Carbon Dot Micelles Synthesized from Leek Seeds in Applications for Cobalt (II) Sensing, Metal Ion Removal, and Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Leek Seed Extract
2.3. Analysis of Leek Seed Extract Through Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Synthesis of CD-Micelles
2.5. Characterization of CD-Micelles
2.6. Selectivity and Sensitivity of CD-Micelles for Metal Ions
2.7. Metal Ion Removal Using CD-Micelles Through Liquid–Liquid Extraction
2.8. Antioxidant Activity of CD-Micelles
2.9. Cytotoxicity of CD-Micelles Against Cisplatin-Resistant Lung Cancer Cells
3. Results and Discussion
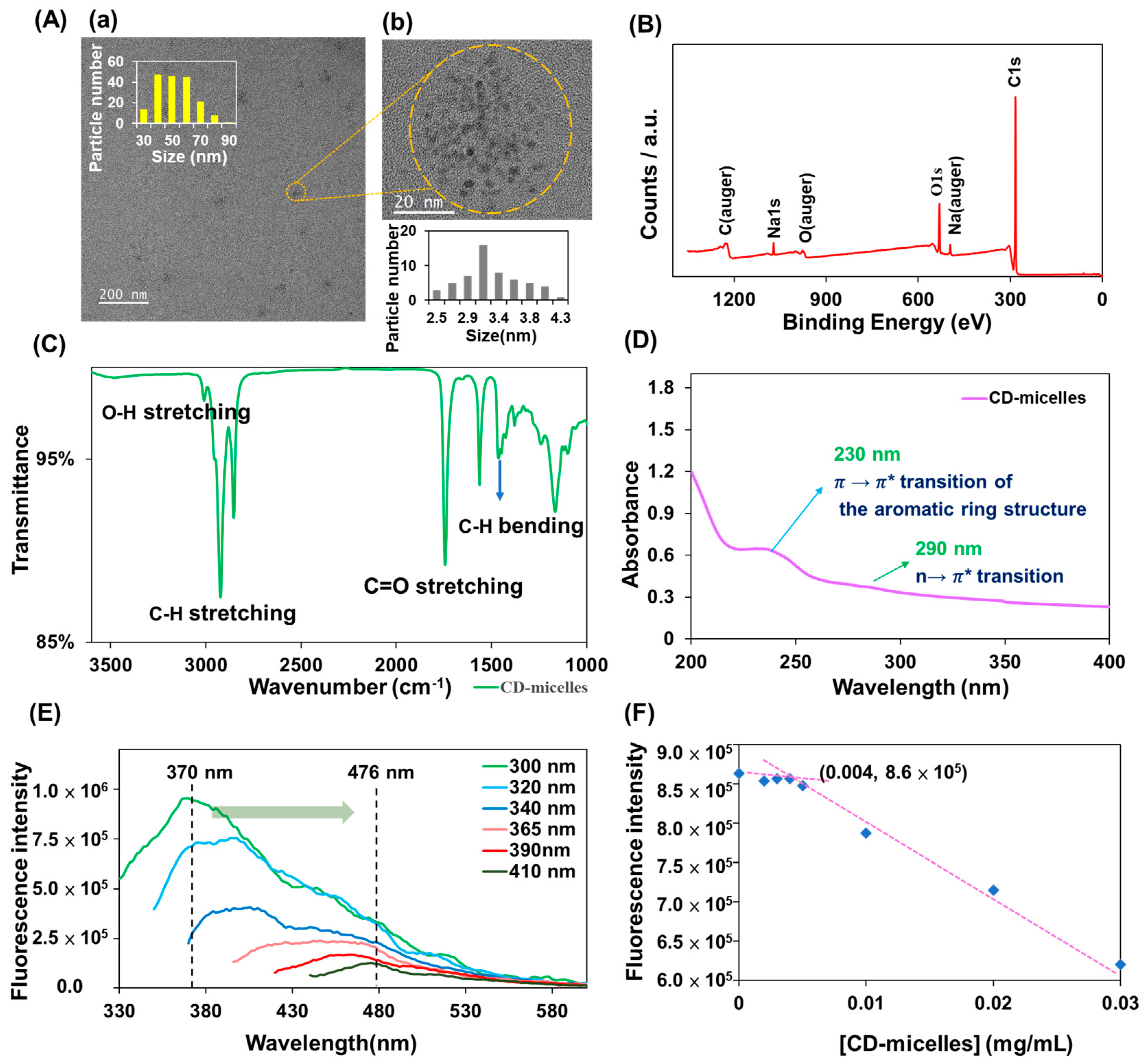
3.1. Characterization of Leek Seed Extract and CD-Micelles
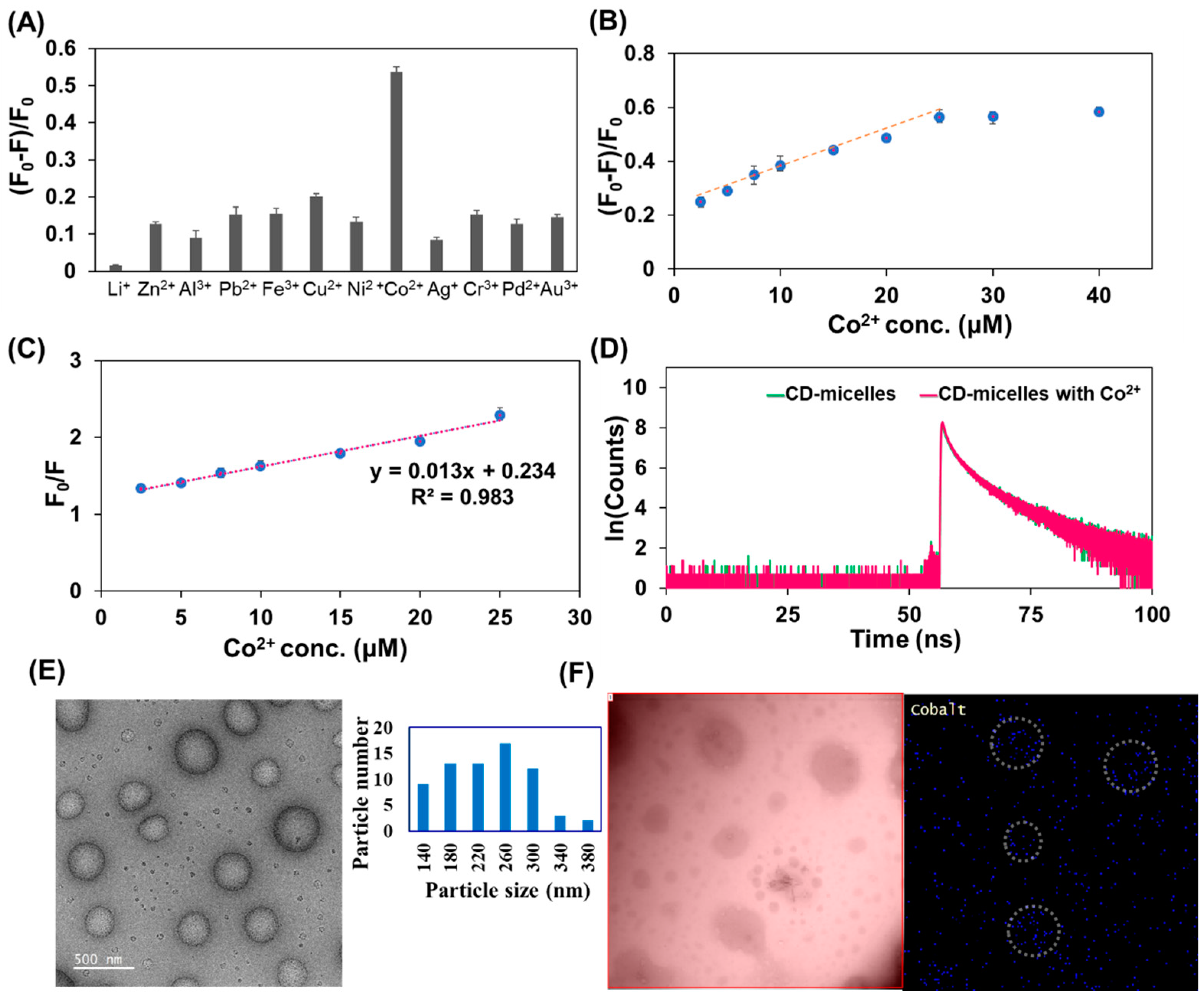
3.2. Detection of Metal Ions Using CD-Micelles
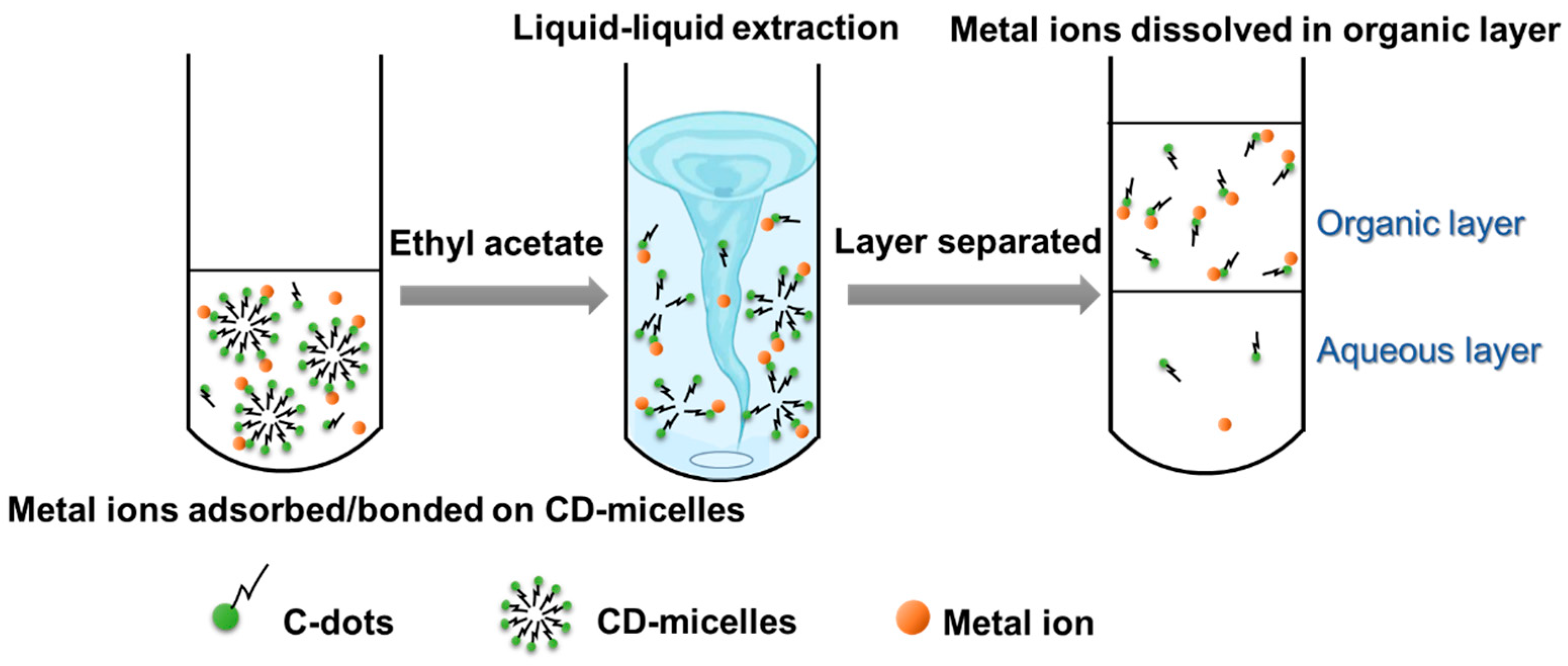
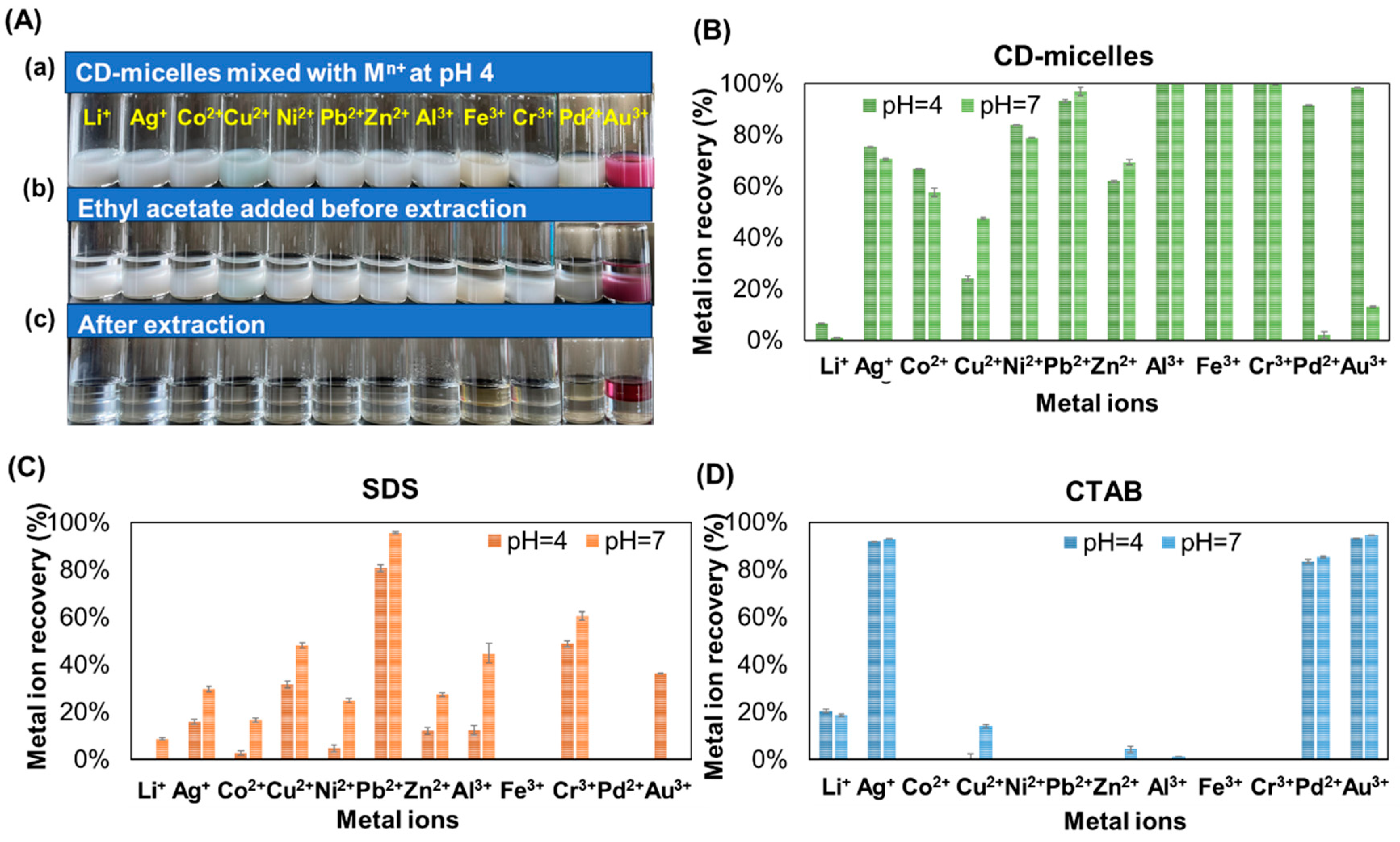
3.3. CD-Micelles for Metal Ion Removal Through Liquid–Liquid Extraction
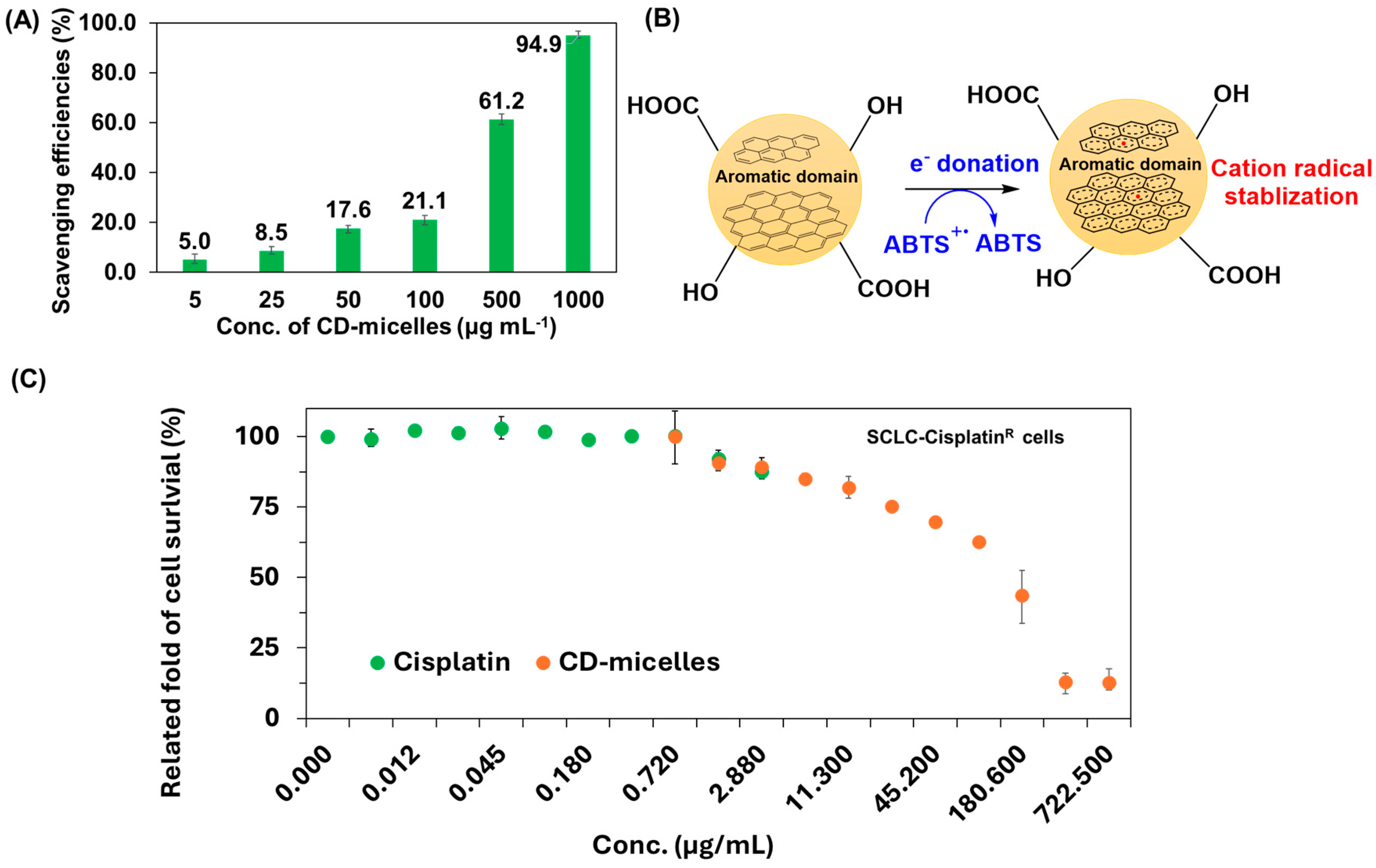
3.4. Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of CD-Micelles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, H.-W.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Anand, A.; Lin, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-C. Carbon quantum dots for the detection of antibiotics and pesticides. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, P.; Negahdari, B.; Eatemadi, A. Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of carbon-based quantum dots: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciortino, A.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. Carbon nanodots: A review—From the current understanding of the fundamental photophysics to the full control of the optical response. C 2018, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-C.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chang, H.-T. Carbon dots as artificial peroxidases for analytical applications. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. Advancement in science and technology of carbon dot-polymer hybrid composites: A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2019, 1, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.; Gopinath, P. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 2015, 140, 4260–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy Padidam, S.; Kadam, B.D.; Thakkellapati, S.; Verma, M.; Raichur, A.M.; Narashimhan Ramana, L. Single-step synthesis of self-assembled carbon dots for enhanced cancer cell retention and theranostics applications. Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Carbon dots—Emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, C.; Tapas, S.; Lei, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Carbon dots modified mesoporous organosilica as an adsorbent for the removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and heavy metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13357–13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya Pudza, M.; Zainal Abidin, Z.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Md Yasin, F.; Noor, A.; Issa, M.A. Eco-friendly sustainable fluorescent carbon dots for the adsorption of heavy metal ions in aqueous environment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.C.; Gomes, C.G.; Pina, J.; Pereira, R.F.; Murtinho, D.; Fajardo, A.R.; Valente, A.J. Carbon quantum dots-containing poly (β-cyclodextrin) for simultaneous removal and detection of metal ions from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, T. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots for determination of nickel ions and morin from aqueous solution simultaneously. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chyueh, S.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Carbon dots functionalized papers for high-throughput sensing of 4-chloroethcathinone and its analogues in crime sites. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 191017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Yen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chang, H. Photoluminescent carbon nanomaterials for sensing of illicit drugs: Focus. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, T.-H.; Chyueh, S.-C.; Chang, H.-T. A carbon-dot sensing probe for screening of date rape drugs: Nitro-containing benzodiazepines. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, J.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, W. Carbon quantum dots: Comprehensively understanding of the internal quenching mechanism and application for catechol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 333, 129557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, F.; Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zho, X. The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: A review on mechanisms and applications. Mikrochim. Acta 2017, 184, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lin, Q.; Chang, H.T. Recent advances and sensing applications of carbon dots. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocito, G.; Calabrese, G.; Forte, S.; Petralia, S.; Puglisi, C.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Conoci, S. Carbon dots as promising tools for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, K.; Nan, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Wang, P. Recent advances and prospects of carbon dots in cancer nanotheranostics. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, Y.; Tin, M.S.; Lok, V.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., III; Xu, W.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Elcarte, E. Distribution, risk factors, and temporal trends for lung cancer incidence and mortality: A global analysis. Chest 2022, 161, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bade, B.C.; Cruz, C.S.D. Lung cancer 2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.A.; Fawell, S.; Floc’h, N.; Flemington, V.; McKerrecher, D.; Smith, P.D. Challenges and opportunities in cancer drug resistance. Chem. Rev. 2020, 121, 3297–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Yu, M.; Xu, J.; Li, B.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kankala, R.K. Overcoming cancer multi-drug resistance (MDR): Reasons, mechanisms, nanotherapeutic solutions, and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Chua, H.J.; Zhao, Y. Carbon-dot-mediated Co-administration of chemotherapeutic agents for reversing cisplatin resistance in cancer therapy. ChemNanoMat 2018, 4, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, A.; Lizundia, E. Luminescent carbon dots obtained from polymeric waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswoyo, T.A.; Mardiana, E.; Lee, K.O.; Hoshokawa, K. Isolation and characterization of antioxidant protein fractions from melinjo (Gnetum gnemon) seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5648–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognyanov, M.; Nikolova, M.; Yanakieva, I.; Kussovski, V.; Kratchanova, M. Influence of composition on the biological activity of pectic polysaccharides from leek. J. BioSci. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Chen, T.-T.; Hu, P.; Wang, S.-Y. A novel antibacterial tripeptide from Chinese leek seeds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, C.; Yan, X.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M. Versatile carbon dots with superoxide dismutase-like nanozyme activity and red fluorescence for inflammatory bowel disease therapeutics. Carbon 2023, 204, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Chen, J.; Tu, K.; Tuo, H.; Wu, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D. Carbon dot nanozymes as free radicals scavengers for the management of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the liver inflammatory network and inhibiting apoptosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-G.; Pan, Z.-Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Cao, Q.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W. Precisely assembled nanoparticles against cisplatin resistance via cancer-specific targeting of mitochondria and imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43444–43455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Graphene quantum dots enhance anticancer activity of cisplatin via increasing its cellular and nuclear uptake. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, Y.; Furuichi, M.; Song, R.; Van, N.T.; Mulcahy, R.T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuo, M.T. Expression of multidrug resistance protein/GS-X pump and gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase genes is regulated by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31075–31085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.S.; Savaraj, N.; Siddik, Z.H.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Wu, C.J.; Kuo, M.T. Role of human copper transporter Ctr1 in the transport of platinum-based antitumor agents in cisplatin-sensitive and cisplatin-resistant cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, T.; Song, L.; Jiang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Salloum, R.G.; Warren, G.W.; Kaye, F.J.; Fujioka, N.; Jin, L.; et al. Reducing Chemotherapy-Induced DNA Damage via nAChR-Mediated Redox Reprograming-A New Mechanism for SCLC Chemoresistance Boosted by Nicotinem. Cancers 2022, 14, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norodin, N.; Salleh, L.; Mustafa, N.M. Supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction of essential oil from swietenia mahagoni seeds. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 162, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ahmad, A. Antioxidant activity of essential oil extracted by SC-CO2 from seeds of Trachyspermum ammi. Medicines 2017, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehdi, I.A.; Sbihi, H.M.; Tan, C.P.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Rashid, U.; Al-Misned, F.A.; El-Serehy, H.A. Chemical composition, oxidative stability, and antioxidant activity of Allium ampeloprasum L. (Wild Leek) seed oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Synthesis of high-quality carbon nanodots from hydrophilic compounds: Role of functional groups. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3984–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.; Chen, P.-C.; Periasamy, A.P.; Chen, Y.-N.; Chang, H.-T. Photoluminescent carbon nanodots: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and analytical applications. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XianáGuo, C. Na+-functionalized carbon quantum dots: A new draw solute in forward osmosis for seawater desalination. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7318–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinathan, K.; Samayanan, S.; Marimuthu, K.; Yim, J.-H. Green synthesis of multicolour fluorescence carbon quantum dots from sugarcane waste: Investigation of mercury (II) ion sensing, and bio-imaging applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 601, 154266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supchocksoonthorn, P.; Hanchaina, R.; Sinoy, M.C.A.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Kangsamaksin, T.; Paoprasert, P. Novel solution-and paper-based sensors based on label-free fluorescent carbon dots for the selective detection of pyrimethanil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 564, 150372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.; Karak, N. A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8286–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Su, H.; Wang, K.; Wong, W.K.; Zhu, X. Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots from porphyrins as efficient probes for bioimaging and biosensing in living cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7375–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, I.; Bera, M.K. Microwave-Assisted Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Calotropis Gigantea as a Fluorescent Probe for Bioimaging. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charisiadis, P.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Tzakos, A.G.; Siskos, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P. 1H-NMR as a structural and analytical tool of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds of phenol-containing natural products and model compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 13643–13682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, H. Photoluminescent carbon dots derived from sugarcane molasses: Synthesis, properties, and applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47840–47847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, G.N.; El-Shaheny, R.; Shabana, R.A.; Hassan, A.H. Inherent photocatalytic activity of luminescent multi-doped carbon dots manufactured from expired medicine and its application for efficient water remediation and nanosensing. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaseem, A.M.; Alhazzani, K.; Alanazi, A.Z.; Alsanad, S.M.; Alkhamees, O.A.; Alasiri, G.; El-Wekil, M.M.; Ali, A.-M.B.H. Dual-Modulation ratiometric fluorescence strategy for cobalt and topotecan detection using Red-Emissive carbon dots. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.J.; Kwak, B.E.; Kim, D.H. Self-quenching origin of carbon dots and the guideline for their solid-state luminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27124–27131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Lu, S. Aggregation in carbon dots. Aggregate 2022, 3, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Guan, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, C.; Lan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Effect of aggregation configuration of molecular fluorophore CZA on photoluminescence properties of carbon dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 659, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, J.K.; El-Nahhal, I.M.; Salama, S.F. Determination of the critical micelle concentration by absorbance and fluorescence techniques using fluorescein probe. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 730, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noun, F.; Jury, E.A.; Naccache, R. Elucidating the quenching mechanism in carbon dot-metal interactions–designing sensitive and selective optical probes. Sensors 2021, 21, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, J. Carbon quantum dots activated metal organic frameworks for selective detection of Cu (II) and Fe (III). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 588, 124378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Suo, T.; Xie, S.; Xia, A.; Ma, Y.-J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q. Rational design, synthesis, and applications of carbon dots@ metal–organic frameworks (CD@MOF) based sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, P. Dynamic aggregation of carbon dots self-stabilizes symmetry breaking for exceptional hydrogen production with near-infrared light. Aggregate 2024, 5, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yan, F.; Han, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, L. Cobalt(II) ions detection using carbon dots as an sensitive and selective fluorescent probe. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67481–67487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, E. Phase distortion-free paramagnetic NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 8–9, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Ge, L.; Li, Y.; Mukhtar, M.; Shen, B.; Yang, D.; Li, J. Carbon dots derived from flax straw for highly sensitive and selective detections of cobalt, chromium, and ascorbic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 579, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkian, I.; Sutanto, H.; Hadiyanto, B.; Prasetio, A.; Aprimanti Utami, B. Facile synthesized carbon dots for simple and selective detection of cobalt ions in aqueous media. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2033467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Y. Green and microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon dots and application for visual detection of cobalt (II) ions and pH sensing. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, M.A.; Salam, K.A.; Evuti, A.M. Continuous removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from synthetic aqueous solutions in a fixed-bed packed column with surfactant-modified activated carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhari, P.; Abdi, S.; Nasiri, M. Effect of various types of anions and anionic surfactants on the performance of micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration process in the removal of Pb (II) ions: An optimization with the response surface methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 187, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri Zare, S.; Raouf, F.; Miveei, L.; Roshan Zekavat, S.; Abedin Pour Farahmand, R. Investigation on the lead adsorption capacity of Iranian natural zeolite: Modifications, structural effects, adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and mechanism studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2691–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-L.; Zhang, M.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.-T.; Geng, B.-Y.; Meng, R.-B.; Yang, Y.-Z.; Zhong, Y.-S.; Liu, H.-Y. Surface modification of coconut-based activated carbon by SDS and its effects on Pb2+ adsorption. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Singh, T.; Hussain, J.I.; Hashmi, A.A. Au (III)–CTAB reduction by ascorbic acid: Preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 104, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shen, J.; Du, A.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles with high concentration via a CTAB-induced silver mirror reaction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 400, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagireddi, S. Effect of cetrimonium bromide (CTAB) surfactant on Pd (II) removal efficiency from electroless plating solutions. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Geng, H.; Yang, Q.; Tong, Y.; He, W. Au/N-doped carbon dot nanozymes as light-controlled anti-and pro-oxidants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 7253–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, B. Dual-mode colorimetric/fluorometric sensor for the detection of glutathione based on the peroxidase-like activity of carbon quantum dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 136, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I. Evaluation of anticancer, antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of Artemisia absinthium L. extract. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaklabi, A.; Arif, I.A.; Ahamed, A.; Kumar, R.S.; Idhayadhulla, A. Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activities of chemical constituents of the Saururus chinensis root extracts. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, B.; Nice, E.; Xu, J.; Huang, C. Antioxidant therapy in cancer: Rationale and progress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Abrahamse, H. Redox potential of antioxidants in cancer progression and prevention. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memarzia, A.; Saadat, S.; Asgharzadeh, F.; Behrouz, S.; Folkerts, G.; Boskabady, M.H. Therapeutic effects of medicinal plants and their constituents on lung cancer, in vitro, in vivo and clinical evidence. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 2841–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thara, C.R.; Mathew, S.; Chacko, A.R.; Mathew, B. Dual functional carbon nitride dots as electrochemical sensor and anticancer agent with chemotherapic and photodynamic effect. Microchem. J. 2023, 187, 108379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzycka-Ayoush, M.; Kowalik, P.; Kowalczyk, A.; Bujak, P.; Nowicka, A.M.; Wojewodzka, M.; Kruszewski, M.; Grudzinski, I.P. Quantum dots as targeted doxorubicin drug delivery nanosystems in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | Compound | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 3.43 |
| 2 | 9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid | 3.75 |
| 3 | Octadecanoic acid | 3.78 |
| 4 | (Z, E)-7,11-Hexadecadien-1-yl acetate | 4.14 |
| 5 | Eicosanoic acid | 4.22 |
| 6 | Butyl 9,12-octadecadienoate | 4.53 |
| 7 | Palmitin [hexadecanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl ester] | 4.65 |
| 8 | Linolein [9,12-octadecadienoic acid (Z, Z)-, 2-hydroxy-1-(Hydroxymethyl)ethyl ester] | 5.31 |
| 9 | Squalene | 5.82 |
| 10 | Cholesterol | 8.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, T.-H.; Lo, W.; Wang, H.-Y.; Tsai, T.-L. Carbon Dot Micelles Synthesized from Leek Seeds in Applications for Cobalt (II) Sensing, Metal Ion Removal, and Cancer Therapy. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15110347
Tsai T-H, Lo W, Wang H-Y, Tsai T-L. Carbon Dot Micelles Synthesized from Leek Seeds in Applications for Cobalt (II) Sensing, Metal Ion Removal, and Cancer Therapy. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2024; 15(11):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15110347
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Teh-Hua, Wei Lo, Hsiu-Yun Wang, and Tsung-Lin Tsai. 2024. "Carbon Dot Micelles Synthesized from Leek Seeds in Applications for Cobalt (II) Sensing, Metal Ion Removal, and Cancer Therapy" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 15, no. 11: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15110347
APA StyleTsai, T.-H., Lo, W., Wang, H.-Y., & Tsai, T.-L. (2024). Carbon Dot Micelles Synthesized from Leek Seeds in Applications for Cobalt (II) Sensing, Metal Ion Removal, and Cancer Therapy. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 15(11), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15110347







