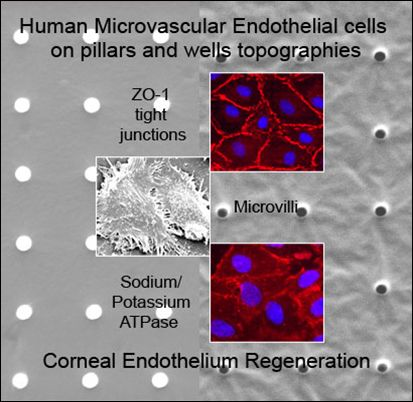
Cultivation of Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells on Topographical Substrates to Mimic the Human Corneal Endothelium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Polydimethylsiloxane Substrates Surface Pattern and Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HMVEC) Cultivation

| Topography | Designed dimensions (nm) | Measured dimensions (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Diameter | Pitch | |
| 1 μm pillars | 1000 | 1500 ± 20 | 6810 ± 60 |
| 1 μm wells | 1000 | 1180 ± 40 | 6890 ± 60 |
| 200 nm pillars | 200 | 193 ± 11 | 333 ± 18 |
| 250 nm wells | 250 | 223 ± 21 | 391 ± 16 |
2.2. Formation of Tight Junctions: Zonula Occludens (ZO1) Staining
2.3. Cell Morphology: Polygonal Cell Shape and Cell Circularity


2.4. Cell Area, Area Coefficient of Variance and Cell Proliferation

2.5. Fluid Pump Function: Na+/K+ Adenine Triphosphatase (ATPase) Staining and the Presence of Microvilli


2.6. Data Summary
| Variable | Cell circularity | Hexagonal shape factor | Cell area | Cell area coefficient of variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | <0.0001*** | 0.0013*** | 0.003*** | <0.0001*** |
| Topography | 0.0162* | 0.0758 | 0.0006*** | 0.0171* |
| Interaction | 0.0031*** | 0.0428* | <0.0001*** | 0.007** |
| Topography | Medium | Cell area | Cell circularity | HSF | CV | ZO-1 | Na+/K+ ATPase | SEM | Scoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 µm Pillars | EGM-2MV | −* | ++** | ++ | + | + | + | + | 8 |
| Medium B | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | −3 | |
| 1 µm Wells | EGM-2MV | − | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | 6 |
| Medium B | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | −3 | |
| 200 nm Pillars | EGM-2MV | −*** | + | + | ++** | + | + | + | 5 |
| Medium B | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | 3 | |
| 200 nm Wells | EGM-2MV | ++ | + | − | − | + | + | + | 4 |
| Medium B | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | −3 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Polydimethylsiloxane Substrates
3.2. Vascular Endothelial Cell Culture on PDMS Substrates
3.3. Immunofluorescence Staining of ZO-1 and Na+/K+-ATPase, BrdU Proliferation Assay
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy of HMVECS on Different Topographies
3.5. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
References
- Gipson, I.K.; Joyce, N.C.; Zieske, J.D. The anatomy and cell biology of the human cornea, limbus, conjunctiva, and adnexa. In Smolin and Thoft’s the Cornea: Scientific Foundations and Clinical Practice; Foster, C.S., Azar, D.T., Dohlman, C.H., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, N.C. Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2003, 22, 359–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Huang, M.C.; Carley, F.; Hillarby, M.C.; Vasileiadis, G.T.; Tullo, A. The influence of donor and recipient factors in allograft rejection of the human cornea. Eye 2009, 24, 334–339. [Google Scholar]
- Barile, F.A. Validating and troubleshooting ocular in vitro toxicology tests. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 61, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Nishida, K.; Yamato, M.; Sumide, T.; Utsumi, M.; Nozaki, T.; Kikuchi, A.; Okano, T.; Tano, Y. Structural characterization of bioengineered human corneal endothelial cell sheets fabricated on temperature-responsive culture dishes. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishino, Y.; Sano, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Connon, C.J.; Rigby, H.; Fullwood, N.J.; Kinoshita, S. Amniotic membrane as a carrier for cultivated human corneal endothelial cell transplantation. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, D.A.; Yu, H.; Young, D.L.; Caldwell, D.R. Matrix stimulates the proliferation of human corneal endothelial cells in culture. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ebihara, N.; Shima, N.; Kimoto, M.; Funaki, T.; Yokoo, S.; Murakami, A.; Yamagami, S. Adhesion, migration, and proliferation of cultured human corneal endothelial cells by la minin-5. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, N.; Sakamoto, Y.; Okumura, N.; Tsuchiya, H.; Torii, R.; Cooper, L.J.; Ban, Y.; Tanioka, H.; Kinoshita, S. Cultivated corneal endothelial transplantation in a primate: Possible future clinical application in corneal endothelial regenerative medicine. Cornea 2008, 27, S48–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, T.; Amano, S.; Usui, T.; Araie, M.; Ono, K.; Akihiro, H.; Yokoo, S.; Yamagami, S. Transplantation of corneas reconstructed with cultured adult human corneal endothelial cells in nude rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 79, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proulx, S.; Bensaoula, T.; Nada, O.; Audet, C.; Uwamaliya, J.A.; Devaux, A.; Allaire, G.; Germain, L.; Brunette, I. Transplantation of a tissue-engineered corneal endothelium reconstructed on a devitalized carrier in the feline model. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, G.S.L.; Beuerman, R.W.; Colman, A.; Tan, D.T.; Mehta, J.S. Human corneal endothelial cell expansion for corneal endothelium transplantation: An overview. Transplantation 2011, 91, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, I.; Sieber, M.; Chang, J.; Jester, J.V.; Kao, W. Cell therapy of congenital corneal diseases with umbilical mesenchymal stem cells: Lumican null mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10707. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, N.C.; Harris, D.L.; Markov, V.; Zhang, Z.; Saitta, B. Potential of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells to heal damaged corneal endothelium. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 547–564. [Google Scholar]
- Murgatroyd, H.; Bembridge, J. Intraocular pressure. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2008, 8, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, A.R.; Secomb, T.W. Blood flow in microvascular networks. In Microcirculation, 2nd; Ronald, F.T., Walter, N.D., Klaus, L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yi, W.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y. Replacement of corneal endothelium with auto-vascular endothelium. Chin. Ophthal. Res. 2008, 26, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Luo, Z.; Huang, G. Experimental study on the corneal endothelial cells substituted by the vascular endothelial cells (VEC) cultivated on the amniotic membrane as its growth carrier. J. Kunming Med. Coll. 2006, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu, M.; Antohe, F. Functional ultrastructure of the vascular endothelium: changes in various pathologies. In The Vascular Endothelium I; Moncada, S., Higgs, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 176/I, pp. 41–69. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, G.A.; Schaus, S.S.; Goodman, S.L.; Nealey, P.F.; Murphy, C.J. Nanoscale topography of the corneal epithelial basement membrane and descemet’s membrane of the human. Cornea 2000, 19, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, E.K.F.; Leong, K.W. Significance of synthetic nanostructures in dictating cellular response. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.M.; George, J.H. Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science 2005, 310, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, B.K.K.; Goh, K.J.; Ng, Z.J.; Koo, S.; Yim, E.K.F. Functional reconstruction of corneal endothelium using nanotopography for tissue-engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Dalby, M.J.; Riehle, M.O.; Johnstone, H.; Affrossman, S.; Curtis, A.S.G. In vitro reaction of endothelial cells to polymer demixed nanotopography. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2945–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, M. Basement membrane proteins: Structure, assembly, and cellular interactions. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. 1992, 27, 93–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.E.; Senger, D.R. Endothelial extracellular matrix. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, S.; Yamagami, S.; Mimura, T.; Uchida, S.; Yokoo, S. Corneal stromal and endothelial cell precursors. Cornea 2006, 25, 73–1. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, K.; Drake, J.; Osakabe, Y.; Hosokawa, Y.; Hwang, D.; Soya, K.; Oshika, T.; Amano, S. Effect of donor age on morphologic variation of cultured human corneal endothelial cells. Cornea 2001, 20, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroll, W.M.; Hsu, J.K.W.; Bean, J.; Cavanagh, H.D.; Center, J.V. The spatial organization of apical junctional complex-associated proteins in feline and human corneal endothelium. Curr. Eye Res. 1999, 18, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, M.J. Prevalence of “non-hexagonal” cells in the corneal endothelium of young Caucasian adults, and their inter-relationships. Ophthal. Physl. Opt. 1998, 18, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Doughty, M.J.; Wright, L. Reassessment of the corneal endothelial cell organisation in children. Brit. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 84, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, G.S.L.; Toh, K.P.; Wu, F.Y.; Tan, D.T.; Mehta, J.S. cultivation of human corneal endothelial cells isolated from paired donor corneas. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28310. [Google Scholar]
- Levis, H.J.; Peh, G.S.L.; Toh, K.-P.; Poh, R.; Shortt, A.J.; Drake, R.A.L.; Mehta, J.S.; Daniels, J.T. Plastic compressed collagen as a novel carrier for expanded human corneal endothelial cells for transplantation. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behndig, A.; Karlsson, K.; Brännström, T.; Sentman, M.L.; Marklund, S.L. Corneal endothelial integrity in mice lacking extracellular superoxide dismutase. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 2784–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, C.C.; Campbell, G.; Spadiccino, A.; Robertson, M.; Curtis, A.S.G. The influence of microscale topography on fibroblast attachment and motility. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5781–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, M.J.; Gadegaard, N.; Riehle, M.O.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Curtis, A.S.G. Investigating filopodia sensing using arrays of defined nano-pits down to 35 nm diameter in size. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. B 2004, 36, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.A.; McFarland, G.A.; Steele, J.G. Stimulation of epithelial tissue migration by certain porous topographies is independent of fluid flux. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 56, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, R.K.; McDonald, M.B.; Srivannaboon, S.; Tan, A.L.; Doubrava, M.W.; Kim, C.K. Normal human corneal cell populations evaluated by in vivo scanning slit confocal microscopy. Cornea 1998, 17, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefansson, A.; Müller, O.; Sundmacher, R. Non-contact specular microscopy of the normal corneal endothelium. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1982, 218, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, M.J.; Riehle, M.O.; Johnstone, H.J.H.; Affrossman, S.; Curtis, A.S.G. Polymer-demixed nanotopography: Control of fibroblast spreading and proliferation. TissueEng. 2002, 8, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.A.; Assoian, R.K. Integrins and cell proliferation regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases via cytoplasmic signaling pathways. J. Cell. Sci. 2001, 114, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Chen, C.S.; Ingber, D.E. Control of cyclin D1, p27Kip1, and cell cycle progression in human capillary endothelial cells by cell shape and cytoskeletal tension. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1998, 9, 3179–3193. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, T. Cornea; Krachmer, J.H., Mannis, M.J., Holland, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, M.; Yee, R.W.; Edelhauser, H.F. Comparison of the corneal endothelium in an american and a japanese population. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1985, 103, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, M.D.; Sibayan, S.A.; Gonzales, C. Corneal endothelial cell density and morphology in normal filipino eyes. Cornea 2004, 23, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.K.; Sen, P.R.; Fogla, R.; Gangadharan, S.; Padmanabhan, P.; Badrinath, S.S. Corneal endothelial cell density and morphology in normal indian eyes. Cornea 2000, 19, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lam, D.S.C.; Rao, S.K. Corneal endothelial cell density and morphology in healthy chinese eyes. Cornea 2007, 26, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, J.A. Identity and regulation of ion transport mechanisms in the corneal endothelium. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2003, 22, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.P.; Collin, H.B. A comparative study of the corneal endothelium in vertebrates. Clin. Exp. Optom. 1998, 81, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.A.; Chiba, K.; Tsubota, K.; Oak, S.S. Metabolic and morphologic changes in the corneal endothelium. The effects of potassium cyanide, iodoacetamide, and ouabain. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Rueda, B.; Spanel-Borowski, K. Microvascular endothelial cells of the corpus luteum. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chua, J.S.; Liew, L.X.; Yim, E.K.F. Cultivation of Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells on Topographical Substrates to Mimic the Human Corneal Endothelium. J. Funct. Biomater. 2013, 4, 38-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb4010038
Chua JS, Liew LX, Yim EKF. Cultivation of Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells on Topographical Substrates to Mimic the Human Corneal Endothelium. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2013; 4(1):38-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb4010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleChua, Jie Shi, Li Xiang Liew, and Evelyn K.F. Yim. 2013. "Cultivation of Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells on Topographical Substrates to Mimic the Human Corneal Endothelium" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 4, no. 1: 38-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb4010038
APA StyleChua, J. S., Liew, L. X., & Yim, E. K. F. (2013). Cultivation of Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells on Topographical Substrates to Mimic the Human Corneal Endothelium. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 4(1), 38-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb4010038