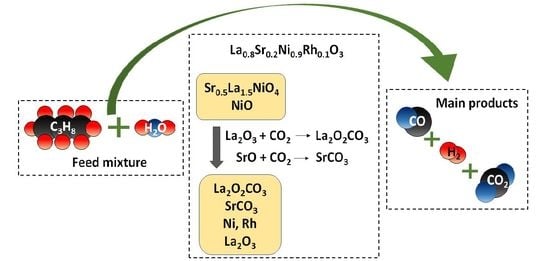
Propane Steam Reforming over Catalysts Derived from Noble Metal (Ru, Rh)-Substituted LaNiO3 and La0.8Sr0.2NiO3 Perovskite Precursors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Perovskite-Type Oxides
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Performance Tests
2.4. Temperature-Programmed Oxidation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of the as-Prepared Perovskite Samples
3.2. Catalytic Performance Tests
3.3. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Used Catalyst Samples
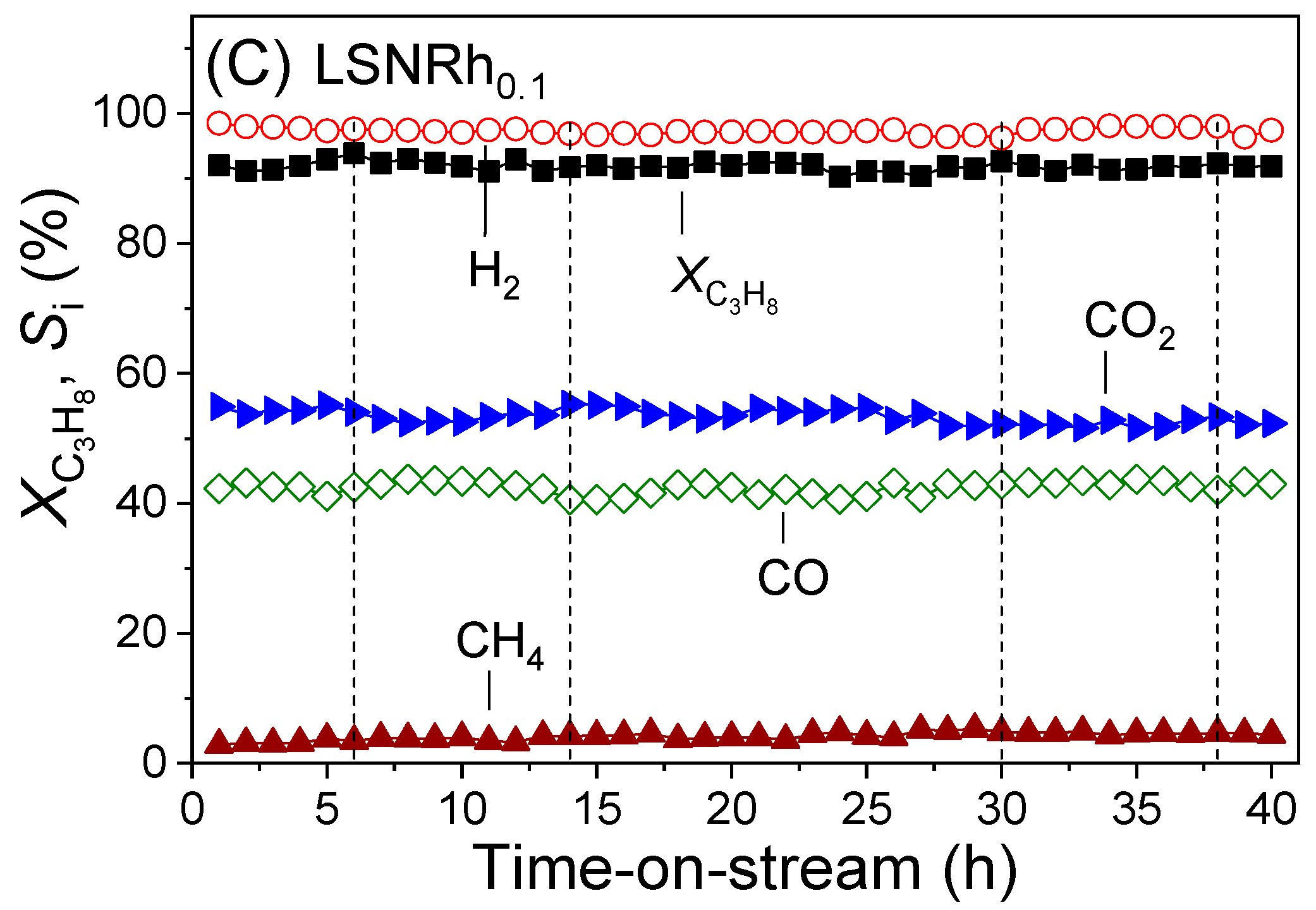
3.4. Long-Term Stability Tests
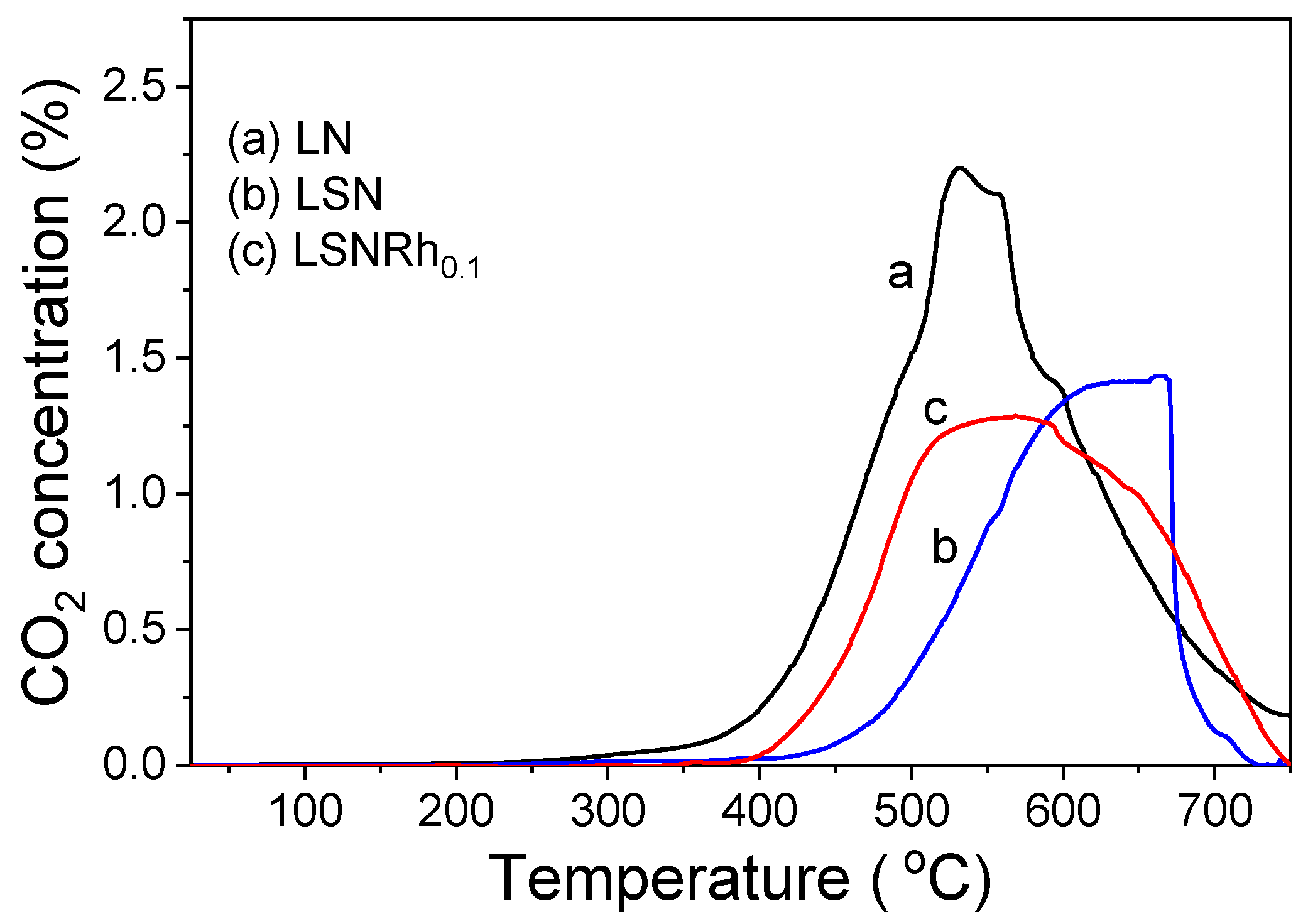
3.5. Carbon Accumulation on the Catalyst Surface
4. Conclusions
- Incorporation of noble metals in the matrix of LN and LSN perovskites resulted in an increase in the specific surface area (SSA), a shift of the XRD lines toward lower angles, and a decrease in the mean primary crystallite size of the materials. These modifications of the physicochemical characteristics of the perovskites, which are more pronounced for samples with higher noble metal content, have been attributed to the distortion of the perovskite structure induced by the incorporation of Ru or Rh in the matrix;
- Exposure of the perovskite samples to PSR reaction conditions resulted in the destruction of the perovskite structure and the development of new phases, accompanied by a considerable increase in the specific surface areas of the materials. Specifically, the in situ reduction of the parent perovskites resulted in the exsolution of Ni (as well as Rh or Ru) and the formation of well-dispersed metal nanoparticles on the resulting support, which consisted mainly of La2O2CO3 produced from the interaction of La2O3 with CO2. The main phases detected with XRD for the LNRux-derived samples included metallic Ni and La2O2CO3 whereas the LNSRux and LNSRhx-derived catalysts also contained La2SrOx, La2O3, and SrCO3. The presence of noble metals in the derived catalysts was confirmed by SEM/EDS measurements;
- The LN-derived catalyst exhibited higher activity compared to LSN, and its performance for the title reaction did not change appreciably following partial substitution of Ru in the B-sites of the perovskite. In contrast, incorporation of Ru and, especially, Rh in the perovskite matrix resulted in the development of catalysts with significantly improved catalytic performance, which increased with an increase in the noble metal content;
- Results of long-term stability test obtained at 600 °C using the LN, LSN, and LSNRh0.1 samples showed that all catalysts were characterized by high stability for 40 hours-on-stream, which was reflected in the accumulation of relatively small amounts of carbon deposits on the catalyst surfaces. This has been attributed to the in situ formation of La2O2CO3 under reaction conditions, which facilitates the oxidation of accumulated carbon, thereby preventing catalyst deactivation; and
- Best results were obtained for the LSNRh0.1-derived catalyst, which was characterized by high activity (XC3H8 = 92%) and selectivity toward H2 (SH2 = 97%) at 600 °C as well as excellent stability for 40 hours-on-stream. This has been attributed to the presence of well dispersed Rh crystallites on the catalyst surface, which act synergistically with Ni0 species.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rusman, N.A.A.; Dahari, M. A review on the current progress of metal hydrides material for solid-state hydrogen storage applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 12108–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, P.A.; Asumadu-Sarkodie, S. A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1167990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Hongmanorom, P.; Zhong, W.; Kawi, S. A review on perovskite catalysts for reforming of methane to hydrogen production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazali, N. Emerging technologies by hydrogen: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 18753–18771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, P.; Papadopoulou, C.; Matralis, H.; Verykios, X. Production of Renewable Hydrogen by Reformation of Biofuels. Adv. Bioenergy 2016, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kalamaras, C.M.; Efstathiou, A.M. Hydrogen Production Technologies: Current State and Future Developments. Conf. Pap. Energy 2013, 2013, 690627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Elgowainy, A. By-product hydrogen from steam cracking of natural gas liquids (NGLs): Potential for large-scale hydrogen fuel production, life-cycle air emissions reduction, and economic benefit. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 20143–20160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, A.T.; Cheetham, A.K.; Foord, J.S.; Green, M.L.H.; Grey, C.P.; Murrell, A.J.; Vernon, P.D.F. Selective oxidation of methane to synthesis gas using transition metal catalysts. Nature 1990, 344, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, A.T.; Cheetham, A.K.; Green, M.L.H.; Vernon, P.D.F. Partial oxidation of methane to synthesis gas using carbon dioxide. Nature 1991, 352, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.P.; Ferreira, R.A.R.; Noronha, F.B.; Hori, C.E. Hydrogen production from steam and oxidative steam reforming of liquefied petroleum gas over cerium and strontium doped LaNiO3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2017, 289, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kwak, B.S.; Do, J.Y.; Kang, M. Effective hydrogen production from propane steam reforming using M/NiO/YSZ catalysts (M = Ru, Rh, Pd, and Ag). Catal. Today 2018, 303, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.A.; Grace, J.R.; Lim, C.J.; Elnashaie, S.S.E.H.; Ghiasi, B. Steam reforming of propane in a fluidized bed membrane reactor for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 6276–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Son, M.; Park, M.-J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Choi, J.-H.; Bae, J.W. Adjusted interactions of nickel nanoparticles with cobalt-modified MgAl2O4-SiC for an enhanced catalytic stability during steam reforming of propane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 549, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, C.; Karadeniz, H.; Maier, L.; Deutschmann, O. Surface Reaction Kinetics of the Oxidation and Reforming of Propane over Rh/Al2O3 Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, N.-K.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, S.T.; Kang, M. Synthesis and characterization of Ni2−xPdxMnO4/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for hydrogen production via propane steam reforming. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegari, F.; Kazemeini, M.; Farhadi, F.; Rezaei, M.; Keshavarz, A. Preparation of mesoporous nanostructure NiO–MgO–SiO2 catalysts for syngas production via propane steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 6604–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.Y.; Kwak, B.S.; Park, N.-K.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, S.T.; Jo, S.W.; Cha, M.S.; Jeon, M.-K.; Kang, M. Effect of acidity on the performance of a Ni-based catalyst for hydrogen production through propane steam reforming: K-AlSixOy support with different Si/Al ratios. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 22687–22697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönsch, S.; Schneider, J.; Matthischke, S.; Schlüter, M.; Götz, M.; Lefebvre, J.; Prabhakaran, P.; Bajohr, S. Review on methanation—From fundamentals to current projects. Fuel 2016, 166, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambo, Y.; Adamu, S.; Abdulrasheed, A.A.; Lucky, R.A.; Ba-Shammakh, M.S.; Hossain, M.M. Catalyst design and tuning for oxidative dehydrogenation of propane—A review. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 609, 117914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, C.; Xia, H.; Deng, T.; Niu, J.; Ran, J.; Wu, C. Highly active and stable Ni/perovskite catalysts in steam methane reforming for hydrogen production. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentekakis, I.V.; Goula, G. Biogas Management: Advanced Utilization for Production of Renewable Energy and Added-value Chemicals. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.M.; Kwak, B.S.; Park, N.-K.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, S.T.; Kang, M. Effective hydrogen production from propane steam reforming over bimetallic co-doped NiFe/Al2O3 catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 46, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokka, A.; Katsoni, A.; Yentekakis, I.V.; Panagiotopoulou, P. Hydrogen production via steam reforming of propane over supported metal catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 14849–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaibari, Z.O.; Croiset, E.; Amin, A.; Epling, W. Effect of interactions between Ni and Mo on catalytic properties of a bimetallic Ni-Mo/Al2O3 propane reforming catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 490, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaneh, R.; Fard, A.A.; Bazyari, A.; Alavi, S.M.; Abnavi, F.J. Effects of Ce, La, Cu, and Fe promoters on Ni/MgAl2O4 catalysts in steam reforming of propane. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Sato, K.; Nagaoka, K. Rh/Ce0.25Zr0.75O2 Catalyst for Steam Reforming of Propane at Low Temperature. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modafferi, V.; Panzera, G.; Baglio, V.; Frusteri, F.; Antonucci, P.L. Propane reforming on Ni–Ru/GDC catalyst: H2 production for IT-SOFCs under SR and ATR conditions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 334, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartun, I.; Silberova, B.; Venvik, H.; Pfeifer, P.; Görke, O.; Schubert, K.; Holmen, A. Hydrogen production from propane in Rh-impregnated metallic microchannel reactors and alumina foams. Catal. Today 2005, 105, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, G.; Zapf, R.; Hessel, V.; Löwe, H. Propane steam reforming in micro-channels—results from catalyst screening and optimisation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 277, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartun, I.; Gjervan, T.; Venvik, H.; Görke, O.; Pfeifer, P.; Fathi, M.; Holmen, A.; Schubert, K. Catalytic conversion of propane to hydrogen in microstructured reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 101, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, S.; Duprez, D.; Can, F.; Courtois, X.; Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Laassiri, S.; Alamdari, H. Perovskites as substitutes of noble metals for heterogeneous catalysis: Dream or reality. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10292–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liang, D.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Tang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Recent advances during CH4 dry reforming for syngas production: A mini review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 5852–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattar, S.; Abedin, M.A.; Kanitkar, S.; Spivey, J.J. A review on dry reforming of methane over perovskite derived catalysts. Catal. Today 2021, 365, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cuaspud, J.; CA, P.; Schmal, M. Nanostructured La0.8Sr0.2Fe0.8Cr0.2O3 Perovskite for the Steam Methane Reforming. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 2504–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, C.; Modak, J.M.; Madras, G. Syngas production via CO2 reforming of methane over noble metal (Ru, Pt, and Pd) doped LaAlO3 perovskite catalyst. Mol. Catal. 2020, 484, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.C.; Bastos, P.H.C.; Junior, R.B.S.; Checca, N.R.; Fréty, R.; Brandão, S.T. Perovskite-type catalysts based on nickel applied in the Oxy-CO2 reforming of CH4: Effect of catalyst nature and operative conditions. Catal. Today 2020, 369, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Jang, J.S.; Ra, E.C.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, J.S. Reduced perovskite LaNiO3 catalysts modified with Co and Mn for low coke formation in dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 575, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvula, S.; Sagar, T.V.; Valluri, D.K.; Sai Prasad, P.S. Selective substitution of Ni by Ti in LaNiO3 perovskites: A parameter governing the oxy-carbon dioxide reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 4136–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, T.; Dong, X.; Li, M.; Wang, H. Effects of Ce substitution at the A-site of LaNi0.5Fe0.5O3 perovskite on the enhanced catalytic activity for dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, X.; Zhao, T.; Yu, H.; Li, M. Dry reforming of methane over bimetallic Ni-Co catalyst prepared from La(CoxNi1-x)0.5Fe0.5O3 perovskite precursor: Catalytic activity and coking resistance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 245, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Jia, L.; Luo, J.-L.; Chi, B.; Pu, J.; Li, J. CO2 dry reforming of CH4 with Sr and Ni co-doped LaCrO3 perovskite catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.K.; Das, T. Production of syngas from carbon dioxide reforming of methane by using LaNixFe1−xO3 perovskite type catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, L.; Han, X.; Zhou, L. Catalytic performance of perovskite-like oxide doped cerium (La2 − xCexCoO4 ± y) as catalysts for dry reforming of methane. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, R.B.S.; Rabelo-Neto, R.C.; Gomes, R.S.; Noronha, F.B.; Fréty, R.; Brandão, S.T. Steam reforming of acetic acid over Ni-based catalysts derived from La1−xCaxNiO3 perovskite type oxides. Fuel 2019, 254, 115714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, B.; Tang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Z. Hydrogen generation by acetic acid steam reforming over Ni-based catalysts derived from La1−xCexNiO3 perovskite. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 6795–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ou, Z.; Qin, C.; Ran, J.; Wu, C. Roles of alkali/alkaline earth metals in steam reforming of biomass tar for hydrogen production over perovskite supported Ni catalysts. Fuel 2019, 257, 116032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Pei, C.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Liu, R.; Gong, J. Chemical looping steam reforming of methane over Ce-doped perovskites. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 223, 115707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, N.; Navarro, R.M.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.C.; Al-Zahrani, S.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Hydrogen production by reforming of diesel fuel over catalysts derived from LaCo1−xRuxO3 perovskites: Effect of the partial substitution of Co by Ru (x = 0.01–0.1). J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9087–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, N.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.C.; Al-Zahrani, S.M.; Navarro, R.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Diesel fuel reforming over catalysts derived from LaCo1-xRuxO3 perovskites with high Ru loading. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 7056–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.M.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.C.; Villoria, J.A.; González-Jiménez, I.D.; Rosa, F.; Fierro, J.L.G. Effect of Ru on LaCoO3 perovskite-derived catalyst properties tested in oxidative reforming of diesel. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 73, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yan, B.; Yao, S.; Xie, Z.; Wu, Q.; Ran, R.; Weng, D.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.G. LaFe0.9Ni0.1O3 perovskite catalyst with enhanced activity and coke-resistance for dry reforming of ethane. J. Catal. 2018, 358, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.H.; Lopez, E.; Cadús, L.E.; Agüero, F.N. Elucidation of the role of support in Rh/perovskite catalysts used in ethanol steam reforming reaction. Catal. Today 2021, 372, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, S.M.; da Silva, A.M.; da Costa, L.O.O.; Assaf, J.M.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H.; Mattos, L.V.; Noronha, F.B. Evaluation of the performance of Ni/La2O3 catalyst prepared from LaNiO3 perovskite-type oxides for the production of hydrogen through steam reforming and oxidative steam reforming of ethanol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 377, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Chi, B.; Pu, J.; Li, J. High performance Ni exsolved and Cu added La0.8Ce0.2Mn0.6Ni0.4O3-based perovskites for ethanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 16458–16468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, D.; Radwan, D.; Ebaid, M.; Mikhail, S.; van Steen, E. Comparing nickel and cobalt perovskites for steam reforming of glycerol. Mol. Catal. 2018, 452, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamonsuangkasem, K.; Therdthianwong, S.; Therdthianwong, A.; Thammajak, N. Remarkable activity and stability of Ni catalyst supported on CeO2-Al2O3 via CeAlO3 perovskite towards glycerol steam reforming for hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baamran, K.S.; Tahir, M. Ni-embedded TiO2-ZnTiO3 reducible perovskite composite with synergistic effect of metal/support towards enhanced H2 production via phenol steam reforming. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 200, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takise, K.; Manabe, S.; Muraguchi, K.; Higo, T.; Ogo, S.; Sekine, Y. Anchoring effect and oxygen redox property of Co/La0.7Sr0.3AlO3-δ perovskite catalyst on toluene steam reforming reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 538, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, C.; Ou, Z.; Ran, J. Resistance of Ni/perovskite catalysts to H2S in toluene steam reforming for H2 production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 26800–26811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Moon, D.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, N.-C.; Shin, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-C. Autothermal reforming of propane over Ce modified Ni/LaAlO3 perovskite-type catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSP, S.; Hossain, M.M.; Gnanasekaran, G.; Mok, Y.S. Dry Reforming of Propane over γ-Al2O3 and Nickel Foam Supported Novel SrNiO3 Perovskite Catalyst. Catalysts 2019, 9, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Yeyongchaiwat, J.; Matsumoto, H.; Ishihara, T. Oxidative reforming of propane with oxygen permeating membrane reactor using Pr2Ni0.75Cu0.25Ga0.05O4 perovskite related mixed conductor. Solid State Ion. 2017, 301, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Gallego, G.A.S.; Mondragon, F.; Barrault, J.; Tatibouët, J.M. CO2 reforming of methane over LaNiO3 as precursor material. Catal. Today 2005, 107, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthiumporn, K.; Kawi, S. Promotional effect of alkaline earth over Ni-La2O3 catalyst for CO2 reforming of CH4: Role of surface oxygen species on H2 production and carbon suppression. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 14435–14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, G.; Goldwasser, M.R.; Navarro, C.U.D.; Tatibouët, J.M.; Barrault, J.; Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Martínez, F. Dry reforming of methane over Ni perovskite type oxides. Catal. Today 2005, 107, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.H.; Noh, Y.S.; Hong, G.H.; Moon, D.J. Combined steam and CO2 reforming of methane over La1-xSrxNiO3 perovskite oxides. Catal. Today 2018, 299, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.; Bak Hansen, J.H. CO2-reforming of methane over transition metals. J. Catal. 1993, 144, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.P.; Moura, L.G.; Spivey, J.J.; Noronha, F.B.; Hori, C.E. Hydrogen production by steam reforming of LPG using supported perovskite type precursors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 21166–21177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safakas, A.; Bampos, G.; Bebelis, S. Oxygen reduction reaction on La0.8Sr0.2CoxFe1-xO3−δ perovskite/carbon black electrocatalysts in alkaline medium. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 244, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampos, G.; Bebelis, S.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X. Comparison of the Activity of Pd–M (M: Ag, Co, Cu, Fe, Ni, Zn) Bimetallic Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampos, G.; Bika, P.; Panagiotopoulou, P.; Verykios, X.E. Reactive adsorption of CO from low CO concentrations streams on the surface of Pd/CeO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 588, 117305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.E.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Goldwasser, M.R.; Pietri, E.; Pérez-Zurita, M.J.; Griboval-Constant, A.; Leclercq, G. Structural features and performance of LaNi1-xRhxO3 system for the dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 344, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, N.A.; Barbero, B.P.; Grange, P.; Cadús, L.E. La1-xCaxCoO3 perovskite-type oxides: Preparation, characterisation, stability, and catalytic potentiality for the total oxidation of propane. J. Catal. 2005, 231, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Li, F.; Gao, P.; Zhao, N.; Xiao, F.; Wei, W.; Zhong, L.; Sun, Y. Methanol synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation over La-M-Cu-Zn-O (M = Y, Ce, Mg, Zr) catalysts derived from perovskite-type precursors. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Zhong, L.; Xiao, P.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J. Perovskite oxides: Preparation, characterizations, and applications in heterogeneous catalysis. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2917–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, C.; Baiyee, Z.M.; Shao, Z.; Ciucci, F. Nonstoichiometric Oxides as Low-Cost and Highly-Efficient Oxygen Reduction/Evolution Catalysts for Low-Temperature Electrochemical Devices. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9869–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Senyshyn, A.; Zhecheva, E.; Tenchev, K.; Stoyanova, R.; Fuess, H. Crystal structure, microstructure and reducibility of LaNixCo1-xO3 and LaFexCo1-xO3 Perovskites (0 < x ≤ 0.5). J. Solid State Chem. 2010, 183, 940–950. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor-Pérez, L.; Baibars, F.; Le Sache, E.; Arellano-García, H.; Gu, S.; Reina, T.R. CO2 valorisation via Reverse Water-Gas Shift reaction using advanced Cs doped Fe-Cu/Al2O3 catalysts. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rynkowski, J.; Samulkiewicz, P.; Ladavos, A.K.; Pomonis, P.J. Catalytic performance of reduced La2-xSrxNiO 4 perovskite-like oxides for CO2 reforming of CH 4. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 263, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, G.; Urbina De Navarro, C.; Goldwasser, M.R. CO2 reforming of CH4 over Co-La-based perovskite-type catalyst precursors. J. Power Sources 2013, 234, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, G.; Kiennemann, A.; Goldwasser, M.R. La-Sr-Ni-Co-O based perovskite-type solid solutions as catalyst precursors in the CO2 reforming of methane. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhad, P.D.K.; Bekheet, M.F.; Bonmassar, N.; Schlicker, L.; Gili, A.; Kamutzki, F.; Gurlo, A.; Doran, A.; Gao, Y.; Heggen, M.; et al. Mechanistic in situ insights into the formation, structural and catalytic aspects of the La2NiO4 intermediate phase in the dry reforming of methane over Ni-based perovskite catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 612, 117984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmassar, N.; Bekheet, M.F.; Schlicker, L.; Gili, A.; Gurlo, A.; Doran, A.; Gao, Y.; Heggen, M.; Bernardi, J.; Klötzer, B.; et al. In Situ-Determined Catalytically Active State of LaNiO3 in Methane Dry Reforming. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Verykios, X.E. Mechanistic aspects of carbon dioxide reforming of methane to synthesis gas over Ni catalysts. Catal. Lett. 1996, 38, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Peng, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, N. La2O2CO3 supported Ni-Fe catalysts for hydrogen production from steam reforming of ethanol. J. Rare Earths 2011, 29, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.J.; Li, B.; Chen, W.Q.; Liu, C.W.; Huang, B.W. Ethanol Steam Reforming over La2O2CO3 Supported Ni-Ru Bimetallic Catalysts. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 457–458, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Pei, C.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Gong, J. Dry reforming of methane over La2O2CO3-modified Ni/Al2O3 catalysts with moderate metal support interaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 264, 118448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.C.; Bastos, P.H.C.; Junior, R.B.S.; Checca, N.R.; Costa, D.S.; Fréty, R.; Brandão, S.T. Oxy-CO2 reforming of CH4 on Ni-based catalysts: Evaluation of cerium and aluminum addition on the structure and properties of the reduced materials. Catal. Today 2020. In Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, C.; Bizkarra, K.; Barrio, V.L.; Cambra, J.F.; Pino, L.; Vita, A. Renewable hydrogen production via steam reforming of simulated bio-oil over Ni-based catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 14671–14682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Diéguez, M.; Pieta, I.S.; Herrera, M.C.; Larrubia, M.A.; Alemany, L.J. RhNi nanocatalysts for the CO2 and CO2 + H 2O reforming of methane. Catal. Today 2011, 172, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, L.; Guilhaume, N.; Mirodatos, C. Autothermal syngas production from model gasoline over Ni, Rh and Ni-Rh/Al2O3 monolithic catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 5772–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, B.S.; Melo, D.M.A.; Libs, S.; Kiennemann, A. CO2 reforming of methane over La2NiO4/α-Al2O3 prepared by microwave assisted self-combustion method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 378, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Notation | Nominal Formula | Specific Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Phases Detected with XRD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | Used | Fresh | Used | ||
| LN | LaNiO3 | 3 | 42 | LaNiO3 (rhombohedral, rh) | La2O2CO3 Ni |
| LSN | La0.8Sr0.2NiO3 | 5 | 18 | Sr0.5La1.5NiO4 NiO | La2SrOx La2O2CO3 Ni |
| LNRu0.01 | LaNi0.99Ru0.01O3 | 4 | 56 | LaNiO3 (rh) | La2O2CO3 Ni |
| LNRu0.1 | LaNi0.9Ru0.1O3 | 6 | 71 | LaNiO3 (cubic) | La2O2CO3 La2O3 Ni |
| LSNRu0.01 | La0.8Sr0.2Ni0.99Ru0.01O3 | 6 | 55 | Sr0.5La1.5NiO4 LaNiO3 (rh) SrNiO3 NiO | La2O2CO3 SrCO3 SrC2 Ni |
| LSNRu0.1 | La0.8Sr0.2Ni0.9Ru0.1O3 | 8 | 59 | Sr0.5La1.5NiO4 LaNiO3 (rh) NiO | La2O2CO3 SrCO3 La2O3 Ni |
| LSNRh0.01 | La0.8Sr0.2Ni0.99Rh0.01O3 | 6 | 66 | Sr0.5La1.5NiO4 NiO | La2O2CO3 SrCO3 Ni |
| LSNRh0.1 | La0.8Sr0.2Ni0.9Rh0.1O3 | 6 | 29 | Sr0.5La1.5NiO4 NiO | La2O2CO3 SrCO3 La2O3 Ni |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramantani, T.; Bampos, G.; Vavatsikos, A.; Vatskalis, G.; Kondarides, D.I. Propane Steam Reforming over Catalysts Derived from Noble Metal (Ru, Rh)-Substituted LaNiO3 and La0.8Sr0.2NiO3 Perovskite Precursors. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081931
Ramantani T, Bampos G, Vavatsikos A, Vatskalis G, Kondarides DI. Propane Steam Reforming over Catalysts Derived from Noble Metal (Ru, Rh)-Substituted LaNiO3 and La0.8Sr0.2NiO3 Perovskite Precursors. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081931
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamantani, Theodora, Georgios Bampos, Andreas Vavatsikos, Georgios Vatskalis, and Dimitris I. Kondarides. 2021. "Propane Steam Reforming over Catalysts Derived from Noble Metal (Ru, Rh)-Substituted LaNiO3 and La0.8Sr0.2NiO3 Perovskite Precursors" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081931
APA StyleRamantani, T., Bampos, G., Vavatsikos, A., Vatskalis, G., & Kondarides, D. I. (2021). Propane Steam Reforming over Catalysts Derived from Noble Metal (Ru, Rh)-Substituted LaNiO3 and La0.8Sr0.2NiO3 Perovskite Precursors. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081931