Laser-Tunable Printed ZnO Nanoparticles for Paper-Based UV Sensors with Reduced Humidity Interference
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Device Fabrication
2.2. Laser Treatment
2.3. Device Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
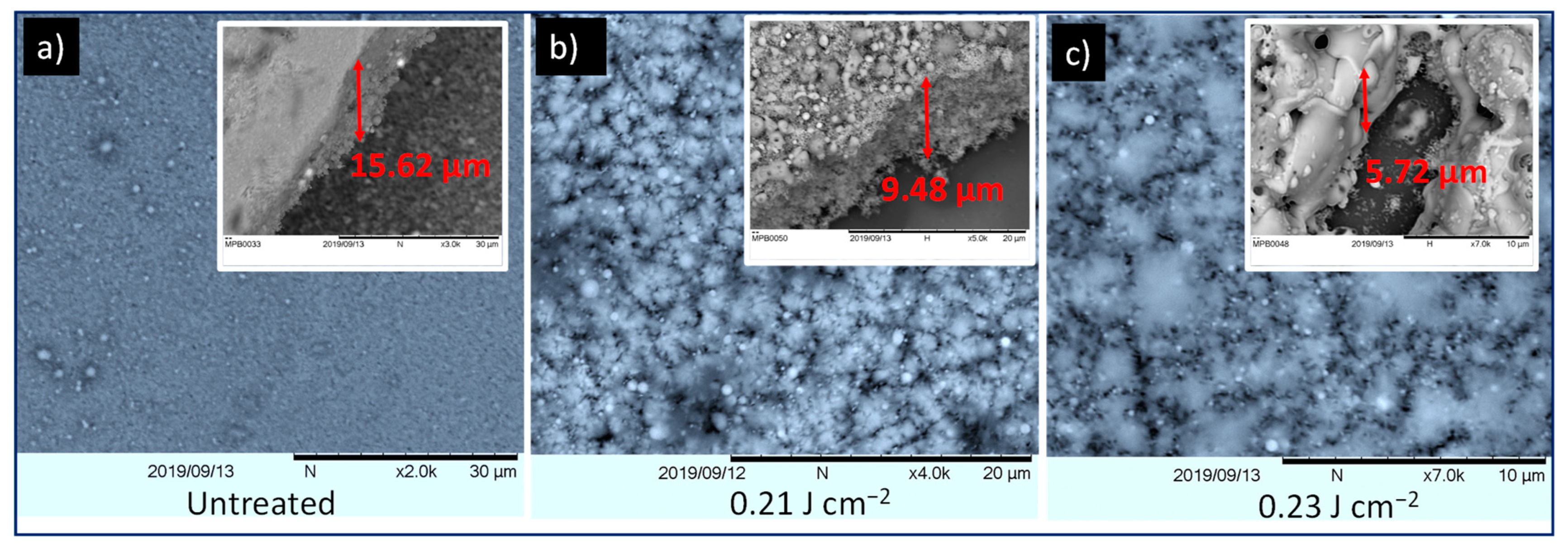
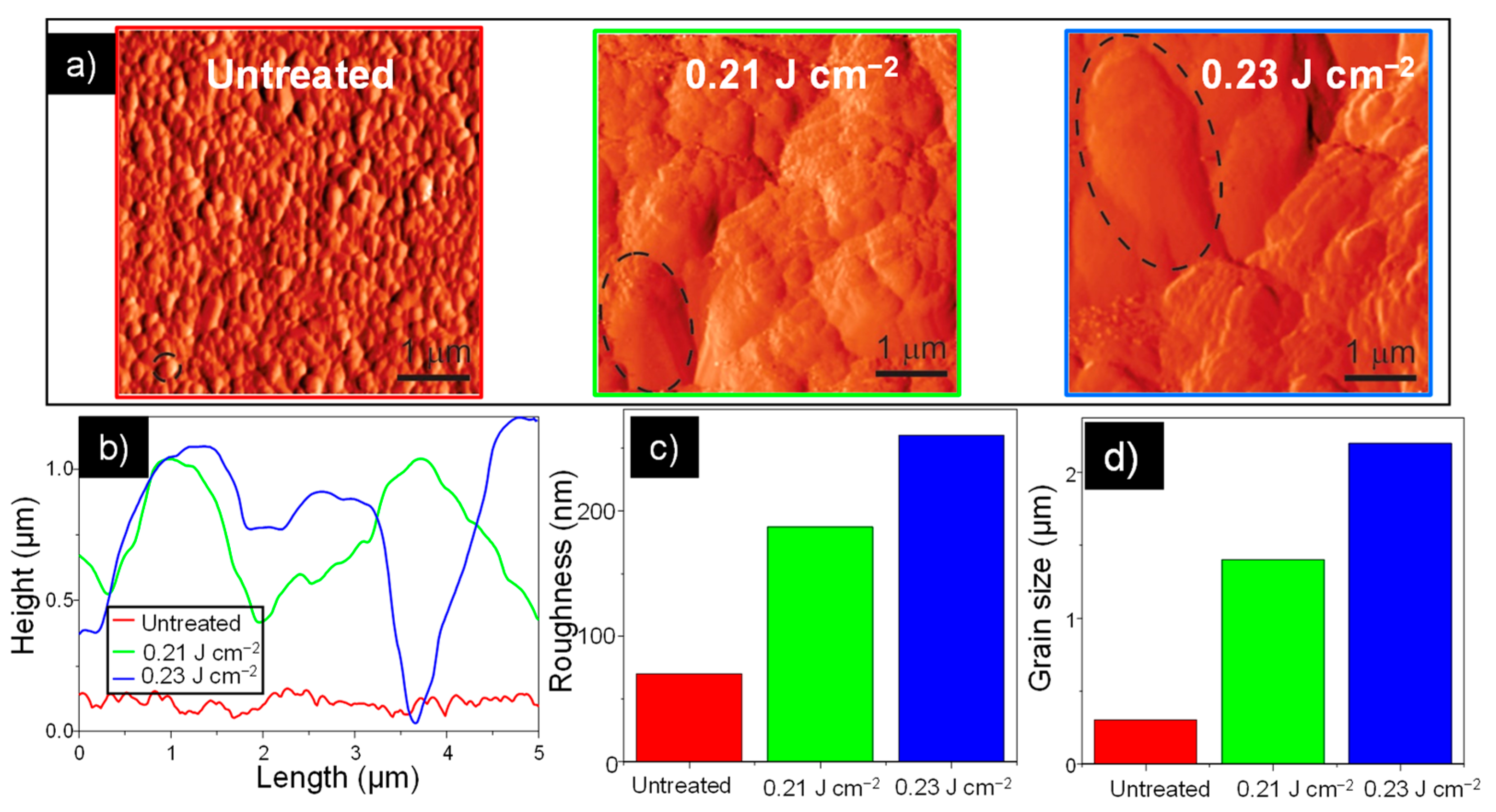
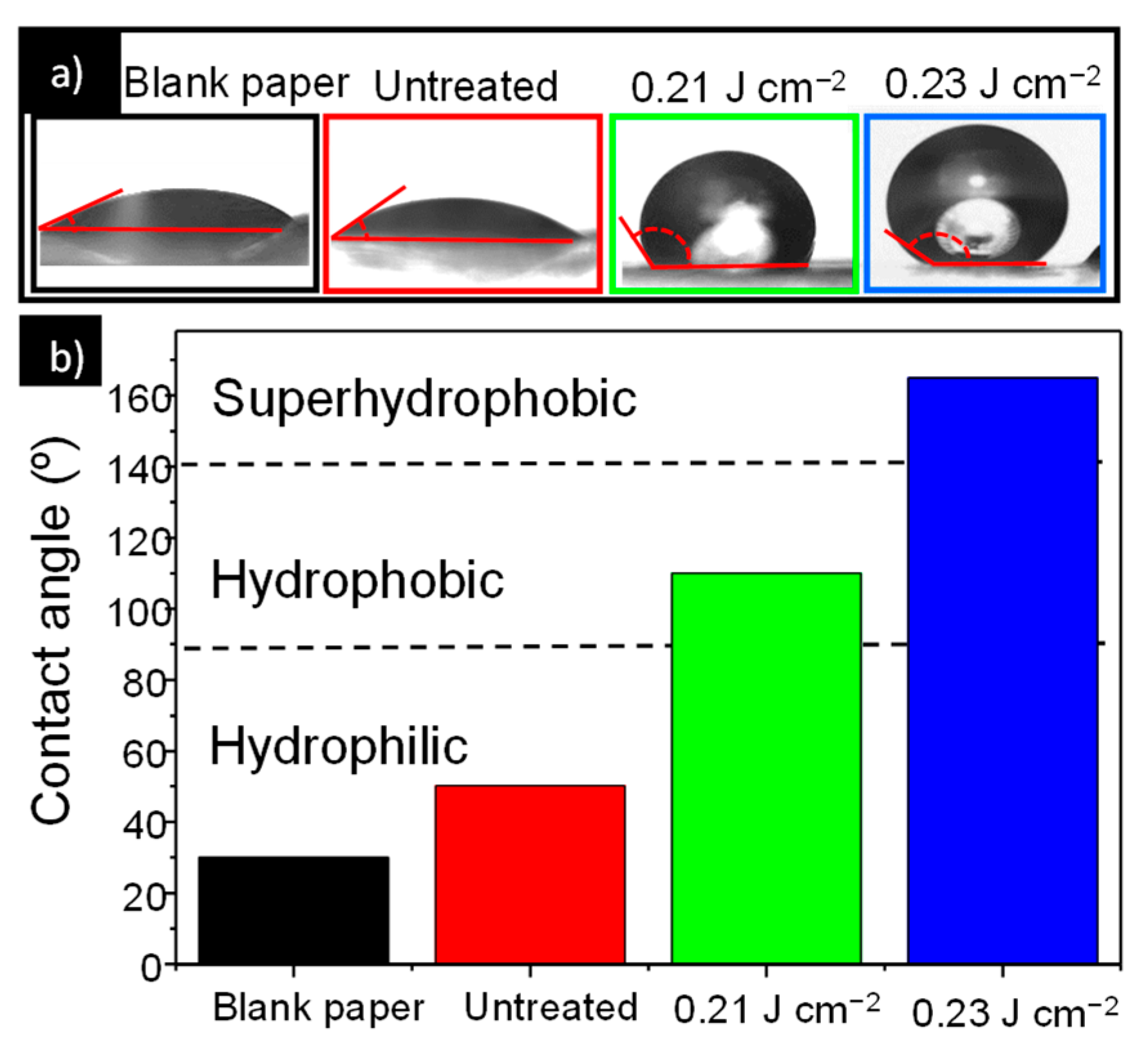
3.1. Characterization of Laser-Treated ZnO Surface
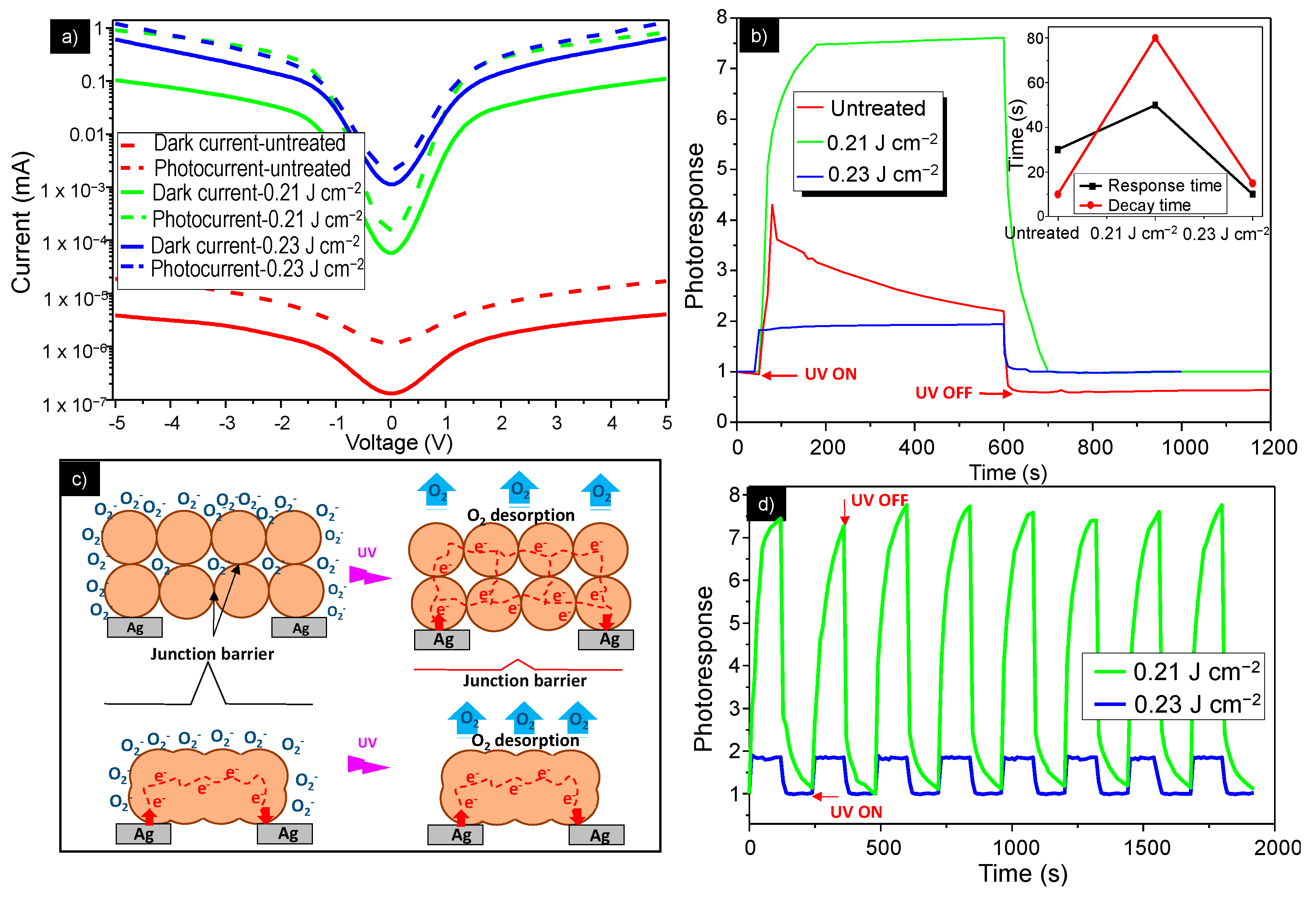
3.2. UV Detection Performances
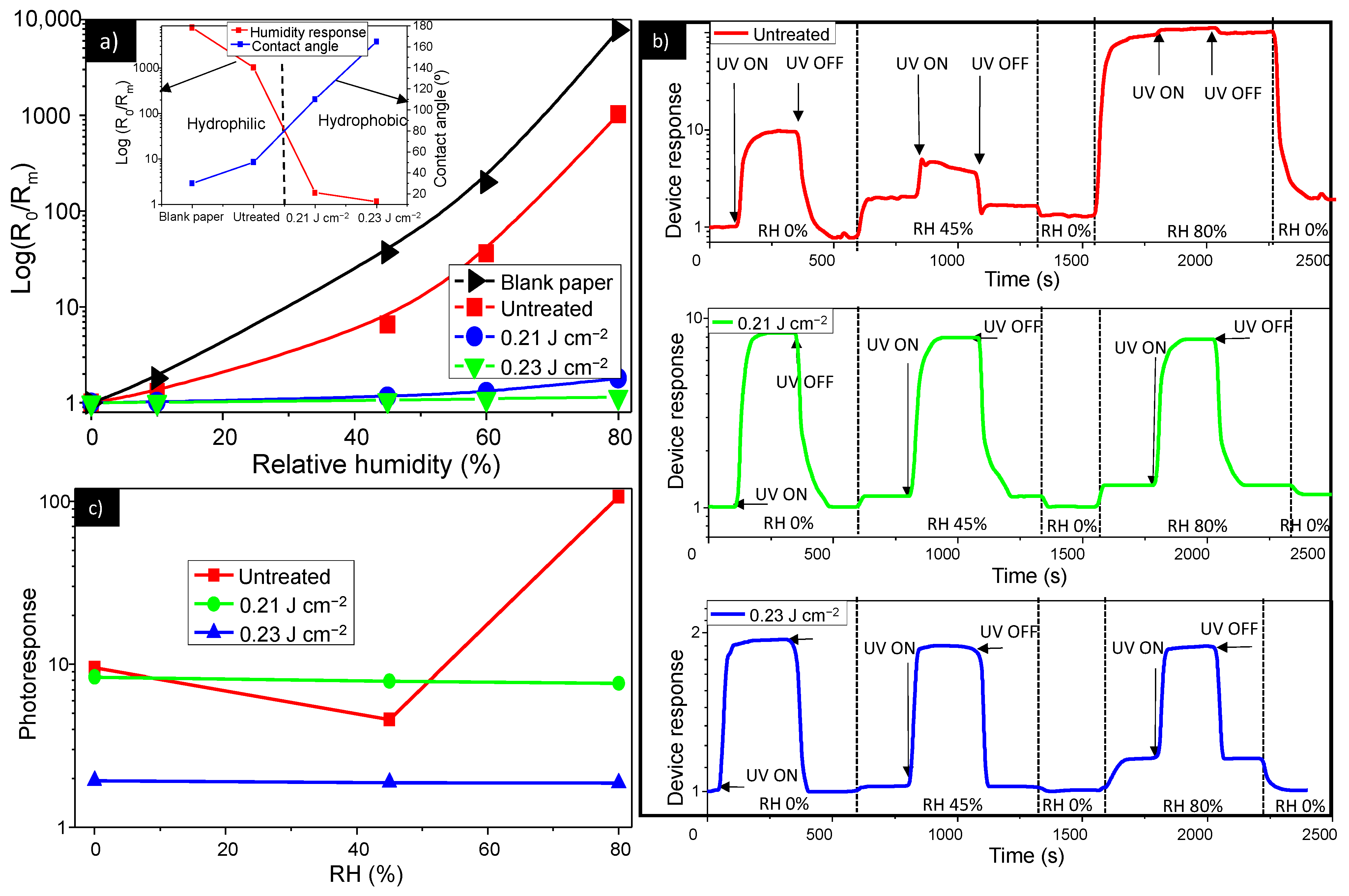
3.3. Suppressed Response to Humidity by Laser-Post Processing Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, D.; Fang, Z.; Zhitenev, N.B. Paper in Electronic and Optoelectronic Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, M.M.; Tashkhourian, J.; Hemmateenejad, B. Structural Elucidation and Ultrasensitive Analyses of Volatile Organic Compounds by Paper-Based Nano-Optoelectronic Noses. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, K.; Stobiecka, M. High-performance modified cellulose paper-based biosensors for medical diagnostics and early cancer screening: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir Kamel, S.; Khattab, T.A. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Biosensors for Medical Diagnosis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradela-Filho, L.A.; Noviana, E.; Araújo, D.A.G.; Takeuchi, R.M.; Santos, A.L.; Henry, C.S. Rapid Analysis in Continuous-Flow Electrochemical Paper-Based Analytical Devices. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummartyotin, S.; Manuspiya, H. A critical review on cellulose: From fundamental to an approach on sensor technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.T.; Araújo, A.; Mendes, M.J.; Nunes, D.; Oliveira, M.J.; Sanchez-Sobrado, O.; Ferreira, M.P.; Águas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.J. Multifunctional cellulose-paper for light harvesting and smart sensing applications. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 3143–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, K.; Mohanty, B.; Biswas, A.; Nayak, J. Role of hexamethylenetetramine in ZnO-cellulose nanocomposite enabled UV and humidity sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 105, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liao, Q.; Ma, M.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Uniformly assembled vanadium doped ZnO microflowers/bacterial cellulose hybrid paper for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators and self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cui, J.; Sheng, X.; Xie, T.; Xu, T.; Feng, X. High-performance photoelectronic sensor using mesostructured ZnO nanowires. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.G.; Santana, G.; Güell, F.; Martínez-Alanis, P.R.; Dutt, A. Photoluminescence of ZnO Nanowires: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.E.; Armani, A.M. Flexible UV exposure sensor based on UV responsive polymer. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.T.; Dubceac, V.; Grey, P.; Cunha, I.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Clausner, A.; Zschech, E.; Pereira, L. Fully Printed Zinc Oxide Electrolyte-Gated Transistors on Paper. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mohr, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fecht, H.J. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators based on a fiber/ZnO nanowires/paper hybrid structure for energy harvesting. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullapalli, H.; Vemuru, V.S.M.; Kumar, A.; Botello-Mendez, A.; Vajtai, R.; Terrones, M.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Ajayan, P.M. Flexible piezoelectric ZnO–paper nanocomposite strain sensor. Small 2010, 6, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.; Samouco, A.; Nunes, D.; Araújo, A.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Ultra-Fast Microwave Synthesis of ZnO Nanorods on Cellulose Substrates for UV Sensor Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Li, H.H.; Hsueh, T.J. Water-and humidity-enhanced UV detector by using p-type La-doped ZnO nanowires on flexible polyimide substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11142–11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Valle, F.D.; Simonnet, M.; Yamada, I.; Delaunay, J. Competitive surface effects of oxygen and water on UV photoresponse of ZnO nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 023110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Tang, R.; Zhu, J.; Oiler, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H. The effects of temperature, relative humidity and reducing gases on the ultraviolet response of ZnO based film bulk acoustic-wave resonator. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 151, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Zhang, H.-D.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.-C.; Zhu, J.-W.; Gong, M.-G.; Wang, X.-X.; Long, Y.-Z. Effects of Ce doping and humidity on UV sensing properties of electrospun ZnO nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Wang, X.X.; Zhao, Y.; Fong, H.; Zhu, Z.T. Effects of humidity on the ultraviolet nanosensors of aligned electrospun ZnO nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobbs, J. The effect of water vapour on the photoconductivity of zinc oxide. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1968, 29, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chao, L.; Hou, M.; Liang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.-D.; Huang, W. Flexible, transparent nanocellulose paper-based perovskite solar cells. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2019, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mates, J.E.; Schutzius, T.M.; Bayer, I.S.; Qin, J.; Waldroup, D.E.; Megaridis, C.M. Water-Based Superhydrophobic Coatings for Nonwoven and Cellulosic Substrates. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollstrom, R.; Pettersson, F.; Dolietis, P.; Preston, J.; Oster-backa, R.; Toivakka, M. Impact of humidity on functionality of on-paper printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 094003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Guo, H.; Guo, Z.; Jin, Y.; Duan, H.; Ren, P.; Yan, D. Highly Bendable and Durable Waterproof Paper for Ultra-High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Polymers 2019, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, H.; Xie, J.; Okagaki, J.; Saji, T. Simple Method for Preparing Superhydrophobic Paper: Spray-Deposited Hydrophobic Silica Nanoparticle Coatings Exhibit High Water-Repellency and Transparency. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4605–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, M.S.; Chanci, D.; Martinez, R.V. Moisture-insensitive, self-powered paper-based flexible electronics. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, A.; Ganayee, M.A.; Jakka Ravindran, S.; Tam, K.C.; Das, S.K.; Ras, R.H.A.; Pradeep, T. Organic Solvent-Free Fabrication of Durable and Multifunctional Superhydrophobic Paper from Waterborne Fluorinated Cellulose Nanofiber Building Blocks. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11091–11099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Duan, X.; Niu, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, T. One-Step Process for Direct Laser Writing Carbonization of NH4H2PO4 Treated Cellulose Paper and Its Use for Facile Fabrication of Multifunctional Force Sensors with Corrugated Structures. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7423–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Chantal, G. Laser processing for bio-microfluidics applications (part I). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balliu, E.; Andersson, H.; Engholm, M.; Ohlund, T.; Nilsson, H.E.; Olin, H. Selective laser sintering of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticle inks on paper substrates to achieve highly conductive patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiep, D.H.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsubara, H.; Ishizaka, S. Fabrication of paper-based microfluidic devices using a laser beam scanning technique. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, S.; Zhou, H.; Nie, J.; Cao, C.; Yang, J.; Pan, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of paper devices via laser-heating-wax-printing for high-tech enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with low-tech pen-type pH meter readout. Analyst 2017, 142, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, G.; Radović, M. Multifunctional Screen-Printed TiO2 Nanoparticles Tuned by Laser Irradiation for a Flexible and Scalable UV Detector and Room-Temperature Ethanol Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6257–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barański, A.; Dutka, D.; Dziembaj, R.; Konieczna-Molenda, A.; Łagan, J.M. Effect of Relative Humidity on the Degradation Rate of Cellulose. Methodology Studies. Restaurator 1970, 25, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, A.F.; Kulik, G.; Sage, D.; Barbieri, L.; Hoffmann, P. A snake-based approach to accurate determination of both contact points and contact angles. Colloid Surf. A 2006, 286, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. A review on special wettability textiles: Theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Chen, B.J.; Suna, X.W.; Fan, W.J. Blueshift of optical band gap in ZnO thin films grown by metal-organic chemical-vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 013505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Futter, J.; Markwitz, A.; Kennedy, J. UV and humidity sensing properties of ZnO nanorods prepared by the arc discharge method. Nanotechnology 2009, 24, 245502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubourg, G.; Radović, M.; Vasić, B. Laser-Tunable Printed ZnO Nanoparticles for Paper-Based UV Sensors with Reduced Humidity Interference. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010080
Dubourg G, Radović M, Vasić B. Laser-Tunable Printed ZnO Nanoparticles for Paper-Based UV Sensors with Reduced Humidity Interference. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubourg, Georges, Marko Radović, and Borislav Vasić. 2021. "Laser-Tunable Printed ZnO Nanoparticles for Paper-Based UV Sensors with Reduced Humidity Interference" Nanomaterials 11, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010080
APA StyleDubourg, G., Radović, M., & Vasić, B. (2021). Laser-Tunable Printed ZnO Nanoparticles for Paper-Based UV Sensors with Reduced Humidity Interference. Nanomaterials, 11(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010080




