Fabrication and Characterization of High-Quality UV Photodetectors Based ZnO Nanorods Using Traditional and Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO Seed Layer Preparations
2.2. ZnO Nanorods Growth
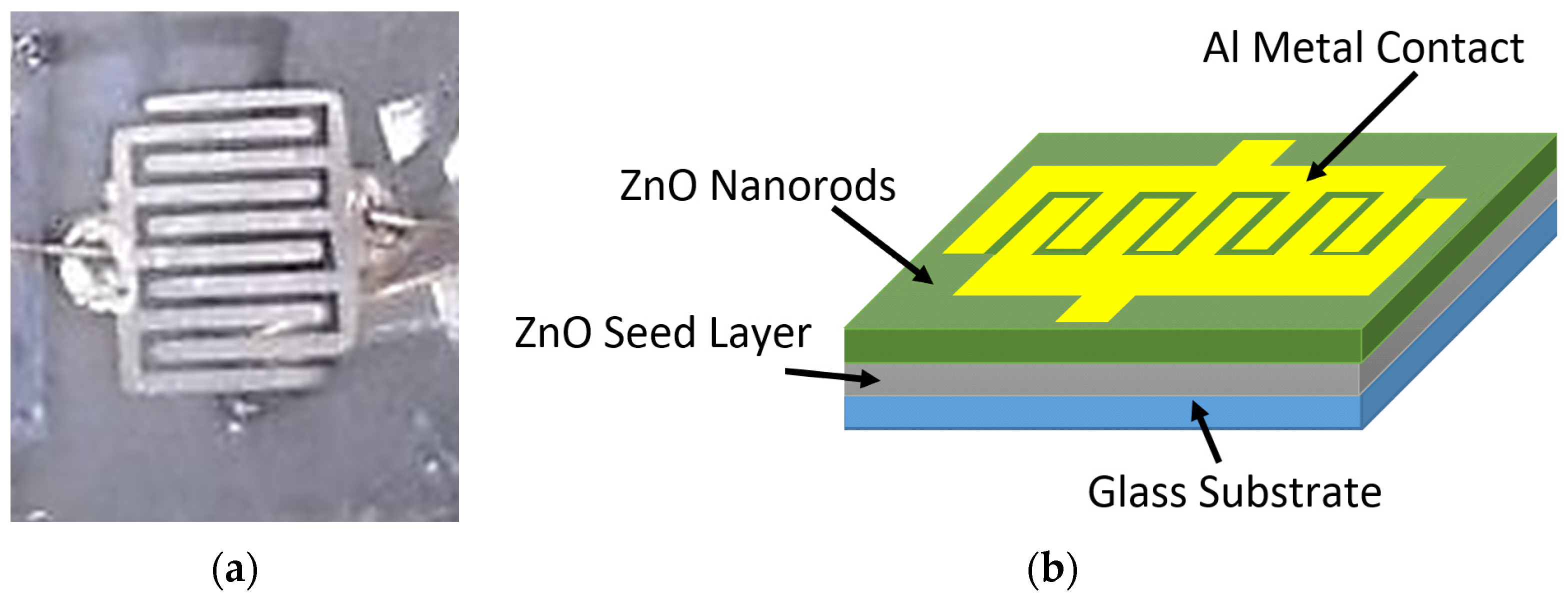
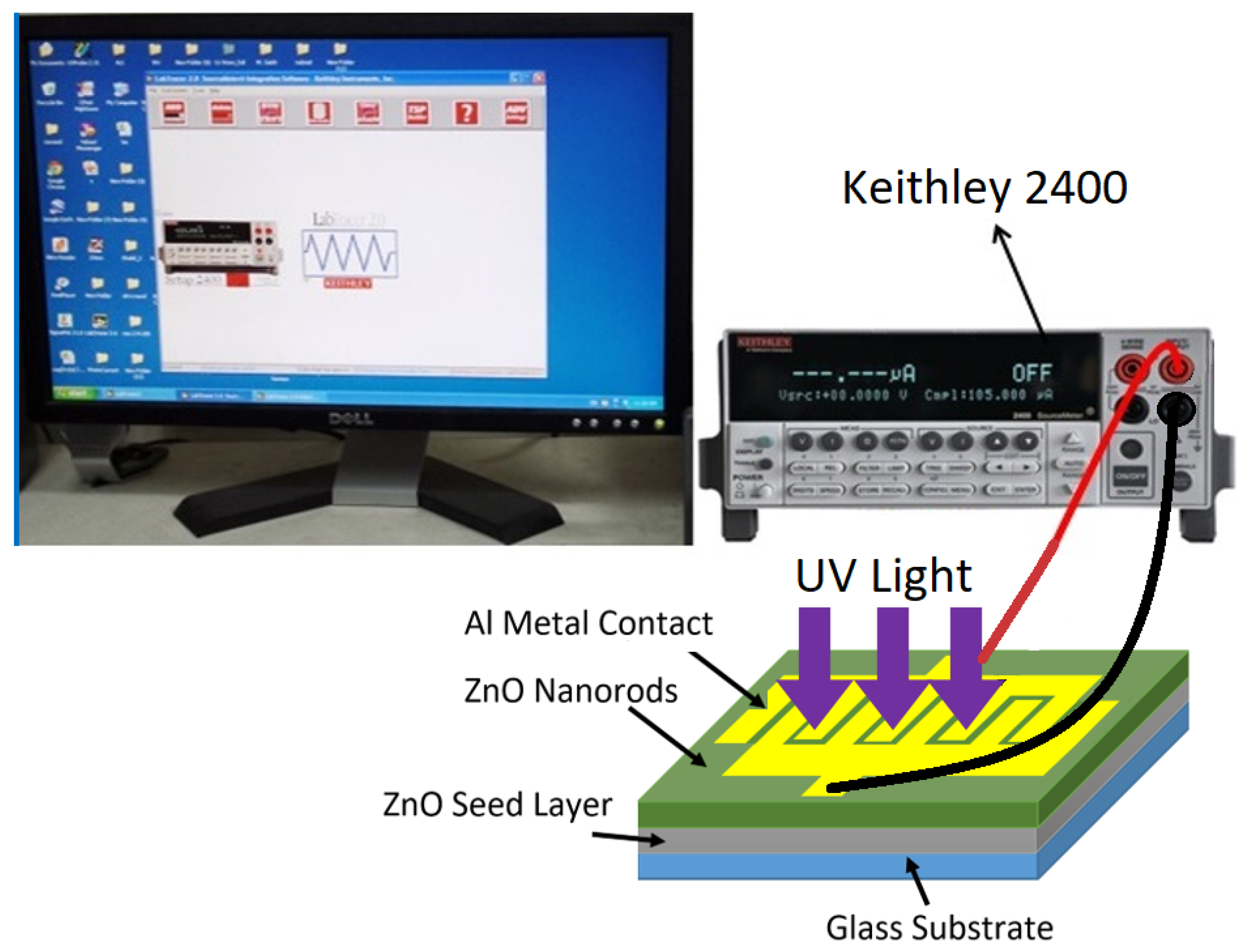
2.3. Fabrication of UV Photodetectors
2.4. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
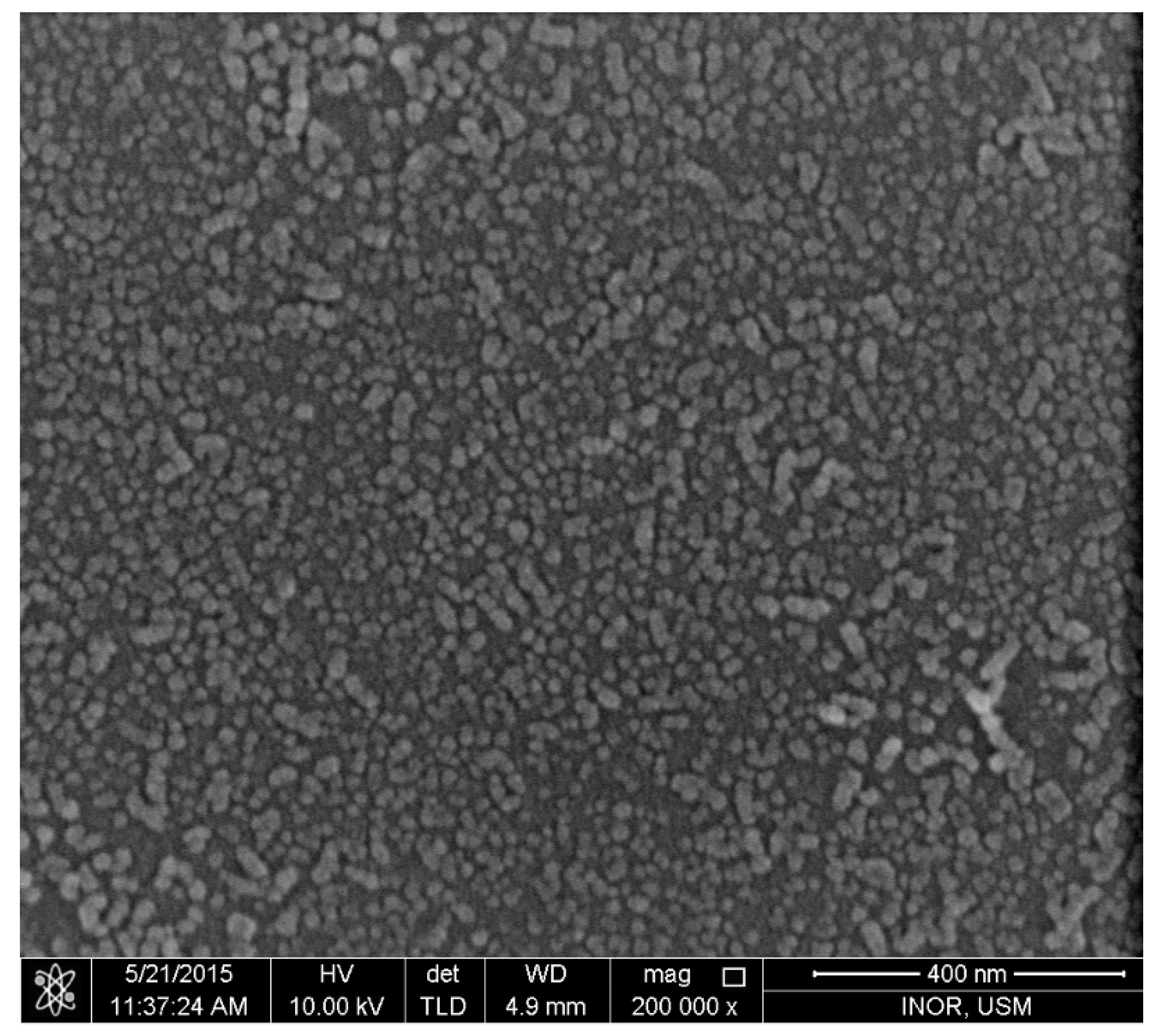
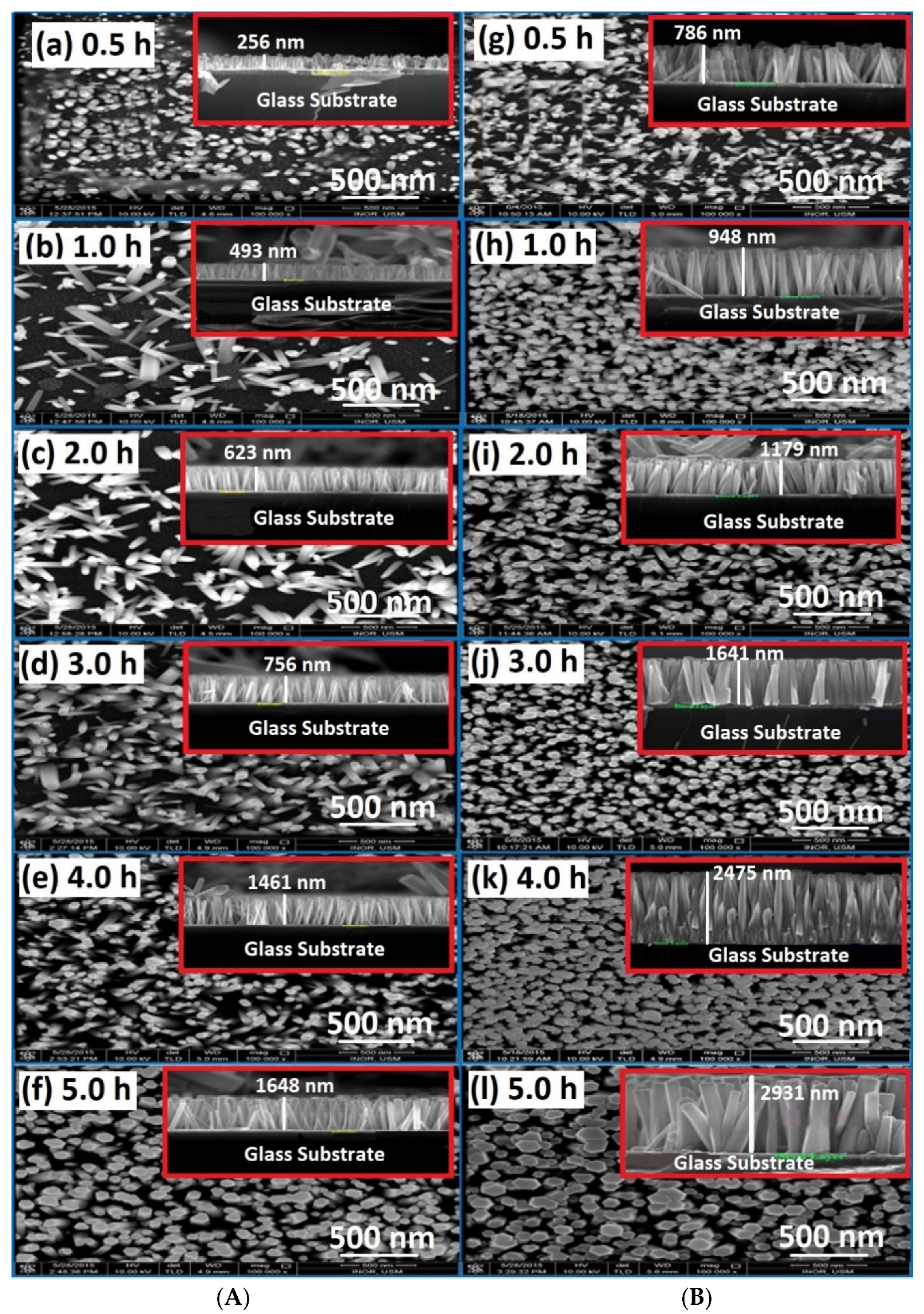
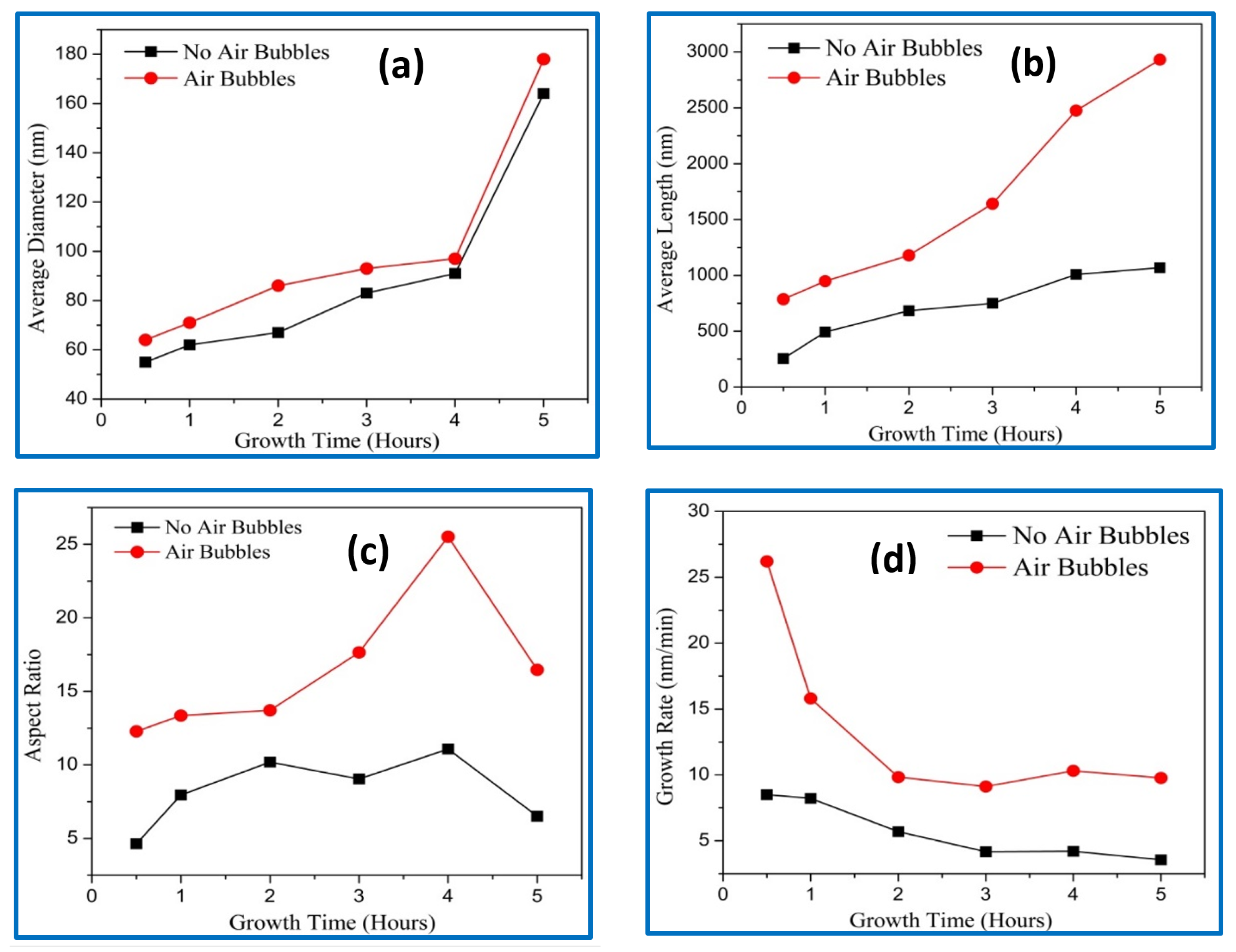
3.1. Morphology Characteristics
3.2. The pH Values of the Growth Solutions
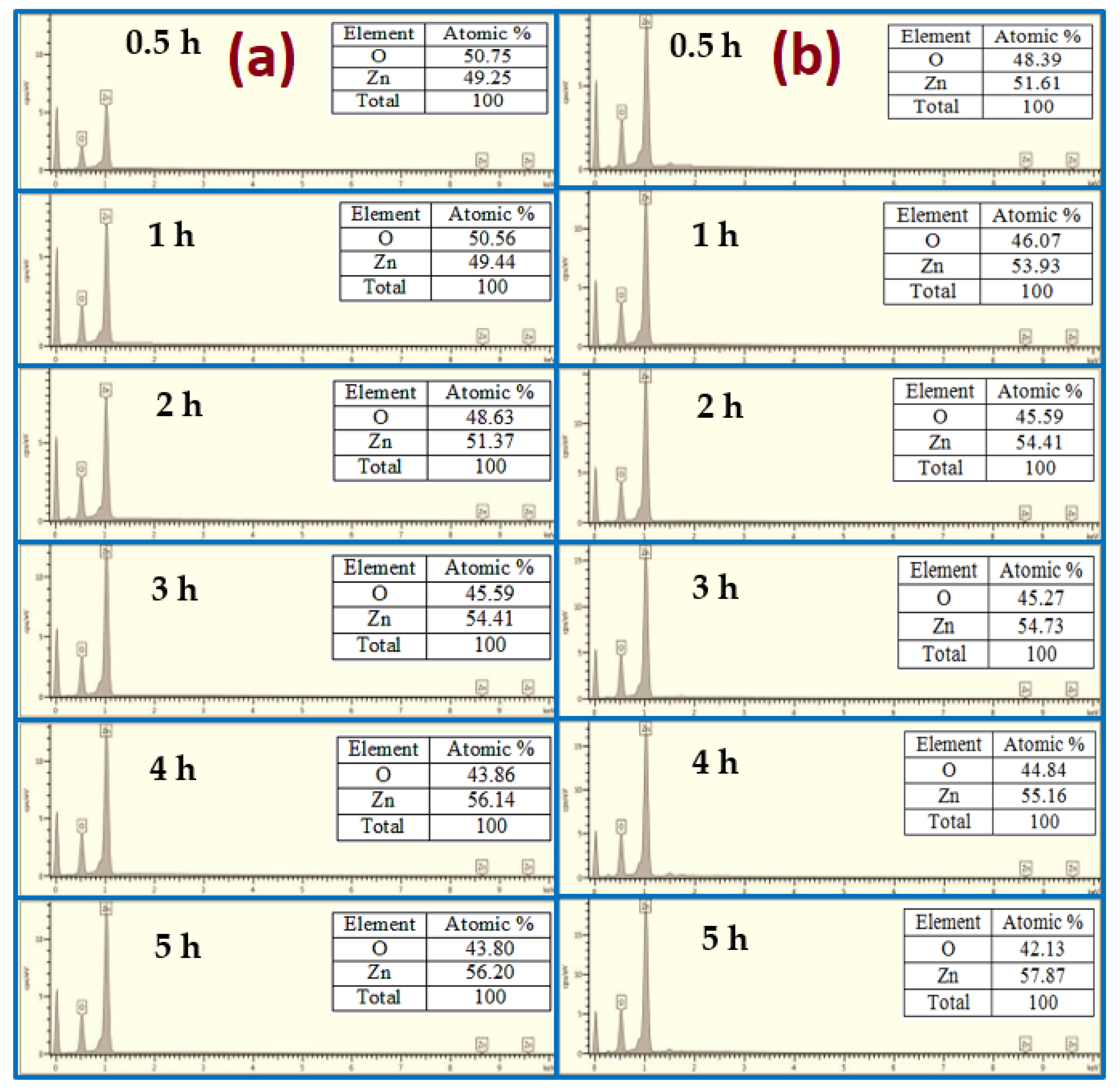
3.3. Chemical Analysis of the Grown ZnO Nanorods
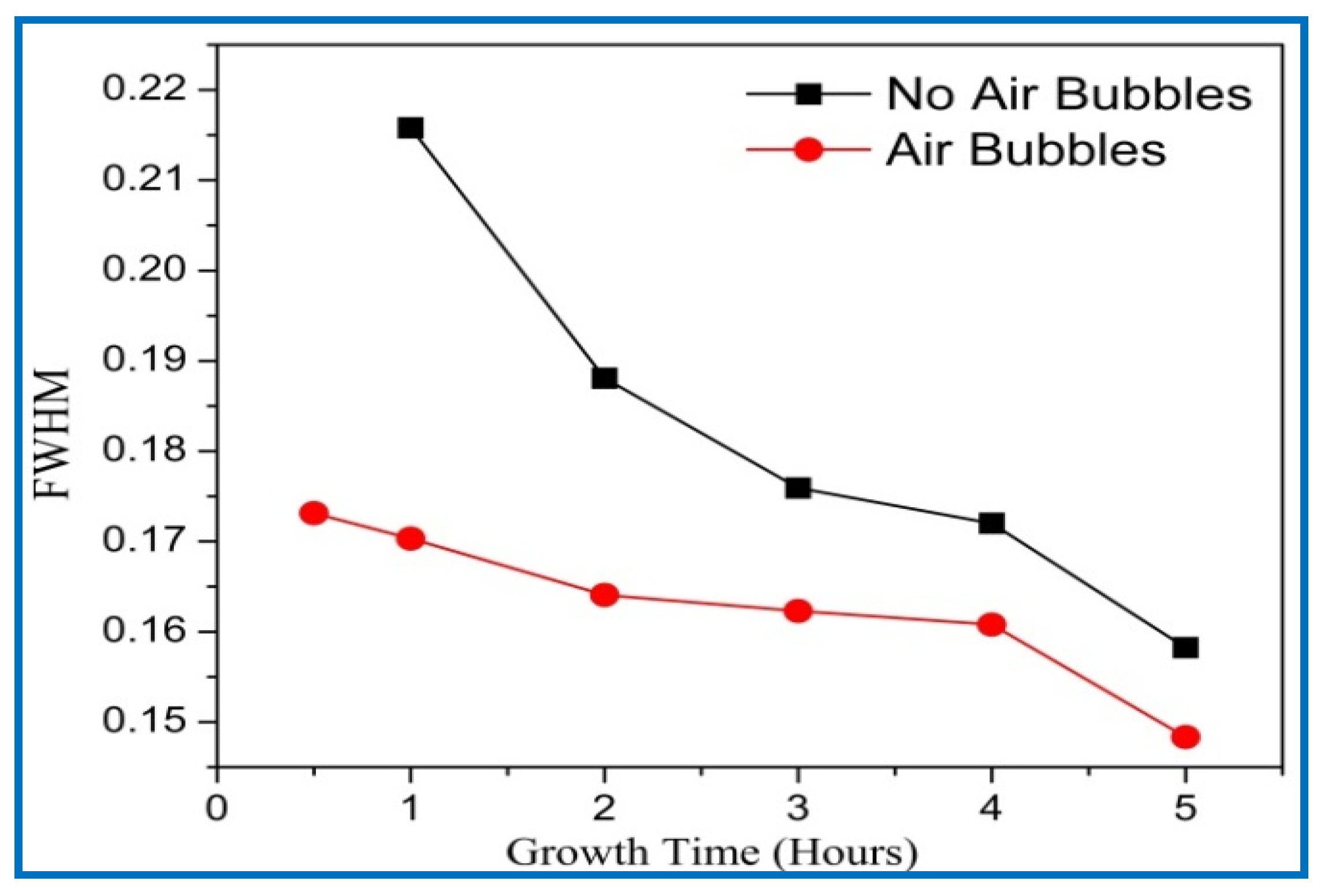
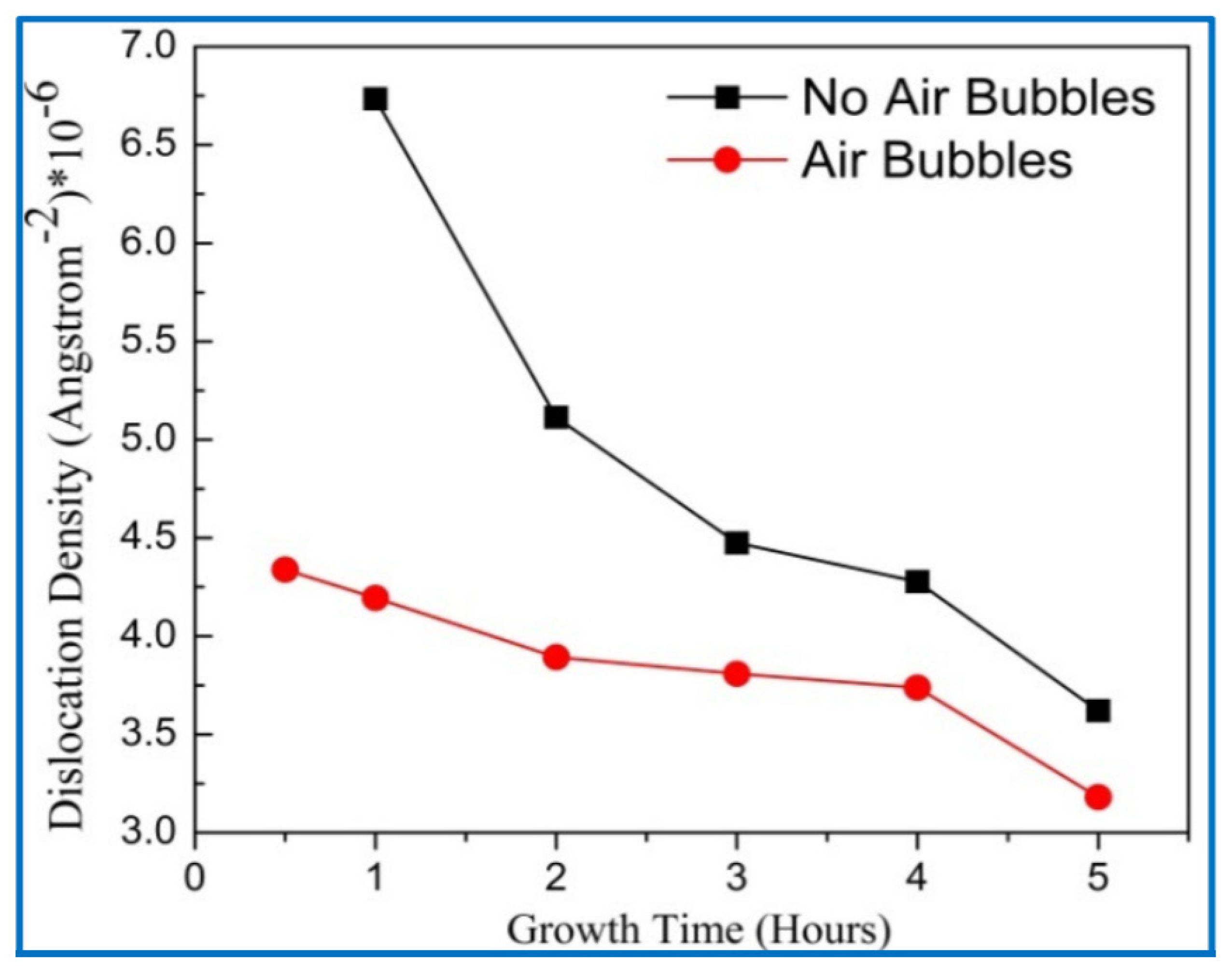
3.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
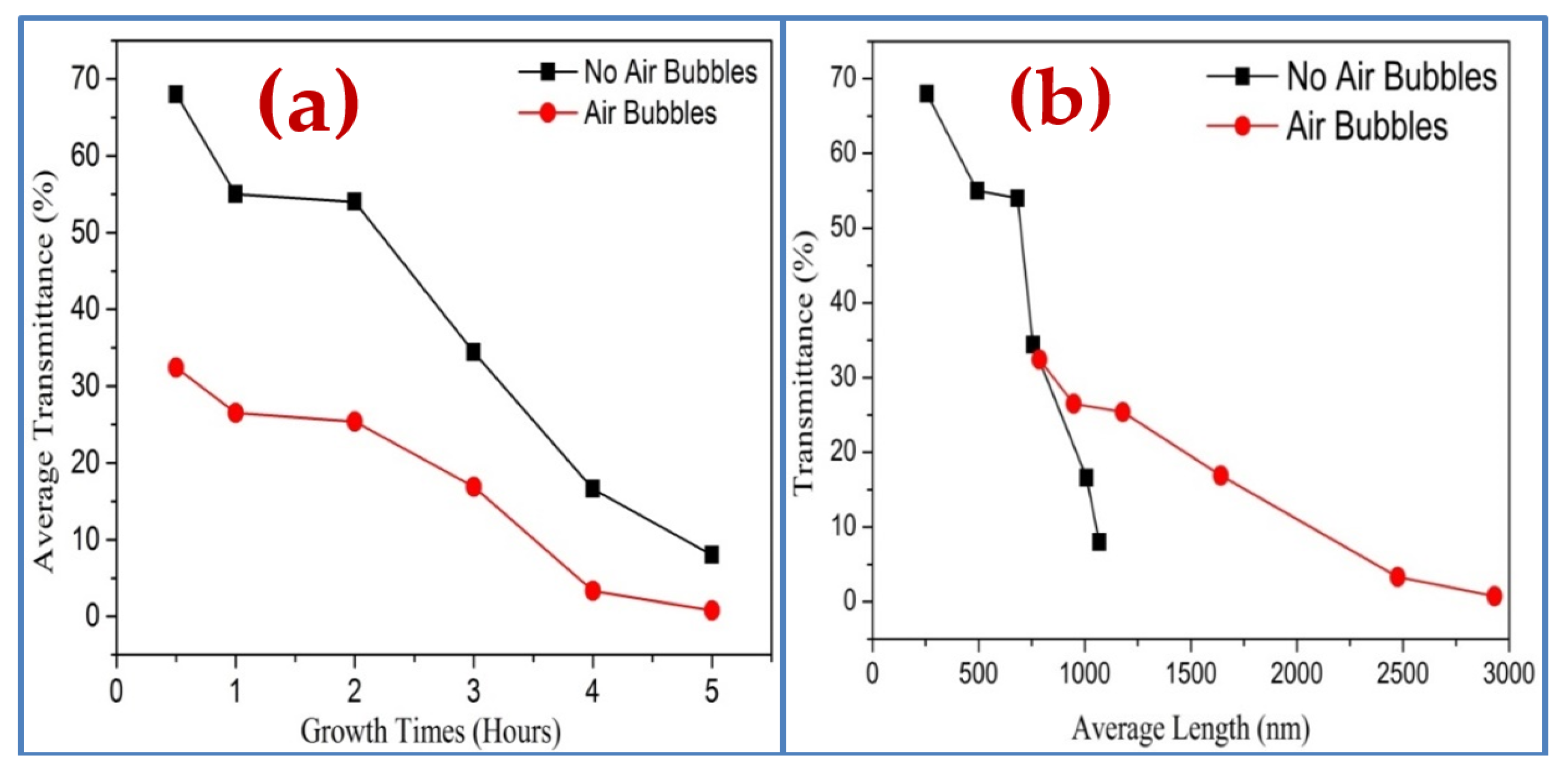
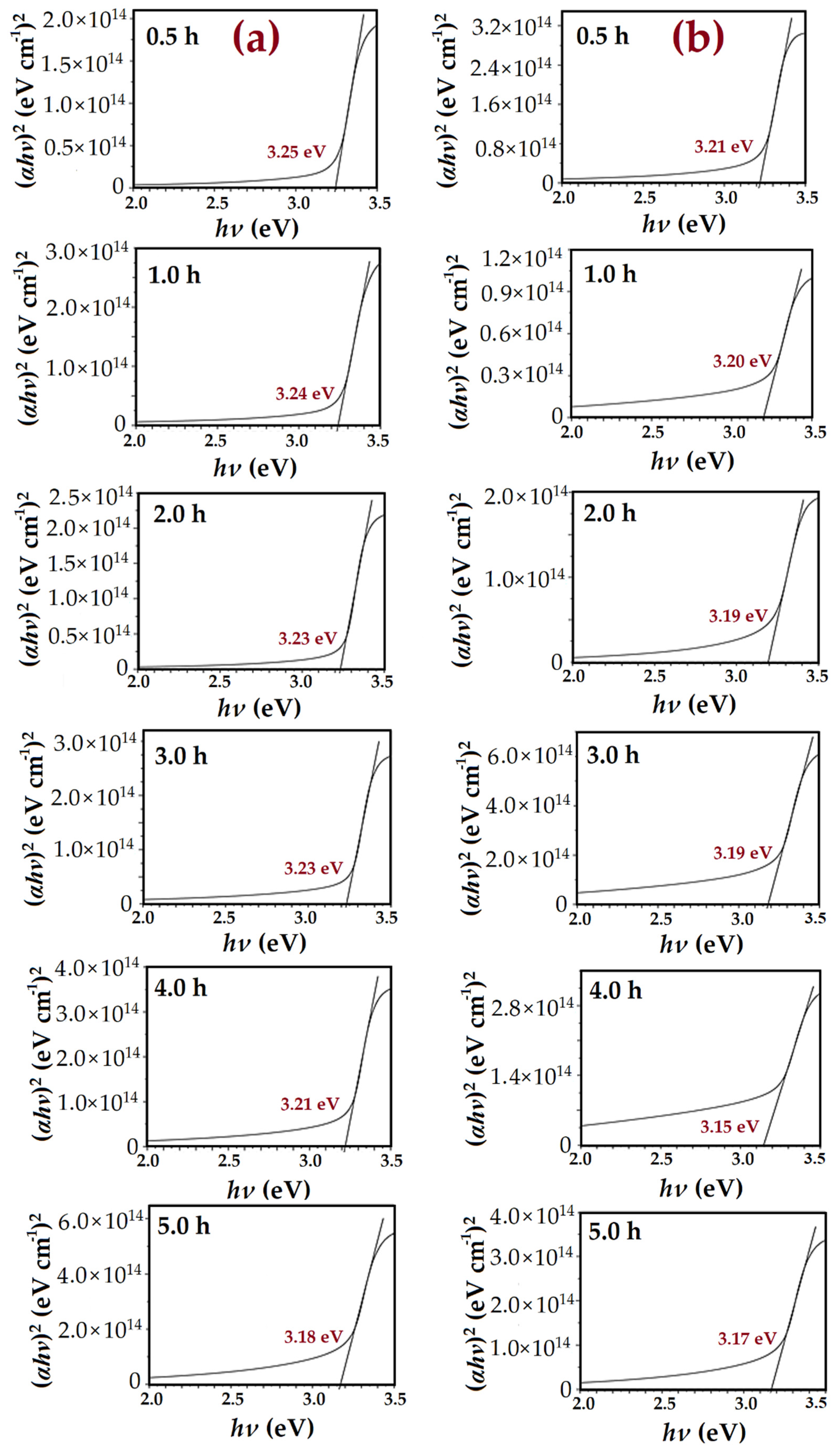
3.5. Optical Properties of ZnO Nanorods
3.6. Photodetection Characterizations of UV Photodetectors Based on ZnO Nanorods
| Bias Voltage (V) | λ (nm) | R (A/W) | Response Time (S) | Recovery Time (S) | S % | Gain | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 380 | 0.43246 | 2.649 | 1.321 | 300.834 | 4.008 | No Air Bubbles |
| 5 | 380 | 2.2851 | 0.9684 | 0.5037 | 3172.811 | 32.728 | Air Bubbles |
| 5 | 365 | 1.22 | - | - | 81.26 | 1.8 | [76] |
| 1.8 | 365 | 0.199 | - | - | 109.415 | 2.095 | [77] |
| 5 | 380 | 102 | 55.5 | 33.1 | 1720 | - | [78] |
| 3 | 365 | 41.3 | 30.7 | 465.2 | - | [79] | |
| 2 | 365 | 0.22 | 3 | 4 | - | - | [80] |
| 3 | 365 | - | 80 | 20 | - | - | [81] |
| 1 | 325 | 1.738 | 0.032 | 0.041 | 20 | [82] | |
| 5 | 365 | 0.0706 | - | - | 815.4 | 9.15 | [83] |
| 3 | 325 | 2.856 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 1175 | 12.75 | [84] |
| 5 | 365 | 0.39 | 3.9 | 2.6 | 2319 | 24.2 | [85] |
| 5 | 365 | 12 | 9 | 1575 | - | [86] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaie, Z.; Nejad, S.M.; Yousefi, M. Recent advances in ultraviolet photodetectors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 29, 16–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghaei, J.; Fallahzadeh, A.; Saghaei, T. Vapor treatment as a new method for photocurrent enhancement of UV photodetectors based on ZnO nanorods. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsultany, F.H.; Hassan, Z.; Ahmed, N.M.; Elafadill, N.G.; Abd, H.R. Effects of ZnO seed layer thickness on catalyst-free growth of ZnO nanostructures for enhanced UV photoresponse. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 98, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Novel process using oxygen and air bubbling in chemical bath deposition method for vertically well aligned arrays of zno nanorods. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2016, 11, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Hamad, S.M.; Barzinjy, A.A. Effect of Growth Temperature on Morphological, Structural, and Optical Properties of ZnO Nanorods Using Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Method. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-B.; Ryu, H.; Lee, W.-J. Effects of copper precursor concentration on the growth of cupric oxide nanorods for photoelectrode using a modified chemical bath deposition method. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 620, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, L.; Navarrete-Astorga, E.; Pereyra, C.J.; Cuevas, A.; Romero, R.; Ariosa, D.; Henríquez, R.; Muñoz, E.; Marotti, R.E.; Martín, F. The effect of a sputtered Al-doped ZnO seed layer on the morphological, structural and optical properties of electrochemically grown ZnO nanorod arrays. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, D392–D400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.-J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-H.; Chang, S.-J.; Wang, B.-C.; Kao, T.-H.; Tsai, K.-S.; Wu, S.-L. ZnO-based ultraviolet photodetectors with novel nanosheet structures. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2014, 13, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Effect of the growth time on the optical properties of ZnO nanorods grown by low temperature method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2017, 12, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M. The Influence of the Growth Time on the Size and Alignment of ZnO Nanorods. Sci. J. Univ. Zakho 2017, 5, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Umakoshi, T.; Abe, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Kiba, T. Determination of effective growth time for zinc oxide nanorods using chemical solution deposition. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 88, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Syafinaz, R.; Lockman, Z.; Aziz, A.A.; Razak, K.A. Properties of Al-doped ZnO nanorods synthesized using low temperature hydrothermal method. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 846, 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ainuddin, A.R.; Darus, M.A.A.; Ismail, N.S.; Kamdi, Z.; Yunos, M.Z.; Hatta, M.N.M.; Hussin, R.; Ibrahim, S.A. The Effect of Water Bath Temperature during Electrochemical Deposition of Zinc Oxide. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 9, 102481704. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, W.; Leem, J.-Y. Effect of an Electrochemically Oxidized ZnO Seed Layer on ZnO Nanorods Grown by using Electrodeposition. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.N.; Ganesh, R.S.; Karthigeyan, A. Effect of annealing temperature on structural, optical and electrical properties of hydrothermal assisted zinc oxide nanorods. Thin Solid Film. 2016, 598, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.N.; Bidin, N. Morphological driven photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 394, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.-C.; Moon, S.W.; Yu, J.S.; Choi, S. Highly reproducible Au-decorated ZnO nanorod array on a graphite sensor for classification of human aqueous humors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5891–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayathulhan, R.; Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. Nucleation and growth of zinc oxide nanorods directly on metal wire by sonochemical method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liu, X. Flexible physical sensors made from paper substrates integrated with zinc oxide nanostructures. Flex. Print. Electron. 2017, 2, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yang, R.; Zhu, K.; Hu, M. Room temperature acetone-sensing properties of branch-like VO2 (B)@ ZnO hierarchical hetero-nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 3780–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, O.; Halim, M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Oglat, A.A.; Abuelsamen, A.; Bououdina, M.; Qaeed, M. A study of the effects of aligned vertically growth time on ZnO nanorods deposited for the first time on Teflon substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Zhu, X.; Yang, D. Vertically aligned ZnO nanorods arrays grown by chemical bath deposition for ultraviolet photodetectors with high response performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efafi, B.; Mazandarani, H.; Ara, M.H.M.; Ghafary, B. Improvement in photoluminescence behavior of well-aligned ZnO nanorods by optimization of thermodynamic parameters. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 579, 411915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebil, W.; Gokarna, A.; Fouzri, A.; Hamdaoui, N.; Nomenyo, K.; Lerondel, G. Study of the growth time effect on the structural, morphological and electrical characteristics of ZnO/p-Si heterojunction diodes grown by sol-gel assisted chemical bath deposition method. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, N.; Sinthiya, M.M.A.; Kumar, M.P.; Ravichandran, S.; Babu, R.R.; Sethurman, K.; Ramamurthi, K. Investigation on the g-C3N4 encapsulated ZnO nanorods heterojunction coupled with GO for effective photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2826–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-H.; Ryu, H.; Lee, W.-J. Fast vertical growth of ZnO nanorods using a modified chemical bath deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 597, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. pH-dependent growth of zinc oxide nanorods. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 2549–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, O.; Halim, M.; Abdullah, M.; Ali, M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Allam, N.K. Growth of vertically aligned ZnO nanorods on Teflon as a novel substrate for low-power flexible light sensors. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, X.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Hu, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Synthesis, characterization and room temperature photoluminescence properties of Al doped ZnO nanorods. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2012, 44, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-P.; Lin, D.-Y.; Lu, C.-Y.; Ko, T.-S.; Chen, H.-Z. Effect of lithium doping on microstructural and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystalline films prepared by the sol-gel method. Crystals 2018, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominov, R.V.; Vakulov, Z.E.; Avilov, V.I.; Khakhulin, D.A.; Fedotov, A.A.; Zamburg, E.G.; Smirnov, V.A.; Ageev, O.A. Synthesis and Memristor Effect of a Forming-Free ZnO Nanocrystalline Films. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azlinda, A.A.; Khusaimi, Z.; Abdullah, S.; Rusop, M. Characterization of urea versus HMTA in the preparation of zinc oxide nanostructures by solution-immersion method grown on gold-seeded silicon substrate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 364, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathy, N.; Ahn, M.-S.; Hahn, Y.-B. Highly stable hydrazine chemical sensor based on vertically-aligned ZnO nanorods grown on electrode. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjith, K.; Kumar, R.R. Facile construction of vertically aligned ZnO nanorod/PEDOT: PSS hybrid heterojunction-based ultraviolet light sensors: Efficient performance and mechanism. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 095304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holi, A.M.; Zainal, Z.; Talib, Z.A.; Lim, H.-N.; Yap, C.-C.; Chang, S.-K.; Ayal, A.K. Effect of hydrothermal growth time on ZnO nanorod arrays photoelectrode performance. Optik 2016, 127, 11111–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammel, R.S.; Sabry, R.S. Effects of the aspect ratio of ZnO nanorods on the performance of piezoelectric nanogenerators. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Enhancement of ZnO Nanorods Properties Using Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Method: Effect of Precursor Concentration. Crystals 2020, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Sánchez, V.; Cano, A.D.; Mendoza, L.R. Characterization of vertically aligned zinc oxide nanorods via a rapid microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis process. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2017, 941–949. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Different substrates effects on the topography and the structure of the ZnO nanorods grown by chemical bath deposition method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2016, 11, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, G.; Asif, M.; Zainelabdin, A.; Zaman, S.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Influence of pH, precursor concentration, growth time, and temperature on the morphology of ZnO nanostructures grown by the hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 269692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuyisa, P.; Ndwandwe, O.; Cepek, C. Controlled growth of zinc oxide nanorods synthesised by the hydrothermal method. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 578, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwankemwa, B.S.; Nambala, F.J.; Kyeyune, F.; Hlatshwayo, T.T.; Nel, J.M.; Diale, M. Influence of ammonia concentration on the microstructure, electrical and raman properties of low temperature chemical bath deposited ZnO nanorods. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 71, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Fabrication, characterization of ZnO nanorods on the flexible substrate (Kapton tape) via chemical bath deposition for UV photodetector applications. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2017; p. 020004. [Google Scholar]
- Shewale, P.; Yu, Y. Structural, surface morphological and UV photodetection properties of pulsed laser deposited Mg-doped ZnO nanorods: Effect of growth time. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 654, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-F.; Shen, C.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Shih, P.-Y.; Chou, W.-H.; Su, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-S.; Liao, C.-H.; Chang, W.-M.; Kiang, Y.-W. Void structures in regularly patterned ZnO nanorods grown with the hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 756401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, M.N.; Manavizadeh, N.; Nayeri, F.D.; Bidgoli, M.M.; Nadimi, E.; Boroumand, F.A. Effect of seed layers on low-temperature, chemical bath deposited ZnO nanorods-based near UV-OLED performance. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4937–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, F.; Viorica, M.; Nicolae, T.; Silviu, P.; Ana, P.; Sofia, F.; Daniela, G.; Tomás, C.; Rodrigo, M.; Elvira, F. ZnO nanostructures grown on ITO coated glass substrate by hybrid microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Optik 2020, 208, 164372. [Google Scholar]
- Lah, N.A.C.; Kamaruzaman, A. The optical quantification measurement on aggregated aqueous ZnO nanostructures upon exposure to tannic acid. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125046. [Google Scholar]
- Akhiruddin, A.; Sugianto, S.; Irmansyah, I. The Influence of Hydrothermal Duration on Structures and Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2015, 2, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.F.; Mamat, M.H.; Soga, T.; Rahman, S.A.; Bakar, S.A.; Ismail, A.S.; Mohamed, R.; Alrokayan, S.A.; Khan, H.A.; Mahmood, M.R. Thickness-controlled synthesis of vertically aligned c-axis oriented ZnO nanorod arrays: Effect of growth time via novel dual sonication sol–gel process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 55, 01AE15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.C.; Hwang, S.M.; Lee, S.M.; Choi, J.H.; Song, K.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Eum, S.-J.; Jung, S.-B.; Lim, J.H. Hydrothermally grown in-doped ZnO nanorods on p-GaN films for color-tunable heterojunction light-emitting-diodes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M. Investigation of Optical Properties of ZnO Nanorods Grown on Different Substrates. Sci. J. Univ. Zakho 2018, 6, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Kaur, K.; Vasisth, A.; Verma, N. Synthesis and characterization of Gd-doped ZnO nanorods. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; p. 020015. [Google Scholar]
- Shewale, P.; Yu, Y. The effects of pulse repetition rate on the structural, surface morphological and UV photodetection properties of pulsed laser deposited Mg-doped ZnO nanorods. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 7125–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezbicke, B.D.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.E.; Birnie, D.P., III. Evaluation of the Tauc method for optical absorption edge determination: ZnO thin films as a model system. Phys. Status Solidi 2015, 252, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimpoor, A.; Erb, U.; Aust, K.; Palumbo, G. High strength nanocrystalline cobalt with high tensile ductility. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israr, M.Q.; Sadaf, J.R.; Yang, L.-L.; Nur, O.; Willander, M.; Palisaitis, J.; Persson, P.Å. Trimming of aqueous chemically grown ZnO nanorods into ZnO nanotubes and their comparative optical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 073114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, F.; Talin, A.A. Electrical contacts to one-and two-dimensional nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, A.M.; Hassan, Z.; Husham, M.; Ahmed, N.M. A high-sensitivity, fast-response, rapid-recovery p–n heterojunction photodiode based on rutile TiO2 nanorod array on p-Si (1 1 1). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, B.; Jöesaar, M.J.; Polcik, P.; Kolozsvari, S.; Håkansson, G.; Johnson, L.; Ahlgren, M.; Odén, M. Effect of work function and cohesive energy of the constituent phases of Ti-50 at.% Al cathode during arc deposition of Ti-Al-N coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 357, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Lee, K.; Yoon, M.-H.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J.; Janes, D.B. High performance ZnO nanowire field effect transistors with organic gate nanodielectrics: Effects of metal contacts and ozone treatment. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 155201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.-J.; Park, K.-S.; Heo, J.-H.; Park, J.-G.; Nahm, S.; Choi, K.J. Synthesis of ZnxCd1−xSe (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) alloyed nanowires for variable-wavelength photodetectors. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2386–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabannia, R. High-sensitivity UV photodetector based on oblique and vertical Co-doped ZnO nanorods. Mater. Lett. 2018, 214, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, M.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, S. Influences of different interdigital spacing on the performance of UV photodetectors based on ZnO nanofibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, K.; Yue, C.Y.; Wei, J.; Pan, Y. Recent progress in synthesis, properties and potential applications of SiC nanomaterials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M. Progress in semiconductor diamond photodetectors and MEMS sensors. Funct. Diam. 2021, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Hashim, M.; Allam, N.K. Low power UV photodetection characteristics of cross-linked ZnO nanorods/nanotetrapods grown on silicon chip. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 192, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayatian, A.; Kashi, M.A.; Azimirad, R.; Safa, S.; Akhtarian, S.A. Effect of annealing process in tuning of defects in ZnO nanorods and their application in UV photodetectors. Optik 2016, 127, 4675–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, S.; Mokhtari, S.; Khayatian, A.; Azimirad, R. Improving ultraviolet photodetection of ZnO nanorods by Cr doped ZnO encapsulation process. Opt. Commun. 2018, 413, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Ganbavale, V.; Mohite, S.; Patil, U.; Rajpure, K. ZnO nanorod based highly selective visible blind ultra-violet photodetector and highly sensitive NO2 gas sensor. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 120, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Li, C.; Yin, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, S. Synthesis of single-crystalline GeS nanoribbons for high sensitivity visible-light photodetectors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8074–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N.; Hashim, M. Porous-shaped silicon carbide ultraviolet photodetectors on porous silicon substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 552, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Zhu, X.; Yang, D. Effect of annealing temperature on the performance of photoconductive ultraviolet detectors based on ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabbina, P.K.; Kaushik, A.; Pokhrel, N.; Bhansali, S.; Pala, N. Electrochemical cortisol immunosensors based on sonochemically synthesized zinc oxide 1D nanorods and 2D nanoflakes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingying, L.; Chuanwei, C.; Xiang, D.; Junshan, G.; Haiqian, Z. Facile fabrication of UV photodetectors based on ZnO nanorod networks across trenched electrodes. J. Semicond. 2009, 30, 063004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, Y.; Kumar, H.; Vyas, S.; Periasamy, C.; Chakrabarti, P.; Jit, S.; Park, S.-H. A study of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorod-based metal-semiconductor-metal UV detectors on glass substrates. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2017, 7, 1847980417702144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, J.S. Metal-semiconductor-metal near-ultraviolet (~380 nm) photodetectors by selective area growth of ZnO nanorods and SiO 2 passivation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodwihok, C.; Choopun, S.; Ruankham, P.; Gardchareon, A.; Phadungdhitidhada, S.; Wongratanaphisan, D. UV sensing properties of ZnO nanowires/nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 477, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, G.; Liu, N.; Zhao, X. Ultraviolet photodetectors based on ZnO nanorods-seed layer effect and metal oxide modifying layer effect. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiss, B.A.; AL-Akhras, M.-A.; Obaidat, I. Ultraviolet photodetector based on ZnO nanorods grown on a flexible PDMS substrate. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabannia, R.; Hassan, H.A.; Mahmodi, H.; Naderi, N.; Abd, H. ZnO nanorod ultraviolet photodetector on porous silicon substrate. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2013, 28, 115007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Hassan, Z.; Ahmed, N.M.; Al-Hardan, N.; Bououdina, M. Fabrication of low cost UV photo detector using ZnO nanorods grown onto nylon substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabannia, R.; Hassan, H.A. Characteristics of photoconductive UV photodetector based on ZnO nanorods grown on polyethylene naphthalate substrate by chemical bath deposition method. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2014, 10, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsultany, F.H.; Hassan, Z.; Ahmed, N.M. A high-sensitivity, fast-response, rapid-recovery UV photodetector fabricated based on catalyst-free growth of ZnO nanowire networks on glass substrate. Opt. Mater. 2016, 60, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, Y.; Numai, T.; Kasahara, K.; Kuboto, K. Light detection sensitivity of a vertical cavity structure used in an optical switch device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


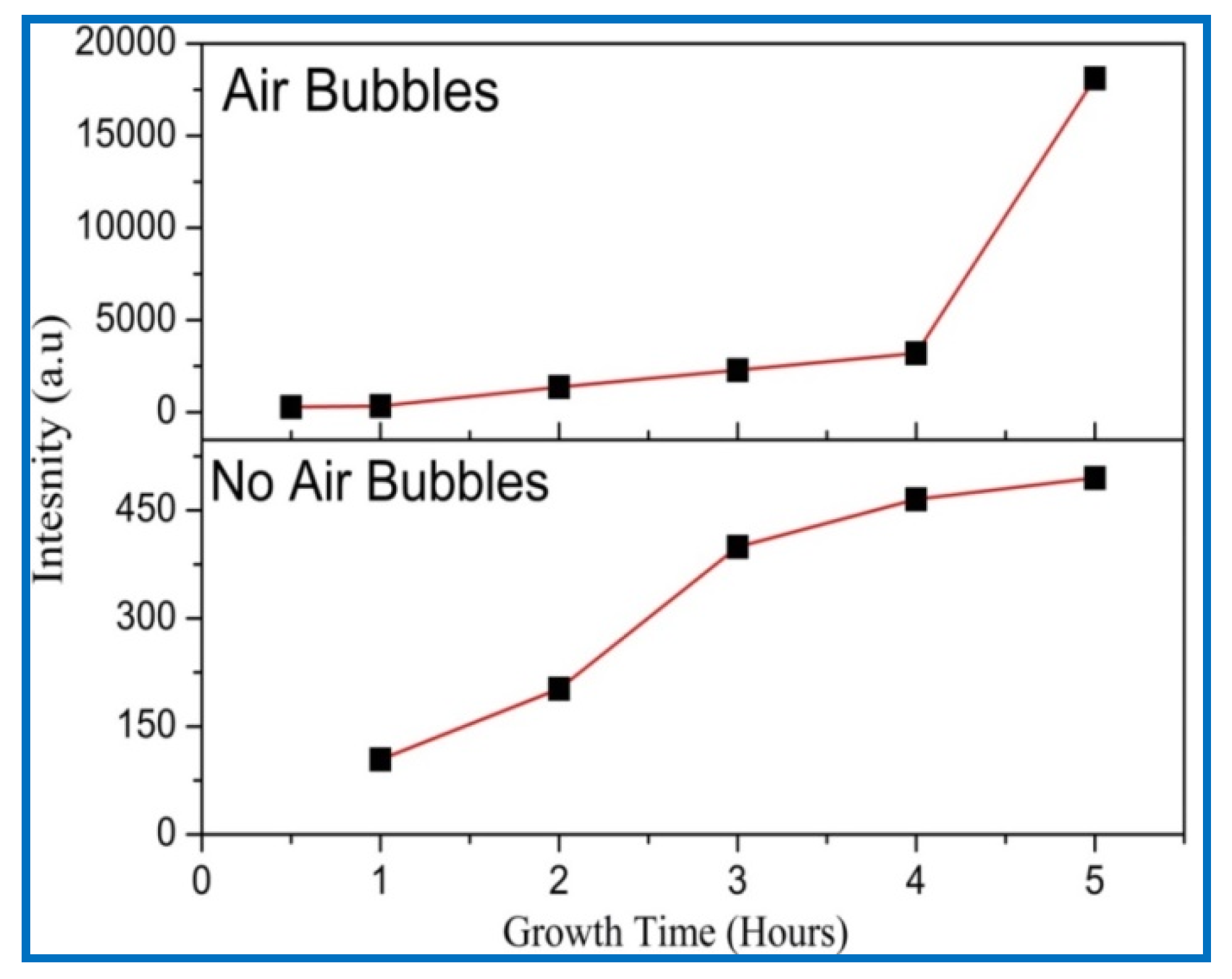
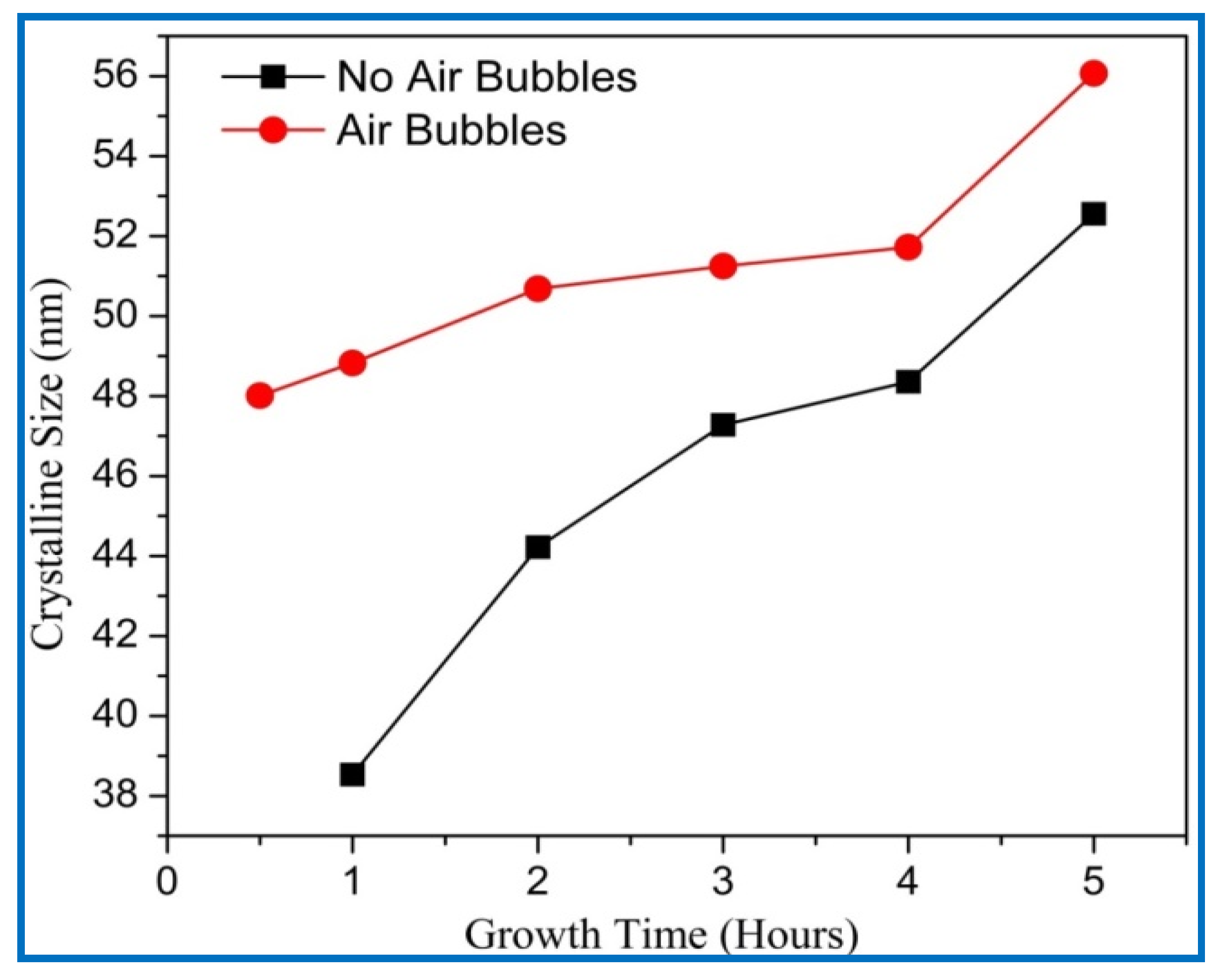


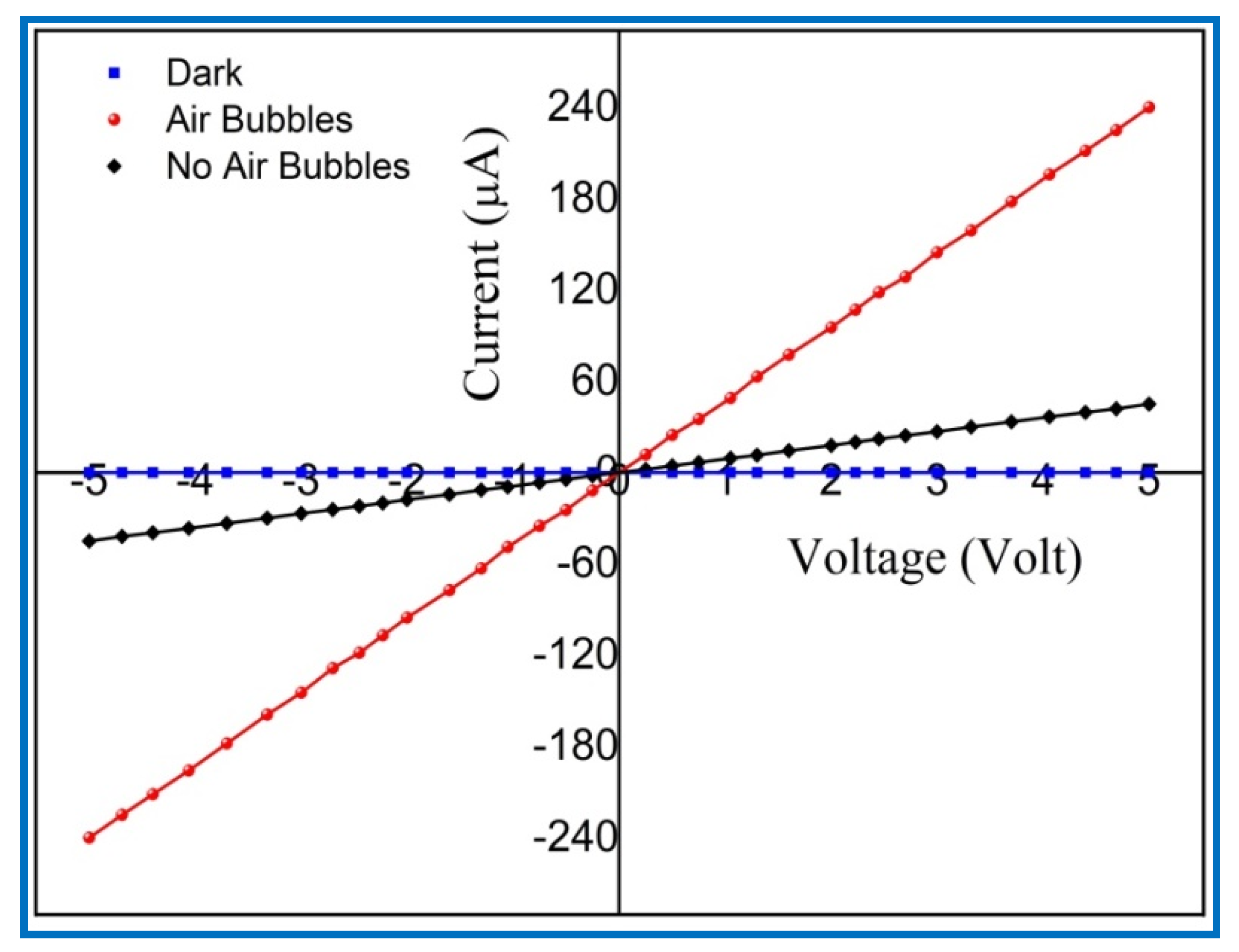
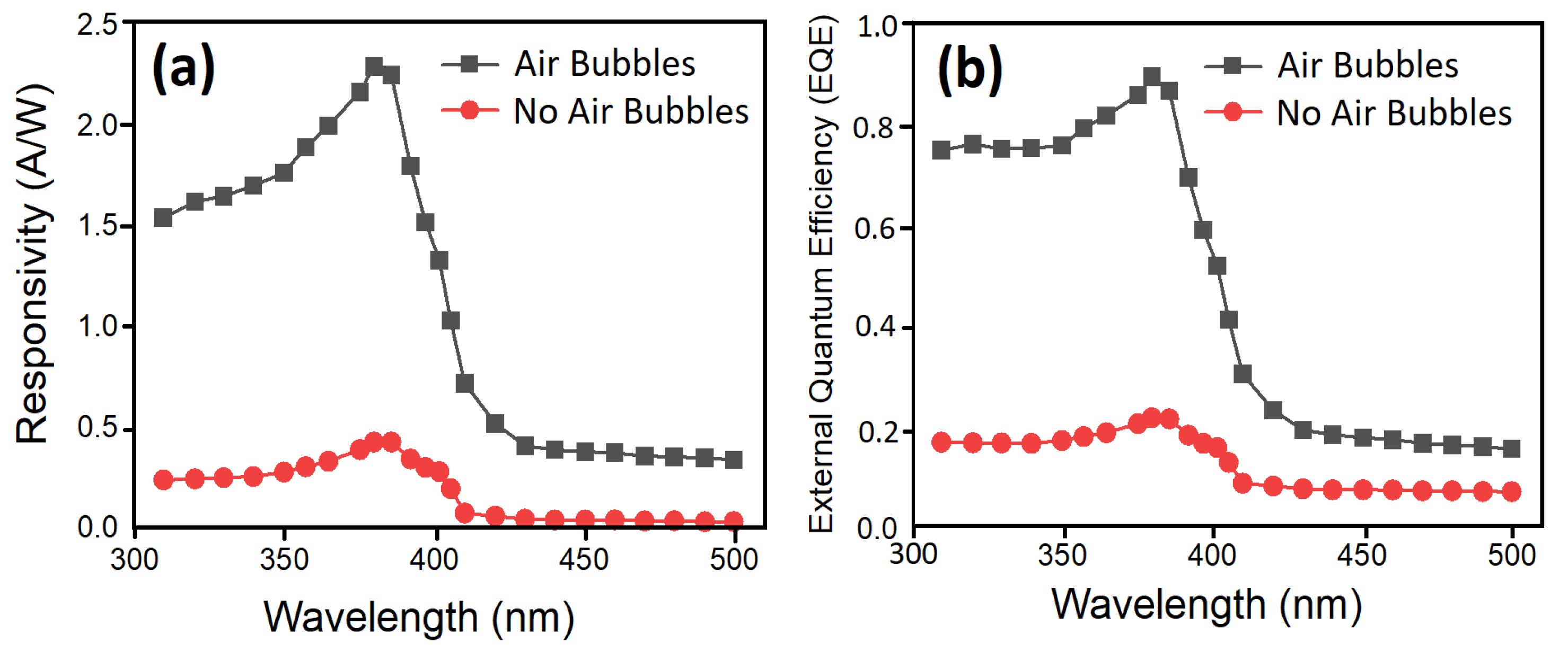

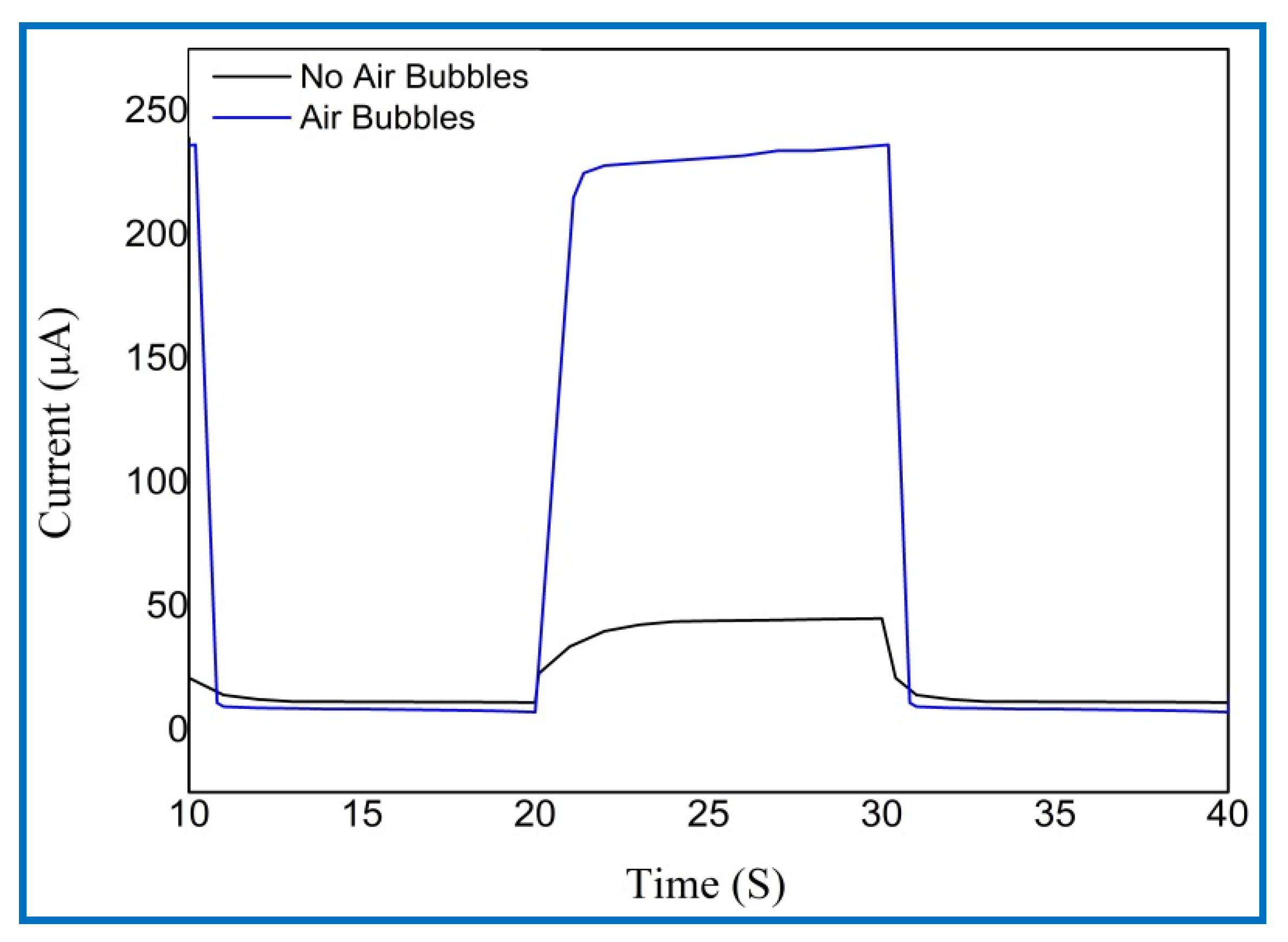
| Growth Duration (h) | 2θ | I (a. u) | a (Å) | c (Å) | Ƹa% | Ƹc% | d (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34.375 | 104 | 3.0100 | 5.213 | −7.483 | −0.029 | 2.606 |
| 2 | 34.425 | 202 | 3.0058 | 5.206 | −7.625 | −0.069 | 2.603 |
| 3 | 34.425 | 399 | 3.0058 | 5.206 | −7.625 | −0.069 | 2.603 |
| 4 | 34.425 | 465 | 3.0058 | 5.206 | −7.625 | −0.069 | 2.603 |
| 5 | 34.375 | 495 | 3.0100 | 5.213 | −7.483 | −0.029 | 2.606 |
| Growth Duration (h) | 2θ | I (a. u) | a (Å) | c (Å) | Ƹa% | Ƹc% | d (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 34.375 | 282 | 3.01004 | 5.2135 | −7.483 | −0.0299 | 2.6067 |
| 1 | 34.382 | 328 | 3.00941 | 5.2125 | −7.502 | −0.0507 | 2.6062 |
| 2 | 34.383 | 1373 | 3.00931 | 5.2123 | −7.505 | −0.0541 | 2.6061 |
| 3 | 34.393 | 2284 | 3.00853 | 5.2109 | −7.529 | −0.0800 | 2.6055 |
| 4 | 34.400 | 3206 | 3.00786 | 5.2097 | −7.550 | −0.1023 | 2.6049 |
| 5 | 34.425 | 18,114 | 3.00580 | 5.2062 | −7.613 | −0.1707 | 2.6031 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Fabrication and Characterization of High-Quality UV Photodetectors Based ZnO Nanorods Using Traditional and Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Methods. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030677
Abdulrahman AF, Ahmed SM, Barzinjy AA, Hamad SM, Ahmed NM, Almessiere MA. Fabrication and Characterization of High-Quality UV Photodetectors Based ZnO Nanorods Using Traditional and Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Methods. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030677
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdulrahman, Ahmed Fattah, Sabah Mohammed Ahmed, Azeez Abdullah Barzinjy, Samir Mustafa Hamad, Naser Mahmoud Ahmed, and Munirah Abullah Almessiere. 2021. "Fabrication and Characterization of High-Quality UV Photodetectors Based ZnO Nanorods Using Traditional and Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Methods" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030677
APA StyleAbdulrahman, A. F., Ahmed, S. M., Barzinjy, A. A., Hamad, S. M., Ahmed, N. M., & Almessiere, M. A. (2021). Fabrication and Characterization of High-Quality UV Photodetectors Based ZnO Nanorods Using Traditional and Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Methods. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030677










