Effects of Functional Biomaterials on the Attributes of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Loaded with Furosemide Nanoparticles: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Formulation and Optimization of the FUR Nanoparticles
2.2.2. Characterization of FUR Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Formulation of ODTs Loaded with FUR Nanoparticles by the Sublimation Method
2.2.4. In Vivo Study of Diuretic Activity in Rats
2.2.5. Stability Studies
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of FUR Nanoparticles
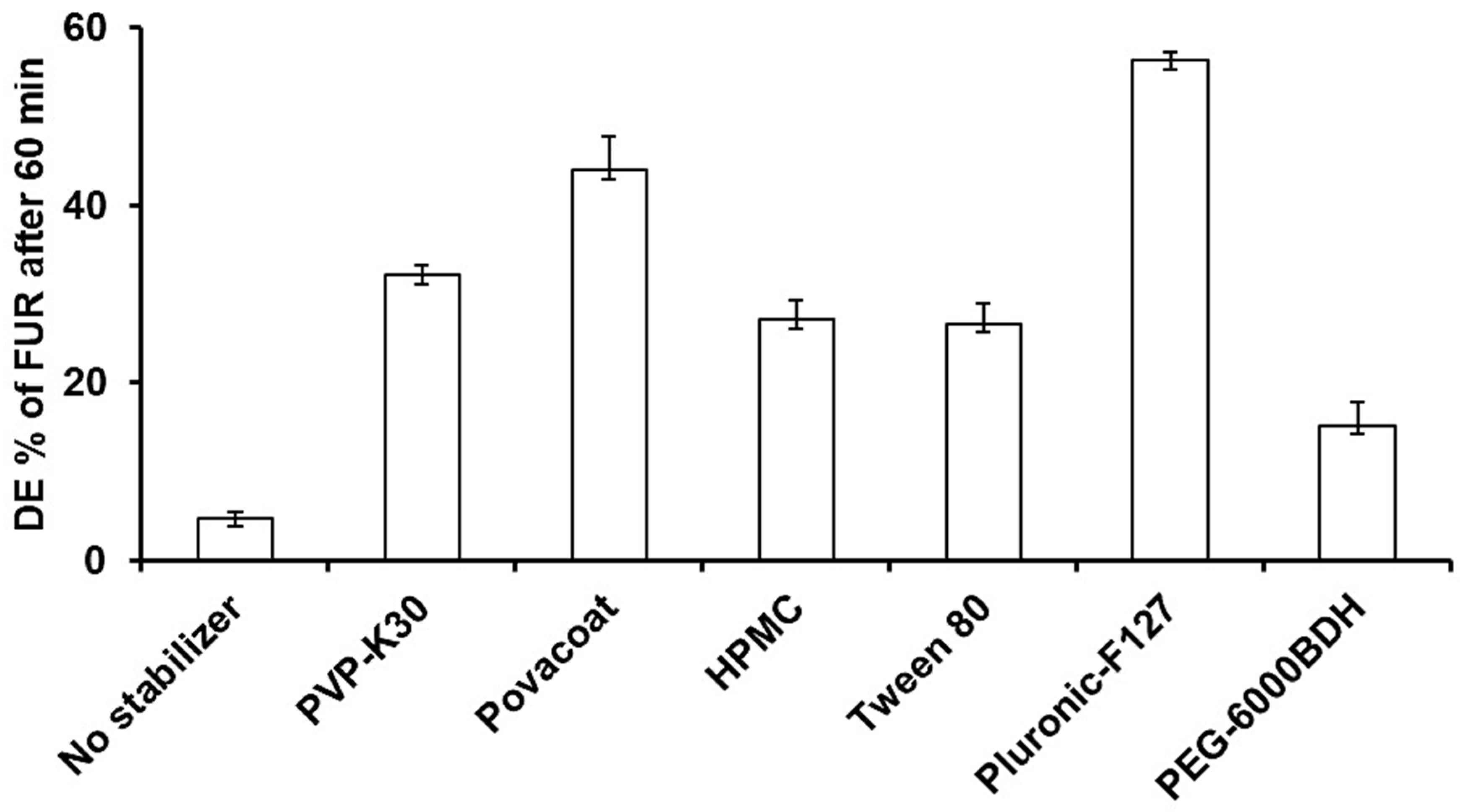
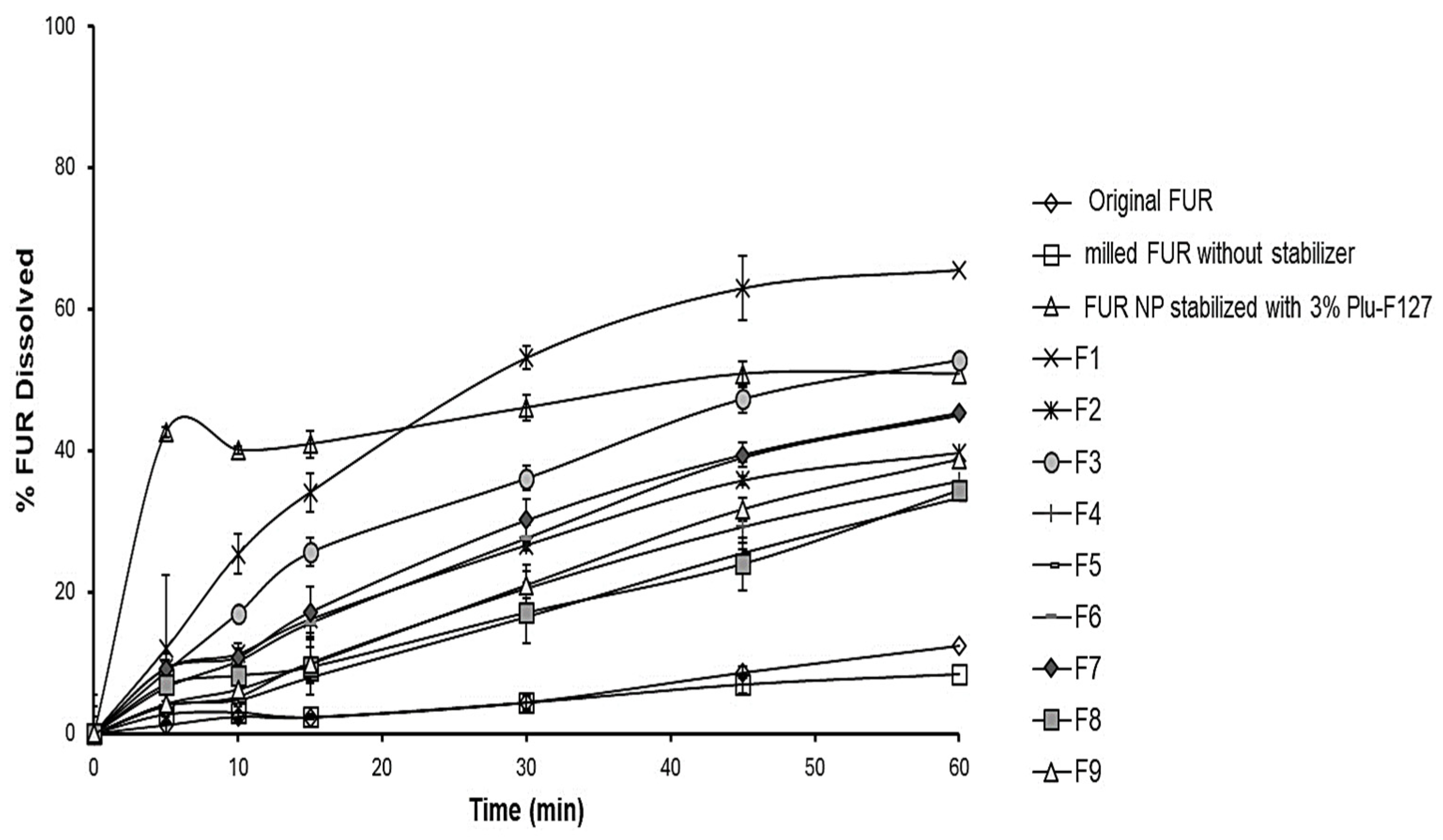
3.1.1. Effect of Different Stabilizer Types on FUR Nanoparticles’ Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Dissolution Rate
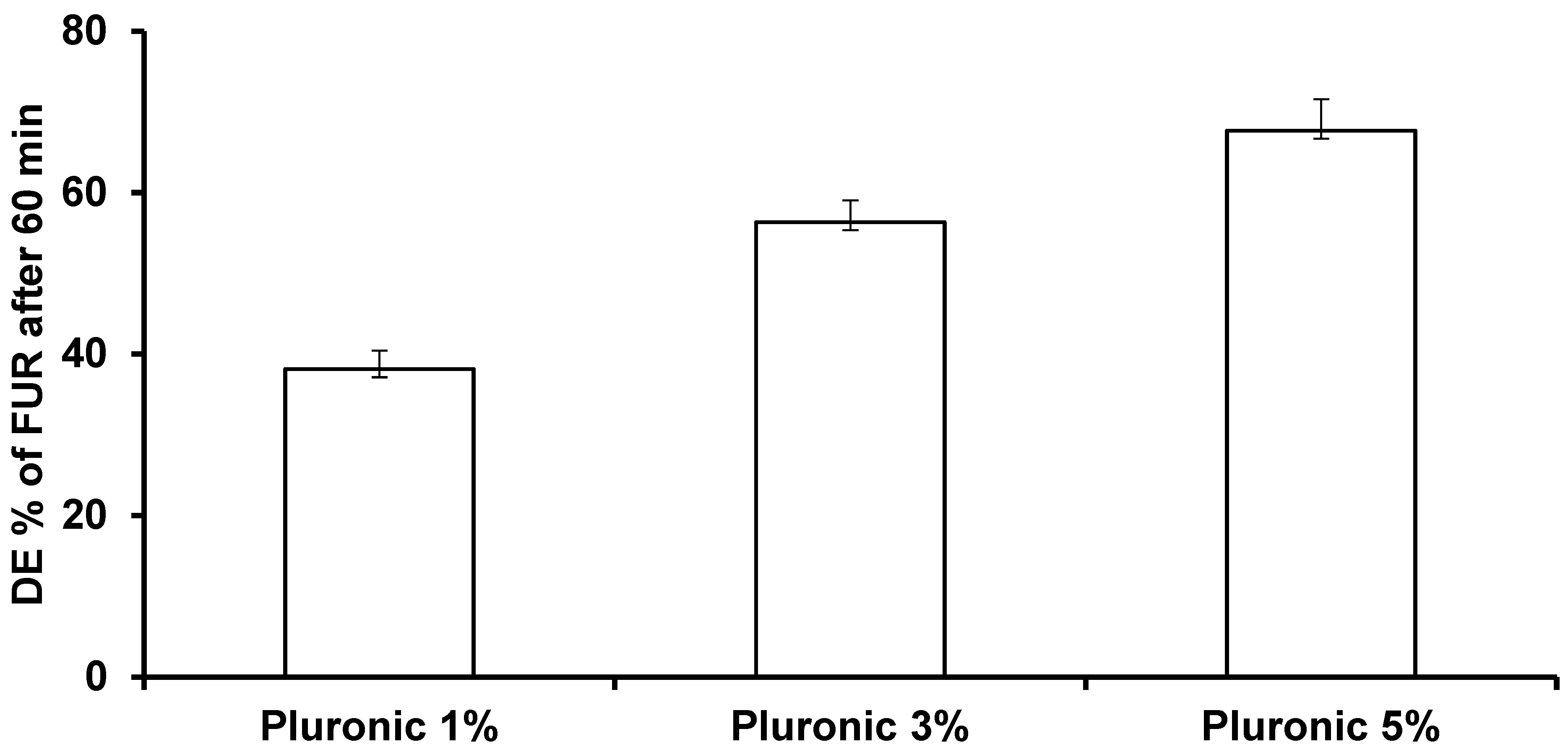
3.1.2. Effect of Different Concentrations of Pluronic F-127 on the FUR Nanoparticles’ Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Dissolution Rate
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Optimized FUR Nanoparticles after Freeze-Drying
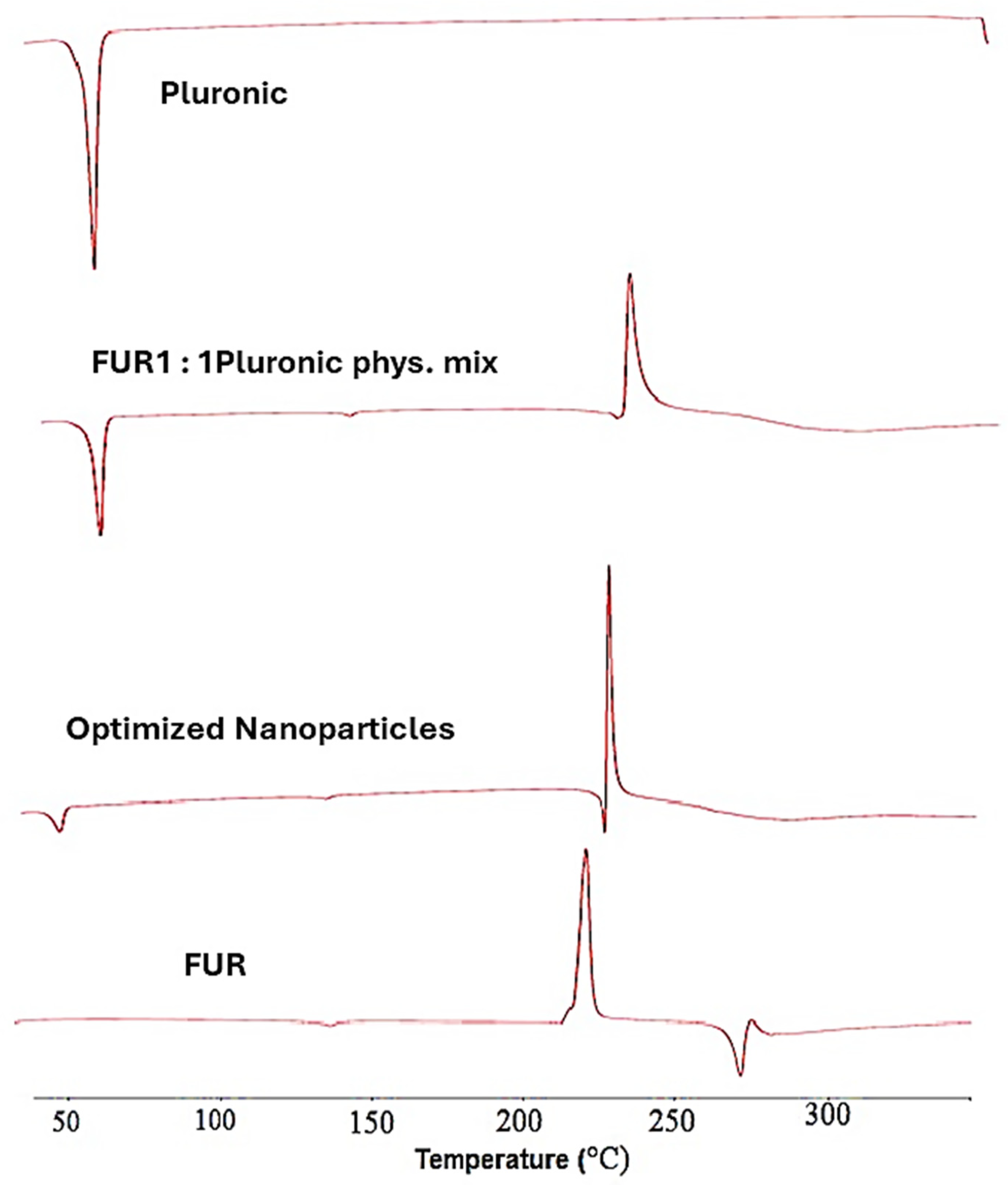
3.2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT)
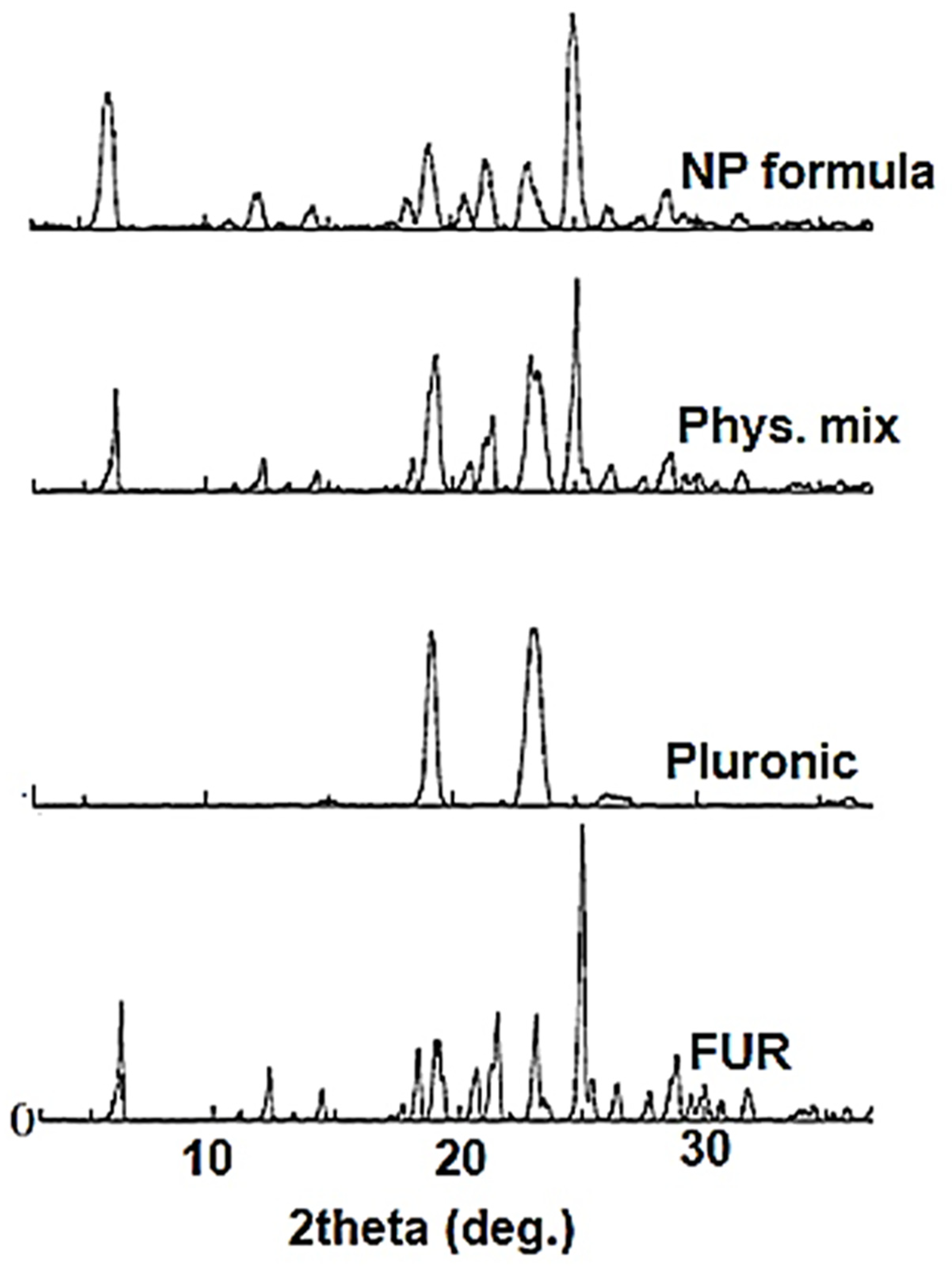
3.2.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.3. ODT Formulations Loaded with FUR Nanoparticles by the Sublimation Method
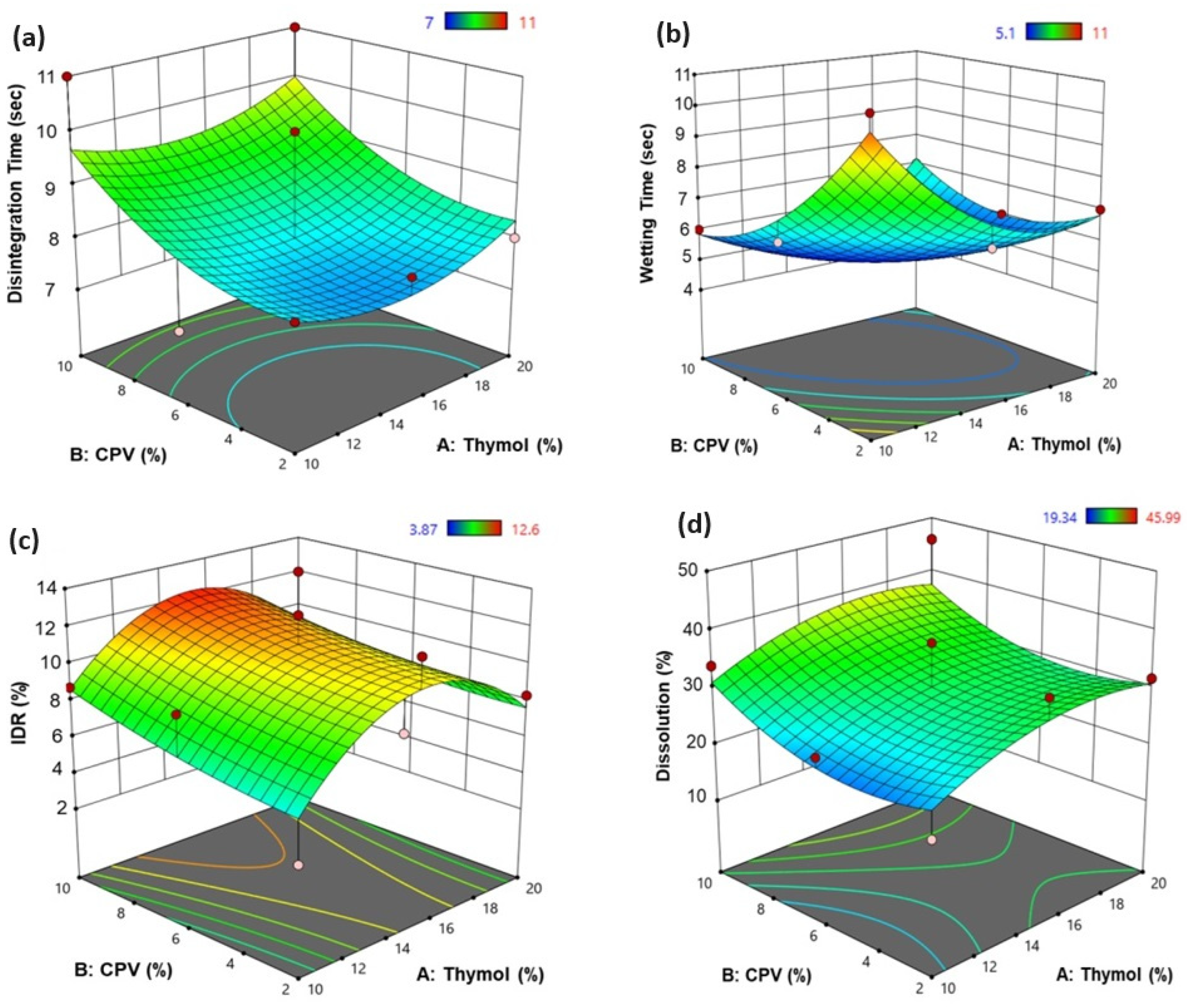
3.3.1. Effect of Each Independent Parameter on the Disintegration Time
3.3.2. Effect of Each Independent Parameter on the Wetting Time
3.3.3. Effect of Each Independent Parameter on the Initial Dissolution Rate
3.3.4. Effect of Each Independent Parameter on the Dissolution Efficiency, DE60%
3.4. Optimization of FUR ODT
3.5. Pharmacodynamics Evaluation of Diuretic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.S.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, C.M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Böhm, M.; Butler, J.; et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: A report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure: Endorsed by the Canadian Heart Failure Society, Heart Failure Association of India, Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and Chinese Heart Failure Association. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 352–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atherton, J.J.; Sindone, A.; De Pasquale, C.G.; Driscoll, A.; MacDonald, P.S.; Hopper, I.; Kistler, P.M.; Briffa, T.; Wong, J.; Abhayaratna, W.; et al. National Heart Foundation of Australia and Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand: Guidelines for the prevention, detection, and management of heart failure in Australia 2018. Heart Lung Circ. 2018, 27, 1123–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, W.; Damman, K.; Harjola, V.P.; Mebazaa, A.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.-P.; Martens, P.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.H.W.; Orso, F.; Rossignol, P.; et al. The use of diuretics in heart failure with congestion—A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felker, G.M.; Ellison, D.H.; Mullens, W.; Cox, Z.L.; Testani, J.M. Diuretic therapy for patients with heart failure: JACC Stateof-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannenfelser, R.M.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Data base of aqueous solubility for organic non-electrolytes. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 109–110, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshora, D.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Alanazi, F.K. Nanotechnology from particle size reduction to enhancing aqueous solubility. In Surface Chemistry of Nanobiomaterials. Application of Nanobiomaterials; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 163–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, P.R.; Karimunnisa, S.S.; Pravin, D.C. Application of liquisolid technology for enhancing solubility and dissolution of rosuvastatin. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Alshora, D.H.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Elzayat, E.; Almeanazel, O.T.; Alanazi, F. Rosuvastatin calcium nanoparticles: Improving bioavailability by formulation and stabilization codesign. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshora, D.H.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Elzayat, E.; Almeanazel, O.T.; Alanazi, F. Defining the process parameters affecting the fabrication of rosuvastatin calcium nanoparticles by planetary ball mill. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4625–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshora, D.; Alsaif, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Ezzeldin, E.; Almeanazel, O.T.; Abou El Ela, A.E.S.; Ashri, L.Y. Co-stabilization of pioglitazone HCL nanoparticles prepared by planetary ball milling: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Pharm. Develop. Technol. 2020, 25, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppersack, C.; Flach, F.; Prziwara, P.; Damm, C.; Breitung-Faes, S.; Peukert, W.; Kwade, A. Conceptual stabilizer selection for nanomilling based on dispersibility parameters. Adv. Powder Tech. 2023, 34, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tho, I. Orally disintegrating tablets—Advantages and drawbacks. NIH 2012, 132, 424–425. [Google Scholar]
- Dalavi, A.; Mahale, A. Fast Dissolving Tablet by Sublimation Technique: A Review. JETIR 2022, 9, c887–c897. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.A. The concept of dissolution efficiency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1975, 27, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.; Gardouh, A.R.; Abogresha, N.M.; Gad, S. Factorial design, formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of rapid orally disintegrating tablets prepared by sublimation technique using captopril as a model drug. JDDST 2020, 57, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. 〈905〉 Uniformity of Dosage Units; The United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shoukri, R.A.; Ahmed, I.S.; Shamma, R.N. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of nimesulide lyophilized orally disintegrating tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Deng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yan, G.; Deng, X.; Wu, L.; Liang, Q.; Fang, F.; Feng, X.; Yu, M.; et al. Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation of Orally Disintegrating/Modified-Release Praziquantel Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipschitz, W.L.; Hadidian, Z.; Kerpcsar, A. Bioassay of diuretics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1943, 79, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. Stability of nanosuspensions in drug delivery. J. Control Release 2013, 172, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Rong, X.; Laru, J.; Van Veen, B.; Kiesvaara, J.; Hirvonen, J.; Laaksonen, T.; Peltonen, L. Nanosuspensions of poorly soluble drugs: Preparation and development by wet milling. Int J Pharm 2011, 411, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomela, A.; Hirvonen, J.; Peltonen, L. Stabilizing Agents for Drug Nanocrystals: Effect on Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeike, J.; Müllera, R. Nanosuspensions a promising formulation for the new phospholipase A2 inhibitor PX-18. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 31, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfandi, E.; Ramezani, V.; Vatanara, A.; Rouholamini, A.; Hadipour, S.P. Clarithromycin dissolution enhancement by preparation of aqueous nanosuspensions using sonoprecipitation technique. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barick, P.; Saha, B.P.; Mitra, R.; Joshi, S.V. Effect of concentration and molecular weight of polyethylenimine on zeta potential, isoelectric point of nanocrystalline silicon carbide in aqueous and ethanol medium. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 4289–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboutaleb, A.E.; Abdel-Rahman, S.I.; Ahmed, M.O.; Younis, M.A. Improvement of Domperidone Solubility and Dissolution Rate by Dispersion in Various Hydrophilic Carriers. JAPS 2016, 6, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boles, P.L.; Schoenwald, R.D. Furosemide (fusemide): A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic review. Part I. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 18, 381–408. [Google Scholar]
- Spamer, E.; Müller, D.G.; Wessels, P.L.; Venter, J.P. Characterization of the complexes of furosemide with 2-hydroxypropyl-bcyclodextrin and sulfobutylether-7-b-cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 16, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; El Sayeh, A.F. Optimized furosemide taste masked orally disintegrating tablets. SPJ 2017, 25, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farcas, A.; Jarroux, N.; Farcas, A.M.; Guegan, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Furosemide Complex in ß-Cyclodextrain. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2006, 1, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.P.; Patel, D.J.; Bhimani, D.B.; Patel, J.K. Physicochemical characterization and dissolution study of solid dispersions of furosemide with polyethylene glycol 6000 and polyvinylpyrrolidone K30. Dissolution Technol. 2008, 15, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, K.S. Formulation and Pharmacokinetics of Flurbiprofen Sublimated Fast Dissolving Tablets. Open Pharm. Sci. J. 2015, 2, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thio, D.R.; Heng, P.W.; Chan, L.W. MUPS Tableting-Comparison between Crospovidone and Microcrystalline Cellulose Core Pellets. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, N.; Morin, M.; Bjork, E.; Edsman, K. Physicochemical interactions between drugs and superdisintegrants. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahrous, G.M.; Kassem, M.G.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Auda, S. Formulation and evaluation of orally disintegrating clopidogrel tablets. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kuo, G.; Chang, C.H. Diuretic effect of co-administration of furosemide and albumin in comparison to furosemide therapy alone: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capogrosso, P.; Ventimiglia, E.; Boeri, L.; Serino, A.; Russo, A.; La Croce, G.; Capitanio, U.; Dehò, F.; Montorsi, F.; Salonia, A. Time of onset of vardenafil orodispersible tablet in a real-life setting—Looking beyond randomized clinical trials. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Independent Parameters | Low Level (−1) | Medium Level (0) | High Level (+1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thymol (A) (%) | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| CPV (B) (%) | 2 | 6 | 10 |
| Dependent Parameters Disintegration time (S) Wetting time (S) IDR (%) DE (%) | |||
| Formula | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUR NPs | Equivalent to 20 mg | ||||||||
| Thymol (%) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| CPV (%) | 2 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 6 |
| Sodium Stearyl Fumarate (SSF) | 1% | ||||||||
| Filler (Avicel–Lactose) (1:1) | To 200 mg | ||||||||
| Stabilizer | Type of Stabilizer | Particle Size Avg ± SD (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | DE60% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No stabilizer | - | 1170.33 ± 30.99 | −6.72 ± 4.42 | 4.77 ± 0.71 |
| PVP K30 | Steric | 300.87 ± 9.13 | −10.3 ± 5.81 | 32.15 ± 1.13 |
| Povacoat | Steric | 559.17 ± 19.93 | −14.9 ± 4.07 | 43.95 ± 3.83 |
| HPMC | Steric | 470.73 ± 76.38 | −11.5 ± 4.11 | 27.14 ± 2.12 |
| Tween 80 | Static | 655.53 ± 46.92 | −5.03 ± 3.82 | 26.65 ± 2.20 |
| PEG-6000 BDH | Steric | 2053 ± 264.78 | −32.6 ± 4.8 | 15.17 ± 0.95 |
| Pluronic F-127 | Steric | 354.07 ± 6.44 | −25.3 ± 5.65 | 56.34 ± 2.68 |
| Stabilizer | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | DE60% |
|---|---|---|---|
| No stabilizer | 1170.33 ± 30.99 | −6.72 ± 4.42 | 4.77 ± 0.71 |
| Pluronic F127 1% | 412.73 ± 45.14 | −21.3 ± 4.42 | 38.13 ± 2.32 |
| Pluronic F-127 3% | 354.07 ± 6.44 | −25.3 ± 5.65 | 56.34 ± 2.68 |
| Pluronic F-127 5% | 434.57 ± 40.17 | −19.2 ± 6.23 | 67.67 ± 3.89 |
| Formula (Thymol/CPV) (%) | Drug Content (AV) | Weight Variation | Disintegration Time (s) | Wetting Time (s) | IDR% | DE60% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (15/2) | 5.5 | 0.1912 | 8 | 6.5 | 12.16 ± 2.01 | 34.88 ± 0.16 |
| F2 (15/6) | 10.99 | 0.1784 | 10 | 5.8 | 12.6 ± 4.66 | 37.87 ± 2.59 |
| F3 (15/10) | 7.07 | 0.18793 | 7 | 5.1 | 9.17 ± 1.03 | 26.56 ± 1.66 |
| F4 (20/2) | 13.31 | 0.1922 | 8 | 7 | 8.31 ± 1.09 | 31.73 ± 0.65 |
| F5 (20/10) | 12.6 | 0.1989 | 11 | 7 | 12.01 ± 5.4 | 45.99 ± 4.5 |
| F6 (10/6) | 14.27 | 0.1948 | 7 | 6.5 | 9.24 ± 2.3 | 24.98 ± 0.64 |
| F7 (10/10) | 3.17 | 0.1978 | 11 | 6 | 8.74 ± 0.83 | 33.88 ± 1.99 |
| F8 (10/2) | 15 | 0.1901 | 8 | 11 | 3.87 ± 0.11 | 19.34 ± 2.23 |
| F9 (20/6) | 13.42 | 0.2039 | 8 | 6 | 4.17 ± 1.00 | 20.51 ± 1.62 |
| Source | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disintegration Time | A-Thymol | 0.166 | 0.03 | 0.8653 |
| B-CPV | 4.17 | 0.85 | 0.4240 | |
| AB | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.0000 | |
| A2 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.7701 | |
| B2 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.7701 | |
| Wetting Time | A-Thymol | 2.04 | 3.53 | 0.1570 |
| B-CPV | 6.83 | 11.79 | 0.0414 | |
| AB | 6.25 | 10.80 | 0.0462 | |
| A2 | 4.21 | 7.26 | 0.0741 | |
| B2 | 2.00 | 3.45 | 0.1600 | |
| IDR % | A-Thymol | 1.16 | 0.0704 | 0.8080 |
| B-CPV | 5.19 | 0.3144 | 0.6142 | |
| AB | 0.342 | 0.0207 | 0.8946 | |
| A2 | 25.73 | 1.56 | 0.3004 | |
| B2 | 0.278 | 0.0169 | 0.9048 | |
| DE % | A-Thymol | 66.87 | 0.5068 | 0.5279 |
| B-CPV | 69.91 | 0.5298 | 0.5193 | |
| AB | 0.0196 | 0.0001 | 0.9910 | |
| A2 | 27.36 | 0.2073 | 0.6798 | |
| B2 | 36.58 | 0.2772 | 0.6350 |
| Optimized Formula Composition | Response | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Desirability | Predicted | Observed | |
| Thymol (A) = 15.39% CPV (B) = 9.13% | Y1: Disintegration time (s) | Minimum | 8.97 | 10 |
| Y2: Wetting time (s) | Minimum | 4.95 | 5.7 | |
| Y3: IDR (%) | Maximum | 12.013 | 10.29 ± 2.15 | |
| Y4: DE60 (%) | Maximum | 35.78 | 22.14 ± 2.64 | |
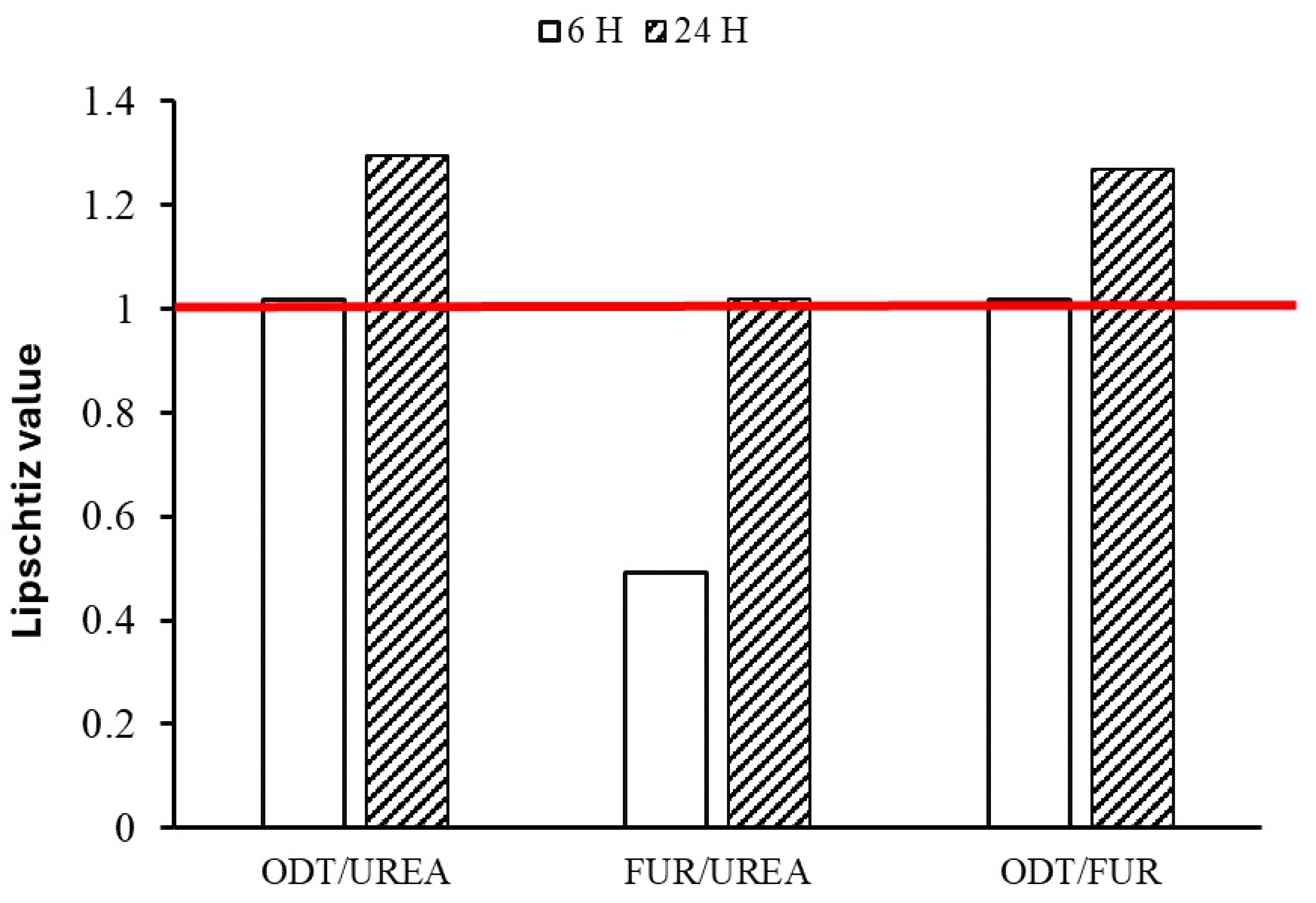
| Group | Urinary Excretion (%) | Diuretic Action | Diuretic Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6th Hour | 24th Hour | 6th Hour | 24th Hour | 6th Hour | 24th Hour | |
| Group I, urea | 7 ± 0.22 | 7.28 ± 0.62 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Group II, pure FUR | 2.18 ± 0.91 | 6.62 ± 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.90 | NA | NA |
| Group III, ODT FUR NPs | 7.08 ± 0.11 | 11.48 ± 0.11 | 1.01 | 1.57 | 3.23 | 1.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshora, D.; Alyousef, W.; Ibrahim, M. Effects of Functional Biomaterials on the Attributes of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Loaded with Furosemide Nanoparticles: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060161
Alshora D, Alyousef W, Ibrahim M. Effects of Functional Biomaterials on the Attributes of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Loaded with Furosemide Nanoparticles: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2024; 15(6):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060161
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshora, Doaa, Wejdan Alyousef, and Mohamed Ibrahim. 2024. "Effects of Functional Biomaterials on the Attributes of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Loaded with Furosemide Nanoparticles: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 15, no. 6: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060161
APA StyleAlshora, D., Alyousef, W., & Ibrahim, M. (2024). Effects of Functional Biomaterials on the Attributes of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Loaded with Furosemide Nanoparticles: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 15(6), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15060161







