Induction of Apoptosis with Silver Nanoparticles Obtained Using Thermophilic Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Geobacillus spp. AgNPs in Sorbitol and YPD Growth Medium
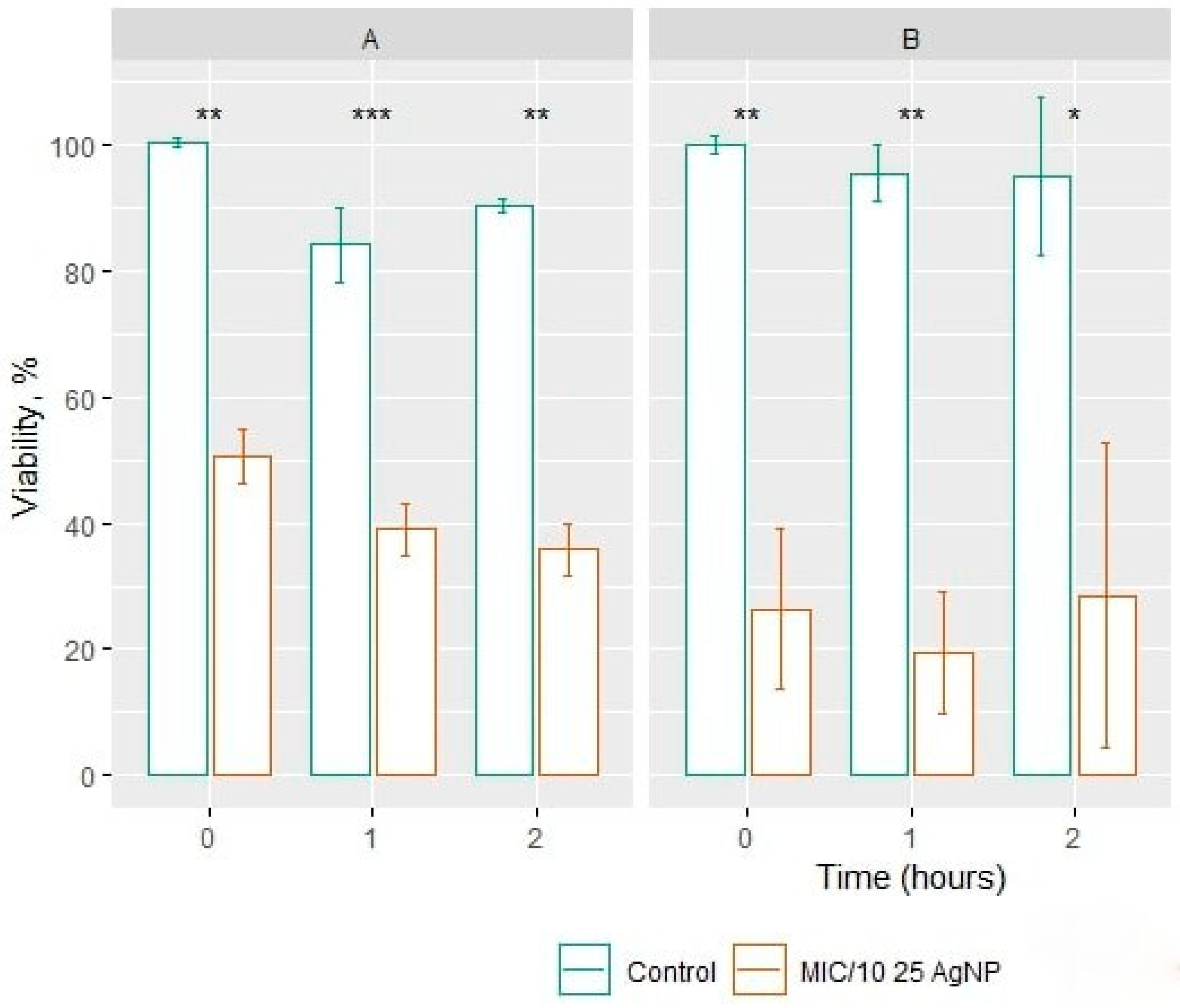
3.2. Determination of Silver Nanopaticles MIC and Cell Viability
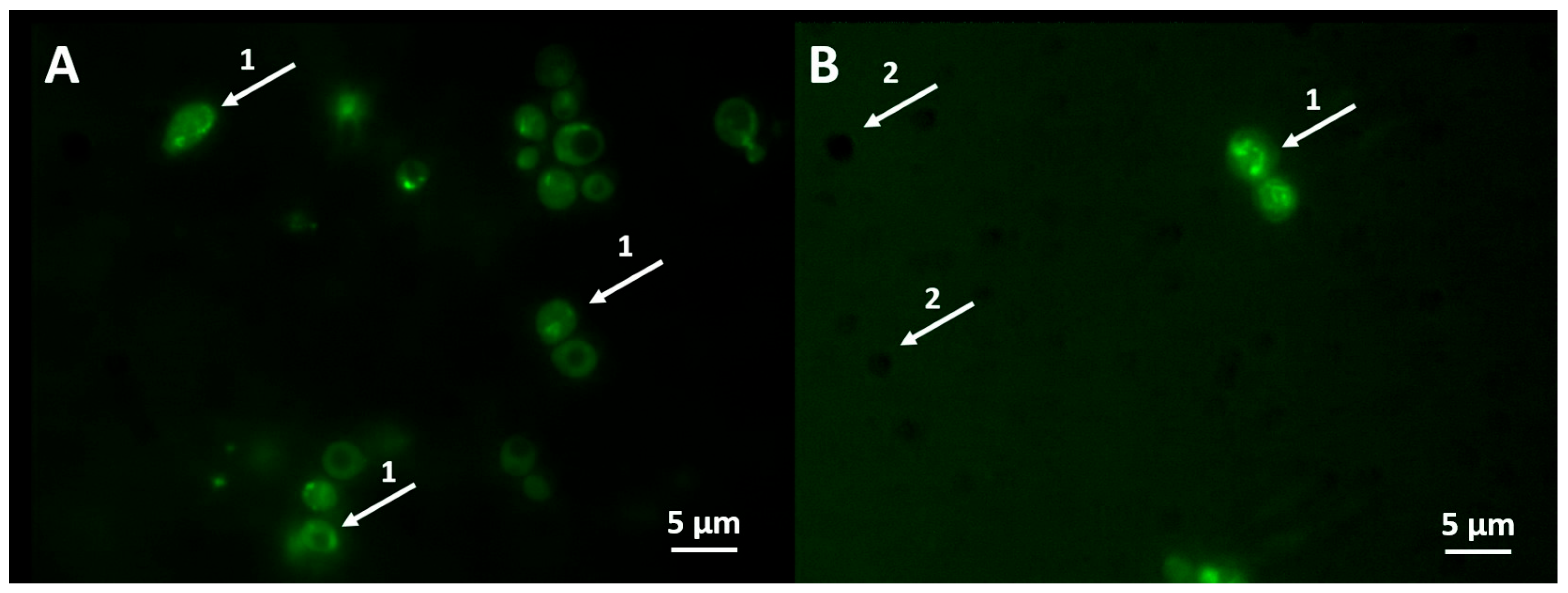
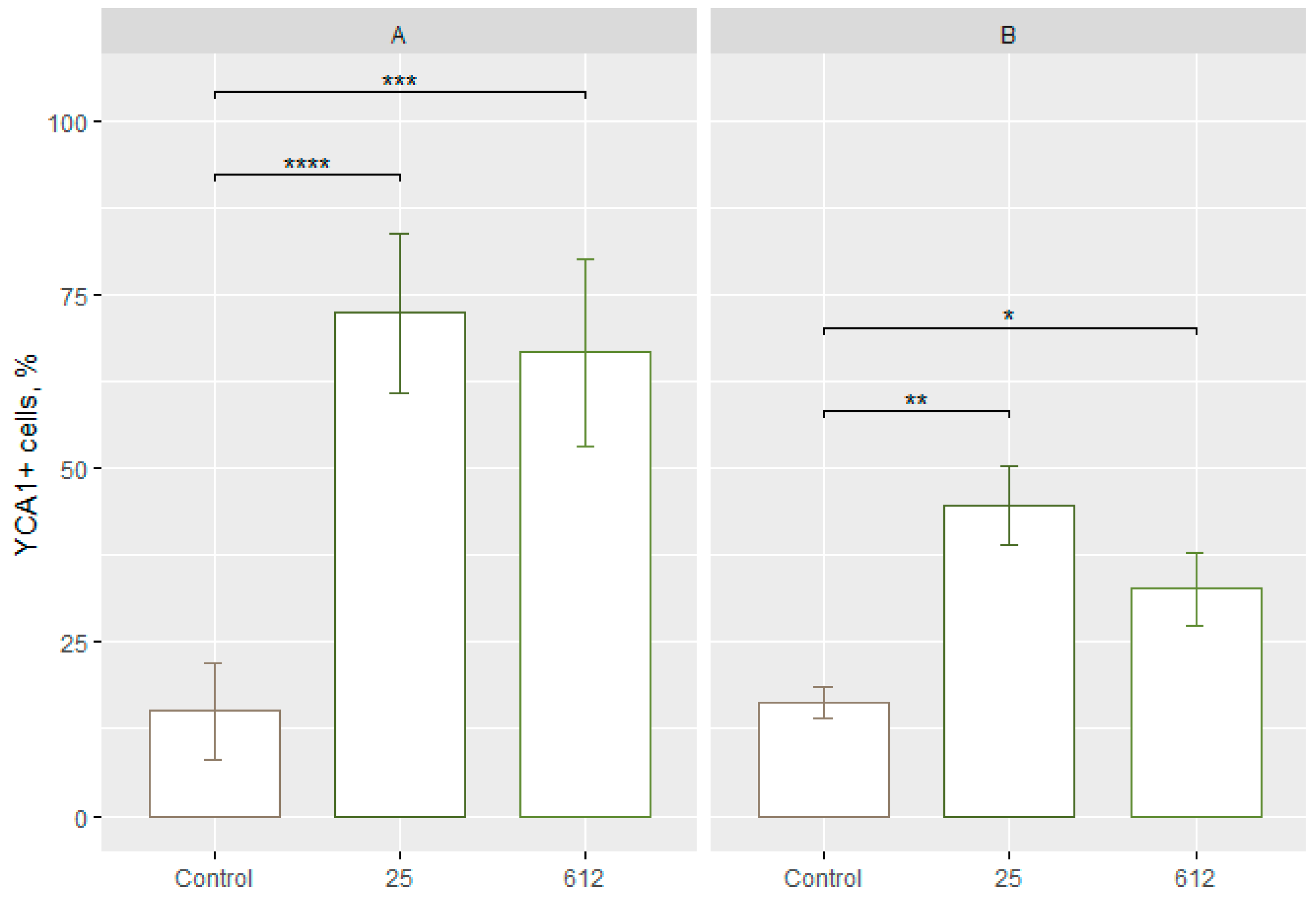
3.3. Detection of the Active Caspases
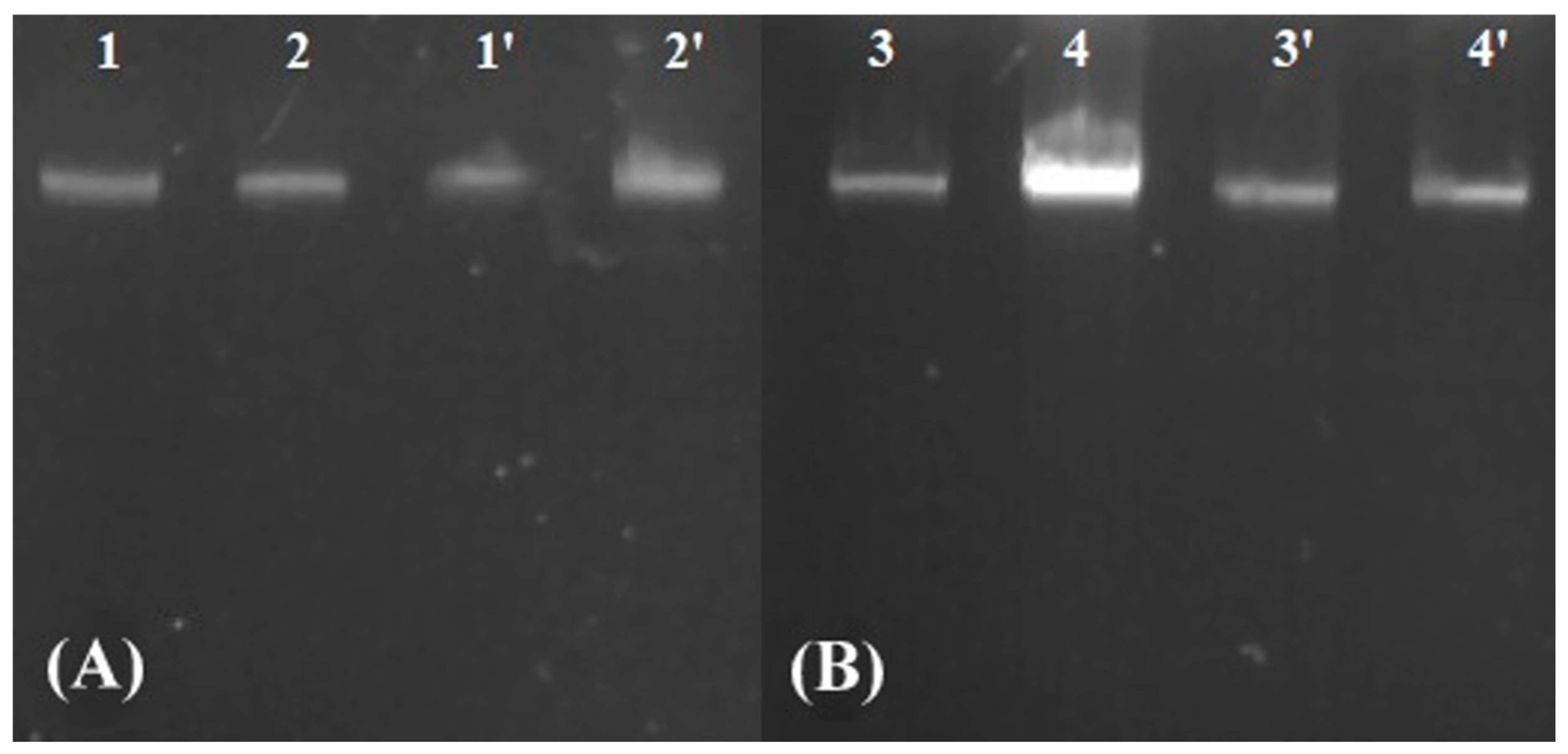
3.4. Evaluation of DNA Fragmentation
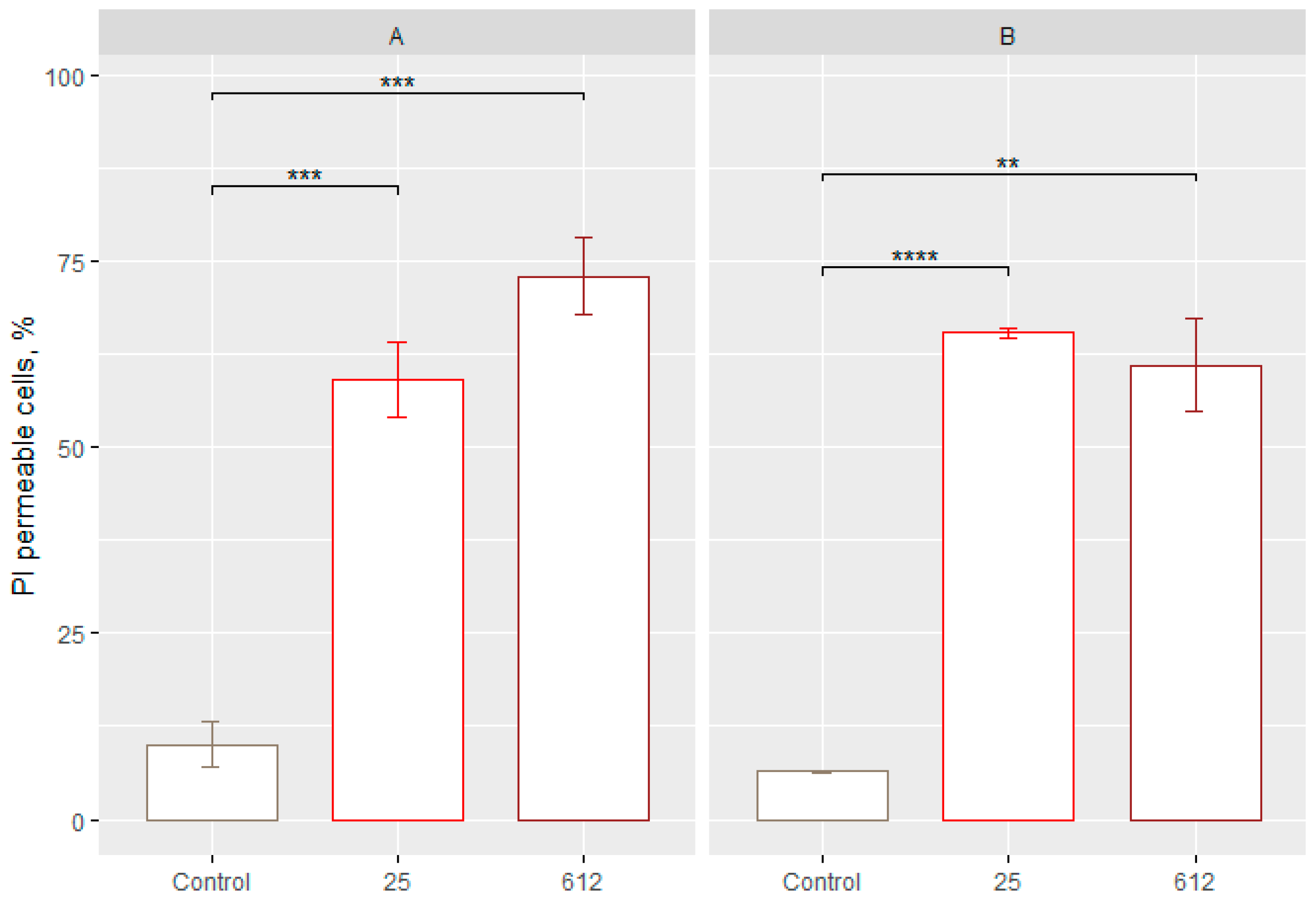
3.5. Determination of the Cell Membrane Permeability
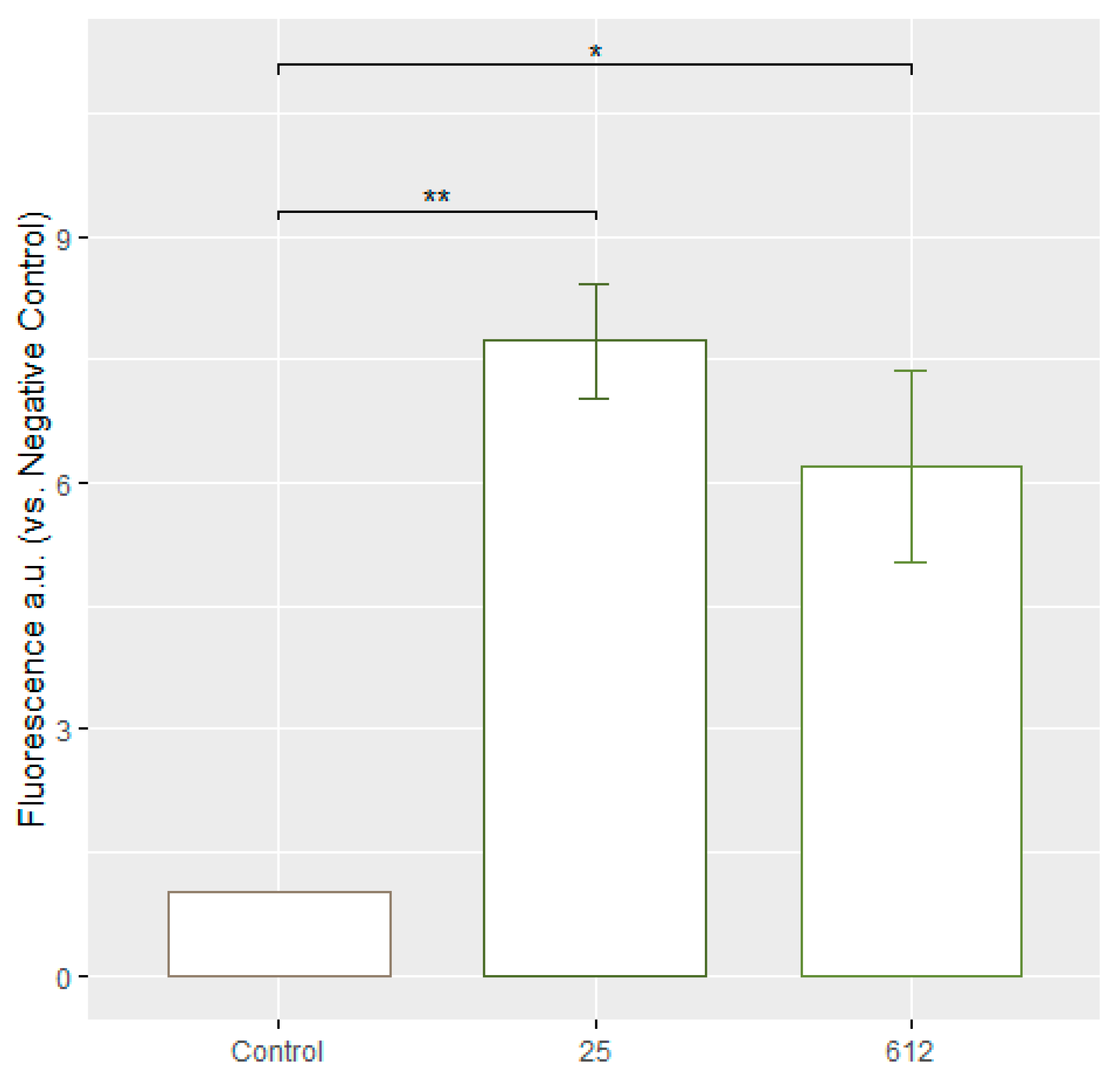
3.6. Evaluation of ROS Formation
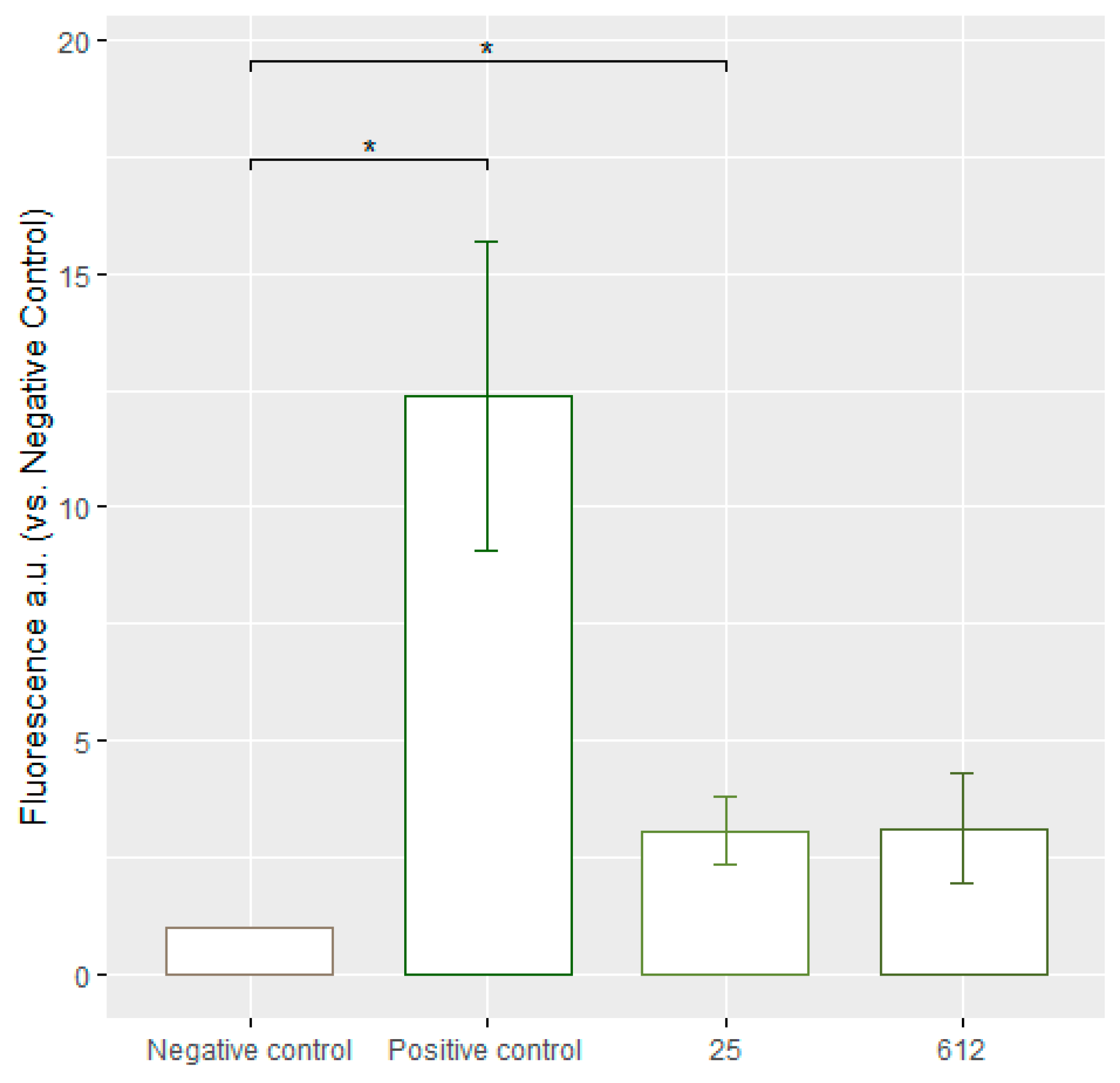
3.7. Assessment of Lipid Peroxidation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benedetti, V.P.; Savi, D.C.; Aluizio, R.; Adamoski, D.; Kava-Cordeiro, V.; Galli-Terasawa, L.V.; Glienke, C. Analysis of the Genetic Diversity of Candida Isolates Obtained from Diabetic Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Drummond, R.A.; Hohl, T.M. Immune Responses to Human Fungal Pathogens and Therapeutic Prospects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marak, M.B.; Dhanashree, B. Antifungal Susceptibility and Biofilm Production of Candida Spp. Isolated from Clinical Samples. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 7495218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Epidemiology of Invasive Candidiasis: A Persistent Public Health Problem. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Lee, M.J.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, K.; Choi, I.-H.; Park, S. Silver Nanoparticles Induce Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Cell Cycle Delay and Synergistic Cytotoxicity with 3-Bromopyruvate in Candida Albicans, but Not in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4801–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Infections Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Bae, S.; Lee, S.; Hong, I.S.; Kim, S. Ion-release Kinetics and Ecotoxicity Effects of Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Toxic. Chem. 2012, 31, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perween, N.; Khan, H.M.; Fatima, N. Silver Nanoparticles: An Upcoming Therapeutic Agent for the Resistant Candida Infections. J. Microbiol. Exp. 2019, 7, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.F.; Paschoal, A.C.C.; Klimeck, T.D.F.; Kuligovski, C.; Marcon, B.H.; De Aguiar, A.M.; Murray, P.G. Biological Synthesis of Low Cytotoxicity Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) by the Fungus Chaetomium Thermophilum—Sustainable Nanotechnology. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekuolyte, K.; Gudiukaite, R.; Klimkevicius, V.; Mazrimaite, V.; Maneikis, A.; Lastauskiene, E. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Produced Using Geobacillus Spp. Bacteria. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giray, G.; Gonca, S.; Özdemir, S.; Isik, Z.; Yılmaz, E.; Soylak, M.; Dizge, N. Novel Extracellular Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Thermophilic Anoxybacillus Flavithermus and Geobacillus Stearothermophilus and Their Evaluation as Nanodrugs. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 54, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed Fayaz, A.; Girilal, M.; Rahman, M.; Venkatesan, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Biosynthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Using Thermophilic Bacterium Geobacillus Stearothermophilus. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1958–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosfeld, E.V.; Bidiuk, V.A.; Mitkevich, O.V.; Ghazy, E.S.M.O.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Alexandrov, A.I. A Systematic Survey of Characteristic Features of Yeast Cell Death Triggered by External Factors. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arandjelovic, S.; Ravichandran, K.S. Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells in Homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asare, N.; Instanes, C.; Sandberg, W.J.; Refsnes, M.; Schwarze, P.; Kruszewski, M.; Brunborg, G. Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Silver Nanoparticles in Testicular Cells. Toxicology 2012, 291, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awashra, M.; Młynarz, P. The Toxicity of Nanoparticles and Their Interaction with Cells: An in Vitro Metabolomic Perspective. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 2674–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipke, P.N.; Ovalle, R. Cell Wall Architecture in Yeast: New Structure and New Challenges. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Arias, M.J.; Hernández-Chávez, M.J.; Garcia-Carnero, L.C.; Amezcua-Hernández, D.G.; Lozoya-Pérez, N.E.; Estrada-Mata, E.; Martínez-Duncker, I.; Franco, B.; Mora-Montes, H.M. Differential Recognition of Candida Tropicalis, Candida Guilliermondii, Candida Krusei, and Candida Auris by Human Innate Immune Cells. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastauskienė, E.; Zinkevičienė, A.; Girkontaitė, I.; Kaunietis, A.; Kvedarienė, V. Formic Acid and Acetic Acid Induce a Programmed Cell Death in Pathogenic Candida Species. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 69, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppi, S.; Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Künnis-Beres, K.; Sihtmäe, M.; Kurvet, I.; Aruoja, V.; Kahru, A. A Novel Method for Comparison of Biocidal Properties of Nanomaterials to Bacteria, Yeasts and Algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Bauer, M.A.; Zimmermann, A.; Aguilera, A.; Austriaco, N.; Ayscough, K.; Balzan, R.; Bar-Nun, S.; Barrientos, A.; Belenky, P.; et al. Guidelines and Recommendations on Yeast Cell Death Nomenclature. Microb. Cell 2018, 5, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sri Ramkumar, S.R.; Sivakumar, N.; Selvakumar, G.; Selvankumar, T.; Sudhakar, C.; Ashokkumar, B.; Karthi, S. Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Garcinia Imberti Bourd and Their Impact on Root Canal Pathogens and HepG2 Cell Lines. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 34548–34555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaiah, V.; Harikrishnan, H.; Al-Harbi, N.S.; Shine, K.; Khaled, J.M.; Balasubramanian, N.; Kumar, R.S. Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Streptomyces sp. VSMGT1014 and their antimicrobial efficiency. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2015, 10, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Biocidal Properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, S.B.; Reed, S.I. Improved Flow Cytometric Analysis of the Budding Yeast Cell Cycle. Cell Cycle 2002, 1, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBel, C.P. Evaluation of the Probe 2’,7’-Dichiorofluorescin as an Indicator of Reactive Oxygen Species Formation and Oxidative Stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1992, 5, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.d.S.; Mano, J. Lipid Peroxide-Derived Reactive Carbonyl Species as Mediators of Oxidative Stress and Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 720867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayır, H.; Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Patel, S.J.; Amoscato, A.A.; Lamade, A.M.; Yang, Q.; Vladimirov, G.K.; Philpott, C.C.; Kagan, V.E. Achieving Life through Death: Redox Biology of Lipid Peroxidation in Ferroptosis. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbahnasawy, M.A.; Shehabeldine, A.M.; Khattab, A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Hashem, A.H. Green Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Novel Endophytic Rothia Endophytica: Characterization and Anticandidal Activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diameter of AgNPs (nm) | Geobacillus sp. 25 AgNPs | Geobacillus sp. 612 AgNPs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 M Sorbitol | YPD Medium | 1 M Sorbitol | YPD Medium | |
| <10 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 10–20 | 25 | 3 | 18 | 1 |
| 20–30 | 26 | 7 | 20 | 5 |
| 30–40 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 5 |
| 40–50 | 13 | 10 | 11 | 7 |
| 50–60 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 9 |
| 60–70 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| 70–80 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 5 |
| 80–90 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 |
| 90–100 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 5 |
| >100 | 8 | 48 | 13 | 57 |
| Geobacillus spp. Strain | 25 | 612 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution | |||
| 1 M sorbitol | −30.03 ± 0.05 | −30.13 ± 0.28 | |
| YPD medium | −30.93 ± 0.21 | −28.37 ± 0.14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čekuolytė, K.; Šapaitė, D.; Žemgulytė, E.; Gudiukaitė, R.; Lastauskienė, E. Induction of Apoptosis with Silver Nanoparticles Obtained Using Thermophilic Bacteria. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060142
Čekuolytė K, Šapaitė D, Žemgulytė E, Gudiukaitė R, Lastauskienė E. Induction of Apoptosis with Silver Nanoparticles Obtained Using Thermophilic Bacteria. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2024; 15(6):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060142
Chicago/Turabian StyleČekuolytė, Kotryna, Diana Šapaitė, Estera Žemgulytė, Renata Gudiukaitė, and Eglė Lastauskienė. 2024. "Induction of Apoptosis with Silver Nanoparticles Obtained Using Thermophilic Bacteria" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 15, no. 6: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060142
APA StyleČekuolytė, K., Šapaitė, D., Žemgulytė, E., Gudiukaitė, R., & Lastauskienė, E. (2024). Induction of Apoptosis with Silver Nanoparticles Obtained Using Thermophilic Bacteria. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 15(6), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060142






