Revealing the Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Structural, Optical, and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CeO2 Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Antibacterial Activity
2.4.1. Antibacterial Testing
2.4.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
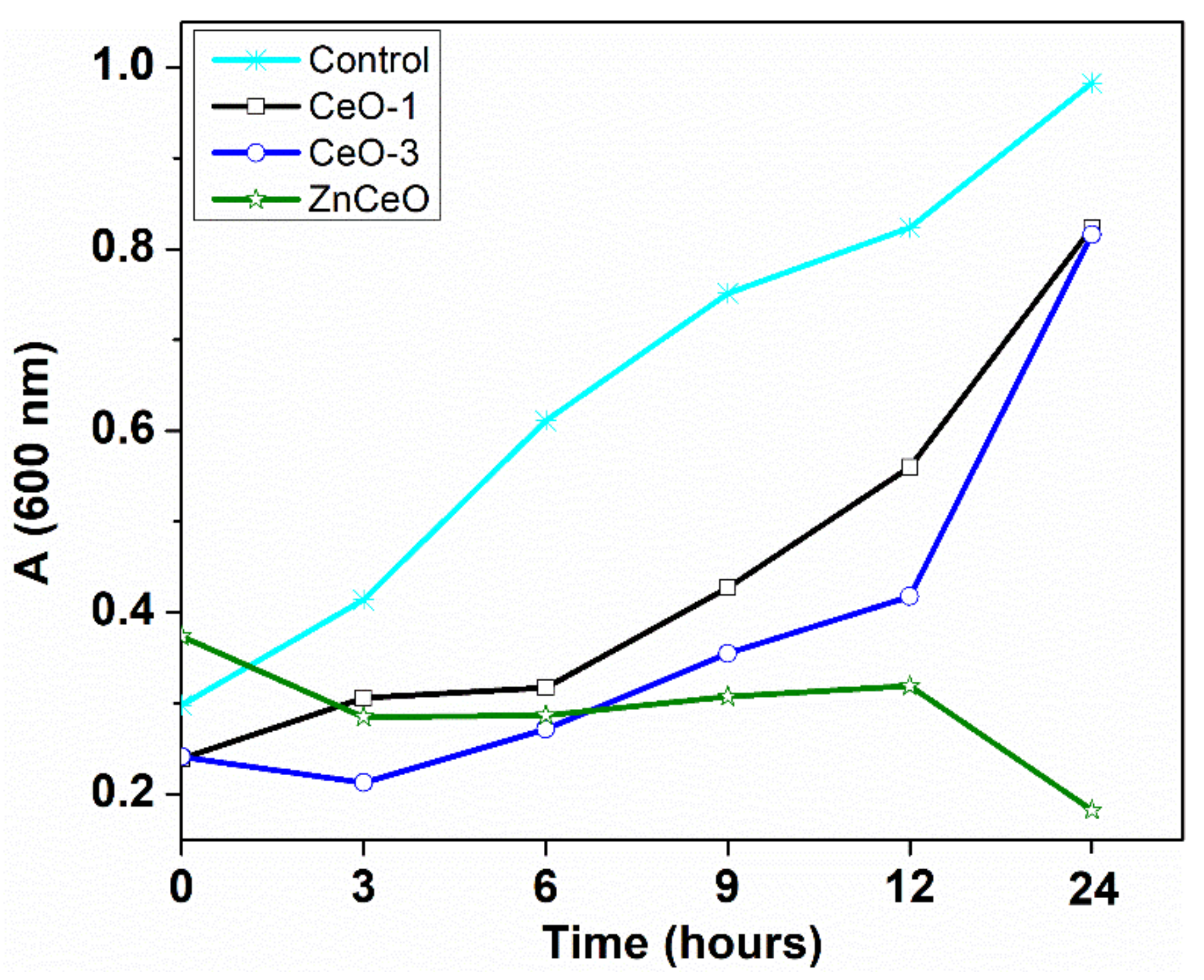
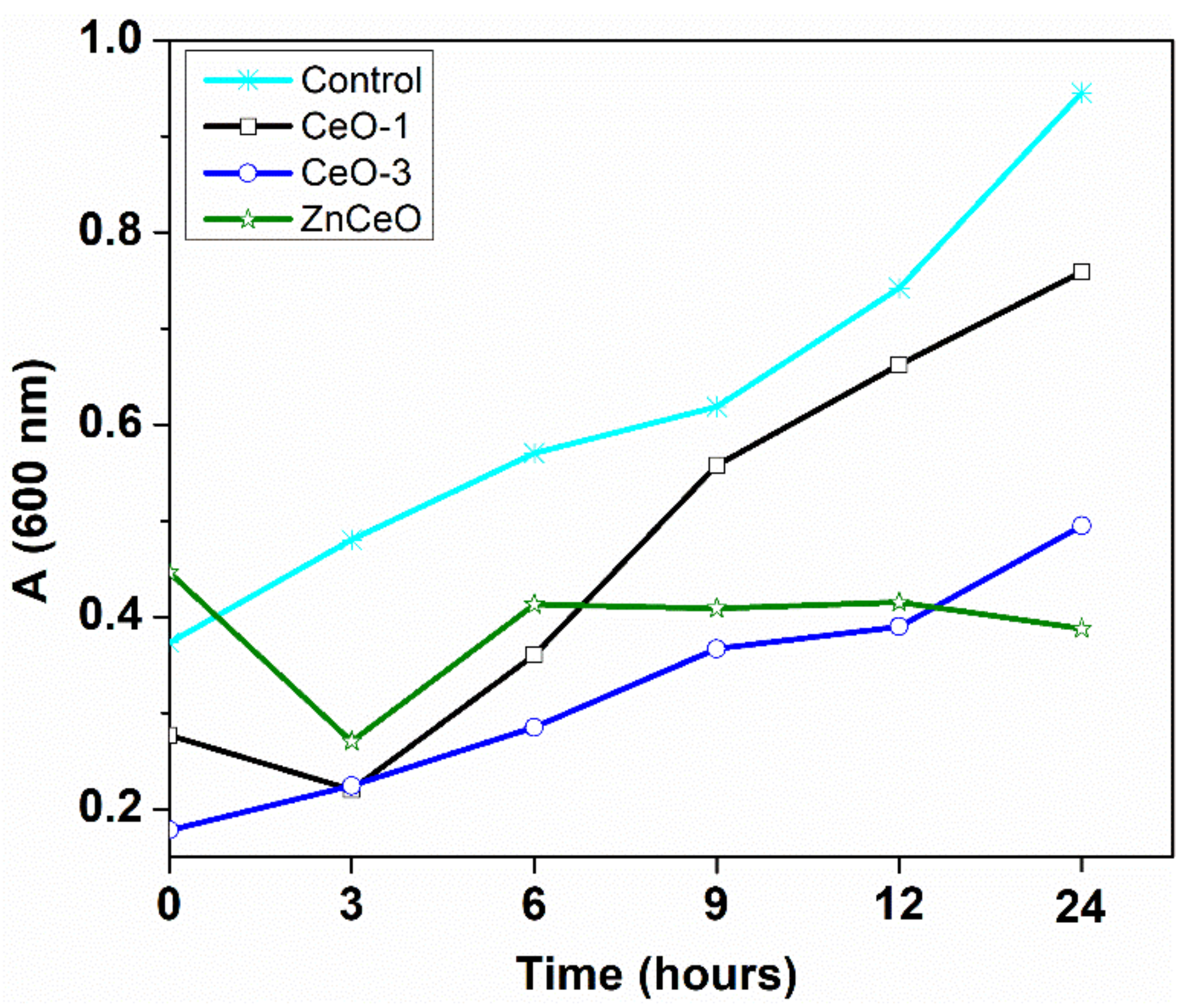
2.4.3. Bacterial Growth Curve
3. Results and Discussion
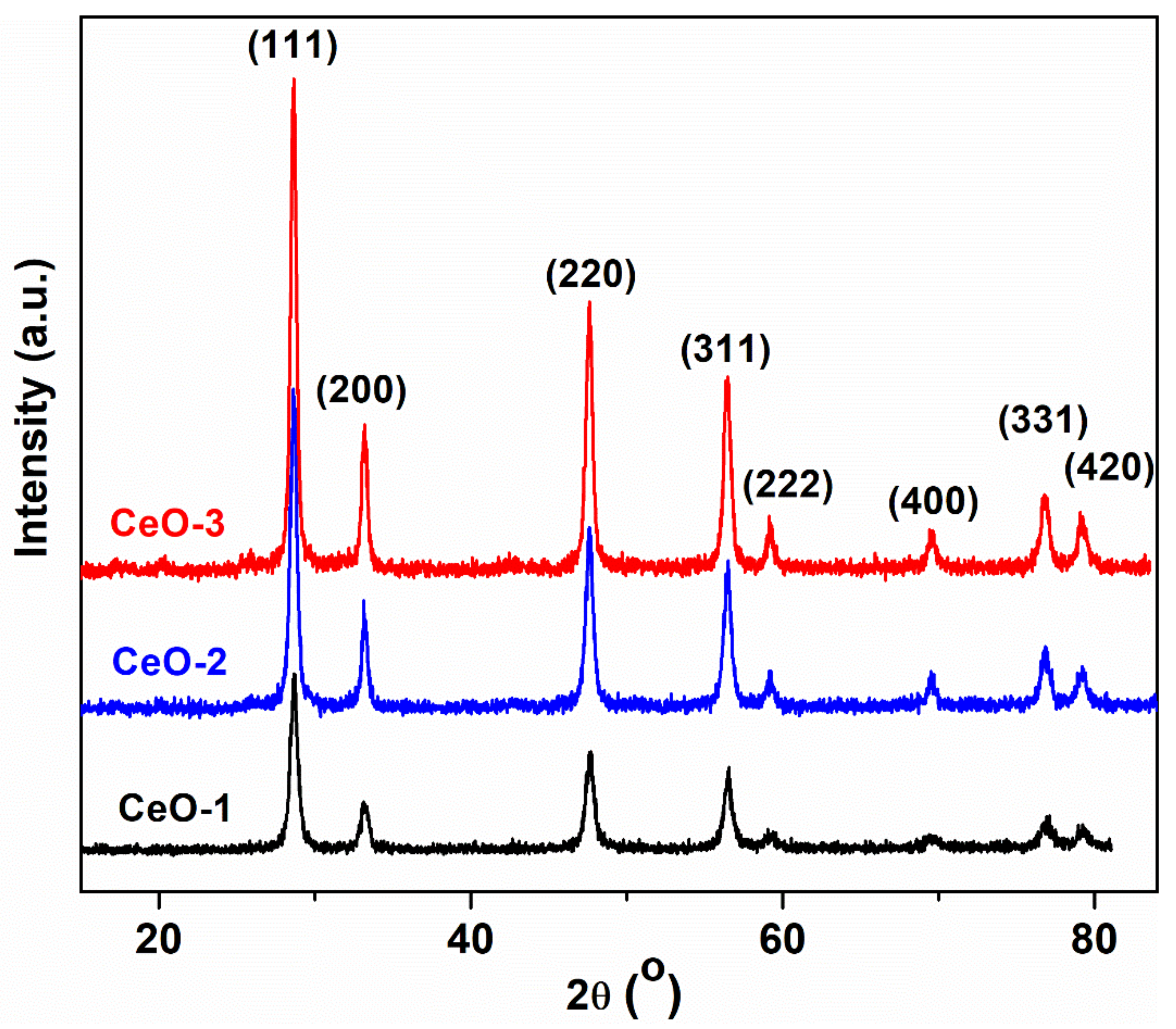
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Investigation
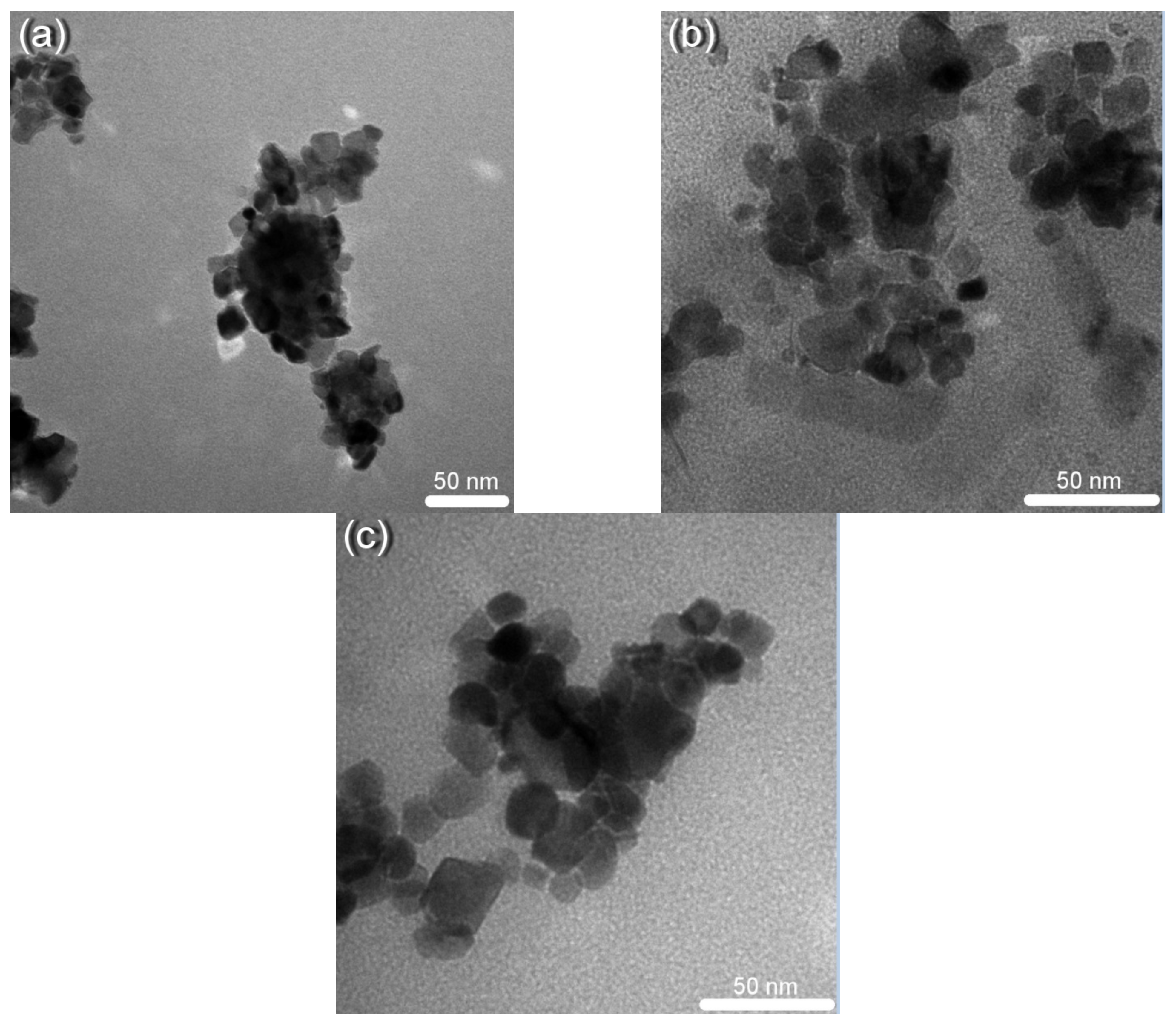
3.2. TEM Analysis
3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
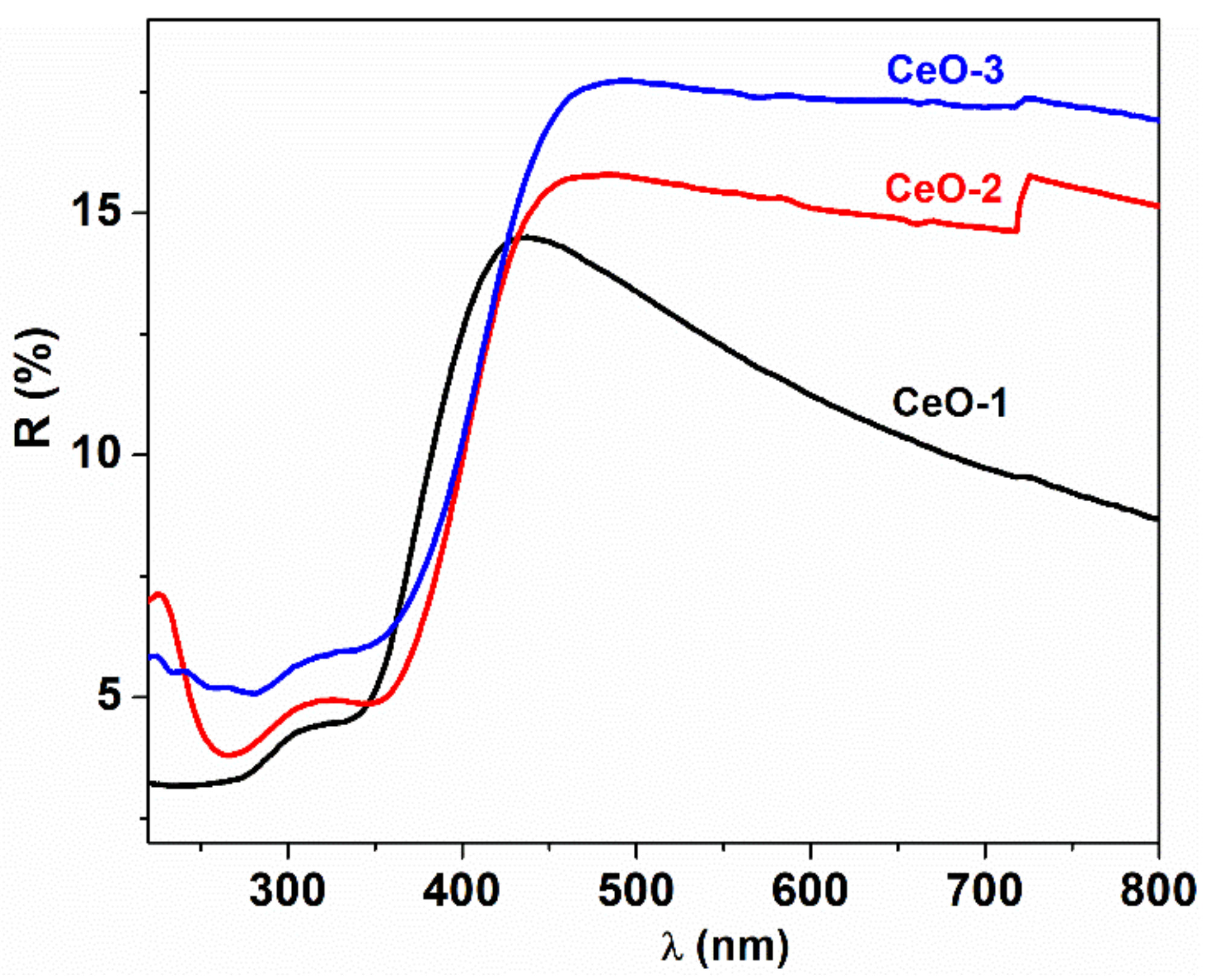
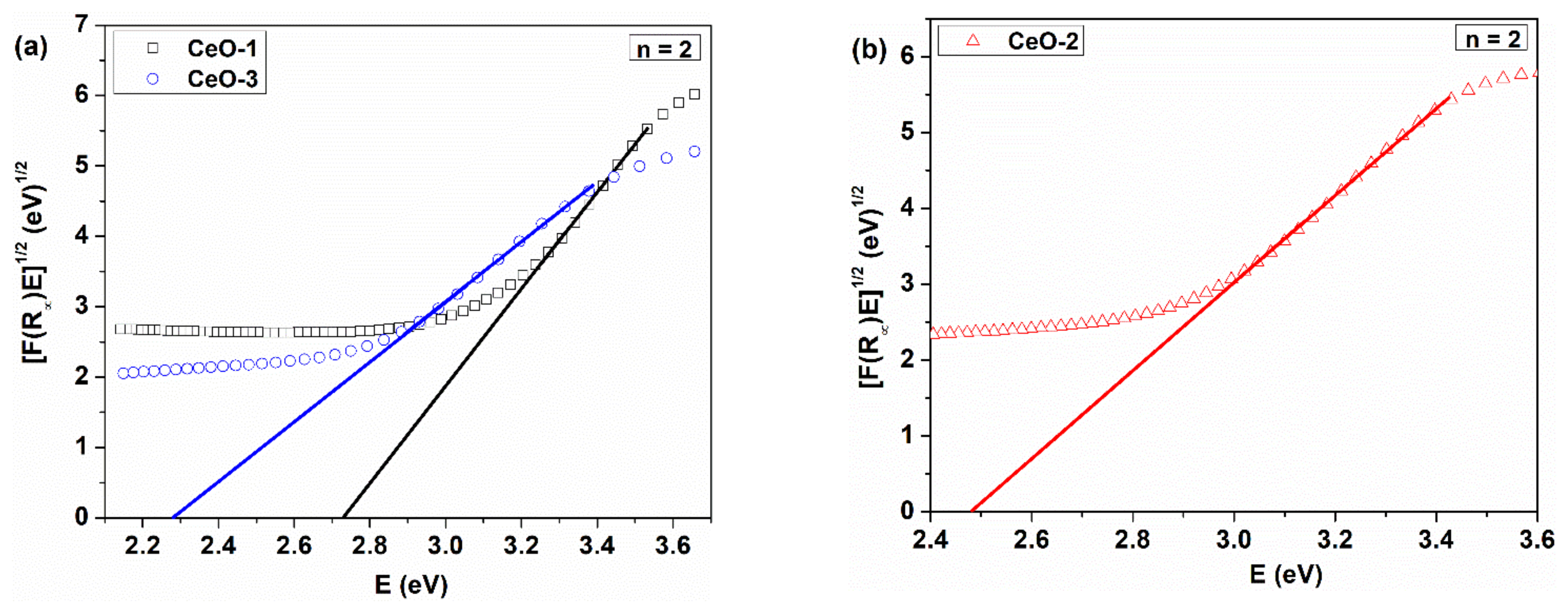
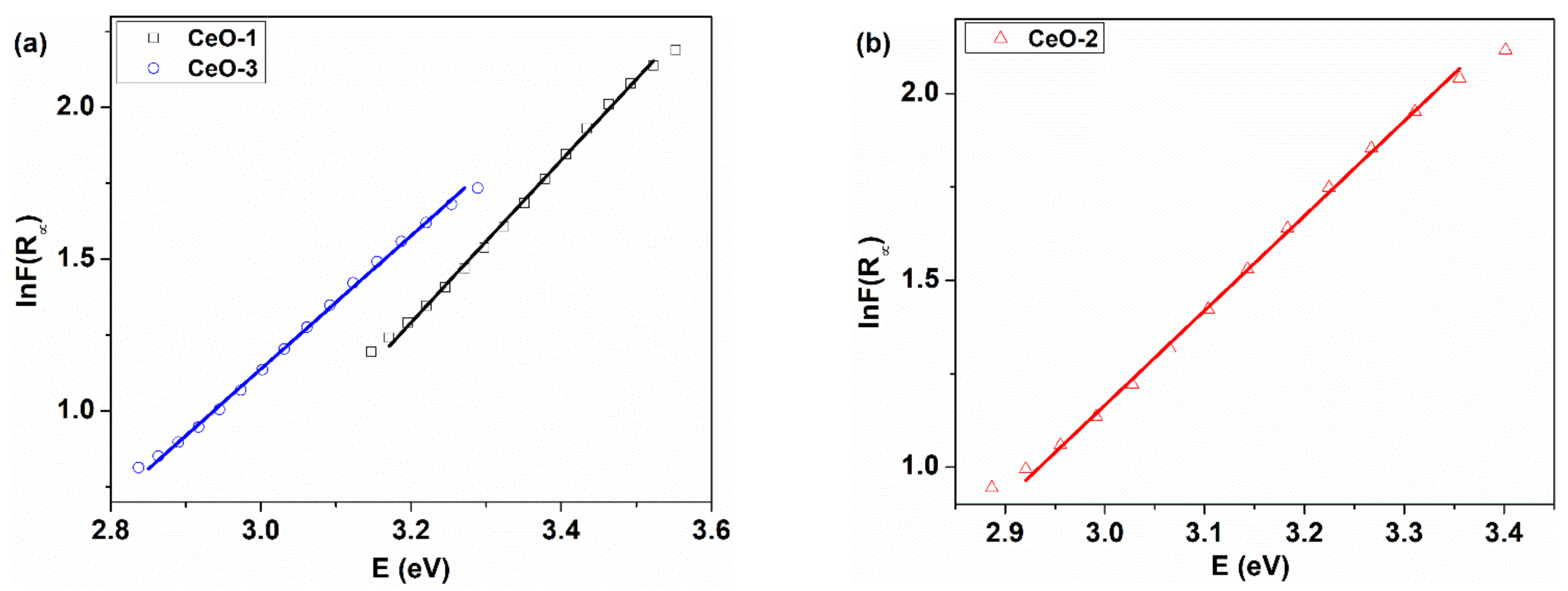
3.4. Optical Properties
3.5. Fluorescence Spectra
3.6. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez-Asencio, R.; Corkery, R.W.; Ahniyaz, A. Solventless synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles and their application in UV protective clear coatings. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14818–14825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izu, N.; Shin, W.; Murayama, N.; Kanzaki, S. Resistive oxygen gas sensors based on CeO2 fine powder prepared using mist pyrolysis. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2002, 87, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Schwank, J.W. A review on oxygen storage capacity of CeO2-based materials: Influence factors, measurement techniques, and applications in reactions related to catalytic automotive emissions control. Catal. Today 2019, 327, 90–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2 based materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Yubero, F.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Lambert, R.M. Microstructural engineering and use of efficient poison resistant Au-doped Ni-GDC ultrathin anodes in methane-fed solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulicovski, J.; Nenadović, S.; Kljajević, L.; Mirković, M.; Nišavić, M.; Kragović, M.; Stojmenović, M. Geopolymer/CeO2 as solid electrolyte for IT-SOFC. Polymers 2020, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Beltrán, A.M.; Yubero, F.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Lambert, R.M. High performance novel gadolinium doped ceria/yttria stabilized zirconia/nickel layered and hybrid thin film anodes for application in solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wason, M.S.; Lu, H.; Yu, L.; Lahiri, S.K.; Mukherjee, D.; Shen, C.; Das, S.; Seal, S.; Zhao, J. Cerium oxide nanoparticles sensitize pancreatic cancer to radiation therapy through oxidative activation of the JNK apoptotic pathway. Cancers 2018, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Datta, A.; Mishra, S.; Manna, K.; Saha, K.D.; Mukherjee, S.; Roy, S. Pro-oxidant therapeutic activities of cerium oxide nanoparticles in colorectal carcinoma cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9714–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhall, A.; Self, W. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: A brief review of their synthesis methods and biomedical applications. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coduri, M.; Checchia, S.; Longhi, M.; Ceresoli, D.; Scavini, M. Rare earth doped ceria: The complex connection between structure and properties. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowding, J.M.; Das, S.; Kumar, A.; Dosani, T.; McCormack, R.; Gupta, A.; Sayle, T.X.T.; Sayle, D.C.; von Kalm, L.; Seal, S.; et al. Cellular interaction and toxicity depend on physicochemical properties and surface modification of redox-active nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4855–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Ran, J.; Niu, J.; Yang, G.; Ou, Z.; He, S. Insight into the effect of facet-dependent surface and oxygen vacancies of CeO2 for Hg removal: From theoretical and experimental studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Kobayashi, S. Positional disorder of oxygen ions in ceria at high temperatures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.D.; Huebner, W. Size-induced lattice relaxation in CeO₂ nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 3512–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, G.; Sahartov, A.; Sadia, Y.; Porat, Z.; Zabicky, J.; Dvir, E. Non-monotonic lattice parameters variation in CeO2. J. Mater. Res. Tech. 2021, 12, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, Z. Chitosan capped noble metal doped CeO2 nanomaterial: Synthesis, and their enhanced catalytic activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soren, S.; Bessoi, M.; Parhi, P. A rapid microwave initiated polyol synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticle using different cerium precursors. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8114–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offner, H.G.; Skoog, D.A. Hydrolysis constant of quadrivalent cerium from spectrometric measurements. Anal. Chem. 1966, 38, 1520–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.L.; Chen, I.W. Reactive cerium(IV) oxide powders by the homogeneous precipitation method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guilbaulat, G.G.; McCurdy, D.W.H., Jr. Mechanism and kinetics of the oxidation of glycerol by cerium(iv) in sulfuric and perchloric acids. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifere, N.; Airinei, A.; Timpu, D.; Rotaru, A.; Sacarescu, L.; Ursu, L. New insights into structural and magnetic properties of of Ce doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compds. 2018, 757, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemer, J.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1973, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Filimon, A.; Avram, E.; Dunca, S.; Stoica, I.; Ioan, S. Surface properties and antibacterial activity of quaternized polysulfones. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaiescu, D.E.; Grumazescu, A.M.; Buteica, A.S.; Mogosanu, D.; Balaure, P.C.; Mihaiescu, O.M.; Traistaru, V.; Vasile, B.S. Bioassay and electrochemical evaluation of controlled release behavior of cephalosporins from magnetic nanoparticles. Digest, J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2012, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Kumar, J.; Thakur, S.; Sharma, S. Antibacterial study of silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. Drug Invent Today 2020, 5, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Sahani, K. In vitro antimicrobial activity and MIC of the extracellular ethyl acetate crude extract of endophytic fungi Fusarium sp. isolated from Terphrosia purpurea root. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Choudhury, A. Ce3+ and oxygen vacancy mediated tuning of structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 131, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouedj, N.; Elaziouti, A.; Benhadria, N.; Bekka, A. CeO2 nanoscale particles: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity under UVA light irradiation. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.; Patil, S.; Kuchibhatla, S.V.N.T.; Seal, S. Size dependency variation in lattice parameter and valency states in nanocrystalline cerium oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 133113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fleming, P.; Morris, V.; Holmes, J.D.; Morris, M.A. Size-related lattice parameter changes and surface defects in ceria nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12909–12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachimuthu, P.; Shih, W.C.; Liu, R.S.; Jang, L.Y.; Chen, J.M. The study of nanocrystalline cerium oxide by X-Ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Solid State Chem. 2000, 149, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cresi, J.S.P.; Spadaro, M.C.; D’Addato, S.; Valeri, S.; Amidani, L.; Boscherini, F.; Bertori, G.; Deiana, D.; Luches, P. Contraction, cation oxidation state and size effects in cerium oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 495702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungár, T.; Tichy, G.; Gubicza, J.; Hellmig, R.J. Correlation between subgrains and coherently scattering domains. Powder Diffr. 2005, 20, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masui, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Machida, K.; Adachi, G.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H. Characterization of cerium(IV) oxide ultrafine particles prepared using reversed micelles. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, P.; Hamnett, A.; Orchard, A.F.; Thornton, G. Satellite structure in the X-ray photoelectron spectra of some binary and mixed oxides of lanthanum and cerium. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1976, 17, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Z.; Gong, J.; Li, A.; Ding, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wu, G. Hydrothermal synthesis of hexagonal CeO2 nanosheets and their room temperature ferromagnetism. J. Alloys Comps. 2015, 647, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Meng, F. Oxygen vacancy and Ce3+ ion dependent magnetism of monocrystal CeO2 nanopoles synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3492–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Quan, X.; Lu, S. Catalytic performance and an insight into the mechanism of CeO2 nanocrystals with different exposed facets in catalytic ozonation of p-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal. B Env. 2019, 248, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuizen, D.N.; Motaung, D.E.; Swart, H.C. Gas sensors based on CeO2 nanoparticles prepared by chemical precipitation method and their temperature-dependent selectivity towards H2S and NO2 gases. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, F.; Gong, J.; Fan, Z.; Qin, R. Structural, morphological and optical properties of shuttle-like CeO2 synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compds. 2017, 722, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvache Muñoz, J.; Prado, F.A.; Tirado, L.; Daza Gomez, L.C.; Cuervo Ochoa, G.; Calambas, H.; Rodríguez Páez, J.E. Structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles synthesized by modified polymer complex method. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 29, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado, J.P.; Munuera, G.; Espinos, J.P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. XPS study of oxidation processes of CeO defective layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 158, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, J.C.; Gonbeau, D.; Vinatier, P.; Levasseur, A. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoko, E.; Smith, M.F.; McKenzie, R.H. Charge distribution near bulk oxygen vacancies in cerium oxides. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 2010, 22, 223201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo Morales, A.; Sanchez Mora, E.; Pal, U. Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Rev. Mex. Fis. S Rev. 2007, 53, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Marabelli, F.; Wachter, P. Covalent insulator: Optical reflectivity measurements. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 36, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Arwin, H.; Jacobsen, S.N.; Jarrendahl, K.; Helmersson, U. A spectroscopic ellipsometry study of cerium dioxide thin films grown of sapphire by rf magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.H.; Moussa, M.E.; Bedair, S.M.; Leonard, R.; Liu, S.X.; El-Masry, N. Violet/blue emission from epitaxial cerium oxide films on silicon substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorodumova, N.V.; Ahuja, R.; Simak, S.I.; Abrikosov, I.A.; Johansson, B.; Lundqvist, B.I. Electronic, bonding, and optical properties of CeO2 and Ce2O3 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 115108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullgren, J.; Castleton, C.W.M.; Müller, C.; Muñoz Ramo, D.; Hermansson, K. B3LYP calculations of cerium oxides. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 054110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patsalas, P.; Logothetidis, S.; Sygellou, L.; Kennou, S. Structure-dependent electronic properties of nanocrystalline cerium oxide film. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 035104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvache-Muñoz, J.; Prado, F.A.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and tentative mechanism of particle formation. Coll. Surf. A 2017, 529, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maensiri, S.; Masingboon, C.; Laokul, P.; Jareonboon, W.; Promarak, V.; Anderson, P.L.; Seraphin, S. Egg white synthesis and photoluminescence of platelike clusters of CeO2 nanoparticles. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhukova, I.N.; Sokovnin, S.Y.; Ilves, V.G.; Myshkina, A.V.; Vazirov, R.A.; Pizurova, N.; Kasyanova, V.V. Luminescence and optical properties of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2019, 92, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Samdarshi, S.K.; Bojja, S.; Paul, S.; Choudhury, B. A novel thermophotocatalyst of mixed-phase cerium oxide (CeO2/Ce2O3) homocomposite nanostructure: Role of interface and oxygen vacancies. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 141, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, F. The long-wavelength of photographic sensitivity and of the electronic absorption of solids. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.; Davis, E. Electron Processes in Nanocrystaline Materials; Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1982; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, S.; Fujishiro, F. The photoluminescence properties of reversible photoinduced spectral change of CeO2 bulk, film and nanocrystals. Phys. Status Solidi B 2009, 246, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, R.C.; Ciola Amoresi, R.A.; Marana, N.L.; Zaghete, M.A.; Ponce, M.; Chiqito, A.J.; Sambrano, J.R.; Longo, E.; Simoes, A.Z. Influence of synthesis time on the morphology and properties of CeO2 nanoparticles: An experimental-theoretical study. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 5031–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Chetri, C.; Choudhury, A. Oxygen defects and formation of Ce3+ affecting the photocatalytic performance of CeO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaz, F.; Farooq, U.; Ahmad, T. Ceria as an efficient nanocatalyst for organic transformations. In Nanocatalysts; Sinha, I., Shukla, M., Eds.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, M.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, L. Cerium and its oxidant-based nanomaterials for antimicrobial applications: A state-of-the-art review. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, I.A.P.; Lima dos Santos, C.C.; Sampaio, F.C. Antimicrobial activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles on opportunistic microorganisms: A systematic review. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1923606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pop, O.L.; Mesaros, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Suharovschi, R.; Tabaran, F.; Magerrusan, L.; Todor, I.S.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Balint, A.; Ciontea, L.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles and their efficient antibacterial applications in vitro against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugan, A.; Karthikeyan, C.; Karthika, A.S.H. Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. lead extract and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.M.; Mahendhiran, M.; Diaz, M.C.; Hernandez-Como, N.; Hernandez-Eligio, A.; Torres-Torres, G.; Godavarthi, S.; Martinez-Gomez, L. Green synthesis of Ce+3 rich CeO2 nanoparticles and its antimicrobial studies. Mater. Lett. 2018, 214, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalane, C.M.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Raja, A.; Arularasu, M.V.; Mola, G.T.; Isaev, A.B.; Al-Zhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V.; Jeyaraj, B.; Kennedy, J.; et al. Photocatalytic decomposition effect of erbium doped cerium oxide nanostructures driven by visible light irradiation Investigation of cytoxicity, antibacterial growth inhibition using catalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 185, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, L.S.; Manjunath, K.; Archana, B.; Madhu, C.; Naika, H.R.; Nagabnishane, H.; Raviatha, C.; Nagaraju, G. Fruit price extract mediated synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles for antibacterial and photocatalytic activities. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2016, 131, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.K.; Sundrarajan, M. A green approach for the synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticle: Characterization and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanosci. 2014, 13, 1450018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, Z.N.; Sahar, S.; Riaz, S.; Messem, S. Tuning of optical and antibacterial characteristics of ZnO thin films: Role of Ce content. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 3930–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, M.V.; Thirumamagal, R.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Ayeshamariam, A.; Kumar, D.S.; Punithavelan, N.; Jayachandran, M. Green chemical approach towards the synthesis of CeO2 doped with seashell and its bacterial applications intermediated with fruit extracts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | T (°C) | Precipitating Agent | D (nm) | a (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO-1 | 80 | NaOH | 13.62 | 5.3691 |
| CeO-2 | 25 | NaOH | 15.48 | 5.3802 |
| CeO-3 | 25 | NH4OH | 17.61 | 5.3765 |
| Sample | x | x′ | Δx = x − x′ | [Ce3+] (%) | [OA] (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO-1 | 1.93 | 1.4 | 0.53 | 14.69 | 15.01 |
| CeO-2 | 1.89 | 2.17 | −0.28 | 21.02 | 39.38 |
| CeO-3 | 1.85 | 2.3 | −0.45 | 30.55 | 47.04 |
| Sample | Synthesis Conditions | Ed1 * (eV) | Ed2 * (eV) | Ei ** (eV) | EU (meV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO-1 | 80 °C, NaOH | 3.28 | 3.76 | 2.72 | 374.30 |
| CeO-2 | 25 °C, NaOH | 3.10 | 3.66 | 2.47 | 394.45 |
| CeO-3 | 25 °C, NH4OH | 3.00 | 3.39 | 2.28 | 455.38 |
| Sample | Concentration (mg/mL) | Diameter of Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | ||
| CeO-1 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 5.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10.0 | 6 | 10 | |
| 20.0 | 9 | 11 | |
| CeO-3 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 5.0 | 10 | 0 | |
| 10.0 | 11 | 10 | |
| 20.0 | 13 | 12 | |
| ZnCeO | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 5.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 20.0 | 11 | 0 | |
| Sample | Bacterial Strain | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| CeO-1 | 2.5 | 5.0 |
| CeO-3 | 2.5 | 5.0 |
| CeOZn | 20.0 | 20.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fifere, N.; Airinei, A.; Dobromir, M.; Sacarescu, L.; Dunca, S.I. Revealing the Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Structural, Optical, and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102596
Fifere N, Airinei A, Dobromir M, Sacarescu L, Dunca SI. Revealing the Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Structural, Optical, and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102596
Chicago/Turabian StyleFifere, Nicusor, Anton Airinei, Marius Dobromir, Liviu Sacarescu, and Simona I. Dunca. 2021. "Revealing the Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Structural, Optical, and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102596
APA StyleFifere, N., Airinei, A., Dobromir, M., Sacarescu, L., & Dunca, S. I. (2021). Revealing the Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Structural, Optical, and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102596





