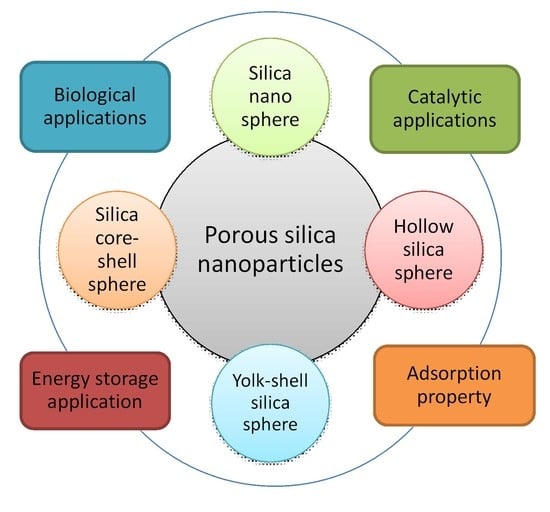
Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis Pathway for Morphology-Controlled Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
2.1. Porous Silica Nanosphere
2.2. Mesoporous Silica Hollow Sphere
2.3. Core-Shell Silica Nanoparticles
2.4. Others Morphologies of Silica Nanoparticles
3. Applications of Morphology-Controlled Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
3.1. Catalysis
3.2. Biological Applications
3.2.1. Drug Delivery
3.2.2. Bioimaging
3.2.3. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity
3.2.4. Biodegradation
3.2.5. Antimicrobial Activity
3.2.6. Biosensing Study
3.3. Energy Storage Application
4. Summary and Future Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| MCM-41 | Mobil Composition of Matter-41 |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| SDA | Structure directing agents |
| PMOs | Periodic mesoporous silicas |
| pH | -log[H+] |
| CMC | Critical miceller concentration |
| nm | Nanometer |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl orthosilicate |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| C16TMACl | Cetyltrimethylammonium chloride |
| CPB | Cetylpyridinium bromide |
| 3D | Three dimensional |
| TEA | Triethanolamine |
| TBOS | Tetrabutyl orthosilicate |
| HMS | Hollow mesoporous silica |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| SBF | Simulated body fluid |
| PMAA | Poly(methacrylic acid) |
| DSSC | Dye-sensitized solar cell |
| MSN | Mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| EtOAc | Ethyl acetate |
| BTDS | bis [3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl] disulphide |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| RB | Rhodamine B |
| µM | Micromolar |
| FC | Fluorocarbon |
| TMOS | Tetramethyl orthosilicate |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
References
- Du, X.; He, J. Spherical silica micro/nanomaterials with hierarchical structures: Synthesis and applications. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3984–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Cho, E.-B.; Kim, D. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica/ceria–silica composites and their high catalytic performance for solvent-free oxidation of benzyl alcohol at room temperature. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9213–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, M.U.A.; Kaur, B.; Srivastava, R. Direct synthesis of metal oxide incorporated mesoporous SBA-15 and their applications in non-enzymatic sensing of glucose. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 381, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhenga, S.; Zhua, S.; Maa, J.; Suna, Z.; Farid, M. Evaluation of paraffin infiltrated in various porous silica matrices as shape stabilized phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Schelch, S.; Mayr, T.; Nidetzky, B. Mesoporous silica materials labelled for optical oxygen sensing and their application to development of a silica-supported oxidoreductase biocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5984–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, C.; Mishrab, A.; Nayak, D.; Chakraborty, A. Drug delivery system composed of mesoporous silica and hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres for chemotherapeutic drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.L.; Beau, R.; Duchene, J. Porous Silica Particles Containing a Crystallized Phase and Method. U.S. Patent 3493341D, 23 January 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Direnzo, F.; Cambon, H.; Dutartre, R. A 28-year-old synthesis of micelle-templated mesoporous silica. Micropor. Mater. 1997, 10, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W. A New Family of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Prepared with Liquid Crystal Templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, N.; Bhaumik, A. Soft templating strategies for the synthesis of mesoporous materials: Inorganic, organic–inorganic hybrid and purely organic solids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 189–190, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.P.; Elangovan, S.P.; Tatsuya, O.; Sokolov, I. Morphology control of mesoporous silica particles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11168–11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ray, S.; Bhanja, P.; Bhaumik, A.; Mukhopadhyay, C. Serendipitous observation of liquid-phase size selectivity inside a mesoporous silica nanoreactor in the reaction of chromene with formic acid. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2260–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Elzatahry, A.; Lu, G.; Zhao, D. Mesoporous organosilica hollow nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1707612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 6397, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Margolese, D.I.; Ciesla, U.D.; Demuth, G.; Feng, P.; Gier, T.E.; Sieger, P.; Chmelka, B.F.; Schuth, F.; Stucky, G.D. Generalized synthesis of periodic surfactant/inorganic composite materials. Nature 1994, 368, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao, D. On the controllable soft-templating approach to mesoporous silicates. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2821–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Ryoo, R. Synthesis and pore size control of cubic mesoporous silica SBA-1. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, G. Das komplexehemische Verhalten der Kieselsure. Ph.D. Thesis, Friedrich-Schiller Universität, Jena, Germany, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, B.; Xu, J.-Q.; Xiang, X.-C.; Ren, D.-F.; Yang, T.-Q.; Ma, S.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Q.-M. Non-surfactant self-templating strategy for mesoporous silica nanospheres: Beyond Stöber method. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Galarneau, A.; Renzo, F.D.; Fajula, F.; Plee, D. Morphological control of MCM-41 by pseudomorphic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Ranade, A.; Du, G.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Haller, G.L. Pseudomorphic synthesis of large-particle Co-MCM-41. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5584–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, B.; Clinard, C.; Durand, D.; Vérona, E.; Massiot, D. New routes to mesoporous silica-based spheres with functionalised surfaces. Chem. Commun. 2005, 13, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, T.; Karouji, T.; Ohta, S.; Kondo, J.N.; Tatsumi, T. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanospheres promoted by basic amino acids and their catalytic application. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.-A.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles via controlled hydrolysis and condensation of silicon alkoxide. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, P.; Thorn, P.; Gu, W.; Yu, C. A simple approach to prepare monodisperse mesoporous silica nanospheres with adjustable sizes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 376, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Kim, S.-G.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 120, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polshettiwar, V.; Cha, D.; Zhang, X.; Basset, J.M. High-surface-area silica nanospheres (KCC-1) with a fibrous morphology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9652–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuge, K.; Murakami, T.; Kikukawa, N.; Takemori, M. Direct Synthesis of Porous Pure and Thiol-Functional Silica Spheres through the S+X−I+ Assembly Pathway. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3184–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuge, K.; Singh, P.S. Rapid synthesis of Al-containing mesoporous silica hard spheres of 30–50 µm diameter. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 2476–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, F. Fluorescence turn-on chemodosimeter-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7175–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooney, R.I.; Thirunavukkarasu, D.; Chen, Y.; Josephs, R.; Ostafin, A.E. Synthesis of nanoscale mesoporous silica spheres with controlled particle size. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4721–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuge, K.; Kikukawa, N.; Takemori, M. One-step preparation of porous silica spheres from sodium silicate using triblock copolymer templating. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4181–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Chung, P.-W.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Facile synthesis of monodisperse spherical MCM-48 mesoporous silica nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5093–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Cui, X.; Cui, F.; Guo, L.; Shi, J. Size-controlled synthesis of monodispersed mesoporous silica nano-spheres under a neutral condition. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 117, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.V.R.; López, G.P.; Bravo, J.; Pham, H.; Datye, A.K.; Xu, H.F.; Ward, T.L. Monodisperse mesoporous silica microspheres formed by evaporation-induced self-assembly of surfactant templates in aerosols. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.H.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; He, M.-Y. A facile synthesis of monodispersed mesoporous silica nanospheres with Pm3n structure. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 220, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Schüth, F.; Stucky, G.D. Preparation of hard mesoporous silica spheres. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ying, J.Y. Generalized fluorocarbon-surfactant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles with various mesoporous structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobler, J.; Möller, K.; Bein, T. Colloidal suspensions of functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Urata, C.; Aoyama, Y.; Osada, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Preparation of colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different diameters and their unique degradation behavior in static aqueous systems. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobler, J.; Bein, T. Porous thin films of functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datz, S.; Engelke, H.; Schirnding, C.V.; Nguyen, L.; Bein, T. Lipid bilayer-coated curcumin-based mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for cellular delivery. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 225, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.-L.; Jiang, J.-G.; Calin, N.; Lam, K.-F.; Zhang, S.-J.; Wu, H.-H.; Wu, G.-D.; Albela, B.; Bonneviot, L.; et al. Facile large-scale synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous silica nanospheres with tunable pore structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-J.; Xing, J.-L.; Pang, J.-L.; Jiang, S.-H.; Lam, K.-F.; Yang, T.-Q.; Xue, Q.-S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, P. Facile synthesis of size controllable dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22655–22665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwe, R.P.; Hilliard, L.R.; Tan, W. Surface modification of silica nanoparticles to reduce aggregation and nonspecific binding. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4357–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, K.; Landry, C.C. Diffusion-based deprotection in mesoporous materials: A strategy for differential functionalization of porous silica particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9674–9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebbin, V.; Jakubowski, M.; Pötz, S.; Fröba, M. Synthesis and characterisation of spherical periodic mesoporous organosilicas (sph-PMOs) with variable pore diameters. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2004, 72, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Mokaya, R. High surface area ethylene-bridged mesoporous and supermicroporous organosilica spheres. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 86, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.U.; Wei, N.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, D. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres: Controllable template synthesis and their application in drug delivery. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 14122–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xin, H.; Meng, Q.; Fang, Y.; Li, F.; Li, X. Synthesis and catalytic application of hollow silica nanospheres. Mater. Focus 2015, 4, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, P.J.; Kim, A.Y.; Liu, J.; Baskaran, S. Mesoporous silica synthesized by solvent evaporation: Spun fibers and spray-dried hollow spheres. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2507–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poostforooshan, J.; Belbekhouche, S.; Shaban, M.; Alphonse, V.; Habert, D.; Bousserrhine, N.; Courty, J.; Weber, A.P. Aerosol-assisted synthesis of tailor-made hollow mesoporous silica microspheres for controlled release of antibacterial and anticancer agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6885–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, H.M.; Zawrah, M.F.; Harbrecht, B. Facile one-pot fabrication of hollow porous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Zheng, N. A cationic surfactant assisted selective etching strategy to hollow mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ru, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Reversible pore-structure evolution in hollow silica nanocapsules: Large pores for siRNA delivery and nanoparticle collecting. Small 2011, 7, 2935–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Su, X.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, G.; Tian, C.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, G. Mesoporous silica hollow spheres with ordered radial mesochannels by a spontaneous self-transformation approach. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-L.; Park, J.H.; Choe, H.-S.; Lee, M.-S.; Park, J.-M.; Harada, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Yanai, N.; Kimizuka, N.; Zhu, J.; et al. Upconverting oil-laden hollow mesoporous silica microcapsules for anti-Stokes-based biophotonic applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26571–26580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Long, D.J.; Haynes, C.L. Preparation of colloidally stable positively charged hollow silica nanoparticles: Effect of minimizing hydrolysis on ζ potentials. Langmuir 2019, 35, 7985–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, A.; Inoue, Y.; Yada, M.; Nakashima, K. Synthesis of silica hollow nanoparticles templated by polymeric micelle with core-shell-corona structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1534–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zea, C.; Alcántara, J.; Barranco-García, R.; Morcillo, M.; de la Fuente, D. Synthesis and characterization of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for smart corrosion protection. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Akane, Y.; Ogi, T.; Okuyama, K. Mesopore-free hollow silica particles with controllable diameter and shell thickness via additive-free synthesis. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8616–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas, H.; Save, M.; Pasetto, P.; Boissière, C.; Sanchez, C.; Charleux, B. Elaboration of monodisperse spherical hollow particles with ordered mesoporous silica shells via dual latex/surfactant templating: Radial orientation of mesopore channels. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13132–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kruk, M. Single-micelle-templated synthesis of hollow silica nanospheres with tunable pore structures. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69870–69877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, L.; Moreno-Atanasio, R.; Neville, F. Synthesis of hollow silica nanoparticle aggregates from asymmetric methyltrimethoxysilane using a modified SBA-15 method. Langmuir 2019, 35, 7896–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q. Organo-functionalized silica hollow nanospheres: Synthesis and catalytic application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chang, J.-H.; Yeh, Y.-Q.; Wu, S.-H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Mou, C.-Y. Formation of hollow silica nanospheres by reverse microemulsion. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9614–9626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, S.P.H.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Ghandehari, H. Glutathione-sensitive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 282, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, S.Z.; Jin, Y.G.; Chen, Z.G.; Gu, H.C.; Lu, G.Q. Magnetic hollow spheres of periodic mesoporous organosilica and Fe3O4 nanocrystals: Fabrication and structure Control. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y. Preparation of novel magnetic hollow mesoporous silica microspheres and their efficient adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Su, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. A facile multi-interface transformation approach to monodisperse multiple-shelled periodic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7935–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Abbaraju, P.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, G.; Yu, C. Multi-shelled dendritic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres: Roles of composition and architecture in cancer immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8446–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Guo, Z.; Teng, S.; Xia, H.; Wang, D.; Han, M.-Y.; Yang, W. Rationalized fabrication of structure-tailored multishelled hollow silica spheres. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 7470–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, S.; Ding, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S. An organosilane-directed growth-induced etching strategy for preparing hollow/yolk-shell mesoporous organosilica nanospheres with perpendicular mesochannels and amphiphilic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 12403–12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. Molecularly organic/inorganic hybrid hollow mesoporous organosilica nanocapsules with tumor-specific biodegradability and enhanced chemotherapeutic functionality. Biomaterials 2017, 125, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Bouchmella, K.; Budimir, J.; Raehm, L.; Cardoso, M.B.; Trens, P.; Durand, J.-O.; Charnay, C. Degradable hollow organosilica nanoparticles for antibacterial activity. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djojoputro, H.; Zhou, X.F.; Qiao, S.Z.; Wang, L.Z.; Yu, C.Z.; Lu, G.Q. Periodic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres with tunable wall thickness. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6320–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.Z.; Lin, C.X.; Jin, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, Z.; Hao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lu, G.Q. (Max) Surface-functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 8673–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Tu, S.; Chen, M.; Wu, L. Novel polymeric organosilica precursor and emulsion stabilizer: Toward highly elastic hollow organosilica nanospheres. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11524–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.B.; Choi, E.; Yang, S.; Jaroniec, M. Hollow mesoporous organosilica nanospheres templated with flower-like micelles of pentablock copolymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 528, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Ow, H.; Wiesner, U. Fluorescent core–shell silica nanoparticles: Towards ‘‘Lab on a Particle’’ architectures for nanobiotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Asefa, T.; Guo, H.; Biradar, A.V.; Peng, D.-L.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Core–shell nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications in catalysis and electrocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7540–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ow, H.; Larson, D.R.; Srivastava, M.; Baird, B.A.; Webb, W.W.; Wiesner, U. Bright and stable core–shell fluorescent silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, E.; Marchincin, T.; Connelly, L.; Bonner, D.; Burns, A.; Switalski, S.; Wiesner, U. Relative quantum Yield Measurements of Coumarin Encapsulated in Core-Shell Silica Nanoparticles. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauda, V.; Schlossbauer, A.; Kecht, J.; Zürner, A.; Bein, T. Multiple core-shell functionalized colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11361–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allouche, J.; Dupin, J.-C.; Gonbeau, D. Generation of a mesoporous silica MSU shell onto solid core silica nanoparticles using a simple two-step sol–gel process. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7476–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchel, G.; Unger, K.K.; Matsumoto, A.; Tsutsumi, K. A novel pathway for synthesis of submicrometer-size solid core/mesoporous shell silica spheres. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteewong, T.; Sai, H.; Hovden, R.; Muller, D.; Bradbury, M.S.; Gruner, S.M.; Wiesner, U. Multicompartment mesoporous silica nanoparticles with branched shapes: An epitaxial growth mechanism. Science 2013, 340, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Cheng, X.; Alghamdi, A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica with tunable morphologies and pore sizes via a nonpolar solvent-assisted Stöber method. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Stucky, G.D. Morphological control of highly ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Biphase stratification approach to three-dimensional dendritic biodegradable mesoporous silica nanospheres. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; He, A.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Song, J. Fabrication of hollow silica nanorods using nanocrystalline cellulose as templates. Bioresources 2012, 7, 2319–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vo, N.T.; Patra, A.K.; Kim, D. Synthesis of hollow doughnut shape mesoporous silica nanoparticle: A case of self-assembly composite templates. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Wu, S.-H.; Hung, Y.; Chou, Y.-H.; Chang, C.; Lin, M.-L.; Tsai, C.-P.; Mou, C.-Y. Multifunctional composite nanoparticles: Magnetic, luminescent, and mesoporous. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5170–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.-S.; Lee, J.-K. Tunable synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with radial wrinkle structure. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12341–12347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, S.; Wiench, J.W.; Yoo, J.-C.; Pruski, M.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Organic functionalization and morphology control of mesoporous silicas via a co-condensation synthesis method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4247–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelebaeva, E.; Raehm, L.; Durand, J.-O.; Guari, Y.; Larionova, J.; Guérin, C.; Trifonov, A.; Willinger, M.; Thangavel, K.; Lascialfari, A.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles combining two-photon excited fluorescence and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palantavida, S.; Peng, B.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright fluorescent silica particles with a large number of complex spectra excited with a single wavelength for multiplex applications. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4881–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, D.O.; Cho, E.-B.; Sokolov, I. Synthesis of ultrabright nanoporous fluorescent silica discoids using an inorganic silica precursor. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, T.; Tuo, X.; Guo, J.; Gong, Y. Formaldehyde-controlled Synthesis of Multishelled Hollow Mesoporous SiO2 Microspheres. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14517–14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, K.; Kao, T.; Spoth, K.A.; Sai, H.; Zhang, D.; Kourkoutis, L.F.; Elser, V.; Wiesner, U. Formation pathways of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with dodecagonal tiling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Banerjee, S.; Choi, E.; Cho, E.-B. Facile one-pot synthesis of yolk-shell structured Ni doped mesoporous silica and its application in enzyme-free glucose sensor. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 6029–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Im, S.; Cho, E.-B.; Kim, H.; Park, J. Superparamagnetic NiO-doped mesoporous silica flower-like microspheres with high nickel content. J. Indus. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Mukherjee, I.; Chatterjee, S.; Cho, E.-B. Surfactant-assisted synthesis of ceria–titania-rich mesoporous silica materials and their catalytic activity towards photodegradation of organic dyes. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 9577–9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Cho, E.-B.; Kim, D.; Jaroniec, M. Mn-doped ordered mesoporous ceria–silica composites and their catalytic properties toward biofuel production. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 15892–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, M.; Chalke, B.; Polshettiwar, V. Efficient synthesis of monodisperse metal (Rh, Ru, Pd) nanoparticles supported on fibrous nanosilica (KCC-1) for catalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3224–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; He, J. Amino-functionalized silica nanoparticles with center-radially hierarchical mesopores as ideal catalyst carriers. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhrara, M.; Ranga, C.; Fihri, A.; Shaikh, R.R.; Sarawade, P.; Emwas, A.-H.; Hedhili, M.N.; Polshettiwar, V. Nitridated fibrous silica (KCC-1) as a sustainable solid base nanocatalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.W.; Jang, H.-G.; Sim, H.-I.; Shin, C.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Seo, G. Preparation of dandelion-type silica spheres and their application as catalyst supports. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Chen, Q.; Hao, L.; Tian, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Synthesis and catalytic properties of nickel–silica composite hollow nanospheres. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6311–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabzadeh, M.; Khalifeh, R.; Eshghi, H.; Sorouri, M. Design and preparation of hallow mesoporous silica spheres include Cuo and its catalytic performance for synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole compounds via the Click reaction in water. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liao, S.; Zeng, J.; Liang, Z. A mesoporous hollow silica sphere (MHSS): Synthesis through a facile emulsion approach and application of support for high performance Pd/MHSS catalyst for phenol hydrogenation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4472–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, L.; Han, J.; Xu, X.; He, C.; Wang, P.; Wei, Q.; Yang, W. Facile synthesis of palladium nanoparticles on hierarchical hollow silica spheres and its catalytic properties in Suzuki-reaction. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Kango, H.; Yamashita, H. Pd nanoparticles and aminopolymers confined in hollow silica spheres as efficient and reusable heterogeneous catalysts for semihydrogenation of alkynes. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.T.; Patra, A.K.; Kim, D. Reductant-free synthesis of silver nanoparticles by functionalized hollow doughnut mesoporous silica nanoparticles for preparation of catalytic nanoreactor. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Tseng, C.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.-Y. Catalytic nano-rattle of Au hollow silica: Towards a poison-resistant nanocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y. Co-templating synthesis of mesoporous hollow silica spheres and their application in catalytic oxidation with low Pt loading. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Bai, S.; Wang, P.; Zhong, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, C. The nanocomposites of SO3H-hollow-nanosphere and chiral amine for asymmetric aldol reaction. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8580–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verho, O.; Zheng, H.; Gustafson, K.P.J.; Nagendiran, A.; Zou, X.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Application of Pd nanoparticles supported on mesoporous hollow silica nanospheres for the efficient and selective semihydrogenation of alkynes. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, J.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xue, G. Facile and controllable fabrication of gold nanoparticles-immobilized hollow silica particles and their high catalytic activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12471–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of hollow silica nanospheres with ultra-high acid density for efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Catalysts 2019, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Cao, C.-Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Song, W.-G. Core-shell structured mesoporous silica as acid–base bifunctional catalyst with designated diffusion path for cascade reaction sequences. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10541–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Liu, Z.; Hsieh, M.-F.; Chen, M.; Liu, P.; Chen, C.; Zheng, N. Hollow mesoporous aluminosilica spheres with perpendicular pore channels as catalytic nanoreactors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4434–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrani, A.; Rostami, A.A.; Emamgholizadeh, A. Electrocatalytically active nanocomposite carbon paste electrode modified with SiO2/poly(p-phenylendiamine) core/shell nanoparticles: Application toward electro-oxidation of hydrazine. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tao, K.; Xiong, C.; Zhou, S. Controlled synthesis of Pd–NiO@SiO2 mesoporous core–shell nanoparticles and their enhanced catalytic performance for p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation with H2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, B.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Han, S. Current advances in precious metal core–shell catalyst design. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 043502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Tsung, C.-K.; Yamada, Y.; Yang, P.; Somorjai, G.A. Thermally stable Pt/mesoporous silica core–shell nanocatalysts for high-temperature reactions. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zou, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of core-shell-structured mesoporous silica nanospheres with dual-pores for biphasic catalysis. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 5833–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otari, S.V.; Yadav, H.M.; Thorat, N.D.; Patil, R.M.; Lee, J.K.; Pawar, S.H. Facile one pot synthesis of core shell AgSiO2 nanoparticles for catalytic and antimicrobial activity. Mater. Lett. 2016, 167, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Cui, G.; Tian, Y.; Yan, S. Multifunctional magnetic core-shell dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres decorated with tiny Ag nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Kana, C.; Ni, Y.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, D. Construction of silica-encapsulated gold-silver core-shell nanorod: Atomic facets enrichment and plasmon enhanced catalytic activity with high stability and reusability. Mater. Des. 2019, 177, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and characterization of novel immobilized Fe3O4@SiO2@mSiO2–Pd (0) catalyst with large pore-size mesoporous for Suzuki coupling reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 459, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Han, L.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. One-pot synthesis of thermally stable gold mesoporous silica core–shell nanospheres with catalytic activity. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Lan, Y. One-pot synthesis of core-shell Cu@SiO2 nanospheres and their catalysis for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane and hydrazine borane. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Werth, C.J.; Strathmann, T.J. Palladium nanoparticles encapsulated in core–shell silica: A structured hydrogenation catalyst with enhanced activity for reduction of oxyanion water pollutants. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3551–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, G.D. Yolk–shell nanostructures: Syntheses and applications for lithium-ion battery anodes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, S.; Zhang, H.; Bian, Y.; Li, H.; Li, H. Yolk–Shell Nanoarchitectures with a Ru-Containing Core and a Radially Oriented Mesoporous Silica Shell: Facile Synthesis and Application for One-Pot Biomass Conversion by Combining with Enzyme. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20851–20859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Cui, T.; Fang, X.; Cui, F.; Wu, J. Preparation of yolk–shell FexOy/Pd mesoporous SiO2 composites with high stability and their application in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W. Yolk–shell catalyst of single au nanoparticle encapsulated within hollow mesoporous silica microspheres. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, N.; Lin, H.; Cen, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, N.; Tang, J.; Teng, Z. Multiple silver nanoparticles anchored hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres by polyacrylic acid aggregate templating approach for catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 8307–8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Sheng, X.; Wang, K. Fabrication of ellipsoidal silica yolk–shell magnetic structures with extremely stable Au nanoparticles as highly reactive and recoverable catalysts. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2698–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Xuan, S.; Gong, X.; Leung, K.C.-F. Mesoporous SiO2 yolk shell confined core-satellite Ag nanoparticles: Preparation and catalytic activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 680, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.Q.; Kleitz, F.; Chen, Z.G.; Yang, T.; Strounina, E.; Lu, G.Q.; Qiao, S.Z. Yolk–shell hybrid materials with a periodic mesoporous organosilica shell: Ideal nanoreactors for selective alcohol oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Design and synthesis of NiCe@m-SiO2 yolk-shell framework catalysts with improved coke- and sintering-resistance in dry reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; He, G. Rapidly constructing multiple AuPt nanoalloy yolk shell hollow particles in ordered mesoporous silica microspheres for highly efficient catalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Cheng, T.; Xiong, X.; Wu, L.; Han, B.; Liu, G. Yolk–shell-structured mesoporous silica: A bifunctional catalyst for nitroaldol–Michael one-pot cascade reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 5714–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, M.; Khalifeh, R.; Eshghi, H.; Hafizi, A. Design and Synthesis of CuO-SiO2 multi-yolk shell and its application as a new catalyst for CO2 fixation reaction under solventless condition. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 89, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Sun, Q.; Fan, D.; Fu, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, R. Facile synthesis of yolk/core-shell structured TS-1 mesosilica composites for enhanced hydroxylation of phenol. Catalysts 2015, 5, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Z.-A.; Huo, Q. Architecture yolk-shell structured mesoporous silica nanospheres for catalytic applications. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 9072–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedicalapplications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, D.; Ashley, C.E.; Xue, M.; Carnes, E.C.; Zink, J.I.; Brinker, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle nanocarriers: Biofunctionality and biocompatibility. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratiwi, F.W.; Kuo, C.W.; Wu, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-P.; Mou, C.Y.; Chen, P. The bioimaging applications of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. In The Enzymes; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 123–153. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 2007, 3, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-J.; Hu, S.-H.; Hsiao, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, D.-M.; Chen, S.-Y. Multifunctional magnetically removable nanogated lids of Fe3O4–capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release and MR imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Guo, J.; Liu, C.; Qian, J.; Yang, W. Surface functionalization of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9941–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. Metalloporphyrin-encapsulated biodegradable nanosystems for highly efficient magnetic resonance imaging-guided sonodynamic cancer therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.-H.; Liao, W.-N.; Chen, L.-M.; Lee, C.-H. pH-Controllable release using functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an oral drug delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7130–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Shi, J.; Chen, F.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, L. An anticancer drug delivery system based on surfactant-templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3335–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, N. Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarani, G.M.; Malmir, M.; Lashgari, N.; Badiei, A. The role of hollow magnetic nanoparticles in drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25094–25106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Structures for Controlled Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, C.; Shan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Q. Fluorophore-free luminescent double-shelled hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pesticide delivery vehicles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20354–20365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tsui, C.P.; Tang, C.Y.; Gu, L. Effects of compositional tailoring on drug delivery behaviours of silica xerogel/polymer core-shell composite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, R.; Ruan, L. Microwave thermal-triggered drug delivery using thermosensitive peptide-coated core–shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 6118–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Cricq, P.; Deshayes, S.; Zink, J.I.; Kasko, A.M. Magnetic field activated drug delivery using thermodegradable azo-functionalised PEG-coated core-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13168–13172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirthalingam, T.; Kalirajan, J.; Chockalingam, A. Use of silica-gold core shell structured nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery system. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, S.Z.; Hartono, S.B.; Lu, G.Q. Monodisperse yolk–shell nanoparticles with a hierarchical porous structure for delivery vehicles and nanoreactors. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 4981–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Zeng, L. Design of yolk–shell Fe3O4 PMAA composite microspheres for adsorption of metal ions and pH-controlled drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7065–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zeng, B.; Mai, Z.; Deng, J.; Fan, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, W. Novel drug delivery nanosystems based on out-inside bifunctionalized mesoporous silica yolk–shell magnetic nanostars used as nanocarriers for curcumin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.-W.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Chen, F.; Qi, C.; Lu, B.-Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, C.-Q. Superparamagnetic yolk–shell porous nanospheres of iron oxide magnesium silicate: Synthesis and application in high-performance anticancer drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103399–103411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, H.; Cai, K. Facile synthesis of yolk–shell silica nanoparticles for targeted tumor therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8303–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Su, X.; Tang, Y.; Dang, M.; Tian, Y.; Yuwen, L.; Weng, L.; et al. Facile synthesis of yolk–shell-structured triple-hybridized periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for biomedicine. Small 2016, 12, 3550–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Li, C.; Hu, J.; Zou, R.; Xu, K.; Han, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Qin, Z.; et al. A simple transformation from silica core–shell–shell to yolk–shell nanostructures: A useful platform for effective cell imaging and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17011–17018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palantavida, S.; Guz, N.V.; Woodworth, C.D.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles for prescreening of cervical cancer. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Huang, W. Core–shell structured phosphorescent nanoparticles for detection of exogenous and endogenous hypochlorite in live cells via ratiometric imaging and photoluminescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Bu, W.; Chen, F.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Peng, W.; Xiao, Q.; Xing, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Rattle-structured multifunctional nanotheranostics for synergetic chemo-/radiotherapy and simultaneous magnetic/luminescent dual-mode imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6494–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqua, A.J.D.; Sharma, K.K.; Shi, Y.-L.; Toms, B.B.; Ouellette, W.; Dabrowiak, J.C.; Asefa, T. Cytotoxicity of mesoporous silica nanomaterials. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubi, F.; Deezagi, A.; Singh, G.; Oghabian, M.A.; Fatemi, S.S.A.; Arpanaei, A. Preparation and characterization of double shell Fe3O4 cluster nonporous SiO2 mesoporous SiO2 nanocomposite spheres and investigation of their in vitro biocompatibility. Iran. J. Biotech. 2015, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, M.; Tang, J.; Qiao, Q.; Wu, T.; Qi, Y.; Tan, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z. Biodegradable hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for regulating tumor microenvironment and enhancing antitumor efficiency. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3276–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Bein, T. Degradable drug carriers: Vanishing mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4364–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratirotjanakul, W.; Suteewong, T.; Polpanichc, D.; Tangboriboonrata, P. Amino acid as a biodegradation accelerator of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 282, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hélary, C.; Haye, B.; Coradin, T. Extracellular versus intracellular degradation of nanostructured silica particles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Wen, L.-X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Chen, J.-F. Immobilization of silver on hollow silica nanospheres and nanotubes and their antibacterial effects. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Hua, H.; Zhua, M. Synthesis of core-shell structured ZnO@m-SiO2 with excellent reinforcing effect and antimicrobial activity for dental resin composites. Dental Mater. 2018, 34, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Jayawardana, K.W.; Chen, X.; Yan, M. One-step synthesis of amine-functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as efficient antibacterial and anticancer materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjani, M.; Sathishkumar, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoo, D.J.; Kim, A.R.; Kumar, G.G. Ni–Co alloy nanostructures anchored on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for non-enzymatic glucose sensor applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 57804–57814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, J.; Deng, Y. Rational design of yolk-shell CuO/Silicalite-1@mSiO2 composites for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. Langmuir 2018, 34, 7663–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Xu, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Yao, Y.; Liu, S.; Yao, C. An electrochemical enzymatic nanoreactor based on dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for living cell H2O2 detection. Analyst 2019, 144, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ni, N.; Cao, L.; Song, X.; Alhamoud, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, H. Silver doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles based electrochemical enzyme-less sensor for determination of H2O2 released from live cells. Micromachines 2019, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimomura, T.; Itoh, T.; Sumiya, T.; Hanaoka, T.; Mizukami, F.; Ono, M. Amperometric detection of phenolic compounds with enzyme immobilized in mesoporous silica prepared by electrophoretic deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 153, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Tao, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Meng, C. Magnetic loading of tyrosinase-Fe3O4/mesoporous silica core/shell microspheres for high sensitive electrochemical biosensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 686, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Gao, T.; Zhou, G. Laccase biosensor fabricated on flower–shaped yolk–shell SiO2 nanospheres for catechol detection. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascón, V.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Blanco, R.M. Successful encapsulation of β-glucosidase during the synthesis of siliceous mesostructured materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califano, V.; Costantini, A. Immobilization of cellulolytic enzymes in mesostructured silica materials. Catalysts 2020, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, C.T.; Chiu, Y.T.; Wu, K.C.W. An effective cellulose-to-glucose-to-fructose conversion sequence by using enzyme immobilized Fe3O4-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as recyclable biocatalysts. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmoko, C.; Sucipto, K.I.; Retnoningtyas, E.S.; Hartono, S.B. Vinyl functionalized cubic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as supporting material to enhance cellulase enzyme stability. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar]
- Venezia, V.; Sannino, F.; Costantini, A.; Silvestri, B.; Cimino, S.; Califano, V. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for β-glucosidase immobilization by templating with a green material: Tannic acid. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 302, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Mustansar, S.; Siddiq, A.M.; Niu, L. Mesoporous silica wrapped with graphene oxide-conducting PANI nanowires as a novel hybrid electrode for supercapacitor. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 113, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, A.K.; Tsumori, N.; Xu, Q. Palladium silica nanosphere-catalyzed decomposition of formic acid for chemical hydrogen storage. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19146–19150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umegaki, T.; Yan, J.-M.; Zhang, X.B.; Shioyama, H.; Kuriyama, N.; Xu, Q. Hollow Ni-SiO2 nanosphere-catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane for chemical hydrogen storage. J. Power Sources 2009, 191, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.A.; Shyla, J.M.; Xavier, F.P. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2/SiO2 nano composites for solar cell applications. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-W.; Chiang, Y.-D.; Kung, C.W.; Sakai, N.; Ikegami, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K.C.-W.; Miyasaka, T.; Ho, K.-C. Highly efficient plastic-based quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with light-harvesting mesoporous silica nanoparticles gel-electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vilà, N.; Walcarius, A. Redox-active vertically-aligned mesoporous silica thin films as transparent surfaces for energy storage applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24262–24270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkatulov, A.I.; Joosten, R.; Fischer, H.R.; Huinink, H. Core-shell encapsulation of salt hydrates into mesoporous silica shells for thermochemical energy storage. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 6860–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Kim, T.; Park, J.-S.; Cho, E.-B. Synthesis of ordered Ca- and Li-doped mesoporous silicas for H2 and CO2 adsorption at ambient temperature and pressure. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 35294–35305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Huang, Y. Nitrogen rich core–shell magnetic mesoporous silica as an effective adsorbent for removal of silver nanoparticles from water. J. Hazardous Mater. 2017, 337, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pal, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.-B. Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112122
Pal N, Lee J-H, Cho E-B. Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112122
Chicago/Turabian StylePal, Nabanita, Jun-Hyeok Lee, and Eun-Bum Cho. 2020. "Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112122
APA StylePal, N., Lee, J. -H., & Cho, E. -B. (2020). Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112122