Diagnosis and Simultaneous Treatment of Musculoskeletal Injury Using H2O2-Triggered Echogenic Antioxidant Polymer Nanoparticles in a Rat Model of Contusion Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
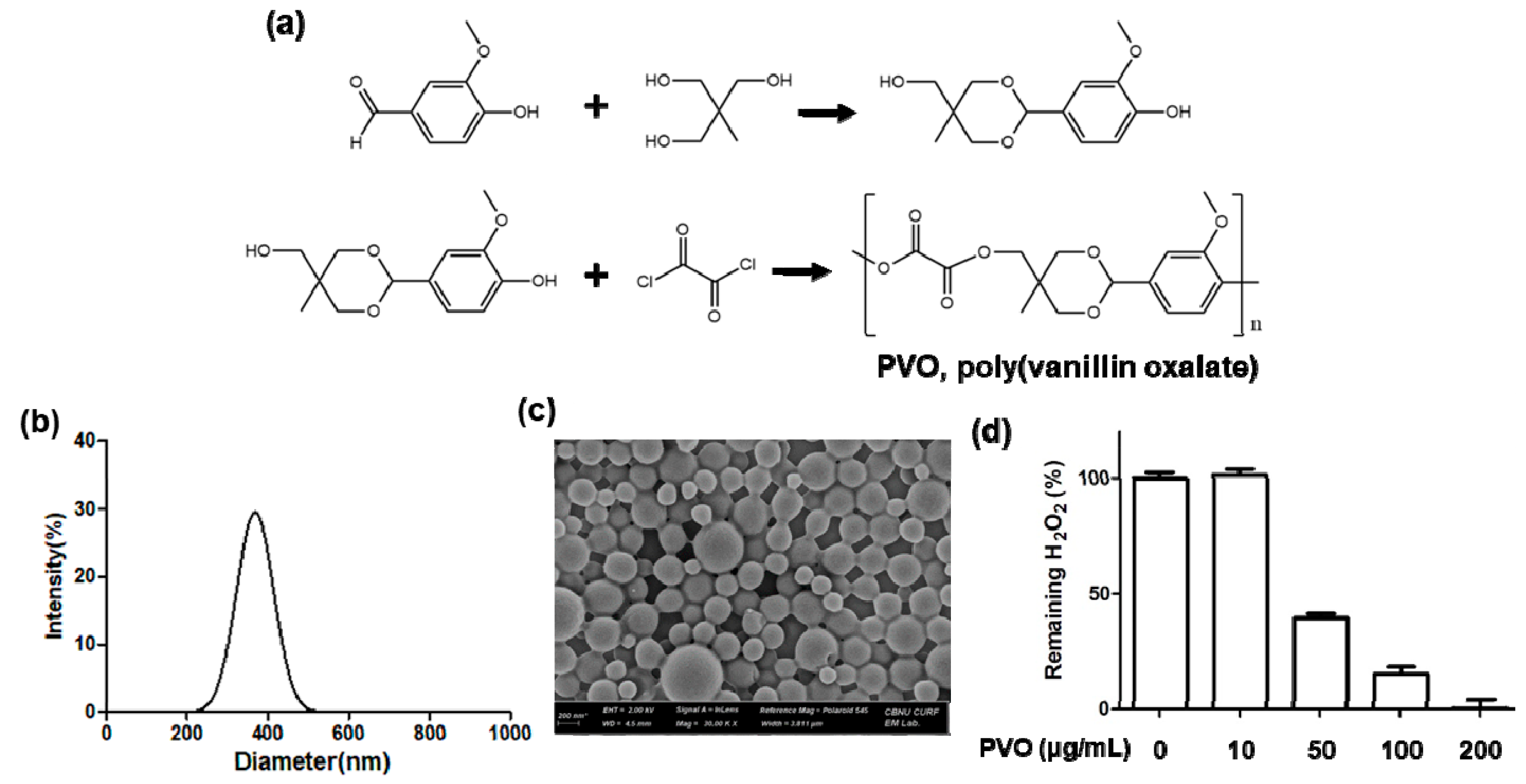
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of PVO Nanoparticles
2.2. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of PVO Nanoparticles on Fibroblast Cells
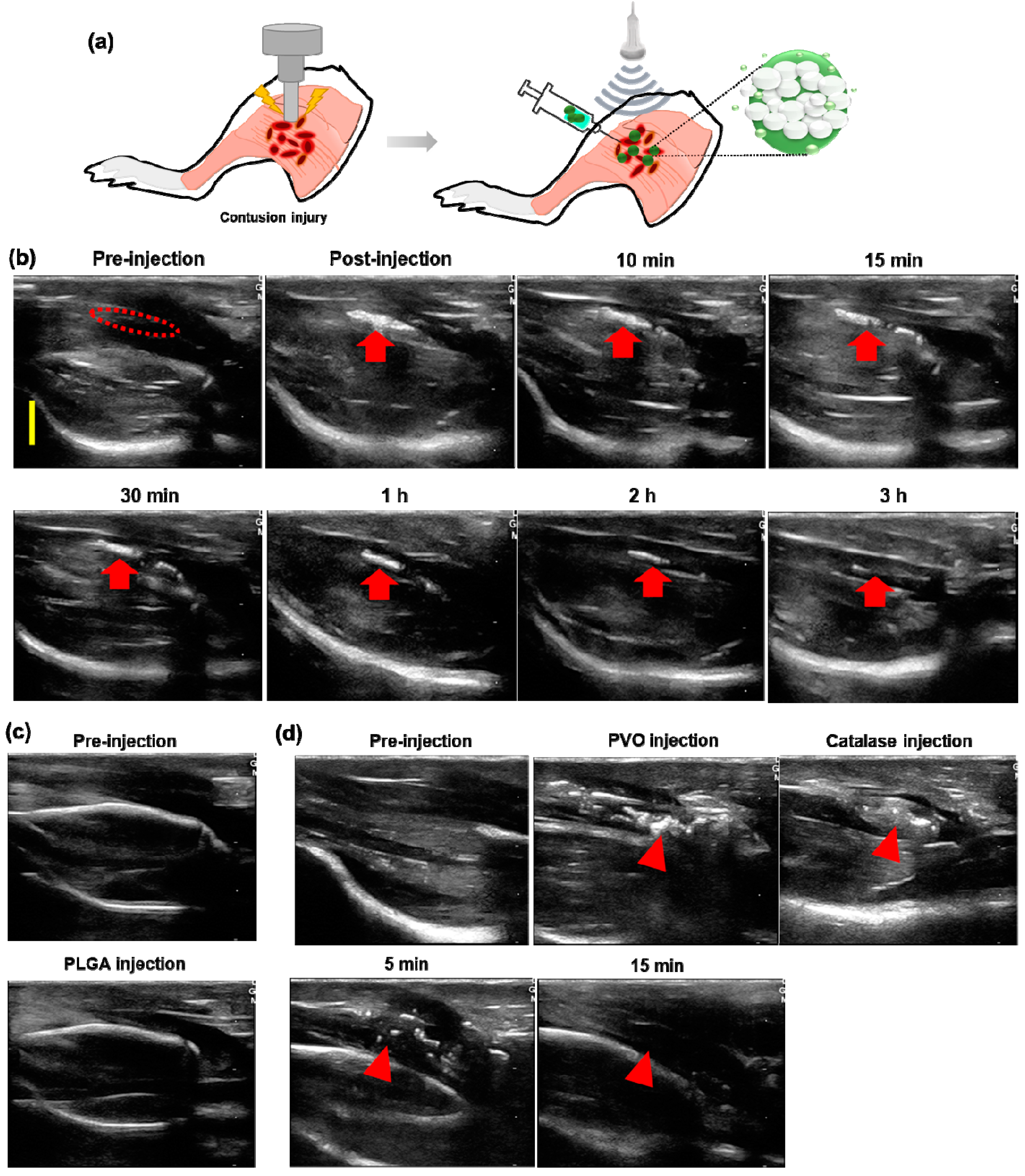
2.3. A Rat Model of Skeletal Muscle Contusion Injury
2.4. Fluorescence Imaging and US Imaging of Contusion Injury
2.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
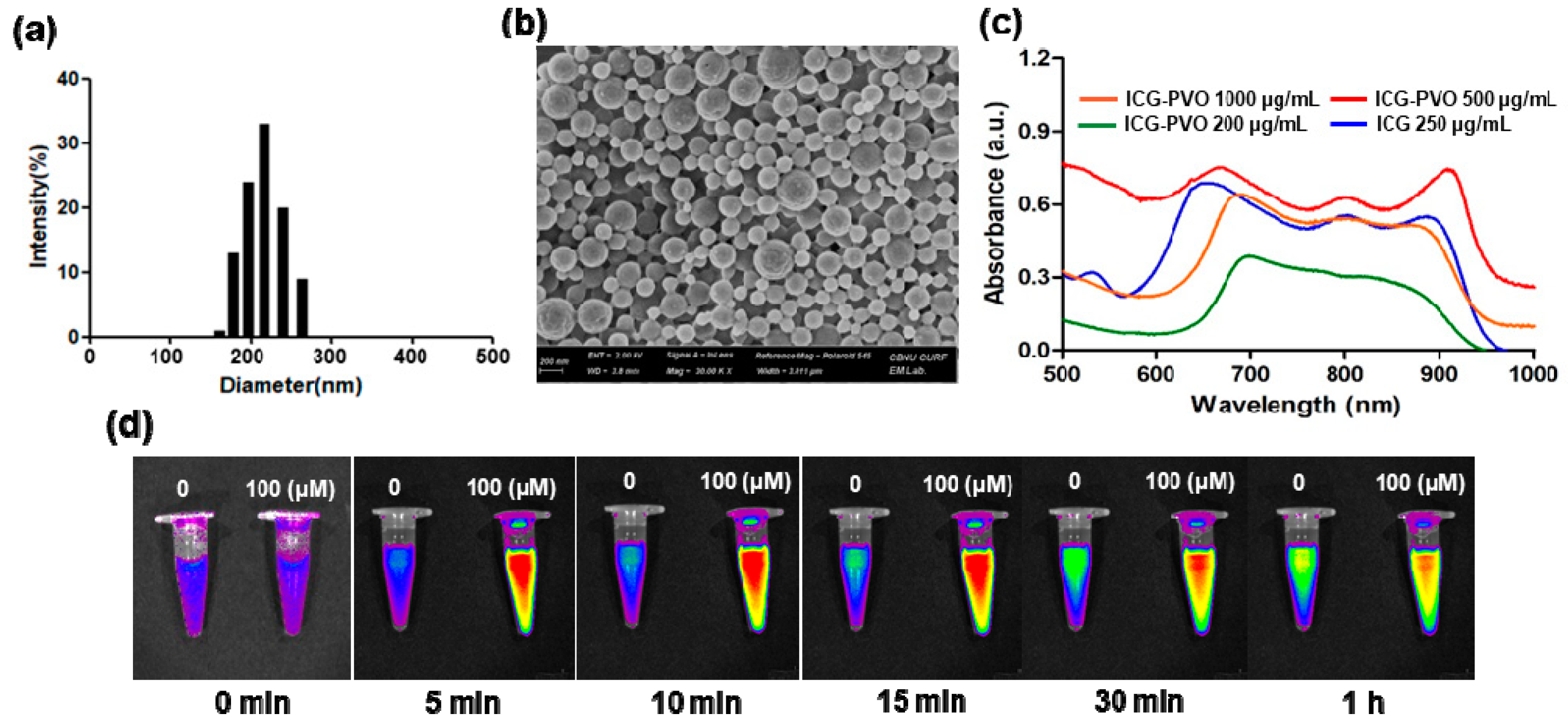
3.1. Characterization of PVO Nanoparticles
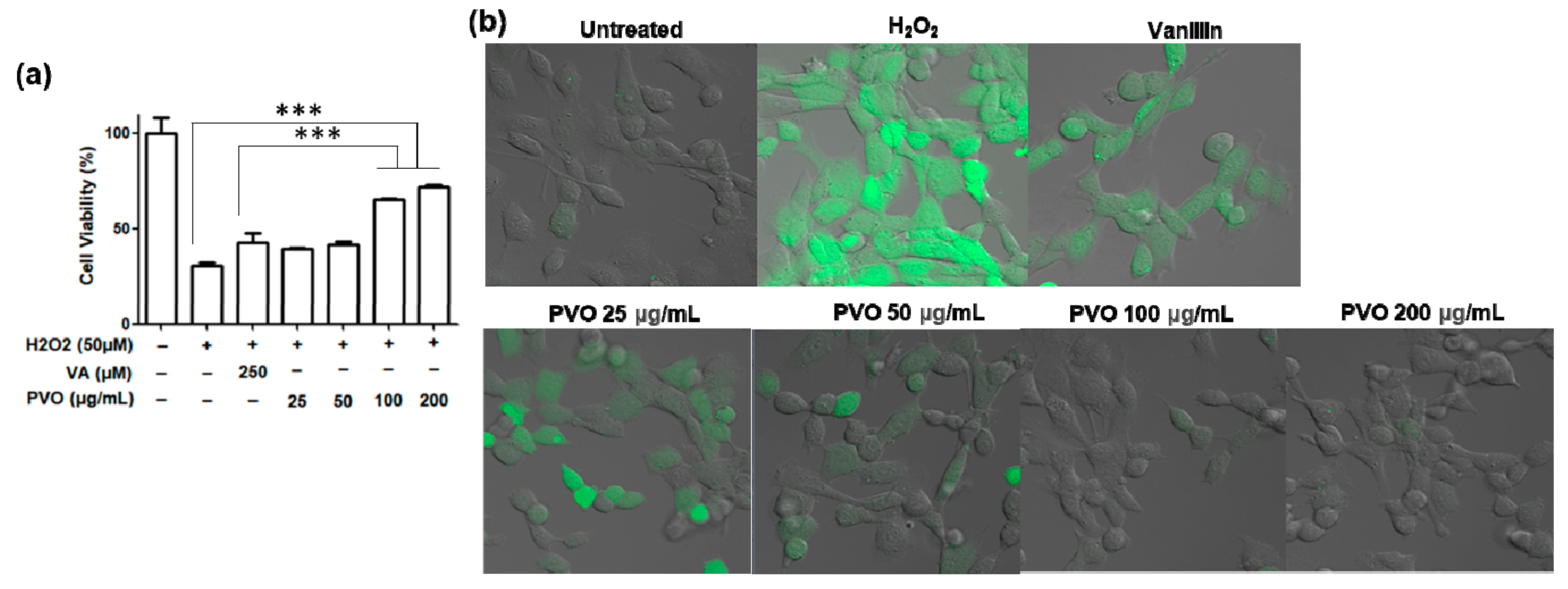
3.2. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of PVO Nanoparticles In Vitro
3.3. US Imaging of PVO Nanoparticles in Agarose Gel Phantom
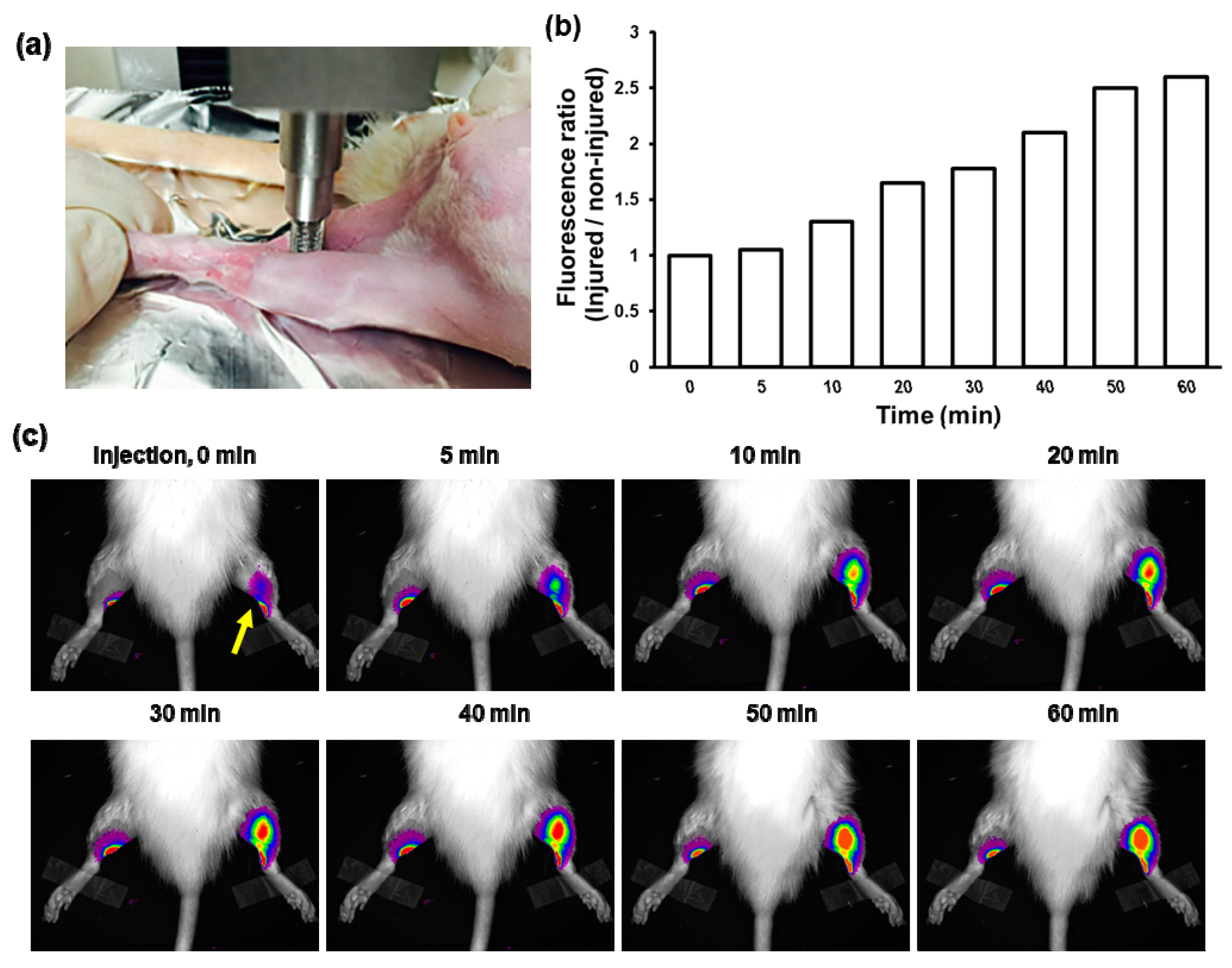
3.4. Fluorescence Imaging of Contusion-Induced Triceps Surae Muscle Injury
3.5. US Imaging of Contusion-Induced Triceps Surae Muscle Injury
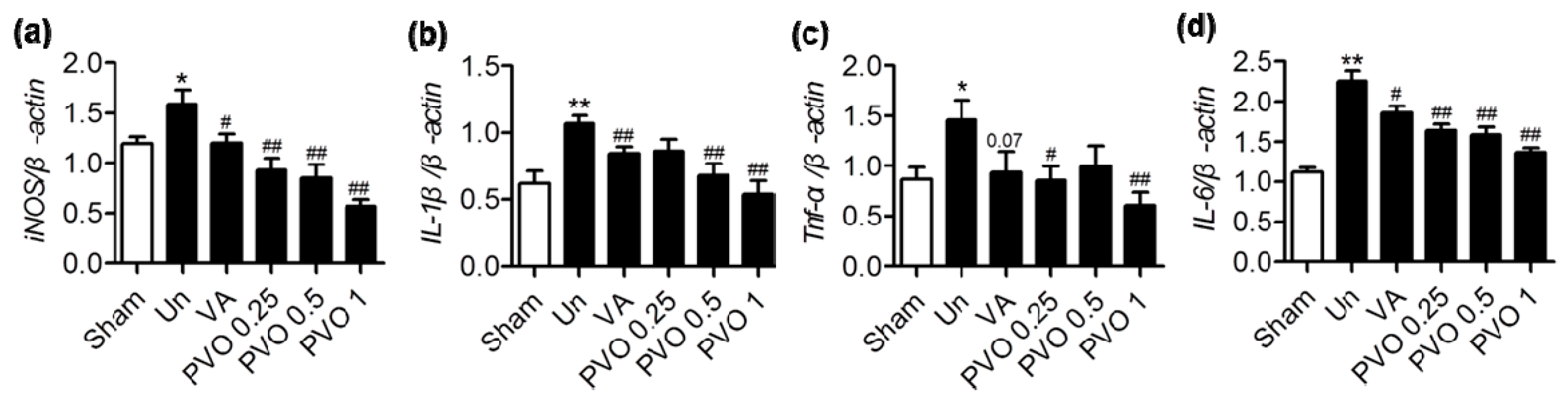
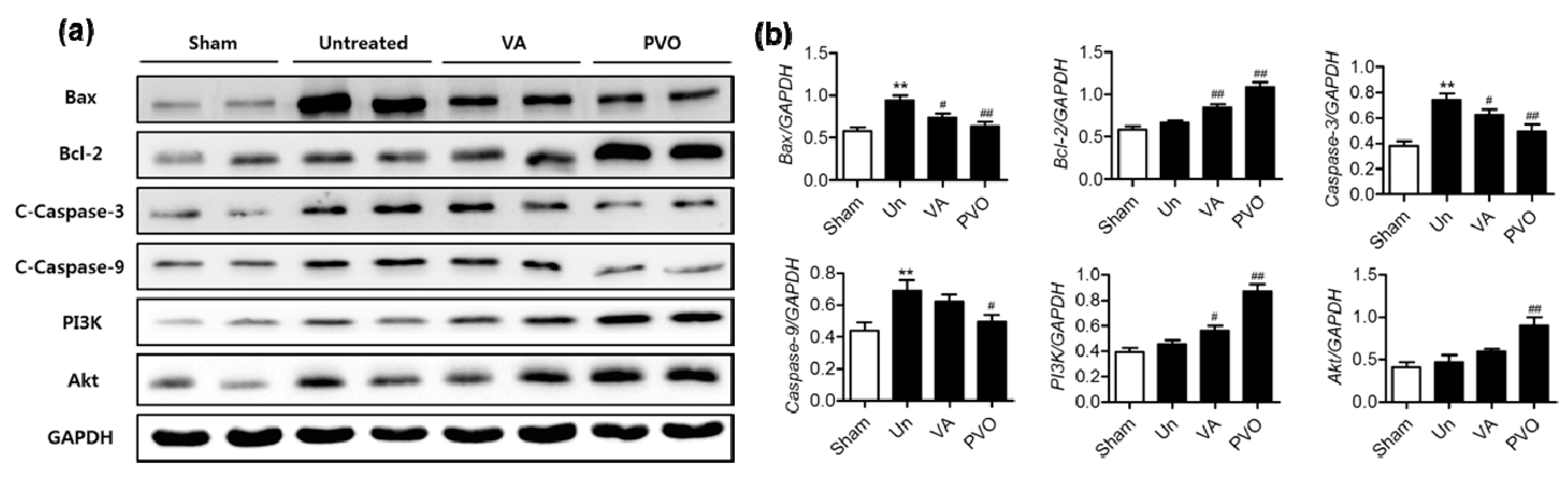
3.6. Therapeutic Effects of PVO Nanoparticles on Contusion-Induced Triceps Surae Muscle Injury
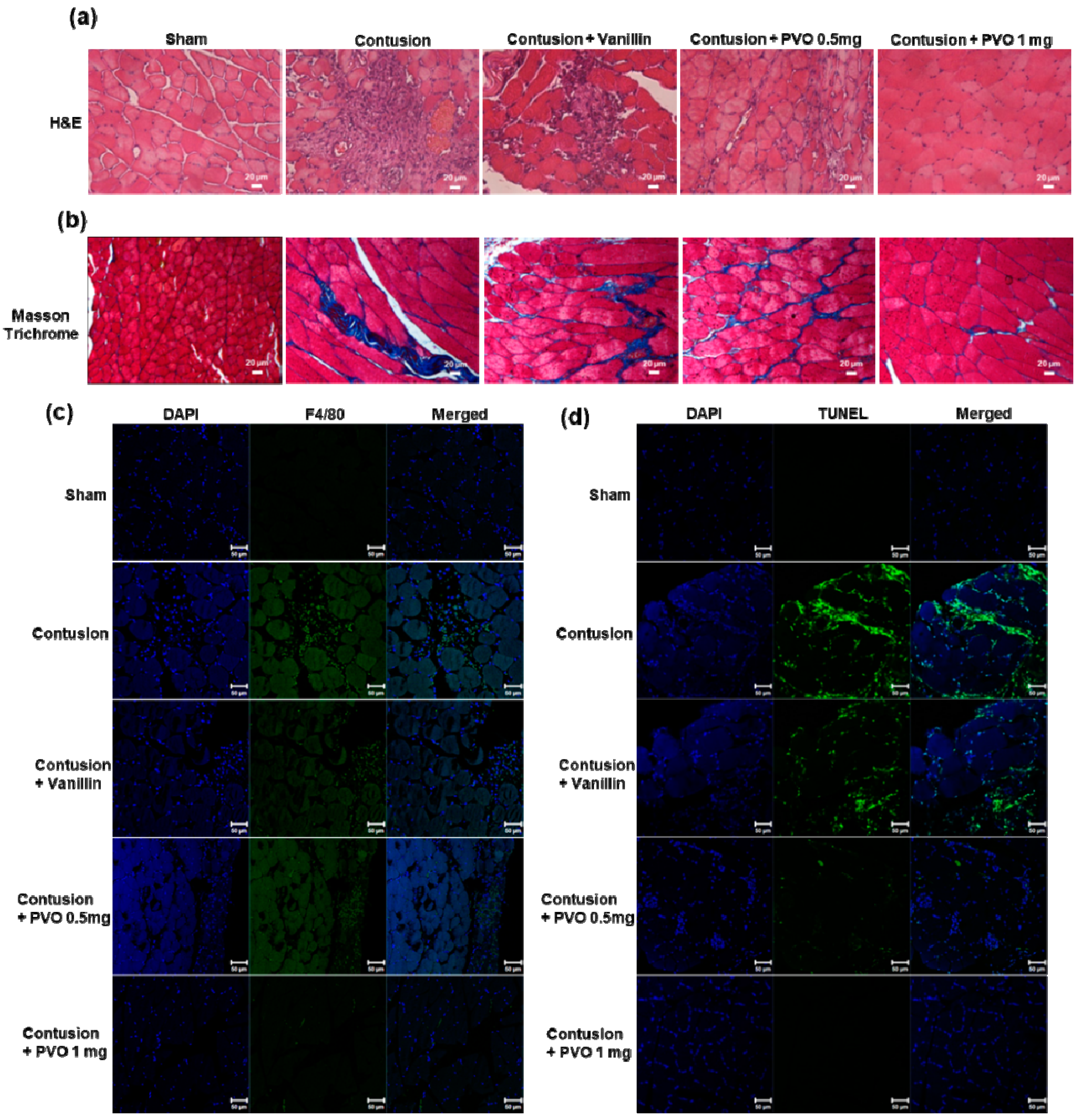
3.7. Histological Examination of Contusion-Induced Triceps Surae Muscle Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piccolo, C.L.; Galluzzo, M.; Ianniello, S.; Trinci, M.; Russo, A.; Rossi, E.; Zeccolini, M.; La Porta, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Miele, V. Pediatric musculoskeletal injuries: Role of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2017, 101, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtgen, B.J.; Ward, C.L.; Garg, K.; Pollot, B.E.; Goldman, S.M.; McKinley, T.O.; Wenke, J.C.; Corona, B.T. Severe muscle trauma triggers heightened and prolonged local musculoskeletal inflammation and impairs adjacent tibia fracture healing. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2016, 16, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jarvinen, T.; Jarvinen, T.L.N.; Kaariainen, M.; Kalimo, A.; Jarvinen, M. Muscle injuries: Biology and treatment. Am. J. Sports Med. 2005, 33, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.P.; Lonbani, Z.B.; Woodruff, M.A.; Parker, T.J.; Steck, R.; Peake, J.M. Effects of Topical Icing on Inflammation, Angiogenesis, Revascularization, and Myofiber Regeneration in Skeletal Muscle Following Contusion Injury. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baoge, L.; Steen, E.V.D.; Rimbaut, S.; Philips, N.; Witvrouw, E.; Almqvist, K.F.; Vanderstraeten, G.; Bossche, L.C.V. Treatment of Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Review. ISRN Orthop. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tidball, J.G. Mechanisms of Muscle Injury, Repair, and Regeneration. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 2029–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.-W.; Kang, C.; Oh, Y.-B.; Ko, M.-H.; Seo, J.-H.; Lee, D. Ultrasonographic Imaging and Anti-inflammatory Therapy of Muscle and Tendon Injuries Using Polymer Nanoparticles. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2463–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Ozcakar, L. Ultrasound Imaging and Rehabilitation of Muscle Disorders Part 1. Traumatic Injuries. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 98, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakonaki, E.E.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Sinopidis, C.; Givissis, P.; Practice, H.I.R. High resolution ultrasound for imaging complications of muscle injury: Is there an additional role for elastography? J. Ultrason. 2019, 19, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Qiu, S.; Mao, L.; Chen, F.; Chen, S. Non-invasive Assessment of Changes in Muscle Injury by Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography: An Experimental Study in Contusion Model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, K.; Taratula, O.; Farsad, K. Applications of nanoparticles in biomedical imaging. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, E.; Dufresne, S.S.; Dumont, N.A. Impact of Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Modalities on Skeletal Muscle Healing: From Fundamental Research to the Clinic. Phys. Ther. 2017, 97, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, M.; Gohil, S.V.; Kuyinu, E.; Kan, H.-M.; Knight, B.E.; Baumbauer, K.; Lo, K.W.-H.; Walker, J.; Laurencin, C.T.; Nair, L.S. Injectable nanocomposite analgesic delivery system for musculoskeletal pain management. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otrocka-Domagała, I.; Paździor-Czapula, K.; Gesek, M. Dexamethasone-induced impairment of post-injury skeletal muscle regeneration. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinks, A.; Koes, B.W.; Volkers, A.C.W.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A. Adverse effects of extra-articular corticosteroid injections: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.; Mak, D.; Davies, A.M.; James, S.; Botchu, R. Musculoskeletal Corticosteroid Administration: Current Concepts. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2019, 70, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhanalakshmi, C.; Manivasagam, T.; Nataraj, J.; Thenmozhi, A.J.; Essa, M.M. Neurosupportive Role of Vanillin, a Natural Phenolic Compound, on Rotenone Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bezerra, D.; Soares, A.K.N.; de Sousa, D. Overview of the Role of Vanillin on Redox Status and Cancer Development. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imanishi, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ohta, T.; Shirasu, Y.; Tutikawa, K. Suppression of 6-TG-resistant mutations in V79 cells and recessive spot formations in mice by vanillin. Mutat. Res. Lett. 1990, 243, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.; Yazan, L.S.; Ismail, N.; Ismail, M. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29 induced by vanillin. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Sun, B.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, F.; Huang, M.; Sun, X.; Li, H. Intracellular antioxidant effect of vanillin, 4-methylguaiacol and 4-ethylguaiacol: Three components in Chinese Baijiu. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 46395–46405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, H.; Shimada, A.; Suemitsu, S.; Murakami, S.; Kitamura, N.; Wani, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; et al. Comprehensive behavioral study of the effects of vanillin inhalation in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Khang, G.; Kang, P.M.; Lee, D. Inflammation-Responsive Antioxidant Nanoparticles Based on a Polymeric Prodrug of Vanillin. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, D.K.; Adhikari, S.; Nair, C.K.K.; Devasagayam, T.P.A. DNA protective properties of vanillin against gamma-radiation under different conditions: Possible mechanisms. Mutat. Res. 2007, 634, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.R.; Jiang, Y.S.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, H.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Sun, X.T.; Zhao, M.M. Elucidation of The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Vanillin in Lps-Activated THP-1 Cells. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretti, A.L.; Antunes, J.S.; Lovison, K.; Kunz, R.I.; Castor, L.R.G.; Brancalhão, R.M.C.; Bertolini, G.R.F.; Ribeiro, L.D.F.C. Action of vanillin (Vanilla planifolia) on the morphology of tibialis anterior and soleus muscles after nerve injury. Einstein 2017, 15, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dantas, M.G.B.; Damasceno, C.M.D.; De Barros, V.R.P.; Menezes, E.S.; Fontoura, H.D.S.; De Lima, R.S.; Carvalho, F.O.; Almeida, J. Creation of a contusion injury method for skeletal muscle in rats with differing impacts. Acta Cir. Bras. 2017, 32, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, M.; Meza, R.; Lieber, R.L. Skeletal muscle fibroblasts in health and disease. Differentiation 2016, 92, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prisk, V.; Huard, J. Muscle injuries and repair: The role of prostaglandins and inflammation. Histol. Histopathol. 2003, 18, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, C.J.; Perdiguero, E.; Kharraz, Y.; Aguilar, S.; Pessina, P.; Serrano, A.L.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Aberrant repair and fibrosis development in skeletal muscle. Skelet. Muscle 2011, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bureau, N.J.; Ziegler, D. Economics of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2016, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lento, P.H.; Primack, S. Advances and utility of diagnostic ultrasound in musculoskeletal medicine. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2008, 1, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, J. Musculoskeletal Ultrasound and MRI: Which Do I Choose? Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2005, 9, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ustun, N.; Tok, F.; Yagiz, A.E.; Kizil, N.; Korkmaz, I.; Karazincir, S.; Okuyucu, E.; Turhanoglu, A.D. Ultrasound-Guided vs. Blind Steroid Injections in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome A Single-Blind Randomized Prospective Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Choi, W.A.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.-K. Accuracy of blind versus ultrasound-guided suprapatellar bursal injection. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2011, 40, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, E.; Li, W.; Ong, K.O.; Chen, W.; Bautista, D. Image-guided versus blind corticosteroid injections in adults with shoulder pain: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, G.; Fu, Q.; Wu, R.; Liu, R.; Cui, L.; Xu, Y. Ultrasound and Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injection Have High Accuracy in the Diagnosis of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Atypical Symptoms. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2021, 37, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, C.; Alexander, M.; Kane, D. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of carpal tunnel syndrome: A new paradigm. Rheumatology 2014, 54, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, W.K.; Papadopoulou, V.; Dayton, P.A. Imaging with ultrasound contrast agents: Current status and future. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, S.; Klibanov, A.L. Microbubbles as Ultrasound Contrast Agents for Molecular Imaging: Preparation and Application. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.B.; Qin, L. Inflammation and the musculoskeletal system. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 10, A1–A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth-Kewley, S.; Schmied, E.A.; Highfill-McRoy, R.M.; Sander, T.C.; Blivin, S.J.; Garland, C.F. A Prospective Study of Factors Affecting Recovery from Musculoskeletal Injuries. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2014, 24, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojulari, O.V.; Lee, S.G.; Nam, J.-O. Beneficial Effects of Natural Bioactive Compounds from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. on Obesity. Molecules 2019, 24, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calixto, J.B. The role of natural products in modern drug discovery. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91 (Suppl. S3), e20190105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.-H.; Vederas, J.C. Drug Discovery and Natural Products: End of an Era or an Endless Frontier? Science 2009, 325, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Song, Y.; Seung, K.; Hong, D.; Khang, G.; Lee, D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Releasing Biodegradable Polyoxalate Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, G.; Gunawardena, D.; Raju, R. Hydrogen peroxide mediates pro-inflammatory cell-to-cell signaling: A new therapeutic target for inflammation? Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Sequences for Primers | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | FOR: AGGGAGTGTTGTTCCAGGTG | NM_012611 |
| REV: TCCTCAACCTGCTCCTCACT | ||
| TNF-α | FOR: TGATCCGAGATGTGGAACTG | NM_012675 |
| REV: CCCATTTGGGAACTTCTCCT | ||
| IL-1β | FOR: CAGGAAGGCAGTGTCACTCA | NM_031512 |
| REV: AGACAGCACGAGGCATTTTT | ||
| IL-6 | FOR: AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA | NM_012589 |
| REV:CAGAATTGCCATTGCACAAC | ||
| Β-actin | FOR: TGTCACCAACTGGGACGATA | NM_031144 |
| REV: GGGGTGTTGAAGGTCTCAAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.-W.; Song, N.-H.; Park, M.-R.; Kim, T.-E.; Kim, D.-S.; Oh, Y.-B.; Lee, D.-W. Diagnosis and Simultaneous Treatment of Musculoskeletal Injury Using H2O2-Triggered Echogenic Antioxidant Polymer Nanoparticles in a Rat Model of Contusion Injury. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102571
Kim G-W, Song N-H, Park M-R, Kim T-E, Kim D-S, Oh Y-B, Lee D-W. Diagnosis and Simultaneous Treatment of Musculoskeletal Injury Using H2O2-Triggered Echogenic Antioxidant Polymer Nanoparticles in a Rat Model of Contusion Injury. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102571
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Gi-Wook, Nan-Hee Song, Mi-Ran Park, Tae-Eon Kim, Da-Sol Kim, Young-Bin Oh, and Dong-Won Lee. 2021. "Diagnosis and Simultaneous Treatment of Musculoskeletal Injury Using H2O2-Triggered Echogenic Antioxidant Polymer Nanoparticles in a Rat Model of Contusion Injury" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102571
APA StyleKim, G.-W., Song, N.-H., Park, M.-R., Kim, T.-E., Kim, D.-S., Oh, Y.-B., & Lee, D.-W. (2021). Diagnosis and Simultaneous Treatment of Musculoskeletal Injury Using H2O2-Triggered Echogenic Antioxidant Polymer Nanoparticles in a Rat Model of Contusion Injury. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102571







