Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Hprt Gene Mutations in V79 Hamster Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Nanoparticle Characterization, Dispersion and Cell Exposure
Dispersion Procedure DP1
Dispersion Procedure DP2
2.3. Extrinsic Properties of TiO2 NPs
2.4. Cellular Uptake
2.5. Relative Growth Activity (RGA)
2.6. Plating Efficiency (PE)
2.7. Hprt Mammalian Gene Mutation Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TiO2 Characterization, Extrinsic Properties
3.2. Uptake of TiO2 NPs Measured by the TEM
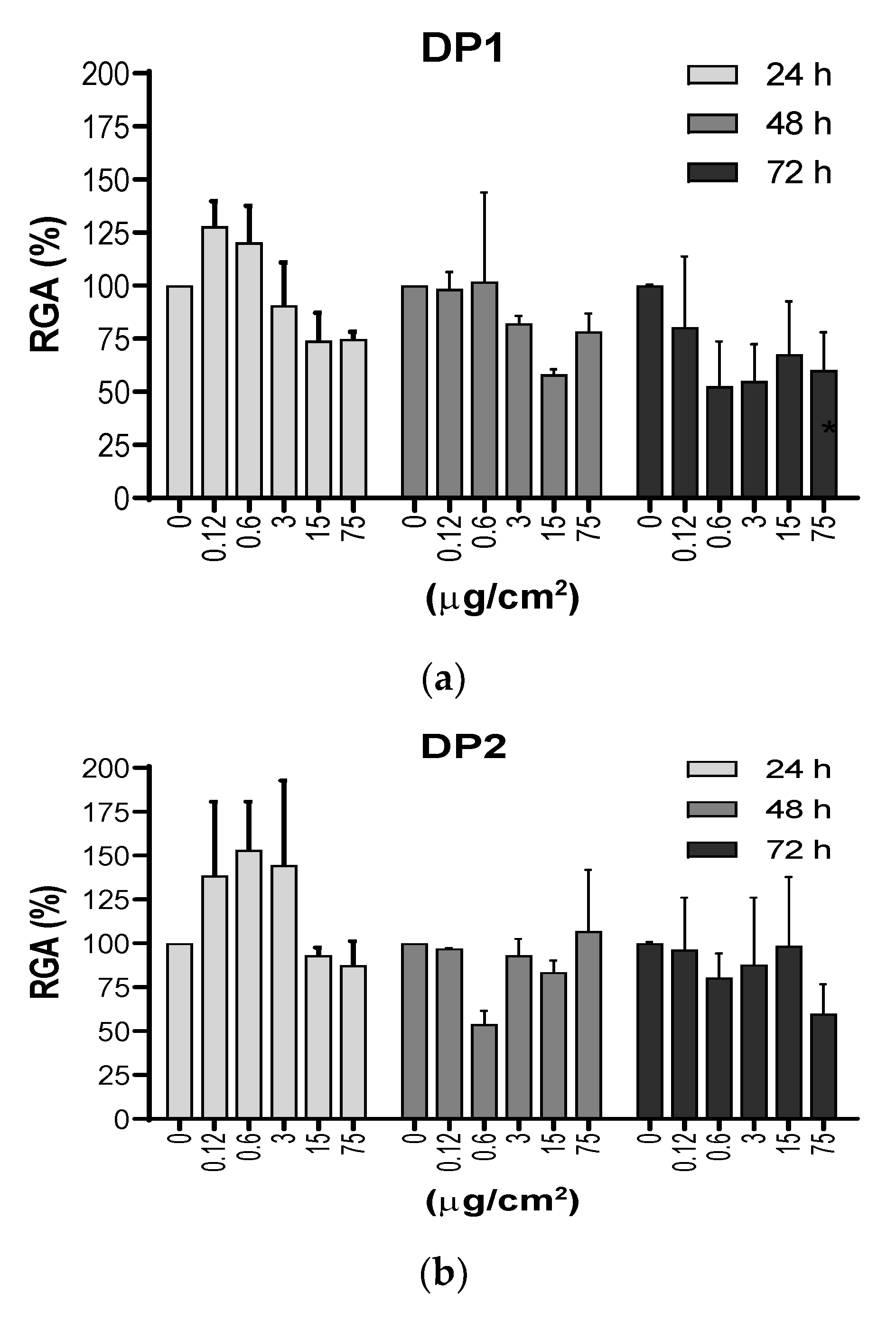
3.3. Cytotoxic Effect of TiO2 NPs on V79-4 Cells
3.4. Mammalian Hprt Gene Mutation Assay, the Effect After TiO2 NPs Exposure
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Cogliano, V. Carcinogenicity of carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Fabricius, L.; von Goetz, N. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 46, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.X.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Y.X.; Cao, A.N.; Liu, J.H.; Du, L.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, H.F. Characterization and preliminary toxicity assay of nano-titaniumdioxide additive in sugar-coated chewing gum. Small 2013, 9, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, H.C.; Notter, T.; Meyer, U.; Naegeli, H. Critical review of the safety assessment of titanium dioxide additives in food. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Magaye, R.; Castranova, V.; Zhao, Z. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Sanderson, B.J.; Wang, H. Cyto- and genotoxicity of ultrafine TiO2 particles in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat. Res. 2007, 628, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ba, T.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.; Chen, T.; Song, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qian, Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Genotoxic evaluation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, A.M.; Louro, H.; Antunes, S.; Quarré, S.; Simar, S.; Temmerman, P.J.D.; Verleysen, E.; Mast, J.; Jensen, K.A.; Norppa, H.; et al. Genotoxicity evaluation of nanosized titanium dioxide, synthetic amorphous silica and multi-walled carbon nanotubes in human lymphocytes. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 28, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yamani, N.; Collins, A.R.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Fjellsbo, L.M.; Shaposhnikov, S.; Zienolddiny, S.; Dusinska, M. In vitro genotoxicity testing of four reference metal nanomaterials, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, cerium oxide and silver: towards reliable hazard assessment. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hunter, L.A.; Arslan, Z.; Wilkerson, M.G.; Wickliffe, J.K. Chronic exposure to nanosized anatase titanium dioxide is not cyto- or genotoxic to Chinese hamster ovary cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2011, 52, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, Y.; Schmit, J.; Darne, C.; Gaté, L.; Goutet, M.; Rousset, D.; Rastoix, O.; Wrobel, R.; Witschger, O.; Martin, A.; et al. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of nanosized and microsized titanium dioxide and iron oxide particles in Syrian hamster embryo cells. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2012, 56, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamzeh, M.; Sunahara, G.I. In vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity studies of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Bilanicova, D.; Pojana, G.; Fjellsbø, L.M.; Hudecova, A.; Hasplova, K.; Marcomini, A.; Dusinska, M. Impact of agglomeration and different dispersions of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the human related in vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Collins, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A.; Stone, V.; Dusinska, M. Mechanisms of genotoxicity. A review of in vitro and in vivo studies with engineered nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.Y.; Wallace, K.; Daniel, K.M.; Tennant, A.H.; Zucker, R.M.; Strickland, J.; Dreher, K.; Kligerman, A.D.; Blackman, C.F.; Demarini, D.M. Effect of treatment media on the agglomeration of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: impact on genotoxicity, cellular interaction, and cell cycle. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1929–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, S.; Jomini, S.; Fessard, V.; Bigorgne-Vizade, E.; Rousselle, C.; Michel, C. Assessment of the in vitro genotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles in a regulatory context. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic. Risks to humans: carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2010, 93, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Doak, S.H.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Singh, N. In vitro genotoxicity testing strategy for nanomaterials and the adaptation of current OECD guidelines. Mutat. Res. 2012, 745, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, M.; Sasaki, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Takaya, M.; Koda, S.; Nagano, K.; Arito, H.; Fukushima, S. Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes in cultured Chinese hamster lung cells in comparison with chrysotile A fibers. J. Occup. Health 2010, 52, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.; El Yamani, N.; Kazimirova, A.; Dusinska, M.; Marcos, R. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (NM401) induce ROS-mediated HPRT mutations in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerlund, E.; Cappellini, F.; Di Bucchianico, S.; Islam, S.; Skoglund, S.; Derr, R.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Hendriks, G.; Karlsson, H.L. Genotoxic and mutagenic properties of Ni and NiO nanoparticles investigated by comet assay, y-H2AX staining, Hprt mutation assay and ToxTracker reporter cell lines. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2018, 59, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dusinska, M.; Boland, S.; Saunders, M.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Tran, L.; Pojana, G.; Marcomini, A.; Volkovova, K.; Tulinska, J.; Knudsen, L.E.; et al. Towards an alternative testing strategy for nanomaterials used in nanomedicine: Lessons from NanoTEST. Nanotoxicology 2015, 7, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annangi, B.; Bach, J.; Vales, G.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Long-term exposures to low doses of cobalt nanoparticles induce cell transformation enhanced by oxidative damage. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huk, A.; Izak-Nau, E.; El Yamani, N.; Uggerud, H.; Vadset, M.; Zasonska, B.; Duschl, A.; Dusinska, M. Impact of nanosilver on various DNA lesions and HPRT gene mutations -effects of charge and surface coating. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Test, No. 476: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests Using the Hprt and xprt Genes. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4: Health Effects; OECD: Paris, France, 2016; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/9789264264809-en.pdf?expires=1582877457&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=AF948B418DF0BC20B908E85A06F87F69 (accessed on 17 August 2016).
- Huk, A.; Izak-Nau, E.; Reidy, B.; Boyles, M.; Duschl, A.; Lynch, I.; Dušinska, M. Is the toxic potential of nanosilver dependent on its size? Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yan, J.; Li, Y. Genotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, Z. Toxicology of nanosized titanium dioxide: an update. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, M.; Jabeen, F.; Shabbir, S.; Asghar, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Chaudhry, A.S. Toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide (TiO2-NP) through various routes of exposure: a review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, P.; Jensen, D.M.; Wils, R.S.; Andersen, M.H.G.; Danielsen, P.H.; Roursgaard, M. Assessment of evidence for nanosized titanium dioxide-generated DNA strand breaks and oxidatively damaged DNA in cells and animal models. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, R.J. HPRT mutations in humans: biomarkers for mechanistic studies. Mutat. Res. 2001, 489, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Senapati, V.A.; Singh, D.; Dubey, K.; Maurya, R.; Pandey, A.K. Impact of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles on mutagenic and genotoxic response in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells (V-79): The role of cellular uptake. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Gao, S.; Hong, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, J. Genotoxicity evaluation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using the mouse lymphoma assay and the Ames test. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 838, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, Y.; Fontana, C.; Chavinier, E.; Terzetti, F.; Gaté, L.; Binet, S.; Darne, C. Cytotoxic and genotoxic evaluation of different synthetic amorphous silica nanomaterials in the V79 cell line. Toxicol. Ind. Health. 2015, 32, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimirova, A.; Barancokova, M.; Staruchova, M.; Drlickova, M.; Volkovova, K.; Dusinska, M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles tested for genotoxicity with the comet and micronucleus assays in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo. Mutat. Res. 2019, 843, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Type of Characteristics | Properties of NM-105 |
|---|---|
| Phase Shape of particles | White ultra-fine powder Irregular/ellipsoidal |
| Particle size (nm) | 15–60 |
| Crystal structure | Anatase/Rutile in ratio of 70:30 or 80:20 |
| Surface area (m2/g) | 61 |
| Pore volume (mL/g) | 0.13 |
| Zeta-potential at pH 7 (mV) | −30.2 |
| Chemical composition of particles | Ti, O |
| Ti purity of particles | >99% |
| Surface chemistry | Uncoated |
| Impurities of concern | Co (920 ppm), Fe (16 ppm) |
| Medium | TiO2 Stock Dispersion DP1 | TiO2 Stock Dispersion DP2 |
|---|---|---|
| DMEM +10% FBS | Bimodal distribution, 112 (± 20) nm and 296 (± 55) nm | 752 (± 397) nm |
| Size stability after 48 h | Stable ~2 days 125 (± 27) nm and 366 (± 65) nm | Large Agglomerates |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazimirova, A.; El Yamani, N.; Rubio, L.; García-Rodríguez, A.; Barancokova, M.; Marcos, R.; Dusinska, M. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Hprt Gene Mutations in V79 Hamster Cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030465
Kazimirova A, El Yamani N, Rubio L, García-Rodríguez A, Barancokova M, Marcos R, Dusinska M. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Hprt Gene Mutations in V79 Hamster Cells. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030465
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazimirova, Alena, Naouale El Yamani, Laura Rubio, Alba García-Rodríguez, Magdalena Barancokova, Ricard Marcos, and Maria Dusinska. 2020. "Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Hprt Gene Mutations in V79 Hamster Cells" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030465
APA StyleKazimirova, A., El Yamani, N., Rubio, L., García-Rodríguez, A., Barancokova, M., Marcos, R., & Dusinska, M. (2020). Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Hprt Gene Mutations in V79 Hamster Cells. Nanomaterials, 10(3), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030465






