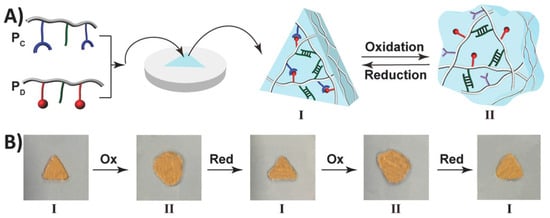
Figure 5.
(A) The formation of a triangle-shaped hydrogel. (B) The redox-switchable transitions and shape-memory functionality of the hydrogel. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [84]. Copyright 2023 John Wiley and Sons.
3. Applications in Wound Repair
Combining the sequential stages of wound healing and their distinctive characteristics, hydrogel-based wound repair strategies often focus on antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, pro-vascularization, and a combination of multiple therapeutic approaches to promote rapid wound healing, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Hydrogels with different therapeutic strategies in wound repair.
3.1. Antibacterial
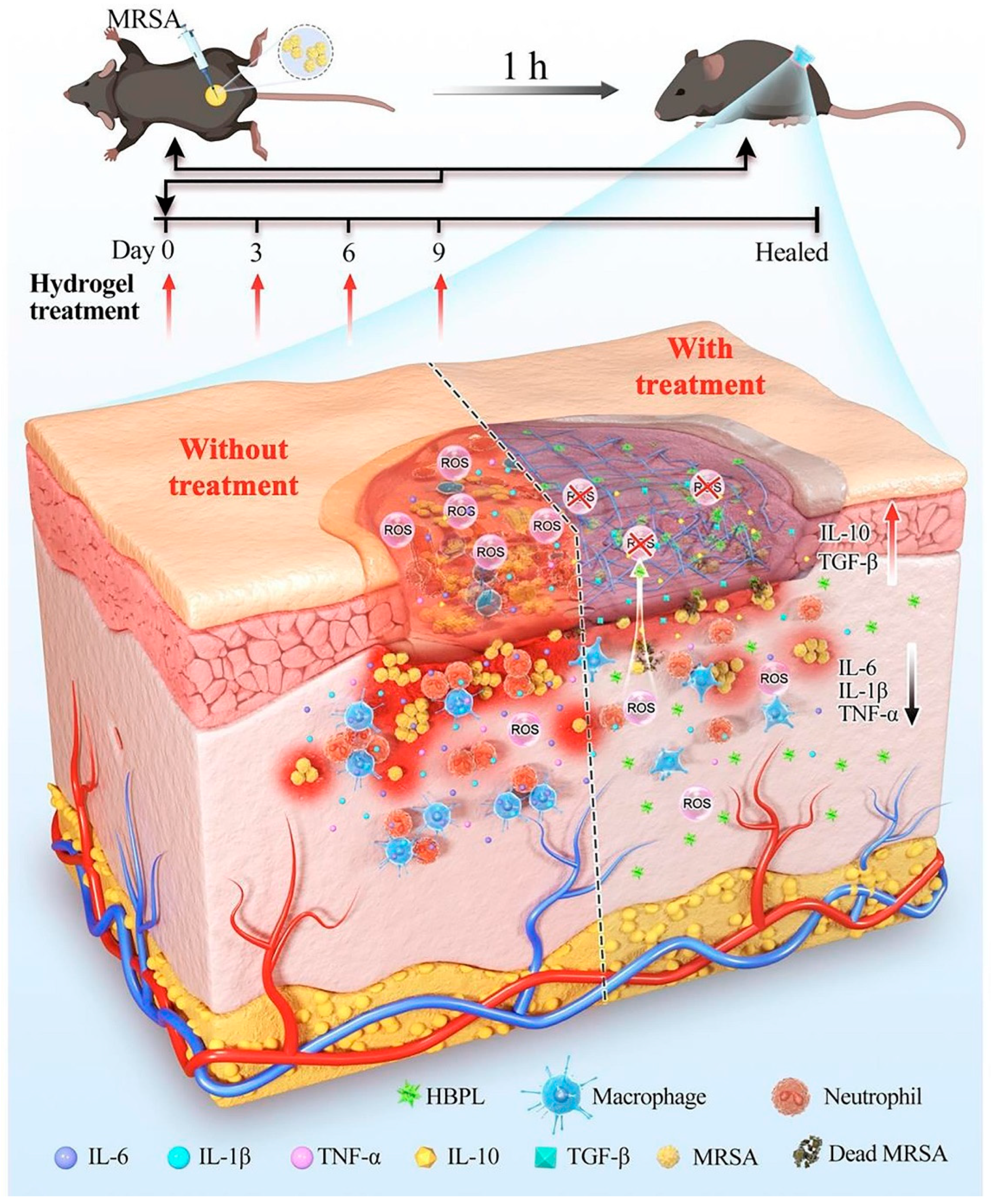
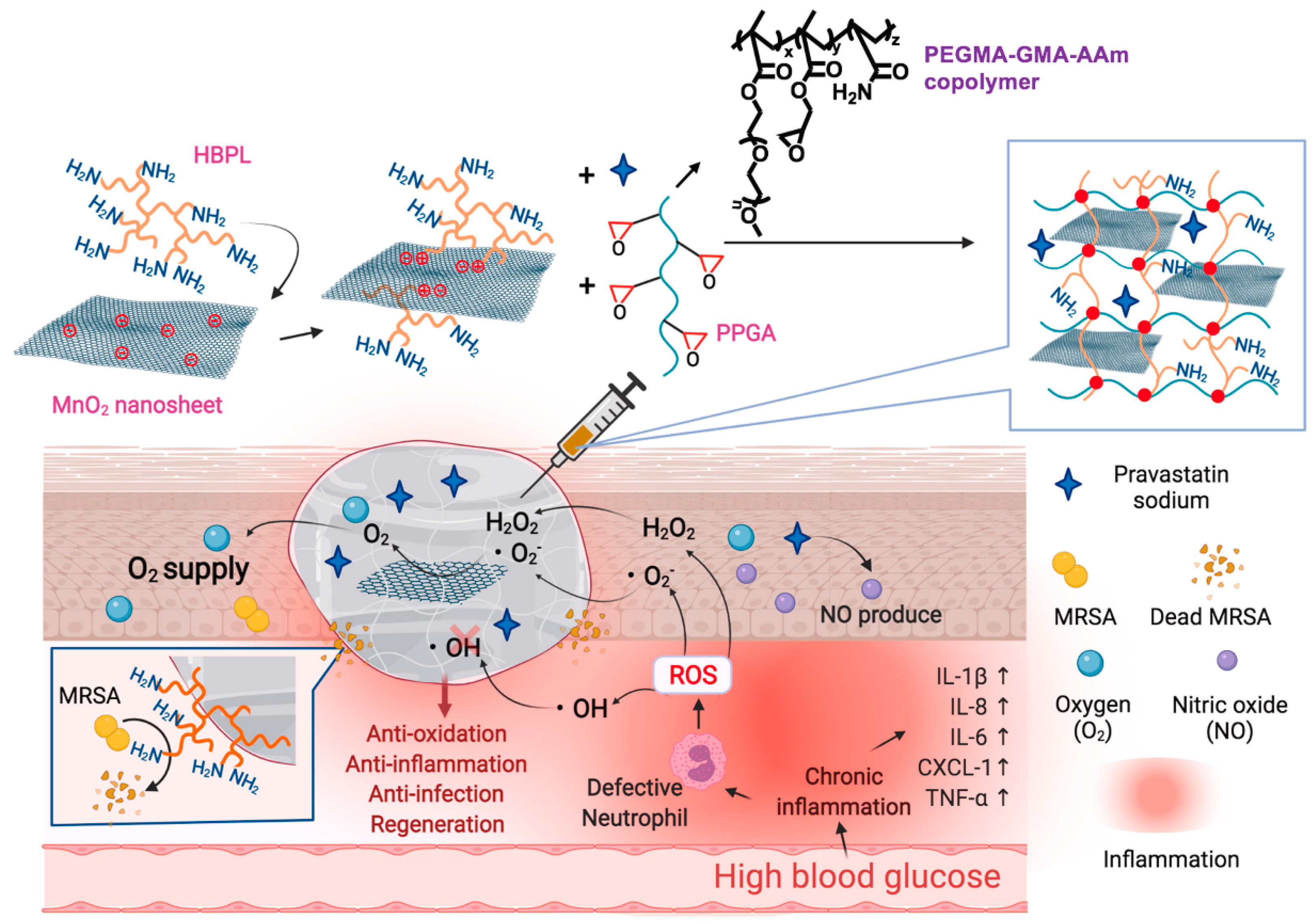
The occurrence of bacterial infections during wound healing presents an unavoidable and urgent challenge. Regrettably, the improper utilization of antibiotics has resulted in the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, thereby exacerbating the already formidable challenges associated with antimicrobial therapy for wound treatment. Addressing the medical bottleneck of achieving efficient antimicrobial efficacy while effectively promoting the wound healing process remains a paramount challenge that necessitates the collective efforts of researchers. There are many kinds of antimicrobial materials, including antibiotics, metal ions (Ag+, Cu2+, etc.), cationic polymers (quaternized chitosan), biomimetic nano-enzymes (MoS2), antimicrobial peptides, etc. [99,100]. Antimicrobial methods also include chemodynamic therapy (CDT), phototherapy (PDT, PTT), and magnetic hyperthermia therapy (MHT), etc. [101,102]. Researchers have constructed corresponding antimicrobial hydrogels to effectively promote healing [22,103]. S. aureus stands as the primary pathogen responsible for skin infections, and the presence and dissemination of MRSA have presented a significant hurdle in treating wound infections due to its formidable drug resistance and potent virulence. Moreover, the excessive production of reactive ROS at the site of skin wounds exacerbates inflammation, resulting in delayed healing and extensive scarring. Drawing from this information, Lu et al. [86] designed an ROS-scavenging hydrogel containing hyperbranched poly-L-lysine (HBPL), a bacterial population-sensing inhibitor, demonstrating effective elimination of MRSA, whether in planktonic form or within biofilm structures. In vivo, this hydrogel effectively promoted the healing of MRSA-infected whole skin defects by impeding quorum sensing (QS), eradicating bacteria, and suppressing inflammation, ultimately promoting the healing process, and this study provided new insights into scarless healing of methicillin-resistant S. aureus-infected skin wounds (Figure 6). Hu et al. [56,104,105,106,107,108] developed a series of smart-responsive hydrogels loaded with antimicrobial drugs for on-demand, controlled release of drugs at the site of the wound to facilitate the healing process. Guo et al. [87] reported a self-healing hydrogel that possessed favorable electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties. The hydrogel was fabricated using quaternized chitosan (QCS), oxidized dextran (OD), tobramycin (TOB), and surface-modified polypyrrole nanowires with polydopamine (PPY@PDA NWs). Additionally, it was crosslinked by Schiff base and could thus achieve the on-demand release of TOB in response to weak acidic pH, killing high concentrations of PA and S. aureus within a short period of time and promoting wound healing. Li et al. [88] integrated iron oxide nanoparticles loaded with polydopamine (PDA) with glucose oxidase (GOx) and hyaluronic acid (HA) grafting onto microneedle (MN) patches and introduced amine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles (AP-MSN) into the substrate, resulting in PFG/M microneedle patches. The experimental results showed that the microneedle patch combined chemical dynamic therapy (CDT), photothermal therapy (PTT), and tip-Fe/PDA@GOx@HA-induced M2 macrophage polarization, exhibiting excellent antimicrobial and immunomodulatory properties. This innovative development holds great promise as a potential clinical candidate for the treatment of infected wounds.
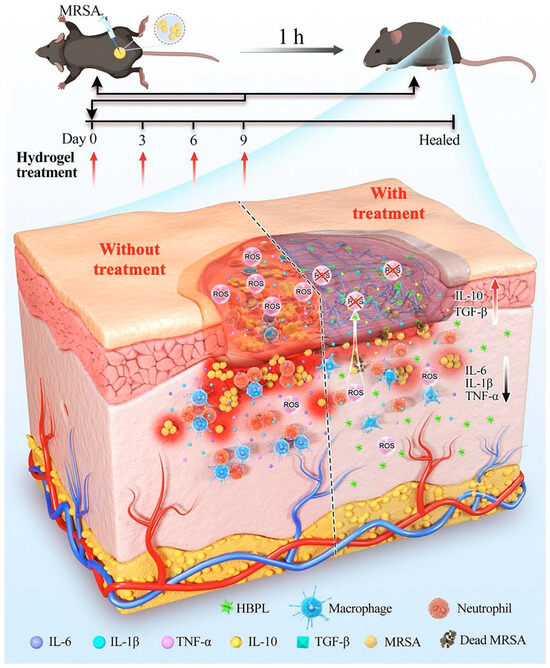
Figure 6.
The mechanism of the ROS-scavenging hydrogel containing hyperbranched poly-L-lysine (HBPL) promoting wound healing. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [86]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier.
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant
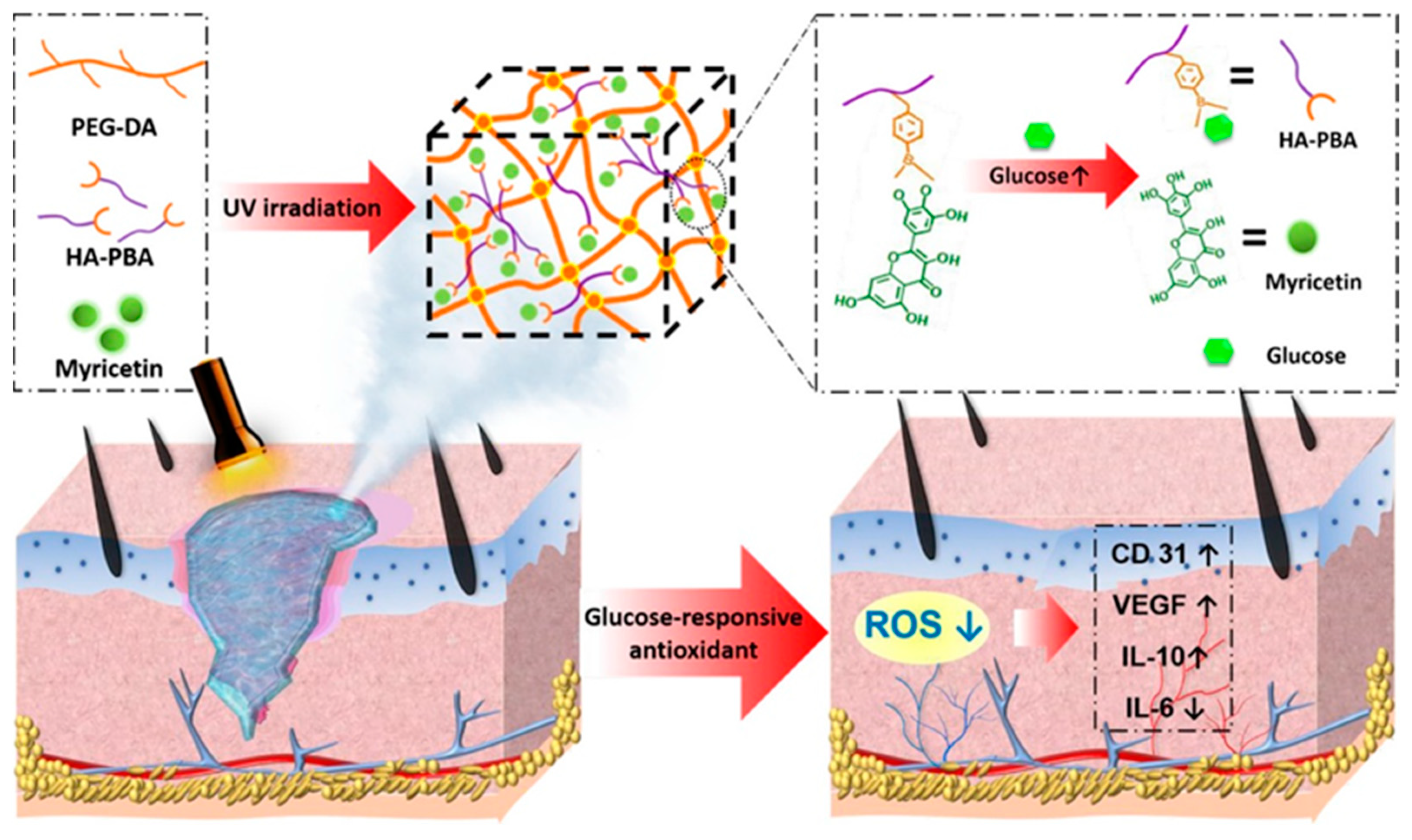
During the second stage of wound healing, known as inflammation, immune cells secrete various inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, etc., to combat bacterial or viral infections and eliminate factors causing physical damage. However, at the same time, oxygen consumption increases, and the accumulation of reactive ROS generated by the “respiratory burst” can lead to DNA damage and apoptosis, further exacerbating inflammation and affecting wound healing. Appropriate inflammation is essential in wound repair, and therefore the regulation of inflammation is important for wound repair. Antioxidants can aid in capturing and neutralizing free radicals, thus eliminating their damaging substances to the organism [109]. The incorporation of well-known natural antioxidants, such as catechins [110], resveratrol [111], anthocyanins [112], and some flavonoids [113], etc., into hydrogels has been employed to harness their antioxidant properties and facilitate the process of wound healing. For example, Xiao et al. [89] developed an injectable self-repairing hydrogel with inherent antimicrobial properties by utilizing the dynamic covalent bond formation between boric acid and catechol moieties within quaternized chitosan as a masonry block, coupled with the in situ encapsulation of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). The authors evaluated the antioxidant efficiency of the hydrogel by measuring its ability to scavenge 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radicals. And the results revealed that the hydrogel demonstrated remarkable antioxidant effects. Wu et al. [90] developed an innovative composite hydrogel with glucose-responsive and antioxidant properties, specifically designed for the purpose of diabetic wound repair. They first prepared glucose-sensitive phenylboronic acid (PBA)-modified hyaluronic acid (HA), which was then combined with polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEG-DA) to form a novel composite hydrogel (PEG-DA/HAPBA). Next, the researchers immobilized poplar plum flavonoid (MY) molecules, known for their potent antioxidant activity, within the hybrid hydrogel (Figure 7). By measuring the DPPH clearance rate and the ROS indicator 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA), the PEG-DA/HA-PBA/MY (PHM) hydrogel was found to effectively scavenge ROS (>80.0%) and revitalize the microenvironment of oxidative wounds. Over the past few years, a series of nanomaterials that can mimic natural antioxidants have been created, such as cerium oxide nanoparticles, iron oxide nanoparticles, and carbon nanomaterials (ceria (CeO2) nanoparticles and manganese oxide (MnO2, Mn2O3, Mn3O4, and MnO2) nanoparticles and carbon nanomaterials), etc. These materials, compared to natural antioxidants, maintain high stability in more complex disease environments [114]. Incorporating them into hydrogels can effectively eliminate ROS at the wound site and promote wound healing [115,116,117]. For instance, Lei et al. [91] prepared multiple coordination-derived bioactive hydrogels (SGPA) by simple multi-metal coordination using sodium alginate, metal ions (Gd3+), and phosphoric acid-functionalized polycitric acid as the raw materials. SGPA has good injectability, self-healing properties, and controlled biodegradability. In addition, it exhibits favorable cytocompatibility and hemocompatibility while also enhancing the migration of endothelial cells. Moreover, the SGPA hydrogel demonstrated notable hemostatic efficacy in an in vivo liver hemorrhage model. In the complete skin wound model, the SGPA hydrogel demonstrated significant effectiveness in promoting wound healing by reducing the expression of inflammatory factors and stimulating angiogenesis in the peri-wound area. Xie et al. [92] developed an in situ hydrogel with a combination of antibacterial, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and wound-adaptive characteristics specifically for the effective treatment of infectious wounds. The hydrogel formulation comprises two naturally derived biopolysaccharides, namely sodium alginate (SA) and carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS). By employing “click” chemical reactions, Schiff base reactions, and other reaction principles, modified derivatives such as sodium maleimido oxidized alginate (AM) and mercapto carboxymethyl chitosan (CS) are crosslinked into gum AxCy (x, y = 3, 4, 5, 6, 7; x + y = 10), which exhibits certain ROS scavenging abilities and can play a pro-infectious wound healing role through resistance to E. coli, S. aureus infection, antioxidant, and macrophage polarization modulation properties.
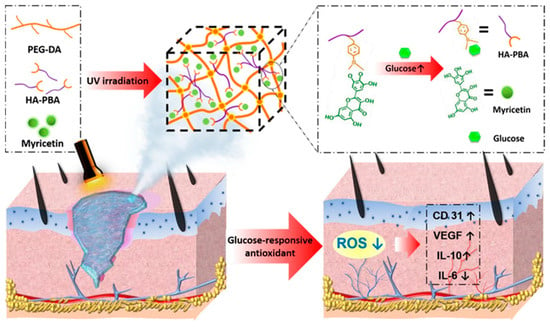
Figure 7.
The preparation process of PHM hydrogel and its mechanism of diabetic wound repair. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [90]. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society.
3.3. Pro-Angiogenic
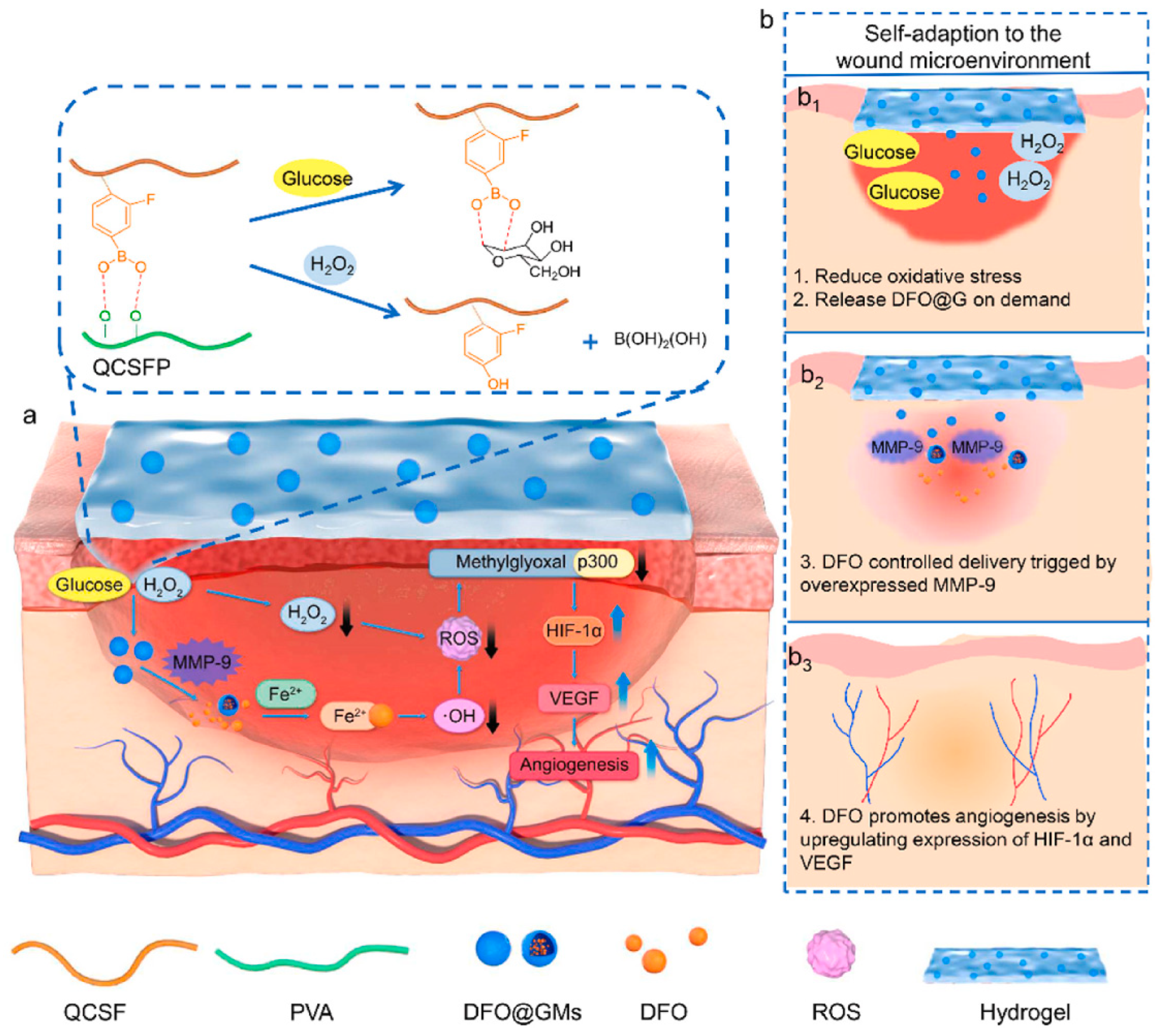
Blood vessels are involved in the transportation of oxygen and other nutrients required for wound healing; therefore, neovascularization is essential for the healing of wounds, and it can be argued that the timely development of blood vessels in the early stages is inherently linked to the rate of wound healing [118]. Over the years, there has been extensive research into the use of growth factors to induce angiogenesis and enhance wound closure in chronic wounds. However, treatment methods based on growth factors have limitations, such as high cost and a short half-life, which restrict their application [119]. Utilizing hydrogels as carriers to deliver small-molecule drugs, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, and other substances that promote vascular formation has become a common treatment for diabetes-related wounds with poor neovascularization [120]. For instance, Xu et al. [121] prepared a hyperbranched poly (β-amino ester) hydrogel using the Schiff base reaction between an amine and acrylic ester. This polyethylene glycol-based hydrogel can undergo controlled degradation and be loaded with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. The measurement of the number of blood vessels formed and the expression levels of VEGF in the wound after treatment with this hydrogel revealed that it effectively promoted angiogenesis and accelerated the healing of diabetic wounds. DFO is an iron chelator that has been approved by the FDA for clinical use. Previous studies have demonstrated that DFO can significantly accelerate the formation of new blood vessels under normal and pathological conditions by upregulating the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and its downstream gene VEGF [122,123]. Zhou et al. [93] synthesized quaternized chitosan (QCS) and then grafted 3-carboxy-4-fluorophenylboronic acid onto the QCS side chains, creating QCSF with grafted phenylboronic acid groups. They used the dynamic boronate ester bonds between the phenylboronic acid groups on QCSF and the hydroxyl groups on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) to develop a drug delivery system involving crosslinked gelatin microspheres for the drug DFO. This DFO-loaded DFO@G-QCSFP hydrogel dynamically regulated the microenvironment by scavenging ROS and releasing DFO as needed, thus promoting vascular regeneration and diabetes wound healing (Figure 8). Guo et al. [94] constructed a pH/glucose dual-responsive metformin hydrogel dressing based on the dual dynamic bonds formed by Schiff base and boronic acid ester. The Schiff base structure possesses pH sensitivity and exhibits instability in acidic conditions, leading to enhanced drug release. The neighboring phenolic structure has the ability to form dynamic boronate ester structures with boronic acid, responding to glucose. The results of immunofluorescence staining demonstrated that treatment with the hydrogel significantly reduced the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the wound and markedly increased the number of newly formed blood vessels. This dual-responsive hydrogel improved wound healing in a rat model of type 2 diabetes by inhibiting inflammation and promoting vascular regeneration. Nitric oxide (NO) has been identified as a crucial molecule in wound healing, playing a vital role in vascular regeneration. Guo et al. [124] developed a multifunctional conductive hydrogel with the ability to release NO under near-infrared laser irradiation to accelerate vascular formation and wound healing. Researchers have found that appropriate thermal stimulation can enhance granulation tissue growth, promote vascular formation, and expedite skin wound healing [125]. Wang et al. [126] developed an injectable, self-healing hydrogel formed through Schiff base bonds between poly (ε-L-lysine) and oxidized hyaluronic acid, leveraging the thermal responsiveness of Pluronic F127. By incorporating exosomes into this hydrogel, they effectively promoted neovascularization in chronic wounds, accelerating their healing. Ren et al. [95] prepared a hybrid hydrogel, Fe\PPHP15, with pro-angiogenic and targeted antibacterial properties. The phenol–iron complex (TA@Fe3+) in the hydrogel served as a photothermal conversion agent, converting light energy into gentle heat at an 808 nm excitation wavelength. The incorporation of iron ions in the hydrogel significantly facilitated the expression of genes related to blood vessel growth, such as bFGF, bFGFR, and HIF-1. The mild thermal effect additionally induced the expression of VEGF. The upregulation of these angiogenesis-related genes promoted vascular formation at the wound site.
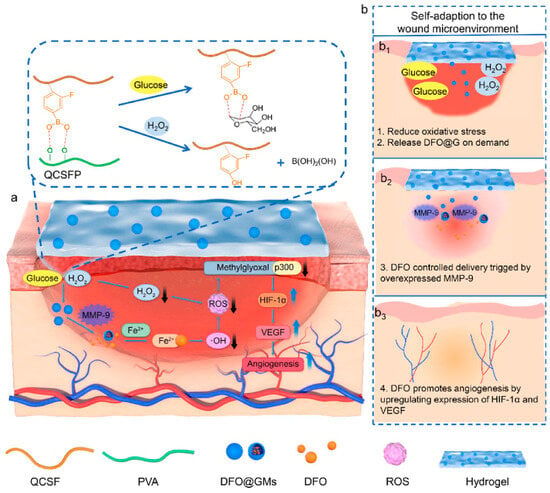
Figure 8.
The preparation of the DFO@G-QCSFP hydrogel and its mechanism for accelerating diabetic wound healing. (a) The chemical structure of the hydrogel and the mechanism of the hydrogel for accelerating diabetic wound healing. (b) The self-adaption of the hydrogel to wound microenvironment. The hydrogel reduced oxidative stress and released DFO@G on demand. Then DFO was released and promoted angiogenesis. Reprinted from Ref. [93].
3.4. Combination Therapy
Wound healing is a complex process that can be impacted by diseases or infections in diverse ways, such as changes in inflammatory responses, altered ROS signaling, and more. Treating wound repair by addressing a single factor is insufficient. In recent years, researchers have developed a variety of combination therapies to address the challenges of wound healing. Wen et al. [127] designed a multifunctional DNA hydrogel by dynamically crosslinking non-immunogenic DNA with polyethyleneimine and incorporating heating-functionalized black phosphorus quantum dots. This DNA hydrogel exhibited remarkable adjustable heating capability, mechanical properties, self-healing ability, and antimicrobial properties. Furthermore, the incorporation of oligomeric proanthocyanidins B2 (OPC B2) endowed the DNA hydrogel with potent free radical scavenging and antioxidant properties. Additionally, the multifunctional DNA hydrogel dressing facilitated the transition of macrophages from the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to the repair-promoting M2 phenotype, thereby maintaining a stable remodeling state at the wound site. Moreover, the DNA hydrogel dressing activated neurons, inducing them to enter a reparative state and accelerating the regeneration of skin nerves and the formation of blood vessels. Chen et al. [96] prepared a hydrogel through coordination crosslinking of multi-arm thiolated polyethylene glycol with silver nitrate. This hydrogel’s self-healing and injectable properties stemmed from dynamic disulfide bonds and ionic coordination bonds. Silver ions endowed the hydrogel with antimicrobial properties. Furthermore, the authors successfully enhanced the healing of diabetic wounds by incorporating the pro-angiogenic drug DFO into the hydrogel. Gao et al. [97] developed a composite antibacterial and antioxidant hydrogel based on hyperbranched poly (β-amino ester) (HBPL) with inhibitory effects on bacterial quorum sensing and manganese dioxide nanosheets (Figure 9). They crosslinked this material with a poly (PEGMA-co-GMA-co-Aam) (PPGA) polymer to create a multifunctional injectable hydrogel dressing. This dressing was employed for effective antibacterial and antioxidant actions as well as continuous oxygen supply in the treatment of diabetic-infected wounds, achieving the goal of inflammation inhibition and repair promotion. Li et al. [98] designed a novel antibacterial and antioxidant dual-functional, low hysteresis, stretchable hydrogel (MPH) through copolymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide, acrylamide, and acrylate Pluronic 127 (PF127-DA), along with functionalization of molybdenum disulfide-polydopamine nanoparticles (MP). This hydrogel, suitable for close adhesion to moving body parts and wound healing, displayed excellent mechanical properties that allowed it to tightly adhere to the wound, resist the invasion of E. coli and S. aureus, and avoid secondary fixation of dressings. Furthermore, the hydrogel’s dual functionality, stemming from its photothermal characteristics and enzyme-like activity, effectively eliminated bacterial infections, mitigated oxidative stress, enhanced the wound microenvironment, and facilitated the process of wound healing.
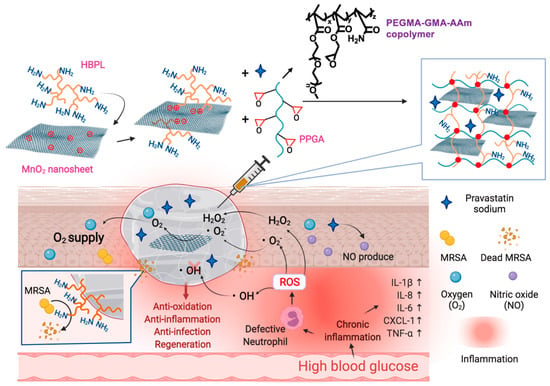
Figure 9.
The chemical structure of the composite antibacterial and antioxidant hydrogel and its mechanism for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [97]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier.
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
The process of wound healing is intricate and time-consuming, significantly impacting the quality of life of countless individuals worldwide. Recently, significant progress has been made in the research of various multifunctional hydrogels, which also show great potential and application in wound repair. We reviewed the therapeutic strategies of multifunctional hydrogels in different stages of wound repair, such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, pro-angiogenic, and a combination of multiple strategies, which provide strong support for wound healing. In addition, multifunctional hydrogels have been combined with other advanced fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing, for personalized wound repair strategies [128,129]. Designing flexible skin sensors is another direction that may significantly impact chronic wound therapy [130,131,132]. In this context, the utilization of hydrogel-based bioelectronic devices offers a promising platform for wound therapy. These devices have the capability to monitor the real-time status of wounds while also enabling the controlled and targeted release of bioactive molecules or drugs as needed.
However, we must also face the challenges faced by multifunctional hydrogels in practical applications, including how to rationally design and combine the functionality and therapeutic strategies of hydrogels, how to prepare hydrogels on a large scale and effectively preserve them, and how to design and screen them more efficiently with the help of artificial intelligence. In addition, patients are not only pursuing the filling of simple defects in the treatment of wounds, but they also have the demand for full functional recovery and aesthetics, and there remains ample opportunity for the further development of therapeutic strategies based on multifunctional hydrogels in the prevention and treatment of scarring, regeneration of hair follicles, and improvement of pigmentation abnormality. It is worth noting that achieving multifunctionality of hydrogels typically involves complex designs of hydrogels, which is contradictory to the simplicity required for clinical translational applications. Therefore, to further enhance the efficacy and clinical application of multifunctional hydrogels in wound repair, we need to actively explore advanced preparation techniques, expand wider application areas, and strengthen the integration of clinical practice and scientific research. Last but not least, multifunctional hydrogels used for wound repair must possess superior safety, biocompatibility, and non-immunogenicity for their clinical application. This ensures that the hydrogel, when in contact with human tissues, does not cause any harmful side effects, including allergies, tissue necrosis, inflammation, or excessive immune system reactions. Therefore, strict control over the selection of raw materials, preparation processes, and quality assurance is necessary to guarantee the effectiveness and safety of hydrogel in clinical use. Overall, the research and application of multifunctional hydrogels in wound repair will bring important innovations and advances to the medical field and substantially improve the health and quality of life of patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and C.H.; methodology, B.W., P.Y. and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; writing—review and editing, C.H. and P.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2023NSFSC0998) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. YJ2021115).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province and Sichuan University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Sun, B.K.; Siprashvili, Z.; Khavari, P.A. Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds. Science 2014, 346, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethi, S.K.; Das, S.; Patra, C.R.; Mukherjee, S. Recent advances in inorganic nanomaterials for wound-healing applications. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2652–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandla, S.; Davenport Huyer, L.; Radisic, M. Review: Multimodal bioactive material approaches for wound healing. APL Bioeng. 2018, 2, 021503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacob, A.-T.; Drăgan, M.; Ionescu, O.-M.; Profire, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Confederat, L.G.; Lupașcu, D. An Overview of Biopolymeric Electrospun Nanofibers Based on Polysaccharides for Wound Healing Management. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korupalli, C.; Li, H.; Nguyen, N.; Mi, F.-L.; Chang, Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Sung, H.-W. Conductive Materials for Healing Wounds: Their Incorporation in Electroactive Wound Dressings, Characterization, and Perspectives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Conductive Biomaterials as Bioactive Wound Dressing for Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Murray, P.J.; Pearce, E.J. Metabolic orchestration of the wound healing response. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1726–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloth, L.C. Discussion: Advanced Technologies to Improve Wound Healing: Electrical Stimulation, Vibration Therapy, and Ultrasound—What Is the Evidence? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 94S–104S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, M.; Alonso-Rasgado, T.; Baguneid, M.; Bayat, A. The efficacy of electrical stimulation in lower extremity cutaneous wound healing: A systematic review. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liang, P.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, P.; Yu, W.; Duan, M.; Guo, L.; Cui, X.; Huang, M.; Huang, X. Hyperbaric oxygen potentiates diabetic wound healing by promoting fibroblast cell proliferation and endothelial cell angiogenesis. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Leavitt, T.; Bayer, L.R.; Orgill, D.P. Effect of negative pressure wound therapy on wound healing. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2014, 51, 301–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, Q.H.; Han, H.A.; Soh, B.-S. Translational stem cell therapy: Vascularized skin grafts in skin repair and regeneration. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.A.; Martinez-Lozano, E.; Sheridan, R.; Rodriguez, E.K.; Nazarian, A.; Grinstaff, M.W. Hydrogels for the management of second-degree burns: Currently available options and future promise. Burn. Trauma 2022, 10, tkac047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in smart-responsive hydrogels for tissue repairing. MedComm–Biomater. Appl. 2022, 1, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yuan, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Recent trends on burn wound care: Hydrogel dressings and scaffolds. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4523–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaziha, M.; Baidya, A.; Annabi, N. Rational Design of Immunomodulatory Hydrogels for Chronic Wound Healing. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Hu, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Lu, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Injectable multifunctional hyaluronic acid/methylcellulose hydrogels for chronic wounds repairing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 289, 119456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, H.L.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.-H.; Chuah, L.H. Application of chitosan-based nanoparticles in skin wound healing. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 299–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Antibacterial biomaterials for skin wound dressing. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.M.; Narayanan, K.B.; Uthappa, U.T.; Park, P.H.; Choi, I.; Han, S.S. Tissue Adhesive, Self-Healing, Biocompatible, Hemostasis, and Antibacterial Properties of Fungal-Derived Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Polydopamine Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Kan, M.; et al. Advances in preparation and application of antibacterial hydrogels. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, M.; Pan, G. Nano-crosslinked dynamic hydrogels for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, D.Y.; Park, S.H.; Son, A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.S. In vivo osteogenic differentiation of human turbinate mesenchymal stem cells in an injectable in situ-forming hydrogel. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5337–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, T.; Yoshihara, R.; Danjo, S.; Fukuhara, Y.; Evans, C.; Tomimatsu, R.; Ohzuno, Y.; Yoshida, M. Hydrophobically-modified gelatin hydrogel as a carrier for charged hydrophilic drugs and hydrophobic drugs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Wang, X.; Park, S.; Jin, X.; Ma, P.X. Rapid Self-Integrating, Injectable Hydrogel for Tissue Complex Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.-G.; Zhu, X.X. Self-Healing Supramolecular Hydrogel Made of Polymers Bearing Cholic Acid and β-Cyclodextrin Pendants. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhuang, X.; He, C.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X. High performance and reversible ionic polypeptide hydrogel based on charge-driven assembly for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.D.; Soranno, D.E.; Rodell, C.B.; Kim, I.L.; Burdick, J.A. Secondary Photocrosslinking of Injectable Shear-Thinning Dock-and-Lock Hydrogels. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.W.; Koshy, S.T.; Bae, H.; Hwang, C.M.; Yamanlar, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espeel, P.; Du Prez, F.E. “Click”-Inspired Chemistry in Macromolecular Science: Matching Recent Progress and User Expectations. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. On-Demand Dissolvable Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Cellulose Nanocrystal for Deep Partial Thickness Burn Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41076–41088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira Teixeira, L.S.; Feijen, J.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Karperien, M. Enzyme-catalyzed crosslinkable hydrogels: Emerging strategies for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Yang, F. Recent Progress in Developing Injectable Matrices for Enhancing Cell Delivery and Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, P.; Diba, M.; Mooney, D.J.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G. Self-Healing Injectable Hydrogels for Tissue Regeneration. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 834–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.K.; Martin, J.R.; Werfel, T.A.; Shen, T.; Page, J.M.; Duvall, C.L. Cell Protective, ABC Triblock Polymer-Based Thermoresponsive Hydrogels with ROS-Triggered Degradation and Drug Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14896–14902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tokatlian, T.; Zhong, J.; Ng, Q.K.T.; Patterson, M.; Lowry, W.E.; Carmichael, S.T.; Segura, T. Physically Associated Synthetic Hydrogels with Long-Term Covalent Stabilization for Cell Culture and Stem Cell Transplantation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5098–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, W.; Long, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, S.; Lu, L.; Fan, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Regeneration of infarcted hearts by myocardial infarction-responsive injectable hydrogels with combined anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammatory and pro-angiogenesis properties. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Xue, W.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Ren, J.; Chi, B. Mechanoadaptive injectable hydrogel based on poly(γ-glutamic acid) and hyaluronic acid regulates fibroblast migration for wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ma, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, F.; Ye, J.; Yang, D.; Li, M.; Wang, P. Injectable multifunctional DNA hydrogel for accelerated wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrador, P.; Esteves, M.R.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F. Stimuli-Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, K.; Stoffelbach, F.; Lyskawa, J.; Fumagalli, M.; Hourdet, D.; Marcellan, A.; Smet, L.D.; de la Rosa, V.R.; Cooke, G.; Hoogenboom, R.; et al. Recognition-Mediated Hydrogel Swelling Controlled by Interaction with a Negative Thermoresponsive LCST Polymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13974–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, W. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based smart hydrogels: Design, properties and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.D.; Babo, P.S.; Costa-Almeida, R.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Mendes, B.B.; Paz, E.; Freitas, P.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Granja, P.L.; Gomes, M.E. Multifunctional magnetic-responsive hydrogels to engineer tendon-to-bone interface. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, X.; Cao, X. Switchable Supramolecular Configurations of Al3+/LysTPY Coordination Polymers in a Hydrogel Network Controlled by Ultrasound and Heat. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40079–40087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Byun, E.; Yoon, Y.J.; Nam, J.; Song, S.H.; Yoon, C. Untethered Actuation of Hybrid Hydrogel Gripper via Ultrasound. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrador, P.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for delivery of bone therapeutics–Barriers and progresses. J. Control. Release 2018, 273, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Shao, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, X. Recent advances in pH-responsive nanomaterials for anti-infective therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10700–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messersmith, P.B.; He, L.; Fullenkamp, D.E. pH responsive self-healing hydrogels formed by boronate-catechol complexation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 47, 7497–7499. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.R.; Duvall, C.L. Chapter Nine-Oxidation State as a Bioresponsive Trigger. In Oxidative Stress and Biomaterials; Dziubla, T., Butterfield, D.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 225–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczak, M. Enzyme-Responsive Hydrogels as Potential Drug Delivery Systems—State of Knowledge and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; You, H. Recent Applications of Point-of-Care Devices for Glucose Detection on the Basis of Stimuli-Responsive Volume Phase Transition of Hydrogel. BioChip J. 2021, 15, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifzadeh, G.; Hosseinkhani, H. Biomolecule-Responsive Hydrogels in Medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, R. Controllable growth of spiral ganglion neurons by magnetic colloidal nanochains. Nano Today 2022, 44, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafipour, A.; Gharieh, A.; Fassihi, A.; Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H.; Mahdavian, A.R. MTX-Loaded Dual Thermoresponsive and pH-Responsive Magnetic Hydrogel Nanocomposite Particles for Combined Controlled Drug Delivery and Hyperthermia Therapy of Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Long, L.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y. A spatiotemporal release platform based on pH/ROS stimuli-responsive hydrogel in wound repairing. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Long, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Dual-crosslinked mussel-inspired smart hydrogels with enhanced antibacterial and angiogenic properties for chronic infected diabetic wound treatment via pH-responsive quick cargo release. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, G.; Chen, J.; Guo, B. Multiple Stimuli-Responsive Nanozyme-Based Cryogels with Controlled NO Release as Self-Adaptive Wound Dressing for Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, G.; LaFontaine, J.; Najafi, B.; Talal, T.K.; Kim, P.; Lavery, L.A. Electrical stimulation to accelerate wound healing. Diabet. Foot Ankle 2013, 4, 22081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, H.; Makin, I.R.S.; Skiba, J.B.; Izadjoo, M.J. Measurement of microelectric potentials in a bioelectrically-active wound care device in the presence of bacteria. J. Wound Care 2014, 24, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, G. Electrical Stimulation of Wound Healing: A Review of Animal Experimental Evidence. Adv. Wound Care 2013, 3, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, D.; Spaulding, S.J.; Burke, S.M.; Houghton, P.E. Electrical stimulation therapy for the treatment of pressure ulcers in individuals with spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wan, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Dai, Z.; Ji, K.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Long, Y. Highly Stretchable, Elastic, and Ionic Conductive Hydrogel for Artificial Soft Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Fan, D. Conductive, adaptive, multifunctional hydrogel combined with electrical stimulation for deep wound repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Song, S.; Lv, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z. Recent Development of Conductive Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Review and Perspective. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2200051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, B.; Dong, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, P.X. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, M.; Liang, Y.; Guo, B. Conductive adhesive self-healing nanocomposite hydrogel wound dressing for photothermal therapy of infected full-thickness skin wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, M.; He, J.; Yin, Z.; Guo, B. Injectable Antimicrobial Conductive Hydrogels for Wound Disinfection and Infectious Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Liu, H.; Ren, X.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shen, C.; Zvyagin, A.V.; Fang, L.; et al. Balloon Inspired Conductive Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Reducing Radiation Damage in Peritumoral Organs during Brachytherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, S.; Yang, K.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Skin-Inspired Antibacterial Conductive Hydrogels for Epidermal Sensors and Diabetic Foot Wound Dressings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ohm, Y.; Liao, J.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Won, P.; Roberts, P.; Carneiro, M.R.; Islam, M.F.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. A self-healing electrically conductive organogel composite. Nat. Electron. 2023, 6, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Huang, K.; Deng, J.; Guo, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.F. Highly Conducting and Stretchable Double-Network Hydrogel for Soft Bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Mu, C.; Li, D.; Ge, L. Antibacterial Conductive Collagen-Based Hydrogels for Accelerated Full-Thickness Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 22817–22829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Zuo, B. Self-Healing, Wet-Adhesion silk fibroin conductive hydrogel as a wearable strain sensor for underwater applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Alsareii, S.A.; Alamri, A.M.; Harraz, F.A.; Guo, B. Antibacterial conductive self-healing hydrogel wound dressing with dual dynamic bonds promotes infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 30, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenberg, C.; Balk, M.; Wischke, C.; Behl, M.; Lendlein, A. Shape-Memory Hydrogels: Evolution of Structural Principles To Enable Shape Switching of Hydrophilic Polymer Networks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Le, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T. Supramolecular shape memory hydrogels: A new bridge between stimuli-responsive polymers and supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, J.M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Naturally biomimicked smart shape memory hydrogels for biomedical functions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Chu, H. Ultra-Stretchable, Variable Modulus, Shape Memory Multi-Purpose Low Hysteresis Hydrogel Derived from Solvent-Induced Dynamic Micelle Sea-Island Structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2011259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Guo, Q.; Jia, L.; Yin, T.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Multifunctional Hydrogels for the Healing of Diabetic Wounds. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 2301885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Tong, Z. NIR-Triggered Rapid Shape Memory PAM–GO–Gelatin Hydrogels with High Mechanical Strength. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12384–12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Gao, H.; Fan, C.; Ma, G.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Cui, C.; et al. Stiffness Self-Tuned Shape Memory Hydrogels for Embolization of Aneurysms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.C.S.; Costa, P.D.C.; Gomes, M.C.; Chandrakar, A.; Wieringa, P.A.; Moroni, L.; Mano, J.F. Universal Strategy for Designing Shape Memory Hydrogels. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fadeev, M.; Vázquez-González, M.; Willner, I. Stimuli-Responsive Donor–Acceptor and DNA-Crosslinked Hydrogels: Application as Shape-Memory and Self-Healing Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, M.A.; Khosrozadeh, A.; Wang, Y.; Ashammakhi, N.; Alem, H.; Erdem, A.; Chang, Q.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Luo, G.; et al. An Alkaline Based Method for Generating Crystalline, Strong, and Shape Memory Polyvinyl Alcohol Biomaterials. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Tu, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, W.; Deng, L.; et al. A ROS-scavenging hydrogel loaded with bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor hyperbranched poly-L-lysine promotes the wound scar-free healing of infected skin in vivo. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Bacterial Growth-Induced Tobramycin Smart Release Self-Healing Hydrogel for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13022–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Song, H.; Zheng, Y. Microneedle Patches with Antimicrobial and Immunomodulating Properties for Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Seidi, F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Injectable chitosan hydrogels tailored with antibacterial and antioxidant dual functions for regenerative wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. Novel Glucose-Responsive Antioxidant Hybrid Hydrogel for Enhanced Diabetic Wound Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7680–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; Xie, C.; Lei, B. Multiple Coordination-Derived Bioactive Hydrogel with Proangiogenic Hemostatic Capacity for Wound Repair. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2200722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.-X.; Zou, C.-Y.; Hu, J.-J.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Zhao, L.-M.; He, T.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Li, Y.-X.; Li-Ling, J.; et al. Click-crosslinked in-situ hydrogel improves the therapeutic effect in wound infections through antibacterial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, T.; Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, S. Wound microenvironment self-adaptive hydrogel with efficient angiogenesis for promoting diabetic wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, B. pH/Glucose Dual Responsive Metformin Release Hydrogel Dressings with Adhesion and Self-Healing via Dual-Dynamic Bonding for Athletic Diabetic Foot Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3194–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, H.; Cai, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Ren, L. Poly(pentahydropyrimidine)-Based Hybrid Hydrogel with Synergistic Antibacterial and Pro-Angiogenic Ability for the Therapy of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2303147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tam, A.; Yan, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.S.; Qi, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. An injectable self-healing coordinative hydrogel with antibacterial and angiogenic properties for diabetic skin wound repair. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Lu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Deng, L.; Cao, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Ding, J.; et al. Promoting the healing of infected diabetic wound by an anti-bacterial and nano-enzyme-containing hydrogel with inflammation-suppressing, ROS-scavenging, oxygen and nitric oxide-generating properties. Biomaterials 2022, 286, 121597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Wen, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Chu, H. Nanozyme-Based Stretchable Hydrogel of Low Hysteresis with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Dual Functions for Closely Fitting and Wound Healing in Movable Parts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Cai, G.; Fu, S.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Z. Reactive incorporation of Ag into porous TiO2 coating and its influence on its microstructure, in vitro antibacterial efficacy and cytocompatibility. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2021, 31, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, S.; Xu, W.; Tu, S.; Yan, L.; Zhao, C.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Antibacterial Hydrogels. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Chen, X.; Fu, L.; Zhu, J.; Fan, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Mao, G.; et al. Ultra-efficient Antibacterial System Based on Photodynamic Therapy and CO Gas Therapy for Synergistic Antibacterial and Ablation Biofilms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22479–22491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piksa, M.; Lian, C.; Samuel, I.C.; Pawlik, K.J.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Matczyszyn, K. The role of the light source in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 1697–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, H.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K. Antimicrobial Hydrogels: Potential Materials for Medical Application. Small 2023, 2304047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Long, L.; He, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, N.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y. Responsive multifunctional hydrogels emulating the chronic wounds healing cascade for skin repair. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Long, L.; Yang, L.; Fu, D.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y. Inflammation-Responsive Drug-Loaded Hydrogels with Sequential Hemostasis, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Behavior for Chronically Infected Diabetic Wound Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 33584–33599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, W.; Long, L.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Lu, L.; et al. Microenvironment-responsive multifunctional hydrogels with spatiotemporal sequential release of tailored recombinant human collagen type III for the rapid repair of infected chronic diabetic wounds. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9684–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, F.; Long, L.; Kong, Q.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y. Dual-responsive injectable hydrogels encapsulating drug-loaded micelles for on-demand antimicrobial activity and accelerated wound healing. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, F.; Kong, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y. Synergistic Chemical and Photodynamic Antimicrobial Therapy for Enhanced Wound Healing Mediated by Multifunctional Light-Responsive Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 4581–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pei, D.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; et al. Green Tea Derivative Driven Smart Hydrogels with Desired Functions for Chronic Diabetic Wound Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, S.; Hu, Z.; Yang, W.; Lan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hancharou, A.; Guo, R.; Tang, B. In situ formed anti-inflammatory hydrogel loading plasmid DNA encoding VEGF for burn wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Tang, J.; Jiang, N.; Han, Y.; et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Functional Hydrogel Delivers Procyanidins for the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 33756–33767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.D.F.; Campos, M.G.N.; Ribeiro, G.P.; Salles, B.C.C.; Cardoso, N.S.; Ribeiro, J.R.; Souza, R.M.; Leme, K.C.; Soares, C.B.; de Oliveira, C.M.; et al. Development of a chitosan hydrogel containing flavonoids extracted from Passiflora edulis leaves and the evaluation of its antioxidant and wound healing properties for the treatment of skin lesions in diabetic mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Gao, L. Nanozyme-based medicine for enzymatic therapy: Progress and challenges. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.E.; Kim, J. ROS-Scavenging Therapeutic Hydrogels for Modulation of the Inflammatory Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23002–23021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xiao, B.; Xiang, F.; Tan, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Mao, Z.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Ultrasmall copper-based nanoparticles for reactive oxygen species scavenging and alleviation of inflammation related diseases. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, F.; Shao, W.; Gao, J.; Ling, D. Promoting Angiogenesis in Oxidative Diabetic Wound Microenvironment Using a Nanozyme-Reinforced Self-Protecting Hydrogel. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.H.G.; Rumma, R.T.; Ozaki, C.K.; Edelman, E.R.; Chen, C.S. Vascular Tissue Engineering: Progress, Challenges, and Clinical Promise. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos, S.; Stojadinovic, O.; Golinko, M.S.; Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. PERSPECTIVE ARTICLE: Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, A.P.; Henderson, K.; Spencer, A.; Sligar, A.D.; Baker, A.B. Therapeutic strategies for enhancing angiogenesis in wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Guo, L.; Sigen, A.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Greiser, U.; Creagh-Flynn, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Cutlar, L.; et al. Injectable hyperbranched poly(β-amino ester) hydrogels with on-demand degradation profiles to match wound healing processes. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Baumgarten, K.M.; Sun, H. Hypoxia-Mimicking Nanofibrous Scaffolds Promote Endogenous Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32450–32459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, L.; Wicks, J.; Ling, C.; Zhao, X.; Yan, Y.; Qi, J.; Cui, W.; Deng, L. Quickly promoting angiogenesis by using a DFO-loaded photo-crosslinked gelatin hydrogel for diabetic skin regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3770–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Photothermal antibacterial antioxidant conductive self-healing hydrogel with nitric oxide release accelerates diabetic wound healing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 266, 110985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, E.; Ma, B.; Xu, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Pei, G.; Chang, J. A novel “hot spring”-mimetic hydrogel with excellent angiogenic properties for chronic wound healing. Biomaterials 2021, 264, 120414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Gao, W.; Xu, H.; Lei, B.; Mao, C. Engineering Bioactive Self-Healing Antibacterial Exosomes Hydrogel for Promoting Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Theranostics 2019, 9, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Pi, W.; Cheng, S.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Min, T.; Zhang, W.; Du, H.; Zhang, P.; Wen, Y. Multifunctional DNA Hydrogels with Hydrocolloid-Cotton Structure for Regeneration of Diabetic Infectious Wounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, X.; Jin, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, J.; Qiang, L.; Wang, W.; Deng, Q.; Yang, H.; et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of multicell-laden scaffolds containing bone morphogenic protein-4 for promoting M2 macrophage polarization and accelerating bone defect repair in diabetes mellitus. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadehgiashi, M.; Nemr, C.R.; Chekini, M.; Pinto Ramos, D.; Mittal, N.; Ahmed, S.U.; Khuu, N.; Kelley, S.O.; Kumacheva, E. Multifunctional 3D-Printed Wound Dressings. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12375–12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, J.R.; Wagner, A.M.; Shin, S.R.; Hassan, S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Peppas, N.A. Modular fabrication of intelligent material-tissue interfaces for bioinspired and biomimetic devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Q.; Yang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, K.; Hou, R.; Zhu, Y. Smart wound dressing for advanced wound management: Real-time monitoring and on-demand treatment. Mater. Des. 2023, 229, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, B.; Li, K.; Yang, Q.; Wei, L.; Pan, C.; et al. Bioinspired Self-healing Soft Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).