Biophysical Properties of Lumbricus terrestris Erythrocruorin and Its Potential Use as a Red Blood Cell Substitute
Abstract
:1. Extracellular Hemoglobins: A New Paradigm
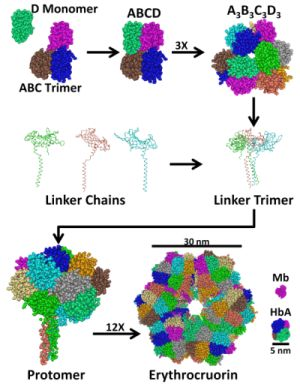
2. Structure and Stability of LtEc

| MW (kDa) | Diameter (nm) | P50 (mm Hg) | n(---) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA | 64 | 5 | 11 | 2.7 |
| AmEc | 3,600 [39] | 30 [39] | 2.6 | 2.5 [39] |
| LtEc | 3,600 | 30 | 28 [40] | 3.7 |
| RBC | --- | 8,000 | 26 [41] | 2.75 [41] |
3. O2 Transport by LtEc
4. Autoxidation of LtEc
| kox (h−1) | Eo (mV) | |
|---|---|---|
| HbA | 0.014 [39] | −50 [53] |
| LtEc | ≤0.010 | +112 [53] |
| AmEc | 0.005 [56] | +63 [53] |
5. Interactions Between LtEc and other Ligands
6. Availability and Economic Analysis of LtEc
7. Preliminary Animal Studies with Ec’s
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Greenburg, A.G.; Kim, H.W. Hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Crit. Care 2004, 8, S61–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.C.; Mazer, C.D.; Martineau, R.; Ralph-Edwards, A.; Karski, J.; Robblee, J.; Finegan, B.; Hall, R.I.; Latimer, R.; Vuylsteke, A. A phase II dose-response study of hemoglobin raffimer (Hemolink) in elective coronary artery bypass surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 127, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, R.M. Red cell substitutes. Semin. Hematol. 2007, 44, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, A.; Menu, P.; Faivre-Fiorina, B.; Labrude, P.; Alayash, A.I.; Vigneron, C. Cardiovascular and hemorheological effects of three modified human hemoglobin solutions in hemodiluted rabbits. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 86, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, S.M.; Grune, F.; Walter, M.; Amr, N.; Erasmi, H.; Buzello, W. The effects of increased doses of bovine hemoglobin on hemodynamics and oxygen transport in patients undergoing preoperative hemodilution for elective abdominal aortic surgery. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 87, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.H.; Goodnough, L.T.; Greilich, P.E.; Parr, G.V.; Stewart, R.W.; Gratz, I.; Wahr, J.; Williams, J.; Comunale, M.E.; Doblar, D.; et al. Polymerized bovine hemoglobin solution as a replacement for allogeneic red blood cell transfusion after cardiac surgery: Results of a randomized, double-blind trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 124, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamuraglia, G.M.; O'hara, P.J.; Baker, W.H.; Naslund, T.C.; Norris, E.J.; Li, J.; Vandermeersch, E. The reduction of the allogenic transfusion requirement in aortic surgery with a hemoglobin-based solution. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprung, J.; Kindscher, J.D.; Wahr, J.A.; Levy, J.H.; Monk, T.G.; Moritz, M.W.; O’hara, P.J. The use of bovine hemoglobin glutamer-250 (Hemopure) in surgical patients: Results of a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded tria. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegriff, K.D.; Malavalli, A.; Wooldridge, J.; Lohman, J.; Winslow, R.M. MP4, a new nonvasoactive PEG-Hb conjugate. Transfusion 2003, 43, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegriff, K.D.; Young, M.A.; Keipert, P.E.; Winslow, R.M. The safety profile of Hemospan®: A new oxygen therapeutic designed using maleimide poly(ethylene) glycol conjugation to human hemoglobin. Transfus. Altern. Transfus. Med. 2007, 9, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegriff, K.D.; Winslow, R.M. Hemospan: Design principles for a new class of oxygen therapeutic. Artif. Organs 2009, 33, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegriff, K.D.; Malavalli, A.; Minn, C.; Jiang, E.; Lohman, J.; Young, M.A.; Samaja, M.; Winslow, R.M. Oxidation and haem loss kinetics of poly(ethylene glycol)-conjugated haemoglobin (MP4): Dissociation between in vitro and in vivo oxidation rates. Biochem. J. 2006, 399, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natanson, C.; Kern, S.J.; Lurie, P.; Banks, S.M.; Wolfe, S.M. Cell-free hemoglobin-based blood substitutes and risk of myocardial infarction and death: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2008, 299, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yubisui, T.; Matsuki, T.; Tanishima, K.; Takeshita, M.; Yoneyama, Y. NADPH-flavin reductase in human erythrocytes and the reduction of methemoglobin through flavin by the enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1977, 76, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuma, F. Properties of methemoglobin reductase and kinetic study of methemoglobin reduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 5518–5523. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, M.D.; Lubin, B.H.; Zuo, L.; Kuypers, F.A. Erythrocyte defense against hydrogen peroxide: Preeminent importance of catalase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1991, 118, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Miller, M.J.; Joshi, M.S.; Sadowska-Krowicka, H.; Clark, D.A.; Lancaster, J.R., Jr. Diffusion-limited reaction of free nitric oxide with erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18709–18713. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, H.F.; Briehl, R.W. The interaction of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate with various human hemoglobins. J. Clin. Invest. 1970, 49, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiancone, E. Dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. II. Human oxyhemoglobin: Gel filtration studies. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger, R.C. Structures of invertebrate hemoglobins. Am. Zool. 1980, 20, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Boffi, A.; Verzili, D.; Chiancone, E.; Leone, M.; Cupane, A.; Militello, V.; Vitrano, E.; Cordone, L.; Yu, W.; di Iorio, E.E. Stereodynamic properties of the cooperative homodimeric Scapharca inaequivalvis hemoglobin studied through optical absorption spectroscopy and ligand rebinding kinetics. Biophys. J. 1994, 67, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, E.; Tavernelli, I.; Yu, W. Dynamic properties of monomeric insect erythrocruorin III from Chironomus thummi-thummi: Relationships between structural flexibility and functional complexity. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zal, F.; Lallier, F.H.; Wall, J.S.; Vinogradov, S.N.; Toulmond, A. The multi-hemoglobin system of the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila. I. Reexamination of the number and masses of its constituents. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8869–8874. [Google Scholar]
- Royer, W.E., Jr.; Sharma, H.; Strand, K.; Knapp, J.E.; Bhyravbhatla, B. Lumbricus erythrocruorin at 3.5 A resolution: Architecture of a megadalton respiratory complex. Structure 2006, 14, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, W.E.; Omartian, M.N.; Knapp, J.E. Low resolution crystal structure of Arenicola erythrocruorin: Influence of coiled coils on the architecture of a megadalton respiratory protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 365, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwilliger, N.; Terwilliger, R.C. Oxygen binding domains of a clam (Cardita borealis) extracellular hemoglobin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 537, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, J.-S.; Yang, D. A new strategy for structure determination of large proteins in solution without deuteration. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, W.E. J.; Strand, K.; van Heel, M.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structural hierarchy in erythrocruorin, the giant respiratory assemblage of annelids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7101–7111. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, K.; Knapp, J.E.; Bhyravbhatla, B.; Royer, W.E., Jr. Crystal structure of the hemoglobin dodecamer from Lumbricus erythrocruorin: Allosteric core of giant annelid respiratory complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 344, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushitani, K.; Matsuura, M.S.; Riggs, A.F. The amino acid sequences of chains a, b, and c that form the trimer subunit of the extracellular hemoglobin from Lumbricus terrestris. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 6502–6517. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Donahue, R.A., Jr.; Schneider, K.; Mirza, U.A.; Haller, I.; Chait, B.T.; Riggs, A.F. Structure of chain d of the gigantic hemoglobin of the earthworm. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1337, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Riggs, A.F. Linker chain L1 of earthworm hemoglobin. Structure of gene and protein: Homology with low density lipoprotein receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 13548–13555. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, W.Y.; Qin, J.; Fushitani, K.; Smith, S.S.; Gorr, T.A.; Riggs, C.K.; Knapp, J.E.; Chait, B.T.; Riggs, A.F. Linker chains of the gigantic hemoglobin of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris: Primary structures of linkers L2, L3, and L4 and analysis of the connectivity of the disulfide bonds in linker L1. Proteins 2006, 63, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Kuchumov, A.R.; Chottard, G.; Martin, P.D.; Wall, J.S.; Vinogradov, S.N. The role of the dodecamer subunit in the dissociation and reassembly of the hexagonal bilayer structure of Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8754–8762. [Google Scholar]
- Lamy, M.L.; Daily, E.K.; Brichant, J.F.; Larbuisson, R.P.; Demeyere, R.H.; Vandermeersch, E.A.; Lehot, J.J.; Parsloe, M.R.; Berridge, J.C.; Sinclair, C.J.; et al. Randomized trial of diaspirin cross-linked hemoglobin solution as an alternative to blood transfusion after cardiac surgery. The DCLHb cardiac surgery trial collaborative group. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numoto, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Kita, A.; Sasayama, Y.; Fukumori, Y.; Miki, K. Structure of an extracellular giant hemoglobin of the gutless beard worm Oligobrachia mashikoi. Proc. Natl. Acad.Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14521–14526. [Google Scholar]
- Lamy, J.; Kuchumov, A.R.; Taveau, J.C.; Vinogradov, S.N.; Lamy, J.N. Reassembly of Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin: A study by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and 3D reconstruction from frozen-hydrated specimens. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 298, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birukou, I.; Soman, J.; Olson, J.S. Blocking the gate to ligand entry in human hemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10515–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselot, M.; Delpy, E.; Drieu La Rochelle, C.; Lagente, V.; Pirow, R.; Rees, J.F.; Hagege, A.; Le Guen, D.; Hourdez, S.; Zal, F. Arenicola marina extracellular hemoglobin: A new promising blood substitute. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.E.; Jelicks, L.A.; Wittenberg, B.A.; Kaul, D.K.; Shear, H.L.; Harrington, J.P. A first evaluation of the natural high molecular weight polymeric Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin as an oxygen carrier. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 1997, 25, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapletal, C.; Bode, A.; Lorenz, M.W.; Gebhard, M.M.; Golling, M. Effects of hemodilution with a hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier (HBOC-201) on ischemia/reperfusion injury in a model of partial warm liver ischemia of the rat. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 78, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standley, P.; Mainwaring, M.G.; Gotoh, T.; Vinogradov, S.N. The calcium, copper and zinc content of some annelid extracellular haemoglobins. Biochem. J. 1988, 249, 915–916. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, J.P. Multimeric Lumbricus hemoglobin stabilization by alkali and alkaline earth cations. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1994, 109, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiancone, E.; Vecchini, P.; Rossi Fanelli, M.R.; Antonini, E. Studies on erythrocruorin. II. Dissociation of earthworm erythrocruorin. J. Mol. Biol. 1972, 70, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.L.; Paul, J.; Ohlsson, P.I.; Paul, K.G. The spontaneous hemin release from Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1997, 118, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushitani, K.; Imai, K.; Riggs, A.F. Oxygenation properties of hemoglobin from the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris. Effects of pH, salts, and temperature. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 8414–8423. [Google Scholar]
- Ochiai, T.; Weber, R.E. Effects of magnesium and calcium on the oxygenation reaction of erythrocruorin from the marine polychaete Arenicola marina and the terrestrial oligochaete Lumbricus terrestris. Zool. Sci. 2002, 19, 999–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Vidugiris, G.; Harrington, J.P.; Friedman, J.M.; Hirsch, R.E. Absence of ligand binding-induced tertiary changes in the multimeric earthworm Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin. A resonance Raman study. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 26190–26192. [Google Scholar]
- Fushitani, K.; Riggs, A.F. The extracellular hemoglobin of the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris. Oxygenation properties of isolated chains, trimer, and a reassociated product. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 10275–10281. [Google Scholar]
- Alayash, A.I. Hemoglobin-based blood substitutes and the hazards of blood radicals. Free Radic. Res. 2000, 33, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellwagen, E. Haem exposure as the determinate of oxidation-reduction potential of haem proteins. Nature 1978, 275, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, A.J.; Payson, A.P.; Bonaventura, J. Invertebrate hemoglobins and nitric oxide: How heme pocket structure controls reactivity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.P.; Kobayashi, S.; Dorman, S.C.; Zito, S.L.; Hirsch, R.E. Acellular invertebrate hemoglobins as model therapeutic oxygen carriers: Unique redox potentials. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2007, 35, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, S.C.; Kenny, C.F.; Miller, L.; Hirsch, R.E.; Harrington, J.P. Role of redox potential of hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers on methemoglobin reduction by plasma components. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2002, 30, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, S.C.; Harrington, J.P.; Martin, M.S.; Johnson, T.V. Determination of the formal reduction potential of Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin using thin layer spectroelectrochemistry. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, T.; Rousselot, M.; Rogniaux, H.; Zal, F. High-level production of recombinant Arenicola marina globin chains in Escherichia coli: A new generation of blood substitute. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2009, 37, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liochev, S.I.; Kuchumov, A.R.; Vinogradov, S.N.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase activity in the giant hemoglobin of the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 330, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, G.M.; Focesi, A., Jr.; Brunori, M.; Wyman, J. Effect of light on carbon monoxide binding by erythrocruorin. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 98, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Giacometti, G.M.; Focesi, A.; Giardina, B.; Brunori, M.; Wyman, J. Kinetics of binding of carbon monoxide to lumbricus erythrocruorin: A possible model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 4313–4316. [Google Scholar]
- Eich, R.; Li, T.; Lemon, D.D.; Doherty, D.H.; Curry, S.; Aitken, J.F.; Johnson, K.A.; Smith, R.D.; Phillips, G.N., Jr.; Olson, J.S. Mechanism of NO-induced oxidation of myoglobin and hemoglobin. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 6976–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S.; Eich, R.F.; Smith, L.P.; Warren, J.J.; Knowles, B.C. Protein engineering strategies for designing more stable hemoglobin-based blood substitutes. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 1997, 25, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, J.; Zorc, K.; Rameez, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cabrales, P.; Palmer, A.F. Hypervolemic infusion of Lumbricus terrestris erythrocruorin purified by tangential flow filtration. Transfusion 2012, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, P.S.; Carvalho, J.W.; Domingues, M.M.; Santos, N.C.; Tabak, M. Thermal stability of extracellular hemoglobin of Glossoscolex paulistus: Determination of activation parameters by optical spectroscopic and differential scanning calorimetric studies. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 152, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourdez, S.; Weber, R.E. Molecular and functional adaptations in deep-sea hemoglobins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachega, J.F.R.; Bleicher, L.; Horjales, E.R.; Santiago, P.S.; Garratt, R.C.; Tabak, M. Crystallization and preliminary structural analysis of the giant haemoglobin from Glossoscolex paulistus at 3.2 Å. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2010, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, A.L.; Moreira, L.M.; Hidalgo, A.A.; Imasato, H. Autoxidation studies of extracellular hemoglobin of Glossoscolex paulistus at pH 9: Cyanide and hydroxyl effect. Biophys. Chem. 2005, 114, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.L.; Moreira, L.M.; Imasato, H. Autoxidation of giant extracellular hemoglobin of Glossoscolex paulistus: Molecular mechanism and oligomeric implications. Spectrochim. Acta A 2011, 82, 306–315. [Google Scholar]
- Agustinho, S.C.; Tinto, M.H.; Imasato, H.; Tominaga, T.T.; Perussi, J.R.; Tabak, M. Spectroscopic studies of the met form of the extracellular hemoglobin from Glossoscolex paulistus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1298, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bispo, J.A.; Santos, J.L.; Landini, G.F.; Goncalves, J.M.; Bonafe, C.F. pH dependence of the dissociation of multimeric hemoglobin probed by high hydrostatic pressure. Biophys. Chem. 2007, 125, 341–349. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, L.M.; Poli, A.L.; Lyon, J.P.; Saade, J.; Costa-Filho, A.J.; Imasato, H. Ferric species of the giant extracellular hemoglobin of Glossoscolex paulistus as function of pH: An EPR study on the irreversibility of the heme transitions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2008, 150, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardillo, F.; de Paula, E.; Oliveira, G.R.; Marangoni, S.; Oliviera, B.; Meirelles, N.C. Erythrocruorin of Glossoscolex paulistus (Oligochaeta, Glossoscolecidae): Modulation of oxygen affinity by specific antibodies. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1997, 41, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Bonafe, C.F.; Villas-Boas, M.; Suarez, M.C.; Silva, J.L. Reassembly of a large multisubunit protein promoted by nonprotein factors. Effects of calcium and glycerol on the association of extracellular hemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 13210–13216. [Google Scholar]
- Shander, A.; Hofmann, A.; Gombotz, H.; Theusinger, O.M.; Spahn, D.R. Estimating the cost of blood: Past, present, and future directions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2007, 21, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmer, J.; Palmer, A.F. Biophysical Properties of Lumbricus terrestris Erythrocruorin and Its Potential Use as a Red Blood Cell Substitute. J. Funct. Biomater. 2012, 3, 49-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3010049
Elmer J, Palmer AF. Biophysical Properties of Lumbricus terrestris Erythrocruorin and Its Potential Use as a Red Blood Cell Substitute. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2012; 3(1):49-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmer, Jacob, and Andre F. Palmer. 2012. "Biophysical Properties of Lumbricus terrestris Erythrocruorin and Its Potential Use as a Red Blood Cell Substitute" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 3, no. 1: 49-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3010049
APA StyleElmer, J., & Palmer, A. F. (2012). Biophysical Properties of Lumbricus terrestris Erythrocruorin and Its Potential Use as a Red Blood Cell Substitute. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 3(1), 49-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3010049