Design and Modeling of Light Emitting Nano-Pixel Structure (LENS) for High Resolution Display (HRD) in a Visible Range
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Need for a Nano-Display
1.2. Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR)
1.3. LENS Proposed Solution
2. Device Concept and Structure
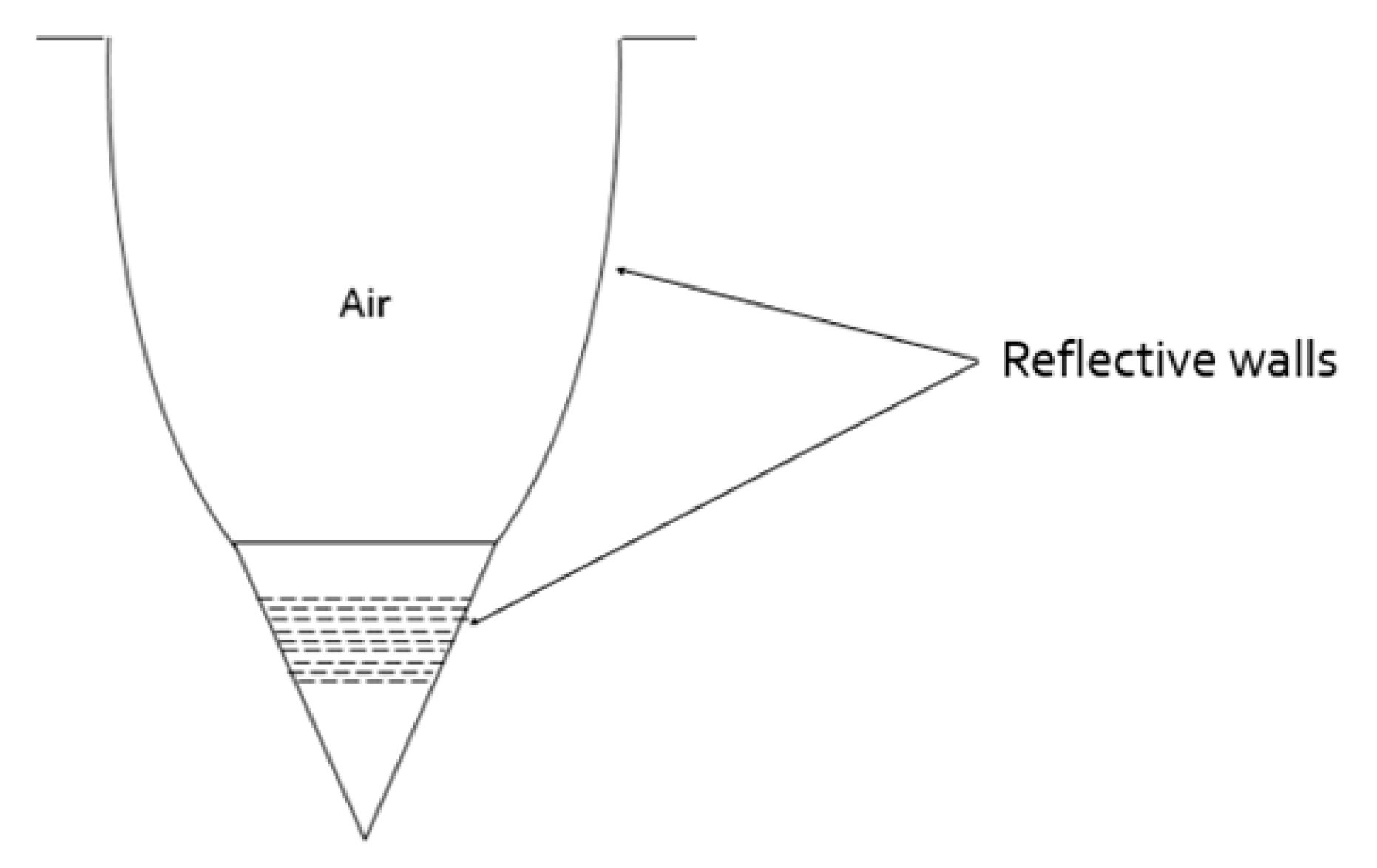
2.1. Existing Technologies in the Industry
- The Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) [17] is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device which uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly, instead using a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.
- The Liquid Crystal-On-Silicon (LCOS) [18] technology has been developed for many years for image and video display applications. This technology combines the unique light-modulating properties of Liquid Crystal (LC) materials and the advantages of high-performance silicon Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) technology through dedicated LCOS assembly processes.
- The Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) [19]: In organic light-emitting diodes, the electro luminescent material comprising the emissive layer of the diode is an organic compound. The organic material is electrically conductive due to the delocalization of electrons caused by conjugation over all or part of the molecule, and the material therefore functions as an organic semiconductor. Through electron–hole recombination, a high-energy molecular state is formed. This state called exciton, behaves like a single molecule with high energy, and generates light after an exciton lifetime period.
- The Digital Light Processing (DLP) [20]: The Digital Mirror Device (DMD) is a Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) device invented in 1987. The DMD is designed for projection usage, where the tilting mirror pixels reflect the light out of the projection lens. Thus, the DMD generates a large, bright and high contrast image in comparison to other display technologies as LCOS, LCD, or OLED displays.
2.2. Recent Progress in Academy
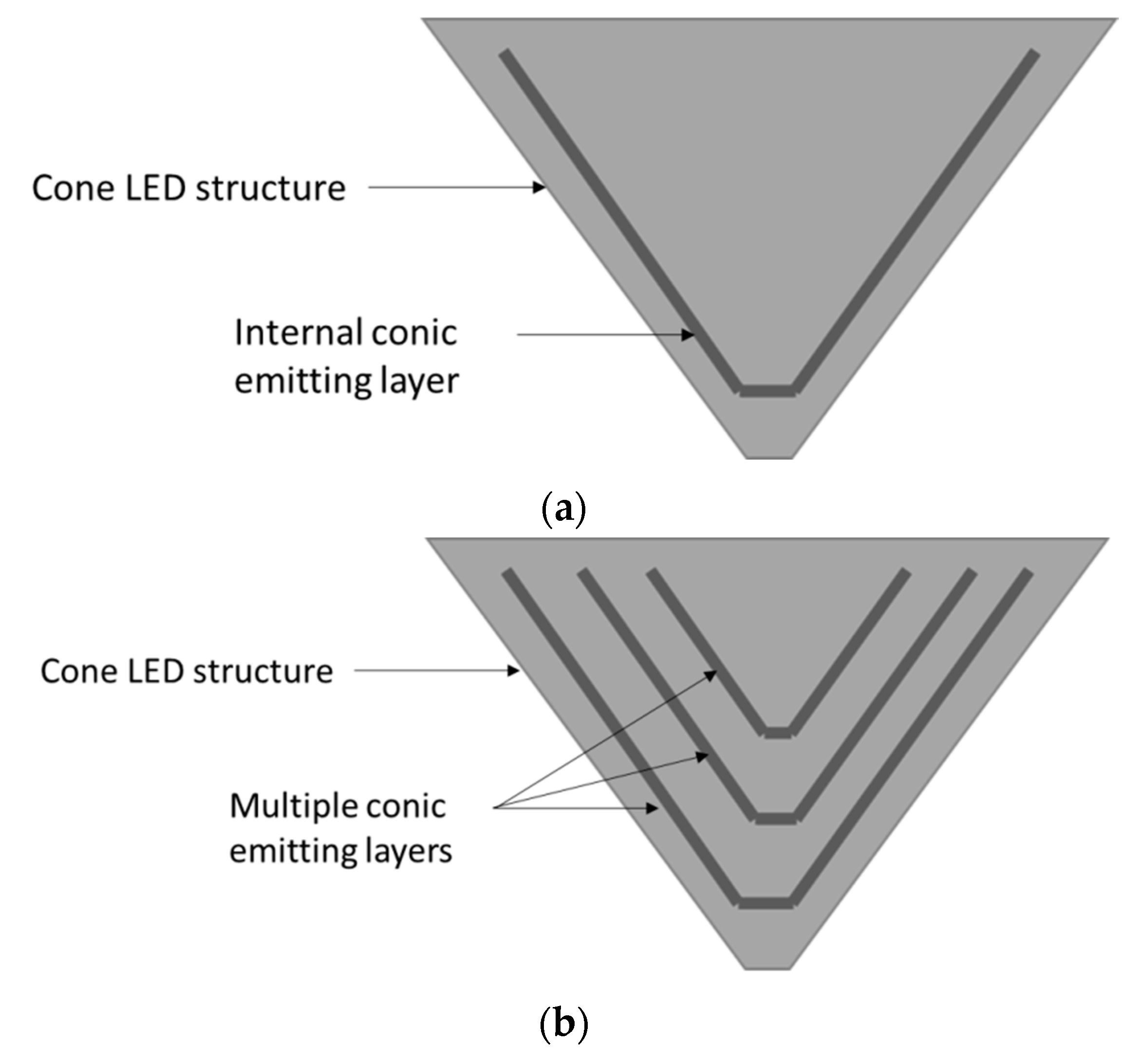
2.3. LENS Proposed Solution: Architecture, Design and Added Values
3. Methods
3.1. Monte Carlo Ray Tracing Using LightTools Simulation Software
3.2. Physical Simualtions vs. Geometry Ray Tracing
4. LightTools—Ray Tracing Results
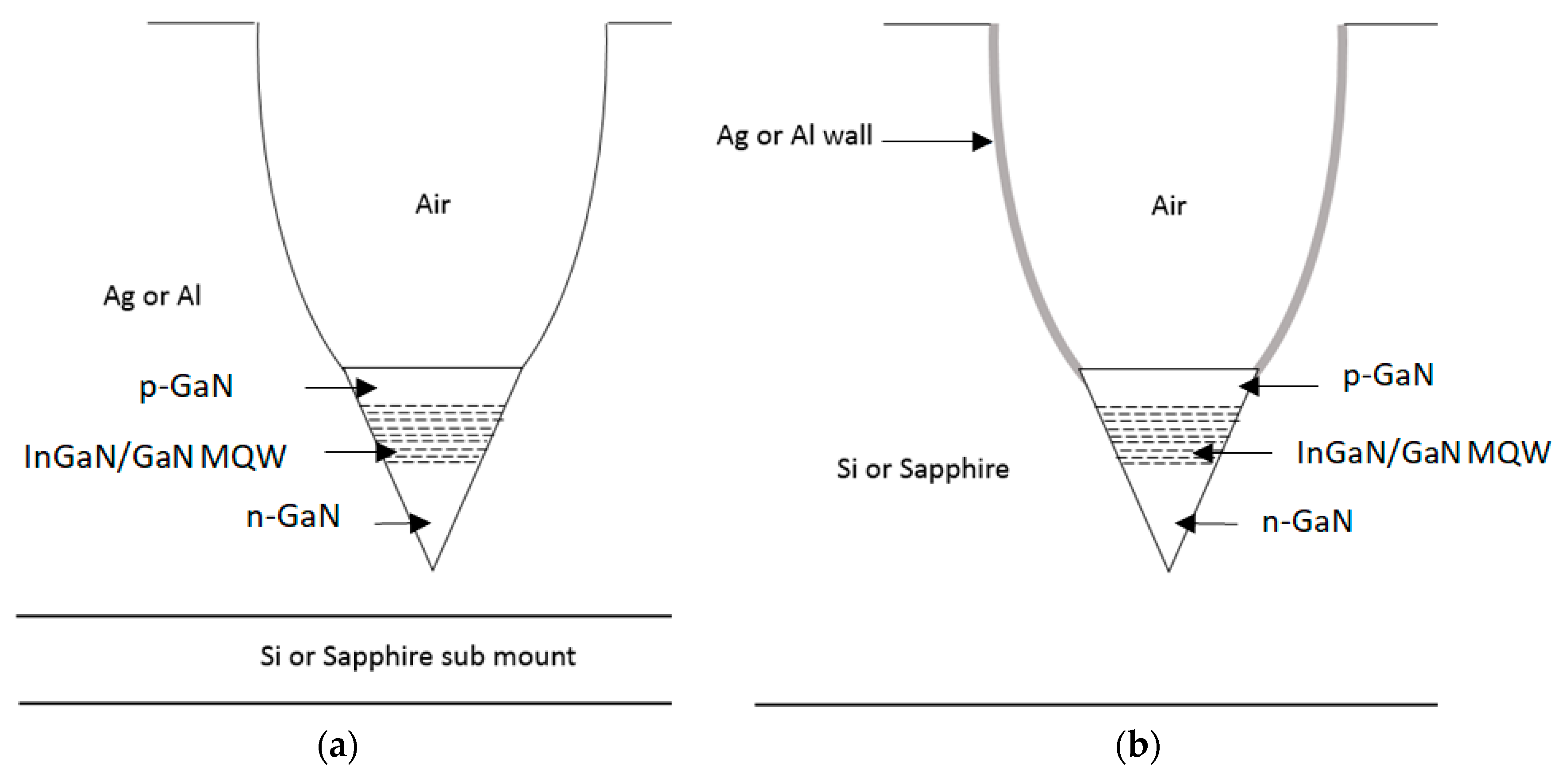
4.1. Reflective Nano-Cone LED
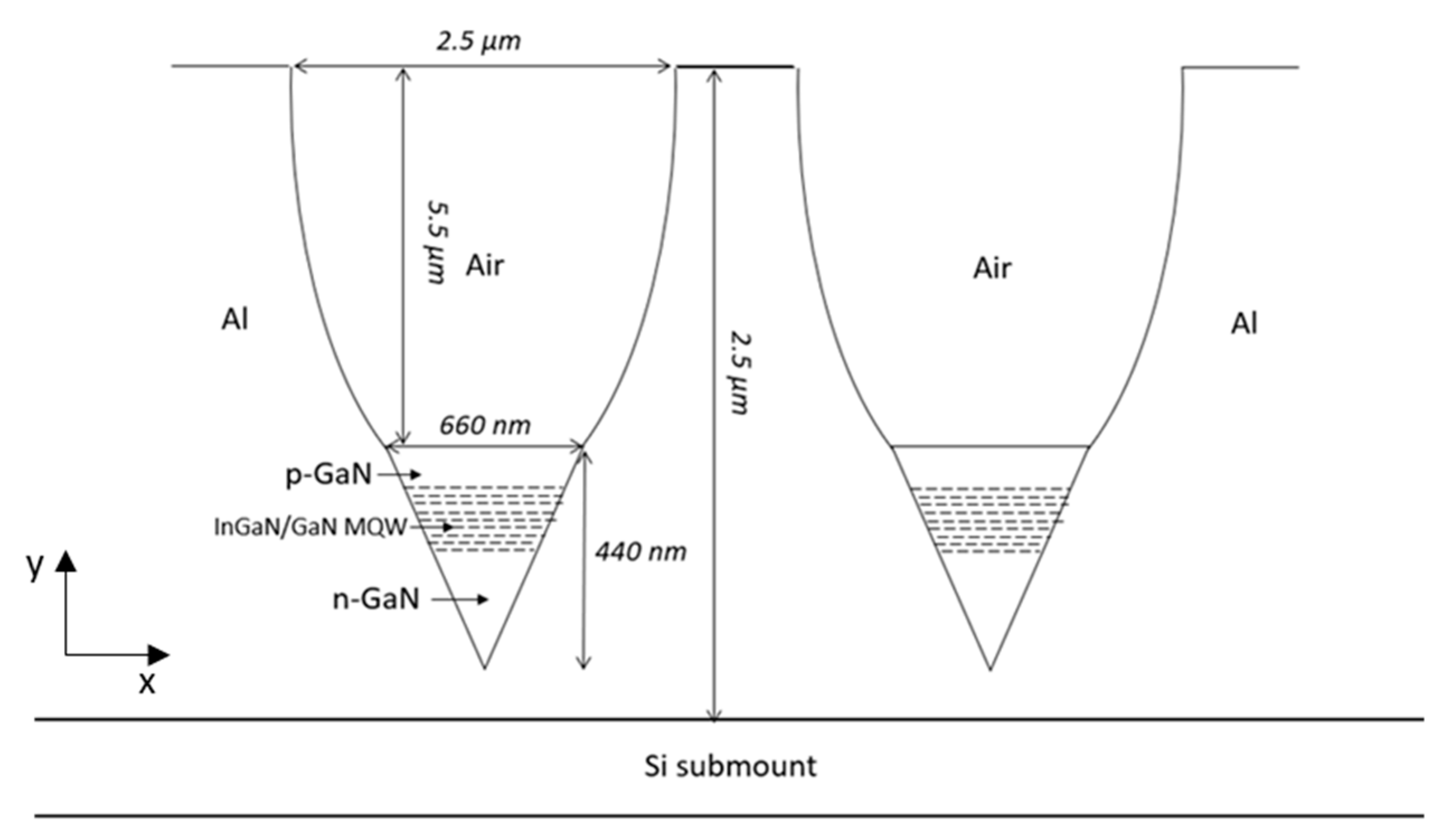
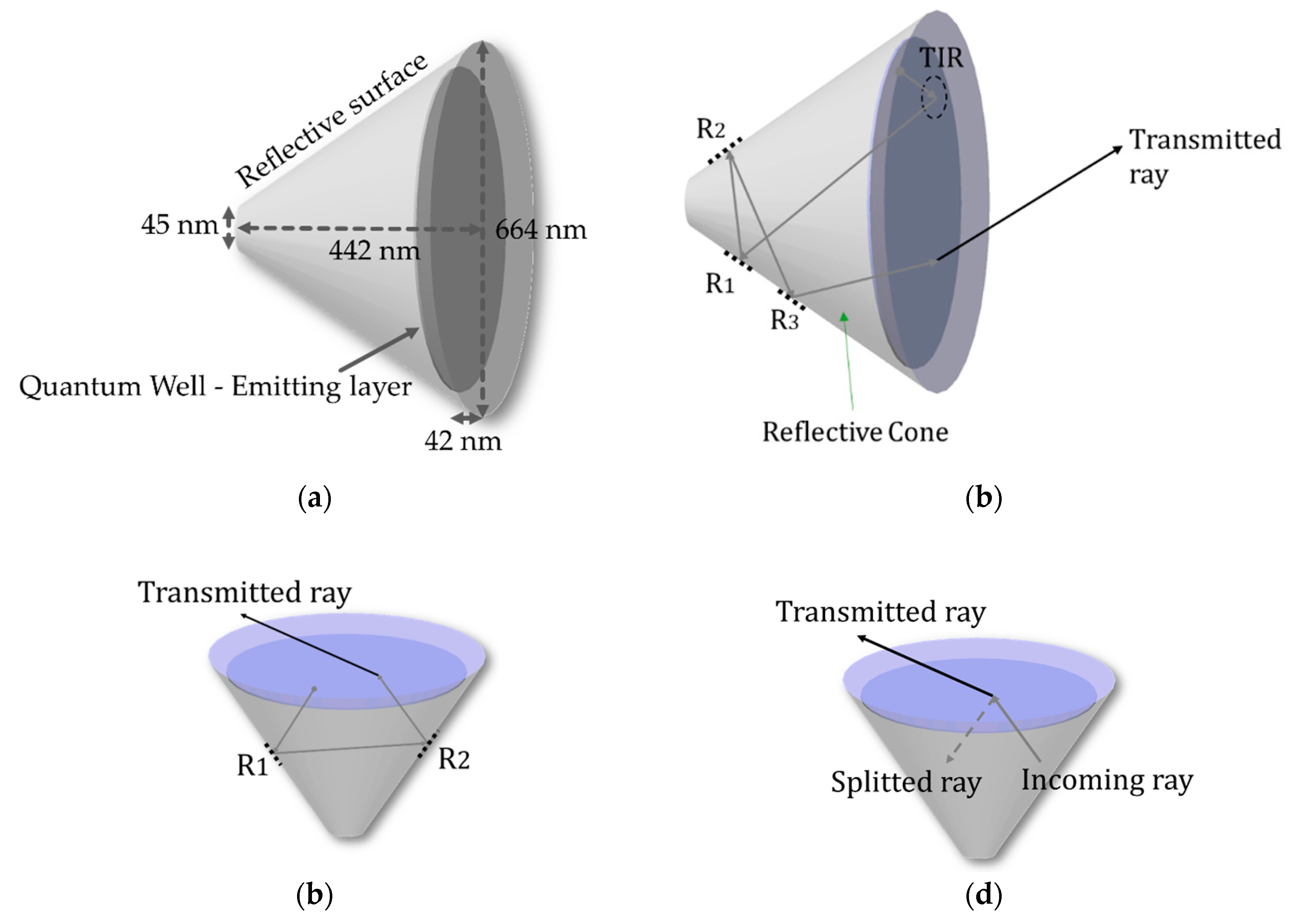
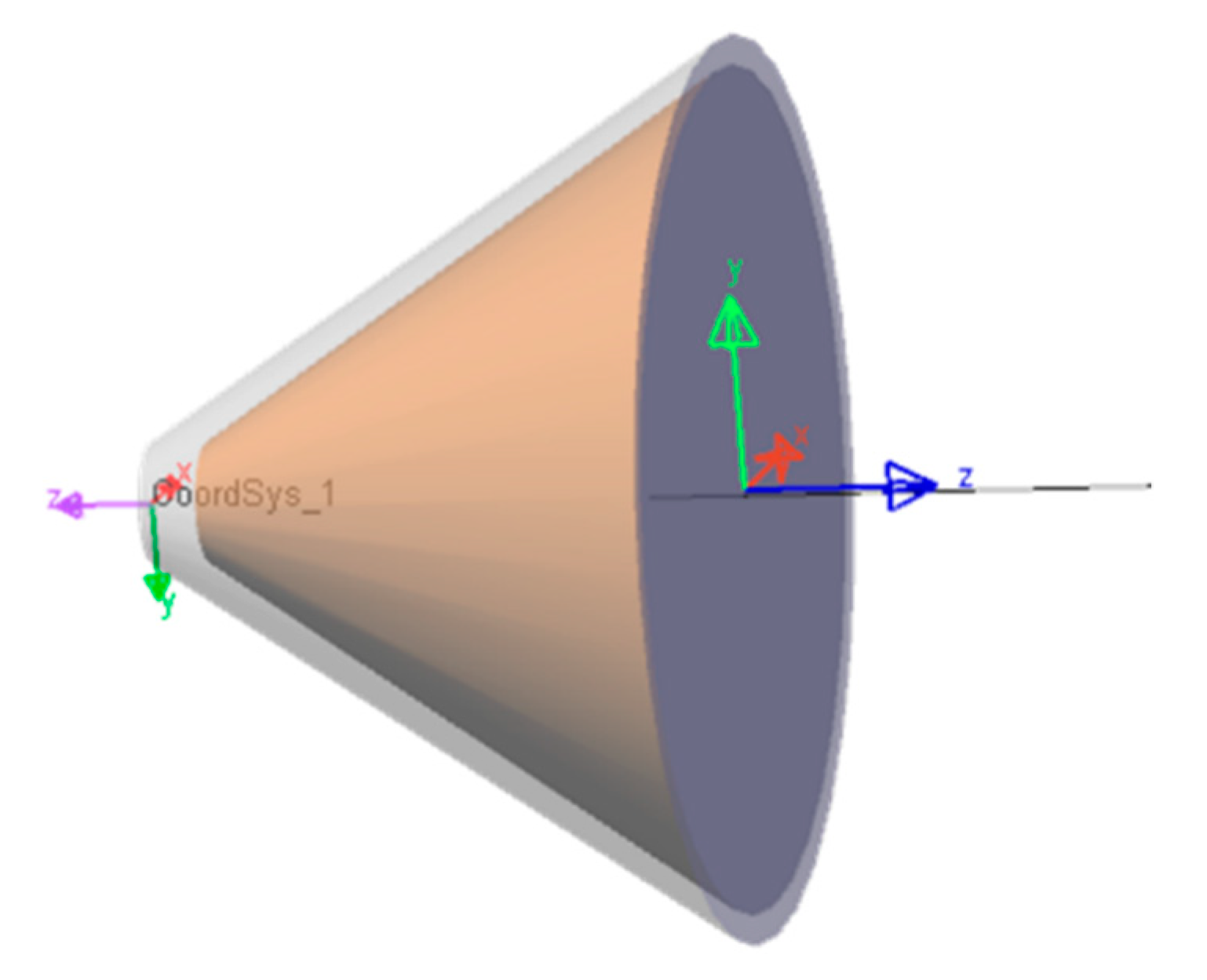
4.1.1. Structure, Dimensions, and Light Path
4.1.2. Light Extraction Efficiency (LEE)
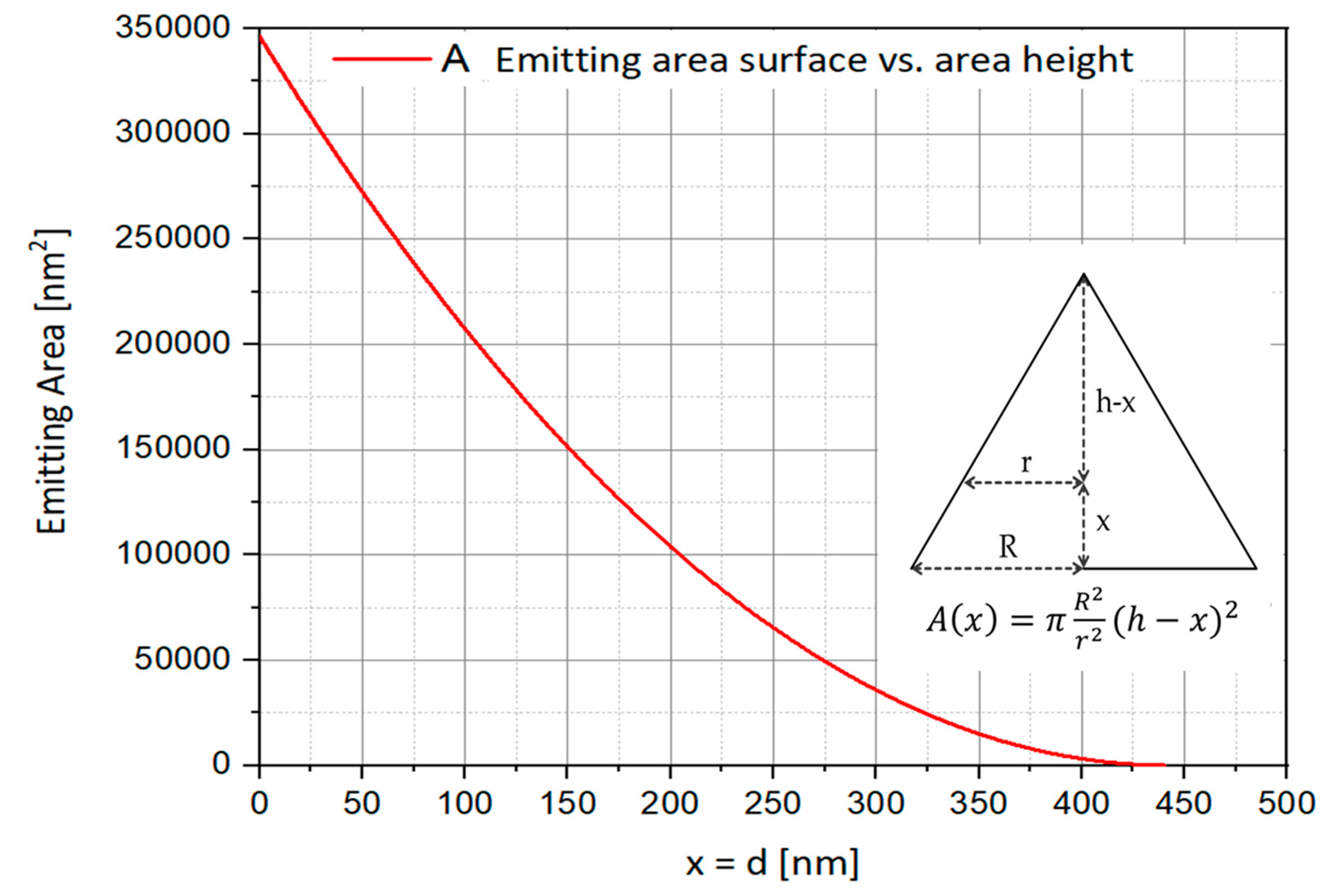
4.1.3. Emitter Position vs. LEE
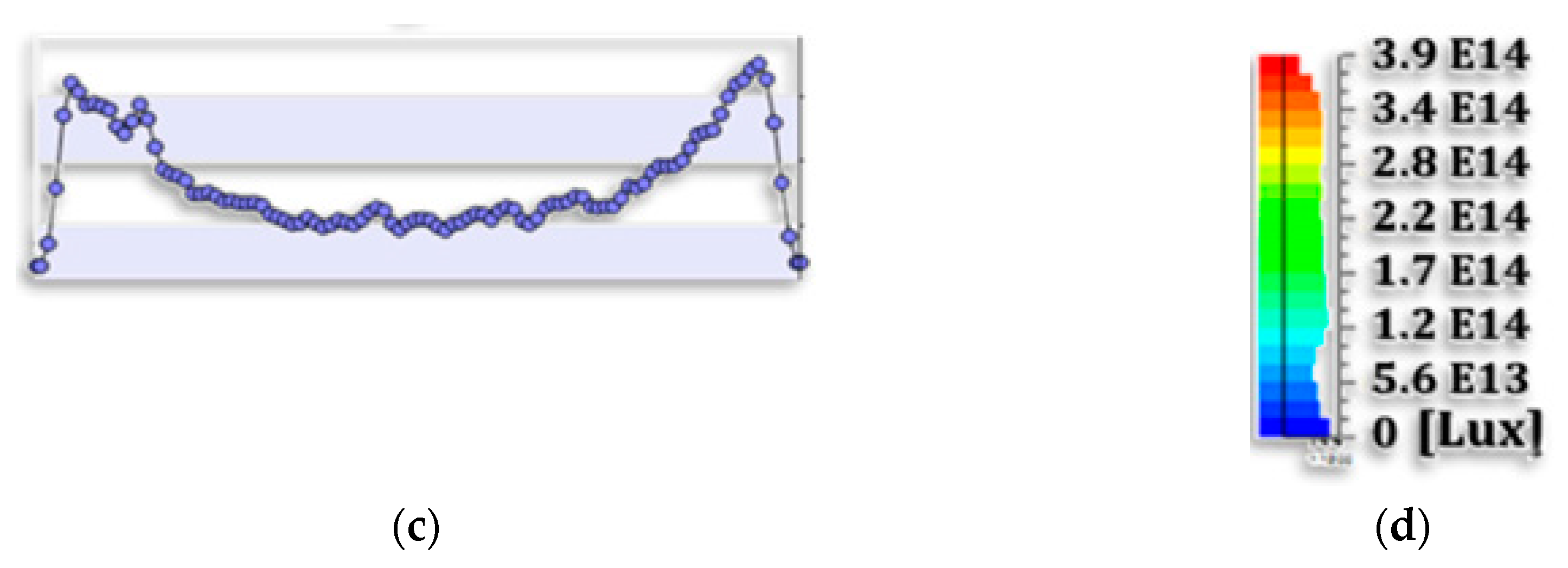
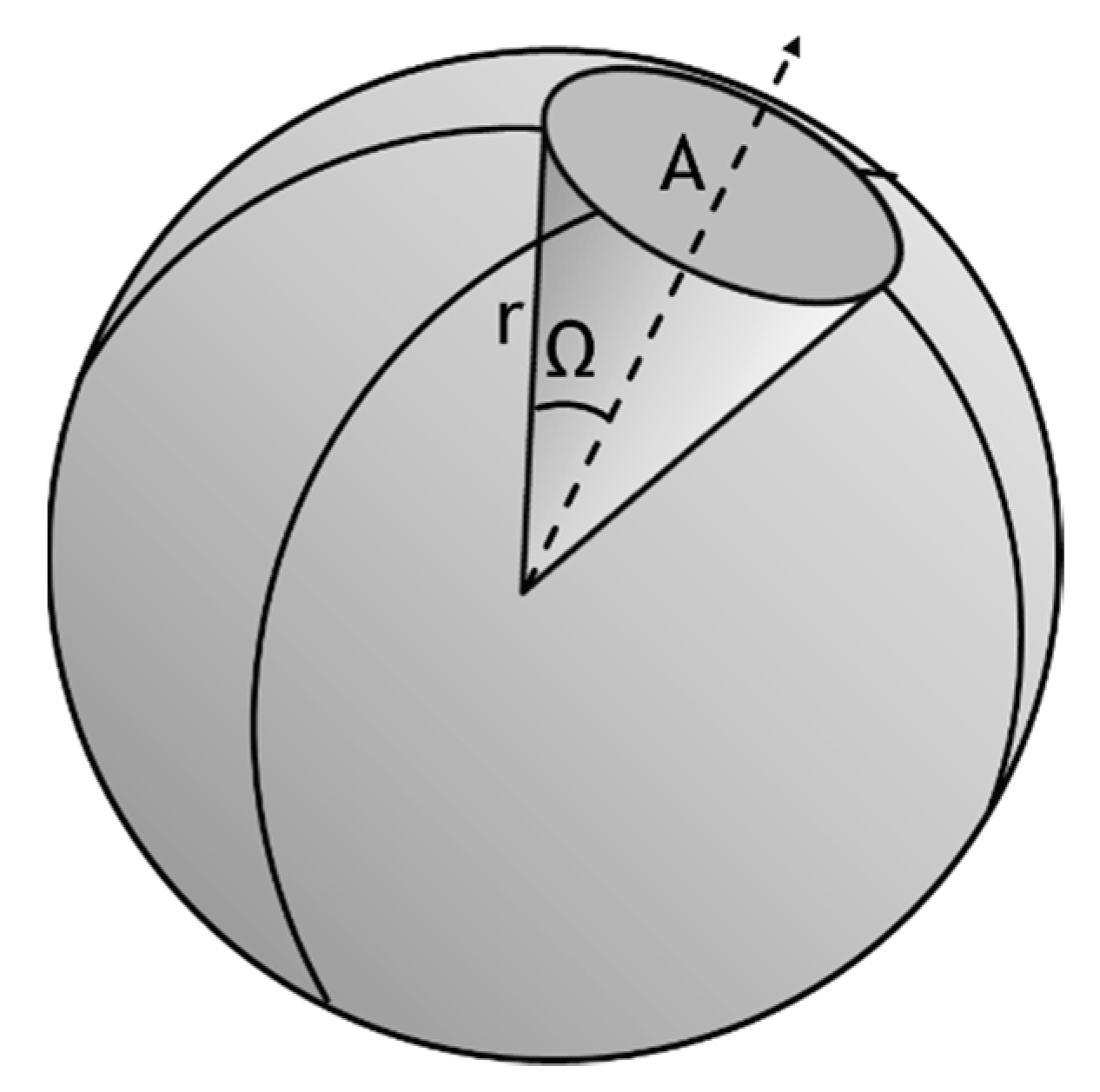
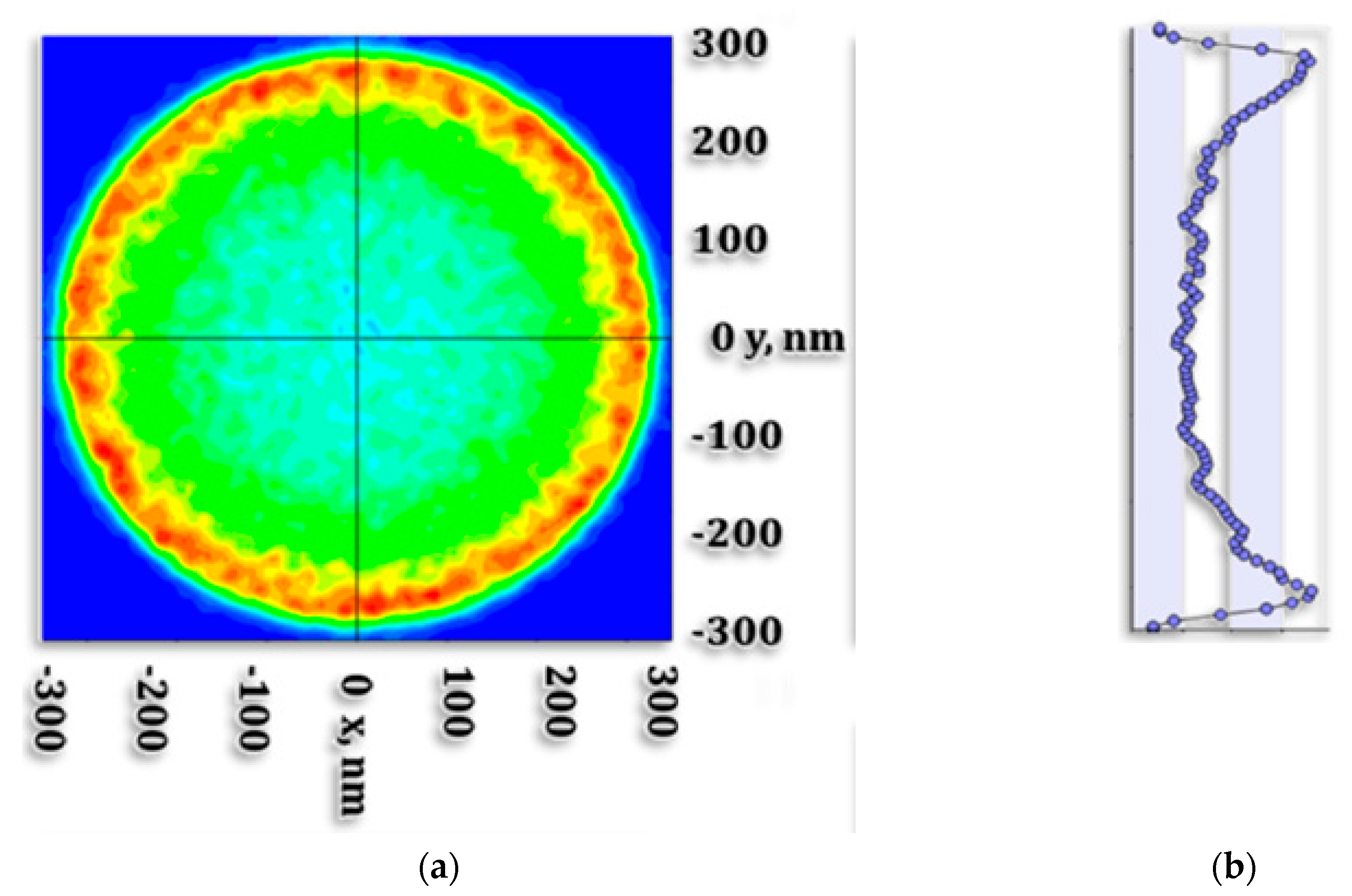
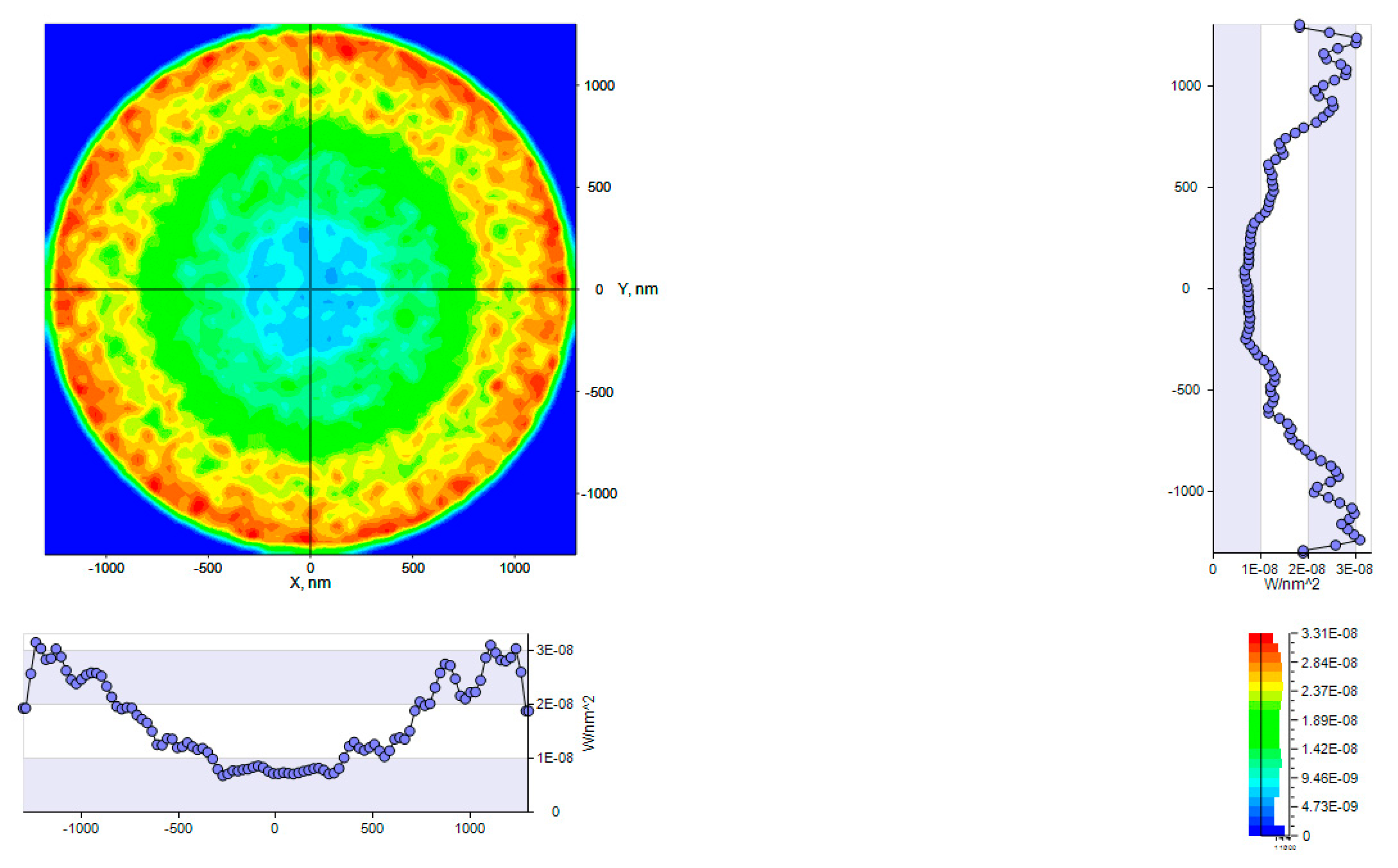
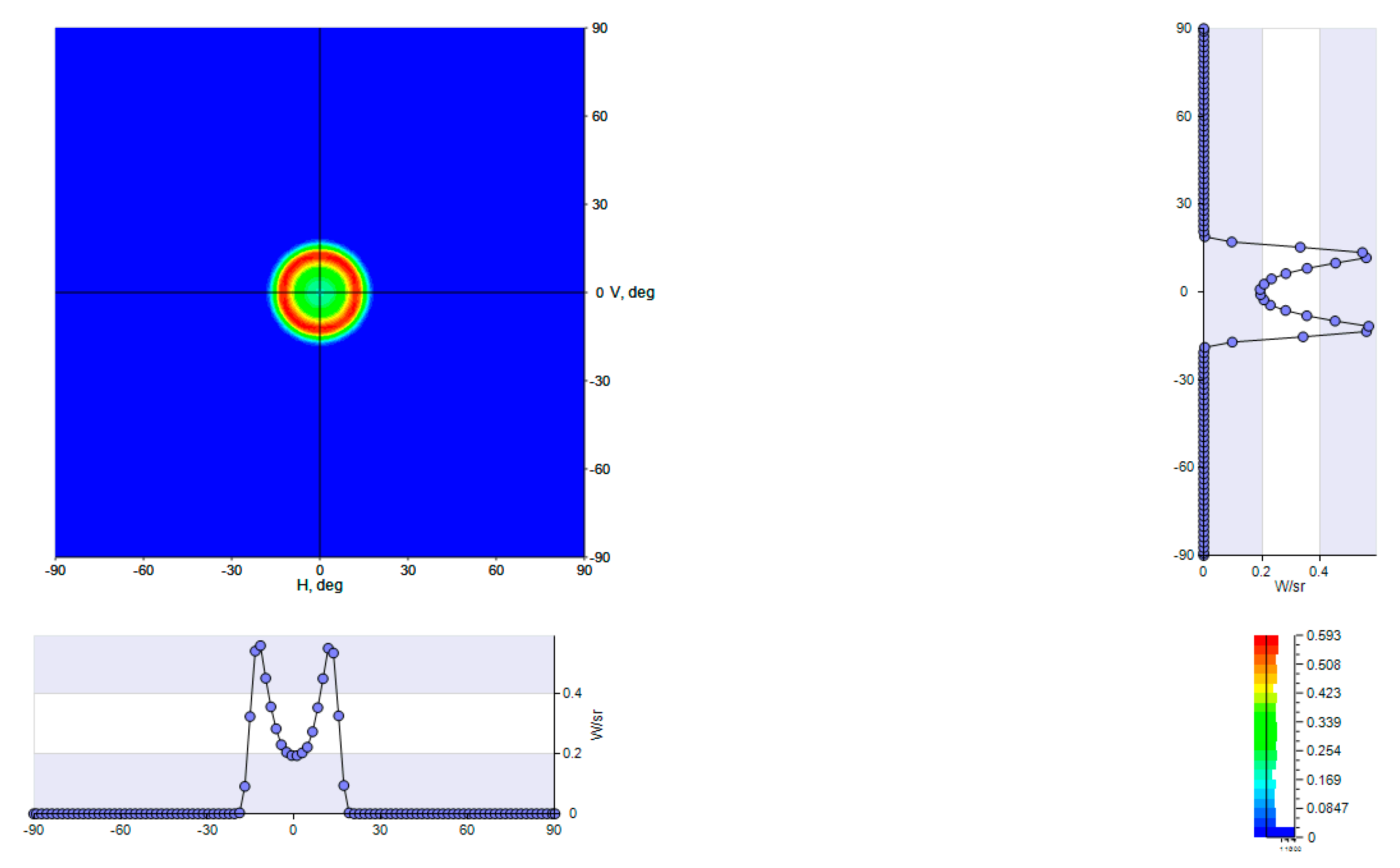
4.1.4. Outgoing Light Angular and Spatial Distribution
4.1.5. High Brightness Conical Emitter Layer
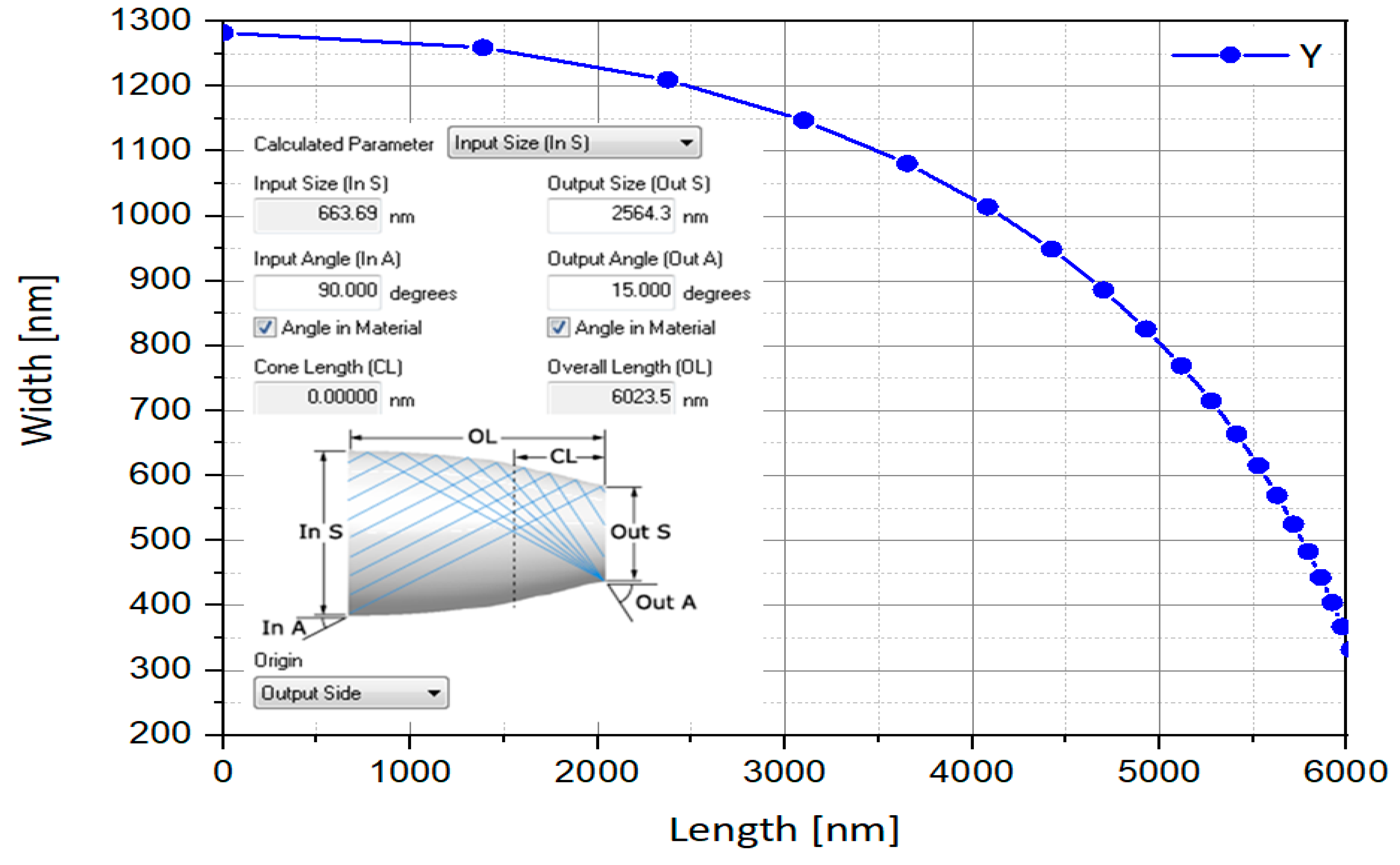
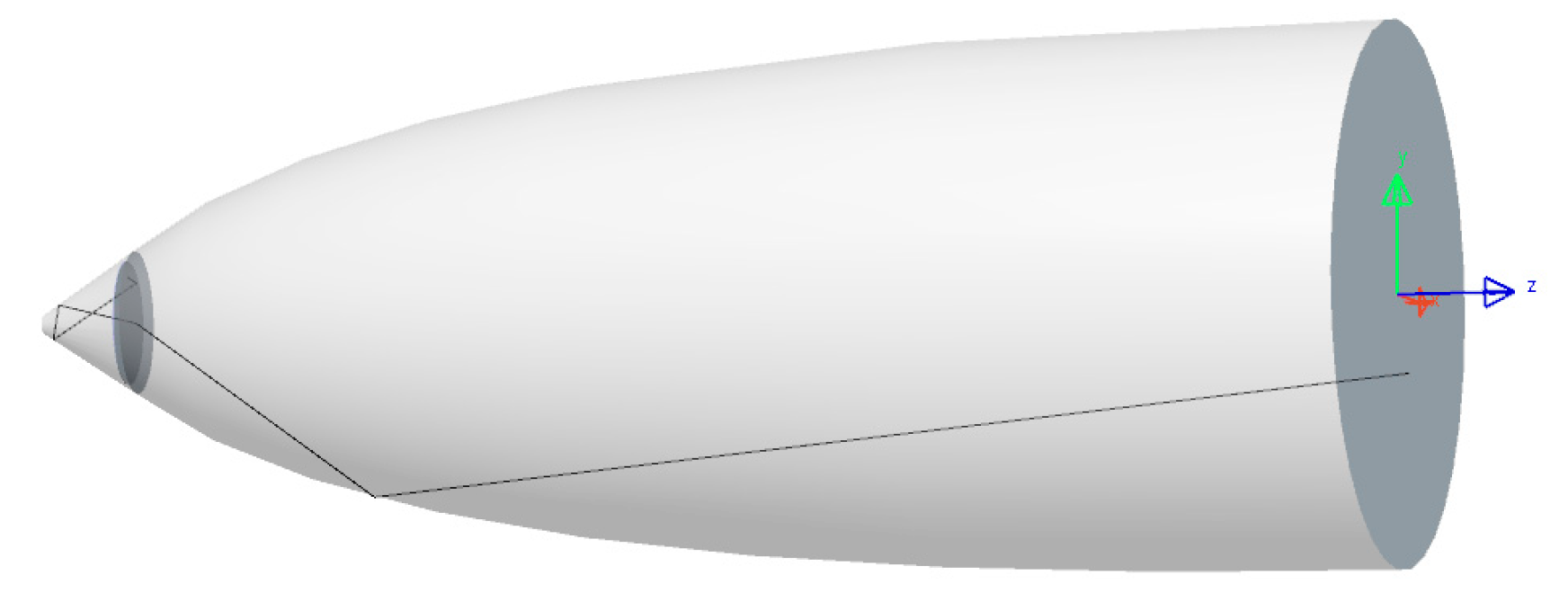
4.2. Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC)
4.3. CPC and Conical LED Assembly
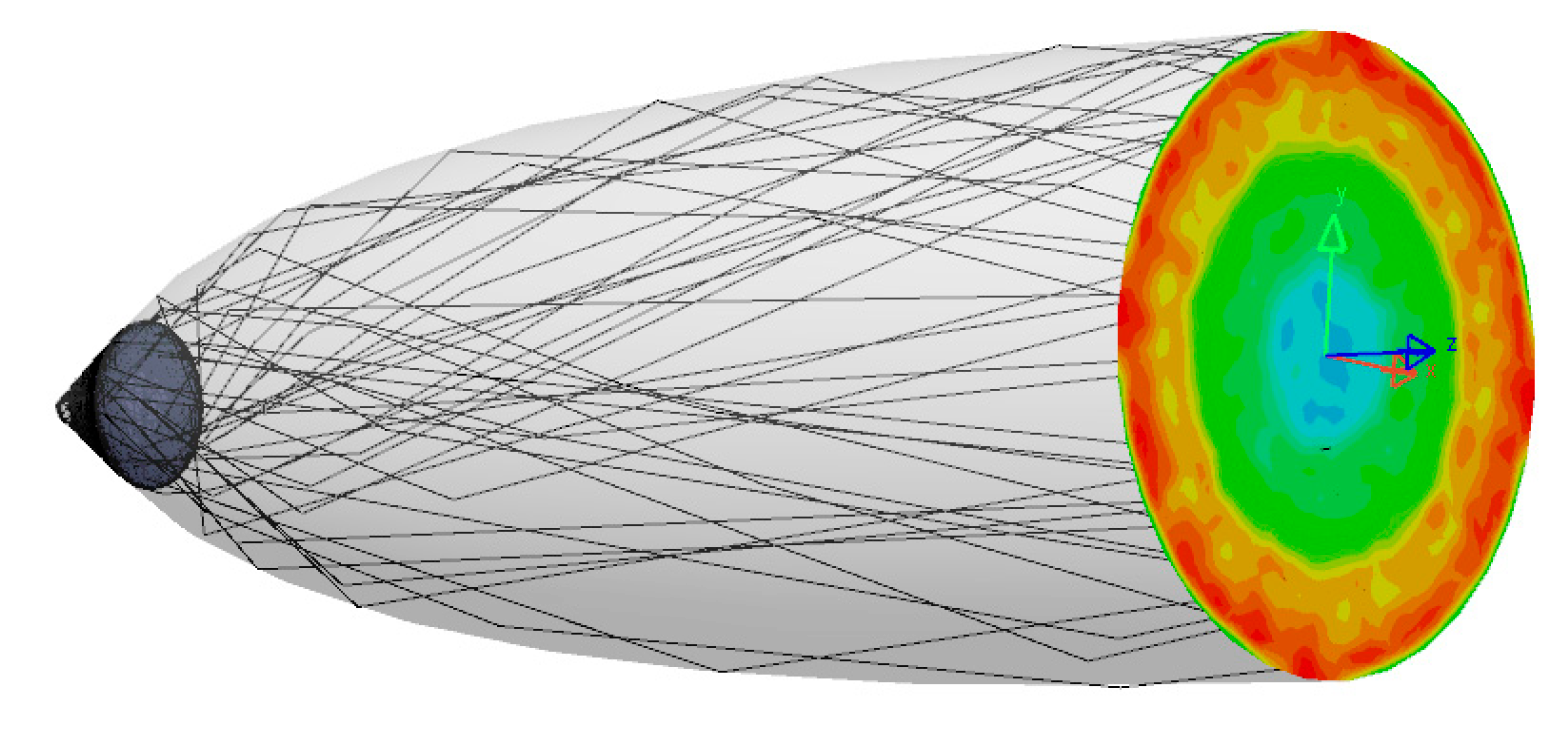
4.3.1. Pixel Assembly Ray Path
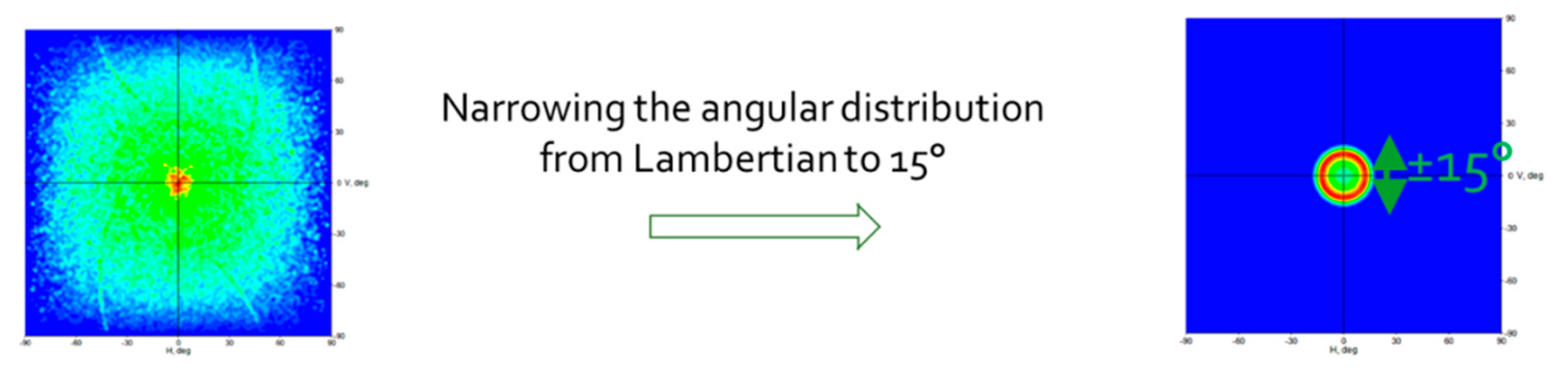
4.3.2. Outgoing Light Angular and Spatial Distribution
4.4. Complete LENS Pixel Assembly Efficiency Improvement
4.4.1. Cone LED LEE Improvement
4.4.2. CPC Brightness Improvement
4.4.3. The Total LENA Pixel Efficiency
4.5. LightTools Parameters Summary
5. Discussion
5.1. Simulation vs. Reality
5.2. Rectangular vs. Circular Aperture Diffraction
5.3. Sub-Wavelength Aperture
5.4. Enhancement of the LENS Pixel Wall Reflection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Market Shipment Share Held by LCD TV Manufacturers from 2008 to 2018. 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/267095/global-market-share-of-lcd-tv-manufacturers (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Betancourt, D.; Del Rio, C. Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors. In Fourth IEEE Workshop on Sensor Array and Multichannel Processing; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lumus Transparent Displays. Available online: https://lumusvision.com/ (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- A New Vision for Compting. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Guttag, K. Near Eye Displays (NEDs): Gaps In Pixel Sizes. 2017. Available online: https://www.kguttag.com/2017/06/07/gaps-in-pixel-sizes (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Theglobalscientist. The Next Big Step in Computers: What Can Physics Offer Us? 2014. Available online: https://theglobalscientist.com/2014/04/07/the-next-big-step-in-computers-what-can-physics-offer-us (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Popular Science. The Incredible Evolution of Supercomputers’ Powers, from 1946 to Today. 2017. Available online: https://www.popsci.com/supercomputers-then-and-now (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Himax Color Sequential LCOS. Available online: http://www.himax.com.tw/products/microdisplay-products/color-sequential-lcos (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Digi-Capita. After Mixed Year, Mobile AR to Drive $108 Billion VR/AR Market by 2021. 2017. Available online: http://www.digi-capital.com (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Carmigniani, J.; Furht, B. Handbook of Augmented Reality; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Carmigniani, J.; Furht, B. Handbook of Augmented Reality; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenfeld, T.; Karsenty, A. Super High Intensity Nano Emitting (SHINE) Pixel for High Resolution and High Brightness Displays. J. Nanophotonics 2020, 14, 016002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Zhang, J.-L.; Wang, G.-X.; Mo, C.-L.; Xu, L.-Q.; Ding, J.; Quan, Z.J.; Wang, X.-L.; Pan, S.; Zheng, C.-D.; et al. Status of GaN-based green light-emitting diodes. Chinese Physics B. 2015, 24, 067804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, L.H.; Hong, K.J. How Bright of Luminance Is Needed for Outdoor Commercial Display? 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Consumer Electronics—Berlin (ICCE-Berlin). Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7684740 (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Herrnsdorf, J.; McKendry, J.J.; Zhang, S.; Xie, E.; Ferreira, R.; Massoubre, D.; Zuhdi, A.M.; Henderson, R.K.; Underwood, I.; Watson, S.; et al. Active-MatrixGaN Micro Light-Emitting Diode Display with Unprecedented Brightness. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmigniani, J.; Furht, B. Handbook of Augmented Reality; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.G.; Chen, J.; Sharp, G.D. Polarization Engineering for LCD Projection; J. Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Berlin, Germany, 2005; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; You, Z.; Chu, D. Fundamentals of phase-only liquid crystal on silicon (LCOS) devices. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N. Sony’s OLED Micro-Display Realizes Both Small Pixel Pitch, High Image Quality. 2017. Available online: http://techon.nikkeibp.co.jp/atclen/news_en/15mk/062001307/?ST=msbe (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Hornbeck, L.J. Digital Light Processing and MEMS: An overview. In Digest IEEE/Leos 1996 Summer Topical Meeting. Advanced Applications of Lasers in Materials and Processing; IEEE: Keystone, CO, USA, 2002; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/540770 (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Hosseini, P.; Wright, C.D.; Bhaskaran, H. An optoelectronic framework enabled by low-dimensional phase-change films. Nature 2014, 511, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ra, Y.H.; Wang, R.; Woo, S.Y.; Djavid, M.; Sadaf, S. Md.; Lee, J.; Botton, G.A.; Mi, Z. Full-Color Single Nanowire Pixels for Projection Displays. Nano Letters 2016, 16, 4608–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Mohiddon, M.A.; Baumgarten, M.; Müllen, K.; Chandrasekar, R. Hierarchical multicolor nano-pixel matrices formed by coordinating luminescent metal ions to a conjugated poly(4′-octyl-2′,6′-bispyrazoyl pyridine) film via contact printing. Nature Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.W.; Hong, K.B.; Tsai, Y.L.; Teng, C.H.; Tzou, A.J.; Chu, Y.C.; Lee, P.T.; Ku, P.C.; Lin, C.C.; Kuo, H.C. Wavelength tunable InGaN/GaN nano-ring LEDs via nano-sphere lithography. Nature Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djuriie, A.B.; Chan, Y.; Li, B.H. Calculations of the refractive index of AlGaN/GaN quantum well. Proc. SPIE 2001, 4283, 630–637. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light, 7th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970; p. 40, eqs. (20), (21). [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, S.Y.; More, S.; Rvindranath, G.; Thipase, S.S. Mathematical modeling and analysis of compound parabolic concentrator using soltrace. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. (IJMET) 2018, 9, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical Constants of the Noble Metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, A.D. Algorithm for the determination of intrinsic optical constants of metal films: Application to aluminum. Appl. Optics 1995, 34, 4755–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970; Chap. 8.5; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.C.; Wang, L.C. A Simple Proof of Thue’s Theorem on Circle Packing; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, September 2010; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1009.4322 (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Schouten, H.F. Light Transmission through Sub-Wavelength Apertures. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, November 2005; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister, P. Optical Coating Technology; SPIE Press—A Publication of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Chap 1.7.5.2; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Harry, G.; Bodiya, T.P.; DeSalvo, R. Optical Coatings and Thermal Noise in Precision Measurement; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; p. 6. [Google Scholar]





| Parameters | Parameters Definition | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Device parameters: | ||
| Dem | Emitting layer distance from top LED surface | 42 nm |
| Rem | Emitting layer Radius | 287 nm |
| Aem | Emitting layer Area | 14.826 µm² |
| Dcbase | Cone base diameter | 45 nm |
| Dctop | Cone top surface diameter | 664 nm |
| OHc | Cone overall height | 442 nm |
| np-GaN | P-GaN refractive index | 2.45 |
| nn-GaN | N-GaN refractive index | 2.42 |
| RAlum | Aluminum reflectance at 525 nm | 91.703% |
| RSilver | Silver reflectance at 525 nm | 98.341% |
| Ratio | Cone LED dimension ratio | 2:3 |
| Dcpcbase | CPC base diameter | 664 nm |
| Dcpctop | CPC top surface diameter | 2564 nm |
| OLcpc | Overall CPC length | 6023 nm |
| InA | CPC Input Angle | 90° |
| OutA | CPC Output Angle | 15° |
| LightTools setup parameters used: | ||
| LUM | Photometric Source flux | 100 Lumen |
| λ | Wavelength LED emission | 525 nm |
| σθ | Emitting layer Angular distribution | Lambertian |
| Measured parameters: | ||
| σ ConeLED | Output Cone LED angular distribution | Lambertian |
| σ assembly | Output Assembly angular distribution | ±15° |
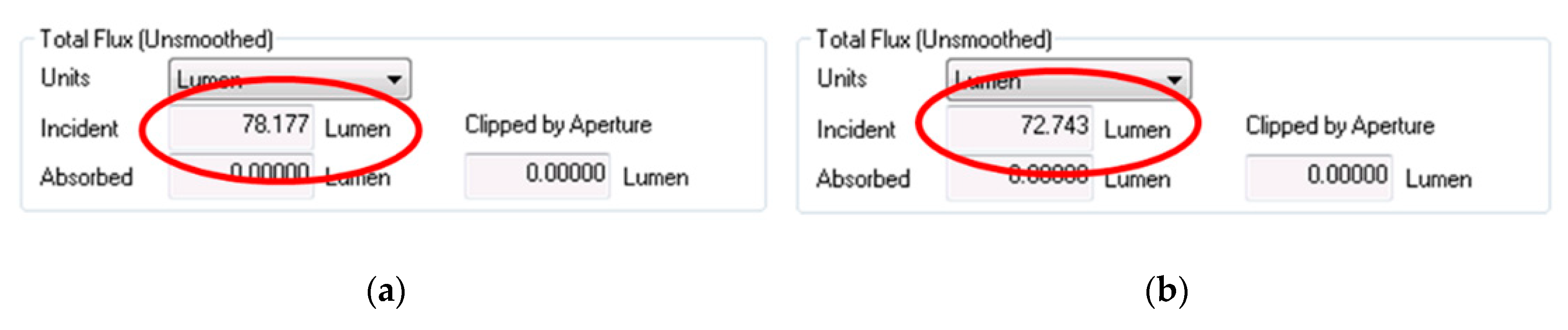
| LAl ConeLED | Output Cone LED light power with Aluminum reflective material | 72.74 Lumen |
| LSi ConeLED | Output Cone LED light power with Silver reflective material | 78.18 Lumen |
| L assembly | Output Cone and CPC assembly light power with Silver reflective material | 76.88 Lumen |
| L assembly | Output Cone and CPC assembly light power with Al reflective material | 66.70 Lumen |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eisenfeld, T.; Karsenty, A. Design and Modeling of Light Emitting Nano-Pixel Structure (LENS) for High Resolution Display (HRD) in a Visible Range. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020214
Eisenfeld T, Karsenty A. Design and Modeling of Light Emitting Nano-Pixel Structure (LENS) for High Resolution Display (HRD) in a Visible Range. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleEisenfeld, Tsion, and Avi Karsenty. 2020. "Design and Modeling of Light Emitting Nano-Pixel Structure (LENS) for High Resolution Display (HRD) in a Visible Range" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020214
APA StyleEisenfeld, T., & Karsenty, A. (2020). Design and Modeling of Light Emitting Nano-Pixel Structure (LENS) for High Resolution Display (HRD) in a Visible Range. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020214






