Aerobic Oil-Phase Cyclic Magnetic Adsorption to Synthesize 1D Fe2O3@TiO2 Nanotube Composites for Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of TiO2 Nanotubes
2.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4@oleic Acid
2.4. Synthesis of 1D Fe2O3@TiO2 Nanotube Composites
2.5. Photocatalytic Experiments
2.6. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
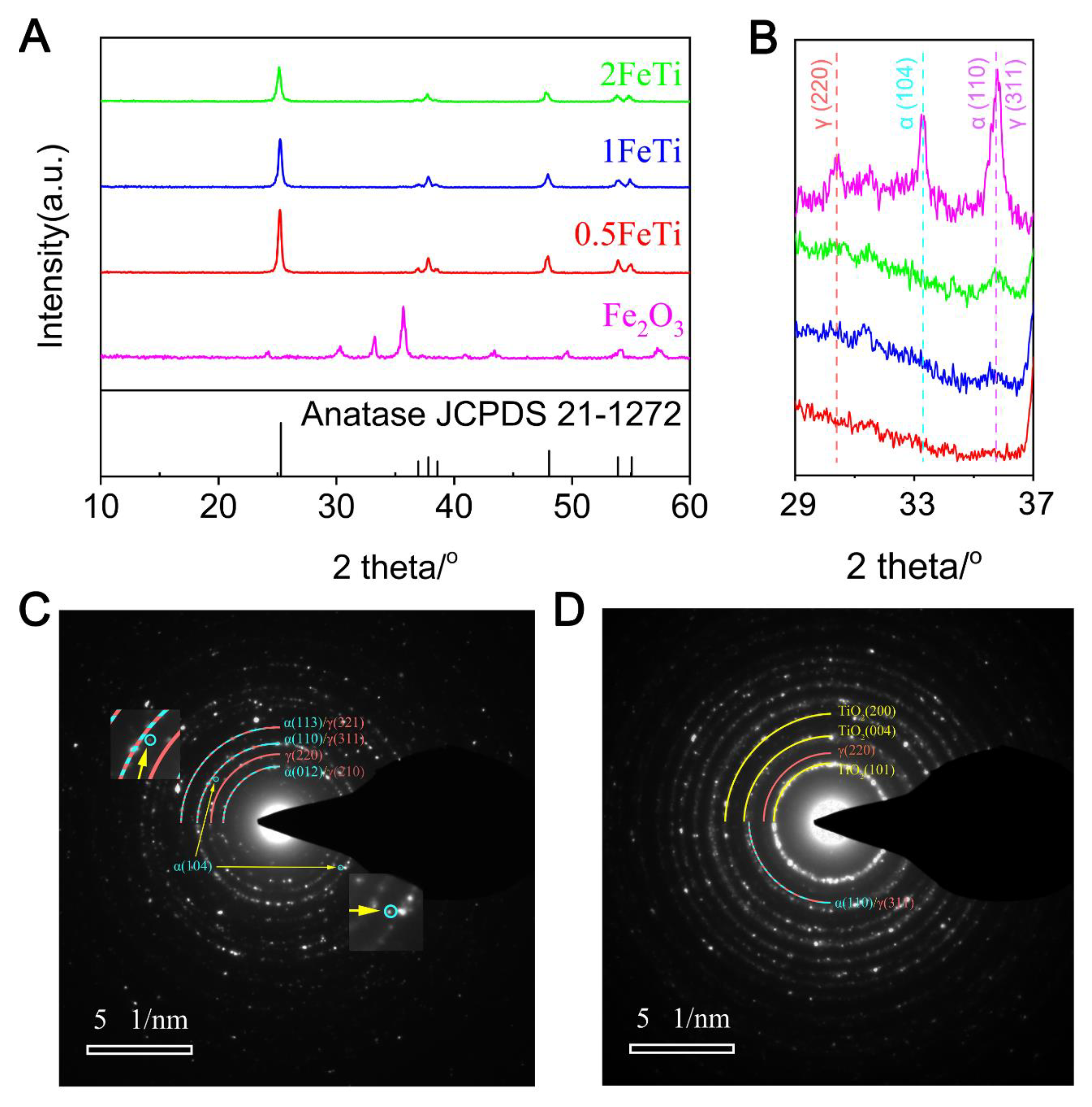
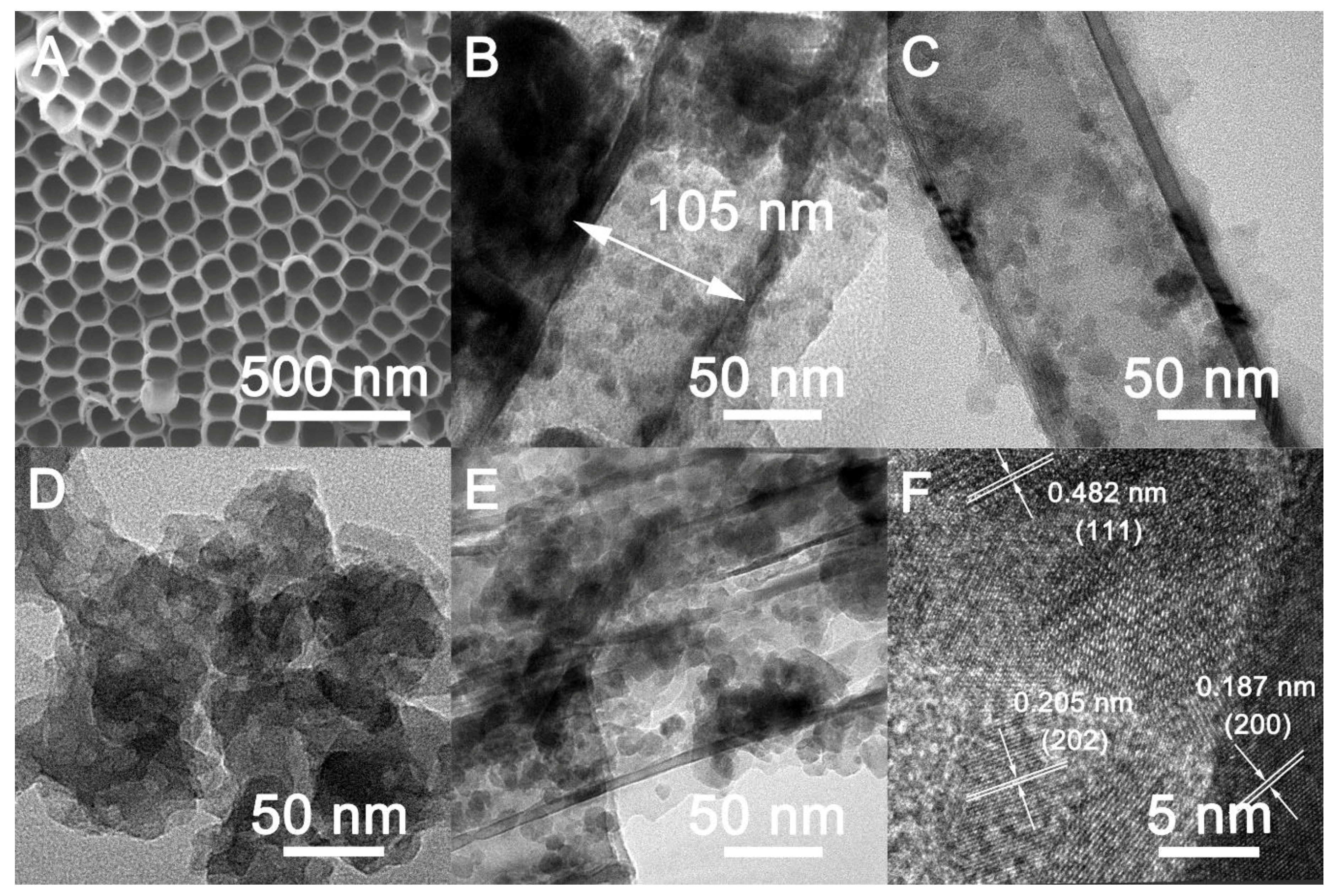
3.1. Structural and Elemental Characterizations
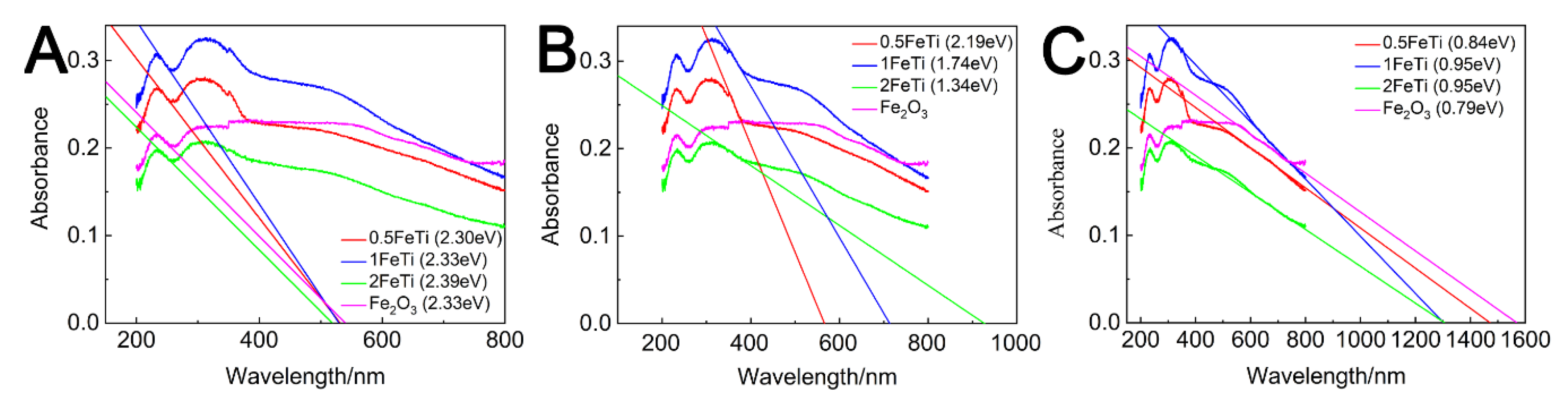
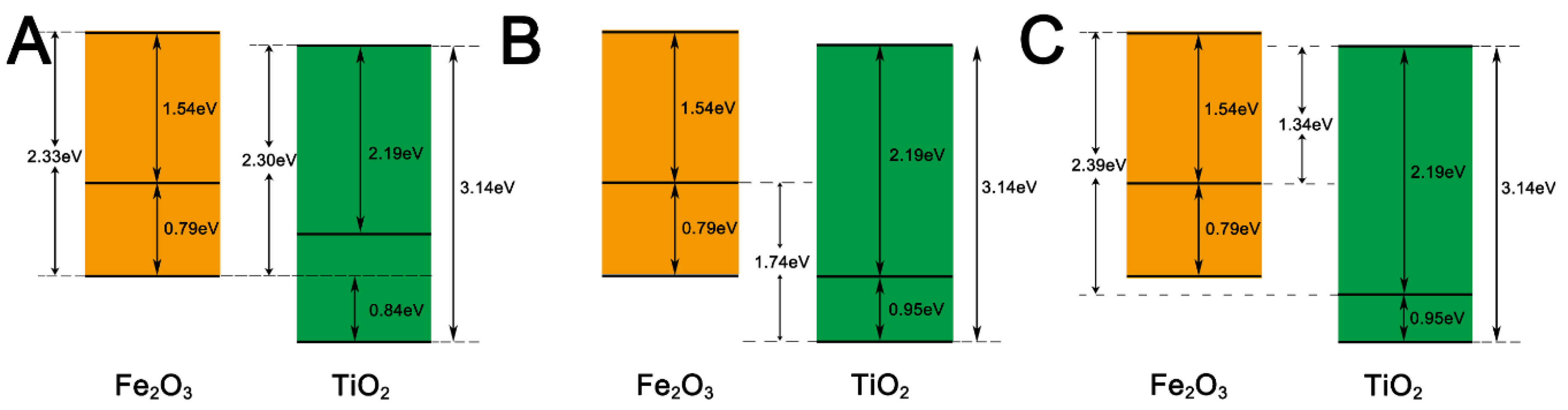
3.2. Photo-Chemical and Bandgap Characterizations
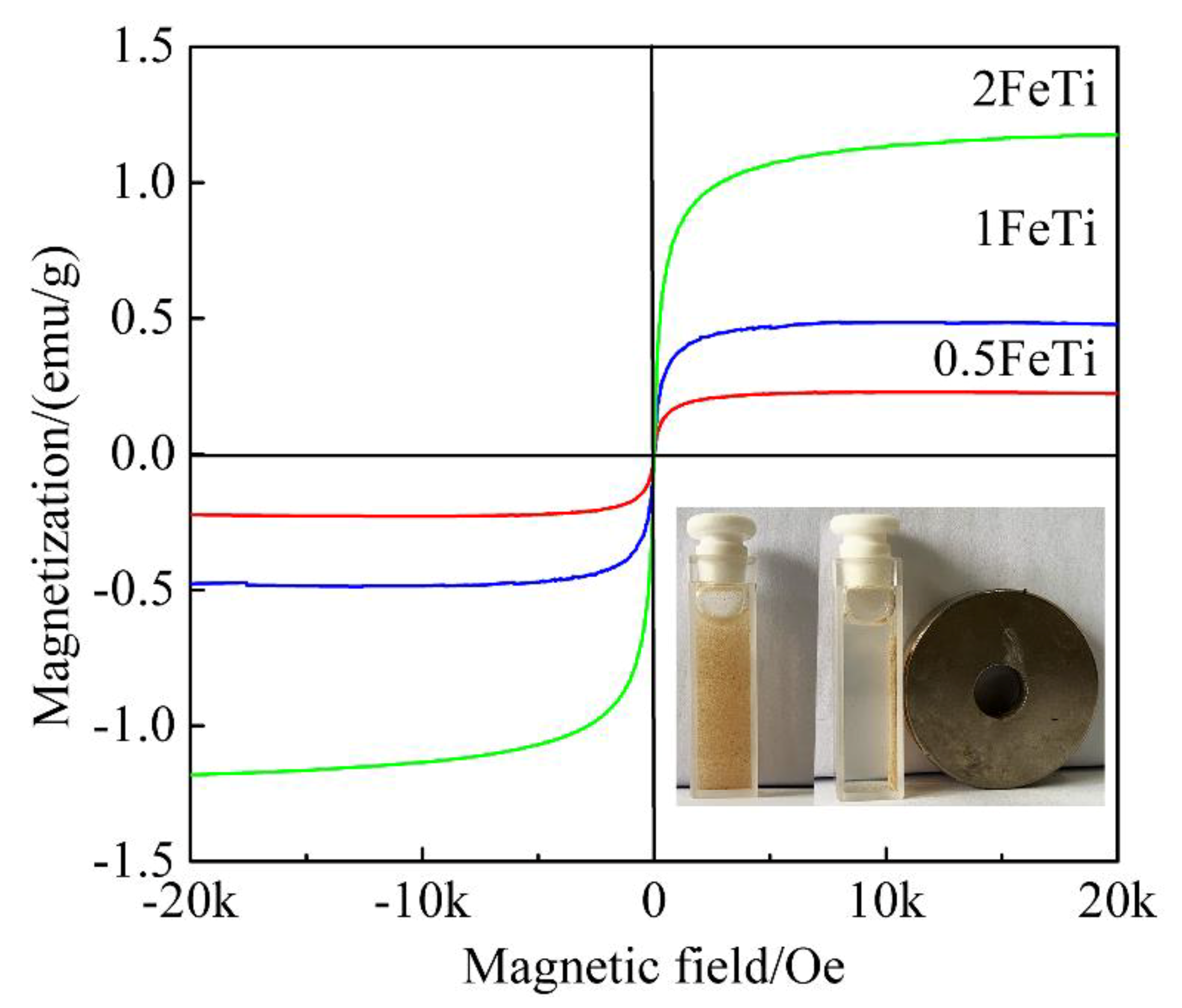
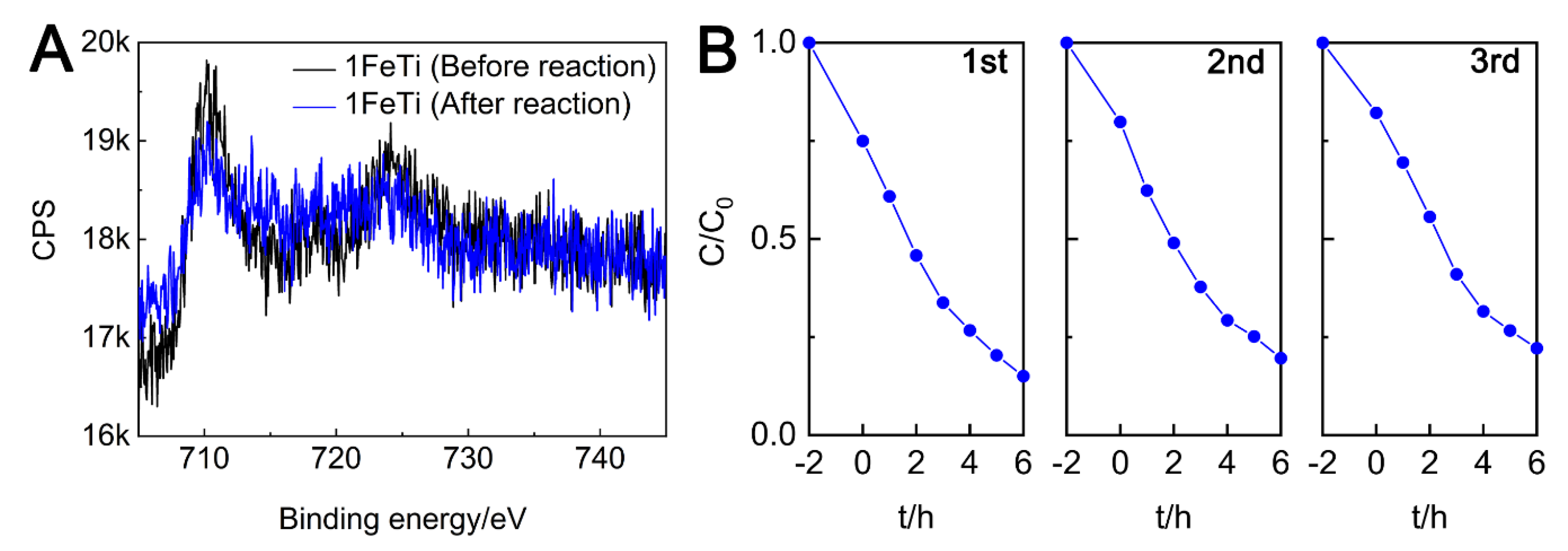
3.3. Magnetic Characterizations
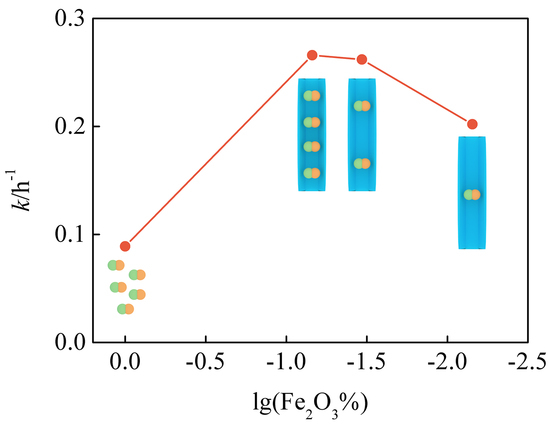
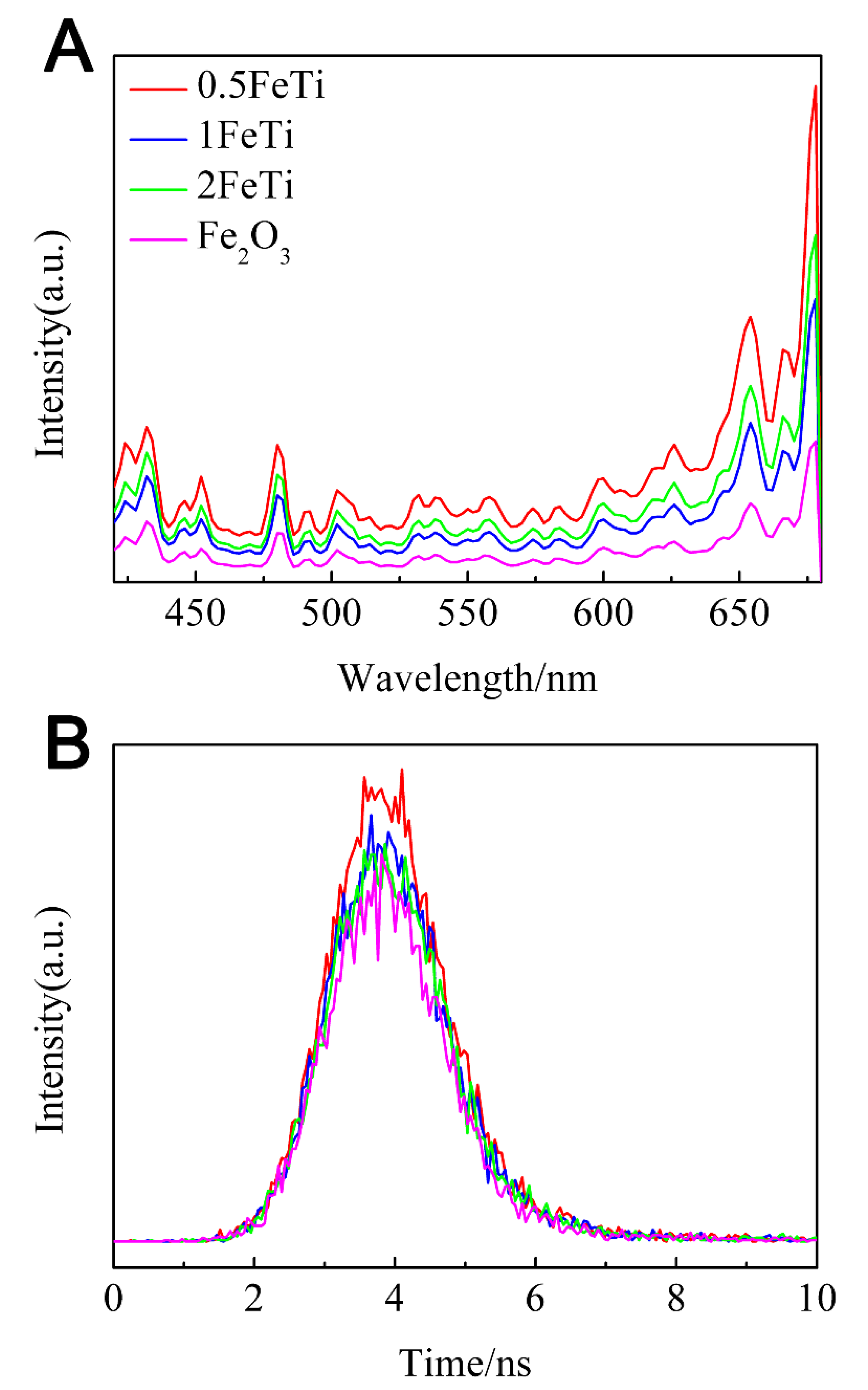
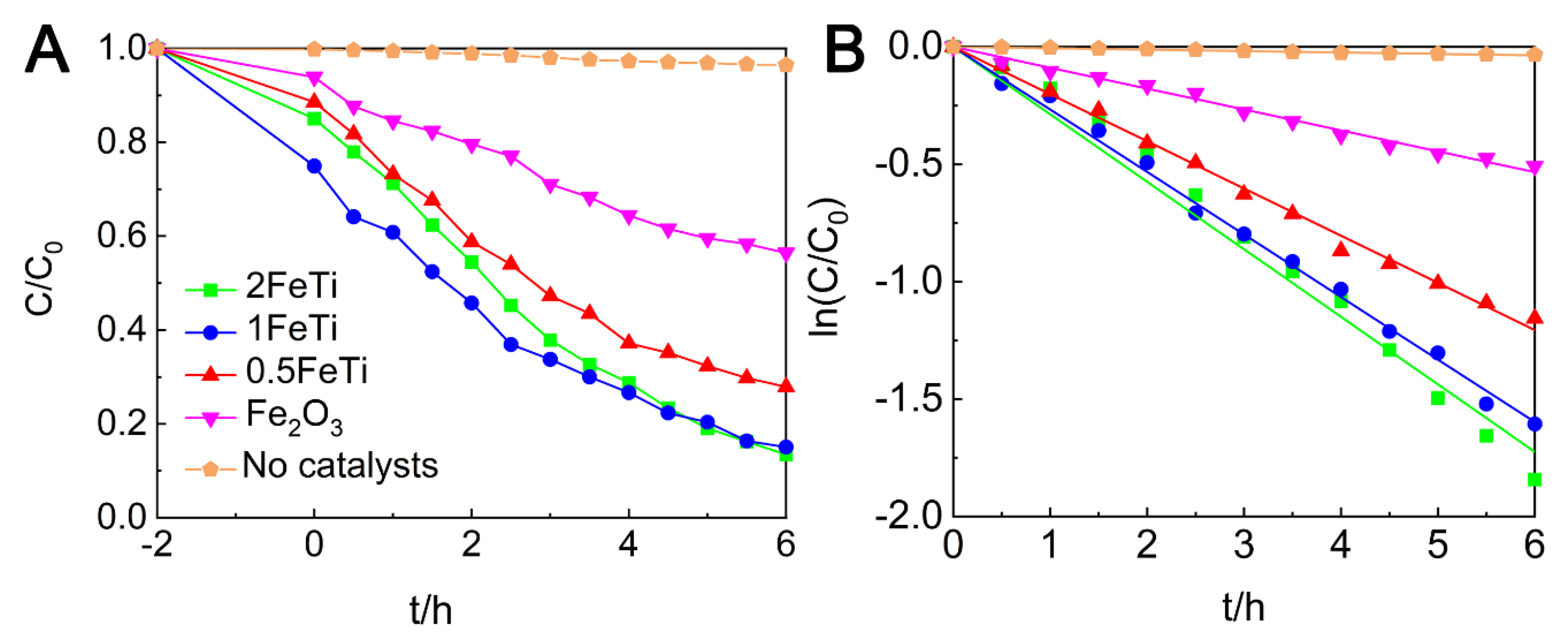
3.4. Photocatalytic Activity
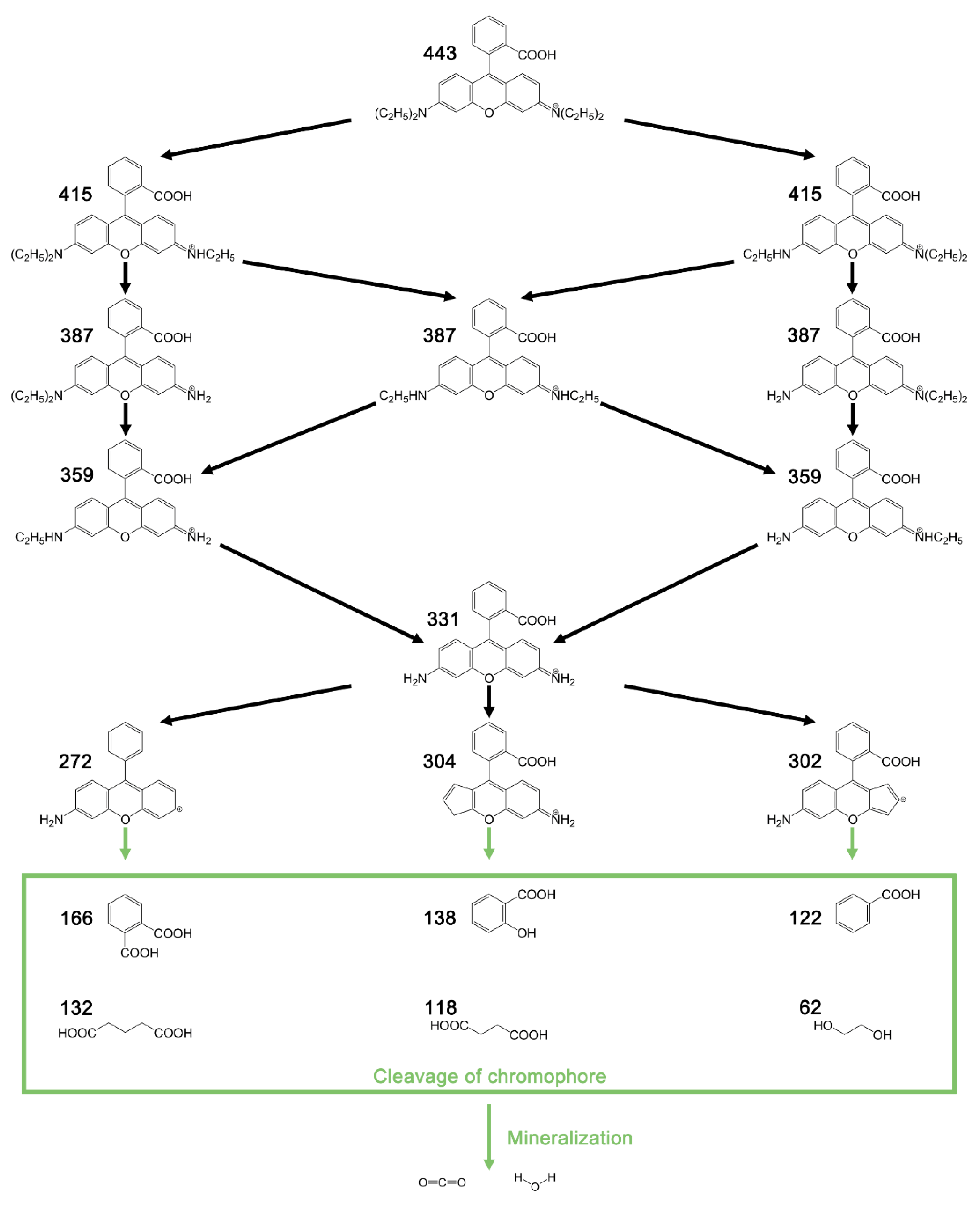
3.5. Intermediate Products and Degradation Pathway of RhB
3.6. Recyclable Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasool, K.; Pandey, R.P.; Rasheed, P.A.; Buczek, S.; Gogotsi, Y.; Mahmoud, K.A. Water treatment and environmental remediation applications of two- dimensional metal carbides (MXenes). Mater. Today 2019, 30, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marĩas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z. Immobilization of carboxyl-modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes in chitosan-based composite membranes for U (VI) sorption. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 317, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Mao, Y.; Luo, L. Partial Oxidation Strategy to Synthesize WS2/WO3 Heterostructure with Enhanced Adsorption Performance for Organic Dyes: Synthesis, Modelling, and Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Bi, J.; Xie, C. Design and synthesis of core e shell Fe3O4@PTMT composite magnetic microspheres for adsorption of heavy metals from high salinity wastewater. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Tao, Q.; Lu, H.; Luo, L.; Li, G.; Hao, H. Self-assembly of immobilized titanate films with different layers for heavy metal ions removal from wastewater: Synthesis, modeling and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bi, W.; Wan, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Yuan, R.; Ju, H.; Chu, W.; Wu, X.; He, L.; et al. Surface etching induced ultrathin sandwich structure realizing enhanced photocatalytic activity. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Jaroniec, M. Direct Z-scheme photocatalysts: Principles, synthesis, and applications. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 1042–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitam, C.N.C.; Jalil, A.A. A review on exploration of Fe2O3 photocatalyst towards degradation of dyes and organic contaminants. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, Z. Fe-based catalysts for heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, C.; Roy, V.A.L. Recent progress in magnetic iron oxide-semiconductor composite nanomaterials as promising photocatalysts. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Duan, F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, F.; Nuansing, W.; Zhang, B.; Qin, Y.; Knez, M. Porous Fe2O3 nanotubes with α-γ phase junction for enhanced charge separation and photocatalytic property produced by molecular layer deposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 248, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusior, A.; Michalec, K.; Jelen, P.; Radecka, M. Shaped Fe2O3 nanoparticles—Synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic degradation towards RhB. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 476, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Yurddaskal, M.; Dikici, T.; Sarıoğlu, C. Fabrication and characterization of novel iodine doped hollow and mesoporous hematite (Fe2O3) particles derived from sol-gel method and their photocatalytic performances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 345, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Fida, H.; You, L.; Zhou, K. Scalable synthesis of Ca-doped α-Fe2O3 with abundant oxygen vacancies for enhanced degradation of organic pollutants through peroxymonosulfate activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 262, 118250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X. Synthesis of Ag2CO3/α-Fe2O3 heterojunction and it high visible light driven photocatalytic activity for elimination of organic pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Guo, R.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Q.; Xie, M.; Cheng, X. Persulfate activation by magnetic γ-Fe2O3/Mn3O4 nanocomposites for degradation of organic pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketova, D.; Motola, M.; Sopha, H.; Michalicka, J.; Cicmancova, V.; Dvorak, F.; Hromadko, L.; Frumarova, B.; Stoica, M.; Macak, J.M. One-Step Decoration of TiO2 Nanotubes with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Photocatalytic and Magnetic Properties. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Nie, G.; Qi, M.; Pan, B. Improved performance and prolonged lifetime of titania-based materials: Sequential use as adsorbent and photocatalyst. Sci. China Chem. 2015, 58, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. Dual Cocatalysts in TiO2 Photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Mazare, A.; Schmuki, P. One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9385–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Sun, L.; Lin, Z.; Cai, J.; Xie, K.; Lin, C. P-n Heterojunction photoelectrodes composed of Cu2O-loaded TiO2 nanotube arrays with enhanced photoelectrochemical and photoelectrocatalytic activities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.X.; Xu, H.; Dong, Y.T.; Lu, X.F.; Tong, Y.X.; Li, G.R. Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysis Using Cobalt Nanotubes Decorated with Titanium Dioxide Nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2960–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challagulla, S.; Nagarjuna, R.; Ganesan, R.; Roy, S. Acrylate-based Polymerizable Sol-Gel Synthesis of Magnetically Recoverable TiO2 Supported Fe3O4 for Cr(VI) Photoreduction in Aerobic Atmosphere. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Huang, Z.W.; Guo, W.L.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.R.; Chai, Z.F.; Shi, W.Q. Enhanced Photocatalytic Removal of Uranium(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Magnetic TiO2/Fe3O4 and Its Graphene Composite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5666–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.J.; Tan, L.L.; Ng, Y.H.; Yong, S.T.; Chai, S.P. Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4)-Based Photocatalysts for Artificial Photosynthesis and Environmental Remediation: Are We a Step Closer to Achieving Sustainability? Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7159–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, H.; Hao, H. Oil-phase cyclic magnetic adsorption to synthesize Fe3O4@C@TiO2-nanotube composites for simultaneous removal of Pb(II) and Rhodamine B. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J. Pb(II) adsorption on magnetic γ-Fe2O3/titanate nanotubes composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cao, Q.; Wang, A.; Duan, J.; Zhou, W.; Sang, Y.; Liu, H. Iron oxide embedded titania nanowires—An active and stable electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution in acidic media. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Berger, S.; Schmuki, P. TiO2 nanotubes: Synthesis and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2904–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Peng, H.; Wen, Y.; Li, N. Re-examination of characteristic FTIR spectrum of secondary layer in bilayer oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.T.; Lee, J.; Seon, J.; Ju, E.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.I.L.; Kim, M.G.; Takemura, Y.; Arbab, A.S.; Kang, K.W.; et al. Giant Magnetic Heat Induction of Magnesium-Doped γ-Fe2O3 Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Completely Killing Tumors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, L.; Yu, P.; Han, S.; Fang, X. Novel Composites of α-Fe2O3 Tetrakaidecahedron and Graphene Oxide as an Effective Photoelectrode with Enhanced Photocurrent Performances. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3331–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Wang, L. Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: Facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Blackman, C.S. Gas-phase synthesis of hybrid nanostructured materials. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 22981–22989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, R.; Pan, L.; Hou, F.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Mi, W.; Shi, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; et al. Regulating the Spin State of Fe III by Atomically Anchoring on Ultrathin Titanium Dioxide for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysis Angewandte. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2313–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jin, R.; Li, A.; Bi, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Sankar, G.; Ma, D.; et al. Highly selective oxidation of methane to methanol at ambient conditions by titanium dioxide-supported iron species. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, H.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, D. Design and synthesis of porous Ag/ZnO nanosheets assemblies as super photocatalysts for enhanced visible-light degradation of 4-nitrophenol and hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 221, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wang, K.; Zhang, G.; Wu, X. A novel α-Fe2O3@g-C3N4 catalyst: Synthesis derived from Fe-based MOF and its superior photo-Fenton performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 469, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthirath Balan, A.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Woellner, C.F.; Sinha, S.K.; Deng, L.; Reyes, C.D.L.; Rao, B.M.; Paulose, M.; Neupane, R.; Apte, A.; et al. Exfoliation of a non-van der Waals material from iron ore hematite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Shi, R. Enhanced photoelectrochemical activity of α-Fe2O3/TiO2 nanoheterojunction by controlling hydrodynamic conditions. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 174002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charanpahari, A.; Umare, S.S.; Gokhale, S.P.; Sudarsan, V.; Sreedhar, B.; Sasikala, R. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of multi-doped TiO2 for the degradation of methyl orange. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 443–444, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Liu, K.; Ni, Y. Synthesis of mesoporous α-Fe2O3 via sol-gel methods using cellulose nano-crystals (CNC) as template and its photo-catalytic properties. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Ni, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhan, W.; Li, Y. Growth of Fe2O3/SnO2 nanobelt arrays on iron foil for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 673, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, X.; Wang, S.; He, D. Preparation and visible-light photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3/γ-Fe2O3 magnetic heterophase photocatalyst. Mater. Lett. 2014, 118, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrpekl, V.; Vejpravová, J.P.; Roca, A.G.; Murafa, N.; Szatmary, L.; Nižňanský, D. Magnetically separable photocatalytic composite γ-Fe2O3@TiO2 synthesized by heterogeneous precipitation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4844–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.S.; Costa, M.J.S.; Oliveira, H.G.; Lima, L.C.B.; Luz, G.E.; Cavalcante, L.S.; Santos, R.S. Effect of the applied potential condition on the photocatalytic properties of Fe2O3/WO3 heterojunction films. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.; Pawar, R.C.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.S. Photocatalytic evaluation of self-assembled porous network structure of ferric oxide film fabricated by dry deposition process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 181, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Sun, C.; Yang, S.; Ding, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Z. Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B by Bi2WO6 with electron accepting agent under microwave irradiation: Mechanism and pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, T.S. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of bismuth-doped TiO2 nanotubes under direct sunlight irradiation for degradation of Rhodamine B dye. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1669–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Ti 2p/% | O 1s/% | Fe 2p/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5FeTi | 32.97 | 66.57 | 0.47 |
| 1FeTi | 30.90 | 67.02 | 2.09 |
| 2FeTi | 29.04 | 66.94 | 4.02 |
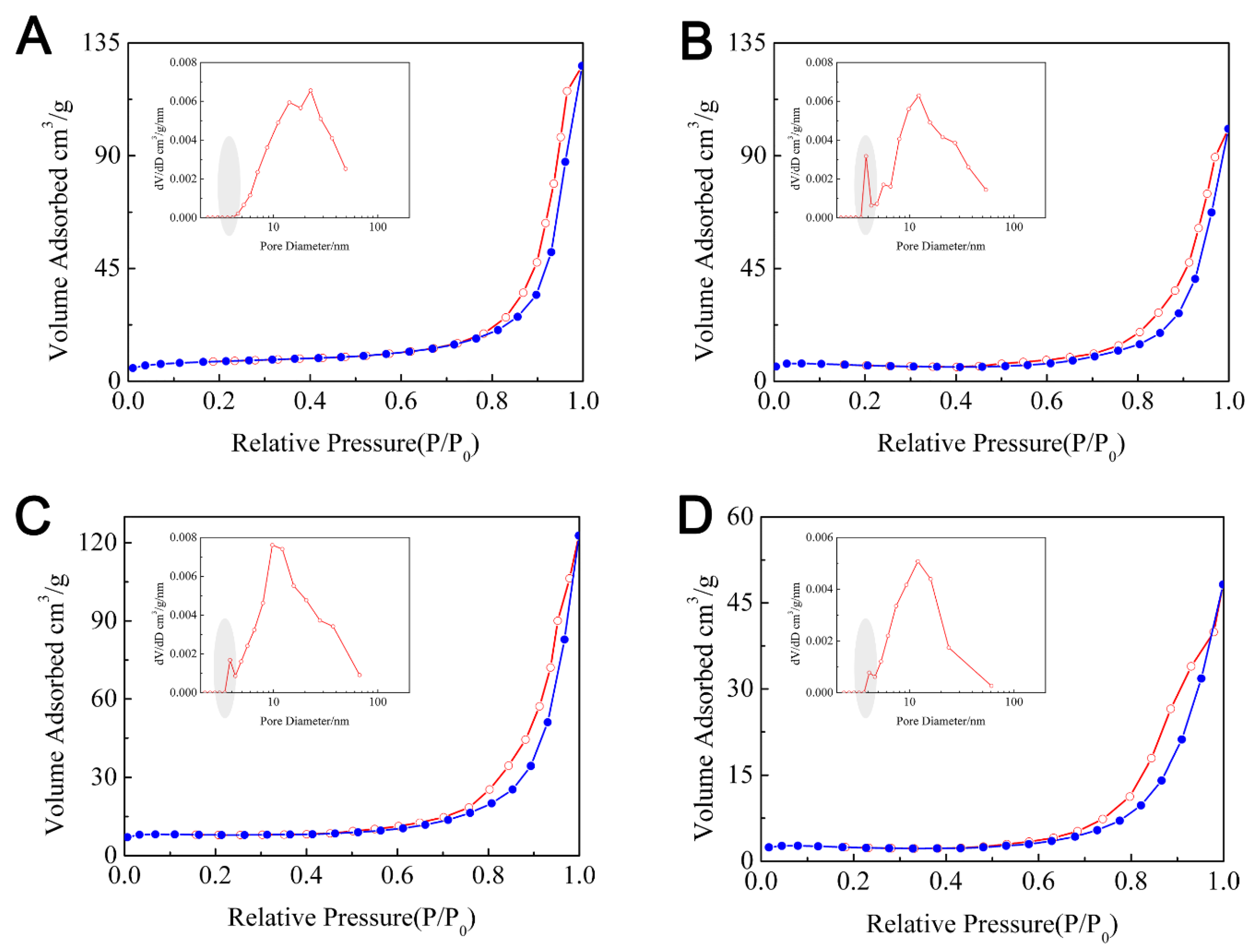
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g−1) | Adsorption Branch | Desorption Branch | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pore Size/nm | Pore Volume/cm3·g−1 | Pore Size/nm | Pore Volume/cm3·g−1 | ||
| 0.5FeTi | 28.46 | 24.77 | 0.195 | 22.72 | 0.186 |
| 1FeTi | 29.36 | 23.31 | 0.160 | 12.23 | 0.148 |
| 2FeTi | 28.29 | 24.42 | 0.192 | 9.76 | 0.174 |
| Fe2O3 | 10.96 | 13.77 | 0.079 | 11.99 | 0.069 |
| Sample | 0.5FeTi | 1FeTi | 2FeTi | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degradation Efficiency (%) | 72.11 | 84.96 | 86.53 | 43.55 |
| k/h−1 | 0.2010 | 0.2663 | 0.2875 | 0.0890 |
| R2 | 0.9985 | 0.9987 | 0.9936 | 0.9972 |
| Materials | Light Source | Time (h) | Photodegradation Amount (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Fe2O3 | Visible light | 3 | 38% MB | [43] |
| Fe2O3/SnO2 | UV light | 4 | 70% MB | [44] |
| α-Fe2O3/γ-Fe2O3 | Visible light | 12 | 90% RhB | [45] |
| γ-Fe2O3@TiO2 | UV light | 5 | ~18% 4-chlophenol | [46] |
| Fe2O3@WO3 | Polychromatic light | 3 | 18% RhB | [47] |
| Fe2O3 | Visible light | 6 | ~70% RhB | [48] |
| 2FeTi | Visible light | 6 | 86.53% RhB | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, Q.; Huang, X.; Bi, J.; Wei, R.; Xie, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L.; Hao, H.; Wang, J. Aerobic Oil-Phase Cyclic Magnetic Adsorption to Synthesize 1D Fe2O3@TiO2 Nanotube Composites for Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071345
Tao Q, Huang X, Bi J, Wei R, Xie C, Zhou Y, Yu L, Hao H, Wang J. Aerobic Oil-Phase Cyclic Magnetic Adsorption to Synthesize 1D Fe2O3@TiO2 Nanotube Composites for Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(7):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071345
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Qingqing, Xin Huang, Jingtao Bi, Rongli Wei, Chuang Xie, Yongzhu Zhou, Lu Yu, Hongxun Hao, and Jingkang Wang. 2020. "Aerobic Oil-Phase Cyclic Magnetic Adsorption to Synthesize 1D Fe2O3@TiO2 Nanotube Composites for Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation" Nanomaterials 10, no. 7: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071345
APA StyleTao, Q., Huang, X., Bi, J., Wei, R., Xie, C., Zhou, Y., Yu, L., Hao, H., & Wang, J. (2020). Aerobic Oil-Phase Cyclic Magnetic Adsorption to Synthesize 1D Fe2O3@TiO2 Nanotube Composites for Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071345