Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of Strontium Adsorption on Graphene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. GO Synthesis
2.3. GO Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. GO Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Studies
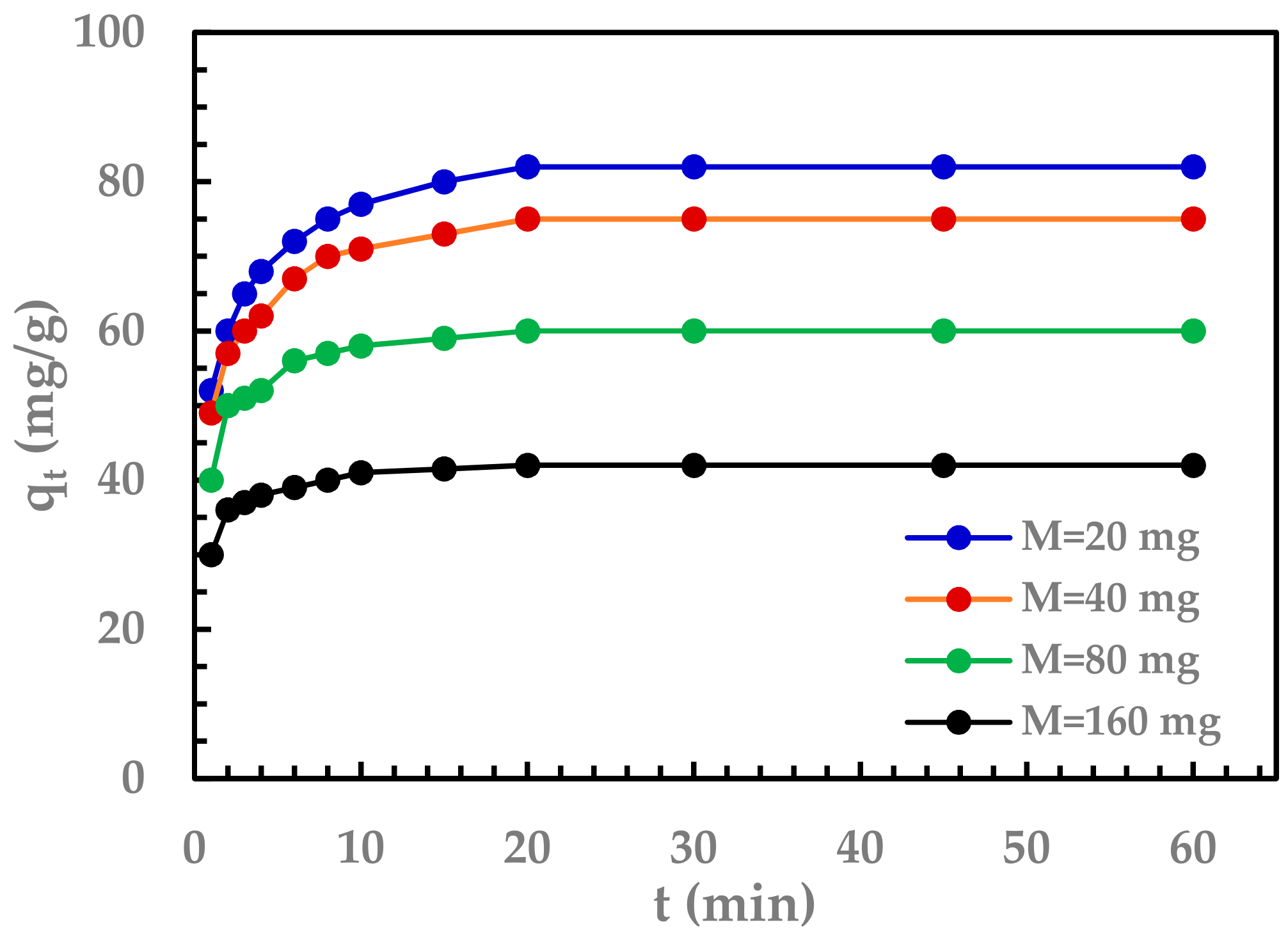
3.2.1. Effect of GO Dosage
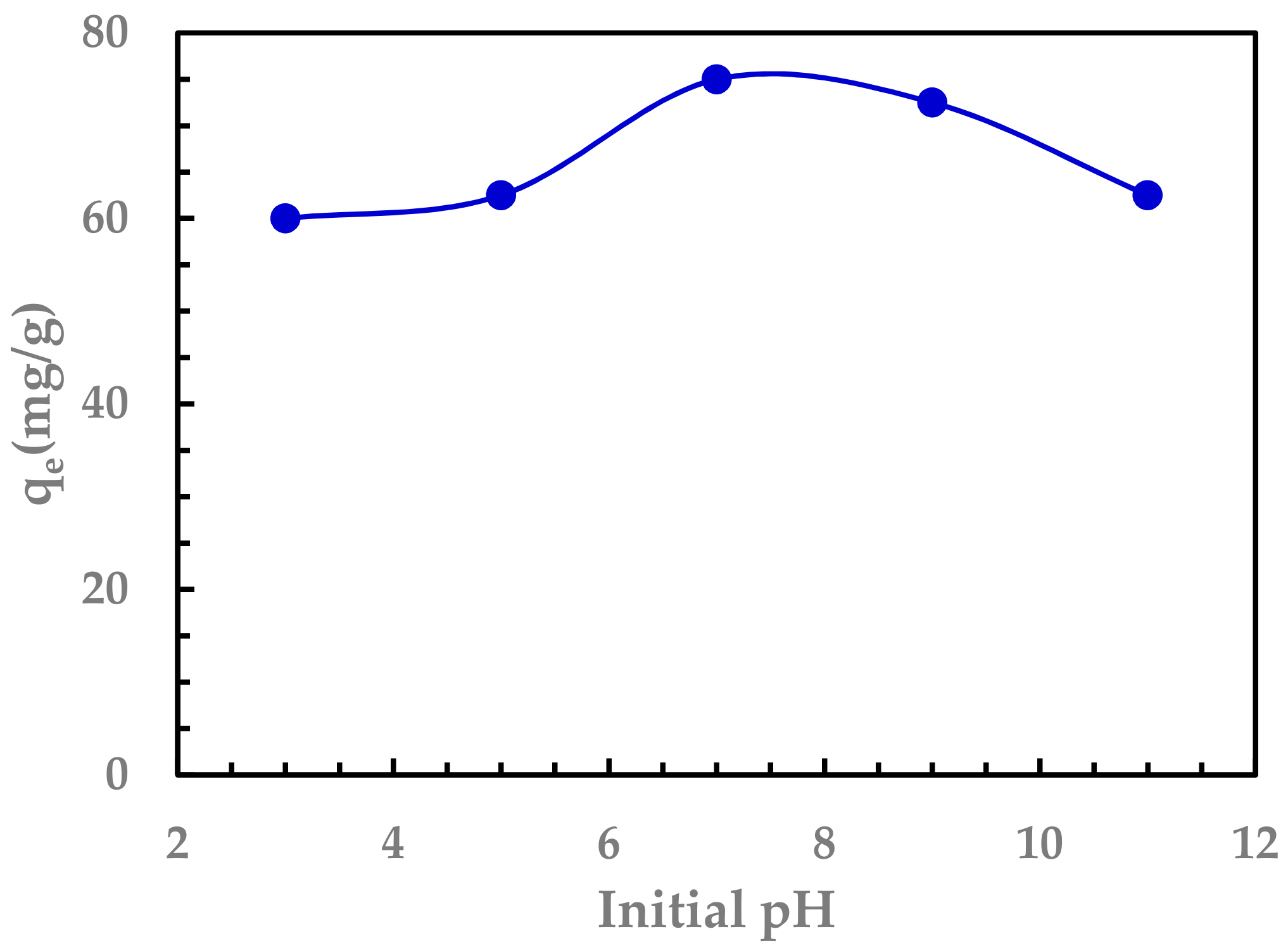
3.2.2. Effect of pH
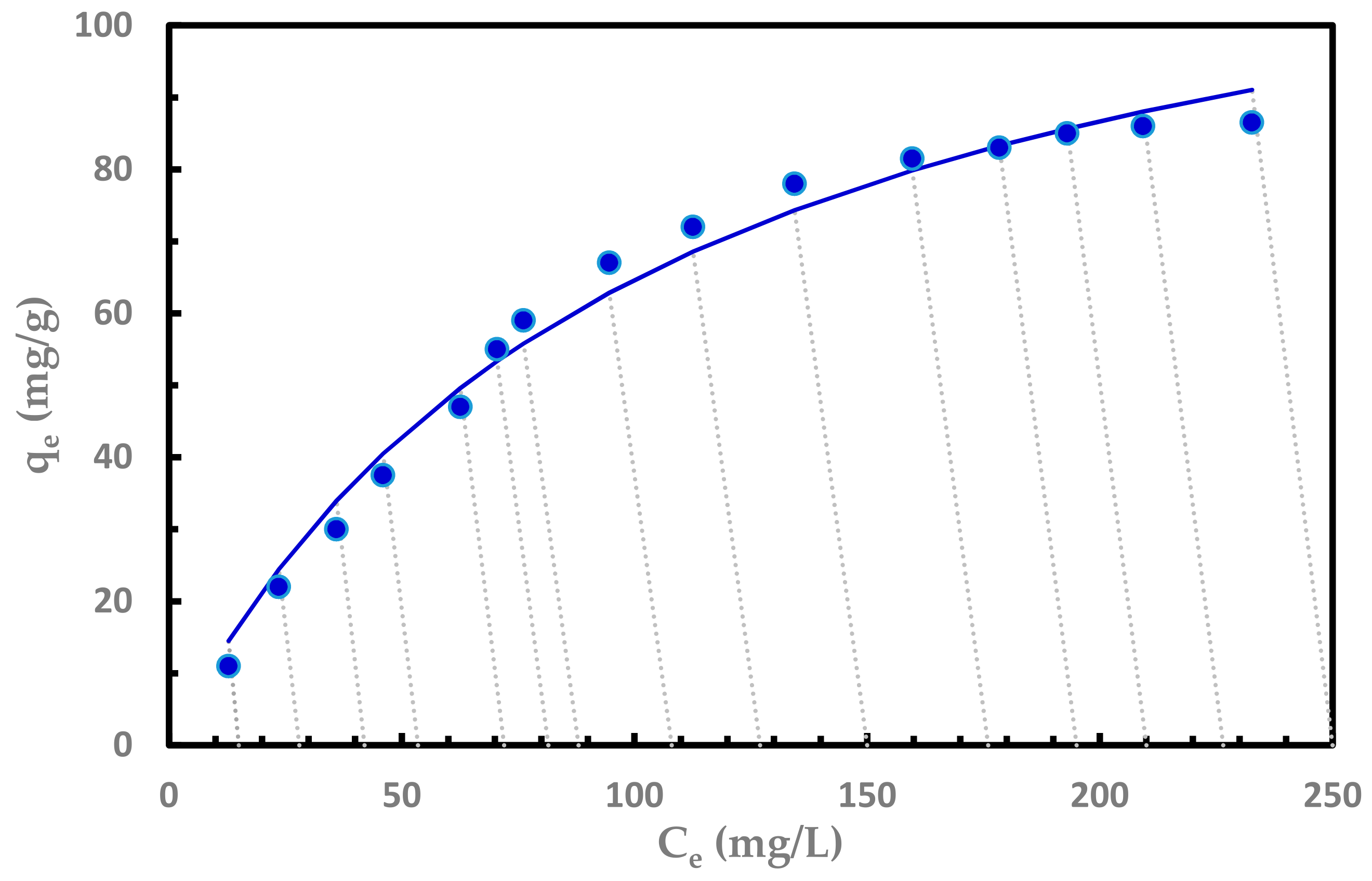
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
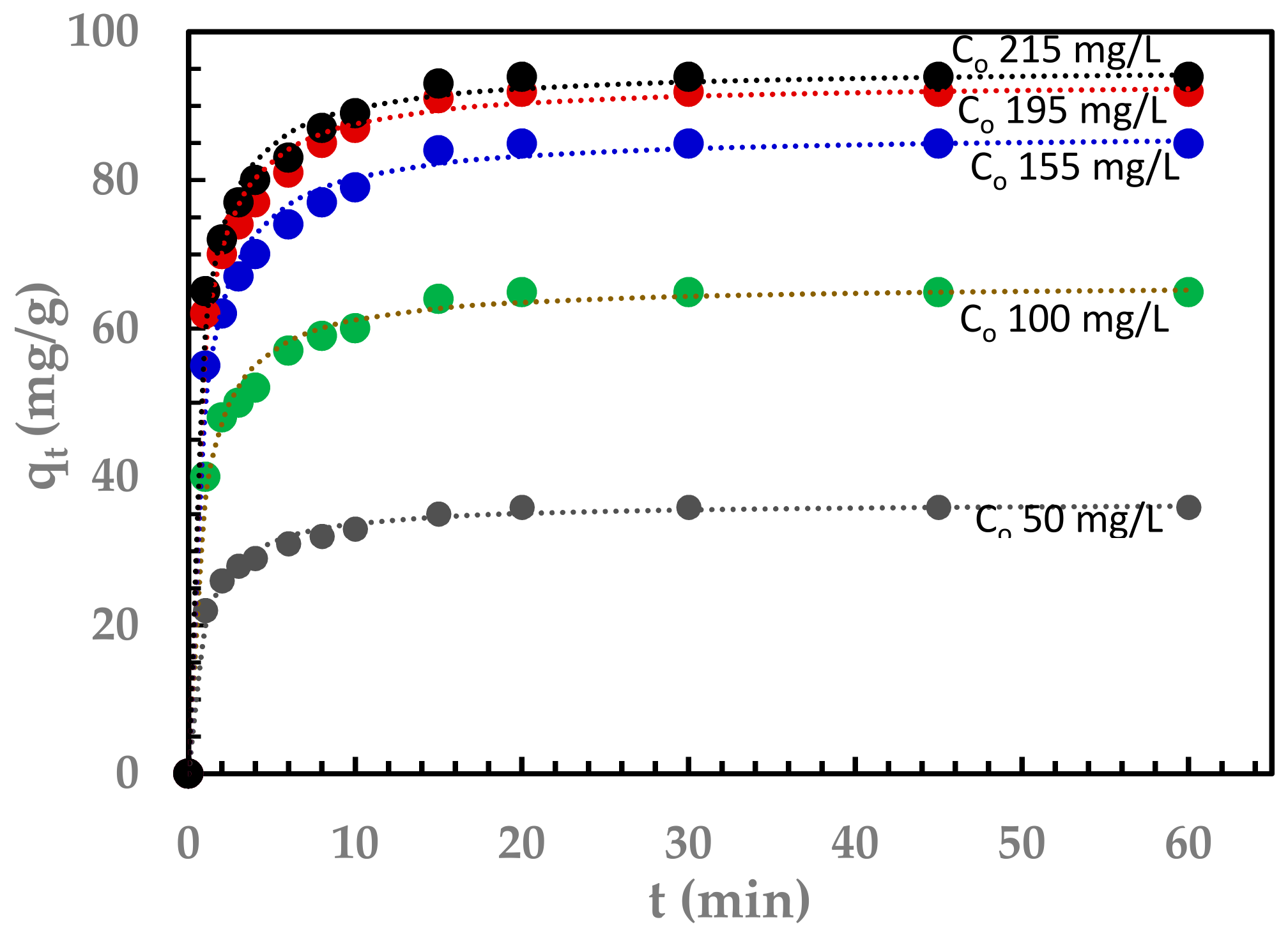
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da̧browski, A.; Hubicki, Z.; Podkościelny, P.; Robens, E. Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Bringas, E.; Tan, N.R.; Ortiz, I.; Ghahramani, M.; Alaei Shahmirzadi, M.A. Recent progress in development of high performance polymeric membranes and materials for metal plating wastewater treatment: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 9, 78–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G. Use of Adsorbents for the Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater; McKay, G., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Gui, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Gas-sensing properties of Ptn-doped WSe2 to SF6 decomposition products. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 97, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Shi, J.; Yang, P.; Li, T.; Tang, C.; Xu, L. Platinum modified MoS2 monolayer for adsorption and gas sensing of SF6 decomposition products: A DFT study. High Volt. 2020, 5, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Du, B.; Wei, Q.; Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Yan, L.; Xu, W. Synthesis of amino functionalized magnetic graphenes composite material and its application to remove Cr(VI), Pb(II), Hg(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) from contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 278, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, A.; Miran, W.; Rasool, K.; Nawaz, M.; Jang, J.; Lim, S.-R.; Lee, D. Heavy metals removal by EDTA-functionalized chitosan graphene oxide nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9764–9771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, N.; Qi, Y. Adsorption characteristics and behaviors of graphene oxide for Zn(II) removal from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghubanshi, H.; Ngobeni, S.M.; Osikoya, A.O.; Shooto, N.D.; Dikio, C.W.; Naidoo, E.B.; Dikio, E.D.; Pandey, R.K.; Prakash, R. Synthesis of graphene oxide and its application for the adsorption of Pb2+ from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, N.; McKay, G.; Abdala, A. Recent advances in applications of hybrid graphene materials for metals removal from wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, I.; Castanheira, I.; Bordado, J.M.; Donard, O.; Silva, J.A.L. Recent developments and trends in the application of strontium and its isotopes in biological related fields. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, D.S. Three-dimensional barium-sulfate-impregnated reduced graphene oxide aerogel for removal of strontium from aqueous solutions. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 504, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, W.; Amer, H.; Salem, W.; Farghali, A.; El Rouby, W. Efficient removal of Co (II) and Sr (II) metals from water using ethylene diamine tera-acetic acid functionalized graphene oxide. Z. Für Anorg. Und Allg. Chem. 2017, 643, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, J. Adsorptive removal of strontium ions from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 29669–29678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Wu, X.; Liu, M.; Xing, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, A.-W. Efficient capture of strontium from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide–hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 7464–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minitha, C.R.; Suresh, R.; Maity, U.K.; Haldorai, Y.; Subramaniam, V.; Manoravi, P.; Joseph, M.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T. Magnetite nanoparticle decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as an efficient and recoverable adsorbent for the removal of cesium and strontium ions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.V.; Pattammattel, A. Graphene composites with inorganic 2-D materials. In Introduction to Graphene; Kumar, C.V., Pattammattel, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliva, M.; Vamvakaki, M. Nanomaterials characterization. In Polymer Science and Nanotechnology; Narain, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 401–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, B.; Toney, M.F. X-ray diffraction for characterizing metallic films. In Metallic Films for Electronic, Optical and Magnetic Applications; Barmak, K., Coffey, K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchoudhury, S.; Baalousha, M.; Lead, J.R. Methods for measuring concentration (mass, surface area and number) of nanomaterials. In Frontiers of Nanoscience; Baalousha, M., Lead, J.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 8, pp. 153–181. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L. A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempkin, M.J.; Pyzhev, V. Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Phys. Chem. 1940, 12, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, J. State equation of the solid-gas interface layers. Acta Chim. Hung. 1971, 69, 311–328. [Google Scholar]
- Kecili, R.; Hussain, C.M. Mechanism of adsorption on nanomaterials. In Nanomaterials in Chromatography; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Kinetics and equilibrium isotherm modeling: Graphene-based nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals from water. In Nanomaterials for Wastewater Remediation; Gautam, R.K., Chattopadhyaya, M.C., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 79–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. I general theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Competitive sorption of copper and nickel ions from aqueous solution using peat. Adsorption 1999, 5, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Clayton, W.R. Application of Elovich equation to the kinetics of phosphate release and sorption in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldowitsch, J. über den mechanismus der katalytischen oxidation von CO a MnO2. URSS Acta Physiochim. 1934, 1, 364–449. [Google Scholar]
- Weber Walter, J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçan, E.; Kütahyalı, C. Adsorption of strontium from aqueous solution using activated carbon produced from textile sewage sludges. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 97, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Gao, P.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Ok, Y.S.; Li, G.; Liu, L. Nanostructured chitosan/molecular sieve-4A an emergent material for the synergistic adsorption of radioactive major pollutants cesium and strontium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironyuk, I.; Tatarchuk, T.; Naushad, M.; Vasylyeva, H.; Mykytyn, I. Highly efficient adsorption of strontium ions by carbonated mesoporous TiO2. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; MacKinnon, G.; Alharthi, A.; Hargreaves, J.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M. A green approach for the removal of Sr(II) from aqueous media: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 257, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, M.R.; Hassan, R.S.; Rashad, G.M. One-pot synthesis of sodium lauryl sulfate-loaded polyacrylonitrile solid-phase extractor for investigating the adsorption behavior of radioactive strontium(II) from aqueous solutions. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 163, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
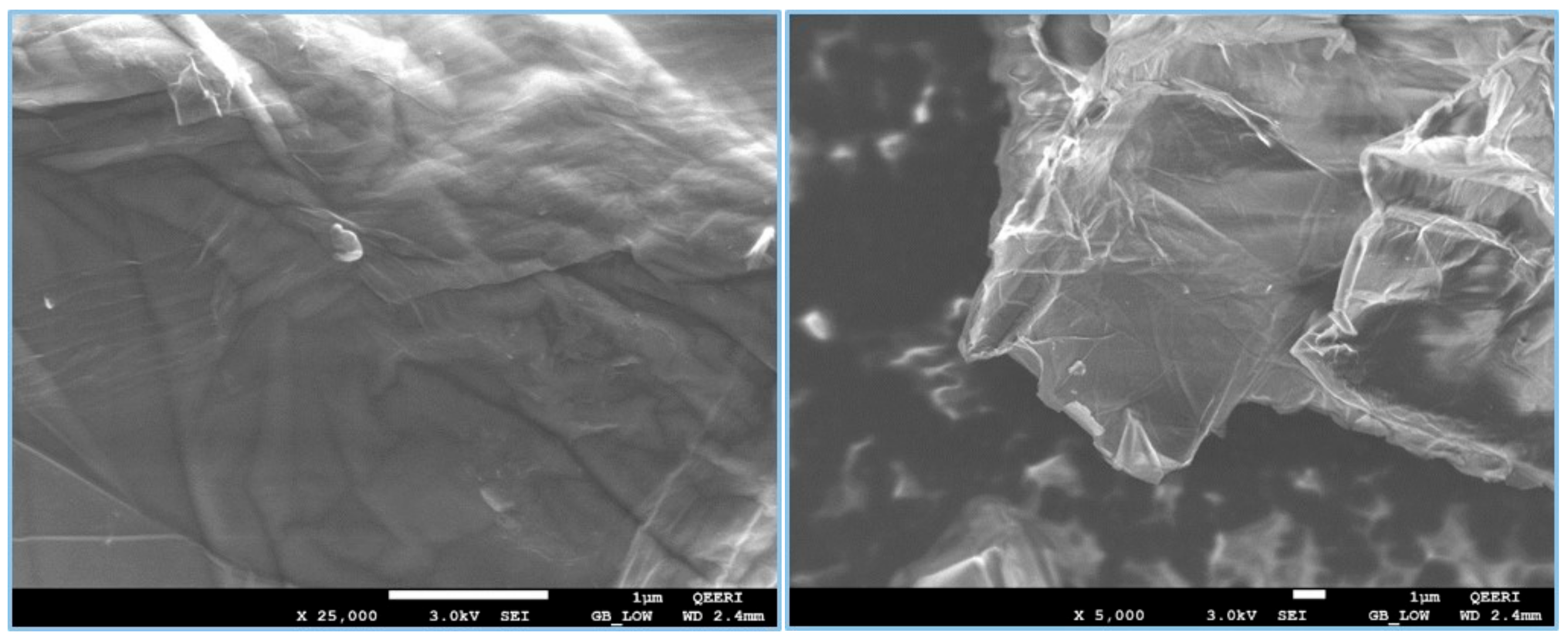
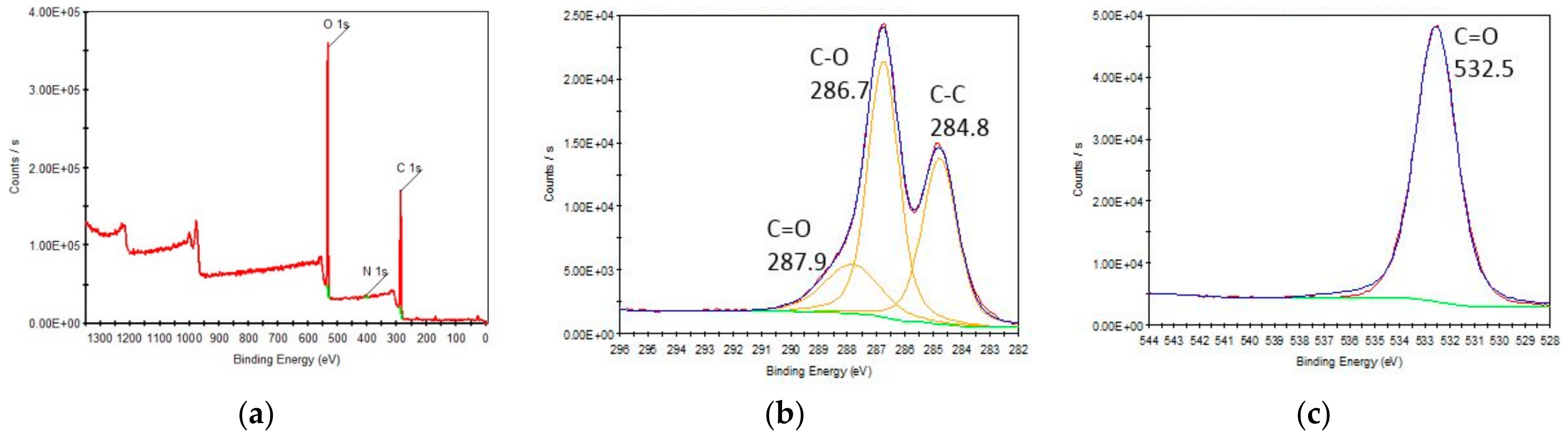

| Name | Peak BE | FWHM eV | Area (P) CPS.eV | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 1s | 258.99 | 4.24 | 691,735.15 | 62.15 |
| O 1s | 532.22 | 3.16 | 1,045,248.53 | 36.98 |
| Isotherm Model | Equation | Model Parameters | Fitting Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | KL = 1.274 L/mg aL = 0.0097 qmax = 131.41 | SSR = 133.4 R2 = 0.985 | |
| Freundlich | aF = 5.359 bF = 0.529 | SSR = 492.0 R2 = 0.945 | |
| Redlich-Peterson | KR = 1.274 aR = 0.0097 bR = 0.999 | SSR = 134.3 R2 = 0.985 | |
| Sips | KLF = 1.27 aLF = 0.0097 nLF = 0.999 | SSR = 134.1 R2 = 0.985 | |
| Temkin | B = 29.32 AT = 0.0930 | SSR = 172.2 R2 = 0.981 | |
| Toth | KT = 103.16 n = 0.999 qmax = 131.40 | SSR = 134.0 R2 = 0.985 |
| Kinetic Model | Equation | Model Parameters | Fitting Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avrami (n = 1) | qe = 11.474 mg/g k1 = −0.00177 | R2 = 0.727 SSR = 14.621 | |
| Pseudo-Second Order | qe = 66.050 mg/g k2 = 0.189 | R2 = 0.999 SSR = 1.59 × 10−4 | |
| Elovich | α = 6952.490 β = 0.160 | R2 = 0.929 SSR = 70.122 | |
| Intra-Particle Diffusion | KIP = 3.226 C = 45.977 | R2 = 0.769 SSR = 229.278 | |
| Avrami | qe = 66.185 mg/g Kav = 0.915 nAV =0.427 | R2 = 0.991 SSR = 9.422 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Nada, A.; Abdala, A.; McKay, G. Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of Strontium Adsorption on Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112780
Abu-Nada A, Abdala A, McKay G. Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of Strontium Adsorption on Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112780
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Nada, Abdulrahman, Ahmed Abdala, and Gordon McKay. 2021. "Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of Strontium Adsorption on Graphene Oxide" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112780
APA StyleAbu-Nada, A., Abdala, A., & McKay, G. (2021). Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of Strontium Adsorption on Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112780







