Combination of Selective Etching and Impregnation toward Hollow Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles
2.2. Synthesis of Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Etching
2.3. Incorporation of Calcium by Impregnation
2.4. Characterization of HMBGNs
2.5. In-Vitro Hydroxyapatite Formation
2.6. Cell Viability
2.7. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
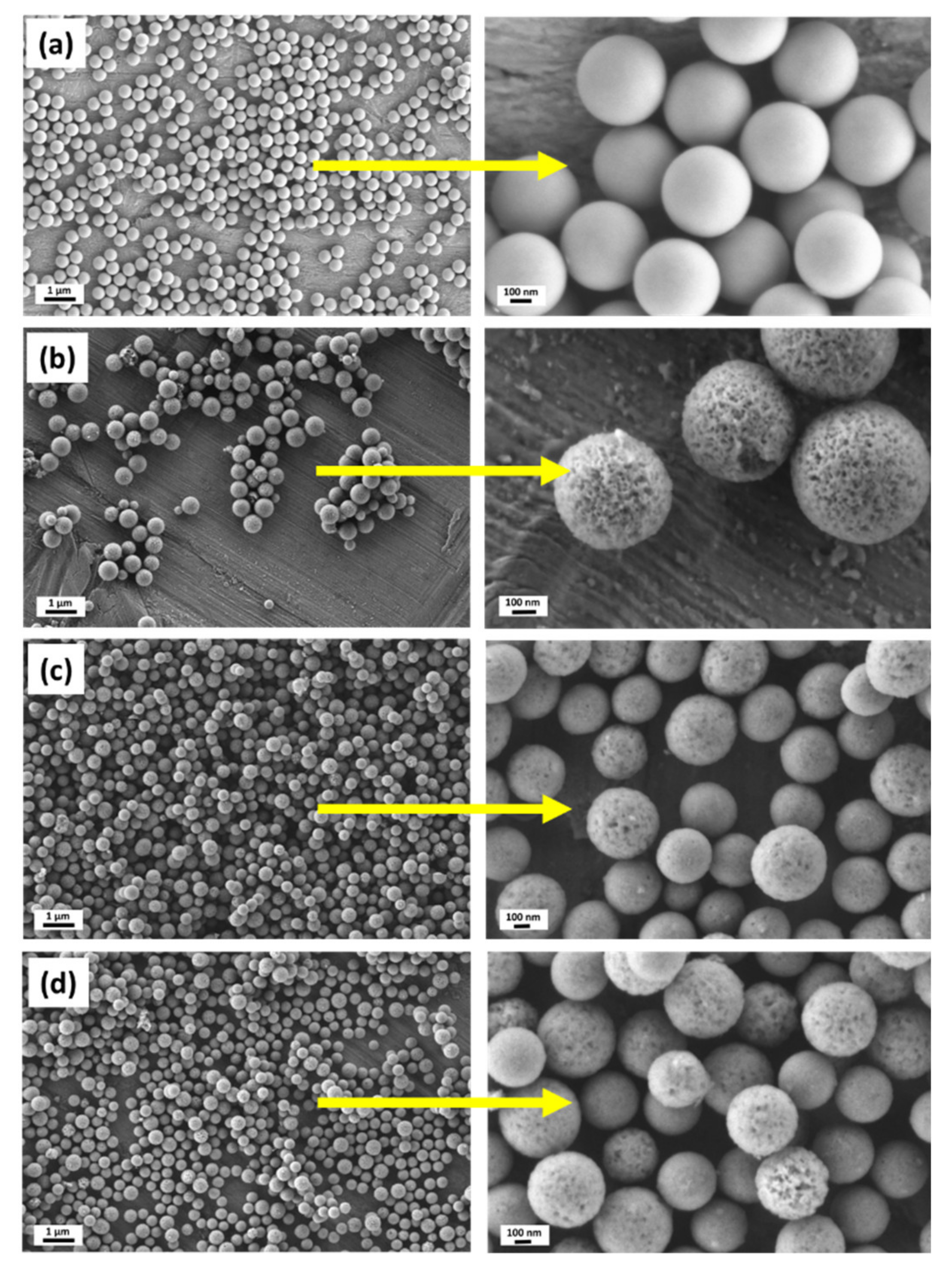
3.1. Synthesis of Hollow Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Particles
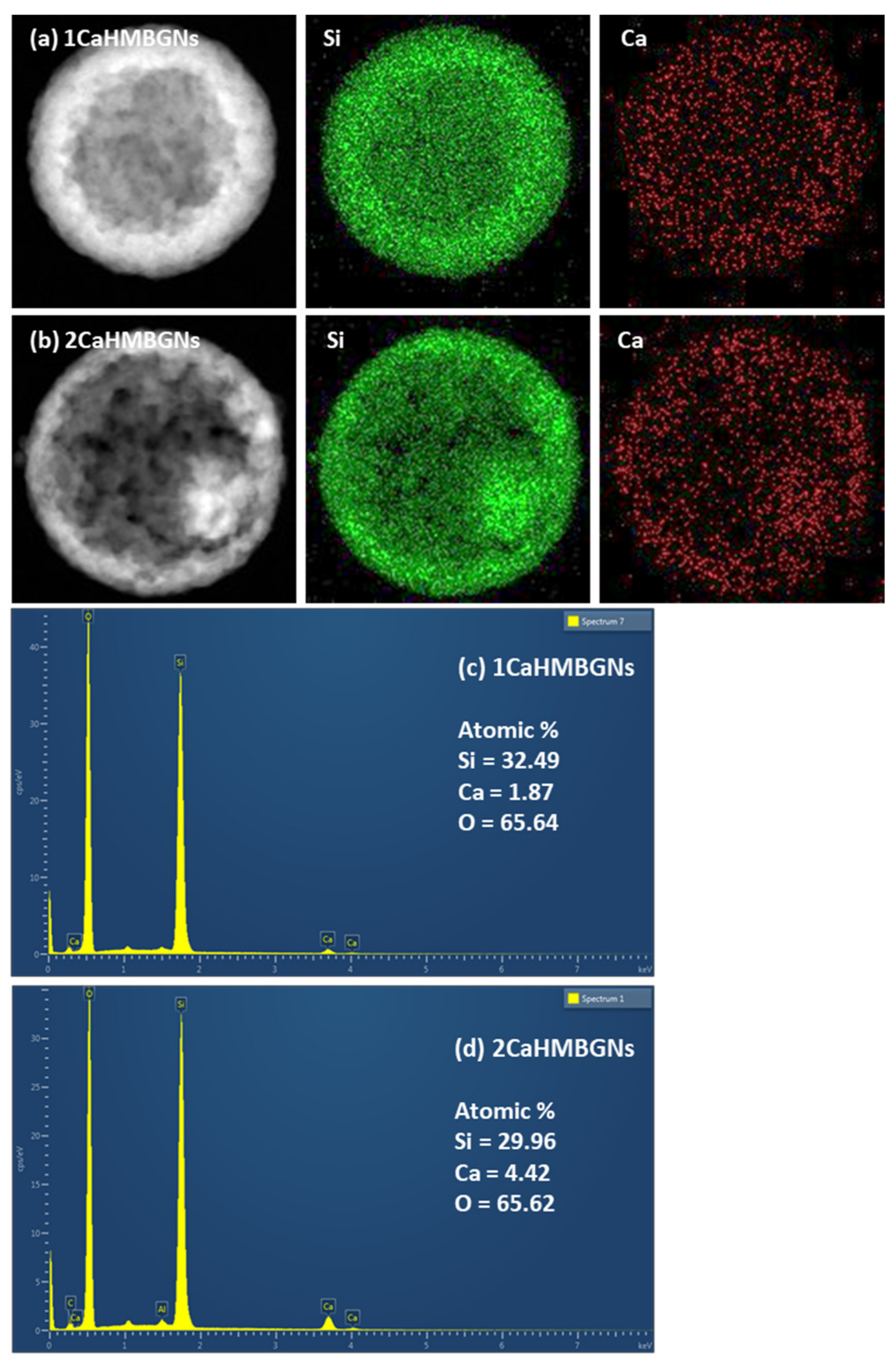
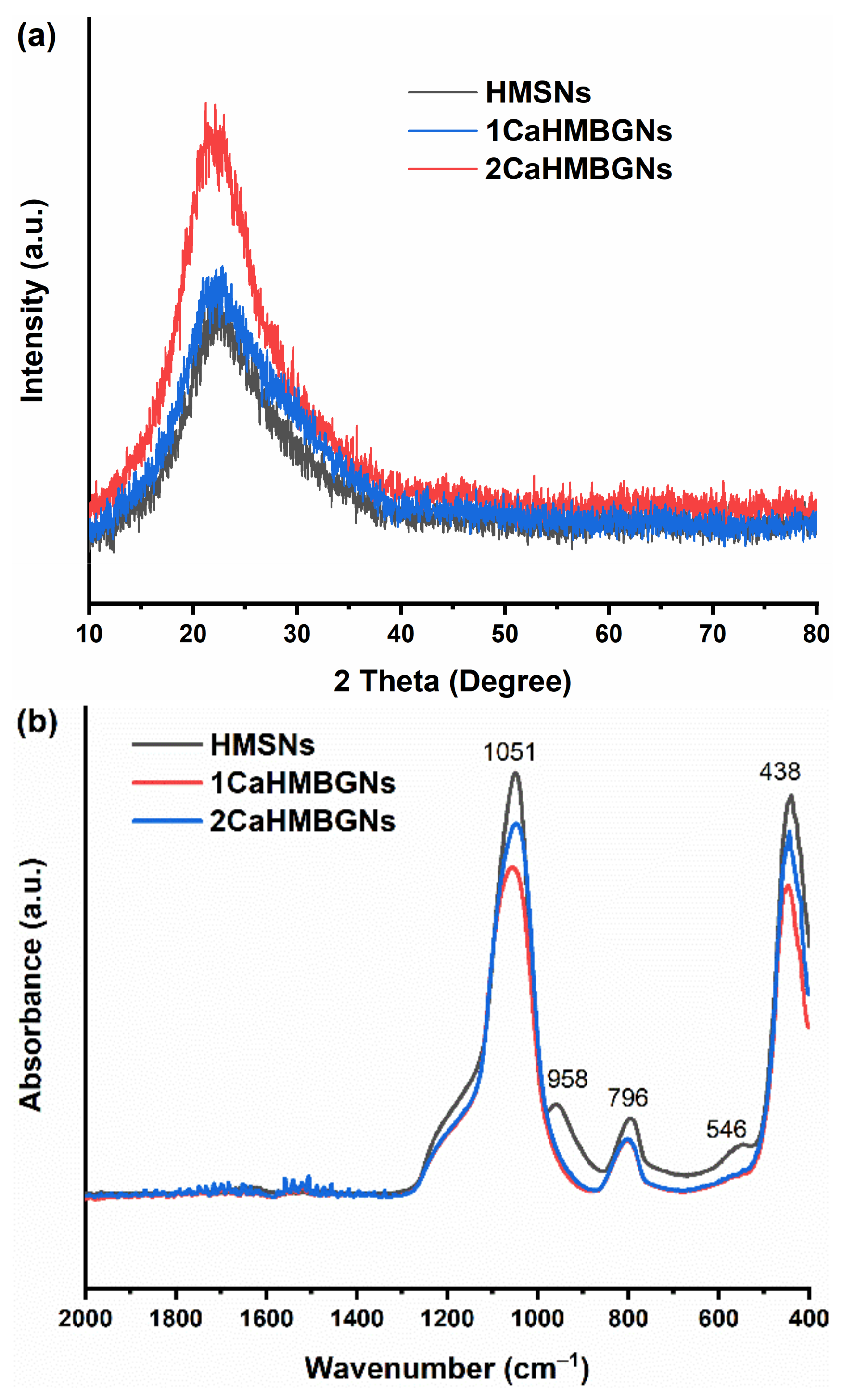
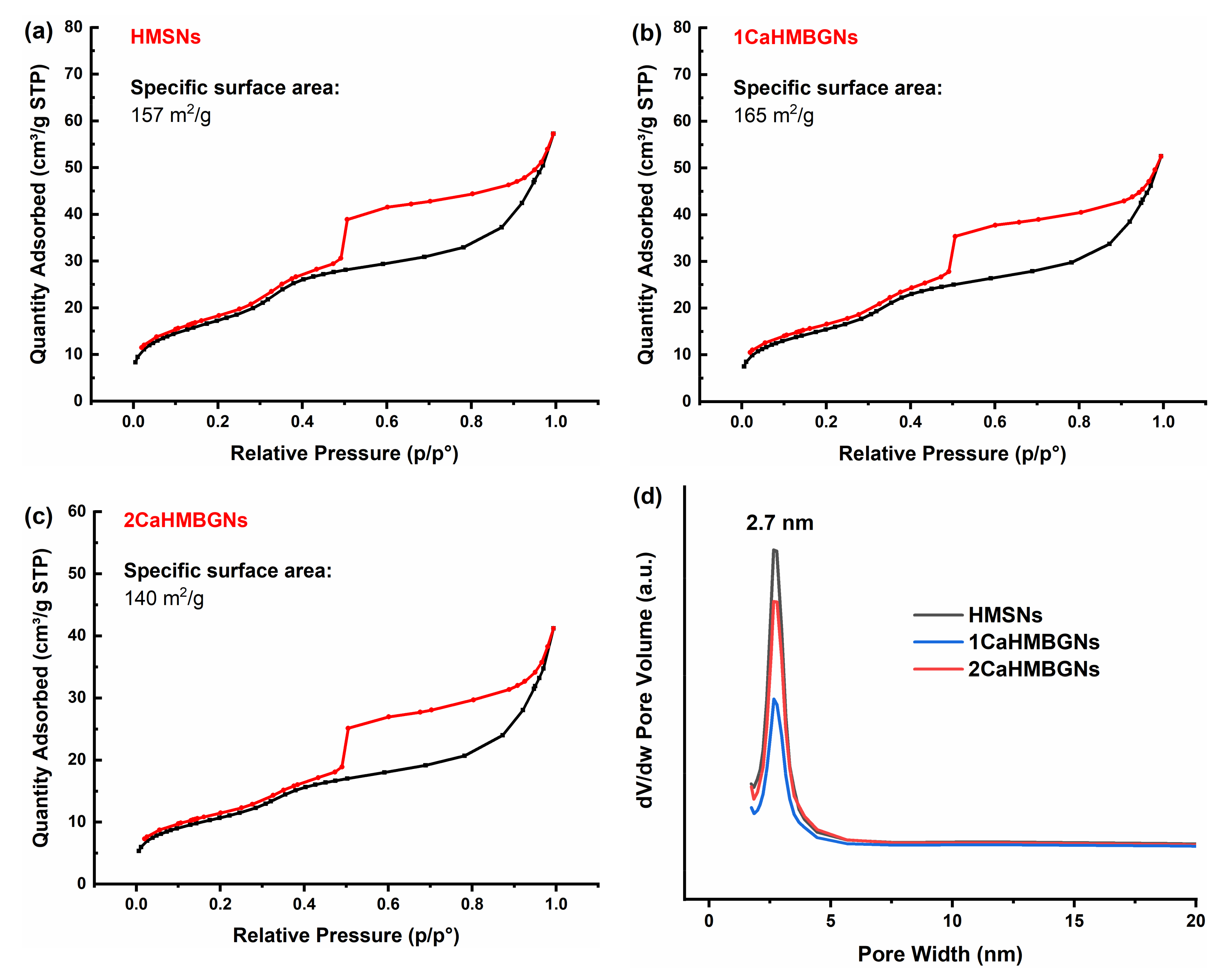
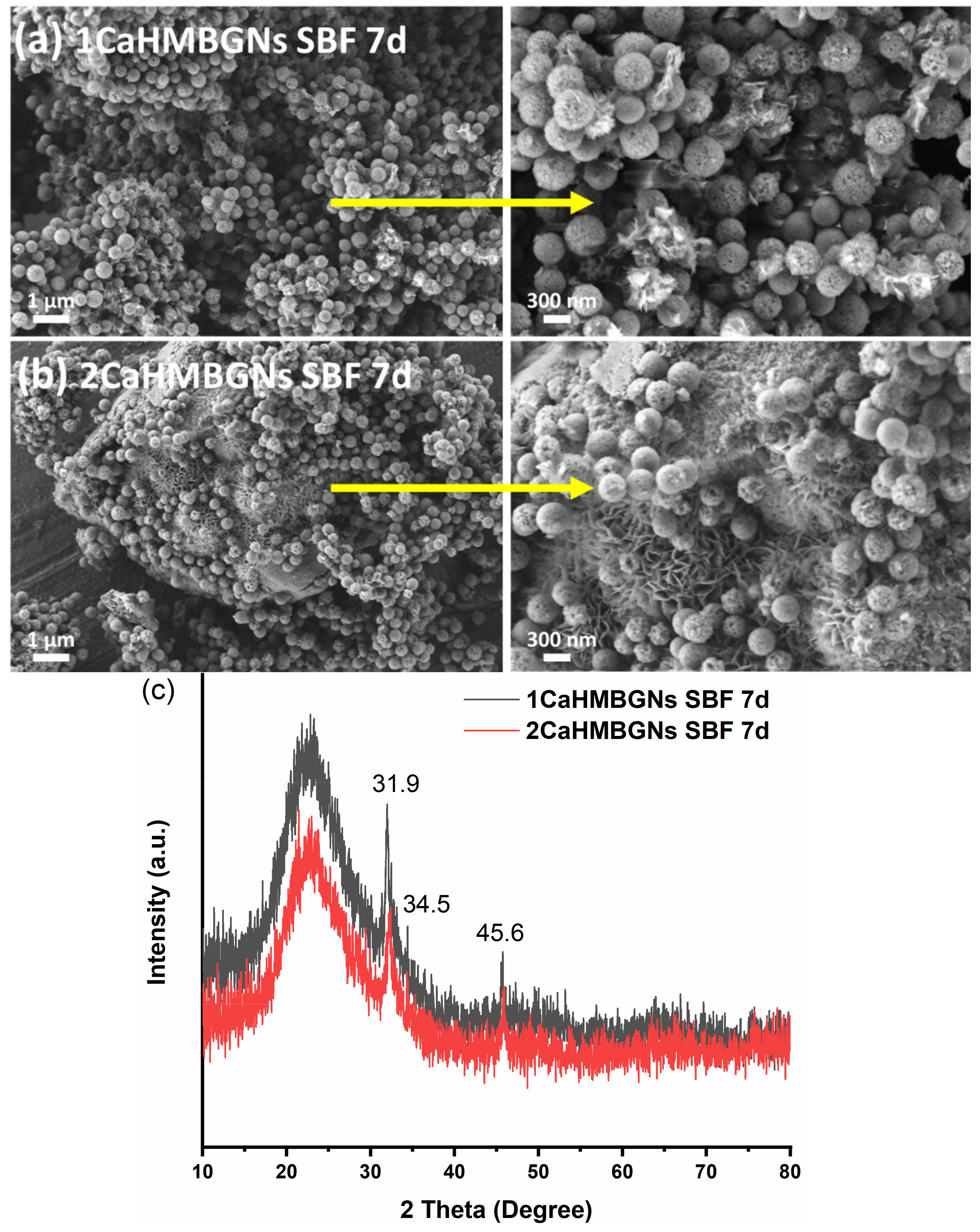
3.2. Structural Characterization and In-Vitro Apatite Forming Ability of HMBGNs
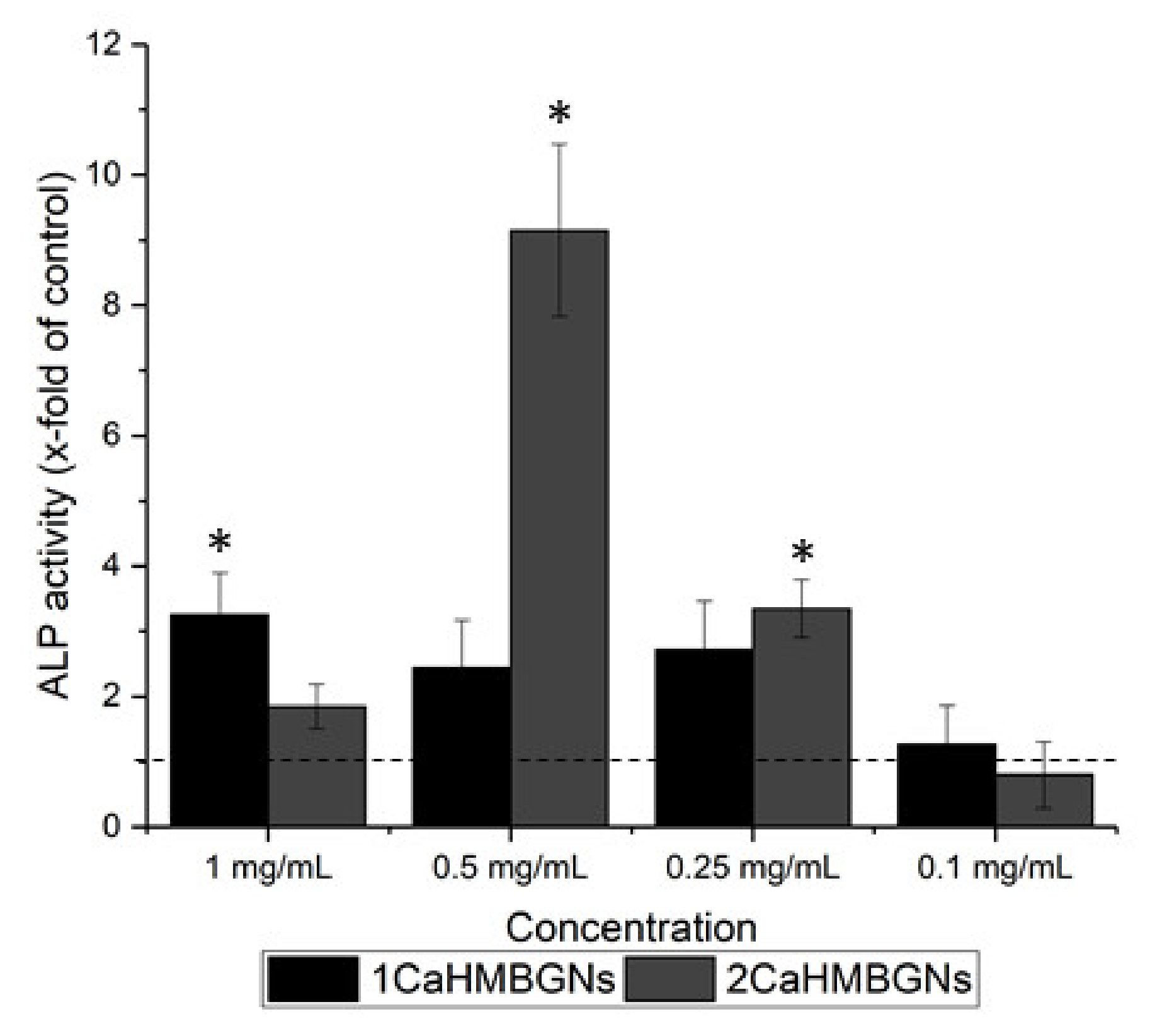
3.3. In-Vitro Cytotoxicity and ALP Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Sol-gel processing of bioactive glass nanoparticles: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R. Reprint of: Review of bioactive glass: From hench to hybrids. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23, S53–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Sui, B.; Ilyas, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Porous bioactive glass micro- and nanospheres with controlled morphology: Developments, properties and emerging biomedical applications. Mater. Horizons 2021, 8, 300–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Diao, J.; Zhao, N.; Ma, Y. Synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glass microspheres with tunable shell thickness by hydrothermal-assisted self-transformation method. Mater. Lett. 2016, 167, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Facile synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glasses with tunable shell thickness and good monodispersity by micro-emulsion method. Mater. Lett. 2017, 189, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, H.; Chen, X. The preparation of hollow mesoporous bioglass nanoparticles with excellent drug delivery capacity for bone tissue regeneration. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Ma, B.; Hung, C.-T.; Li, W.; Zhao, D. Spherical mesoporous materials from single to multilevel architectures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2928–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable structures for controlled drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. Construction of homogenous/heterogeneous hollow mesoporous silica nanostructures by silica-etching chemistry: Principles, synthesis, and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Ning, C.; Chen, X. Facile synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glass sub-micron spheres with a tunable cavity size. Mater. Lett. 2014, 134, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bastakoti, B.P.; Yamauchi, Y. Smart soft-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glass spheres. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 8038–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhang, L.; Zi, Y. Facile synthesis of hollow bioactive glass nanospheres with tunable size. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Synthesis, Properties, and applications of hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10983–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C. Bioactive SiO2-CaO-P2O5 hollow nanospheres for drug delivery. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2016, 447, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Bortuzzo, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Roether, J.; Lu, M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bio-templated bioactive glass particles with hierarchical macro–nano porous structure and drug delivery capability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Torre, E.; Bari, A.; Taccardi, N.; Cassinelli, C.; Morra, M.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Iviglia, G.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antioxidant mesoporous ce-doped bioactive glass nanoparticles with anti-inflammatory and pro-osteogenic activities. Mater. Today Bio 2020, 5, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapp, M.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Zheng, K. Protein adsorption on SiO2-CaO bioactive glass nanoparticles with controllable ca content. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greasley, S.L.; Page, S.J.; Sirovica, S.; Chen, S.; Martin, R.A.; Riveiro, A.; Hanna, J.V.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Controlling particle size in the stöber process and incorporation of calcium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Zheng, N. A cationic surfactant assisted selective etching strategy to hollow mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, N. Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Kang, J.; Rutkowski, B.; Gawȩda, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Founier, N.; Sitarz, M.; Taccardi, N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Toward highly dispersed mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles with high Cu concentration using Cu/ascorbic acid complex as precursor. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, H.; Serra, J.; González, P.; León, B. Structural study of sol-gel silicate glasses by IR and raman spectroscopies. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajda, A.; Sitarz, M. Structural and microstructural comparison of bioactive melt-derived and gel-derived glasses from CaO-SiO2 binary system. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 8856–8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadipour Moghaddam, S.P.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Ghandehari, H. Glutathione-sensitive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 282, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. The story of Bioglass®. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbaf, S.; Tsigkou, O.; Müller, K.H.; Stevens, M.M.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Spherical bioactive glass particles and their interaction with human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. Cytotoxicity of nanopartides. Small 2008, 4, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Y. Intracellular localization and cytotoxicity of spherical mesoporous silica nano-and microparticles. Small 2009, 5, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Park, K. Oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses induced by silica nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 184, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Hu, X.; Sun, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, M.; et al. Toxicity and mechanism of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in eyes. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13637–13653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkou, O.; Labbaf, S.; Stevens, M.M.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Monodispersed bioactive glass submicron particles and their effect on bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mutlu, N.; Beltrán, A.M.; Nawaz, Q.; Michálek, M.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Zheng, K. Combination of Selective Etching and Impregnation toward Hollow Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071846
Mutlu N, Beltrán AM, Nawaz Q, Michálek M, Boccaccini AR, Zheng K. Combination of Selective Etching and Impregnation toward Hollow Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071846
Chicago/Turabian StyleMutlu, Nurshen, Ana Maria Beltrán, Qaisar Nawaz, Martin Michálek, Aldo R. Boccaccini, and Kai Zheng. 2021. "Combination of Selective Etching and Impregnation toward Hollow Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071846
APA StyleMutlu, N., Beltrán, A. M., Nawaz, Q., Michálek, M., Boccaccini, A. R., & Zheng, K. (2021). Combination of Selective Etching and Impregnation toward Hollow Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071846









