Microwave-Assisted Incorporation of AgNP into Chitosan–Alginate Hydrogels for Antimicrobial Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
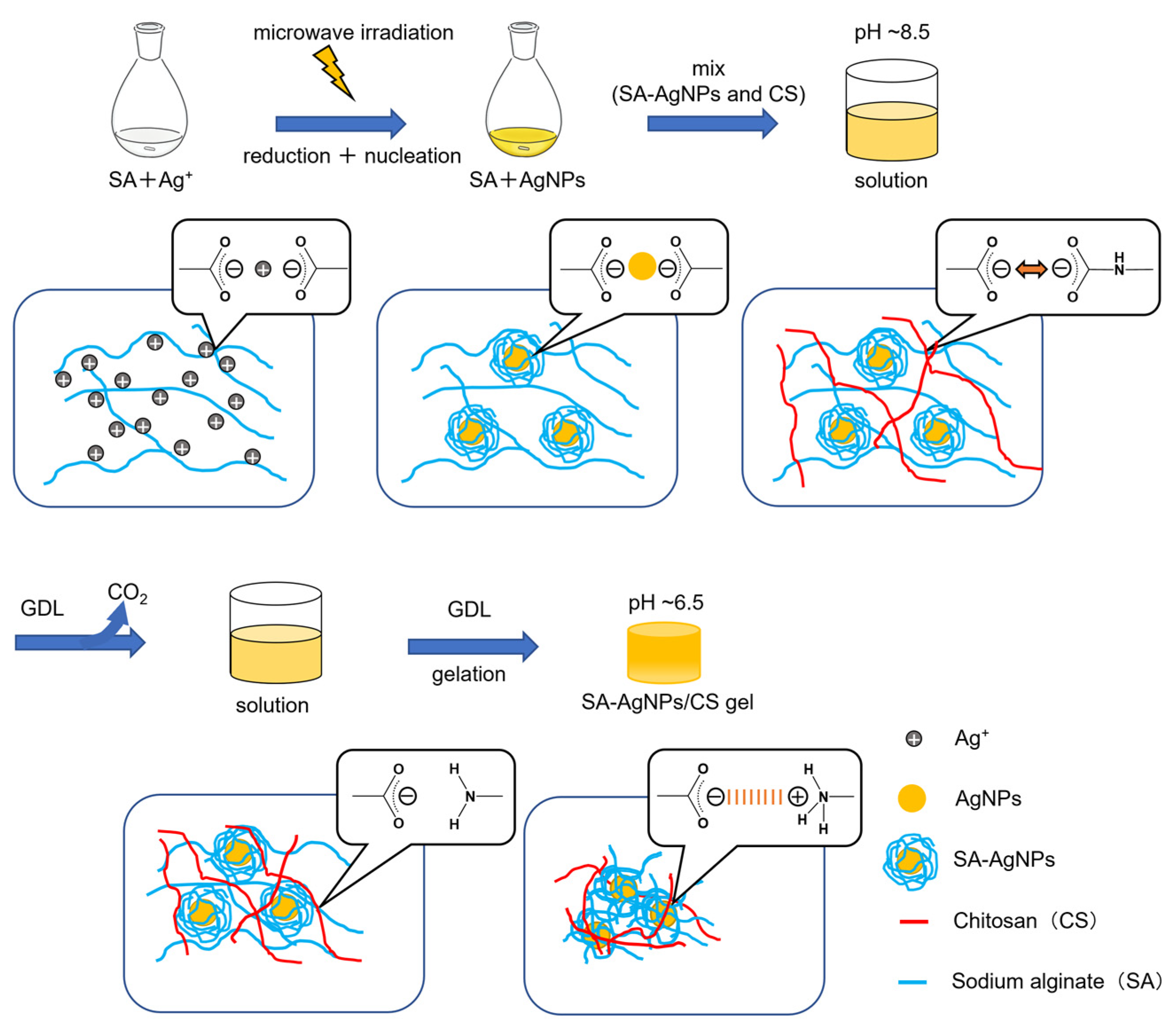
2.2. Preparation of SA-AgNPs
2.2.1. Synthesis without Microwave Irradiation
2.2.2. Synthesis by Microwave Irradiation
2.3. Preparation of the SA-AgNPs/CS gel
2.4. Characterization of the Synthesized AgNPs, SA-AgNPs, and SA-AgNPs/CS Gel
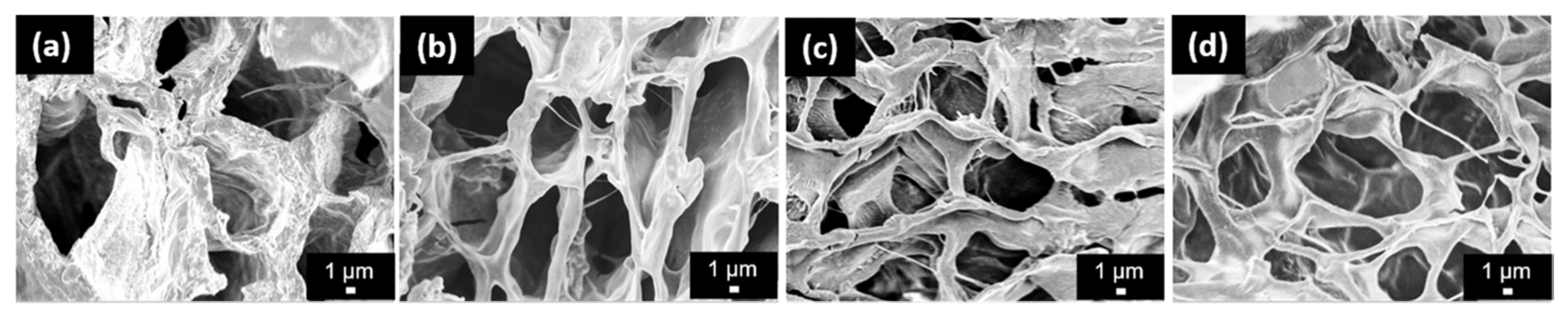
2.5. Compressive Strength, Crosslink Density, and SEM Images of SA-AgNPs Gel
2.6. Water-Resistance Test of the SA-AgNPs/CS Gel
2.7. Antibacterial Test
2.8. Cytotoxicity Test
2.8.1. Cell Propagation for Cytotoxicity Test
2.8.2. Cytotoxicity Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reaction Mechanism of AgNP Formation
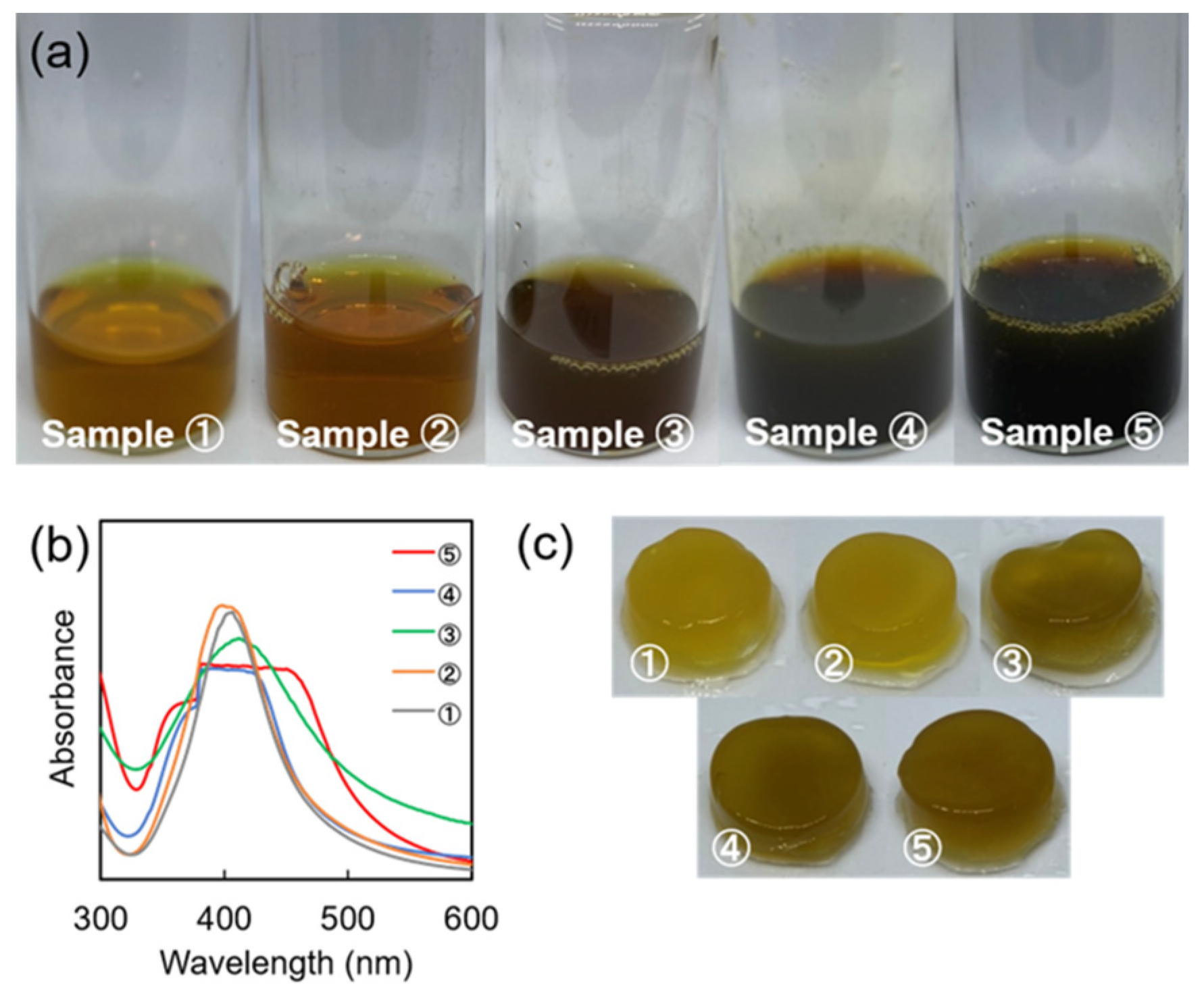
3.2. Confirmation of SA-AgNP Synthesis
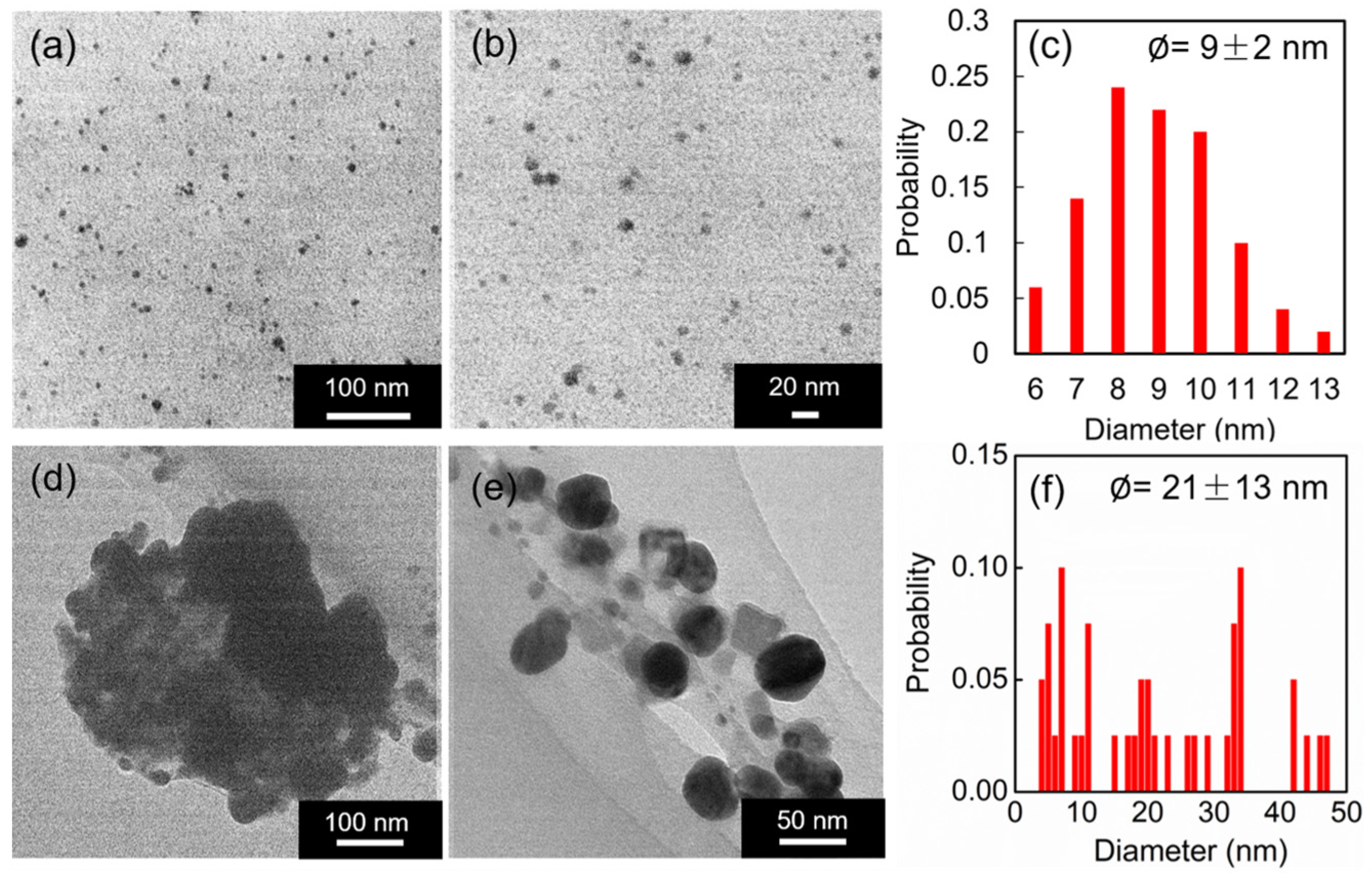
3.2.1. Synthesis without Microwave Irradiation
3.2.2. Synthesis Using Microwave Irradiation
3.3. Preparation of the SA-AgNPs/CS Gel
3.4. Mechanical Properties and SEM Images of the SA-AgNPs/CS Gels
3.5. Water Resistance of the SA-AgNPs/CS Gels
3.6. Antibacterial Activities
3.7. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samadian, H.; Zamiri, S.; Ehterami, A.; Farzamfar, S.; Vaez, A.; Khastar, H.; Alam, M.; Ai, A.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Allahyari, Z.; et al. Electrospun cellulose acetate/gelatin nanofibrous wound dressing containing berberine for diabetic foot ulcer healing: In vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Sun, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, S.; Ma, J.; Zhou, F. Electrospun chitosan nanofibers for wound healing application. Eng. Regen. 2021, 2, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, A.M.; Hudson, S.M.; Rojas, O.J. Antimicrobial wound dressing nanofiber mats from multicomponent (chitosan/silver-NPs/polyvinyl alcohol) systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 100, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Thummavichai, K.; Ola, O.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Y. Antibacterial properties and drug release study of cellulose acetate nanofibers containing ear-like Ag-NPs and Dimethyloxallyl Glycine/beta-cyclodextrin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 153132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Kenawy, E.-R.S.; Tamer, T.M.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Eldin, M.S.M. Poly (vinyl alcohol)-alginate physically crosslinked hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: Characterization and bio-evaluation. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, C.K.; Hamdan, A.D.; Barshes, N.R.; Wyers, M.; Hevelone, N.D.; Belkin, M.; Nguyen, L.L. Prospective, randomized, multi-institutional clinical trial of a silver alginate dressing to reduce lower extremity vascular surgery wound complications. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramli, R.H.; Soon, C.F.; Rus, A.Z.M. Synthesis of Chitosan /Alginate/ Silver Nanoparticles Hydrogel Scaffold. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 78, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mndlovu, H.; du Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Marimuthu, T.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Development of a fluid-absorptive alginate-chitosan bioplatform for potential application as a wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, T.T.; Aarstad, O.A.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Draget, K.I.; Vårum, K.M. Gelling Concept Combining Chitosan and Alginate—Proof of Principle. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoto, D.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Preparation of polyelectrolyte complex gel of sodium alginate with chitosan using basic solution of chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Zheng, P.; Gao, L.; Huo, D.; Cheng, L.; Wei, S. Study on antibacterial wood coatings with soybean protein isolate nano-silver hydrosol. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 165, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, T.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Versatile roles of silver in Ag-based nanoalloys for antibacterial applications. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 449, 214218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Pei, Y.; Tang, K. Soluble soybean polysaccharide films containing in-situ generated silver nanoparticles for antibacterial food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. A wearable, anti-bacterial strain sensor prepared by silver plated cotton/spandex blended fabric for human motion monitoring. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, N.; Siddiqui, S.; Fatima, B.; Sultana, R.; Tara, N.; Hashmi, A.; Ahmad, R.; Mohsin, M.; Nirala, R.; Linh, N.; et al. Silver based hybrid nanocomposite: A novel antibacterial material for water cleansing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocsoy, I.; Temiz, M.; Celik, C.; Altinsoy, B.; Yilmaz, V.; Duman, F. A green approach for formation of silver nanoparticles on magnetic graphene oxide and highly effective antimicrobial activity and reusability. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.G.; Shumilova, A.A.; Shidlovskiy, I.P.; Nikolaeva, E.D.; Sukovatiy, A.G.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Shishatskaya, E.I. Antibacterial properties of films of cellulose composites with silver nanoparticles and antibiotics. Polym. Test. 2018, 65, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, J.; Zhu, R.; Lang, S.; Yan, H.; Liu, G.; Peng, B. Mussel-inspired immobilization of zwitterionic silver nanoparticles toward antibacterial cotton gauze for promoting wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, R.; Kokate, M.; Jambhale, C.; Pawar, S.; Han, S.; Kolekar, S. One-pot synthesis of PVA-capped silver nanoparticles their characterization and biomedical application. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 3015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiragond, C.B.; Kshirsagar, A.S.; Dhapte, V.V.; Khanna, T.; Joshi, P.; More, P.V. Enhanced anti-microbial response of commercial face mask using colloidal silver nanoparticles. Vacuum 2018, 156, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbay, M.; Rey, V.; Dorado, R.D.; Sosa, M.C.; Borsarelli, C.D. Silver nanoparticle-protein interactions and the role of lysozyme as an antagonistic antibacterial agent. Colloids Surf. B. 2021, 208, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, N.; Ghaneialvar, H.; Moradi, R.; Zangeneh, M.; Zangeneh, A. Formulation and characterization of a novel cutaneous wound healing ointment by silver nanoparticles containing Citrus lemon leaf: A chemobiological study. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Shi, J. Antibacterial and wound healing-promoting effect of sponge-like chitosan-loaded silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by iturin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Mariadoss, A.; Wang, M. Biocompatible fungal chitosan encapsulated phytogenic silver nanoparticles enhanced antidiabetic, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.; Soni, S.; Patial, V.; Kulurkar, P.; Kumari, A.; Mahesh, S.; Padwad, Y.; Yadav, S. In vivo diabetic wound healing potential of nanobiocomposites containing bamboo cellulose nanocrystals impregnated with silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarchi, C.; Cruz, A.; Bitencourt, C.; Farias, I.; Ślawska-Waniewska, A.; Nedelko, N.; Dłużewski, P.; Morawiec, K.; Calisto, J.; Martello, R.; et al. Eugenia umbelliflora mediated reduction of silver nanoparticles incorporated into O-carboxymethylchitosan/y-Fe2O3: Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and toxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, Y.; Li, Q.; Ma, X.; Quan, F.; Geng, C.; Han, Z. Microwave-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles using sodium alginate and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, V.; Riabov, S.; Sinelnikov, S.; Radchenko, O.; Kobylinskyi, S.; Rybalchenko, N. Novel approach to synthesis of silver nanoparticles in interpolyelectrolyte complexes based on pectin, chitosan, starch and their derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Saptami, K.; Venkatesan, J.; Rekha, P.D. Microwave–assisted rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fucoidan: Characterization with assessment of biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Zou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, F. Silver nanoparticles in situ synthesized by polysaccharides from Sanghuangporus sanghuang and composites with chitosan to prepare scaffolds for the regeneration of infected full-thickness skin defects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikosou, D.; Saita, S.; Miyata, S.; Miyaji, H.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H.; Kawasaki, H. Aggregation/Self-Assembly-Induced Approach for Efficient AuAg Bimetallic Nanocluster-Based Photosensitizers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 12494–12501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, D. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by sodium alginate to obtain silver-loaded composite wound dressing with enhanced mechanical and antimicrobial property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, T. Polymer Gels, Chapter 2 and 4; Kyoritsu Shuppan CO., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Garavand, F.; Jafari, S. Incorporation of silver nanoparticles into active antimicrobial nanocomposites: Release behavior, analyzing techniques, applications and safety issues. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 293, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yguerabide, J.; Yguerabide, E.E. Light-Scattering Submicroscopic Particles as Highly Fluorescent Analogs and Their Use as Tracer Labels in Clinical and Biological Applications. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 262, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhui, D.; Bar, H.; Sarkar, P.; Sahoo, G.; De, S.; Misra, A. Synthesis and UV–vis spectroscopic study of silver nanoparticles in aqueous SDS solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2009, 145, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, R.L.; Bilderling, C.; Guz, L.; Bernal, C.; Fama, L. Effect of greenly synthetized silver nanoparticles on the properties of active starch films obtained by extrusion and compression molding. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Kanikireddy, V.; Toro, C.; Sadiku, E. Alginate-based composite materials for wound dressing application:A mini review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; Jesus, M.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine 2016, 127, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mohsen, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, R.M.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Vojtova, L.; Uhrova, L.; Hassan, A.F.; Al–Deyab, S.S.; El-Shamy, I.E.; Jancar, J. Preparation characterization and cytotoxicity of schizophyllan/silver nanoparticle composite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Lee, S. Study on aggregation behavior of Cytochrome C–conjugated silver nanoparticles using asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. Talanta 2015, 132, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Yang, A.; Xiong, J. Green, microwave-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles using bamboo hemicelluloses and glucose in an aqueous medium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Formation and Stabilization of Silver Nanoparticles through Reduction by N,N-Dimethylformamide. Langmuir 1999, 15, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle? A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Xue, Y.; Han, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using sodium alginate and tannic acid: Characterization and anti–S. aureus activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhong, L.; Xue, J. Preparation and properties of conductive bacterial cellulose-based graphene oxide-silver nanoparticles antibacterial dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Jain, J.; Rajwade, J.M.; Paknikar, K.M. Interactions of silver nanoparticles with primary mouse fibroblasts and liver cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 236, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M. Antibacterial and catalytic activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 135, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokura, S.; Ueno, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Nishi, N. Molecular Weight Dependent Antimicrobial Activity by Chitosan. Macromol. Symp. 1997, 120, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Cheng, F.; Chiu, H.; Tsai, J.; Fang, C.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y. Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, apoptosis and the autophagic effects of silver nanoparticles in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4706–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample | Average Pore Size (10−3 mm2) |
|---|---|
| SA/CS gel (CS:SA = 0.75:1) | 0.58 ± 0.05 |
| SA-AgNPs/CS gels (CS:SA = 0.5:1) | 0.55 ± 0.02 |
| SA-AgNPs/CS gels (CS:SA = 0.75:1) | 0.37 ± 0.02 |
| SA-AgNPs/CS gels (CS:SA = 1:1) | 0.41 ± 0.02 |
| Bacteria | SA/AgNPs/CS (10 mM) | SA/AgNPs/CS (50 mM) |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | 17 ± 1 mm | 25 ± 2 mm |
| B. subtilis | 16 ± 2 mm | 21 ± 1 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oe, T.; Dechojarassri, D.; Kakinoki, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Microwave-Assisted Incorporation of AgNP into Chitosan–Alginate Hydrogels for Antimicrobial Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040199
Oe T, Dechojarassri D, Kakinoki S, Kawasaki H, Furuike T, Tamura H. Microwave-Assisted Incorporation of AgNP into Chitosan–Alginate Hydrogels for Antimicrobial Applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040199
Chicago/Turabian StyleOe, Takuma, Duangkamol Dechojarassri, Sachiro Kakinoki, Hideya Kawasaki, Tetsuya Furuike, and Hiroshi Tamura. 2023. "Microwave-Assisted Incorporation of AgNP into Chitosan–Alginate Hydrogels for Antimicrobial Applications" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040199
APA StyleOe, T., Dechojarassri, D., Kakinoki, S., Kawasaki, H., Furuike, T., & Tamura, H. (2023). Microwave-Assisted Incorporation of AgNP into Chitosan–Alginate Hydrogels for Antimicrobial Applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040199







