Effect of an In-Office Bleaching Agent with Surface Pre-Reacted Glass-Ionomer Filler on the Enamel Surface: A In-Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
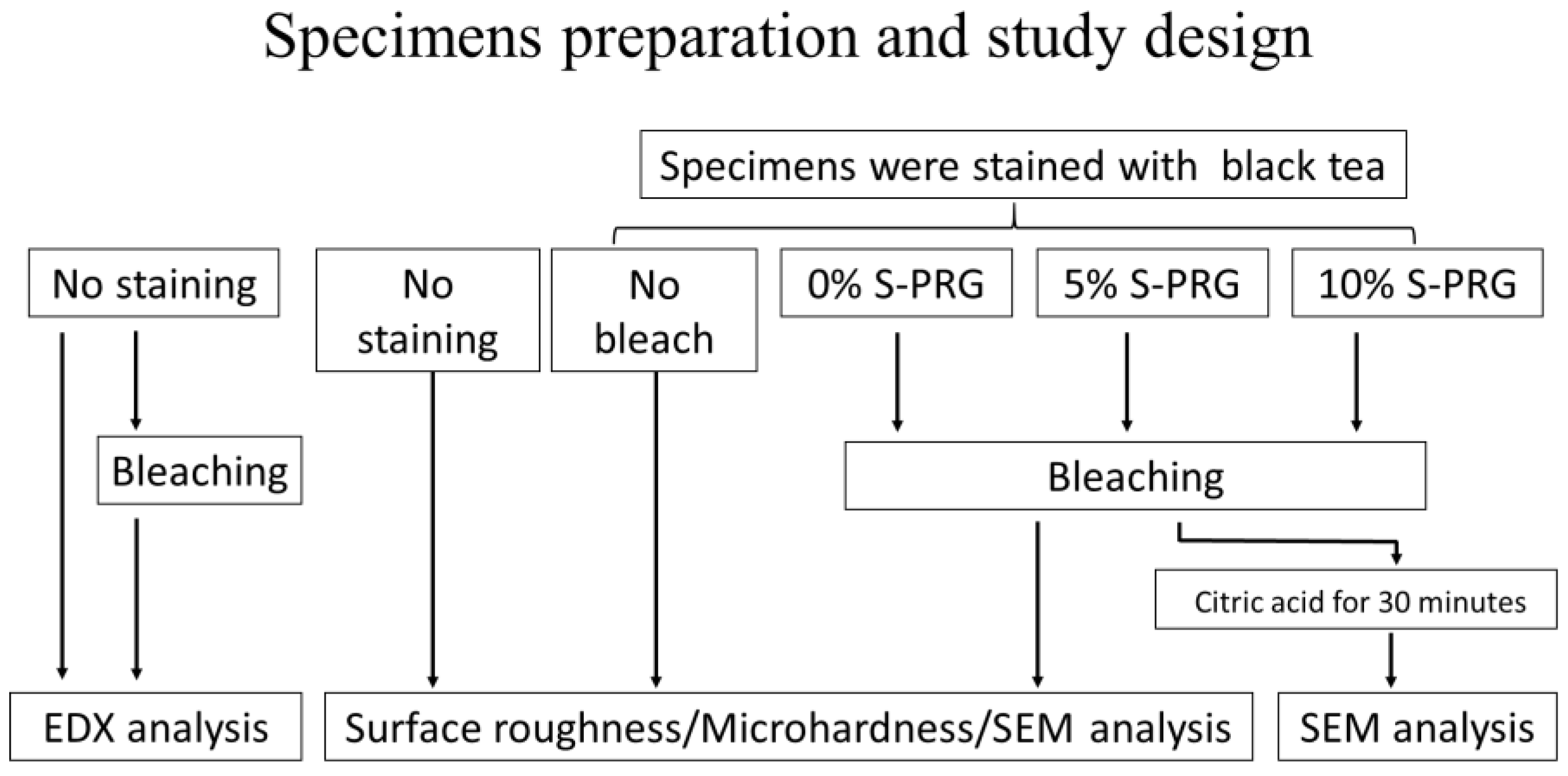
2.1. Specimen Preparation and Bleaching Procedure
- The no staining group— enamel that were not stained.
- The no bleaching group—enamel surfaces unbleached after staining.
- The control (0% S-PRG) group—stained enamel bleached with plain paste without S-PRG filler.
- The 5% S-PRG group—stained enamel bleached with a paste containing 5% S-PRG filler in the powder.
- The 10% S-PRG group—stained enamel bleached with a paste containing 10% S-PRG filler in the powder.
2.2. Assessment of Surface Roughness
2.3. Assessment of Microhardness
2.4. Assessment of Morphological Changes
2.5. Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) Analysis
2.6. Assessment of Erosion by Citric Acid
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surface Roughness
3.2. Microhardness
3.3. Surface Morphology
3.4. EDX
3.5. Erosion by Citric Acid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nathoo, S.A. The chemistry and mechanisms of extrinsic and intrinsic discoloration. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1997, 128, 6s–10s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, M. An overview of tooth discoloration: Extrinsic, intrinsic and internalized stains. Dent. Update 2005, 32, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liang, S.; Sa, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y. Surface alteration of human tooth enamel subjected to acidic and neutral 30% hydrogen peroxide. J. Dent. 2011, 39, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.R.; Wertz, P.W. Review of the Mechanism of Tooth Whitening. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2015, 27, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Xu, J.W.; Shing, C.X. Decomposition rate of hydrogen peroxide bleaching agents under various chemical and physical conditions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1993, 69, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, C.R.; Wiegand, A.; Sener, B.; Attin, T. Influence of chemical activation of a 35% hydrogen peroxide bleaching gel on its penetration and efficacy—In vitro study. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joiner, A. The bleaching of teeth: A review of the literature. J. Dent. 2006, 34, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, A.; Addy, M. Tooth discolouration and staining: A review of the literature. Br. Dent. J. 2001, 190, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.; Valiente, M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J. Tooth whitening: From the established treatments to novel approaches to prevent side effects. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2019, 31, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.B.; Sedarous, M.; Hiltz, G.S. The pH of tooth-whitening products. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2000, 66, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli, V.; Arrais, C.A.; Giannini, M.; Ambrosano, G.M. High-concentrated carbamide peroxide bleaching agents effects on enamel surface. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2004, 31, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bistey, T.; Nagy, I.P.; Simó, A.; Hegedus, C. In vitro FT-IR study of the effects of hydrogen peroxide on superficial tooth enamel. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attin, T.; Müller, T.; Patyk, A.; Lennon, A.M. Influence of different bleaching systems on fracture toughness and hardness of enamel. Oper. Dent. 2004, 29, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wijetunga, C.L.; Otsuki, M.; Abdou, A.; Luong, M.N.; Qi, F.; Tagami, J. The effect of in-office bleaching materials with different pH on the surface topography of bovine enamel. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.; Fairley, P.; Mohan, V.; Jumeaux, C. A study of hydrogen peroxide chemistry and photochemistry in tea stain solution with relevance to clinical tooth whitening. J. Dent. 2012, 40 (Suppl. S2), e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Effects of pH values of hydrogen peroxide bleaching agents on enamel surface properties. Oper. Dent. 2011, 36, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmaier, G.M.; Schulze, I.M.; Attin, T. Fluoride uptake and development of artificial erosions in bleached and fluoridated enamel in vitro. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2002, 29, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschoppe, P.; Neumann, K.; Mueller, J.; Kielbassa, A.M. Effect of fluoridated bleaching gels on the remineralization of predemineralized bovine enamel in vitro. J. Dent. 2009, 37, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Han, A.R.; Kim, K.M.; Kwon, J.S. Effects of incorporating 45S5 bioactive glass into 30% hydrogen peroxide solution on whitening efficacy and enamel surface properties. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2022, 26, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Wen, H.-L.; Dong, X.-L.; Li, F.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhou, X.-D. Effects of 45S5 bioglass on surface properties of dental enamel subjected to 35% hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2013, 5, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Imazato, S.; Chen, J.-H.; Mayanagi, G.; Takahashi, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Nakano, T. Effects of a coating resin containing S-PRG filler to prevent demineralization of root surfaces. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 31, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, S.; Iijima, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Tsukamoto, N.; Mizoguchi, I.; Saito, T. Effects of surface pre-reacted glass-ionomer fillers on mineral induction by phosphoprotein. J. Dent. 2011, 39, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imazato, S.; Nakatsuka, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Sasaki, J.-I.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ito, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Nomura, R.; Nakano, K. Multiple-Ion Releasing Bioactive Surface Pre-Reacted Glass-Ionomer (S-PRG) Filler: Innovative Technology for Dental Treatment and Care. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, Y.; Koulourides, T. Fluoride incorporation into and retention in remineralized enamel. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Saranathan, S.; Cai, F.; Cross, K.J.; Reynolds, E.C. Enamel subsurface lesion remineralisation with casein phosphopeptide stabilised solutions of calcium, phosphate and fluoride. Caries Res. 2008, 42, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedhiya, M.G.; Young, F.; Higuchi, W.I. Mechanism for the retardation of the acid dissolution rate of hydroxapatite by strontium. J. Dent. Res. 1973, 52, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akabane, K.; Hiraishi, N.; Shimojima, M.; Nassar, M.; Qi, F.; Otsuki, M.; Shimada, Y. The bleaching effect of office bleaching agents containing S-PRG filler evaluated by pH value and electron spin resonance. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2023, 27, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassen, G.H.; Platt, J.A.; Hara, A.T. Bovine teeth as substitute for human teeth in dental research: A review of literature. J. Oral. Sci. 2011, 53, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attin, T.; Vollmer, D.; Wiegand, A.; Attin, R.; Betke, H. Subsurface microhardness of enamel and dentin after different external bleaching procedures. Am. J. Dent. 2005, 18, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.H.; Huo, M.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.J. Effects of hydrogen peroxide on the light reflectance and morphology of bovine enamel. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2002, 29, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, B.C.D.; Pinheiro, M.H.M.; Feitosa, D.A.D.S.; Correia, T.C.; Braz, R.; Montes, M.A.J.R.; Pinheiro, I.V.D.A. Preliminary study of a novel in-office bleaching therapy modified with a casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, M.; Addy, M.; Macdonald, E.; Rees, J.S. A safety study in vitro for the effects of an in-office bleaching system on the integrity of enamel and dentine. J. Dent. 2004, 32, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, C.R.; Crastechini, E.; Feitosa, F.A.; Pucci, C.R.; Borges, A.B. Influence of pH on the effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide whitening. Oper. Dent. 2014, 39, E261–E268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cadenaro, M.; Navarra, C.O.; Mazzoni, A.; Nucci, C.; Matis, B.A.; Di Lenarda, R.; Breschi, L. An in vivo study of the effect of a 38 percent hydrogen peroxide in-office whitening agent on enamel. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2010, 141, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imazato, S.; Ma, S.; Chen, J.H.; Xu, H.H. Therapeutic polymers for dental adhesives: Loading resins with bio-active components. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.P.; Chang, C.H.; Liu, J.K.; Chuang, S.F.; Yang, J.Y. Effect of fluoride containing bleaching agents on enamel surface properties. J. Dent. 2008, 36, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akabane, S.T.F.; Danelon, M.; Nunes, G.P.; Gruba, A.S.; de Souza-Costa, C.A.; Duque, C.C.D.O.; Gallinari, M.D.O.; Briso, A.L.F.; Delbem, A.C.B. Evaluation of the aesthetic effect, enamel microhardness and trans-amelodentinal cytotoxicity of a new bleaching agent for professional use containing trimetaphosphate and fluoride. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 114, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenaro, M.; Breschi, L.; Nucci, C.; Antoniolli, F.; Visintini, E.; Prati, C.; Matis, B.A.; Di Lenarda, R.; Cadenaro, L.B.M.; Marson, F.; et al. Effect of two in-office whitening agents on the enamel surface in vivo: A morphological and non-contact profilometric study. Oper. Dent. 2008, 33, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.J.; Cochran, M.A.; Matis, B.A.; Gonzalez, C.; Platt, J.A.; Pund, M.R. Clinical evaluation of 15% carbamide peroxide on the surface microhardness and shear bond strength of human enamel. Oper. Dent. 2007, 32, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippert, F.; Hara, A.T. Strontium and caries: A long and complicated relationship. Caries Res. 2013, 47, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, M.; Ebrahimi Chaharom, M.E.; Daneshpooy, M.; Gholizadeh, S.; Pashayi, H. Effect of bleaching protocols on surface roughness and biofilm formation on silorane-based composite resin. Dent. Res. J. 2019, 16, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Wegehaupt, F.; Wiegand, A. Influence of study design on the impact of bleaching agents on dental enamel microhardness: A review. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Du, W.; Zhou, X.D.; Yu, H.Y. Review of research on the mechanical properties of the human tooth. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2014, 6, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegedüs, C.; Bistey, T.; Flóra-Nagy, E.; Keszthelyi, G.; Jenei, A. An atomic force microscopy study on the effect of bleaching agents on enamel surface. J. Dent. 1999, 27, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.F.; Oliveira, R.; Cavalli, V.; Giannini, M. Peroxide bleaching agent effects on enamel surface microhardness, roughness and morphology. Braz. Oral. Res. 2004, 18, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, R.F.; Galvão, A.; Campolina, M.G.; Mendonça, L.C.; Soares, C.J.; Carvalho, C.N.; da Silva, G.R. Does polishing of bleached enamel affect roughness and tooth color stability after exposure to coffee? J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2022, 34, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarek, A.; Klukowska, M.; Ganowicz, M.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Kwaśny, M. The effect of strip, tray and office peroxide bleaching systems on enamel surfaces in vitro. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owda, R.; Sancakli, H.S. Effects of Different Bleaching Agents on the Surface Topography and the Microhardness of Artificial Carious Lesions. Eur. J. Dent. 2021, 15, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, K.; Tanaka, R.; Shibata, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Hisamitsu, H. In vitro demineralization of tooth enamel subjected to two whitening regimens. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2013, 144, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attin, T.; Meyer, K.; Hellwig, E.; Buchalla, W.; Lennon, A.M. Effect of mineral supplements to citric acid on enamel erosion. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2003, 48, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Chang, H.H.; Chiang, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, C.P. Strontium ion can significantly decrease enamel demineralization and prevent the enamel surface hardness loss in acidic environment. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Product and Manufacturer | Composition |
|---|---|
| Shofu Hi–Lite, Shofu Inc., Kyoto, Japan | Powder: potassium compound, manganese sulphate, hydrated amorphous silica, organic copolymer, green dye Liquid: 35% hydrogen peroxide |
| Surface pre-reacted glass-ionomer filler, Shofu Inc., Kyoto, Japan | S-PRG filler (filler size 1 µm) Lot. BFFG-421 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimojima, M.; Hiraishi, N.; Akabane, K.; Nassar, M.; Otsuki, M.; Shimada, Y. Effect of an In-Office Bleaching Agent with Surface Pre-Reacted Glass-Ionomer Filler on the Enamel Surface: A In-Vitro Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070386
Shimojima M, Hiraishi N, Akabane K, Nassar M, Otsuki M, Shimada Y. Effect of an In-Office Bleaching Agent with Surface Pre-Reacted Glass-Ionomer Filler on the Enamel Surface: A In-Vitro Study. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(7):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070386
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimojima, Mika, Noriko Hiraishi, Kodai Akabane, Mohannad Nassar, Masayuki Otsuki, and Yasushi Shimada. 2023. "Effect of an In-Office Bleaching Agent with Surface Pre-Reacted Glass-Ionomer Filler on the Enamel Surface: A In-Vitro Study" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 7: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070386
APA StyleShimojima, M., Hiraishi, N., Akabane, K., Nassar, M., Otsuki, M., & Shimada, Y. (2023). Effect of an In-Office Bleaching Agent with Surface Pre-Reacted Glass-Ionomer Filler on the Enamel Surface: A In-Vitro Study. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(7), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070386








