Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Green Tea and Its Removal of Hexavalent Chromium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of nFe
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Removal of Cr(VI) by nFe
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Synthesizing Conditions on Removal Efficiency
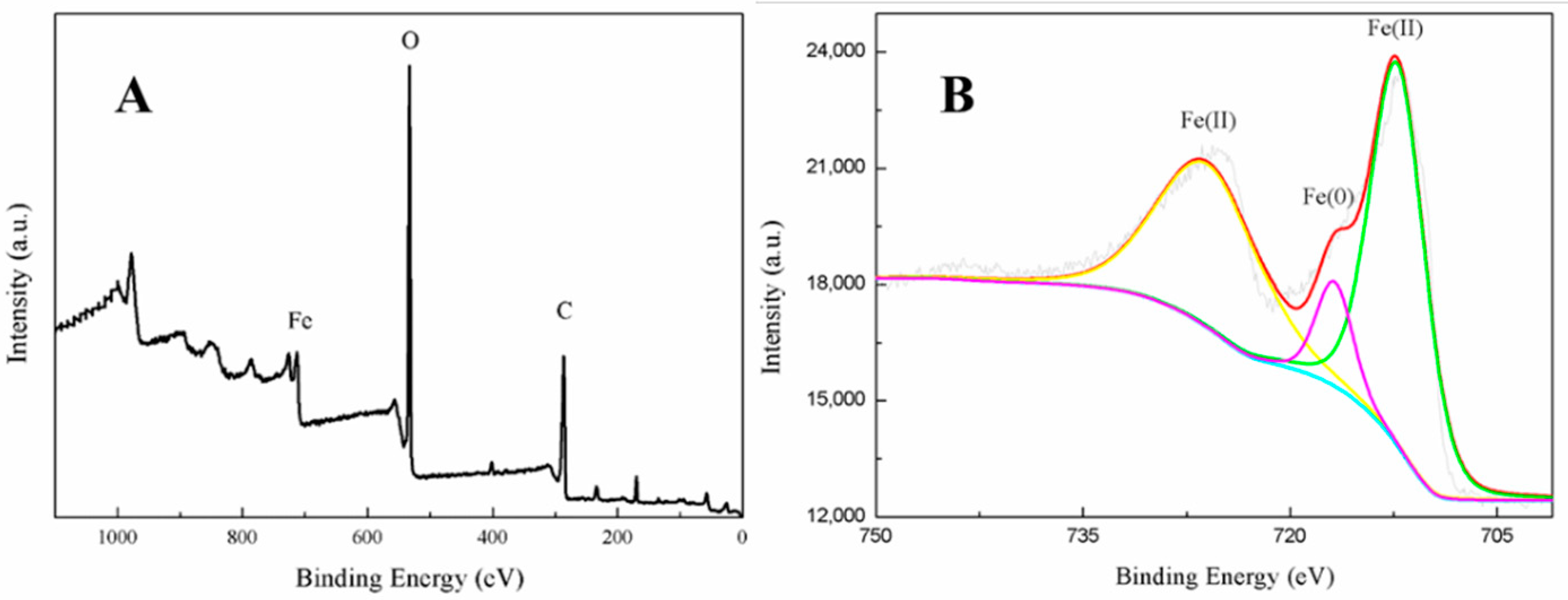
3.2. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.3. Analysis of the Green Tea Extract
3.4. Mechanism
3.5. Stability of nFe Removal Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nur-E-Alam, M.; Mia, M.A.; Ahmad, F.; Rahman, M.M. An overview of chromium removal techniques from tannery effluent. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, N.N.; Aravindhan, R.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U. Solid Waste Removes Toxic Liquid Waste: Adsorption of Chromium(VI) by Iron Complexed Protein Waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2804–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.C.; Cardoso, C.E.D.; Tavares, D.S.; Freitas, R.; Trindade, T.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Chromium removal from contaminated waters using nanomaterials—A review. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Deng, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, T. Facile Preparation of Self-Assembled Chitosan-Based POSS-CNTs-CS Composite as Highly Efficient Dye Absorbent for Wastewater Treatment. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Yin, J.; Ma, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Jiao, T. Exploring the enhanced catalytic performance on nitro dyes via a novel template of flake-network Ni-Ti LDH/GO in-situ deposited with Ag3PO4 NPs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 543, 148821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhang, W.-X. Mapping the reactions of hexavalent chromium [Cr(vi)] in iron nanoparticles using spherical aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy (Cs-STEM). Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3211–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.K.; Chakraborty, S. Adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution on graphene oxide (GO) pre-pared from graphite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.; Abdulhakim, S.A.; Ishaq, K.; Saka, A.A.; Peter, M.S.; Chidinma, O.U. Carbon nanotubes: Mechanism, Langmuir Hinshelwood growth kinetics and it application for the removal of Chromium (VI). J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 100174–100184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Qian, G. A porous Zr-cluster-based cationic metal–organic framework for highly efficient Cr2O72− removal from water. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14732–14734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, S.P.; Owens, G. Evaluation of enhancement techniques for the dechlorination of DDT by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Nanoscale zero-valent iron as a catalyst for heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of amoxicillin. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jin, X.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.; Chen, Z. Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using iron-based nanoparticles and persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Guo, M.; Luo, F.; Chen, Z. One-step green synthesis of bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles by eucalyptus leaf extract: Biomolecules identification, characterization and catalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions via reduction and absorption by green synthesized iron nanoparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Weng, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles using oolong tea extract for the degradation of malachite green. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Wang, Q.P.; Chen, Z.L.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of mon-ochlorobenzene using green synthesis of iron nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 410, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. The formation of iron nanoparticles by Eucalyptus leaf extract and used to remove Cr(VI). Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 627, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extracts for treatment of eutrophic wastewater. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 466–467, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Removal of co-contaminants Cu (II) and ni-trate from aqueous solution using kaolin-Fe/Ni nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Safer, A.M.; Menon, M. Green tea polyphenols and their potential role in health and disease. Inflammopharmacology 2015, 23, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Weng, X.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Mechanism and impact of synthesis conditions on the one-step green synthesis of hybrid RGO@ Fe/Pd nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Panwar, J.; Yun, Y.-S. Biogenic Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles by Plant Extracts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheju, M. Hexavalent Chromium Reduction with Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) in Aquatic Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 222, 103–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njagi, E.C.; Huang, H.; Stafford, L.; Genuino, H.; Galindo, H.M.; Collins, J.B.; Hoag, G.E.; Suib, S.L. Bio-synthesis of Iron and Silver Nanoparticles at Room Temperature Using Aqueous Sorghum Bran Extracts. Langmuir 2011, 27, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahwan, T.; Abu Sirriah, S.; Nairat, M.; Boyacı, E.; Eroğlu, A.; Scott, T.; Hallam, K. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.-N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.-L. Removal of Chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2011, 45, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhang, W.-X. Enrichment and Encapsulation of Uranium with Iron Nanoparticle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2788–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.S.; Lee, J.C.; Rhee, S.H. Effect of precursor concentration and spray pyrolysis temperature upon hdroxyapatite particle size and density. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Sen, S. Optimization of process parameters for the rapid biosynthesis of hematite nano-particles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 159, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; Biesinger, M.C.; McIntyre, N.S. Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, W.; Xiong, Z.; Xia, D.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y. Synergistic effect of iron and copper oxides on the formation of persistent chlorinated aromatics in iron ore sintering based on in situ XPS analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, J.H.; Yoon, J.B.; Jung, H.; Park, J.H. Structural evolution of SiO2–ZrO2 nano-sol intercalated clays upon pillaring reaction. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R.; Shukla, D.P. Synthesis of fly ash based zeolite-reduced graphene oxide composite and its evalua-tion as an adsorbent for arsenic removal. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daboin, V.; Briceño, S.; Suárez, J.; Carrizales-Silva, L.; Alcalá, O.; Silva, P.; Gonzalez, G. Magnetic SiO2-Mn1-xCoxFe2O4 nanocomposites decorated with Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 479, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





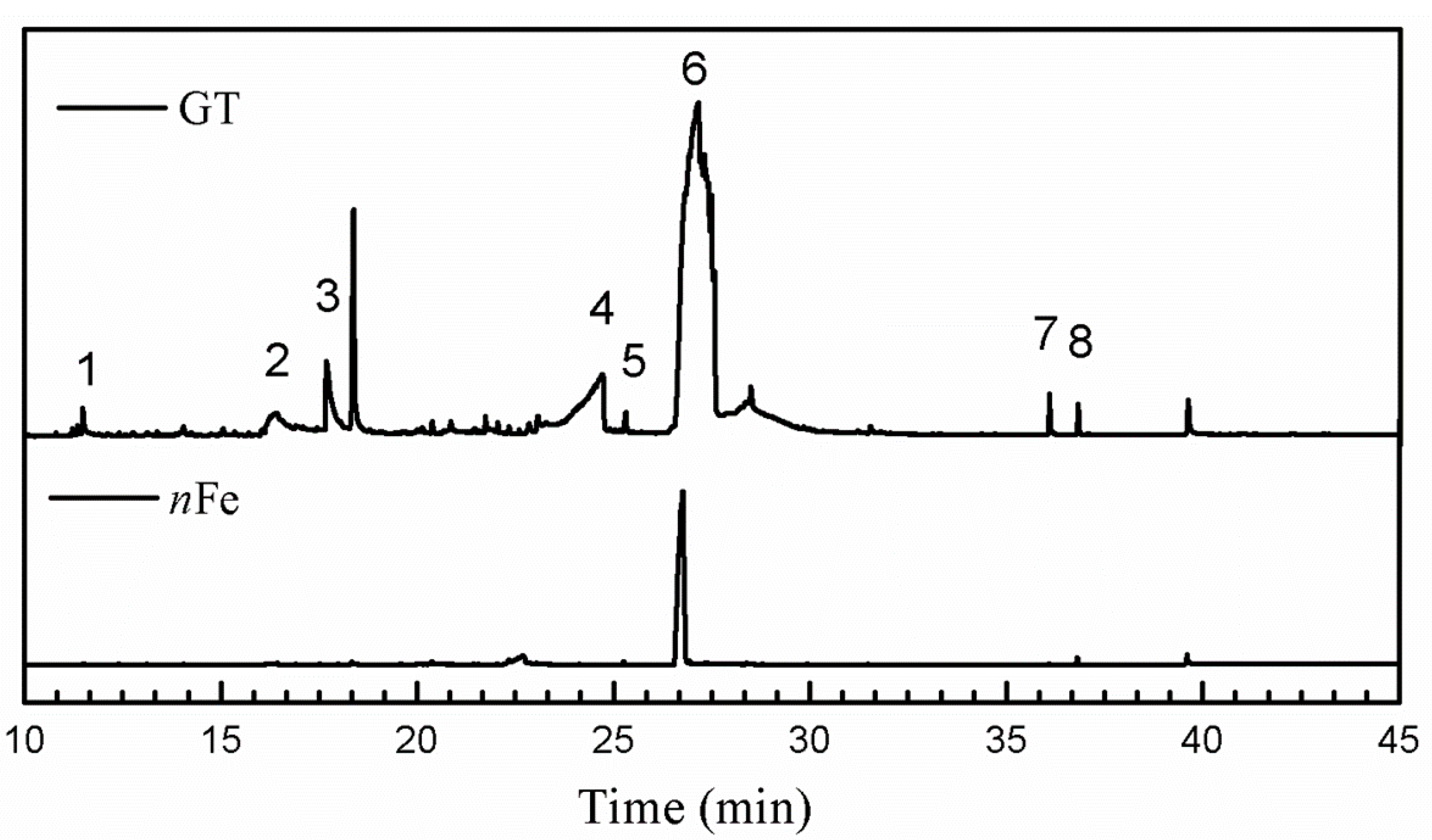


| Entry | RT (min) | The Major Compound Involved Synthesis | Structure |
| 1 | 11.47 | Phenol |  |
| 2 | 16.37 | 1,1′-Biphenyl,2-ethyl- | 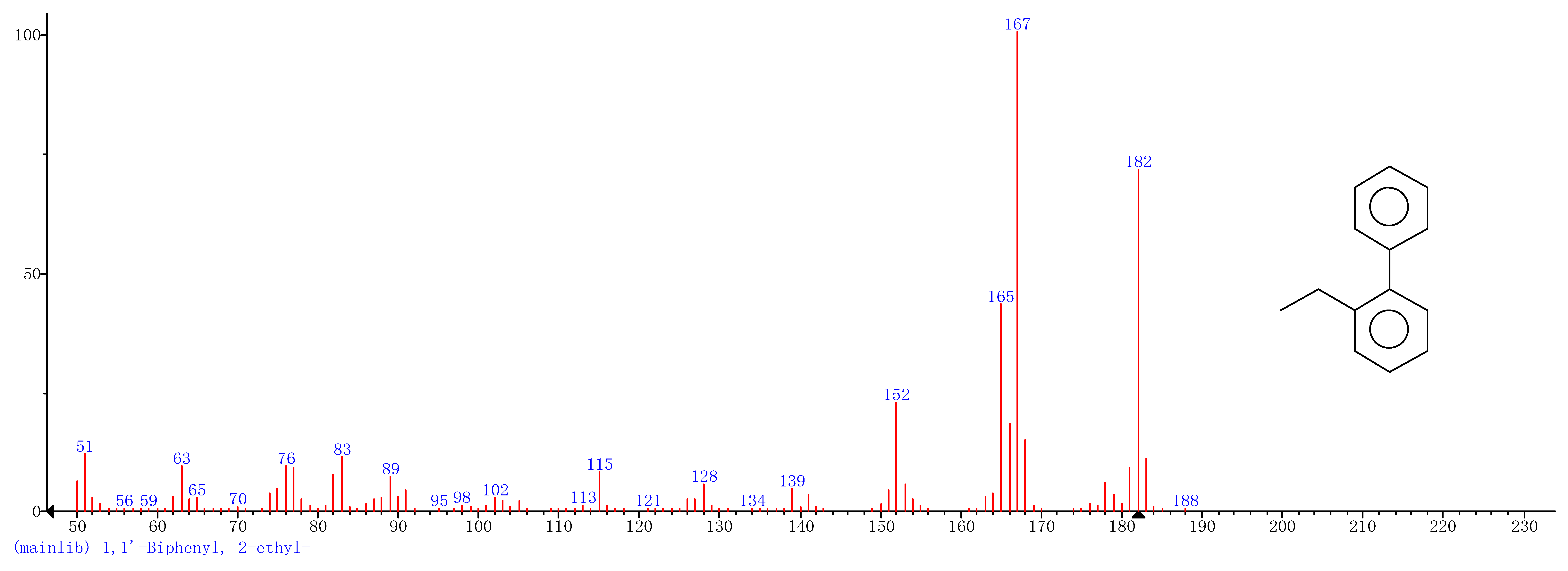 |
| 3 | 17.71 | 1,2,3-Benzenetriol |  |
| 4 | 24.70 | 1,3,5-Benzenetriol | 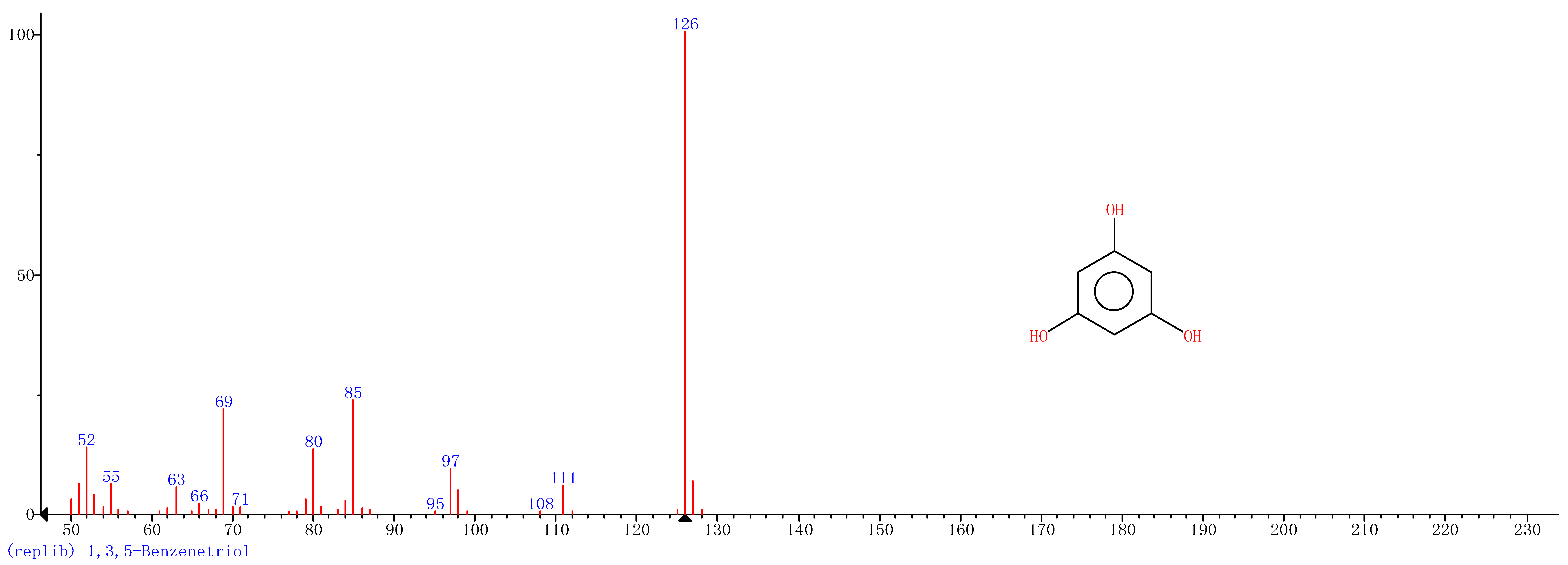 |
| 5 | 25.33 | 6-Hydroxy-4,4,7a-trimethyl-5,6,7a-tetrahydrobenzofuran |  |
| 6 | 27.14 | Caffeine |  |
| 7 | 36.09 | Oleanitrile |  |
| 8 | 36.80 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, T. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Green Tea and Its Removal of Hexavalent Chromium. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030650
Hao R, Li D, Zhang J, Jiao T. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Green Tea and Its Removal of Hexavalent Chromium. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030650
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Runqin, Dong Li, Jie Zhang, and Tifeng Jiao. 2021. "Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Green Tea and Its Removal of Hexavalent Chromium" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030650
APA StyleHao, R., Li, D., Zhang, J., & Jiao, T. (2021). Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Green Tea and Its Removal of Hexavalent Chromium. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030650







