Green Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Natural Product Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chemicals and Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials Used
2.2. Preparation of Aqueous Extract of CT Leaf and 3% (v/v) JC Latex Extract
2.3. Preparation of CT-Fe3O4 NPs
2.4. Preparation of JC-Fe3O4 NPs
2.5. Characterization of CT-Fe3O4 and JC-Fe3O4 NPs
2.6. Dye Adsorption Experiment
2.7. Toxic Metal Adsorption Experiment (with Concentration)
2.8. Antibacterial Assay for Wastewater Treatment
2.9. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteria from the Collected Sample
2.9.1. Disk Diffusion Test
2.9.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
2.9.3. Antibacterial Assay
Bacteria Culture Preparation
2.10. 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical Scavenging Assay
2.11. Measurement of Cytotoxicity Using MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
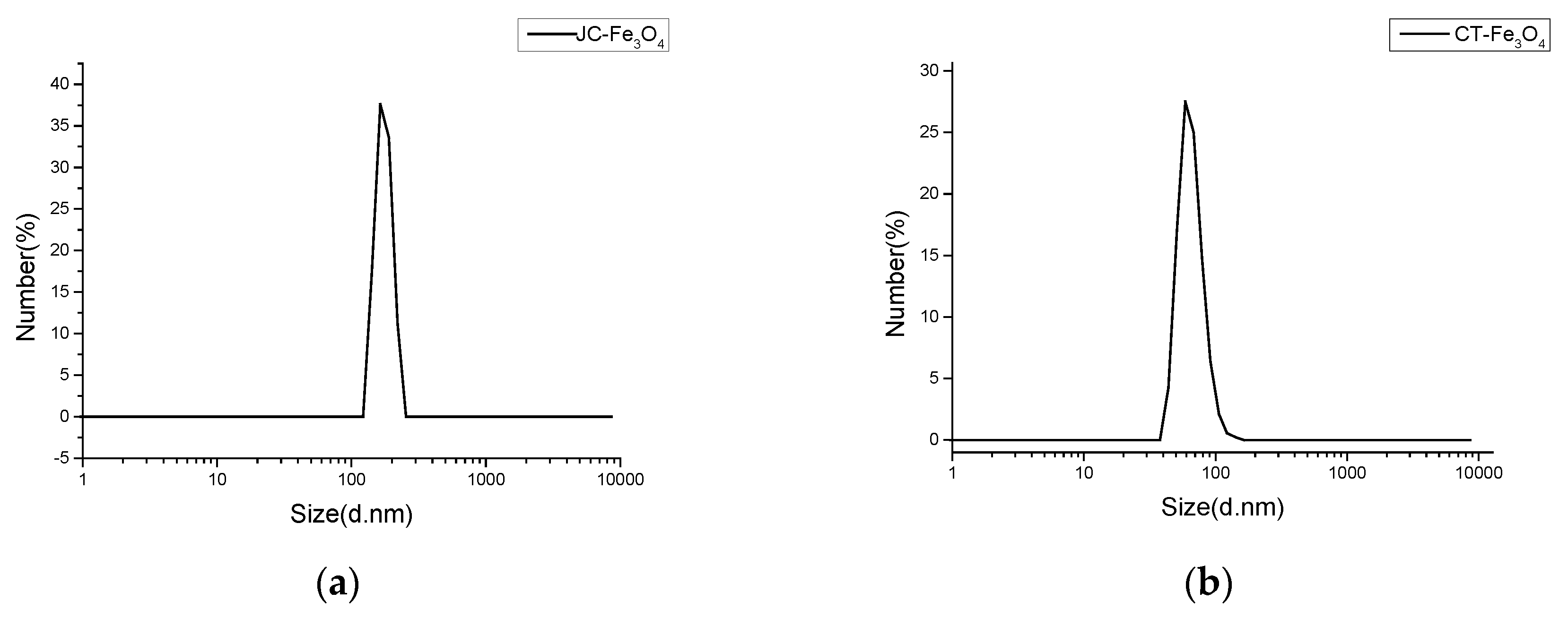
3.2. Dynamic Light Scattering Experiment
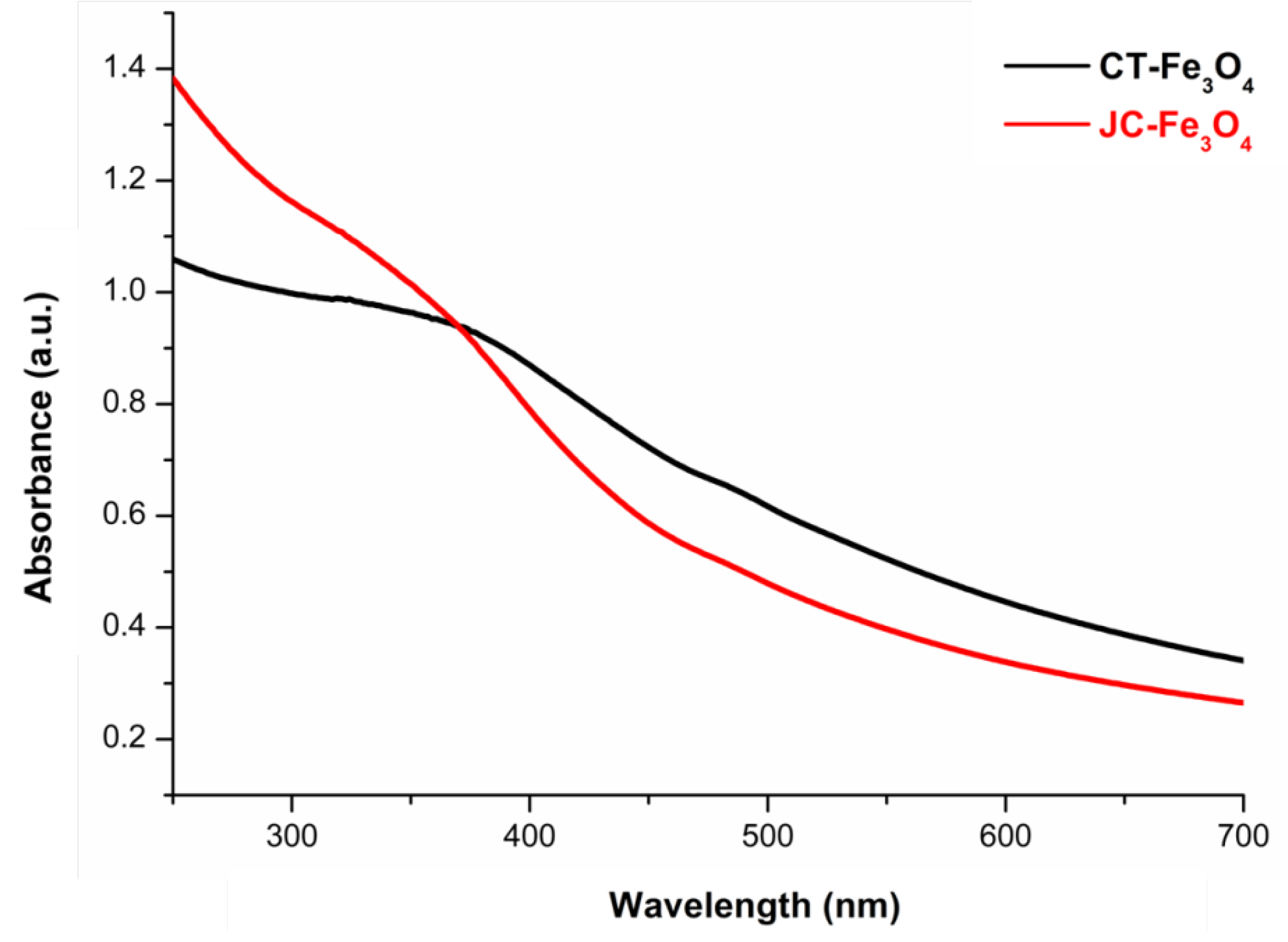
3.3. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
3.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.4.1. FTIR Analysis of JC-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
3.4.2. FTIR Analysis of CT-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
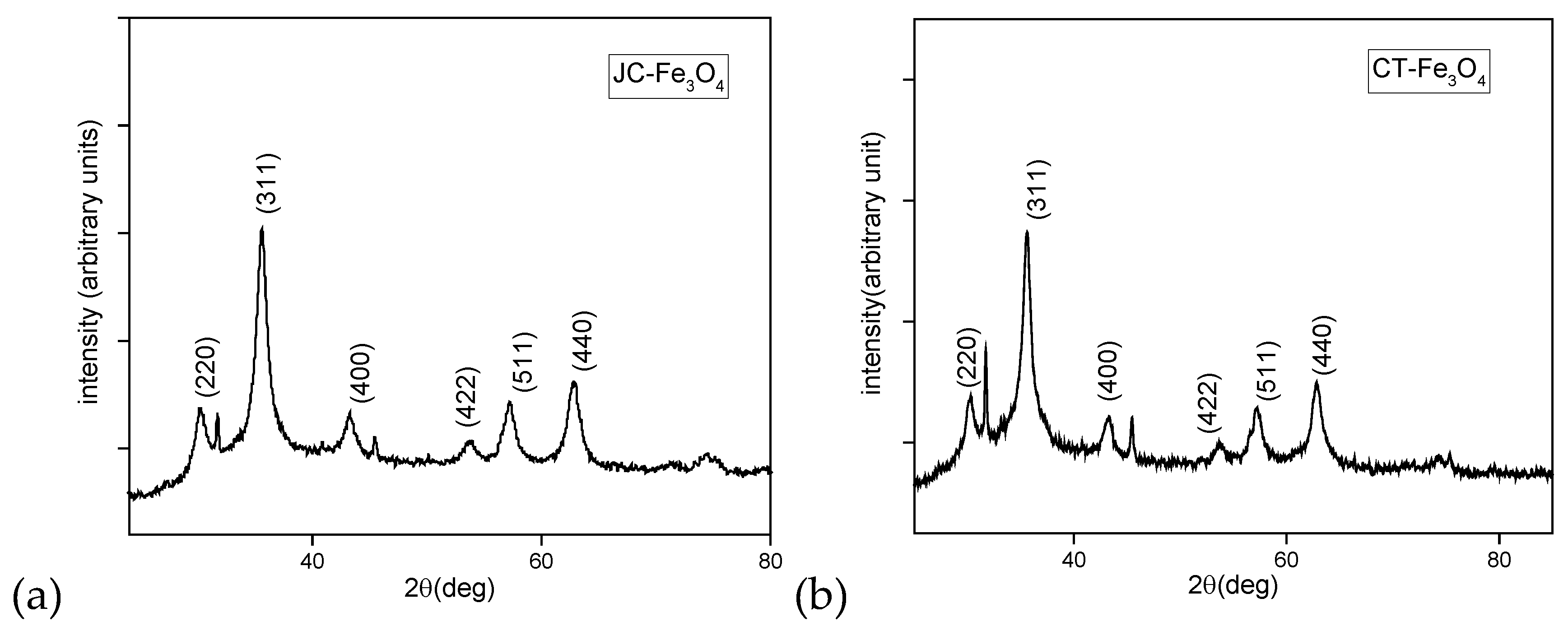
3.5. Powder XRD Analysis of JC-Fe3O4 and CT-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
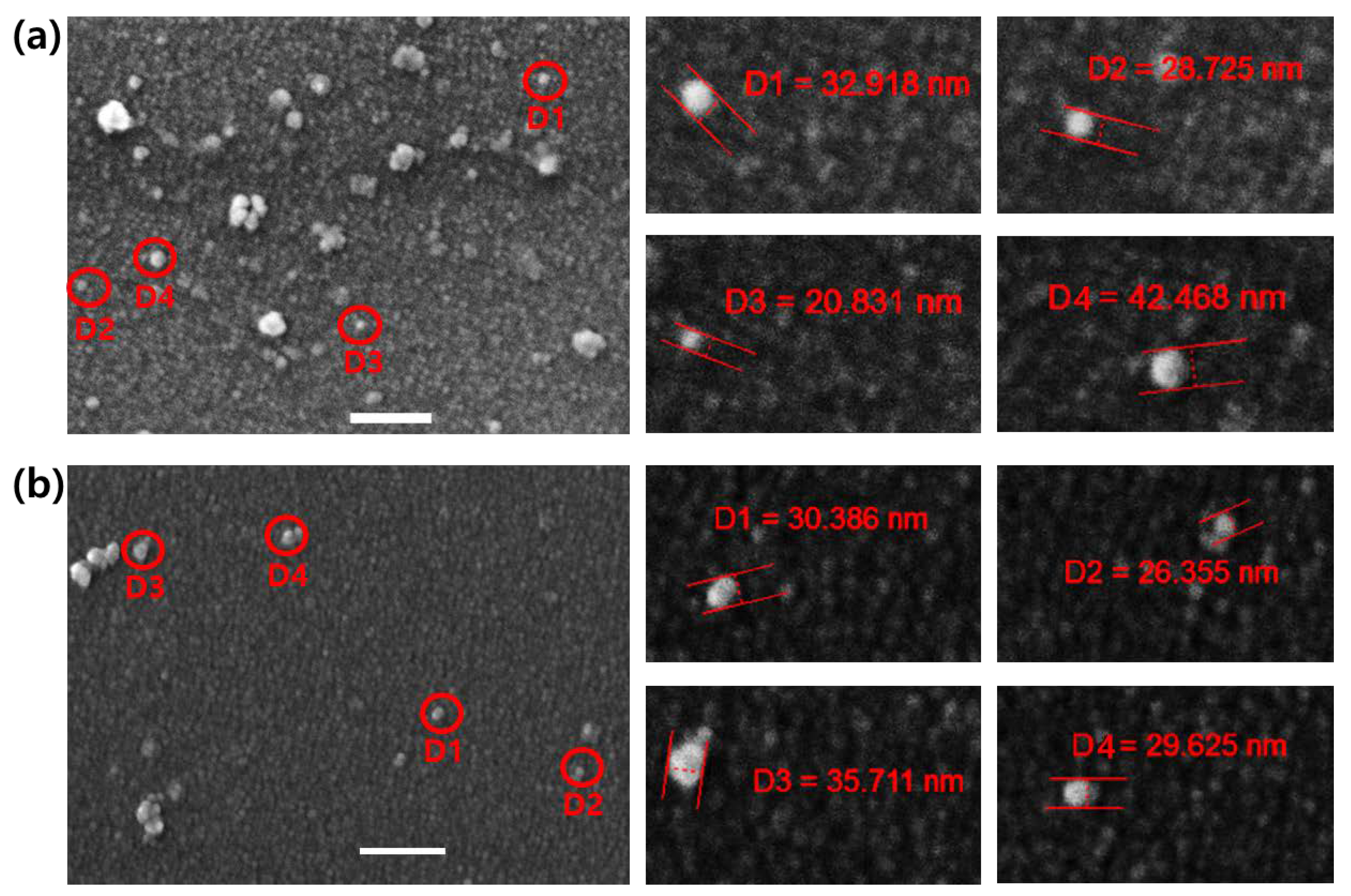
3.6. FE-SEM Analysis
3.7. Dye Adsorption Study
3.7.1. Dye Adsorption Isotherm of MB Dye
3.7.2. Adsorption Kinetics for MB Dye
3.8. Toxic Metal Adsorption Study (with Concentration)
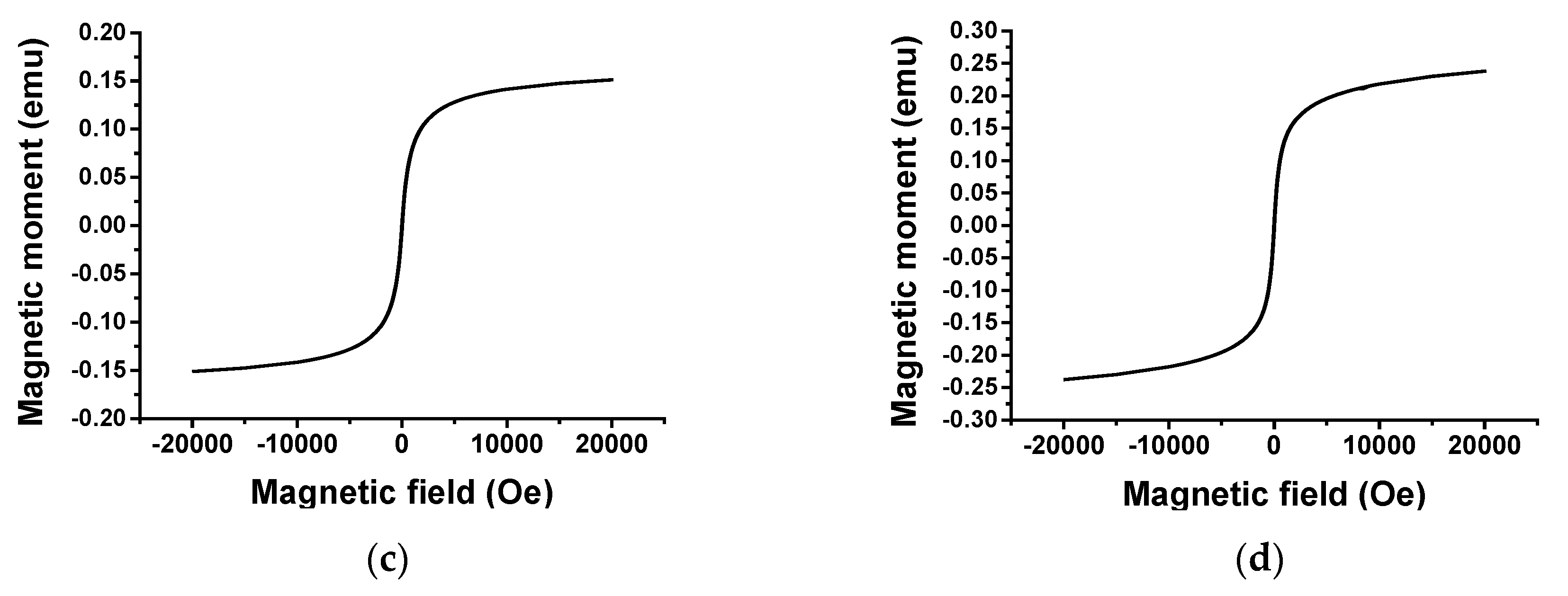
3.9. Magnetic Properties
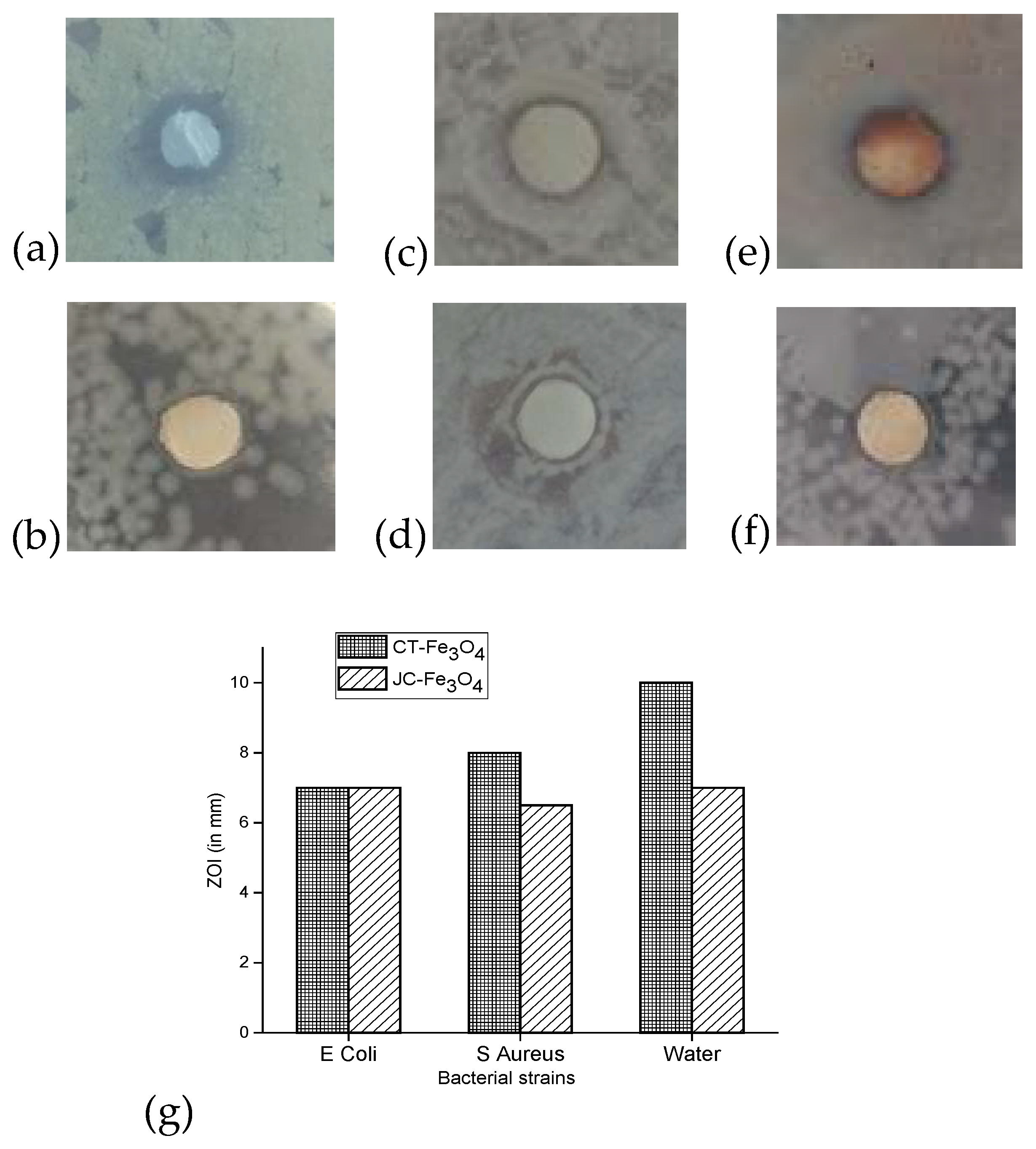
3.10. Antibacterial Assay
3.10.1. Characterization of Bacteria Isolated from Pond Water
3.10.2. Wastewater Treatment
3.10.3. Disk Diffusion
3.10.4. MIC of CT-Fe3O4 and JC-Fe3O4NPs
3.11. DPPH Scavenging Assay
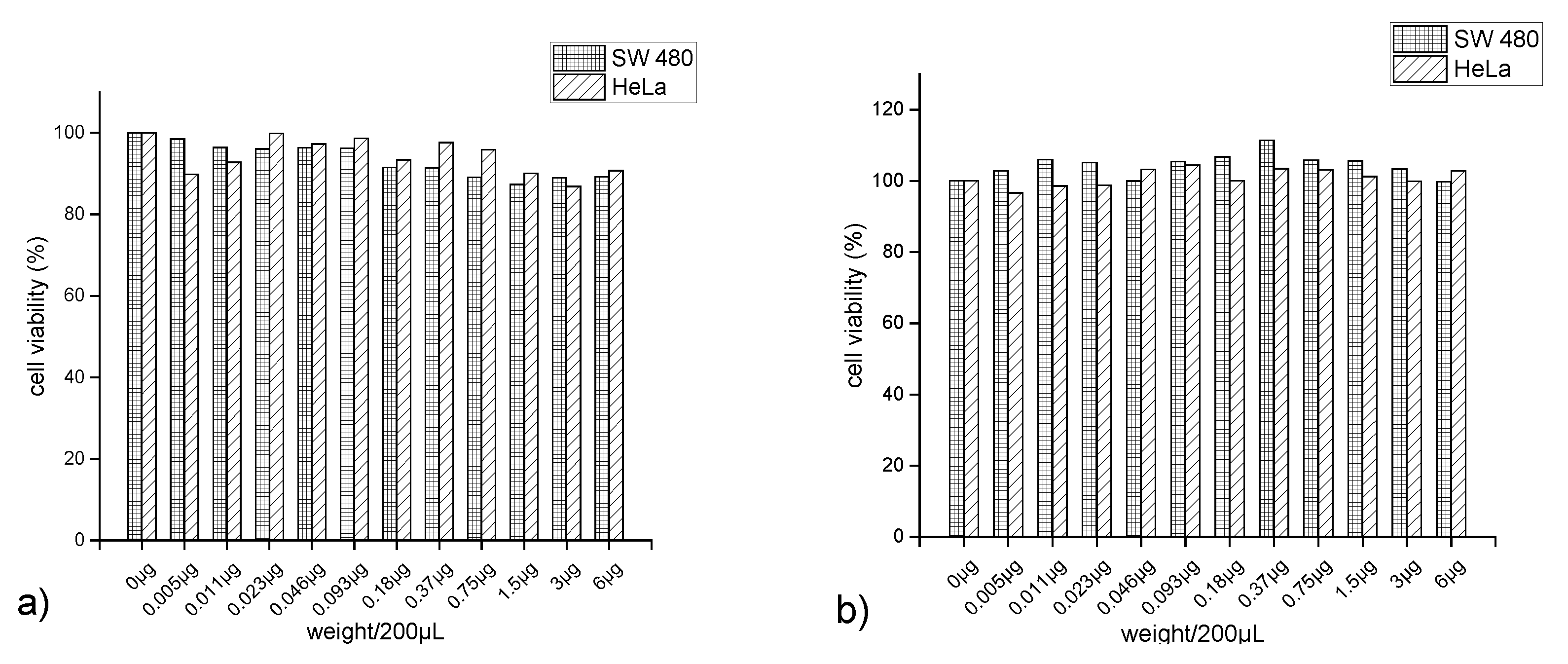
3.12. Measurement of Cytotoxicity Using MTT Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. Npj Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.M.; Dziubla, T.D.; Hilt, J.Z. Recent advances on iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles as sorbents of organic pollutants in water and wastewater treatment. Rev. Environ. Health 2017, 32, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.; Singh, K. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: A review. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2017, 7, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Kariminia, H.-R. Influence of ion interaction on lead removal by a polyamide nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2015, 362, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanets, A.I.; Srivastava, V.; Kitikova, N.V.; Shashkova, I.L.; Sillanpää, M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the Co(II) and Ni(II) ions removal from aqueous solutions by Ca-Mg phosphates. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, H.C.; Woo, S.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Kumar Sarmah, A.; Ivanets, A.; Dotto, G.L.; et al. Removal of various contaminants from water by renewable lignocellulose-derived biosorbents: A comprehensive and critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 2155–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanets, A.I.; Srivastava, V.; Kitikova, N.V.; Shashkova, I.L.; Sillanpää, M. Non-apatite Ca-Mg phosphate sorbent for removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Nagpal, G.; Agrawal, S. Rachna Water purification by using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanets, A.I.; Shashkova, I.L.; Kitikova, N.V.; Drozdova, N.V. Extraction of Co(II) ions from aqueous solutions with thermally activated dolomite. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 87, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.S.; da Silva, A.G.M.; Camargo, P.H.C. Nanocatalysis by noble metal nanoparticles: Controlled synthesis for the optimization and understanding of activities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 5857–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malekzad, H.; SahandiZangabad, P.; Mirshekari, H.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Noble metal nanoparticles in biosensors: Recent studies and applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhirde, A.; Xie, J.; Swierczewska, M.; Chen, X. Nanoparticles for cell labeling. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kannan, U.M.; Giribabu, L.; Jammalamadaka, S.N. Demagnetization field driven charge transport in a TiO2 based dye sensitized solar cell. Sol. Energy 2019, 187, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhathathreyan, K.S.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Balaji, R. Nanomaterials for Fuel Cell Technology. In Nanotechnology for Energy Sustainability; Raj, B., Van de Voorde, M., Mahajan, Y., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; pp. 569–596. ISBN 978-3-527-69610-9. [Google Scholar]
- Venditti, I. Gold Nanoparticles in Photonic Crystals Applications: A Review. Materials 2017, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizvi, S.A.A.; Saleh, A.M. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Boubeta, C.; Simeonidis, K. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Water Purification. In Nanoscale Materials in Water Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 521–552. ISBN 978-0-12-813926-4. [Google Scholar]
- Najafpoor, A.; Norouzian-Ostad, R.; Alidadi, H.; Rohani-Bastami, T.; Davoudi, M.; Barjasteh-Askari, F.; Zanganeh, J. Effect of magnetic nanoparticles and silver-loaded magnetic nanoparticles on advanced wastewater treatment and disinfection. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 303, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Jia, S.; Jia, J.; He, Z.; Li, G.; Zuo, Q.; Zhuang, H. Fe3O4 nanoparticles loading on cow dung based activated carbon as an efficient catalyst for catalytic microbubble ozonation of biologically pretreated coal gasification wastewater. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 267, 110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Ficiarà, E.; Ruffinatti, F.; Stura, I.; Argenziano, M.; Abollino, O.; Cavalli, R.; Guiot, C.; D’Agata, F. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Functionalization for Biomedical Applications in the Central Nervous System. Materials 2019, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gul, S.; Khan, S.B.; Rehman, I.U.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.I. A Comprehensive Review of Magnetic Nanomaterials Modern Day Theranostics. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, L.; Gomaa, H.G.; Ragab, D.; Zhu, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: A review. Particuology 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.F.; Lai, C.W.; Abdul Hamid, S.B. Facile Synthesis Polyethylene Glycol Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for High Colloidal Stability. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fathy, M.M.; Fahmy, H.M.; Saad, O.A.; Elshemey, W.M. Silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as a novel nano-radiosensitizer for electron therapy. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, L.; Yang, L.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; Niu, Y.; Chen, H. Rapid removal of anionic dye from water by poly(ionic liquid)-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.; Masood, M.; Nasim, M.; Sarfraz, M.; Ebokaiwe, A.; Schäfer, K.-H.; Keck, C.; Jacob, C. Natural Nanoparticles: A Particular Matter Inspired by Nature. Antioxidants 2017, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudr, J.; Haddad, Y.; Richtera, L.; Heger, Z.; Cernak, M.; Adam, V.; Zitka, O. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, L.; Pessan, J.; Vieira, A.; Lima, T.; Delbem, A.; Monteiro, D. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: A Perspective on Synthesis, Drugs, Antimicrobial Activity, and Toxicity. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagajyothi, P.C.; Pandurangan, M.; Kim, D.H.; Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Shim, J. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic and In Vitro Anticancer Activities. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Mohamed, F.M.; Marzouq, M.H.; Mustafa, A.B.E.-D.; Alsoudi, A.M.; Ali, O.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mahmoud, F.A. Review of Green Methods of Iron Nanoparticles Synthesis and Applications. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.H.; Luong, N.H. Nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 211–240. ISBN 978-0-08-102814-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pochhi, M.L. An antioxidant activity of Cinnamonumtamala improves histopathological alterations and biochemical parameters in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Asian J. Med. Sci. 2019, 10, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, W.; Zainab Kazmi, S.N. Antimicrobial Activity of Cinnamomumtamala Leaves. J. Nutr. Disord. Ther. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Fu, R.; Peng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F. Antioxidant activity of flavonoids from leaves of Jatropha curcas. ScienceAsia 2014, 40, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bar, H.; Bhui, D.K.; Sahoo, G.P.; Sarkar, P.; De, S.P.; Misra, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Jatropha curcas. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambri, N.D.S.; Taib, N.I.; Abdul Latif, F.; Mohamed, Z. Utilization of Neem Leaf Extract on Biosynthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meenachi, S.; Kandasamy, S. Investigation of tannery liming waste water using green synthesised iron oxide nano particles. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 99, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Setua, S.; Kumari, S.; Dan, N.; Massey, A.; Hafeez, B.B.; Yallapu, M.M.; Stiles, Z.E.; Alabkaa, A.; Yue, J.; et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles of curcumin enhance gemcitabine therapeutic response in pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials 2019, 208, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawafta, R.; Shahwan, T. A comparative study of the removal of methylene blue by iron nanoparticles from water and water-ethanol solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NorouzianBaghani, A.; Mahvi, A.H.; Gholami, M.; Rastkari, N.; Delikhoon, M. One-Pot synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for removal of Cr (VI) and Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almomani, F.; Bhosale, R.; Khraisheh, M.; Kumar, A.; Almomani, T. Heavy metal ions removal from industrial wastewater using magnetic nanoparticles (MNP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, V.; Divya, K.; Gayathri, S.; Jagan Mohan, E.; Keerthanaa, N.; Vinitha, M.; Kirubanandan, S.; Renganathan, S. Applications of iron oxide nano composite in waste water treatment–dye decolourisation and anti‒microbial activity. MOJ Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunha, F.A.; Maia, K.R.; Mallman, E.J.; Cunha, M.D.; Maciel, A.A.; Souza, I.P.; Menezes, E.A.; Fechine, P.B. Silver Nanoparticles-disk diffusion test against Escherichia coli isolates. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. S. Paulo 2016, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A. Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2012, 6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussmann, R.W.; Malca-García, G.; Glenn, A.; Sharon, D.; Chait, G.; Díaz, D.; Pourmand, K.; Jonat, B.; Somogy, S.; Guardado, G.; et al. Minimum inhibitory concentrations of medicinal plants used in Northern Peru as antibacterial remedies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neupane, B.P.; Chaudhary, D.; Paudel, S.; Timsina, S.; Chapagain, B.; Jamarkattel, N.; Tiwari, B.R. Himalayan honey loaded iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and study of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vashisht, S.; Singh, M.P.; Chawla, V. In-vitro Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity of Methanolic Extract of ShorearobustaGaertn. F. Resin. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharm. Res. 2016, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaminger, S.P.; Syhr, C.; Berensmeier, S. Controlled Synthesis of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Magnetite or Maghemite? Crystals 2020, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Bt Ahmad Khairudin, N.B.; Bt Mohamad, S.E.; Lee, K.X. Green Synthesis of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Using Seaweed (Kappaphycusalvarezii) Extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, N.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Malik, A. Antibacterial Potential of Jatropha curcas Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles against Food Borne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nahar, K.; Aziz, S.; Bashar, M.; Haque, M.A.; Al-Reza, S.M. Synthesis and characterization of Silver nanoparticles from Cinnamomumtamala leaf extract and its antibacterial potential. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2020, 11, 88–98. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, H.; Nakara, A.; Menon, S.; Shanmugam, V. Eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cinnamomum Tamala leaf extract and its promising effect towards the antibacterial activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.A.; Andrade, P.L.; Silva, M.P.; Valladares, L.D.; Aguiar, J.A. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with fucan polysaccharides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 343, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakar, A.; Ünlü, A.; Yeşilçayır, T.; Bıyık, İ. Kinetics and thermodynamics of textile dye removal by adsorption onto iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2020, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dib, F.I.; Mohamed, D.E.; El-Shamy, O.A.A.; Mishrif, M.R. Study the adsorption properties of magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of different synthesized surfactants for heavy metal ions removal. Egypt. J. Pet. 2020, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Bi, J.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Yanful, E.K. Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.S.; Chen, D.-H. Fast removal of copper ions by gum arabic modified magnetic nano-adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H.; Chen, D.-H. Rapid removal of heavy metal cations and anions from aqueous solutions by an amino-functionalized magnetic nano-adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Yadav, M.; Kohout, T.; Lahtinen, M.; Garg, V.K.; Sillanpää, M. Development of iron oxide/activated carbon nanoparticle composite for the removal of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. Water Resour. Ind. 2018, 20, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizro, S.; Baseri, H. Removal of Cobalt Ions from Contaminated Water Using Magnetite Based Nanocomposites: Effects of Various Parameters on the Removal Efficiency. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanets, A.I.; Srivastava, V.; Roshchina, M.Y.; Sillanpää, M.; Prozorovich, V.G.; Pankov, V.V. Magnesium ferrite nanoparticles as a magnetic sorbent for the removal of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9097–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrakian, E.; Ghaemi, E.; Ahmadi, M. Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction and Removal of Five Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetite Nanoparticle Loaded Platanusorientalis Waste Leaves. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Nebsen, M.; Salem, M.Y. Removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution with magnetite/pectin and magnetite/silica/pectin hybrid nanocomposites: Kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11461–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshaee, R.; Panahandeh, M. Stabilization of a magnetic nano-adsorbent by extracted pectin to remove methylene blue from aqueous solution: A comparative studying between two kinds of cross-likened pectin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielyan, L.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Gevorgyan, V.; Ananyan, M.; Trchounian, A. Antibacterial effects of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles: Distinguishing concentration-dependent effects with different bacterial cells growth and membrane-associated mechanisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2773–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, Y.T.; Rao, K.V.; Kumari, B.S.; Kumar, V.S.S.; Pavani, T. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its antibacterial application. Int. Nano Lett. 2015, 5, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, D.M.S.A.; Ismail, M.M.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A. Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial potency of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using algae harvested from the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaili, Z.; Yeo, C.C.; Yasin, H.N.; Badaludin, N.A.; Zakaria, Z.A. Antibacterial profile of Jatropha curcas latex extracts against selected human pathogenic bacteria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.M.; Thorat, N.D.; Shete, P.B.; Bedge, P.A.; Gavde, S.; Joshi, M.G.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Bohara, R.A. Comprehensive cytotoxicity studies of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 13, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.; Adireddy, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Mandava, S.; Lee, B.; Chrisey, D. In Vitro/In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation and Quantification of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24417–24450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

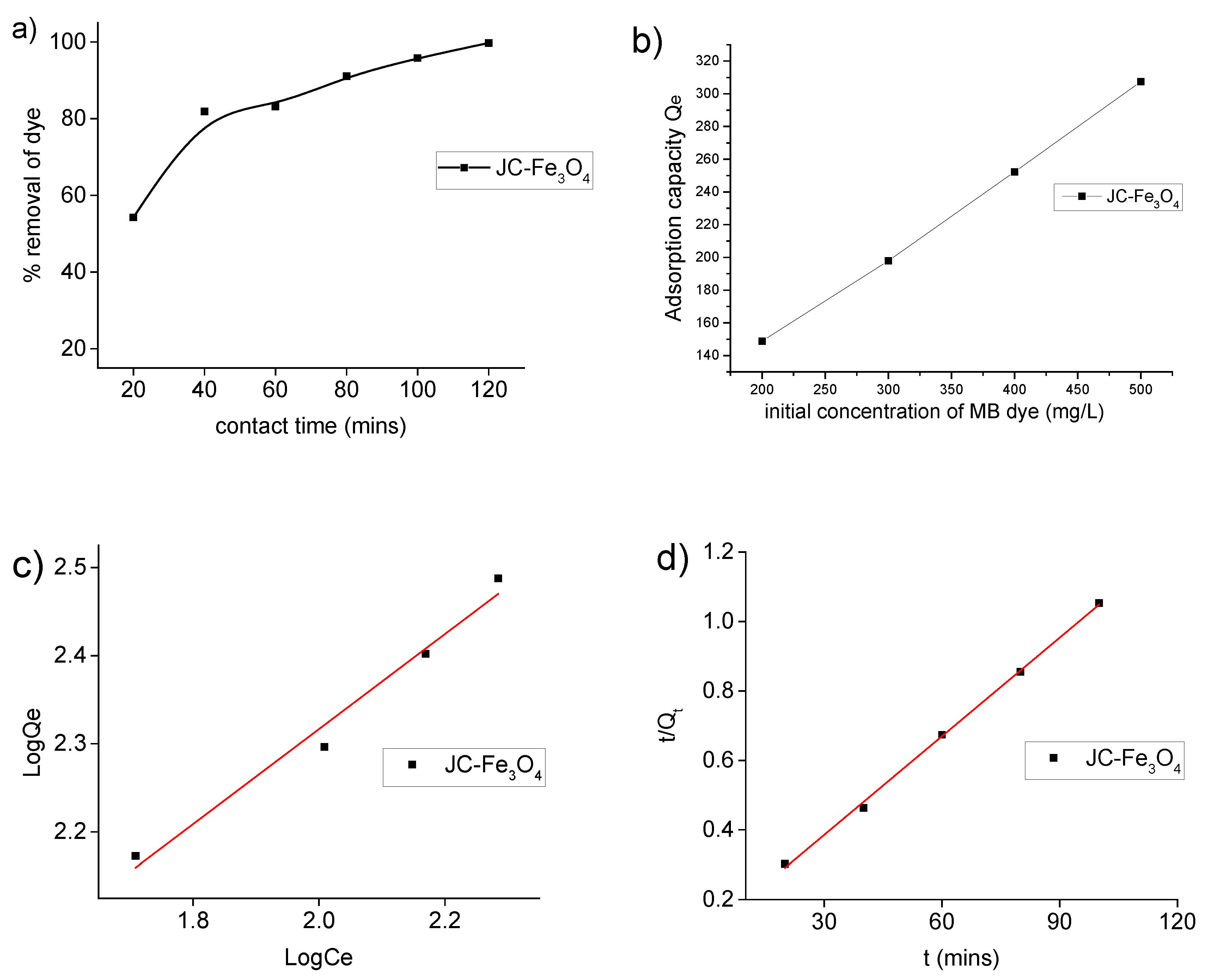





| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm | KL | RL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | ||
| JC-Fe3O4 | MB dye | 466.6 | 0.0078 | 0.204-0.340 | 0.919 | 17.248 | 0.539 | 0.979 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Qe(expt) (mg/g) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe(cal) (mg/g) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe(cal) (mg/g) | K2(g/mg·min) | R2 | |||
| JC-Fe3O4 | MB dye | 96.25 | 57.67 | 0.0368 | 0.980 | 104.82 | 8.02 × 10−4 | 0.998 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm | KL | RL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | ||
| JC-Fe3O4 | Cu2+ | 543.3 | 0.055 | 0.039–0.120 | 0.974 | 1.079 | 0.226 | 0.861 |
| Co2+ | 501.3 | 0.076 | 0.036–0.117 | 0.977 | 1.062 | 0.310 | 0.836 | |
| CT-Fe3O4 | Cu2+ | 463.24 | 0.059 | 0.030–0.130 | 0.954 | 1.086 | 0.159 | 0.697 |
| Co2+ | 513.7 | 0.038 | 0.070–0.209 | 0.956 | 1.222 | 0.312 | 0.916 | |
| Adsorbate | Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | Iron oxide nanoparticles | 17.6 | [61] |
| GA-MNP | 38.5 | [61] | |
| Amino functionalized magnetic nanosorbent | 12.4 | [62] | |
| Fe3O4/AC | 2.7 | [63] | |
| CT-Fe3O4 | 463.2 | Present study | |
| JC-Fe3O4 | 543.3 | Present study | |
| Co2+ | Magnetite-citric acid nanoadsorbent | 43.3 | [64] |
| MgFe2O4 | 135.5 | [65] | |
| CT-Fe3O4 | 513.7 | Present study | |
| JC-Fe3O4 | 501.3 | Present study | |
| MB dye | MNPs-POLP | 128.2 | [66] |
| Magnetite/pectin NPs | 125 | [67] | |
| Magnetite/silica/pectin NPs | 178.6 | [67] | |
| Fe3O4 NPs coated with pectin and crosslinked with adipic acid (FN-PAA) | 221.7 | [68] | |
| JC-Fe3O4 | 466.6 | Present study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, C.; Sen, S.; Singh, T.; Ghosh, T.; Paul, S.S.; Kim, T.W.; Jeon, S.; Maiti, D.K.; Im, J.; Biswas, G. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Natural Product Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081615
Das C, Sen S, Singh T, Ghosh T, Paul SS, Kim TW, Jeon S, Maiti DK, Im J, Biswas G. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Natural Product Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081615
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Chanchal, Subhadeep Sen, Tejinder Singh, Tanmoy Ghosh, Subha Sankar Paul, Tae Wan Kim, Seob Jeon, Dilip K. Maiti, Jungkyun Im, and Goutam Biswas. 2020. "Green Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Natural Product Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081615
APA StyleDas, C., Sen, S., Singh, T., Ghosh, T., Paul, S. S., Kim, T. W., Jeon, S., Maiti, D. K., Im, J., & Biswas, G. (2020). Green Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Natural Product Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081615







