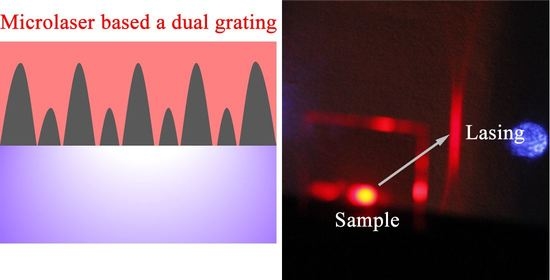
Low-Threshold Microlasers Based on Holographic Dual-Gratings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication Methods
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hide, R.; Díaz-García, M.; Schwartz, B.; Andersson, M.; Pei, Q.; Heeger, A. Semiconducting polymers: A new class of solid-state laser materials. Science 1996, 273, 1833–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, N.; Denton, G.; Friend, R. Lasing from conjugated-polymer microcavities. Nature 1996, 382, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, M.; Glackin, J.M.E.; Schubert, M.; Kronenberg, N.M.; Turnbull, G.A.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Gather, M.C. Flexible and ultra-lightweight polymer membrane lasers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ta, V.; Leck, K.; Tan, B.; Wang, Z.; He, T.; Ohl, C.; Demir, H.V.; Sun, H. Robust whispering-gallery-mode microbubble lasers from colloidal quantum dots. Nano. Lett. 2017, 17, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, N.; Hirano, Y.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W. Influence of an interfacial effect on the laser performance of a rhodamine 6G/cellylose acetate waveguide on a vinylidene fluoride copolymer layer. Langmuir 2018, 34, 7527–7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Oe, K.; Yanag, H. Simultaneous RGB lasing from a single-chip polymer device. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2451–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, A.; Tong, J.; Chen, C.; Niu, L.; Aziz, G.; Zhang, T.Z.X. Multi-wavelength colloidal quantum dot lasers in distributed feedback cavities. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 182401:1–182401:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Precise assembly of particles for zigzag or linearPatterns. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 15348–15352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görrn, P.; Lehnhardt, M.; Kowalsky, W.; Riedl, T.; Wagner, S. Elastically tunable self-organized organic lasers. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingruber, R.; Mohrle, M.; Sigmund, A.; Furst, W. Continuously chirped gratings for DFB-lasers fabricated by direct write electron-beam lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 61, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Cao, F.; Chu, S.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, X. Continuously tunable distributed feedback polymer laser. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 4491–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balslev, S.; Rasmussen, T.; Shi, P.; Kristensen, A. Single mode solid state distributed feedback dye laser is fabricated by gray scale electron beam lithography on a dye doped SU-8 resist. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdas, E.; Tong, M.; Ledochowitsch, P.; Mednick, S.; Yuen, J.; Moses, D.; Heege, A. Low thresholds in polymer lasers on conductive substrates by distributed feedback nanoimprinting: Progress toward electrically pumped plastic lasers. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, E.; Camposeo, A.; Stabile, R.; del Carro, P.; di Benedetto, F.; Persano, L.; Cingolani, R.; Pisignano, D. Polymeric distributed feedback lasers by room-temperature nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 131109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisignano, D.; Persano, L.; Visconti, P.; Cingolani, R.; Gigli, G. Oligomer-based organic distributed feedback lasers by room-temperature nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2545–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Zhang, X.; Pang, Z.; Dou, F. Direct writing of polymer lasers using interference ablation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.H.; Ding, R.; Lu, S.Y.; Wang, L.; Feng, J.; Chen, Q.D.; Sun, H.B. Direct laser interference ablating nanostructures on organic crystals. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Direct writing of tunable multi-wavelength polymer lasers on a flexible substrate. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, S.; Kollosche, M.; Rabe, T.; Stumpe, J.; Kofod, G. Electrically tunable polymer DFB laser. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Chen, C.; Tong, J.; Cui, L.; Zhai, T. Manipulating the performance of polymer lasers using diffraction elements. Org. Electron. 2020, 84, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Mu, Q.; Peng, Z.; Yang, C.; Xuan, L. Second-order distributed feedback polymer laser based on holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal grating. Org. Electron. 2013, 14, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reufer, M.; Riechel, S.; Lupton, J.M.; Feldmann, J. Low-threshold polymeric distributed feedback lasers with metallic contacts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 3262–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Pu, D.; Yang, X.; Wei, G.; Zhou, Z.F.X.; Qiao, W.; Chen, L. A high-order external distributed feedback polymer laser with low working threshold. J. Phys. D 2016, 49, 175106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.L.; Zhai, T.R. Distributed feedback organic lasing in photonics crystals. Front. Optoelectron. 2020, 13, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnutsch, C.; Gyrtner, C.; Haug, V.; Lemmer, U. Low threshold blue conjugated polymer lasers with first- and second-order distributed feedback. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 89, 2011108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnutsch, C.; Pflumm, C.; Heliotis, G.; deMello, J.C.; Bradley, D.D.C.; Wang, J.; Weimann, T.; Haug, V.; Gärtner, C.; Lemmer, U. Improved organic semiconductor lasers based on a mixed-order distributed feedback resonator design. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 131104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazarinov, R.; Henry, C. Second-order distributed feedback lasers with mode selection provided by first-order radiation losses. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1985, 21, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.; Wang, Y.; Kanibolotsky, A.; Skabara, P.; Turnbull, G.; Samuel, I. Low-threshold nanoimprinted lasers using substructured gratings for control of distributed feedback. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2013, 1, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, T.; Han, L.; Ma, X.; Wang, X. Low-Threshold Microlasers Based on Holographic Dual-Gratings. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061530
Zhai T, Han L, Ma X, Wang X. Low-Threshold Microlasers Based on Holographic Dual-Gratings. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Tianrui, Liang Han, Xiaojie Ma, and Xiaolei Wang. 2021. "Low-Threshold Microlasers Based on Holographic Dual-Gratings" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061530
APA StyleZhai, T., Han, L., Ma, X., & Wang, X. (2021). Low-Threshold Microlasers Based on Holographic Dual-Gratings. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061530