Sulfur(VI) Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)-Mediated Synthesis of the Chitosan-PEG Conjugate and Its Supramolecular Hydrogels for Protein Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
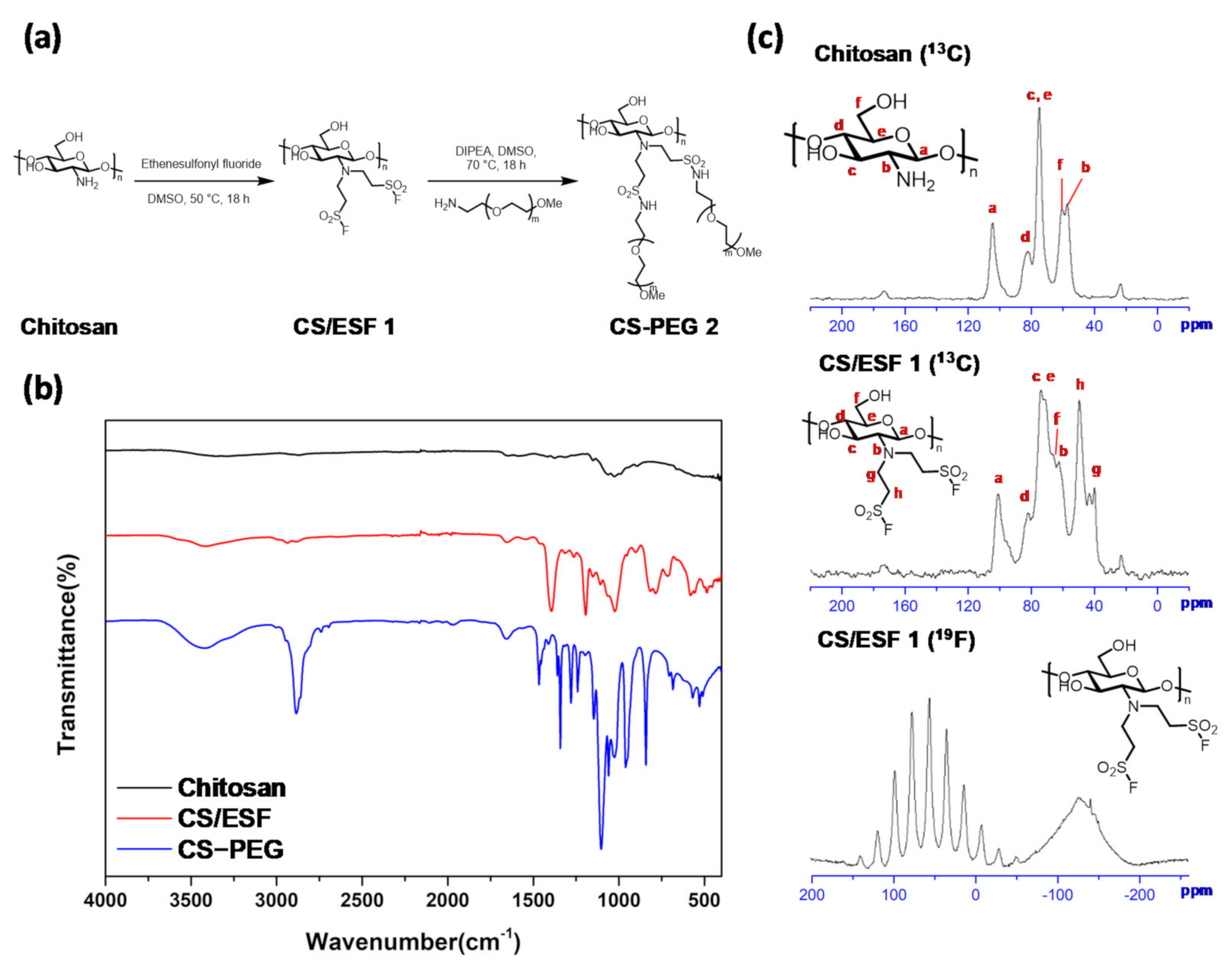
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan Derivatives
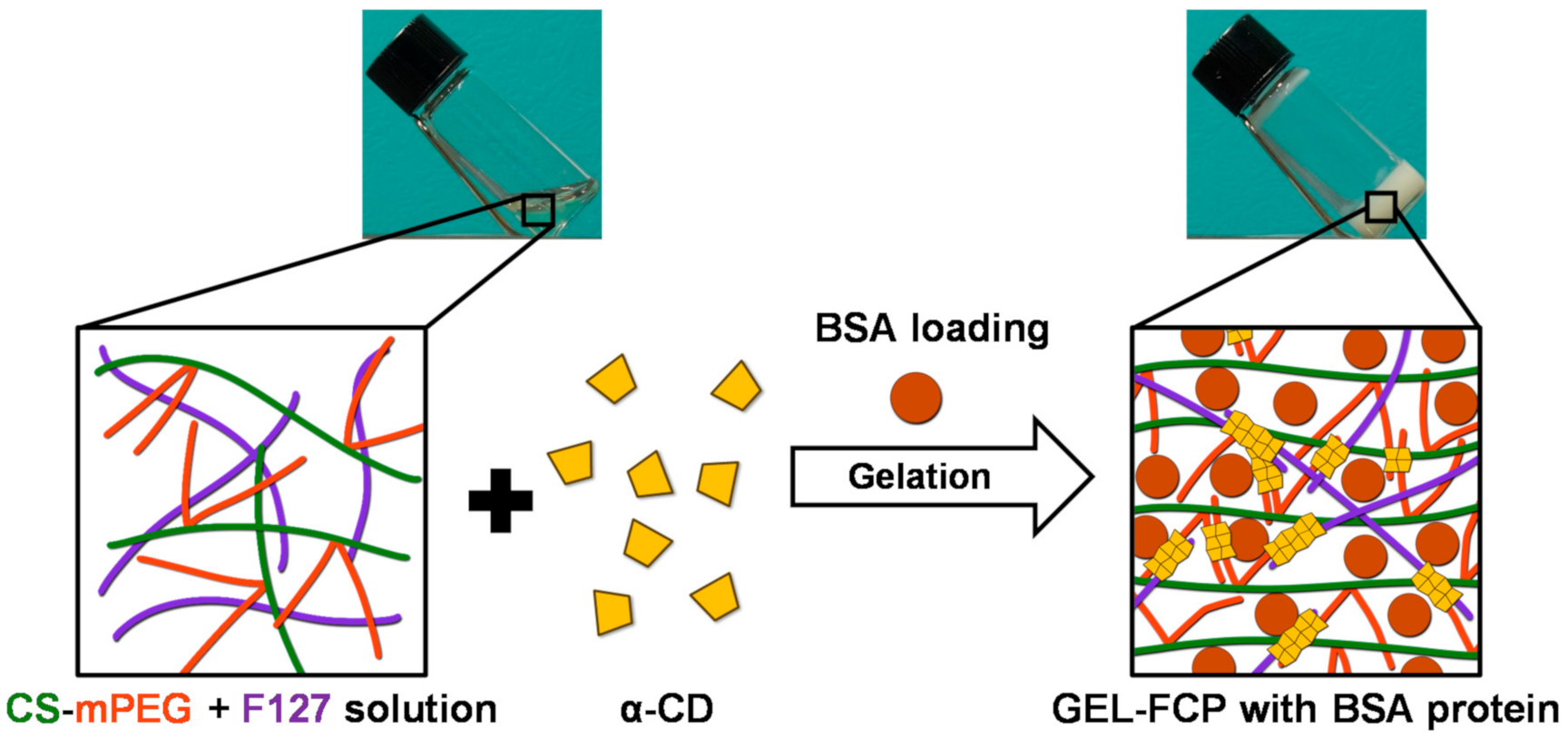
2.2. Hydrogel Preparation
2.3. Characterization of Chitosan Derivatives and Hydrogels
2.4. Gelation Time
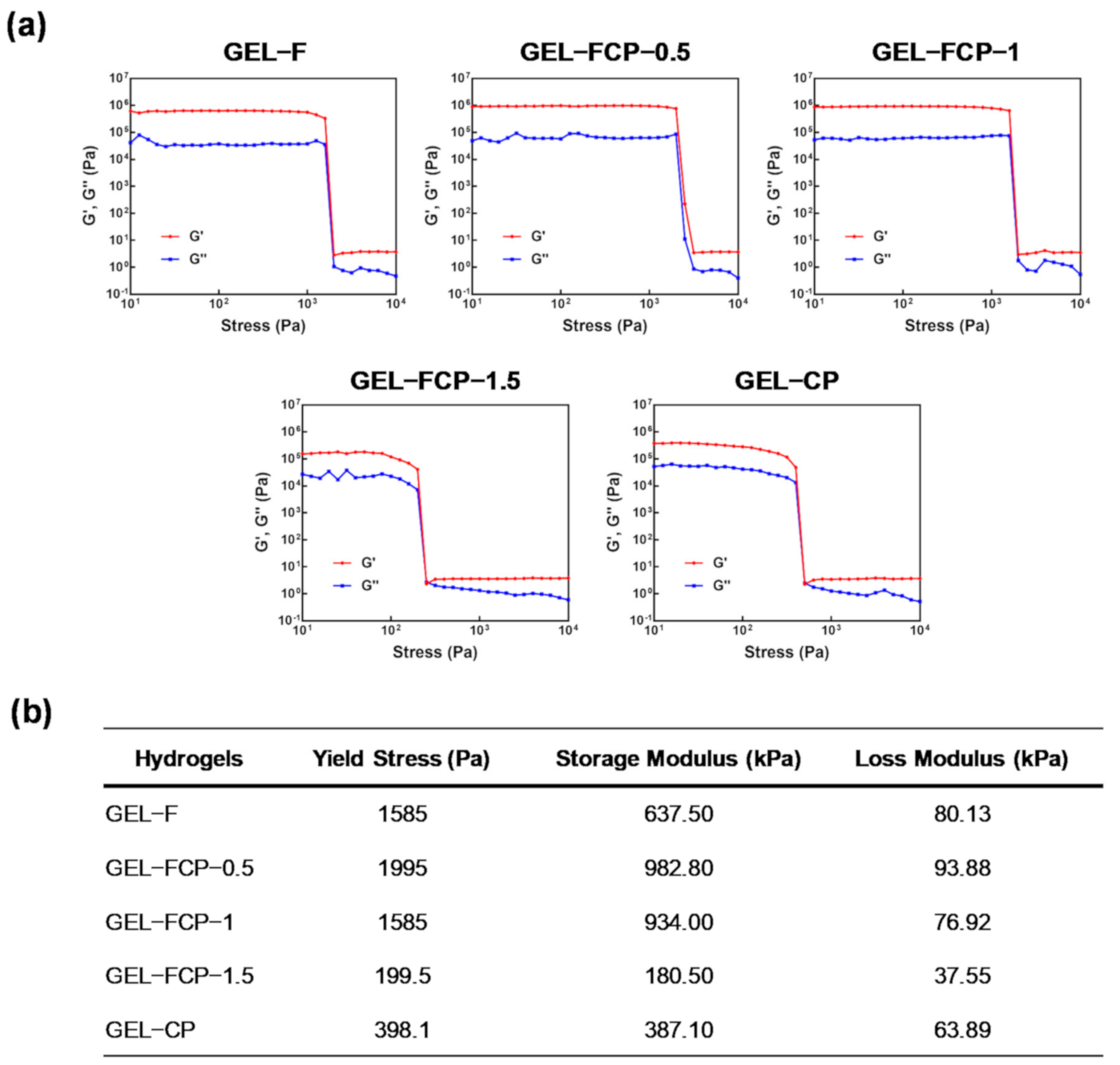
2.5. Rheology Study
2.6. BSA Releasing
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of CS-mPEG Conjugate
3.2. FT-IR Spectra for Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives
3.3. Gelation Time
3.4. Interior Structure
3.5. Rheology Study
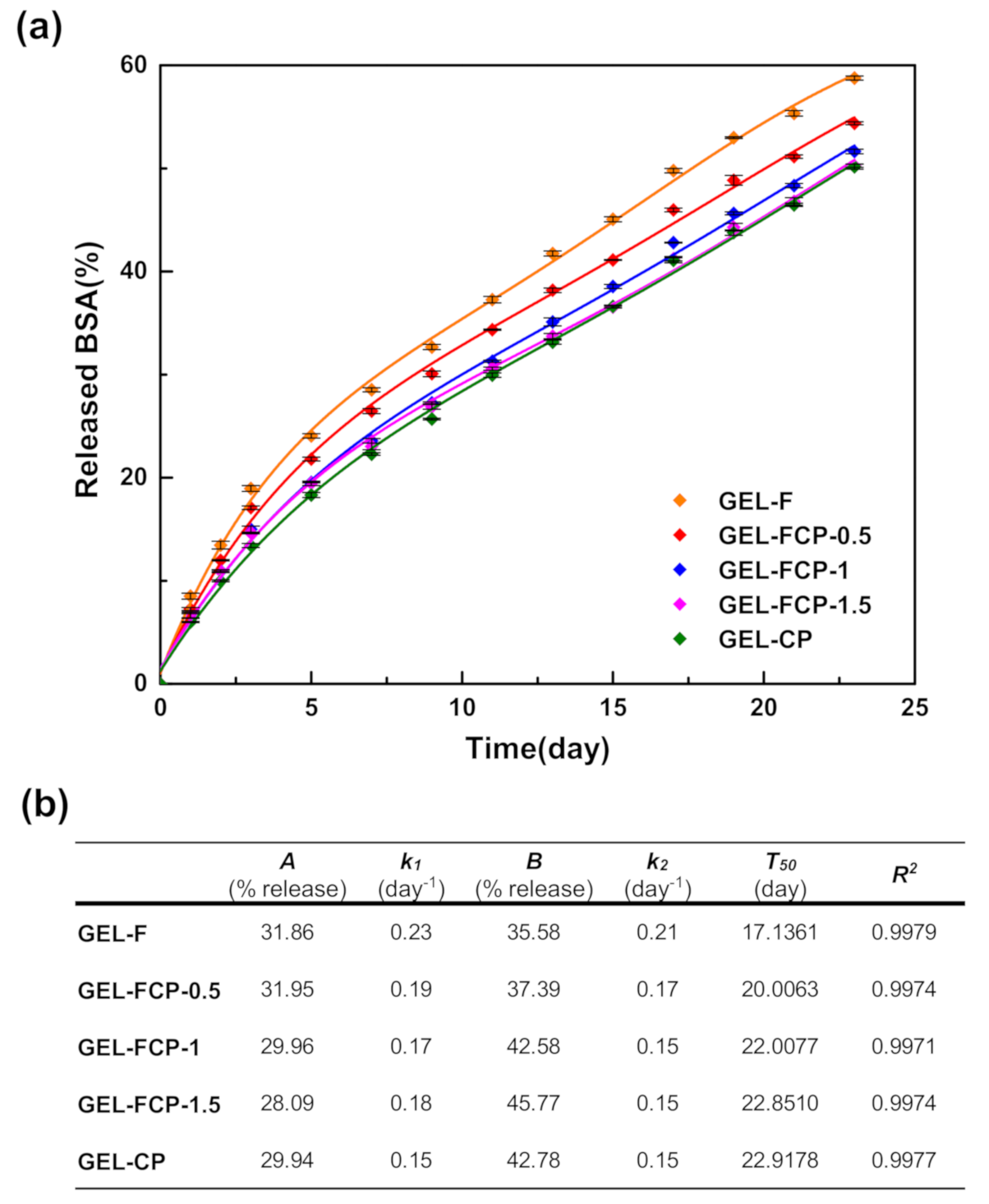
3.6. BSA Release
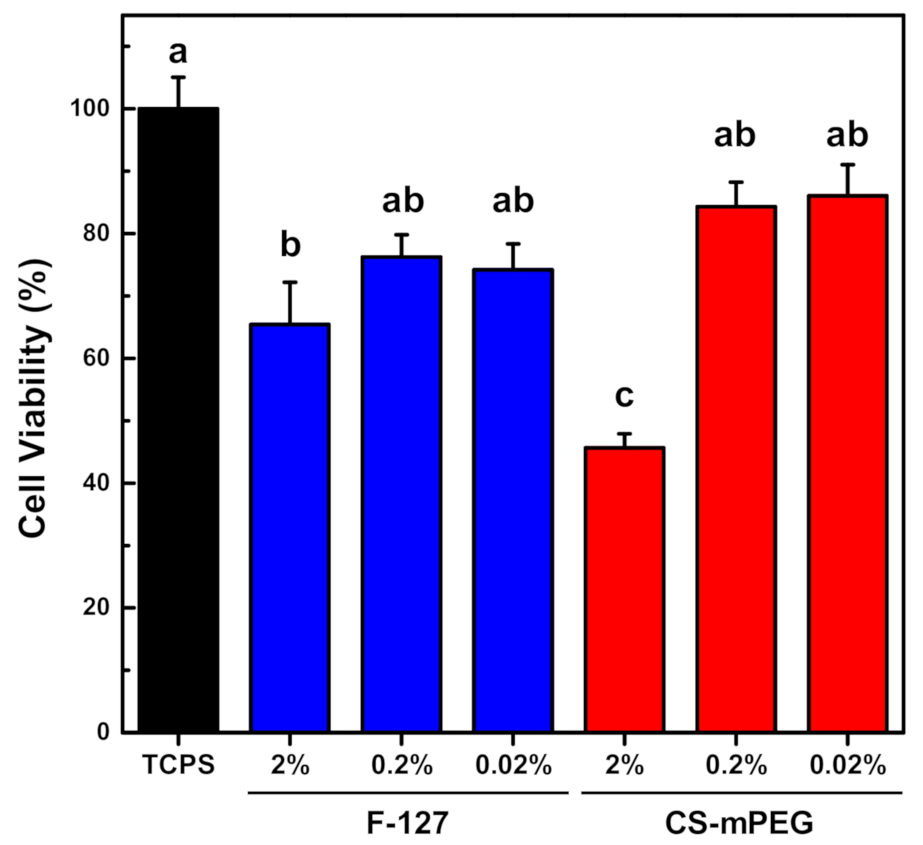
3.7. Cytotoxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spicer, C.D. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: The importance of polymer choice. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 184–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiet, T.; Vandenhaute, M.; Schelfhout, J.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P. A review of trends and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6020–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahranavard, M.; Zamanian, A.; Ghorbani, F.; Shahrezaee, M.H. A critical review on three dimensional-printed chitosan hydrogels for development of tissue engineering. Bioprinting 2020, 17, e00063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Stowers, R.; Lou, J.; Xia, Y.; Chaudhuri, O. Varying PEG density to control stress relaxation in alginate-PEG hydrogels for 3D cell culture studies. Biomaterials 2019, 200, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Huang, H. Review on Magnetic Natural Polymer Constructed Hydrogels as Vehicles for Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2574–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi, H.; Moradi, S.; Hudson, S.M.; Tonelli, A.E. Chitosan based hydrogels and their applications for drug delivery in wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Yuan, Q.; Hollett, G.; Zhao, W.; Kang, Y.; Wu, J. Cyclodextrin-based host–guest supramolecular hydrogel and its application in biomedical fields. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3436–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Krasnova, L.; Finn, M.; Sharpless, K.B. Sulfur (VI) fluoride exchange (SuFEx): Another good reaction for click chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9430–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cohen-Karni, D.; Beringer, L.T.; Wu, C.; Kallick, E.; Edington, H.; Passineau, M.J.; Averick, S. Direct introduction of R-SO2F moieties into proteins and protein-polymer conjugation using SuFEx chemistry. Polymer 2016, 99, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Jung, D.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.M. Chemoselective tyrosine bioconjugation through sulfate click reaction. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 10948–10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.W.; Keum, G.; Jang, S.K.; Kim, B.M. Sulfur (vi) fluoride exchange as a key reaction for synthesizing biaryl sulfate core derivatives as potent hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitors and their structure–activity relationship studies. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31803–31821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelli, R.; Bartolami, E.; Longevial, J.; Bessin, Y. A metal-free synthetic approach to peptide-based iminosugar clusters as novel multivalent glycosidase inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 2210–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelli, R.; Tommasone, S.; Dumy, P.; Marra, A.; Dondoni, A. SuFEx: A metal-free click ligation for multivalent biomolecules. Eur. J. Org. Chem 2016, 7, 5102–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulow, R.W.; Wu, J.W.; Kim, C.; Michaudel, Q. Synthesis of unsymmetrical sulfamides and polysulfamides via SuFEx click chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7807–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Requena, J.V.; Grijalvo, S.; Sampedro, D.; Mayr, J.; Saldías, C.; Marrero-Tellado, J.J.; Eritja, R.; Herrera, R.P.; Díaz, D.D. Sulfonamide as amide isostere for fine-tuning the gelation properties of physical gels. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11481–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, P.X. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular systems for drug delivery: Recent progress and future perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Takashima, Y.; Nakahata, M. Supramolecular polymeric materials via cyclodextrin–guest interactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ha, W.; Sun, J.-N.; Shi, Y.-P. Supramolecular hybrid hydrogel based on host–guest interaction and its application in drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19544–19551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.J.; Park, M.H.; Joo, M.K.; Jeong, B. Temperature-responsive compounds as in situ gelling biomedical materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4860–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Dong, A.; Song, J.; Chen, X. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel systems based on functional PEG/PCL block polymer for local drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 297, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Rodrigues, J.; Tomas, H. Injectable and biodegradable hydrogels: Gelation, biodegradation and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2193–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Li, R.; Qu, L.; Dai, X.; Sui, Y.; Hou, J. Multiple physically cross-linked F127− α-CD hydrogels: Preparation, sol–gel transformation, and controlled release of 5-fluorouracil. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Liu, T.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Kirk, T.B.; Ma, D.; Xue, W. Injectable supramolecular hydrogel formed from α-cyclodextrin and PEGylated arginine-functionalized poly (l-lysine) dendron for sustained MMP-9 shRNA plasmid delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, C.; Cancemi, P.; Mattiello, L.; Marullo, S.; D’Anna, F. Naphthalimide Imidazolium-Based Supramolecular Hydrogels as Bioimaging and Theranostic Soft Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48442–48457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tong, G.; Dong, R.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhu, X. Self-assembly of supramolecularly engineered polymers and their biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11994–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, G.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Carbon quantum dot-based fluorescent vesicles and chiral hydrogels with biosurfactant and biocompatible small molecule. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 6983–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, A.K.; Dewangan, M.; Suresh, P.K. Potential of chitosan-based carrier for periodontal drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Hua, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J. Chemical and physical chitosan hydrogels as prospective carriers for drug delivery: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10050–10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Tsao, C.T.; Chang, C.H.; Lai, Y.T.; Wu, M.F.; Liu, Z.W.; Chuang, C.N.; Chou, H.C.; Wang, C.K.; Hsieh, K.H. Synthesis and characterization of reinforced poly (ethylene glycol)/chitosan hydrogel as wound dressing materials. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Tsao, C.-T.; Chang, C.-H.; Lai, Y.-T.; Wu, M.-F.; Chuang, C.-N.; Chou, H.-C.; Wang, C.-K.; Hsieh, K.-H. Assessment of reinforced poly (ethylene glycol) chitosan hydrogels as dressings in a mouse skin wound defect model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2584–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, J.; Sharpless, K.B. Ethenesulfonyl fluoride (ESF): An on-water procedure for the kilogram-scale preparation. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11360–11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvvuri, S.; Janoria, K.G.; Mitra, A.K. Effect of polymer blending on the release of ganciclovir from PLGA microspheres. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Palazzo, A.; Hennink, W.E.; Kok, R.J. Effect of particle size on drug loading and release kinetics of gefitinib-loaded PLGA microspheres. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Xian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Performances: Preparation, Structure, and Property. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, X.; Shi, S.; Gu, Y.; Yang, L.; Guo, G.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; Qian, Z. Biodegradable MPEG-g-Chitosan and methoxy poly (ethylene glycol)-b-poly (ε-caprolactone) composite films: Part 1. Preparation and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Xing, Y.; Fang, W.; Ren, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, G. NIR-light-and pH-responsive graphene oxide hybrid cyclodextrin-based supramolecular hydrogels. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.L.; Li, J. Supramolecular anchoring of DNA polyplexes in cyclodextrin-based polypseudorotaxane hydrogels for sustained gene delivery. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3162–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
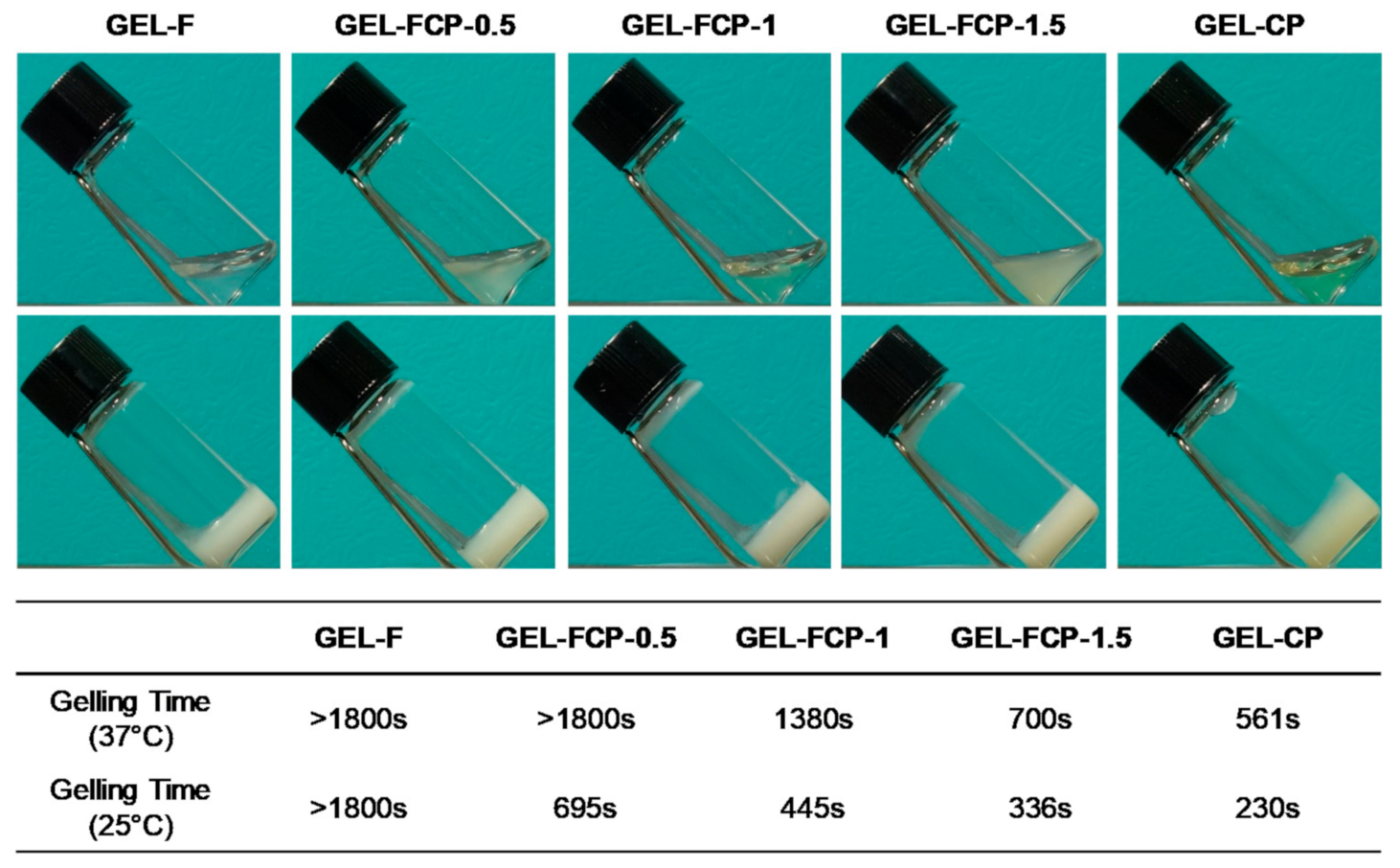


| Hydrogel | Polymers | Mass Ratio (wt%) F127:CS-mPEG | Mass Ratio (wt%) polymer:α-CD |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEL-F | F127 | 100:0 | 20:97 |
| GEL-FCP-0.5 | F127 + CS-mPEG | 75:25 | 20:97 |
| GEL-FCP-1 | F127 + CS-mPEG | 50:50 | 20:97 |
| GEL-FCP-1.5 | F127 + CS-mPEG | 25:75 | 20:97 |
| GEL-CP | CS-mPEG | 0:100 | 20:97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, K.-J.; Lee, W.-S.; Park, S.; Han, J.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, B.M.; Chung, J.H. Sulfur(VI) Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)-Mediated Synthesis of the Chitosan-PEG Conjugate and Its Supramolecular Hydrogels for Protein Delivery. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020318
Jang K-J, Lee W-S, Park S, Han J, Kim JE, Kim BM, Chung JH. Sulfur(VI) Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)-Mediated Synthesis of the Chitosan-PEG Conjugate and Its Supramolecular Hydrogels for Protein Delivery. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Kyoung-Je, Woong-Sup Lee, Sangbae Park, Jinsub Han, Jae Eun Kim, B. Moon Kim, and Jong Hoon Chung. 2021. "Sulfur(VI) Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)-Mediated Synthesis of the Chitosan-PEG Conjugate and Its Supramolecular Hydrogels for Protein Delivery" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020318
APA StyleJang, K.-J., Lee, W.-S., Park, S., Han, J., Kim, J. E., Kim, B. M., & Chung, J. H. (2021). Sulfur(VI) Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)-Mediated Synthesis of the Chitosan-PEG Conjugate and Its Supramolecular Hydrogels for Protein Delivery. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020318







