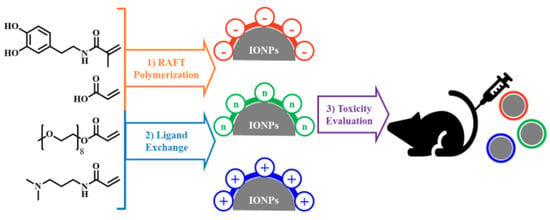
Charge-Modulated Synthesis of Highly Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of OAc-IONPs
2.3. Synthesis of Differently Charged Polymer Ligands
2.4. Synthesis of Charged IONPs
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.7. MTT Assay
2.8. Animals
2.9. Hematological Analysis and Histological Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Differently Charged Ligands
3.2. Synthesis of Charged IONPs Dispersed in the Aqueous Solution
3.3. Stability of IONP in DIW and Cell Culture Media
3.4. Evaluation of In Vitro Toxicity of Differently Charged IONPs
3.5. Evaluation of In Vivo Toxicity of Differently Charged IONPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IONPs | iron oxide nanoparticles |
| RAFT polymerization | reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer-mediated polymerization |
| HD | hydrodynamic diameter |
| (−) ligand | negative ligand |
| (n) ligand | neutral ligand |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| (+) ligand | positive ligand |
| PDI | polydispersity index |
| OAc-IONPs | oleic acid-coated IONPs |
| (−) IONPs | negatively charged IONPs |
| (n) IONPs | neutral IONPs |
| (+) IONPs | positively charged IONPs |
| MTT | thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide |
| DMA | 4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-2-methylprop-2-enamide |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| GPC | gel permeation chromatography |
| DLS | dynamic laser scattering |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CREA | creatinine |
| ALT | alanine aminotransaminase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransaminase |
| TBIL | total bilirubin |
| DP | degree of polymerization |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
References
- Serga, V.; Burve, R.; Maiorov, M.; Krumina, A.; Skaudžius, R.; Zarkov, A.; Kareiva, A.; Popov, A.I. Impact of gadolinium on the structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline powders of iron oxides produced by the extraction-pyrolytic method. Materials 2020, 13, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahil, H.; Faramawy, A.; El-Sayed, H.; Abdel-Sattar, A. Magnetic properties and SAR for gadolinium-doped iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method. Crystals 2021, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Wang, T.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, E.; Shen, C.; Jia, A.; Zhang, Q. Magnetically reusable Fe3O4@NC@Pt catalyst for selective reduction of nitroarenes. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhayal, A.; Fathima, A.; Alhasan, A.H.; Alsharaeh, E.H. PEG coated Fe3O4/RGO nano-cube-like structures for cancer therapy via magnetic hyperthermia. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Shi, X.Y.; Shen, M.W. Intelligent design of ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticle-based theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 45119–45129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Bao, G. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 20, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.B.; Palui, G.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Ji, X.; Grant, S.C.; Mattoussi, H. Multidentate catechol-based polyethylene glycol oligomers provide enhanced stability and biocompatibility to iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2012, 6, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chevallier, P.; Ramrup, P.; Biswas, D.; Vuckovich, D.; Fortin, M.-A.; Oh, J.K. Mussel-inspired multidentate block copolymer to stabilize ultrasmall superparamagnetic Fe3O4 for magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement and excellent colloidal stability. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7100–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstad, E.; Textor, M.; Reimhult, E. Stabilization and functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2819–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ling, D.; Lee, N.; Hyeon, T. Chemical synthesis and assembly of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanot, C.C.; Choi, Y.S.; Anani, T.B.; Soundarrajan, D.; David, A.E. Effects of iron-oxide nanoparticle surface chemistry on uptake kinetics and cytotoxicity in CHO-K1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Laurent, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Hosseinkhani, M. Toxicity evaluations of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Cell “vision” versus physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2011, 5, 7263–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bona, K.R.; Xu, Y.L.; Ramirez, P.A.; DeLaine, J.; Parker, C.; Bao, Y.P.; Rasco, J.F. Surface charge and dosage dependent potential developmental toxicity and biodistribution of iron oxide nanoparticles in pregnant CD-1 mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 50, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, M.; Taylor, A.; Nieves, D.J.; Bogart, L.K.; Mandal, P.; Collins, C.M.; Moore, L.R.; Chalmers, J.J.; Lévy, R.; Williams, S.R.; et al. Tailoring the surface charge of dextran-based polymer coated SPIONs for modulated stem cell uptake and MRI contrast. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakulkhu, U.; Mahmoudi, M.; Maurizi, L.; Coullerez, G.; Hofmann-Amtenbrink, M.; Vries, M.; Motazacker, M.; Rezaee, F.; Hofmann, H. Significance of surface charge and shell material of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION) based core/shell nanoparticles on the composition of the protein corona. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, V.; Kinnear, C.; Moniatte, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Clift, M.J.D.; Fink, A. Surface charge of polymer coated SPIONs influences the serum protein adsorption, colloidal stability and subsequent cell interaction in vitro. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakulkhu, U.; Mahmoudi, M.; Maurizi, L.; Salaklang, J.; Hofmann, H. Protein corona composition of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with various physico-chemical properties and coatings. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calatayud, M.P.; Sanz, B.; Raffa, V.; Riggio, C.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F. The effect of surface charge of functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles on protein adsorption and cell uptake. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6389–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayala, V.; Herrera, A.P.; Latorre-Esteves, M.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Rinaldi, C. Effect of surface charge on the colloidal stability and in vitro uptake of carboxymethyl dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivet, C.J.; Yuan, Y.; Borca-Tasciuc, D.A.; Gilbert, R.J. Altering iron oxide nanoparticle surface properties induce cortical neuron cytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Huang, J.X.; Xiao, K. Uptake, distribution, clearance, and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and coatings. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; Nguyen, H.T.; Fox, K.; Tran, N. In vitro cytotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles: Effects of chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol as stabilizing agents. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 035051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, S.; Leonzino, M.; Drago, C.; Ferretti, A.M.; Usseglio, S.; Maggioni, D.; Tornese, P.; Chini, B.; Ponti, A. Zwitterion-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: Surface chemistry and intracellular uptake by hepatocarcinoma (HepG2) cells. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7381–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.H.; Greytak, A.B.; Lee, J.; Wong, C.R.; Park, J.; Marshall, L.F.; Jiang, W.; Curtin, P.N.; Ting, A.Y.; Nocera, D.G.; et al. Compact biocompatible quantum dots via RAFT-mediated synthesis of imidazole-based random copolymer ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, Y.; Kawano, T.; Shimomura, M.; Yabu, H. Fabrication of mussel-inspired highly adhesive honeycomb films containing catechol groups and their applications for substrate-independent porous templates. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, N.; Endo, T. Functional RAFT agents for radical-controlled polymerization: Quantitative synthesis of trithiocarbonates containing functional groups as RAFT agents using equivalent amount of CS2. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 3702–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, K.J.; Hwang, Y.S.; Park, J.G.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, N.M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Whitaker, R.D.; Nap, R.J.; Paulsen, J.L.; Mathiyazhagan, V.; Doerrer, L.H.; Song, Y.Q.; Hurlimann, M.D.; Szleifer, I.; Wong, J.Y. Stability of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles at different pH values: Experimental and theoretical analysis. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6246–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisciotti, M.L.M.; Lima, E.; Mansilla, M.V.; Tognoli, V.E.; Troiani, H.E.; Pasa, A.A.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B.; Silva, A.H.; Gurman, P.; Colombo, L.; et al. In vitro and in vivo experiments with iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with DEXTRAN or polyethylene glycol for medical applications: Magnetic targeting. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2014, 102, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.J.; David, A.E.; Wang, J.X.; Galban, C.J.; Hill, H.L.; Yang, V.C. Polyethylene glycol modified, cross-linked starch-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic tumor targeting. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Keijsers, J.; van Heek, M.; Stuiver, A.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Kamperman, M. The effect of molecular composition and crosslinking on adhesion of a bio-inspired adhesive. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3121–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Chung, H. Photo-responsive bio-inspired adhesives: Facile control of adhesion strength via a photocleavable crosslinker. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 6300–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Falentin-Daudré, C.; Jérôme, C.; Detrembleur, C. Mussel-inspired protein-repelling ambivalent block copolymers: Controlled synthesis and characterization. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2919–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, D.S.; Hyeon, T. Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small 2013, 9, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Park, M.K.; Lu, C.; Lee, Y.H.; Chai, K.Y. A mussel-inspired chitooligosaccharide based multidentate ligand for highly stabilized nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3730–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholoobi, A.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Shandiz, F.H.; Darroudi, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Meshkat, Z. Synthesis of gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticles capped with oleic acid and their magnetic characterization. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2018, 42, 1889–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiogo, H.T.R.; Lim, M.; Bulmus, V.; Yun, J.; Amal, R. Stabilization of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biological media by fetal bovine serum (FBS). Langmuir 2011, 27, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, U.S.; Adireddy, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Mandava, S.; Lee, B.R.; Chrisey, D.B. In vitro/in vivo toxicity evaluation and quantification of iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24417–24450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Theoretical Value | Calculated Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DMA | PEG | DMA | PEG |
| 10 | 90 | 9 | 91 |
| 20 | 80 | 20 | 80 |
| 30 | 70 | 28 | 72 |
| 40 | 60 | 35 | 65 |
| 50 | 50 | 45 | 55 |
| Sample | DMA:PEG:Functional Group | Mn | DP ([Monomer]/[RAFT]) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Experimental (NMR) | NMR | GPC (PDI) | Theoretical | NMR | GPC | |
| (−) ligand | 20:50:30 | 17:52:31 | 4738 | 5253 (1.28) | 20 | 12 | 13 |
| (n) ligand | 20:80:0 | 18:82:0 | 9745 | 7049 (1.29) | 20 | 22 | 16 |
| (+) ligand | 20:50:30 | 22:53:25 | 7239 | 2509 (1.25) | 20 | 20 | 7 |
| PBS | (−) IONPs | (n) IONPs | (+) IONPs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Fe mg/kg | 10 Fe mg/kg | 2 Fe mg/kg | 10 Fe mg/kg | 2 Fe mg/kg | 10 Fe mg/kg | ||
| Liver Inflammatory cell foci | +(3) | +(1), ++(2) | |||||
| Kidney | +(1) | ||||||
| Basophilic tubules | +(1) | +(1) | |||||
| Inflammatory cell foci | +(1) | +(1) | |||||
| Mineralization | +(1) | ||||||
| Lung | |||||||
| Heart Cardiomyopathy | +(1) | ||||||
| Spleen | |||||||
| Brains | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Cheon, Y.W.; Yoon, S.; Oh, J.-H.; Park, J. Charge-Modulated Synthesis of Highly Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113068
Woo S, Kim S, Kim H, Cheon YW, Yoon S, Oh J-H, Park J. Charge-Modulated Synthesis of Highly Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113068
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Sunyoung, Soojin Kim, Hyunhong Kim, Young Woo Cheon, Seokjoo Yoon, Jung-Hwa Oh, and Jongnam Park. 2021. "Charge-Modulated Synthesis of Highly Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113068
APA StyleWoo, S., Kim, S., Kim, H., Cheon, Y. W., Yoon, S., Oh, J.-H., & Park, J. (2021). Charge-Modulated Synthesis of Highly Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113068